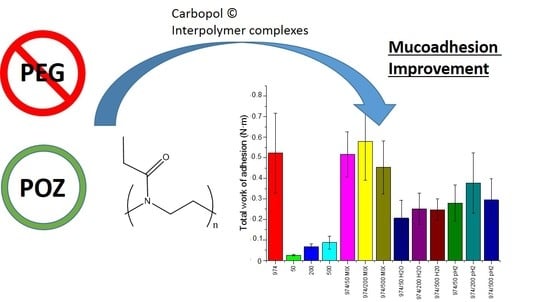
Formulation of Carbopol®/Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)s Mucoadhesive Tablets for Buccal Delivery of Hydrocortisone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
2.2. Complex Formation
2.3. Tablet Formulation and Preparation
2.4. Mucoadhesion of the Tablets
2.5. Swelling Behavior
2.6. Hydrocortisone Release from the Tablets
2.6.1. Instruments and Chromatographic Conditions
2.6.2. Dissolution Tests
3. Results and Discussion
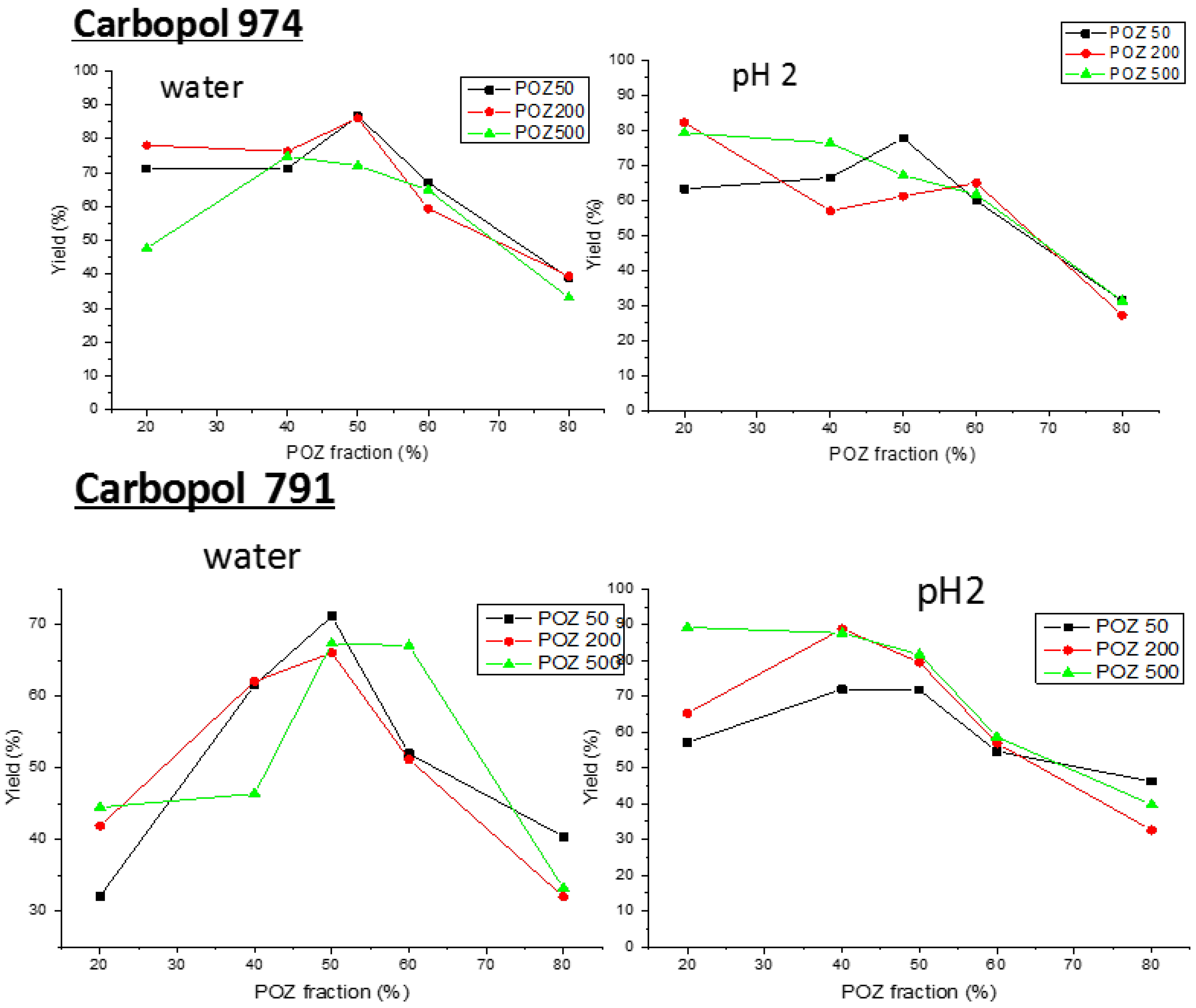
3.1. Fabrication of Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)/Carbopol Interpolymer Complexes
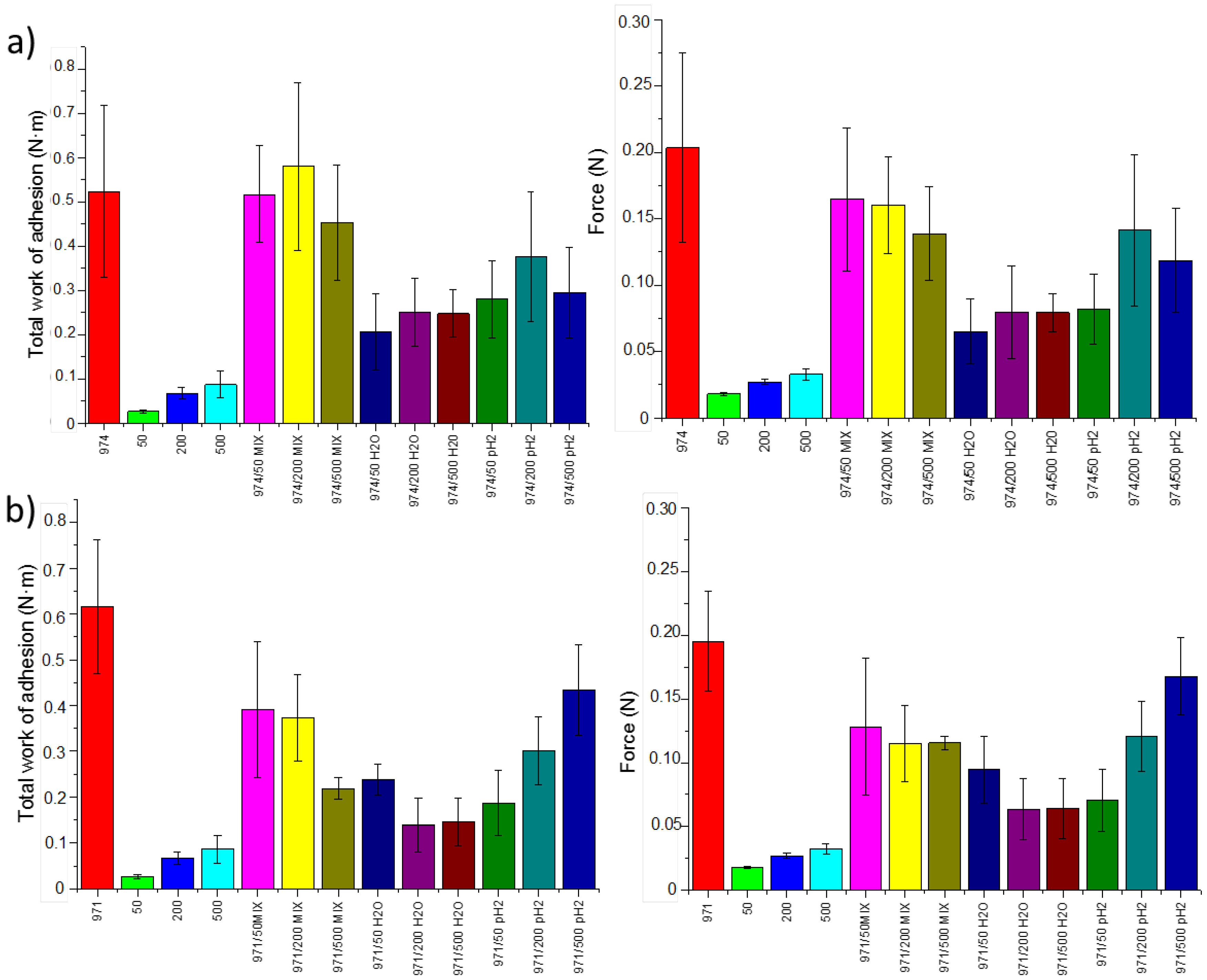
3.2. Mucoadhesion Studies
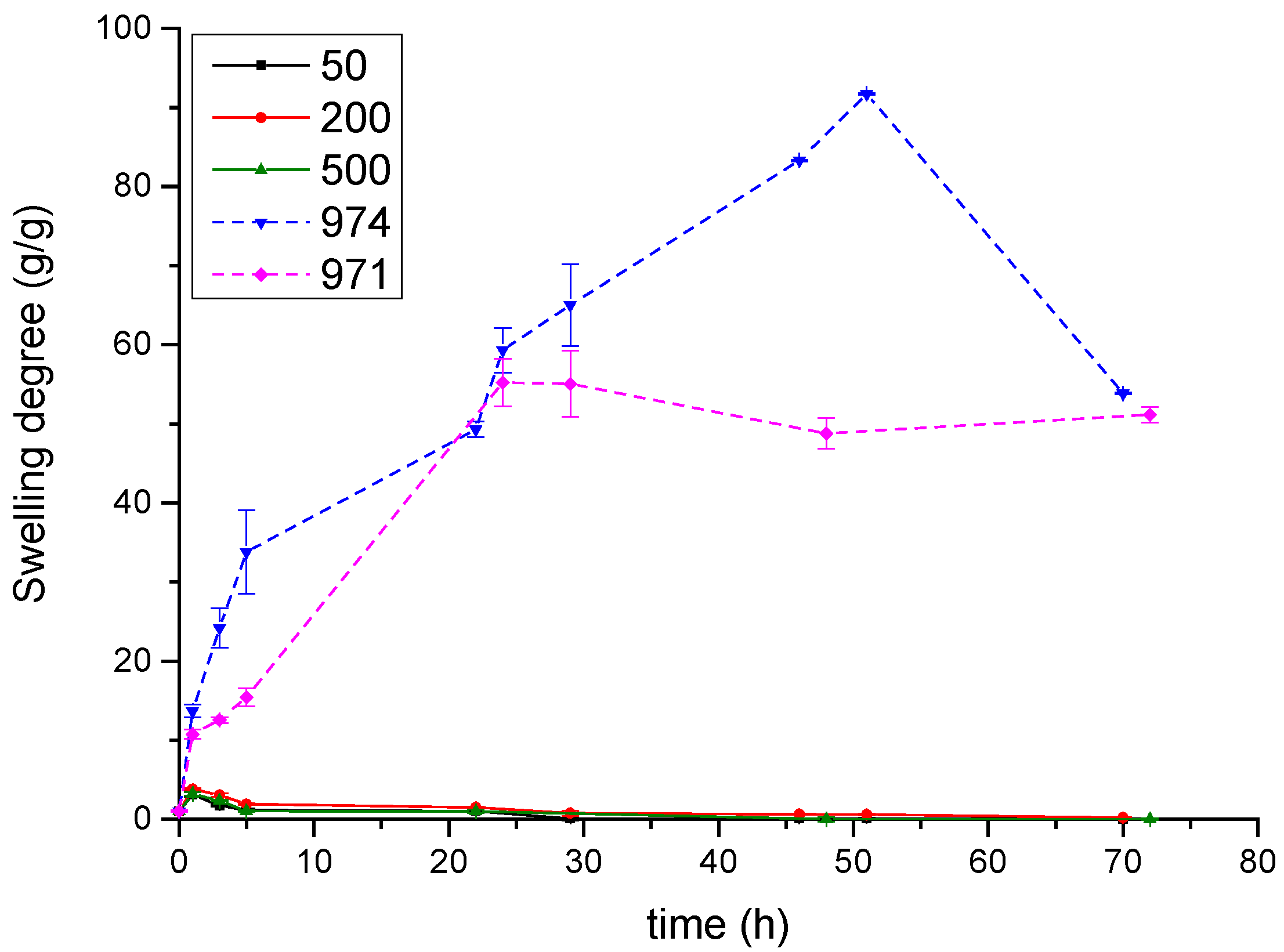
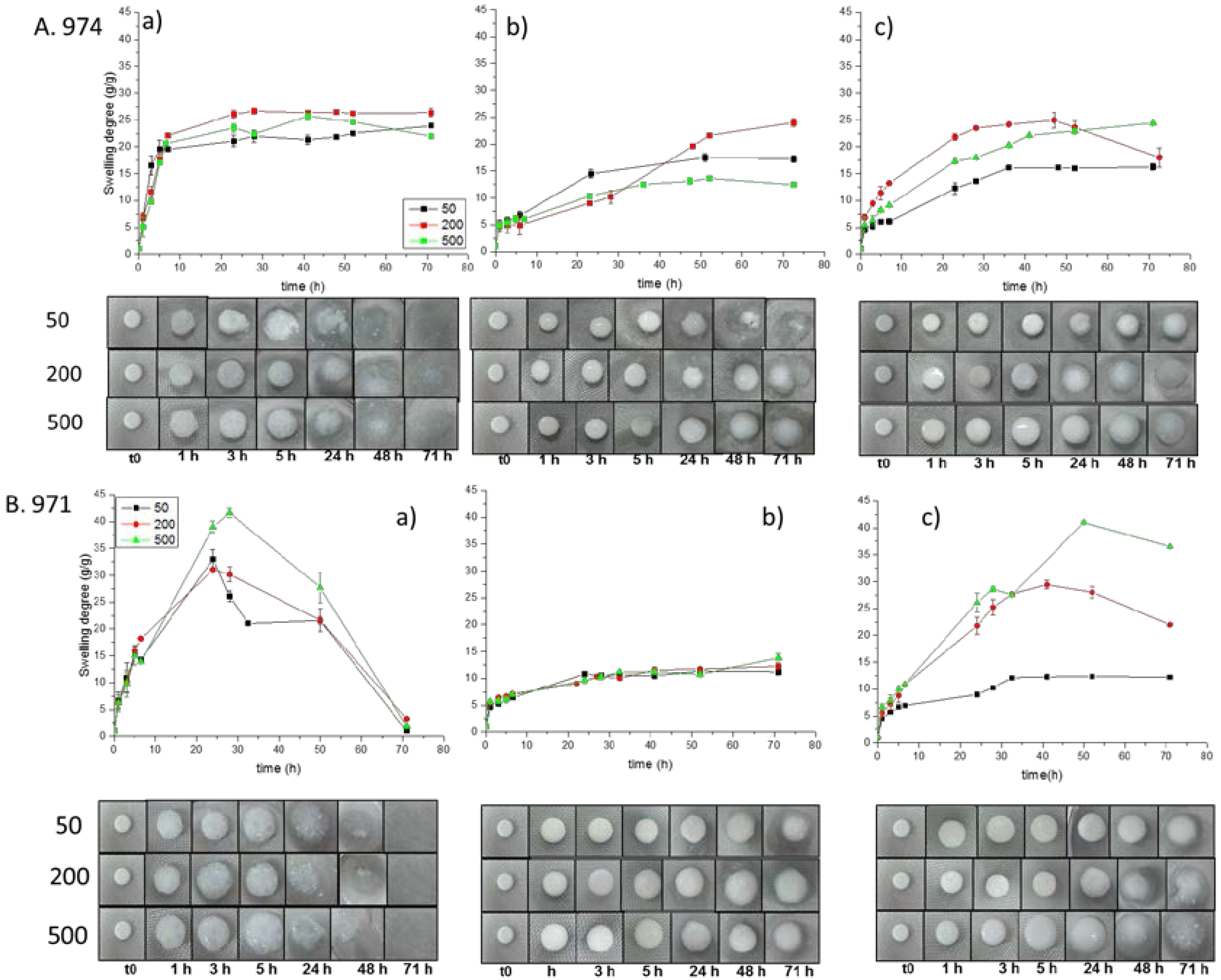
3.3. Swelling Studies
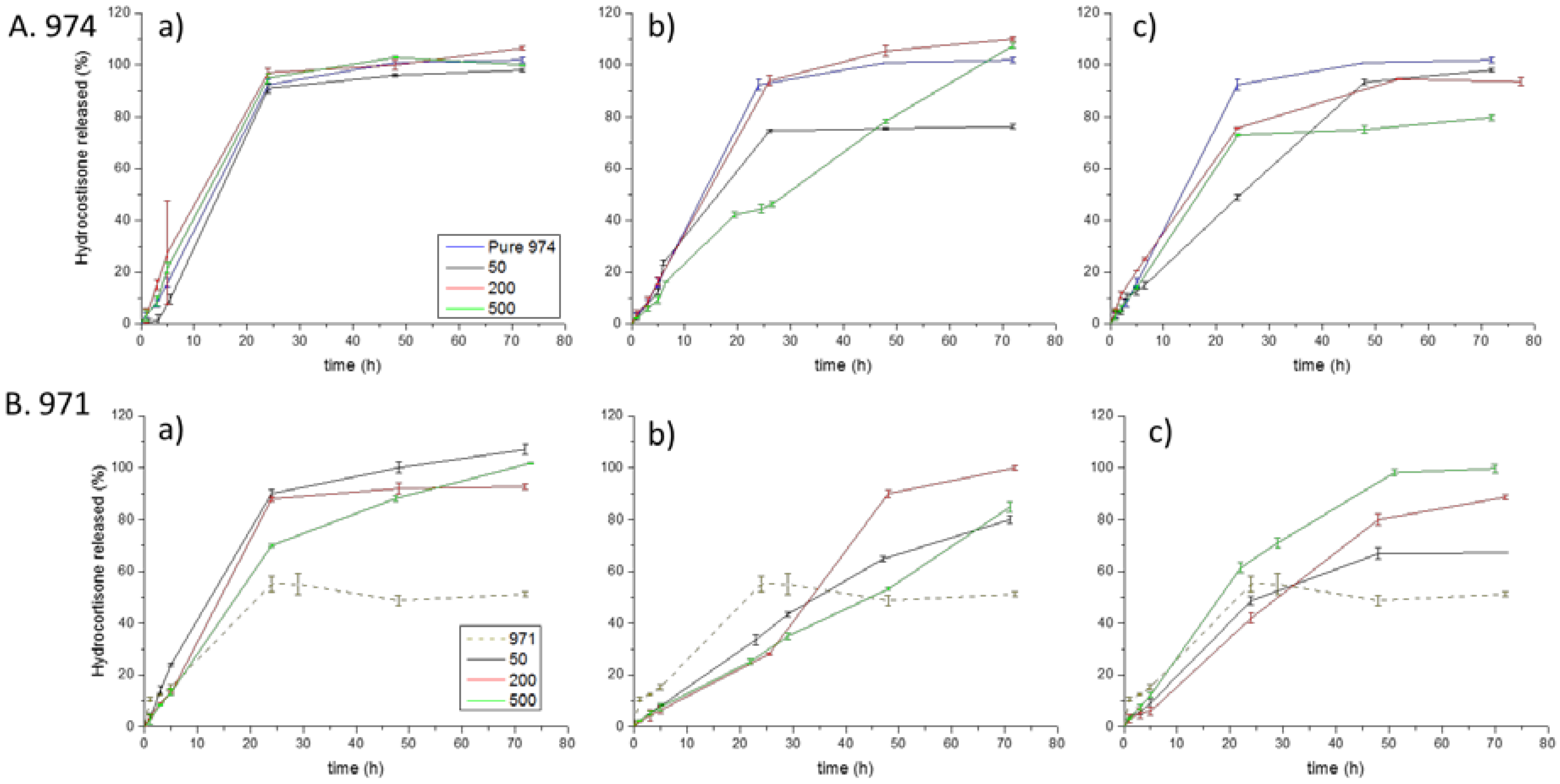
3.4. Dissolution Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stegemann, S.; Leveiller, F.; Franchi, D.; de Jong, H.; Lindén, H. When poor solubility becomes an issue: From early stage to proof of concept. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 31, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadka, P.; Ro, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, I.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, H.; Cho, J.M.; Yun, G.; Lee, J. Pharmaceutical particle technologies: An approach to improve drug solubility, dissolution and bioavailability. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalepu, S.; Nekkanti, V. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: Review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, J.D.R.; Waddington, W.A.; Ell, P.J.; Parsons, G.E.; Coffin, M.D.; Basit, A.W. Concentration-Dependent Effects of Polyethylene Glycol 400 on Gastrointestinal Transit and Drug Absorption. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 1984–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.M.; Dust, J.M.; McGill, R.A.; Harris, P.A.; Edgell, M.J.; Sedaghat-Herati, R.M.; Karr, L.J.; Donnelly, D.L. New Polyethylene Glycols for Biomedical Applications. In Water-Soluble Polymers; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; Volume 467, pp. 27–418. ISBN 0-8412-2101-4. [Google Scholar]
- Knop, K.; Hoogenboom, R.; Fischer, D.; Schubert, U.S. Poly(ethylene glycol) in drug delivery: Pros and cons as well as potential alternatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6288–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuman, E.; Balsam, P.E. Probable anaphylactic reaction to polyethylene glycol electrolyte lavage solution. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1991, 37, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Koker, S.; Hoogenboom, R.; De Geest, B.G. Polymeric multilayer capsules for drug delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, J.C.M.E.; Hoogenboom, R.; Van, V.P.A.A. Drug Delivery System Comprising Polyoxazoline and a Bioactive Agent. U.S. Patent 8,642,080 B2, 28 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hoogenboom, R. Poly(2-oxazoline)s: A polymer class with numerous potential applications. Angew. Chem. 2009, 48, 7978–7994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mero, A.; Pasut, G.; Via, L.D.; Fijten, M.W.M.; Schubert, U.S.; Hoogenboom, R.; Veronese, F.M. Synthesis and characterization of poly(2-ethyl 2-oxazoline)-conjugates with proteins and drugs: Suitable alternatives to PEG-conjugates? J. Control. Release 2008, 125, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barz, M.; Luxenhofer, R.; Zentel, R.; Vicent, M.J. Overcoming the PEG-addiction: Well-defined alternatives to PEG, from structure-property relationships to better defined therapeutics. Polym. Chem. 2011, 1900–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, N.; Schubert, U.S. Poly(2-oxazolines) in biological and biomedical application context. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1504–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, T.; Tabata, Y.; Ikada, Y. Distribution and tissue uptaken of poly(ethylene glycol) with different molecular weights after intravenous administration to mice. J. Pharma Sci. 1994, 83, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longley, B.L.; Zhao, H.; Lozanguiez, Y.L.; Conover, C.D. Biodistribution and excretion of radiolabeled 40 kDa polyethylene glycol following intravenous administration in mice. J. Pharma. Sci. 2013, 102, 2362–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nokhodchi, A.; Raja, S.; Patel, P.; Asare-Addo, K. The role of oral controlled release matrix tablets in drug delivery systems. BioImpacts 2012, 2, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Stilhano, R.S.; Madrigal, J.L.; Wong, K.; Williams, P.A.; Martin, P.K.M.; Yamaguchi, F.S.M.; Samoto, V.Y.; Han, S.W.; Silva, E.A. Injectable alginate hydrogel for enhanced spatiotemporal control of lentivector delivery in murine skeletal muscle. J. Control. Release 2016, 237, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, F.; Bruschi, M.; Evangelista, R.; Gremiao, M. Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems. Brazilian J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 46, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.F. Site-specific drug delivery systems within the gastro-intestinal tract: From the mouth to the colon. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 395, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, A.K.; Chawla, M.; Singh, A. Potential Applications of Carbomer in Oral Mucoadhesive Controlled Drug Delivery System: A Review. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2000, 26, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Chun, M.K.; Choi, H.K. Preparation of an extended-release matrix tablet using chitosan/Carbopol interpolymer complex. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 347, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Hydrogen-bonded interpolymer complexes as materials for pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 334, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, K.D.; Sander, C.; Baldursdottir, S.; Pedersen, A.M.L.; Jacobsen, J. Development of an ex vivo retention model simulating bioadhesion in the oral cavity using human saliva and physiologically relevant irrigation media. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 448, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, P.; Cirri, M.; Mennini, N.; Casella, G.; Maestrelli, F. Polymeric mucoadhesive tablets for topical or systemic buccal delivery of clonazepam: Effect of cyclodextrin complexation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hájková, R.; Solich, P.; Dvořák, J.; Šı́cha, J. Simultaneous determination of methylparaben, propylparaben, hydrocortisone acetate and its degradation products in a topical cream by RP-HPLC. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 32, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Palo, E.F.; Antonelli, G.; Benetazzo, A.; Prearo, M.; Gatti, R. Human saliva cortisone and cortisol simultaneous analysis using reverse phase HPLC technique. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 405, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendela, M.; Kahsay, G.; Baekelandt, I.; Van Schepdael, A.; Adams, E. Simultaneous determination of lidocaine hydrochloride, hydrocortisone and nystatin in a pharmaceutical preparation by RP-LC. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 56, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moribe, K.; Makishima, T.; Higashi, K.; Liu, N.; Limwikrant, W.; Ding, W.; Masuda, M.; Shimizu, T.; Yamamoto, K. Encapsulation of poorly water-soluble drugs into organic nanotubes for improving drug dissolution. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 469, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Rubio, L.; Laza, J.M.; Pérez, L. Polymer–polymer complexes of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and poly (N,N-diethylacrylamide) with poly(carboxylic acids): A comparative study. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamou, A.S.H.; Djadoun, S. Interpolymer complexes of poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide/poly(styrene-co-acrylic acid): Thermal stability and FTIR analysis. Macromol. Symp. 2011, 303, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhu, B.; Inove, Y. Hydrogen bonds in polymer blends. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2004, 29, 1021–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniliuc, L.; David, C. Intermolecular interactions in blends of poly(vinyl alcohol) with poly(acrylic acid): 2. Correlation between the states of sorbed water and the interactions in homopolymers and their blends. Polymer 1996, 37, 5219–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khutoryanskiy, V.V.; Dubolazov, A.V.; Nurkeeva, Z.S.; Mun, G.A. pH effects in the complex formation and blending of poly(acrylic acid) with poly(ethylene oxide). Langmuir 2004, 20, 3785–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayramgil, N.P. Therml degradation of [poly(N-vinylimidazole)-polyacrylic acid] interpolymer complexes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 1504–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Rubio, L.; Álvarez, V.; Lizundia, E.; Vilas, J.L.; Rodriguez, M.; León, L.M. Influence of α-methyl substitutions on interpolymer complexes formation between poly(meth)acrylic acids and poly(N-isopropyl(meth)acrylamide)s. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2015, 293, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Advances in mucoadhesion and mucoadhesive polymers. Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 748–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khutoryanskaya, O.V.; Morrison, P.W.J.; Seilkhanov, S.K.; Mussin, M.N.; Ozhmukhametova, E.K.; Rakhypbekov, T.K.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Hydrogen-bonded complexes and blends of poly(acrylic acid) and methylcellulose: Nanoparticles and mucoadhesive films for ocular delivery of riboflavin. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Tiwary, A.K.; Kaur, G. Investigations on interpolymer complexes of cationic guar gum and xanthan gum for formulation of bioadhesive films. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 5, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamat-Miller, N.; Chittchang, M.; Johnston, T.P. The use of mucoadhesive polymers in buccal drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1666–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.M.; Smart, J.D.; Nevell, T.G.; Ewen, R.J.; Eaton, P.J.; Tsibouklis, J. Mucin/poly(acrylic acid) interactions: A spectroscopic investigation of mucoadhesion. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, E.; Selmin, F.; Baldassari, S.; Gennari, C.G.M.; Caviglioli, G.; Cilurzo, F.; Minghetti, P.; Parodi, B. A focus on mucoadhesive polymers and their application in buccal dosage forms. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Chun, M.K.; Choi, H.K. Preparation of Carbopol/chitosan interpolymer complex as a controlled release tablet matrix; Effect of complex formation medium on drug release characteristics. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2008, 31, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz-Rubio, L.; Alonso, M.L.; Pérez-Álvarez, L.; Alonso, R.M.; Vilas, J.L.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Formulation of Carbopol®/Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)s Mucoadhesive Tablets for Buccal Delivery of Hydrocortisone. Polymers 2018, 10, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020175
Ruiz-Rubio L, Alonso ML, Pérez-Álvarez L, Alonso RM, Vilas JL, Khutoryanskiy VV. Formulation of Carbopol®/Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)s Mucoadhesive Tablets for Buccal Delivery of Hydrocortisone. Polymers. 2018; 10(2):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020175
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz-Rubio, Leire, María Luz Alonso, Leyre Pérez-Álvarez, Rosa Maria Alonso, Jose Luis Vilas, and Vitaliy V. Khutoryanskiy. 2018. "Formulation of Carbopol®/Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)s Mucoadhesive Tablets for Buccal Delivery of Hydrocortisone" Polymers 10, no. 2: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020175
APA StyleRuiz-Rubio, L., Alonso, M. L., Pérez-Álvarez, L., Alonso, R. M., Vilas, J. L., & Khutoryanskiy, V. V. (2018). Formulation of Carbopol®/Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)s Mucoadhesive Tablets for Buccal Delivery of Hydrocortisone. Polymers, 10(2), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020175