Statistical Design of Experimental and Bootstrap Neural Network Modelling Approach for Thermoseparating Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction of Polyhydroxyalkanoates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Production of PHAs
2.3. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
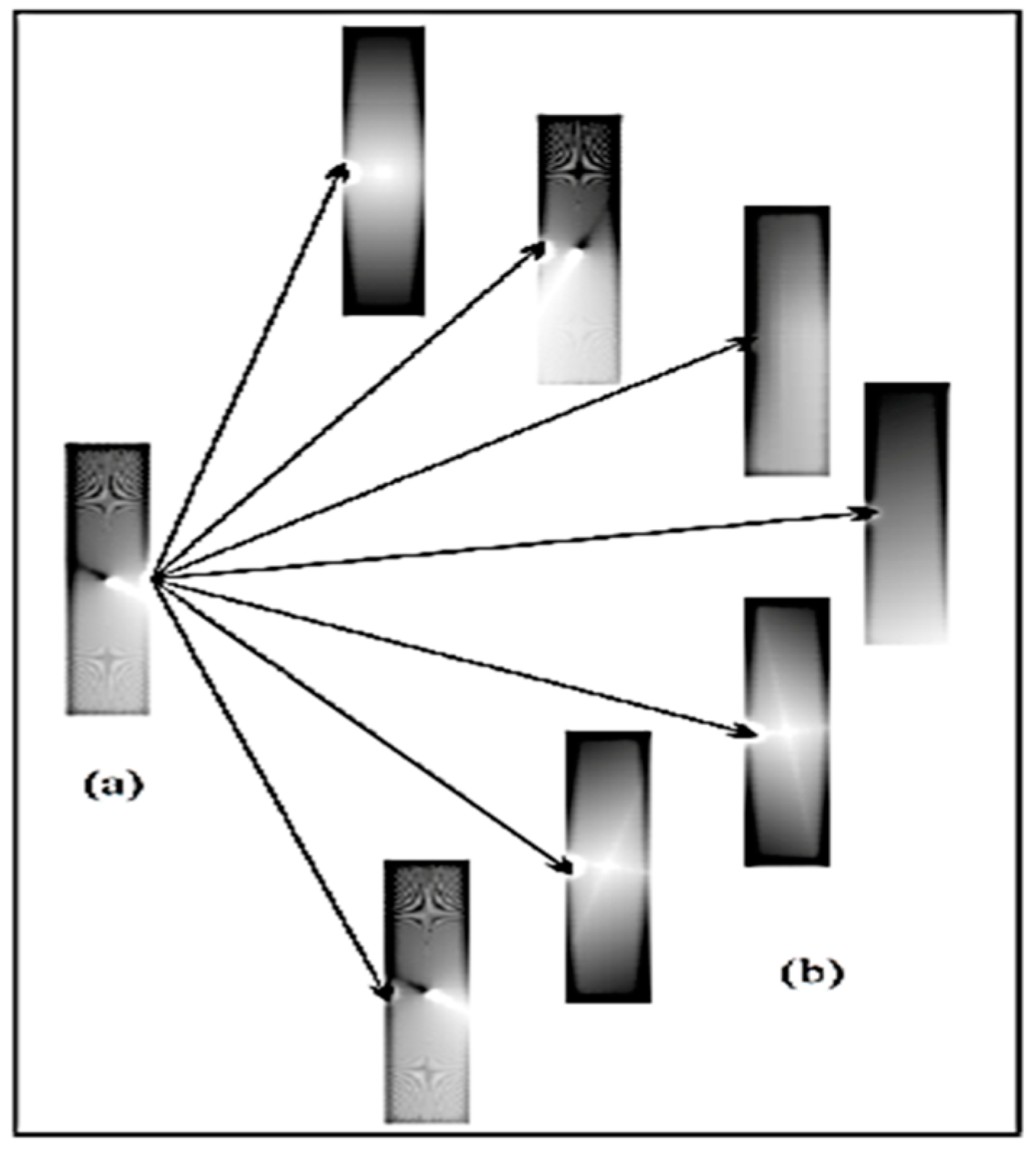
2.4. Partitioning of PHAs in Thermoseparating ATPE
2.5. Quantification of PHAs by Gas Chromatography (GC) Analysis
2.6. Partitioning Behaviors of PHAs
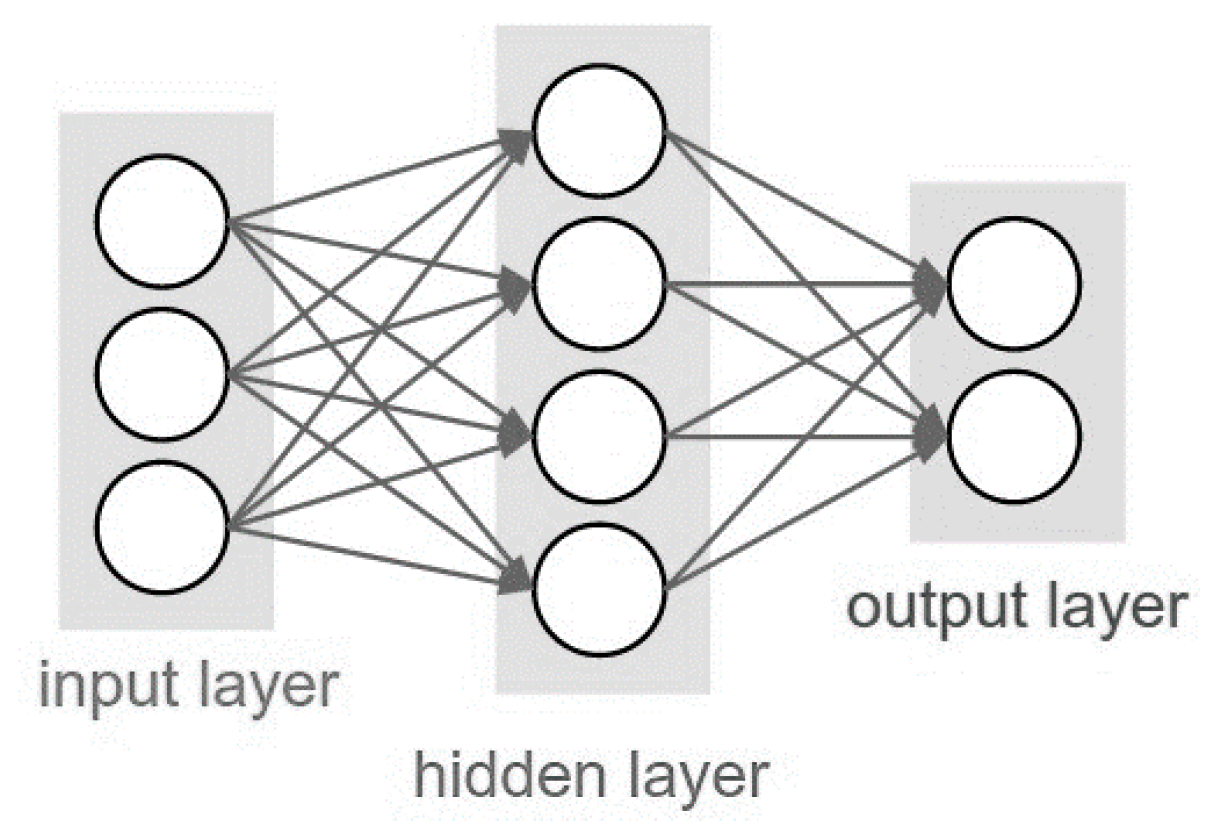
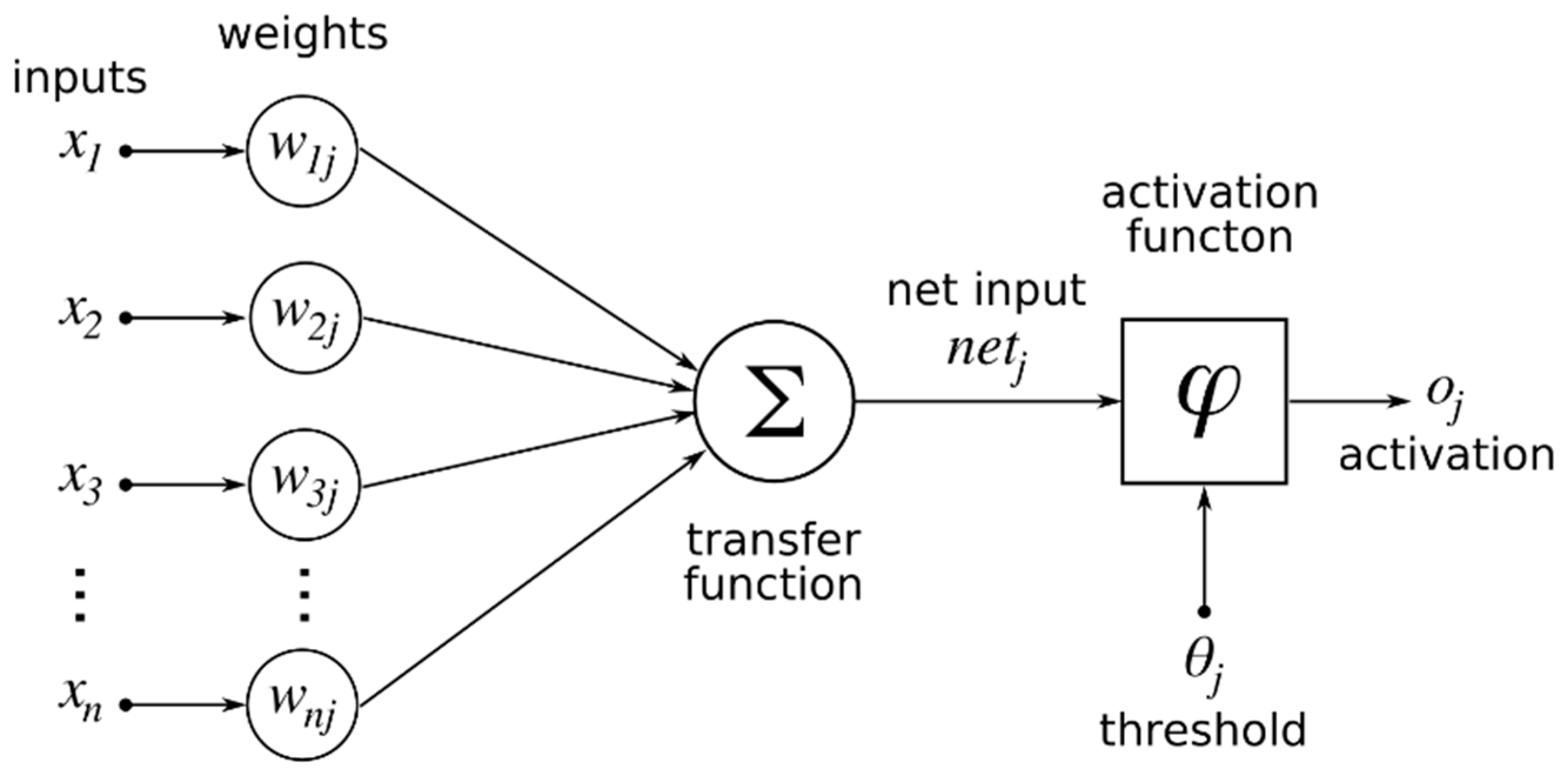
2.7. Neural Network Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Statistical Experimental Result
3.1.1. Effect on the “Yield”
3.1.2. Effect on the “Partition Coefficient”
3.1.3. Effect on the “Purification Factor”
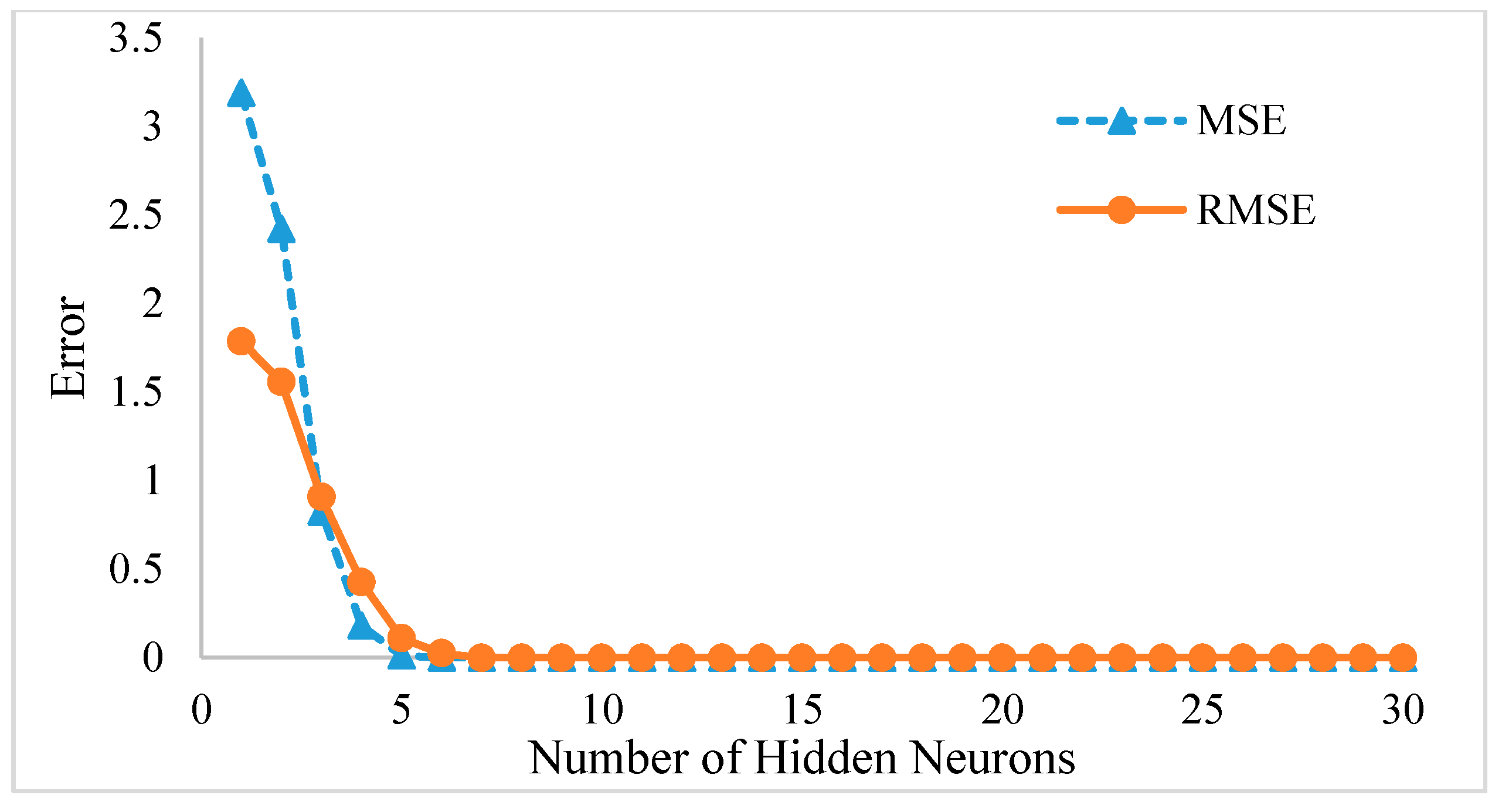
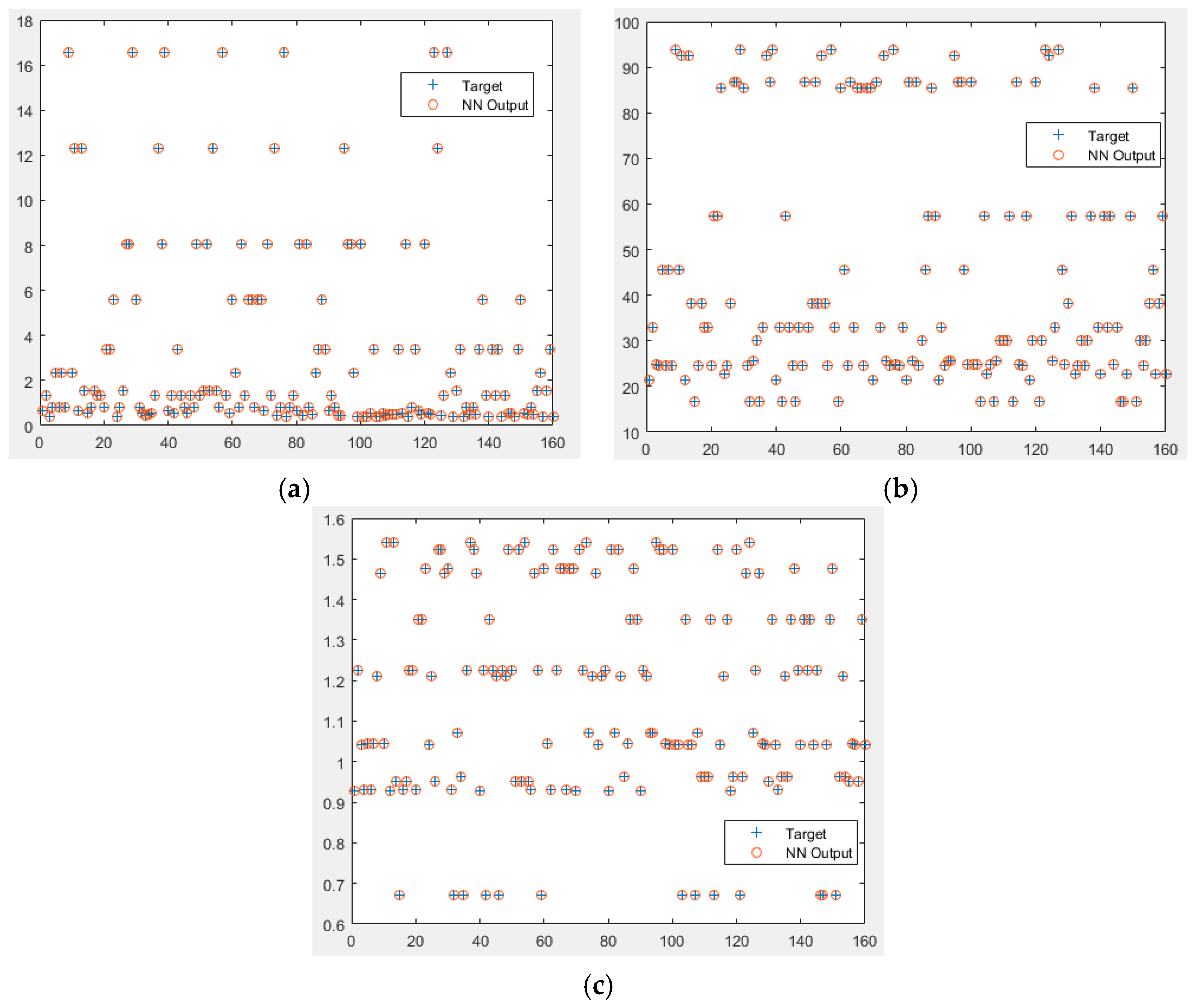
3.2. Feed Forward Neural Network (FFNN) Model Results
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drzyzga, O.; Revelles, O.; Durante-Rodríguez, G.; Díaz, E.; García, J.L.; Prieto, A. New challenges for syngas fermentation: Towards production of biopolymers. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 1735–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaraonye, E.; Keshavarz, T.; Roy, I. Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates: The future green materials of choice. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigmatullin, R.; Thomas, P.; Lukasiewicz, B.; Puthussery, H.; Roy, I. Polyhydroxyalkanoates, a family of natural polymers, and their applications in drug delivery. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.; Keshavarz, T.; Roether, J.A.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Roy, I. Medium chain length polyhydroxyalkanoates, promising new biomedical materials for the future. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2011, 72, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswar Reddy, M.; Nikhil, G.N.; Venkata Mohan, S.; Swamy, Y.V.; Sarma, P.N. Pseudomonas otitidis as a potential biocatalyst for polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) synthesis using synthetic wastewater and acidogenic effluents. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 123, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King-Sern, H.; Rajni, H.K.; Farook, A.; Toshiaki, F.; Kumar, S. Conversion of rice husks to polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) via a three-step process: Optimized alkaline pretreatment, enzymatic hydrolysis, and biosynthesis by Burkholderia cepacia USM (JCM 15050). J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarz, T.; Roy, I. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Bioplastics with a green agenda. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben, M.; Kennes, C.; Veiga, M.C. Optimization of polyhydroxyalkanoate storage using mixed cultures and brewery wastewater. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 2817–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Abelairas, M.; García-Torreiro, M.; Lú-Chau, T.; Lema, J.M.; Steinbüchel, A. Comparison of several methods for the separation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) from Cupriavidus necator H16 cultures. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 93, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunasundari, B. Isolation and recovery of microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Express Polym. Lett. 2011, 5, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquel, N.; Lo, C.-W.; Wei, Y.-H.; Wu, H.-S.; Wang, S.S. Isolation and purification of bacterial poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates). Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 39, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Dong, Q.L.; Yu, J.G.; Jiao, F.P. Extraction of Tryptophan enantiomers by aqueous two-phase systems of ethanol and (NH4)2SO4. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Kim, J.W.; Peeples, T.L. Amylase partitioning and extractive bioconversion of starch using thermoseparating aqueous two-phase systems. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 93, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.S.; Tan, C.P.; Mokhtar, M.N.; Ibrahim, S.; Ariff, A.; Ooi, C.W.; Ling, T.C. Recovery of Bacillus cereus cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and recycling of phase components in an aqueous two-phase system using thermo-separating polymer. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 89, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Trasviña, C.; González-Valdez, J.; Mayolo-Deloisa, K.; Rito-Palomares, M. Impact of aqueous two-phase system design parameters upon the in situ refolding and recovery of invertase. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembczyński, R.; Białas, W.; Jankowski, T. Partitioning of lysozyme in aqueous two-phase systems containing ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer and potassium phosphates. Food Bioprod. Process. 2013, 91, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiendahl, M.; Oelmeier, S.A.; Dismer, F. Hubbuch, J. High-throughput screening-based selection and scale-up of aqueous two-phase systems for pDNA purification. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 3197–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydoğan, Ö.; Bayraktar, E.; Mehmetoğlu, Ü.; Kaeding, T.; Zeng, A.P. Selection and optimization of an aqueous two-phase system for the recovery of 1,3-propandiol from fermentation broth. Eng. Life Sci. 2010, 10, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V.C.; Hasmann, F.A.; Converti, A.; Pessoa, A. Liquid–liquid extraction by mixed micellar systems: A new approach for clavulanic acid recovery from fermented broth. Biochem. Eng. J. 2011, 56, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.A. Review of the applications of neural networks in chemical process control: Simulation and online implementation. Artif. Intell. Eng. 1999, 13, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadlou, A.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Ebrahimzadeh Mousavi, M.; Ehsani, M.R.; Javanmard, M.; Sheehan, D. Response surface optimization of an artificial neural network for predicting the size of re-assembled casein micelles. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2009, 68, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Medeiros e Silva, G.M.; Viana Marques, D.A.; Porto, T.S.; Filho, J.L.L.; Teixeira, J.A.C.; Pessoa-Júnior, A.; Porto, A.L.F. Extraction of fibrinolytic proteases from Streptomyces sp. DPUA1576 using PEG-phosphate aqueous two-phase systems. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2013, 339, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divyashree, M.S.; Shamala, T.R.; Rastogi, N.K. Isolation of polyhydroxyalkanoate from hydrolyzed cells of Bacillus flexus using aqueous two-phase system containing polyethylene glycol and phosphate. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2009, 14, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.K. Extraction and Purification of Green Polymes Using Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction (ATPE). Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Nottingham Malaysia Campus, Broga, Malaysia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Akaraonye, E.; Moreno, C.; Knowles, J.C.; Keshavarz, T.; Roy, I. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production by Bacillus cereus SPV using sugarcane molasses as the main carbon source. Biotechnol. J. 2012, 7, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, F.A.N.; Lona, L.M.F.L. Neural network applications in polymerization processes. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2005, 22, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, R.A.M.; Ahmad, Z. Neural network based soft sensor for prediction of biopolycaprolactone molecular weight using bootstrap neural network technique. In Proceedings of the 2011 3rd Conference on Data Mining and Optimization (DMO), Putrajaya, Malaysia, 28–29 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Developing robust non-linear models through bootstrap aggregated neural networks. Neurocomputing 1999, 25, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.A.; Júnior, A.C.V.F.; Filho, J.L.L.; Converti, A.; Marques, D.A.V.; Carneiro-da-Cunha, M.G.; Porto, A.L.F. Two-phase partitioning and partial characterization of a collagenase from Penicillium aurantiogriseum URM4622: Application to collagen hydrolysis. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 75, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baş, D.; Boyacı, İ.H. Modeling and optimization II: Comparison of estimation capabilities of response surface methodology with artificial neural networks in a biochemical reaction. J. Food Eng. 2007, 78, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammoun, R.; Chouayekh, H.; Abid, H.; Naili, B.; Bejar, S. Purification of CBS 819.72 α-amylase by aqueous two-phase systems: Modelling using Response Surface Methodology. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 46, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Lu, W.; Wang, W.; Guo, Q.; Yang, Y. The optimization of aqueous two-phase extraction of lysozyme from crude hen egg white using response surface methodology. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, C.S.; Porto, T.S.; Nascimento, K.S.; Teixeira, E.H.; Cavada, B.S.; Lima-Filho, J.L.; Porto, A.L.F. Partition of lectin from Canavalia grandiflora Benth in aqueous two-phase systems using factorial design. Biochem. Eng. J. 2011, 53, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Run | X1 (wt %) | X2 (wt %) | X3 | X4 (mM) | Kpa | Yield (%) | PF (fold) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0.814 | 24.6 | 0.93 |
| 2 | 8 | 10 | 8 | 0 | 0.646 | 21.4 | 0.93 |
| 3 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 3.371 | 57.4 | 1.35 |
| 4 | 8 | 18 | 8 | 0 | 0.431 | 25.5 | 1.07 |
| 5 | 8 | 18 | 8 | 100 | 0.402 | 24.8 | 1.04 |
| 6 | 15 | 18 | 10 | 0 | 16.547 | 93.9 | 1.46 |
| 7 | 15 | 18 | 10 | 100 | 5.585 | 85.5 | 1.48 |
| 8 | 15 | 10 | 8 | 0 | 1.554 | 38.3 | 0.95 |
| 9 | 8 | 10 | 8 | 100 | 0.525 | 16.8 | 0.67 |
| 10 | 15 | 18 | 8 | 100 | 12.291 | 92.5 | 1.54 |
| 11 | 15 | 18 | 8 | 0 | 8.047 | 86.8 | 1.52 |
| 12 | 15 | 10 | 8 | 100 | 1.314 | 32.9 | 1.22 |
| 13 | 8 | 18 | 10 | 0 | 0.512 | 30.1 | 0.96 |
| 14 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 100 | 2.322 | 45.5 | 1.04 |
| 15 | 8 | 18 | 10 | 100 | 0.369 | 22.7 | 1.04 |
| 16 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 100 | 0.817 | 24.6 | 1.21 |
| Source | Sum of squares | Degree of freedom | Mean square | F value | Prob>F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 12070.8 | 14 | 862.2 | 1007.687 | 0.0247 |
| X1 | 7323.1 | 1 | 7323.1 | 8558.750 | 0.0069 |
| X2 | 2507.5 | 1 | 2507.5 | 2930.613 | 0.0118 |
| X3 | 128.3 | 1 | 128.3 | 149.897 | 0.0519 |
| X4 | 66.8 | 1 | 66.8 | 78.107 | 0.0717 |
| X1X2 | 1783.0 | 1 | 1783.0 | 2083.799 | 0.0139 |
| X1X3 | 20.9 | 1 | 20.9 | 24.462 | 0.1270 |
| X1X4 | 3.3 | 1 | 3.3 | 3.893 | 0.2986 |
| X2X3 | 100.5 | 1 | 100.5 | 117.459 | 0.0586 |
| X2X4 | 7.7 | 1 | 7.7 | 9.000 | 0.2048 |
| X3X4 | 32.2 | 1 | 32.2 | 37.640 | 0.1029 |
| X1X2X3 | 33.4 | 1 | 33.4 | 38.978 | 0.1011 |
| X1X2X4 | 20.5 | 1 | 20.5 | 23.931 | 0.1284 |
| X1X3X4 | 21.4 | 1 | 21.4 | 25.000 | 0.1257 |
| X2X3X4 | 22.3 | 1 | 22.3 | 26.093 | 0.1231 |
| Residual | 0.9 | 1 | 0.9 | ||
| Cor Total | 12071.7 | 15 | |||
| R2 | 0.9999 | ||||
| R2adj | 0.999 | ||||
| R2pred | 0.982 |
| Source | Sum of squares | Degree of freedom | Mean square | F value | Prob>F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 3.568 | 9 | 0.396 | 221.5 | <0.0001 |
| X1 | 2.891 | 1 | 2.891 | 1615.4 | <0.0001 |
| X3 | 0.052 | 1 | 0.0516 | 28.8 | 0.0015 |
| X4 | 0.033 | 1 | 0.0332 | 18.5 | 0.0057 |
| X1X2 | 0.516 | 1 | 0.516 | 288.5 | <0.0001 |
| X2X3 | 0.046 | 1 | 0.0460 | 25.7 | 0.0022 |
| X2X3X4 | 0.018 | 1 | 0.0179 | 10.0 | 0.0265 |
| Residual | 0.011 | 6 | 0.0018 | ||
| Cor Total | 3.579 | 15 | |||
| R2 | 0.997 | ||||
| R2adj | 0.992 | ||||
| R2pred | 0.979 |
| Source | Sum of squares | Degree of freedom | Mean square | F value | Prob>F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 0.955 | 6 | 0.159 | 42.6 | <0.0001 |
| X1 | 0.459 | 1 | 0.459 | 122.9 | <0.0001 |
| X2 | 0.205 | 1 | 0.205 | 54.8 | <0.0001 |
| X1X2 | 0.072 | 1 | 0.071556 | 19.2 | 0.0018 |
| X2X3 | 0.061 | 1 | 0.061256 | 16.4 | 0.0029 |
| X1X3X4 | 0.095 | 1 | 0.094556 | 25.3 | 0.0007 |
| X1X2X3X4 | 0.064 | 1 | 0.063756 | 17.1 | 0.0026 |
| Residual | 0.034 | 9 | 0.003734 | ||
| Cor Total | 0.988 | 15 | |||
| R2 | 0.966 | ||||
| R2adj | 0.943 | ||||
| R2pred | 0.893 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leong, Y.K.; Chang, C.-K.; Arumugasamy, S.K.; Lan, J.C.-W.; Loh, H.-S.; Muhammad, D.; Show, P.L. Statistical Design of Experimental and Bootstrap Neural Network Modelling Approach for Thermoseparating Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction of Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Polymers 2018, 10, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020132
Leong YK, Chang C-K, Arumugasamy SK, Lan JC-W, Loh H-S, Muhammad D, Show PL. Statistical Design of Experimental and Bootstrap Neural Network Modelling Approach for Thermoseparating Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction of Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Polymers. 2018; 10(2):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020132
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeong, Yoong Kit, Chih-Kai Chang, Senthil Kumar Arumugasamy, John Chi-Wei Lan, Hwei-San Loh, Dinie Muhammad, and Pau Loke Show. 2018. "Statistical Design of Experimental and Bootstrap Neural Network Modelling Approach for Thermoseparating Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction of Polyhydroxyalkanoates" Polymers 10, no. 2: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020132
APA StyleLeong, Y. K., Chang, C.-K., Arumugasamy, S. K., Lan, J. C.-W., Loh, H.-S., Muhammad, D., & Show, P. L. (2018). Statistical Design of Experimental and Bootstrap Neural Network Modelling Approach for Thermoseparating Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction of Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Polymers, 10(2), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020132








