Direct Growth of a Polypyrrole Aerogel on Hollow CuS Hierarchical Microspheres Yields Particles with Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Hollow Hierarchical CuS Microspheres
2.3. Synthesis of Core–Shell Structured CuS@PPy Microspheres
2.4. Characterization and Measurement
3. Results
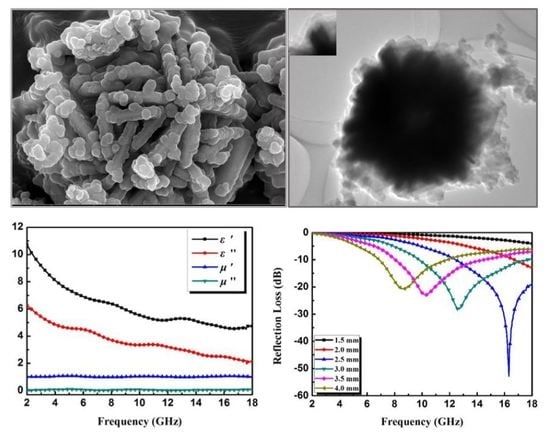
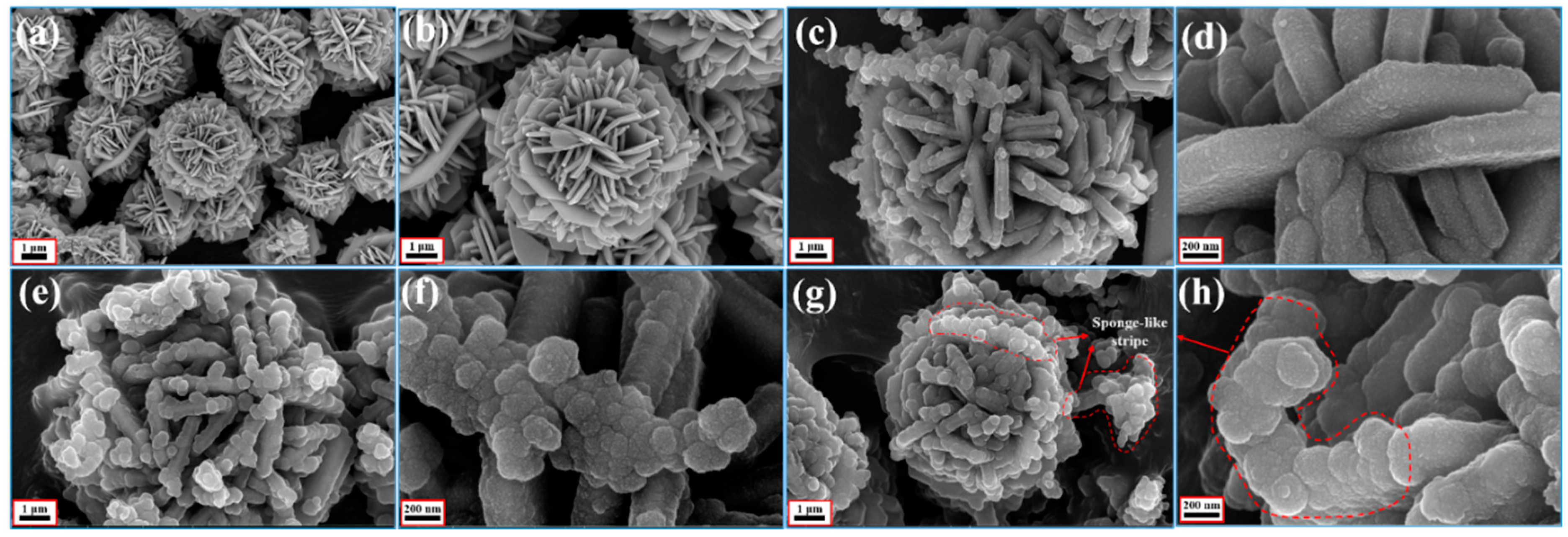
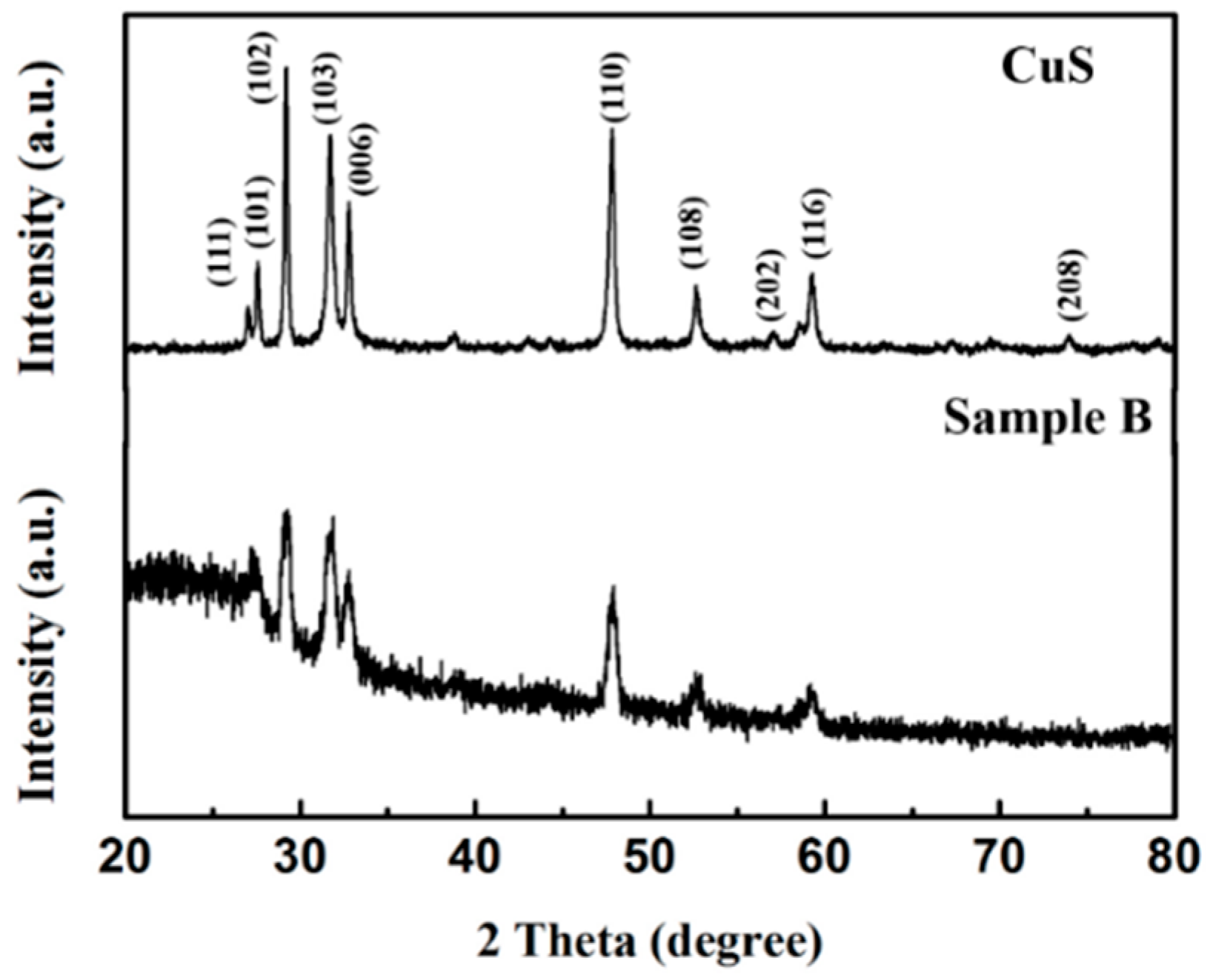
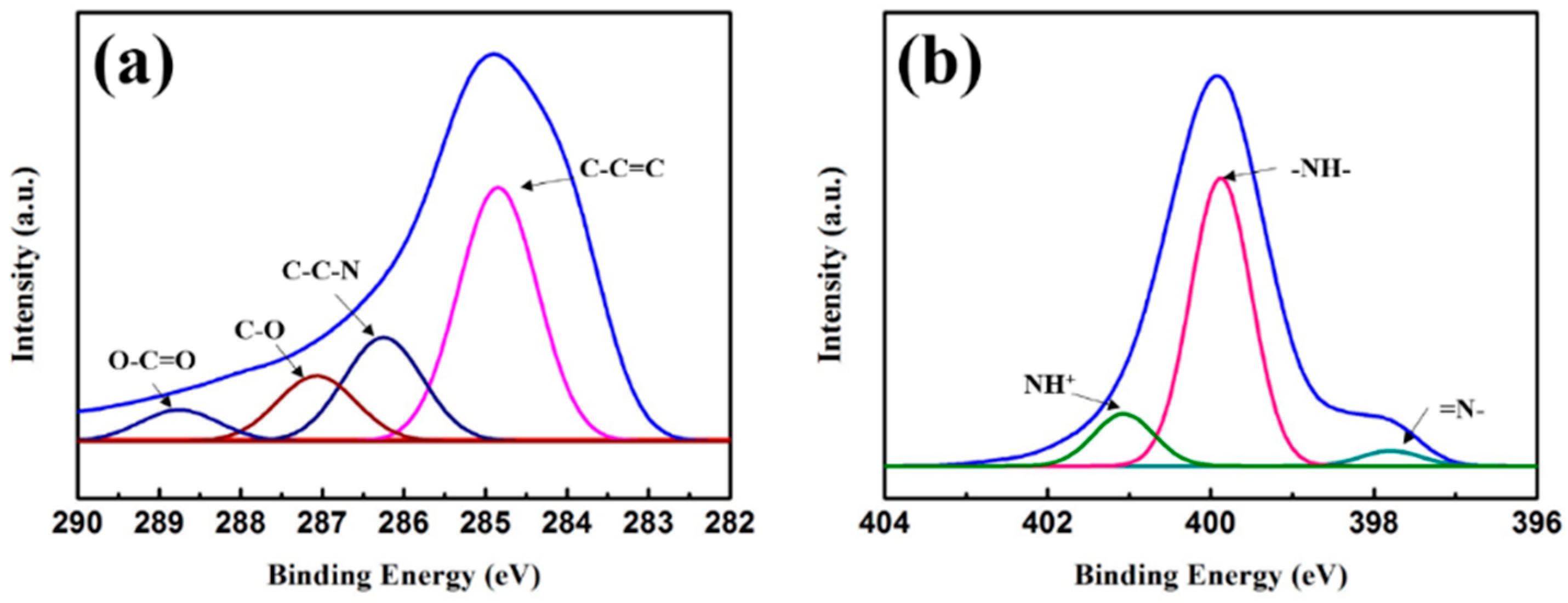
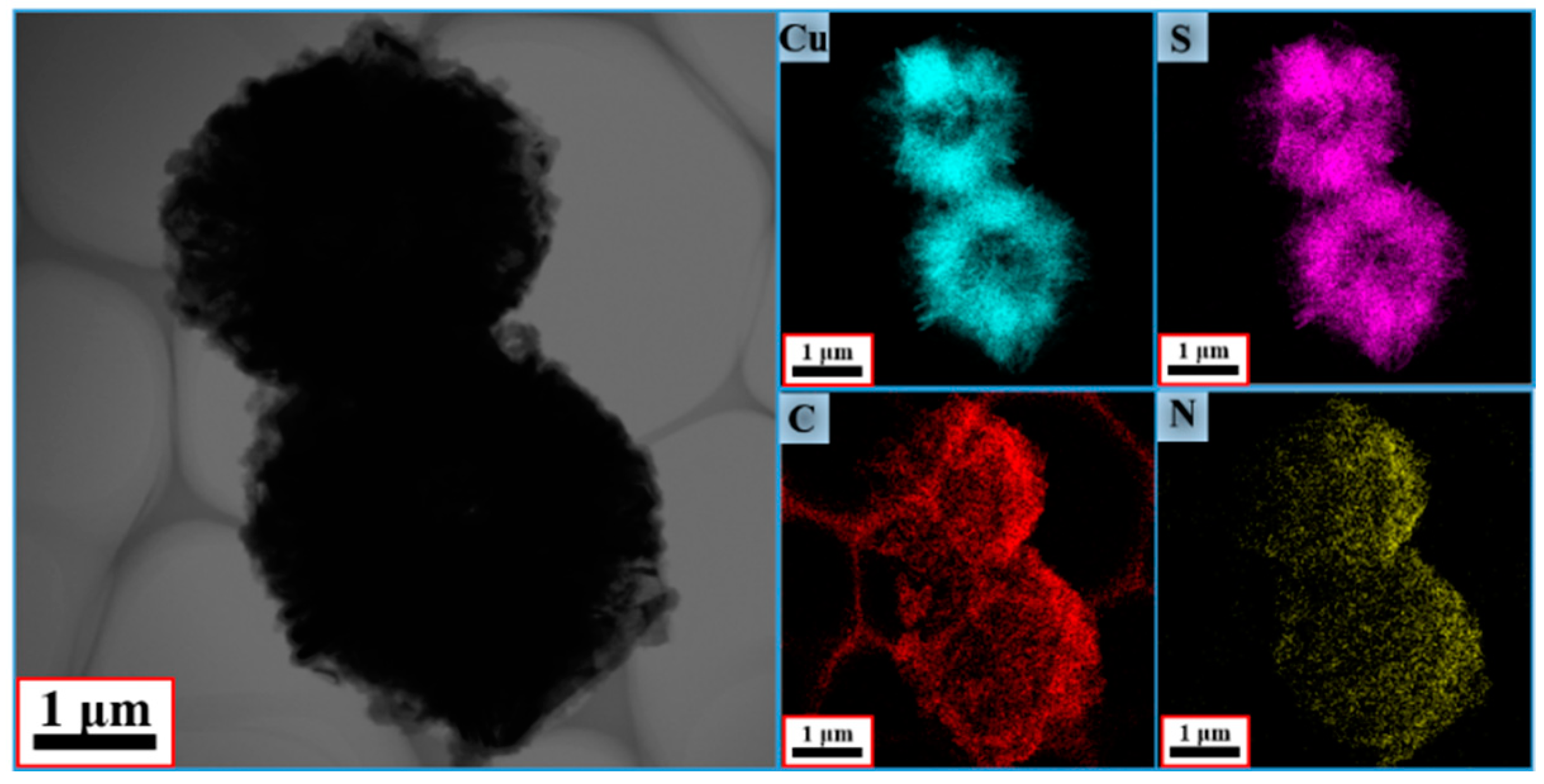
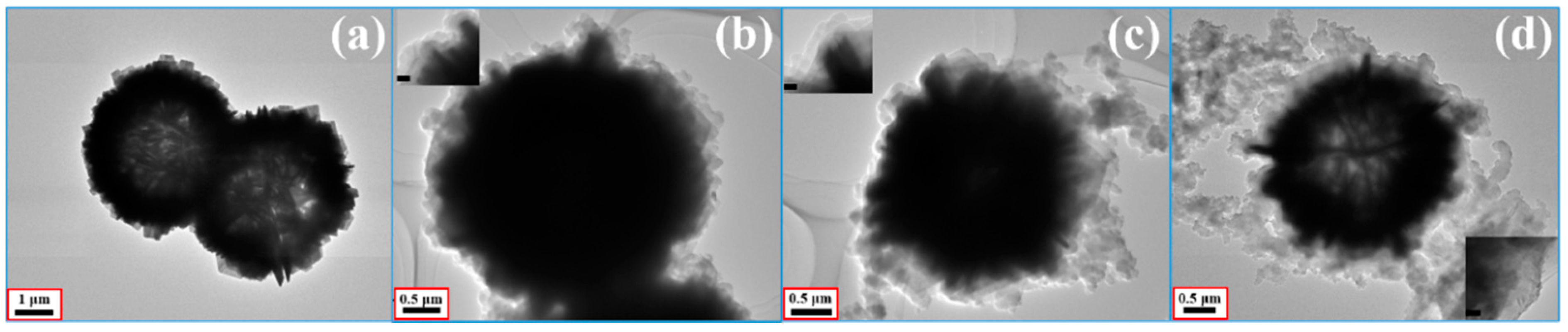
3.1. Sample Characterization
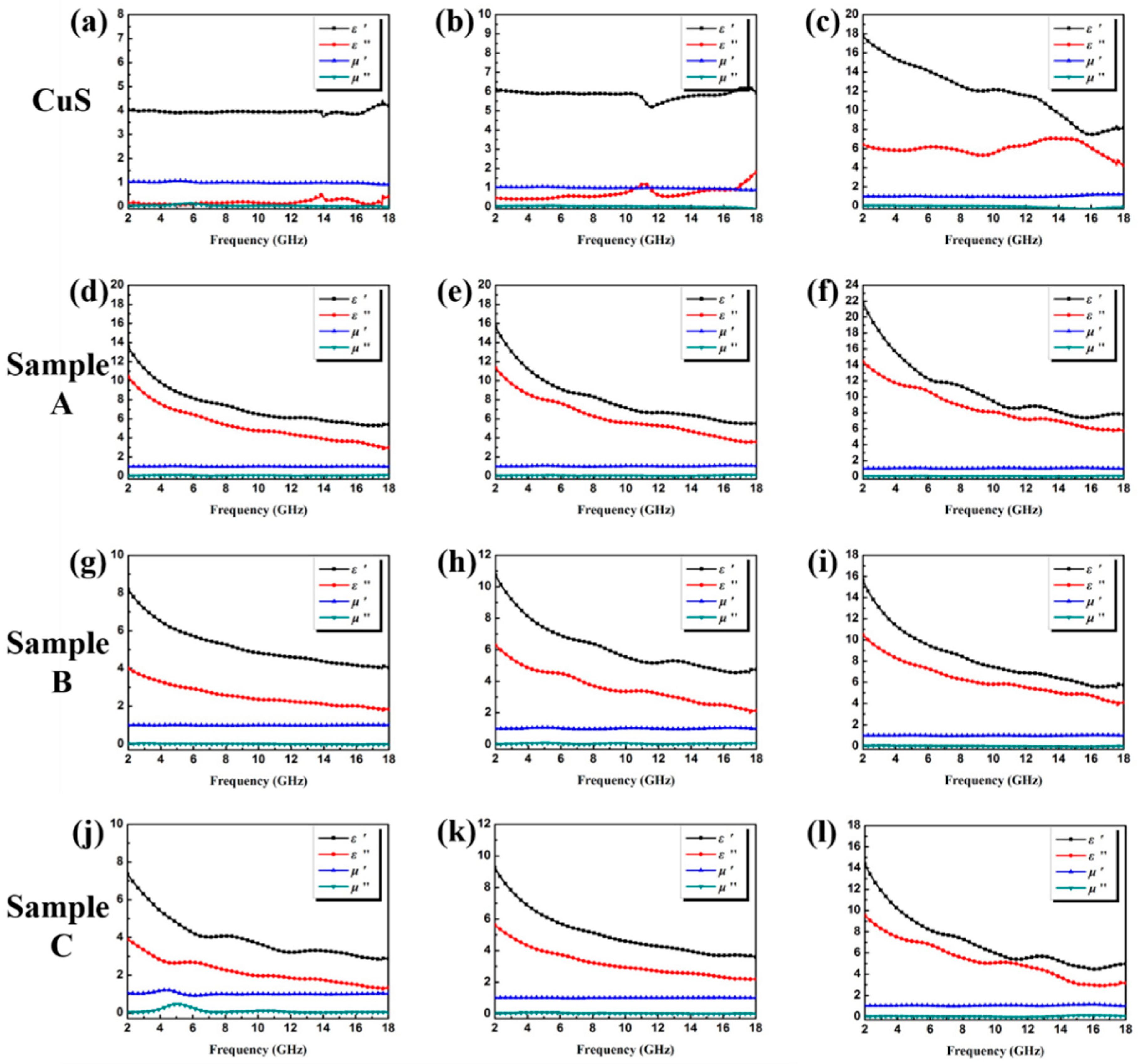
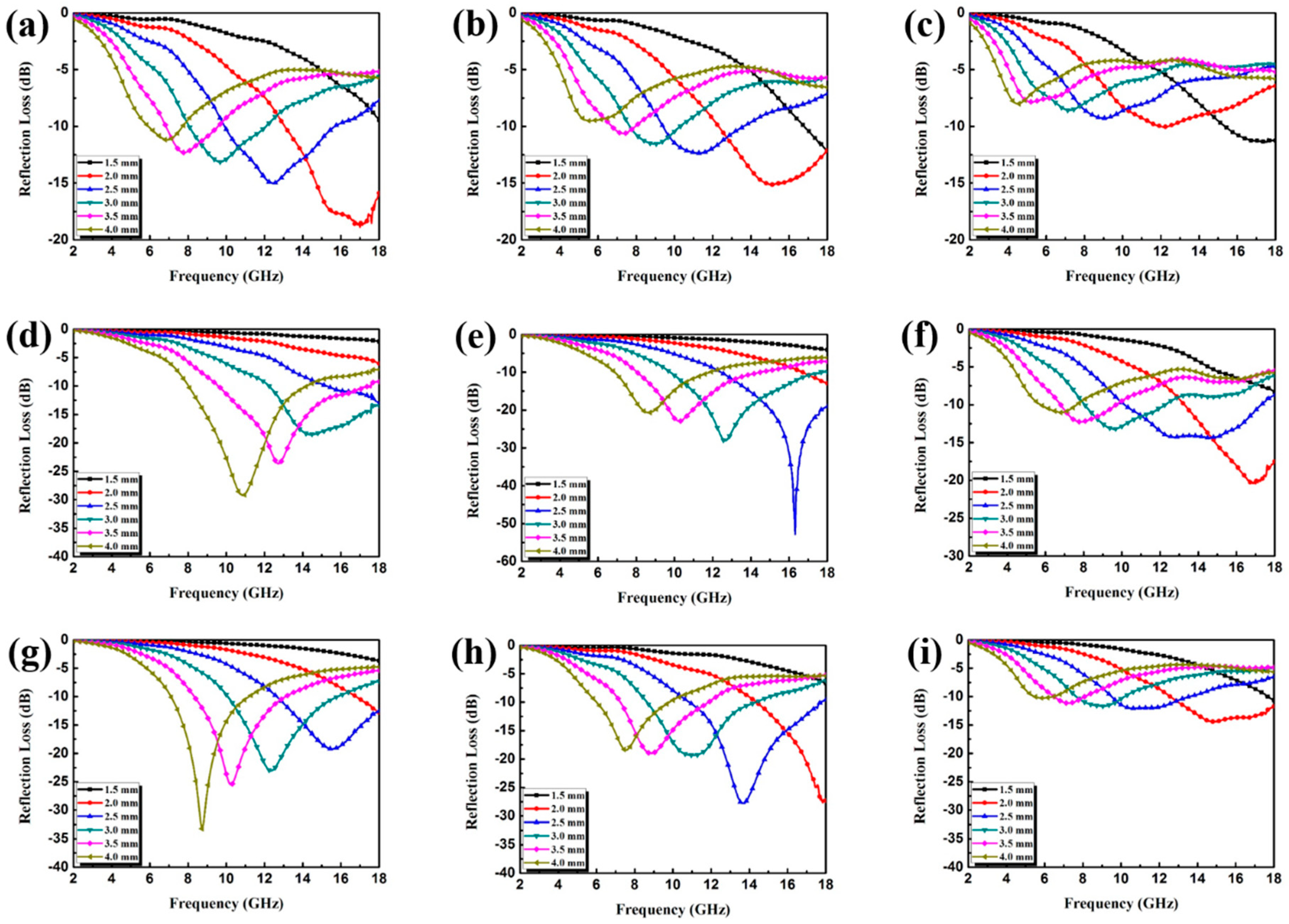
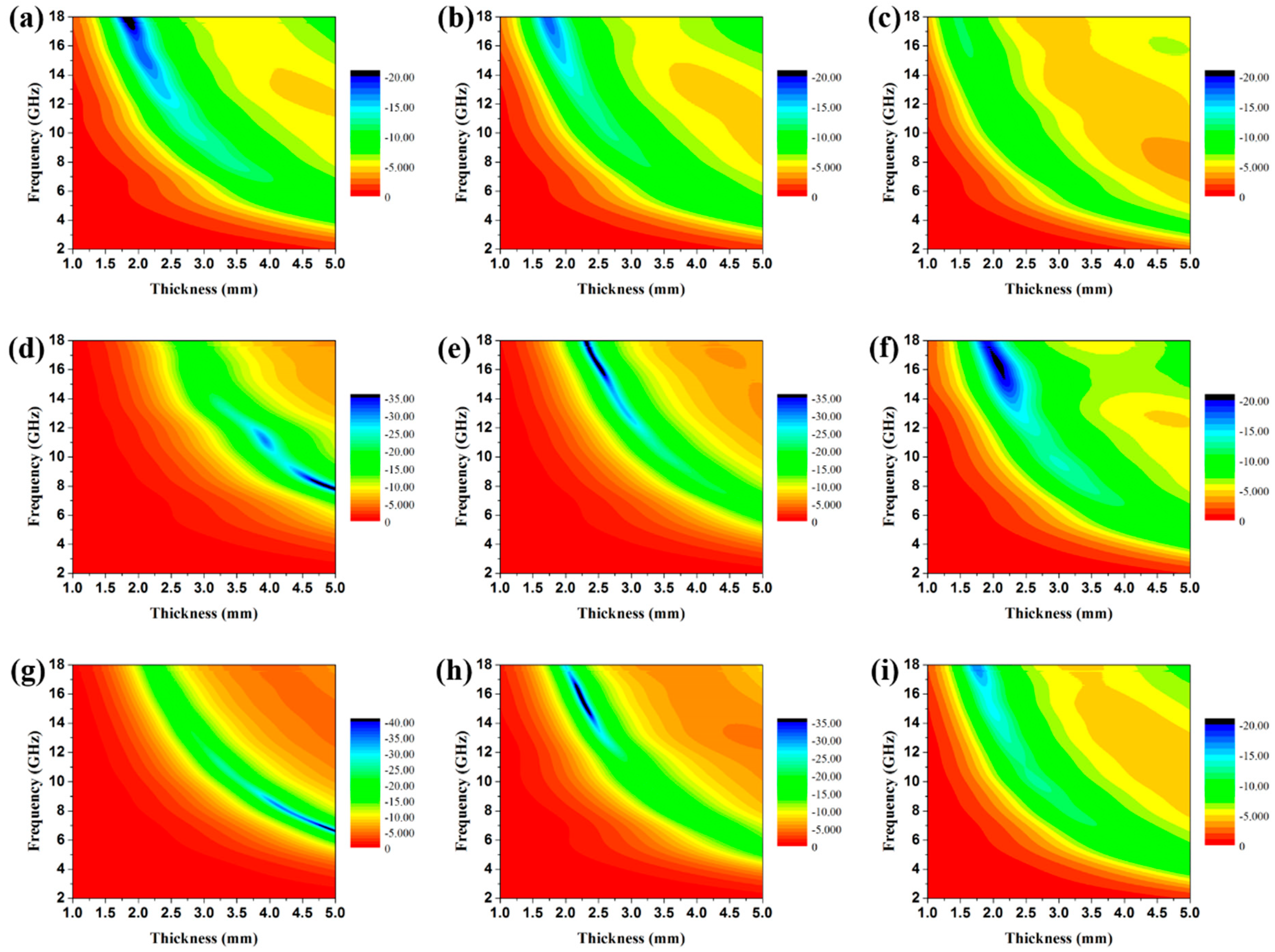
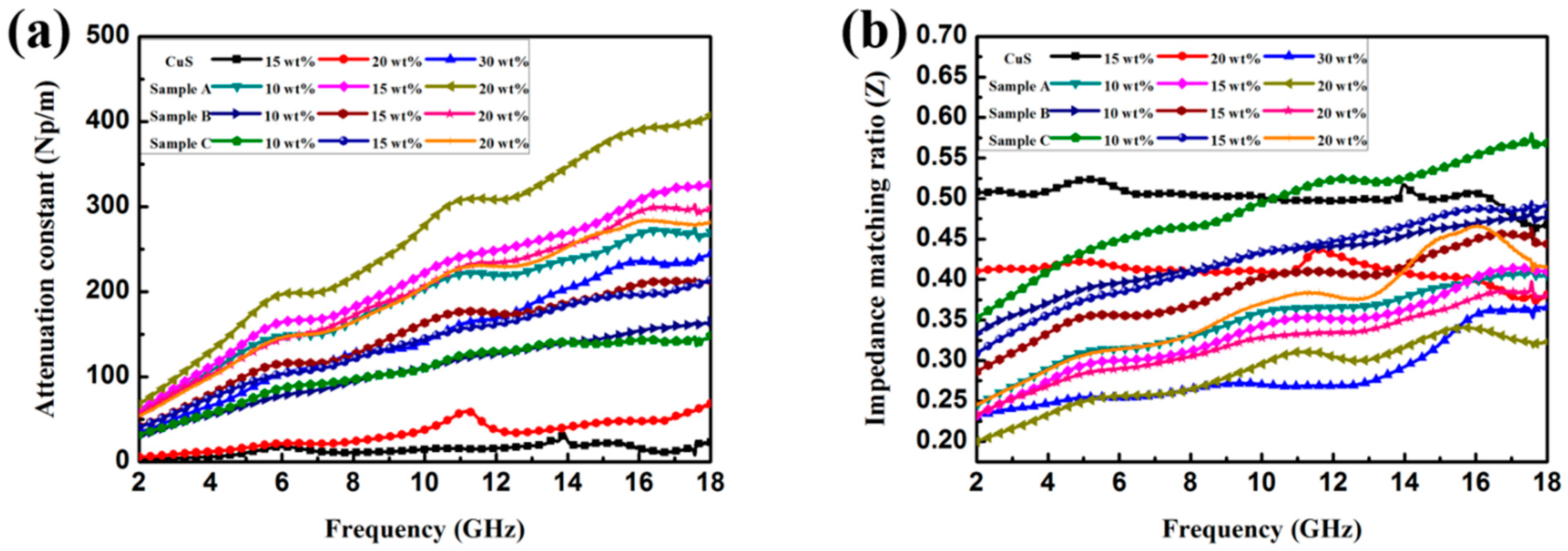
3.2. Electromagnetic Absorption Property
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Green, M.; Tian, L.; Xiang, P.; Murowchick, J.; Tan, X.; Chen, X. FeP nanoparticles: A new material for microwave absorption. Mater. Chem. Front. 2018, 2, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Liu, Z.; You, W.; Zhao, X.; Che, R. Janus-like Fe3O4/PDA vesicles with broadening microwave absorption bandwidth. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 7790–7796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yang, J.; Pu, B.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Niu, X. Excellent microwave absorption of lead halide perovskites with high stability. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 4201–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, B.; Liu, W.; Liang, X.; Ji, G. Tailoring the input impedance of FeCo/C composites with efficient broadband absorption. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 14926–14933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Yang, Q.; Liao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Fu, Y. A novel 3D silver nanowires@polypyrrole sponge loaded with water giving excellent microwave absorption properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 352, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiang, L.; Wei, W.; An, J.; He, J.; Gong, C.; Hou, Y. Efficient and Lightweight Electromagnetic Wave Absorber Derived from Metal Organic Framework-Encapsulated Cobalt Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 42102–42110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, M.; Lü, X.; Xie, A.; Xu, W.; Rong, X.; Wu, G. The synthesis of three-dimensional (3D) polydopamine-functioned carbonyl iron powder@polypyrrole (CIP@PPy) aerogel composites for excellent microwave absorption. Synth. Met. 2015, 210, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.-Z.; Wang, G.-S.; Wu, Y.; Yue, Y.-H.; Wu, J.-T.; Lu, C.; Guo, L. Bioinspired design and assembly of platelet reinforced polymer films with enhanced absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 5516–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Huang, Y.; Yan, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Construction of CuS Nanoflakes Vertically Aligned on Magnetically Decorated Graphene and Their Enhanced Microwave Absorption Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5536–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Chen, K.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Jin, Y. Fabrication and microwave absorbing properties of (Z-type barium ferrite/silica)@polypyrrole composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.; Wang, G.; Huang, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Yu, L.; Peng, X.; Qin, Y. Uniform Fe3O4 coating on flower-like ZnO nanostructures by atomic layer deposition for electromagnetic wave absorption. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 18804–18809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.-F.; Wang, G.-S.; Yue, Y.-H. Fabrication of Fe3O4@SiO2@RGO nanocomposites and their excellent absorption properties with low filler content. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 71718–71723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xie, X.; Pang, Y.; Kobayashi, S. Co/C nanoparticles with low graphitization degree: A high performance microwave-absorbing material. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, R.; Du, Y.; Chen, D.; Ma, W.; Wang, Y.; Xu, P.; Ma, J.; Zhao, H.; Han, X. Electromagnetic functionalized Co/C composites by in situ pyrolysis of metal-organic frameworks (ZIF-67). J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 681, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Liu, J.; Lei, M.; Wang, W.; Lu, Y.; Yang, L.; Yang, Q.; Liu, G.; Su, N. Self-Assembly of Parallelly Aligned NiO Hierarchical Nanostructures with Ultrathin Nanosheet Subunits for Electrochemical Supercapacitor Applications. ACS Appl. Materi. Interfaces 2016, 8, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, G.; Or, S.W.; Sun, Y. Fe/amorphous SnO2 core–shell structured nanocapsules for microwave absorptive and electrochemical performance. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 51389–51394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Shao, G.; Fan, B.; Zhao, W.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, R. ZnS nanowall coated Ni composites: Facile preparation and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 61219–61225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-H.; Tao, R.; Luo, P.; Shu, X.; Ban, G.-D. Preparation and microwave absorbing property of carbon fiber/polyurethane radar absorbing coating. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 46060–46068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Chen, Z.; Liao, X.; Liu, C.; Shi, B. Ferromagnetic hierarchical carbon nanofiber bundles derived from natural collagen fibers: Truly lightweight and high-performance microwave absorption materials. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 10146–10153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Lai, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Towards efficient microwave absorption: Intrinsic heterostructure of fluorinated SWCNTs. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 11847–11855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, E.; Akiba, E. Electromagnetic absorbing materials using nonwoven fabrics coated with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2014, 78, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, B.; Liang, X.; Yi, H.; Gong, H.; Ji, G.; Chen, J.; Xu, G.; Du, Y. Constructing hierarchical porous nanospheres for versatile microwave response approaches: The effect of architectural design. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 14264–14269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arief, I.; Biswas, S.; Bose, S. FeCo-Anchored Reduced Graphene Oxide Framework-Based Soft Composites Containing Carbon Nanotubes as Highly Efficient Microwave Absorbers with Excellent Heat Dissipation Ability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 19202–19214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, P.; Miao, J.; Cao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Xie, A.; Shen, Y. Facile synthesis and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties of flower-like porous RGO/PANI/Cu2O nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 13078–13090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Huang, D.; Lv, R.; Bai, Y.; Huang, Z.-H.; Gu, J.; Kang, F. Three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide powder for efficient microwave absorption in the S-band (2–4 GHz). RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 25773–25779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Sun, M.; Jiang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, F.; Xie, A.; Dong, W. A core–shell polypyrrole@silicon carbide nanowire (PPy@SiC) nanocomposite for the broadband elimination of electromagnetic pollution. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 43056–43059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, N.; Yan, Z.; Deng, L.; He, J.; Hou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, G. Cobalt/polypyrrole nanocomposites with controllable electromagnetic properties. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 7189–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, B.; Liang, X.; Xu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Ji, G.; Du, Y. A permittivity regulating strategy to achieve high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers with compatibility of impedance matching and energy conservation. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yu, Z.; Ji, G.; Lin, X.; Lv, H.; Du, Y. Reduction synthesis of FexOy@SiO2 core–shell nanostructure with enhanced microwave-absorption properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 602, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Gu, A.; Wei, Y.; Fang, B. CuS nanotubes for ultrasensitive nonenzymatic glucose sensors. Chem. Commun. 2008, 45, 5945–5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinpour, Z.; Alemi, A.; Khandar, A.A.; Zhao, X.; Xie, Y. A controlled solvothermal synthesis of CuS hierarchical structures and their natural-light-induced photocatalytic properties. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 5470–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, S.; Rong Dai, Z.; Wang, Z.L. The crystal structure and growth direction of Cu2S nanowire arrays fabricated on a copper surface. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001, 3, 3750–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.-H.; Qu, P.; Guan, X.; Wang, G.-S. Hydrothermal synthesis of hierarchical CuS/ZnS nanocomposites and their photocatalytic and microwave absorption properties. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 15579–15585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Guo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Su, T.; Ma, C.; Zhang, R. Constructing hierarchical hollow CuS microspheres via a galvanic replacement reaction and their use as wide-band microwave absorbers. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 2178–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Wu, F.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, K.; Sun, M.; Wang, M. Chiral induced synthesis of helical polypyrrole (PPy) nano-structures: A lightweight and high-performance material against electromagnetic pollution. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 2175–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Ma, G.; Sun, K.; Mu, J.; Wang, H.; Lei, Z. High-performance supercapacitor based on multi-structural CuS@polypyrrole composites prepared by in situ oxidative polymerization. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 3303–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pang, Y.; Kikuchi, H.; Liu, T. The synergistic effects of carbon coating and micropore structure on the microwave absorption properties of Co/CoO nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 30507–30514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.J.; Hou, Z.L.; Song, W.L.; Liu, X.D.; Cao, W.Q.; Shao, X.H.; Cao, M.S. Unusual continuous dual absorption peaks in Ca-doped BiFeO3 nanostructures for broadened microwave absorption. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 10415–10424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y. Electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of Fe–Sr0.8La0.2Fe11.8Co0.2O19 shell-core composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 2177–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-H.; Wang, H.-W.; Kan, S.-W.; Shen, M.-Z.; Wei, Y.-M.; Chen, S.-Y. Microwave absorbing materials using Ag–NiZn ferrite core–shell nanopowders as fillers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 284, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.L.; Wu, H.Y.; Lu, M.M.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhu, C.L.; Gao, P.; Cao, M.S.; Li, C.Y.; Ouyang, Q.Y. Quaternary nanocomposites consisting of graphene, Fe3O4@Fe core@shell, and ZnO nanoparticles: Synthesis and excellent electromagnetic absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6436–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Kuang, Q.; Zheng, L. MOF-Derived Porous Co/C Nanocomposites with Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 13604–13611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Qi, X.; Cai, H.; Xie, R.; Long, L.; Bai, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Qin, S.; Zhong, W.; Du, Y. Preparation of porous Fe2O3 nanorods-reduced graphene oxide nanohybrids and their excellent microwave absorption properties. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.; Jin, S.; Li, K.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H. Metal organic framework (MOF)-derived carbonaceous Co3O4/Co microframes anchored on RGO with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances. Synth. Met. 2017, 228, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Geng, D.; Wang, Y.; An, J.; He, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z. Excellent microwave-absorption performances by matched magnetic–dielectric properties in double-shelled Co/C/polyaniline nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 40384–40392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, N.; Cui, C.; Bi, N.; Sun, Y. One pot synthesis of Fe3O4/MnO2 core–shell structured nanocomposites and their application as microwave absorbers. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24016–24022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Sun, M.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, K.; Xie, A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M. A self-assembly method for the fabrication of a three-dimensional (3D) polypyrrole (PPy)/poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) hybrid composite with excellent absorption performance against electromagnetic pollution. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Lei, X.; Ma, Y.; Tian, L.; Su, K.; Zhang, Q. Dependency of tunable microwave absorption performance on morphology-controlled hierarchical shells for core-shell Fe3O4@MnO2 composite microspheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Lv, X.; Cui, G.; Sui, M.; Sun, X.; Yu, S. Direct Growth of a Polypyrrole Aerogel on Hollow CuS Hierarchical Microspheres Yields Particles with Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Properties. Polymers 2018, 10, 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10111286
Zhang Z, Lv X, Cui G, Sui M, Sun X, Yu S. Direct Growth of a Polypyrrole Aerogel on Hollow CuS Hierarchical Microspheres Yields Particles with Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Properties. Polymers. 2018; 10(11):1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10111286
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhi, Xuliang Lv, Guangzhen Cui, Mingxu Sui, Xiaodong Sun, and Songlin Yu. 2018. "Direct Growth of a Polypyrrole Aerogel on Hollow CuS Hierarchical Microspheres Yields Particles with Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Properties" Polymers 10, no. 11: 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10111286
APA StyleZhang, Z., Lv, X., Cui, G., Sui, M., Sun, X., & Yu, S. (2018). Direct Growth of a Polypyrrole Aerogel on Hollow CuS Hierarchical Microspheres Yields Particles with Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Properties. Polymers, 10(11), 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10111286