Investigation of Conical Spinneret in Generating More Dense and Compact Electrospun Nanofibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Study
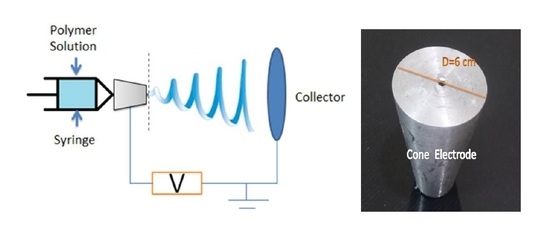
2.1. Electrospinning Process
2.2. Synthesis, Process Parameters, and Characterization of Nanofibers
3. Analytical Study
3.1. Discrete Bead Model
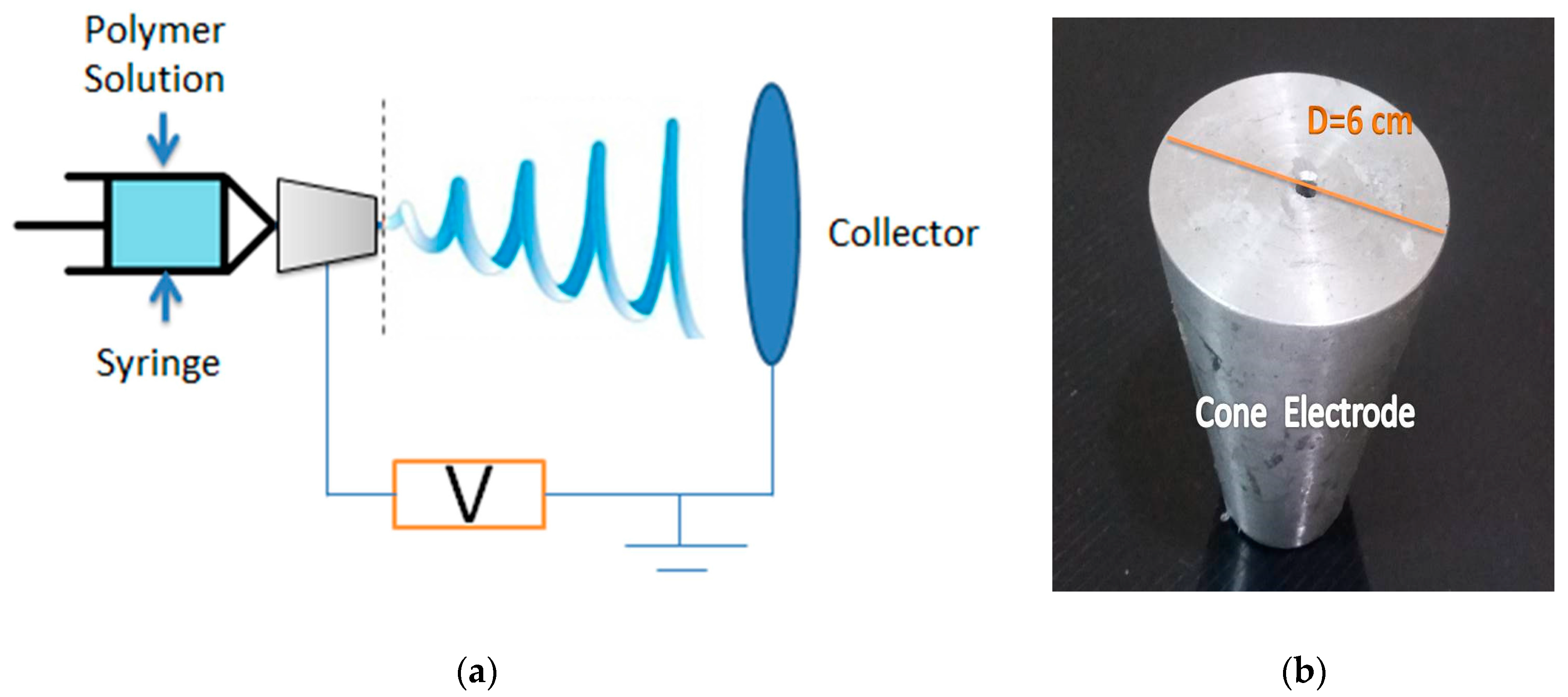
3.2. Finite Element Analysis for Electric Field Distribution
4. Results and Discussion
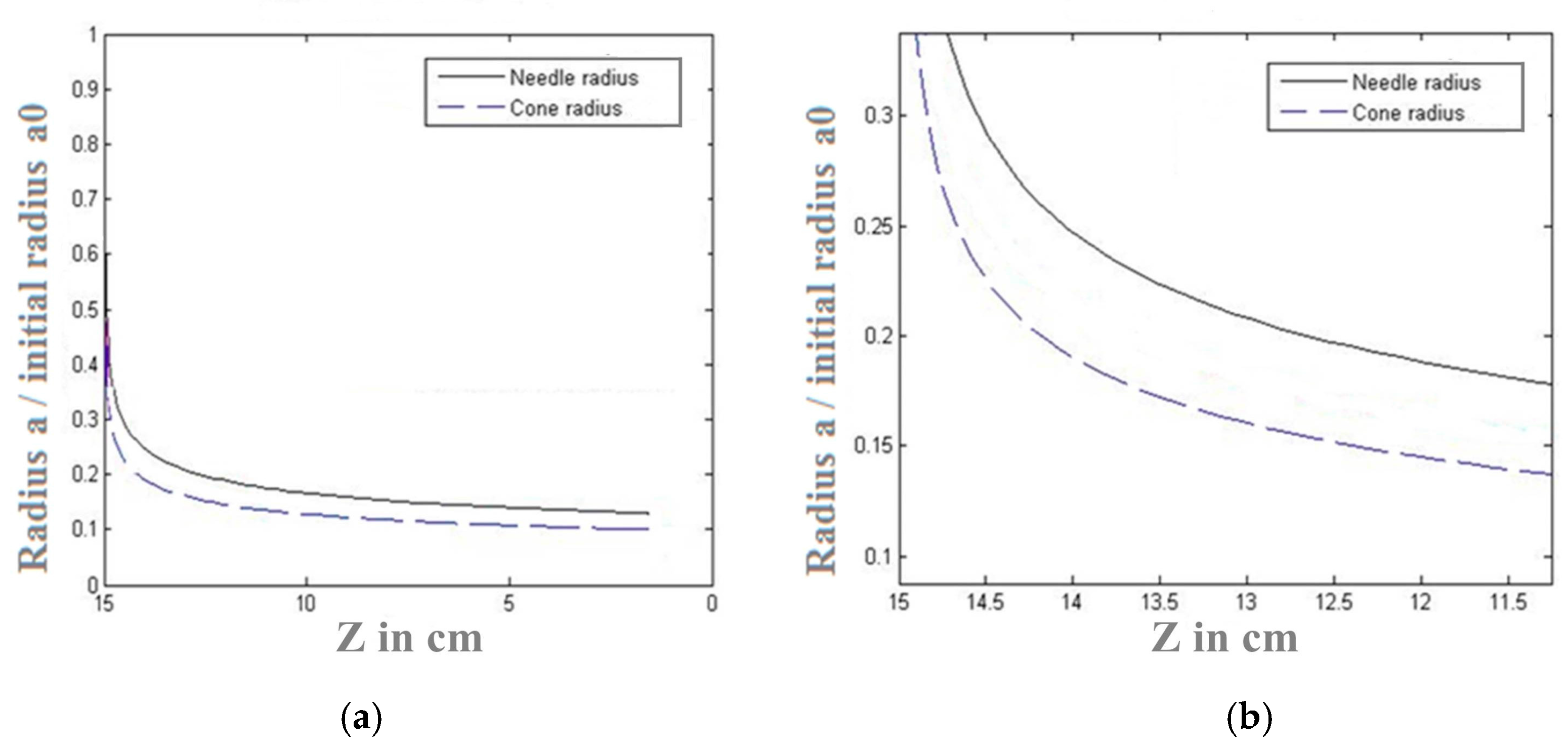
4.1. Electric Field Distribution
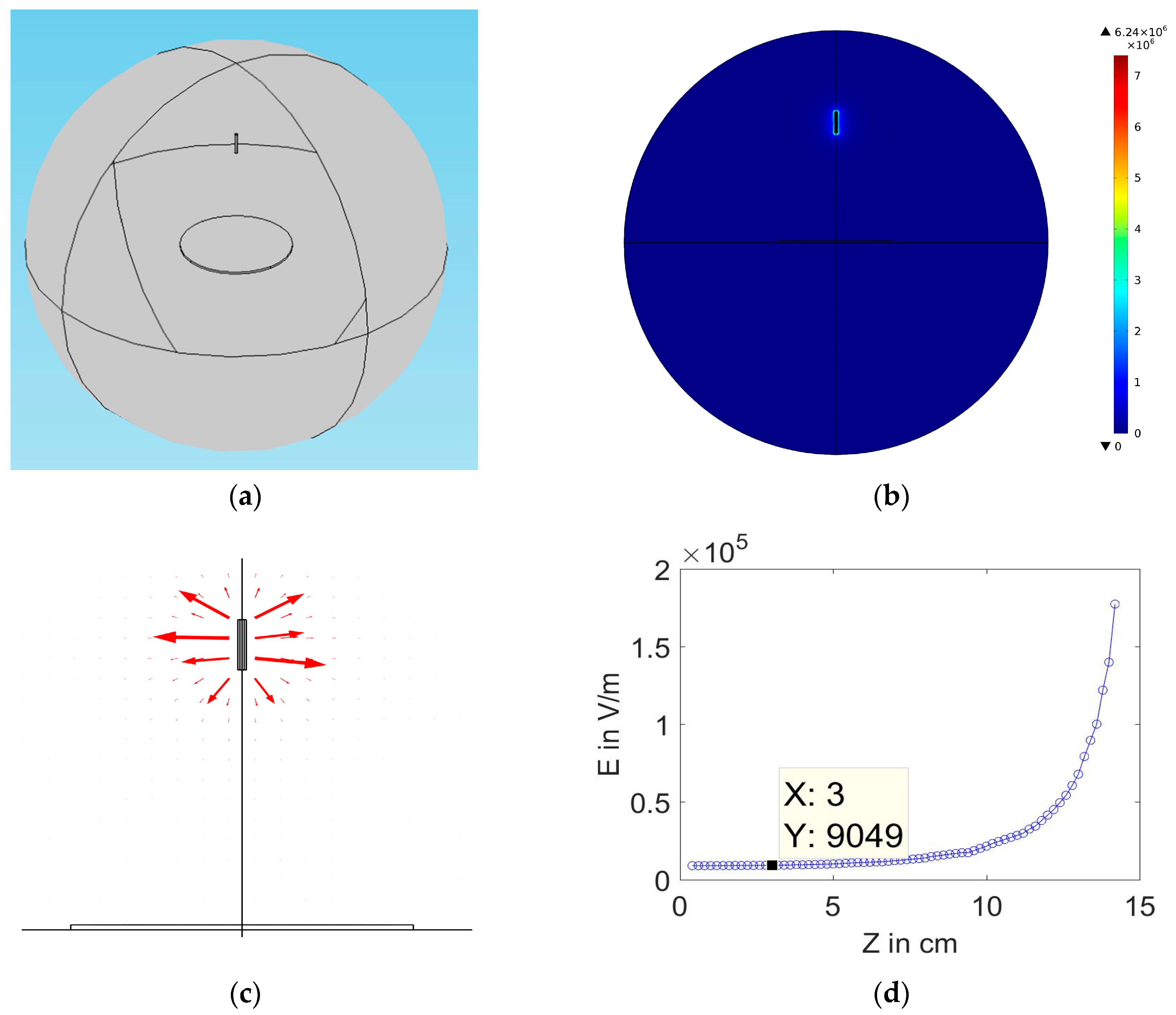
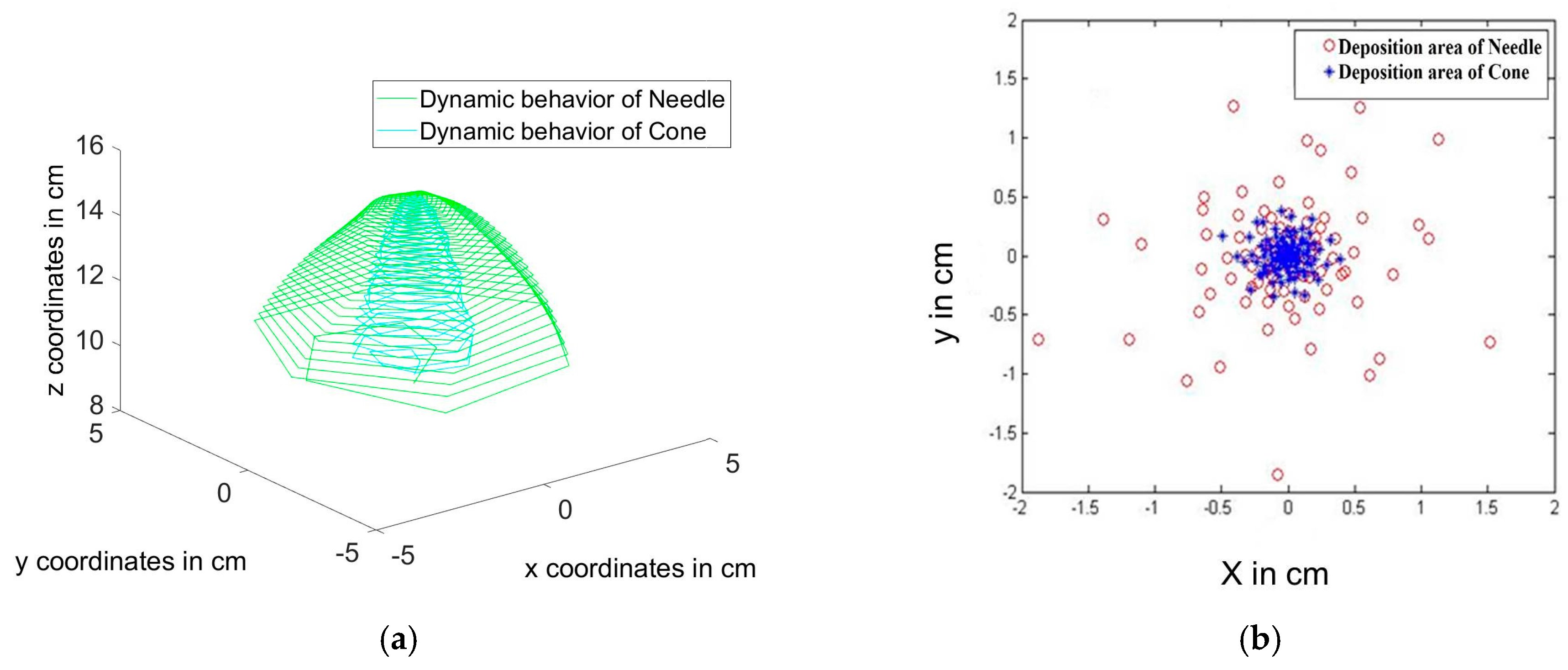
4.2. Comparison between Typical Setup and Proposed Setup
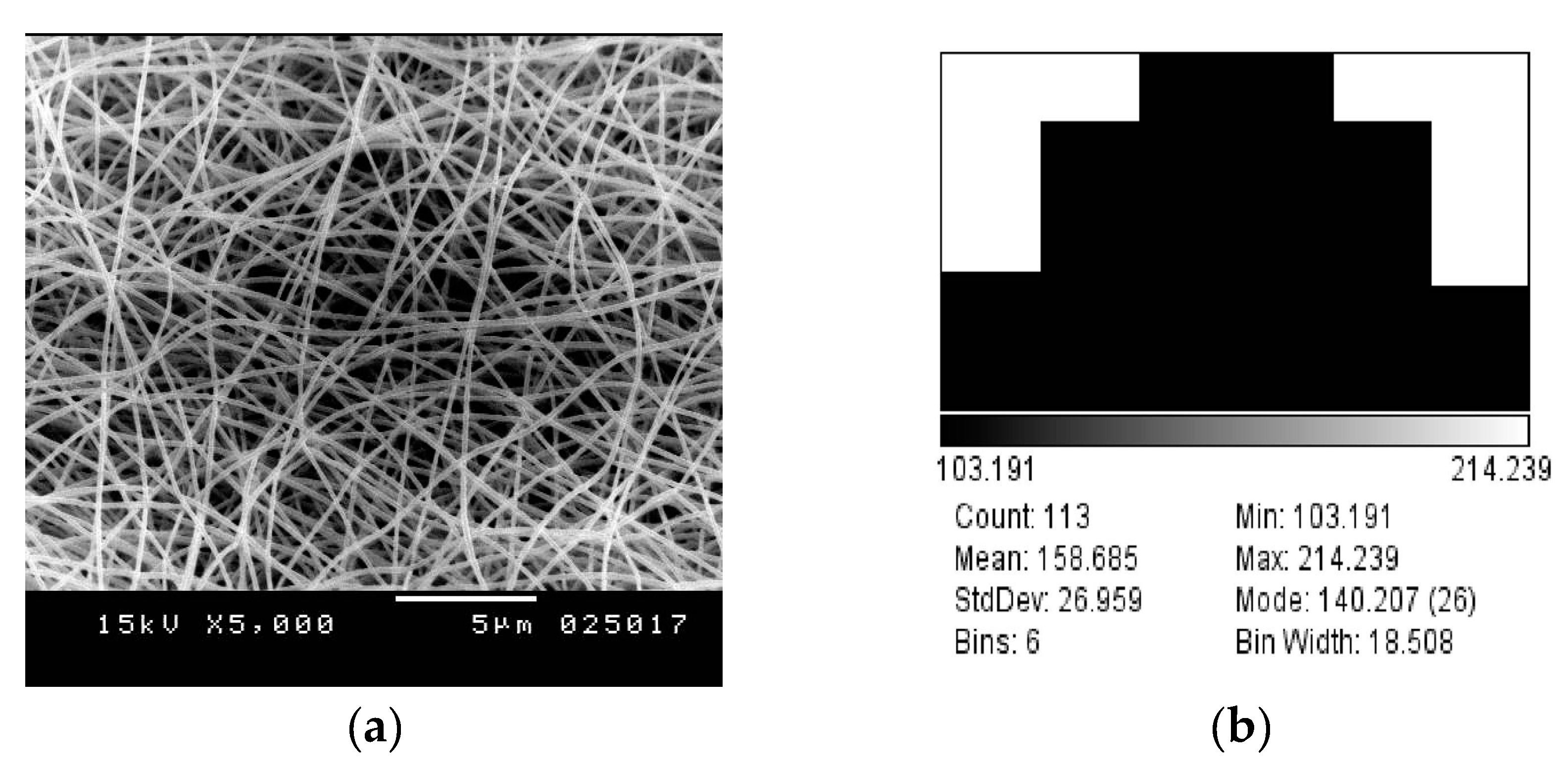
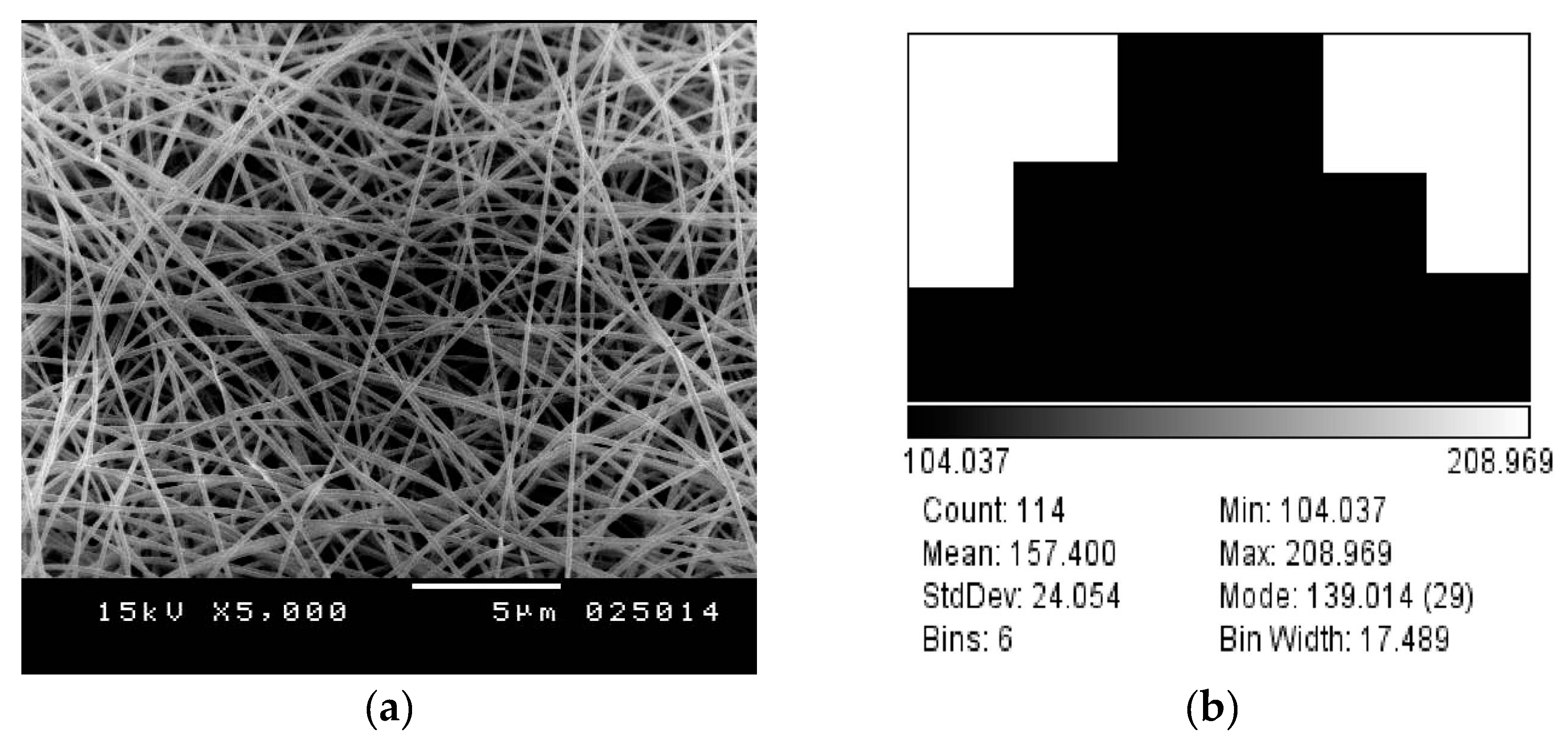
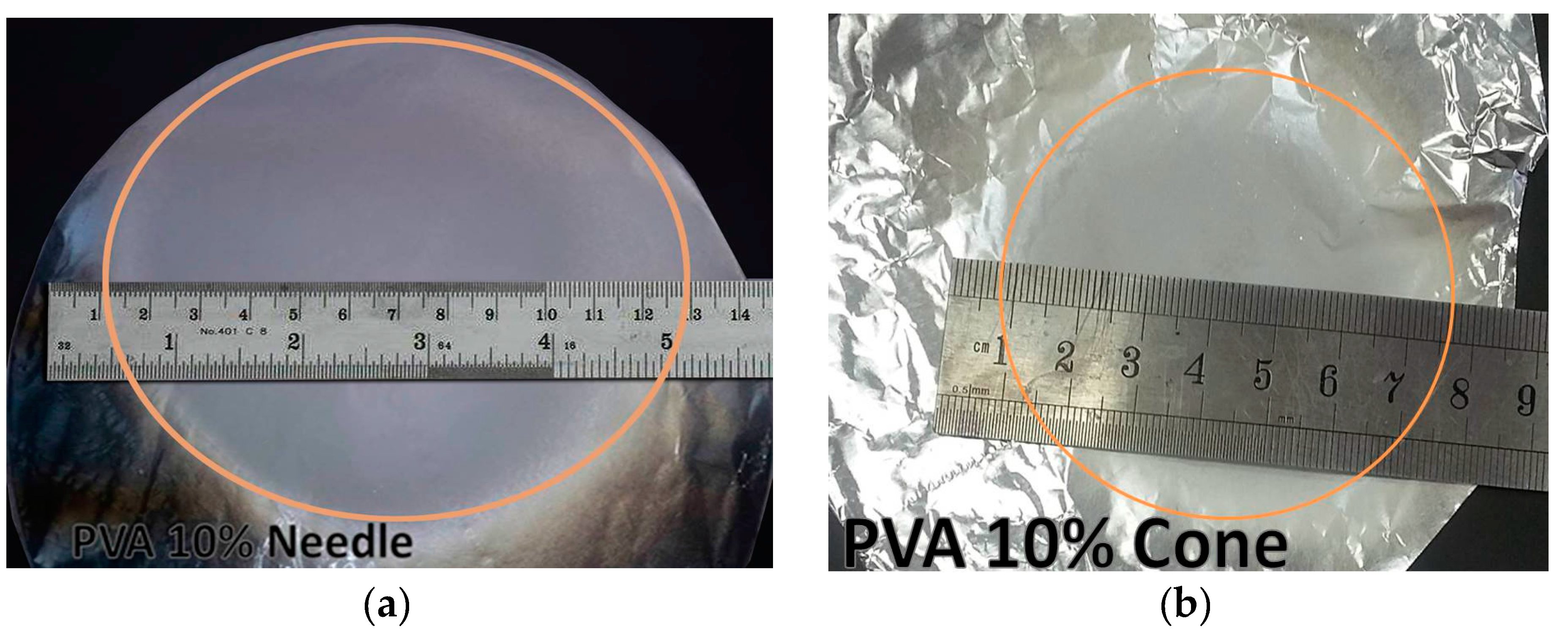
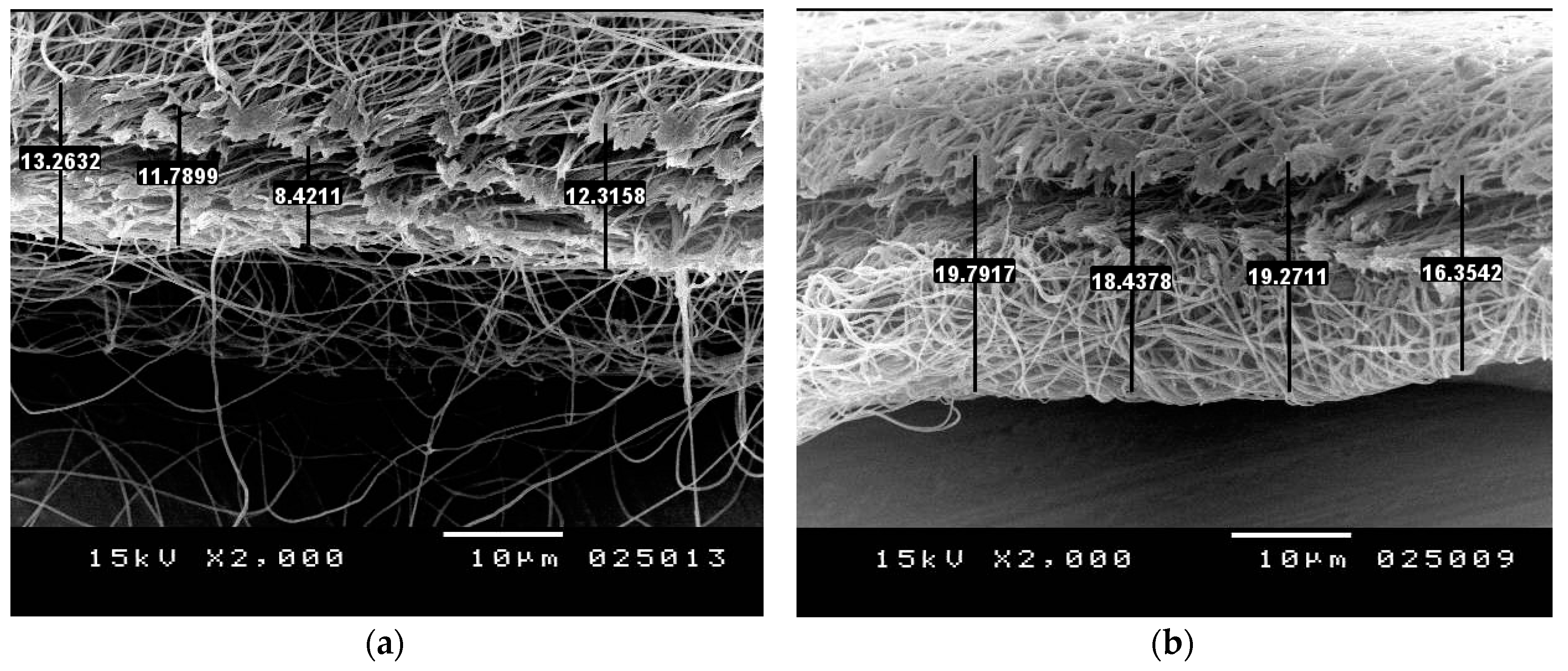
4.3. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of nanofibers: Reinventing the wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fujihara, K.; Teo, W.E.; Lim, T.C.; Ma, Z. An Introduction to Electrospinning and Nanofibers; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2005; ISBN 9812564152. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Functional Applications of Electrospun Nanofibers. In Nanofibers Production, Properities and Functional Applications; Lin, T., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 287–326. ISBN 978-953-307-420-7. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, W.E.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on electrospinning design and nanofibre assemblies. Nanotechnology 2006, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deitzel, J.M.; Kleinmeyer, J.D.; Hirvonen, J.K.; Tan, N.C.B. Controlled deposition of electrospun poly (ethylene oxide) fibers. Polymer (Guildf) 2001, 42, 8163–8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L.; Zussman, E.; Xu, H. Electrospinning of Nanofibers from Polymer Solutions and Melts. Adv. Appl. Mech. 2007, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, R.; Bergshoeft, M.M.; Martin Batlle, C.; Schlinherr Julius Vancso, H.G. Electrospinning of ultra-thin polymer fibers. Macromol. Symp. 1998, 127, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H. Electrospinning process using field-controllable electrodes. J. Polym. Sci. B 2006, 44, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurfaizey, A.H.; Stanger, J.; Tucker, N.; Buunk, N.; Wallace, A.; Staiger, M.P. Manipulation of electrospun fibres in flight: The principle of superposition of electric fields as a control method. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Carnell, L.A.; Clark, R.L. Control of electrospun mat width through the use of parallel auxiliary electrodes. Polymer (Guildf) 2007, 48, 5653–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arras, M.M.L.; Grasl, C.; Bergmeister, H.; Schima, H. Electrospinning of aligned fibers with adjustable orientation using auxiliary electrodes. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubert, S.; Pliszka, D.; Góra, A.; Jaworek, A.; Wintermantel, E.; Ramakrishna, S. Focused deposition of electrospun polymer fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellan, L.M.; Craighead, H.G. Control of an electrospinning jet using electric focusing and jet-steering fields. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2006, 24, 3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, M.; El-chami, I.; Rintoul, L.; Bahreyni, B. Morphology of electrospun poly(ethylene oxide) ultra-fine fibres with incorporated MoO3 nanoparticles. Mater. Des. 2017, 113, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L.; Fong, H.; Koombhongse, S. Bending instability of electrically charged liquid jets of polymer solutions in electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 4531–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vught, R. Simulating the Dynamical Behaviour of Electrospinning Processes; Eindhoven University of Technology: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sohrabi, A.; Shaibani, P.M.; Thundat, T. The effect of applied electric field on the diameter and size distribution of electrospun Nylon6 nanofibers. Scanning 2013, 35, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Symbols | Parameters | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| L | Length scale | |
| Q | charge | |
| V | Voltage | |
| Elastic modulus | ||
| A | Surface tension | |
| H | Distance from pendant drop to collector | |
| Time | ||
| Length of rectilinear part of jet | ||
| Velocity | ||
| Stress |
| Electrode | Maximum E near nozzle (few millimeters from nozzle) in V/m | Convergent E in V/m |
|---|---|---|
| Needle | 1.834 × 105 | 0.9 × 104 |
| Cone | 3.226 × 105 | 3.549 × 104 |
| Symbol | Definition | Values in SI units | Values in gaussian units |
|---|---|---|---|
| a0 | Initial jet radius | 150 µm | 150 × 10−4 cm |
| h | Distance from pendant drop to collector | 0.15 m | 15 cm |
| Applied voltage | 10 kV | 10,000/299.8 statV | |
| α | Surface tension | 0.7 k gs−3 | 700 gs−3 |
| µ | Viscosity | 103 kg/(m·s) | 1 × 104 g/(cm·s) |
| G | Elastic modulus | 105 kg/(m·s2 | 106 g/(cm·s2 |
| e | Charge of bead | 2.83 × 10−4 C | 8.48 statC |
| m | Mass of bead | 0.293 × 10−8 kg | 0.283 × 105 g |
| w | Frequency of perturbation | 104·s−1 | 104·s−1 |
| λ | Wavelength of perturbation | 10−4 m | 10−2 cm |
| Electrode | Area of gaps | Average area of gaps | Ratio of effective area to total area | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region 1 40 | Region 2 40 | Region 3 40 | |||
| Needle | 4.872 | 3.158 | 3.348 | 5.29 | 0.867 |
| Cone | 3.659 | 6.882 | 5.342 | 3.795 | 0.900 |
| Comparison aspect | Needle | Cone |
|---|---|---|
| Fibers diameters | ~158 ± 27 nm | ~157 ± 24 nm |
| Beads formation | No beads | No beads |
| Deposition area | Large diameter > 12 cm covering most of the collector | compact Reduced Diameter ~ 6.8 cm |
| Fiber density | Low density | dense |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamed, A.; Shehata, N.; Elosairy, M. Investigation of Conical Spinneret in Generating More Dense and Compact Electrospun Nanofibers. Polymers 2018, 10, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010012
Hamed A, Shehata N, Elosairy M. Investigation of Conical Spinneret in Generating More Dense and Compact Electrospun Nanofibers. Polymers. 2018; 10(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamed, Aya, Nader Shehata, and Mohammad Elosairy. 2018. "Investigation of Conical Spinneret in Generating More Dense and Compact Electrospun Nanofibers" Polymers 10, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010012
APA StyleHamed, A., Shehata, N., & Elosairy, M. (2018). Investigation of Conical Spinneret in Generating More Dense and Compact Electrospun Nanofibers. Polymers, 10(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010012