Abstract
We have prepared a series of pyridinium-based gemini amphiphiles. They exhibit thermotropic liquid–crystalline behavior depending on their alkyl chain lengths and anion species. By adjusting the alkyl chain lengths and selecting suitable anions, we have obtained an ionic amphiphile that exhibits a normal-type bicontinuous cubic phase from 38 °C to 12 °C on cooling from an isotropic phase. In the bicontinuous cubic liquid–crystalline assembly, the pyridinium-based ionic parts align along a gyroid minimal surface forming a 3D continuous ionic domain while their ionophobic alkyl chains form 3D branched nanochannel networks. This ionic compound can form homogeneous mixtures with a lithium salt and the resultant mixtures keep the ability to form normal-type bicontinuous cubic phases. Ion conduction measurements have been performed for the mixtures on cooling. It has been revealed that the formation of the 3D branched ionophobic nanochannels does not disturb the ion conduction behavior in the ionic domain while it results in the conversion of the state of the mixtures from fluidic liquids to quasi-solids, namely highly viscous liquid crystals. Although the ionic conductivity of the mixtures is in the order of 10–7 S cm–1 at 40 °C, which is far lower than the values for practical use, the present material design has a potential to pave the way for developing advanced solid electrolytes consisting of two task-specific nanosegregated domains: One is an ionic liquid nano-domain with a 3D continuity for high ionic conductivity and the other is ionophobic nanochannel network domains for high mechanical strength.
1. Introduction
Ionic liquids are a class of organic salts forming liquid states at ambient temperature [1,2]. Owing to the strong electrostatic interactions between the component ions, these ionic liquids have several unique properties, such as negligible volatility, flame retardancy, and high ionic conductivity, that are totally different from those of conventional organic solvents. These properties lead scientists to expect that ionic liquids should be new electrolytes for batteries [3,4], solar cells [5], and fuel cells [6], and therefore intensive efforts have been paid for the design of ion conductive materials based on ionic liquids [7]. One of a unique approach for enhancing their ionic conductivities is to align ionic liquids into ordered states [8]. For example, Kato and Ohno succeeded in aligning ionic liquids into 1D [9,10], 2D [11,12], and 3D [13,14] manners by endowing ionic liquids with liquid crystallinity. For the design of liquid-crystalline (LC) ionic liquids (namely ionic liquid crystals), it is important not only to design the shape of molecules and inter/intra-molecular interactions but also to control the volume balance between the ionic and non-ionic parts. The relationships between the molecular structure and molecular assembled structures of ionic liquid crystals are well-summarized in several reviews and papers [8,15,16,17,18].
In 2007, Kato and Ichikawa reported that a series of ammonium-based ionic liquid crystals self-organize into bicontinuous cubic (Cubbi) LC phases with three-dimensionally continuous ionic nanochannel networks (Figure 1a) [13]. This phase can be categorized into an “inverted-type” Cubbi phase. This is a situation where ionic nanochannels (Figure 1a, red) expand three-dimensionally in an ionophobic alkyl chain domain (Figure 1a, blue). In addition, it was revealed that the ionic nanochannels function as ion transporting pathways because the 3D branched nanochannel structure enables ions to transport over LC domain boundaries.
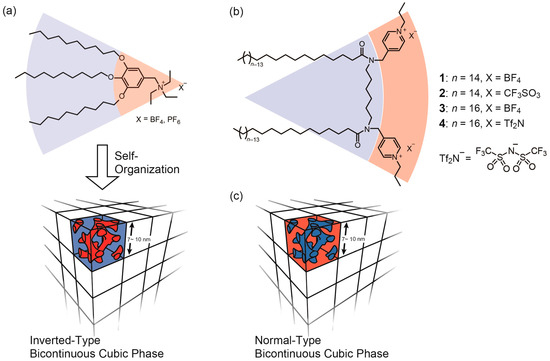
Figure 1.
(a) A series of wedge-shaped ammonium salts forming inverted-type bicontinuous cubic (Cubbi) phases [13]. (b) Molecular structure of gemini-type amphiphile 1–4. (c) A schematic illustration of a normal-type Cubbi phase.
In the course of studies on nanosegregated liquid crystals, it has been well-known that there are “normal-type” nanosegregated LC phases whose nanostructures are the reverse of those of inverted-type LC phases [19,20]. This is applicable in the case of Cubbi phases [21,22,23,24,25]. This well-known fact stimulates us to have an interest in the potential utility of normal-type Cubbi phases (Figure 1c) as ion conductive materials. Here, we have designed an ionic liquid crystal forming a normal-type Cubbi phase and have then evaluated its potential utility as an ion conductive material.
2. Results and Discussion
For the design of ionic liquid crystals forming normal-type Cubbi phases, we focus here on the use of gemini-type amphiphilic structures. One of the reasons that we focus on the gemini design is that there have been a relatively large number of reports on gemini-type amphiphiles exhibiting lyotropic Cubbi phases in the presence of water [26,27,28,29]. Moreover, just recently, we have succeeded in developing gemini-type ionic amphiphiles exhibiting thermotropic Cubbi phases [30,31]. Based on the molecular design in these previous studies, we have designed a series of gemini-type ionic amphiphiles, 1–4, with various alkyl chain lengths and anion species (Figure 1b). The number of carbon atoms in the alkyl chains is 14 or 16. As anion species, tetrafluoroborate (BF4), trifluoromethanesulfonate (Tf), and bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonimide (Tf2N) have been selected because they are known as useful anions for designing ionic liquids with a low glass transition temperature (Tg) [32]. As a cation part, a pyridinium cation has been employed since there have been several reports on the exhibition of Cubbi phases for pyridinium-based amphiphiles [33,34,35,36,37]. As a linker, we have selected a hexyl chain according to several researches on gemini-type amphiphiles [26,27,28,29,30,31].
The phase transition behavior of amphiphiles 1–4 was examined using a polarizing optical microscope (POM), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements. The obtained results are summarized in Table 1. It has been found that 1 shows no birefringence (Figure 2a) while two distinct XRD peaks are found at 2.44° and 2.80° at 30 °C (Figure 2b). The reciprocal ratio of these d-spacing values is √6:√8 and therefore these peaks can be indexed as the reflection of (211) and (220) in a Cubbi phase with Ia3d symmetry. Based on DSC thermograms, we have revealed that 1 forms a Cubbi phase from 38 °C to 12 °C on cooling (Figure 2c). Nanosegregation of the ionic and non-ionic parts is a major driving force for the spontaneous molecular organization. It is of interest that the selection of the anion species plays a critical role for controlling their self-organization behavior. For example, the substitution of BF4 anion with Tf anion causes a loss to its liquid crystallinity. Compound 2 shows no mesomorphic behavior. Considering the difference between the anion radii of these two anions, it is assumed that the strength of electrostatic interactions between the cation and anion is one of the governing factors that influences the spontaneous progress of nanosegregation of the ionic parts and non-ionic parts. Compound 3 has longer alkyl chains than those of 1, yet also exhibits LC behavior while the observed LC phase is not a Cubbi but a Sm phase. The characterization of the Sm phase was carried out in the same way (Figure 2d–f). The disappearance of LC properties is also induced by substituting a BF4 anion with a Tf2N anion with a larger anion radius. Considering that the results of compounds 1 and 3 showed that the elongation of the alkyl chains leads to the change of the mesophase pattern from a Cubbi phase with a curved ionic/non-ionic interface to a smectic A (SmA) phase with flat interfaces, it is presumed that the Cubbi phase is not an inverted-type Cubbi phase, but a normal-type Cubbi phase consisting of an ionic sheath domain and 3D branched ionophobic domains (Figure 1c).

Table 1.
Phase transition behavior of compound 1–5.
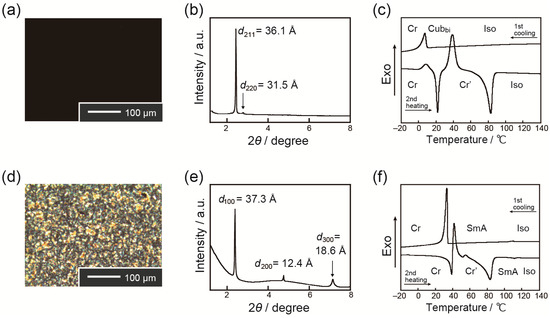
Figure 2.
(a) Polarizing optical microphotograph of 1 in the bicontinuous cubic (Cubbi) phase at 30 °C. (b) X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of 1 in the Cubbi phase at 30 °C. (c) Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) thermograms of 1. (d) Polarizing optical microphotograph of 3 in the smectic A (SmA) phase at 50 °C. (e) XRD pattern of 3 in the Sm phase at 50 °C. (f) DSC thermograms of 3.
With the aim to reveal the importance of the gemini-amphiphilic structures for the exhibition of Cubbi phases, we prepared a control sample, compound 5, with a single-type molecular structure (Figure 3a). Compound 5 shows no mesomorphic behavior, which is confirmed by the DSC measurement (Figure 3b). Comparing the phase behavior of 1 and 5, it has been clearly found that the crystallinity of 5 is higher than that of 1. For example, compound 5 shows a crystallization at 10 °C with an exothermic enthalpy of 38 mJ/mg while compound 1 shows a crystallization at 12 °C with a smaller exothermic enthalpy of 14 mJ/mg (Table 1). We assume that the connection of the two amphiphilic molecules causes two effects. One is that the connection makes it difficult for their alkyl chains to get a suitable position for dense packing, which leads to the lowering of the crystallinity. The other is that the connection enhances the stability of the nanosegregated states, which strengths the self-organization ability of these amphiphiles.
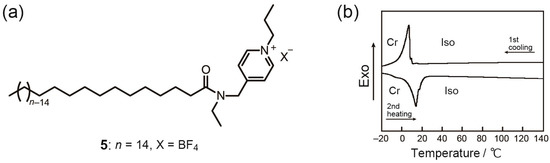
Figure 3.
(a) Molecular structure of single-type compound 5. (b) DSC thermograms of 5.
Compatibility of 1 and a lithium salt, lithium tetrafluoroborate (LiBF4), was examined. Homogeneous mixtures of these two components (1/LiBF4) in various molar ratios were prepared by dissolving the two components into a methanol, and subsequent slow evaporation of the solvent. Here, we define the molar fraction of LiBF4 in the 1/LiBF4 mixtures as X. By observing the obtained mixtures under POM, we found that these two components form homogeneous states where LiBF4 is dissolved into the ionic domains in the nanosegregated states. It is of interest that the 1/LiBF4 mixtures exhibit not only Cubbi phases but also Col phases depending on the temperature and the molar fraction of LiBF4 (X). For example, the 1/LiBF4 (X = 0.09) mixture exhibits a Col phase from 44 °C and then turns into a Cubbi phase at 40 °C on cooling. The phase transition from the Col to Cubbi phase was definitively confirmed by POM observation. Upon cooling from an isotropic liquid state, an appearance of a focal conic fan texture is observed at 44 °C (Figure 4). On further cooling, black domains with non-birefringent domains appear at various positions at 40 °C and they grow until the birefringence disappears entirely. On the other hand, the 1/LiBF4 (X = 0.20) mixture exhibits only a Col phase. The obtained results are summarized as a phase diagram (Figure 5). It can be seen that the addition of LiBF4 induces and stabilizes the exhibition of Col phases. We attribute the exhibition of the Col phases to the increase of the volume ratio of the ionic domains against the non-ionic domains.
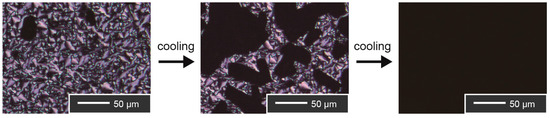
Figure 4.
Polarizing optical microscopic images of the 1/LiBF4 (X = 0.09) mixture on the phase transition from the Col to the Cubbi phase.
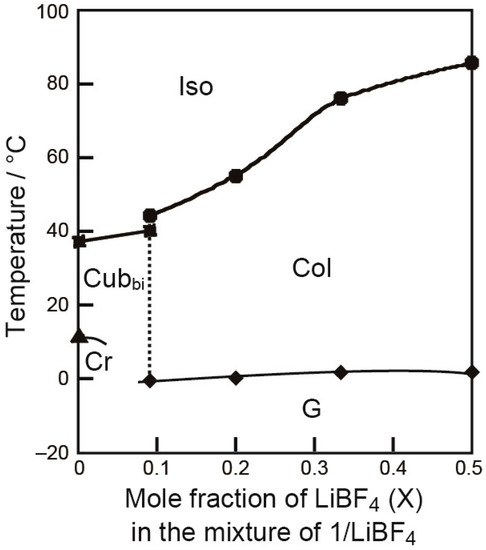
Figure 5.
Phase diagram of the 1/LiBF4 mixtures as a function of the mole fraction of LiBF4 (X) in the mixtures. Cr, crystalline; Col, columnar; Cubbi, bicontinuous cubic; Iso, isotropic.
Ionic conductivity (σ) of 1 and the 1/LiBF4 mixtures was examined using alternating current impedance method with a Schlumberger Solartron 1260 impedance analyzer on cooling at a rate of 1 °C min–1 (frequency range: 10 Hz–10 MHz, applied voltage: 0.3 V). The measurements were carried out upon cooling from 100 °C to room temperature. The ionic conductivity on each temperature was estimated from a Cole–Cole plot (Figure 6a). The estimated σ values are plotted against the reciprocal absolute temperature. It has been found that 1 shows σ of 1.6 × 10–6 S cm–1 at 70 °C, which linearly decreases upon cooling. In general, the ionic conductivity of ionic liquid crystals drastically decreases upon the phase transition from isotropic liquid states to polydomain LC phases [9] for of two reasons. One is the drastic increase of the viscosity of the materials, which largely lowers the diffusion constants of the component ions. The other is the formation of domain boundaries that disturb the macroscopic ion migration. It should be noted that the latter can be overcome when the LC domains are aligned in a macroscopic scale [9]. In the case of compound 1, such drastic decrease of ionic conductivity is not found at 38 °C where 1 shows the phase transition from the isotropic liquid to the Cubbi LC phase with high viscosity, although no alignment control of the LC domains is performed. These results lead us to conclude that the formation of the 3D branched ionophobic nanochannels in the ionic domain does not disturb the ion conduction. Namely, the 3D ionophobic channels endow the ionic domain with a quasi-solidity while it does not act as an obstacle that disturbs the macroscopic ion conduction in the ionic domain. This effect is similar to those that have been found for gelation of ionic liquids by some polymers [38] and supramolecular fibers [39].
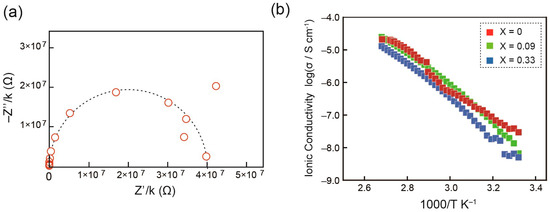
Figure 6.
(a) A Cole–Cole plot for compound 1 at 36 °C in the Cubbi phase. (b) Arrhenius plots of ionic conductivities of compound 1 and the 1/LiBF4 mixtures (X = 0.09 and 0.33).
The ionic conductivities of the 1/LiBF4 (X = 0.09 and 0.33) mixtures were also measured in the same way. The obtained results are compared in Figure 6b. It has been found that the ionic conductivities of the 1/LiBF4 (X = 0.09) mixture are slightly higher than those of pristine 1 while the further addition of LiBF4 results in the lowering of ionic conductivities. These results can be explained by the competition of two effects: one is the increase of ion carrier densities in the mixture and the other is the increase of the viscosity that is induced by the presence of the lithium cation that is harder than the pyridinium cation of 1.
In the decades of studies on ionic liquids, a variety of potential utilities of ionic liquids have been explored for solvents of biopolymers [40,41], gas treatments [42,43], and drug delivery [44]. We expect that organized ionic liquids, including the present systems, will be useful not only for the development of electrolytes but also for these new fields.
3. Materials and Methods
Thermotropic Liquid–Crystalline Properties
Thermotropic liquid–crystalline behaviors of compounds 1–5 and the 1/LiBF4 mixtures were examined by polarizing optical microscope (POM, Olympus BX51) and X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku SmartLab X-Ray Diffractometer) measurements. Some obtained results are shown in the Supplementary Materials. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC, Hitachi DSC7000X) measurements were also performed for the mixtures.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, we have succeeded in designing gemini-type ionic liquid crystals that form normal-type bicontinuous cubic and smectic A phases. For the induction of normal-type bicontinuous cubic phases, the selection of anion species and the employment of long alkyl chains with suitable lengths are found to be important. The normal-type bicontinuous cubic phase consists of two continuous nanosegregated domains: one is a continuous ionic domain and the other is 3D branched ionophobic nanochannel domains that spread around the ionic domain. These liquid-crystalline materials can dissolve lithium salts as well as conventional ionic liquids. The dissolution of lithium salts influences their mesophase behavior. The ionic conductivities of these liquid–crystalline materials are in the order of 10–7 S cm–1 at 36 °C. Although these values are lower than those of conventional ionic liquids, we believe the present material design will be one of the potential approaches for creating a quasi-solid electrolyte consisting of two task-specific domains: One is a 3D continuous ionic domain for high ionic conductivity and the other is 3D continuous ionophobic nanochannels that contribute to endowing the matrix with high mechanical strength without disturbing the ion conduction in the neighbouring ionic domain.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4352/9/6/309/s1.
Author Contributions
T.I., Y.S., T.K., H.O. (Hikaru Oshiro), A.O., and H.O. (Hiroyuki Ohno) conceived and designed the experiments; Y.S., T.K., H.O. (Hikaru Oshiro), and A.O performed the experiments and analyzed the data; Y.S, T.K, H.O. (Hikaru Oshiro), A.O., and T.I. wrote the paper.
Acknowledgments
TI is grateful for financial support from the Precursory Research for Embryonic Science and Technology (PRESTO) from the Japan Science and Technology Corporation (JST) (No. JPMJPR1413). TK is grateful for financial support from the JSPS Research Fellowships for Young Scientists (No. JP 18J21088).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ohno, H. Functional Design of Ionic liquids. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 79, 1665–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, H.; Yoshizawa-Fujita, M.; Kohno, Y. Functional Design of Ionic Liquids Unprecedented Liquids that Contribute to Energy Technology, Bioscience, and Materials Sciences. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 92, 852–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M.; Howlett, P.C.; Kar, M.; Passerini, S.; Pringle, J.M.; Ohno, H.; Watanabe, M.; Yan, F.; Zheng, W.; et al. Ionic liquids and their solid-state analogues as materials for energy generation and storage. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 15005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarra, M.A.; Fujimura, K.; Sgambetterra, M.; Tsurumaki, A.; Panero, S.; Nakamura, N.; Ohno, H.; Scrosati, B. New Ether-functionalized Morpholinium and Piperidinium-based Ionic Liquids as Electrolyte Components in Lithium and Lithium-Ion Batteries. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 2496–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grätzel, M. Dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Photochem. Rev. 2003, 4, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, T.; Watanabe, M. Protic ionic liquids: Fuel cell applications. MRS Bull. 2013, 38, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galinski, M.; Lewandowski, A.; Stepniak, I. Ionic liquids as electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 5567–5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Yoshio, M.; Ichikawa, T.; Soberats, B.; Ohno, H.; Funahashi, M. Transport of ions and electrons in nanostructured liquid crystals. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshio, M.; Mukai, T.; Ohno, H.; Kato, T. One-Dimensional Ion Transport in Self-Organized Columnar Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 994–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshio, M.; Kagata, T.; Hoshino, K.; Mukai, T.; Ohno, H.; Kato, T. One-Dimensional Ion-Conductive Polymer Films: Alignment and Fixation of Ionic Channels Formed by Self-Organization of Polymerizable Columnar Liquid Crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 5570–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshio, M.; Mukai, T.; Kanie, K.; Yoshizawa, M.; Ohno, H.; Kato, T. Layered Ionic Liquids: Anisotropic Ion Conduction in New Self-Organized Liquid-Crystalline Materials. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuda, J.; Yoshio, M.; Ichikawa, T.; Ohno, H.; Kato, T. 2D assemblies of ionic liquid crystals based on imidazolium moieties: Formation of ion-conductive layers. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 4471–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, T.; Yoshio, M.; Hamasaki, A.; Mukai, T.; Ohno, H.; Kato, T. Self-Organization of Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids Exhibiting Liquid-Crystalline Bicontinuous Cubic Phases: Formation of Nano-Ion Channel Networks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 10662–10663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, T.; Yoshio, M.; Hamasaki, A.; Taguchi, S.; Liu, F.; Zeng, X.B.; Ungar, G.; Ohno, H.; Kato, T. Induction of Thermotropic Bicontinuous Cubic Phases in Liquid-Crystalline Ammonium and Phosphonium Salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2634–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, K.; Lava, K.; Bielawski, C.W.; Binnemans, K. Ionic Liquid Crystals: Versatile Materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 4643–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axenov, K.V.; Laschat, S. Thermotropic Ionic Liquid Crystals. Materials 2011, 4, 206–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Slattery, J.M.; Bruce, D.W. Columnar thermotropic mesophases formed by dimeric liquid-crystalline ionic liquids exhibiting large mesophase ranges. New J. Chem. 2011, 35, 2910–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Goossens, K.; Shin, T.J.; Bielawski, C.W. Dicyanamide Salts that Adopt Smectic, Columnar, or Bicontinuous Cubic Liquid-Crystalline Mesophases. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 6399–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodby, J.W.; Collings, P.J.; Kato, T.; Tschierske, C.; Gleeson, H.; Raynes, P. Handbook of Liquid Crystals, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T.; Mizoshita, N.; Kishimoto, K. Functional liquid-crystalline assemblies: Self-organized soft materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 38–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschierske, C. Non-conventional liquid crystals—The importance of micro-segregation for self-organisation. J. Mater. Chem. 1998, 8, 1485–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschierske, C. Liquid crystal engineering-new complex mesophase structures and their relations to polymer morphologies, nanoscale patterning and crystal engineering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1930–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diele, S. On thermotropic cubic mesophases. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 7, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impéror-Clerc, M. Thermotropic cubic mesophases. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 9, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, D.W. Calamitics, Cubics, and Columnars Liquid-Crystalline Complexes of Silver(I). Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Nemade, P.R.; Lu, X.; Zeng, X.; Hatakeyama, E.S.; Noble, R.D.; Gin, D.L. New Type of Membrane Material for Water Desalination Based on a Cross-Linked Bicontinuous Cubic Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9574–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatakeyama, E.S.; Wiesenauer, B.R.; Gabriel, C.J.; Noble, R.D.; Gin, D.L. Nanoporous, Bicontinuous Cubic Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Networks via Polymerizable Gemini Ammonium Surfactants. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 4525–4527. [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson, G.P.; Coppage, K.L.; Mahanthappa, M.K. Unusually Stable Aqueous Lyotropic Gyroid Phases from Gemini Dicarboxylate Surfactants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 14928–14931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensona, G.P.; Mahanthappa, M.K. Unexpected role of linker position on ammonium gemini surfactant lyotropic gyroid phase stability. Soft Mater. 2016, 12, 2408–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Ono, A.; Ichikawa, T.; Kato, T.; Ohno, H. Construction of gyroid-structured matrices through the design of geminized amphiphilic zwitterions and their self-organization. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 12167–12170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, A.; Ohno, H.; Kato, T.; Ichikawa, T. Design of 3D continuous proton conduction pathway by controlling co-organization behavior of gemini amphiphilic zwitterions and acids. Solid State Ion. 2018, 317, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, R.; Warr, G.G.; Atkin, R. Structure and Nanostructure in Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 6357–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, T.; Kato, T.; Ohno, H. 3D Continuous Water Nanosheet as a Gyroid Minimal Surface Formed by Bicontinuous Cubic Liquid-Crystalline Zwitterions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11354–11357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Ichikawa, T.; Kato, T.; Ohno, H. Development of Glassy Bicontinuous Cubic Liquid Crystals for Solid Proton-Conductive Materials. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Ichikawa, T. Design of Viologen-Based Liquid Crystals Exhibiting Bicontinuous Cubic Phases and Their Redox-Active Behavior. Materials 2017, 10, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neve, F.; Impéror-Clerc, M. An Ia3d thermotropic cubic phase from N-alkylpyridinium tetrahalocuprates. Liq. Cryst. 2004, 31, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Li, Y.X.; Ono, A.; Zeng, Z.B. Ichikawa, Gyroid structured aqua-sheets with sub-nanometer thickness enabling 3D fast proton relay conduction. Chem. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, A.; Watanabe, M. Highly conductive polymer electrolytes prepared by in situ polymerization of vinyl monomers in room temperature molten salts. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Functional ionic gels formed by supramolecular assembly of a novel low molecular weight anticorrosive/antioxidative gelator. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 13399–13405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Dissolution of Cellose with Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4974–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukaya, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Wada, M.; Ohno, H. Cellulose dissolution with polar ionic liquids under mild conditions: Required factors for anions. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, E.D.; Mayton, R.D.; Ntai, I.; Davis, J.H., Jr. CO2 Capture by a Task-Specific Ionic Liquid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 926–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittenthal, M.S.; Flowers, B.S.; Bara, J.E.; Whitley, J.W.; Spear, S.K.; Roveda, J.D.; Wallace, D.A.; Shannon, M.S.; Holler, R.; Martens, R.; et al. Ionic Polyimides: Hybrid Polymer Architectures and Composites with Ionic Liquids for Advanced Gas Separation Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 5055–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adawiyah, N.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Hawatulaila, S.; Goto, M. Ionic liquids as a potential tool for drug delivery systems. Med. Chem. Commun. 2016, 7, 1881–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).