The Structure of Ferroselite, FeSe2, at Pressures up to 46 GPa and Temperatures down to 50 K: A Single-Crystal Micro-Diffraction Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ambient Conditions Structural Refinements
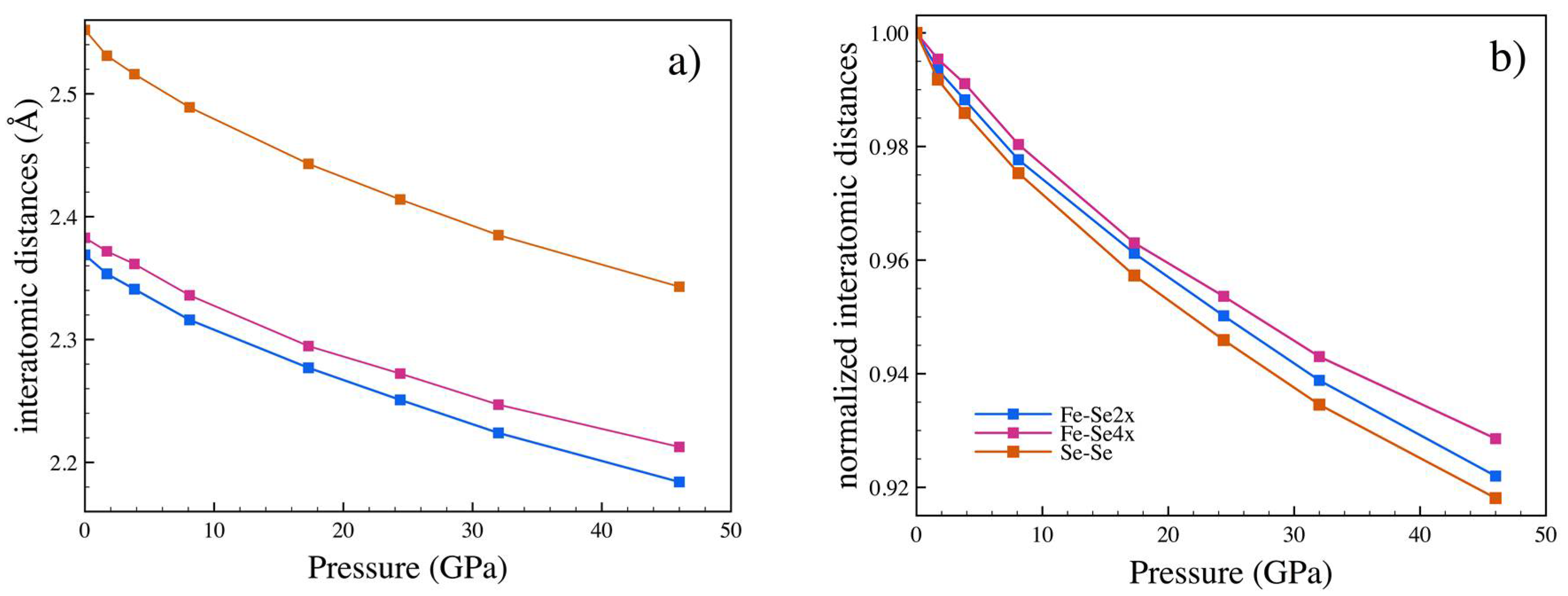
3.2. High Pressure
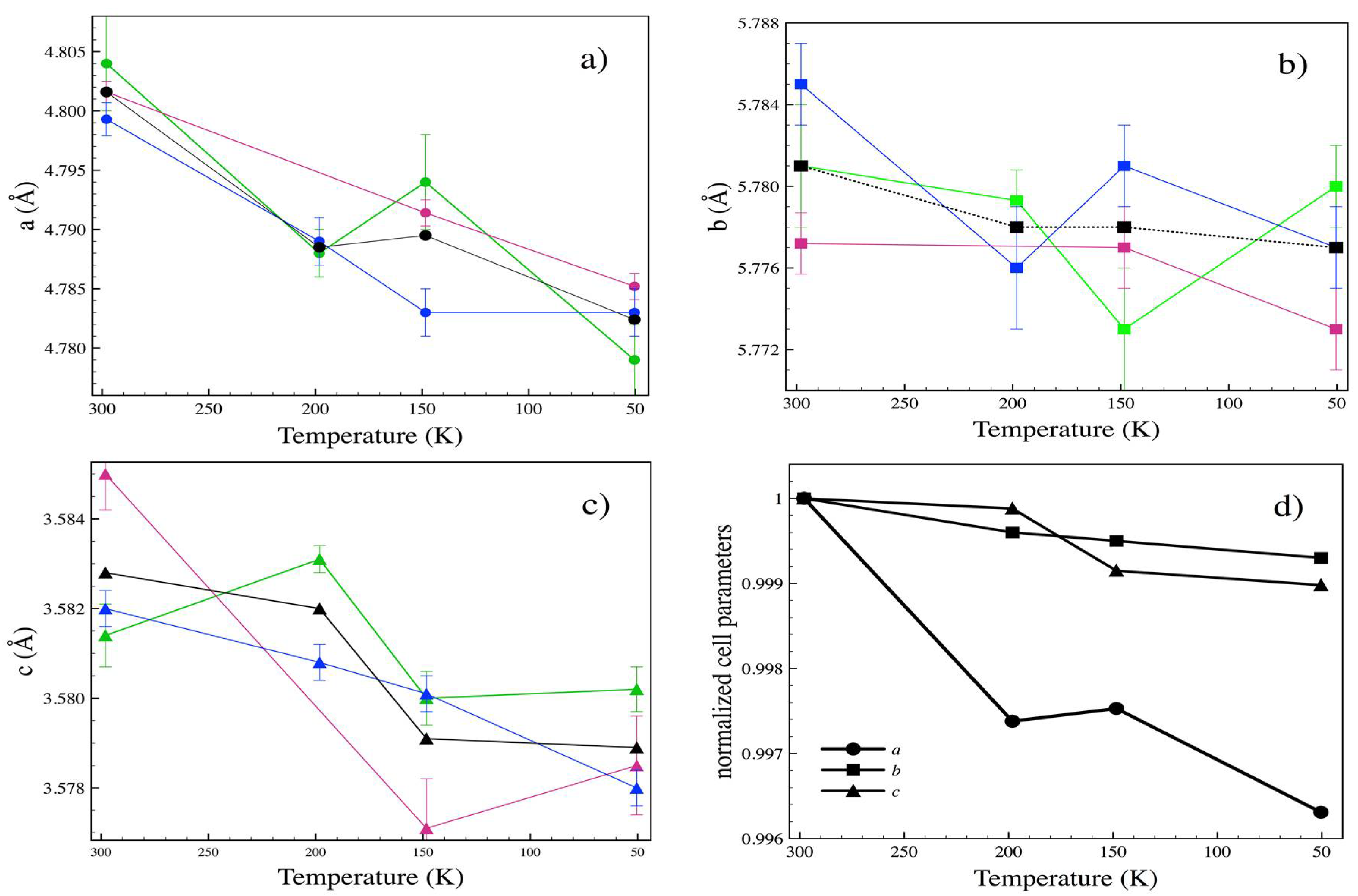
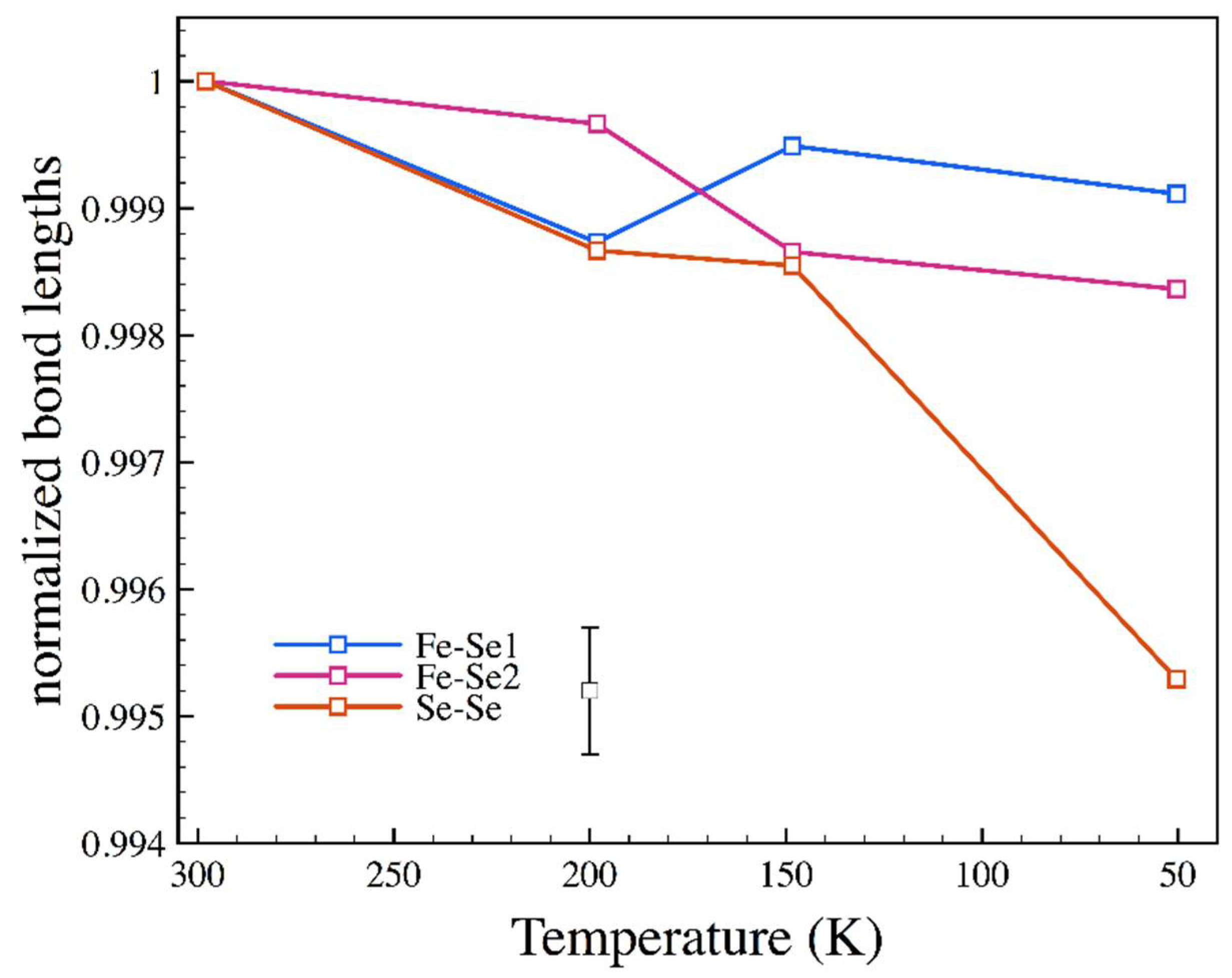
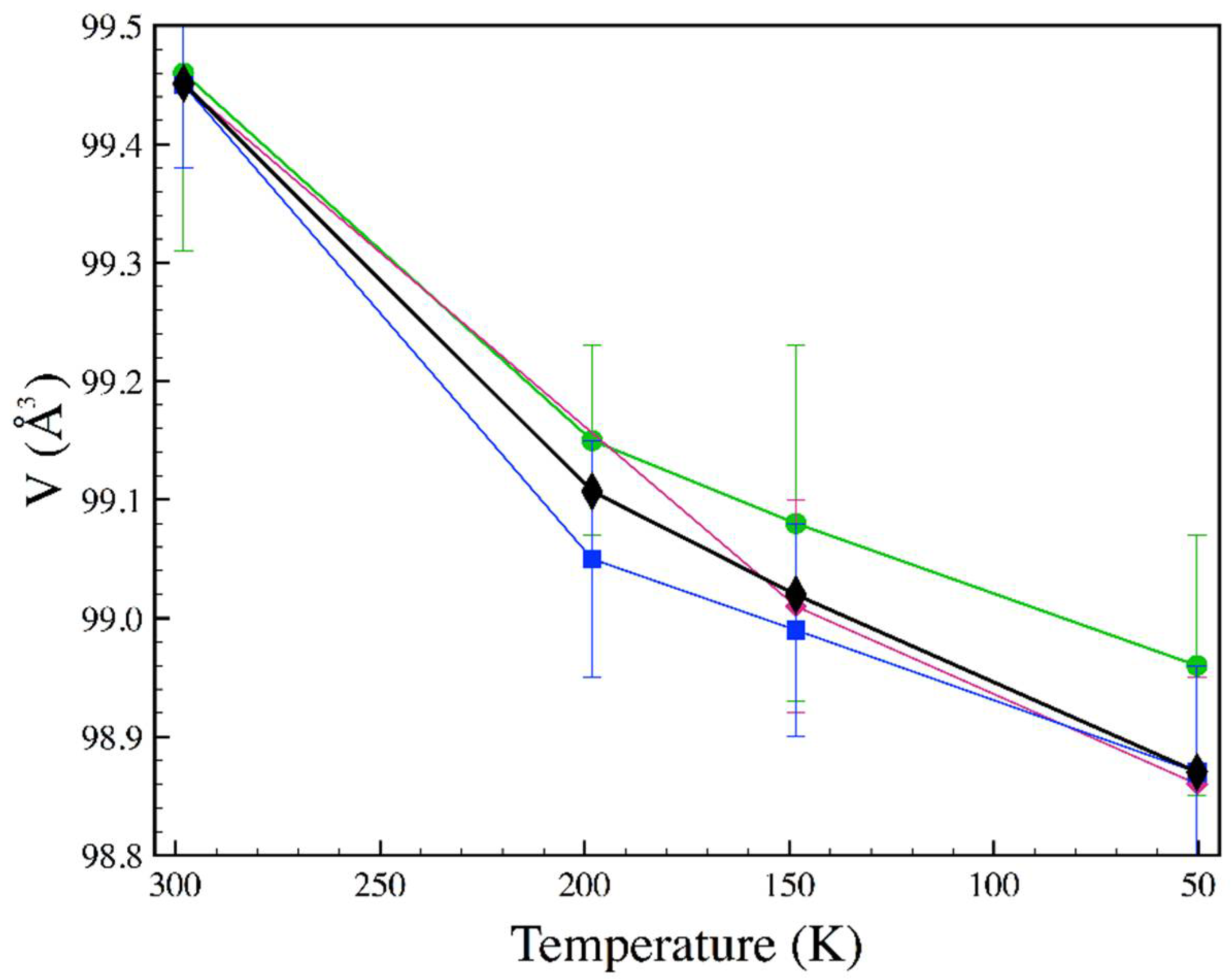
3.3. Low Temperature
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gudelli, V.K.; Kanchana, V.; Vaitheeswaran, G.; Valsakumar, M.C.; Mahanti, S.D. Thermoelectric properties of marcasite and pyrite FeX2 (X = Se, Te): A first principle study. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 9424–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, G.; Zhang, B.; Rao, J.; Gonzalez, D.H.; Blake, G.R.; de Groot, R.A.; Palstra, T.T.M. Effect of vacancies on magnetism, electrical transport, and thermoelectric performance of marcasite FeSe2−δ (δ = 0.05). Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 8220–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Thangavel, R. Electronic structure and optical properties of iron-based chalcogenide FeX2 (X = S, Se, Te) for photovoltaic applications: A first principle study. Indian J. Phys. 2017, 91, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, J.B. Energy bands in TX2 compounds with pyrite, marcasite, and arsenopyrite structures. J. Solid State Chem. 1972, 5, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Arai, M.; Sasaki, T. Marcasite osmium nitride with high bulk modulus: First-principles calculations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 061922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, K.; Dzivenko, D.; Suzuki, K.; Riedel, R.; Troyan, I.; Eremets, M.; Hasegawa, M. High pressure synthesis of marcasite-type rhodium pernitride. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 697–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Harran, I.; Jia, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, N. Prediction and characterization of the marcasite phase of iron pernitride under high pressure. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 702, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjekshus, A.; Rakke, T. Compounds with the marcasite type crystal structure. XI. High temperature studies of chalcogenides. Acta Chem. Scand. 1975, A29, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bither, T.A.; Prewitt, C.T.; Gillson, J.L.; Bierstedt, P.E.; Flippen, R.B.; Young, H.S. New transition metal dichalcogenides formed at high pressure. Solid State Commun. 1966, 4, 533–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bither, T.A.; Bouchard, R.J.; Cloud, W.H.; Donohue, P.C.; Siemons, W.J. Transition metal pyrite dichalcogenides. High-pressure synthesis and correlation of properties. Inorg. Chem. 1968, 7, 2208–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momma, K.; Izumi, F. VESTA3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.E.M.; de Lima, J.C.; Grandi, T.A.; Machado, K.D.; Itié, J.P.; Polian, A. Pressure-induced effects on the structural properties of iron selenides produced by mechano-synthesis. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2004, 16, 8485–8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.-H.; Zhang, J.-M. The structural, elastic, electronic and optical properties of orthorhombic FeX2 (X = S, Se, Te). Superlattices Microstruct. 2018, 119, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente, B.; Downs, R.T.; Yang, H.; Stone, N. The power of databases: The RRUFF project. In Highlights in Mineralogical Crystallography; Armbruster, T., Danisi, R.M., Eds.; W. De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Boehler, R.; De Hantsetters, K. New anvil designs in diamond-cells. High Press. Res. 2004, 24, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toby, B.H.; Von Dreele, R.B. GSAS-II: The genesis of a modern open-source all purpose crystallography software package. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2013, 46, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Ito, E.; Katsura, T.; Yamazaki, D.; Yoshino, T.; Yokoyama, A.; Funakoshi, K.I. The temperature-pressure-volume equation of state of platinum. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 013505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Xu, J.; Bell, P. Calibration of the ruby pressure gauge to 800-Kbar under quasi-hydrostatic conditions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth Planets 1986, 91, 4673–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dera, P.; Zhuravlev, K.; Prakapenka, V.; Rivers, M.L.; Finkelstein, G.J.; Grubor-Urosevic, O.; Tschauner, O.; Clark, S.M.; Downs, R.T. High pressure single-crystal micro X-ray diffraction analysis with GSE_ADA and RSV software. High Press. Res. 2013, 33, 466–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, L.J. WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: An update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescher, C.; Prakapenka, V.B. DIOPTAS: A program for reduction of two-dimensional X-ray diffraction data and data exploration. High Press. Res. 2015, 35, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjekshus, A.; Rakke, T.; Andresen, A.F. Compounds with the marcasite type crystal structure. IX. Structural data for FeAs2, FeSe2, NiAs2, NiSb2, and CuSe2. Acta Chem. Scand. 1974, A28, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickardt, J.; Reuter, B.; Riedel, E.; Söchtig, J. On the formation of FeSe2 single crystals by chemical transport reactions. J. Solid State Chem. 1975, 15, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.-H.; Zhang, J.-M. The structural, elastic and electronic properties of marcasite FeS2 under pressure. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 118, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
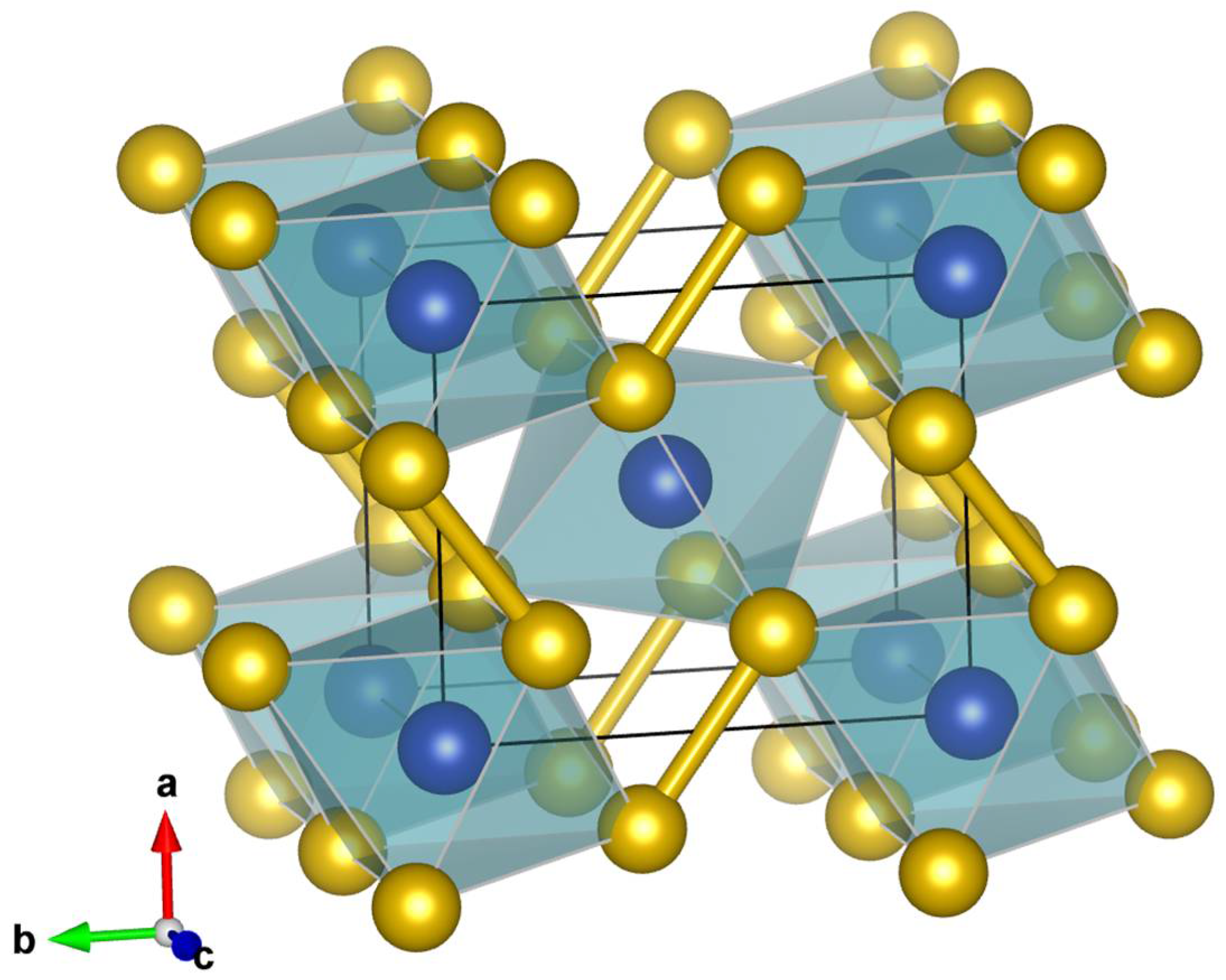
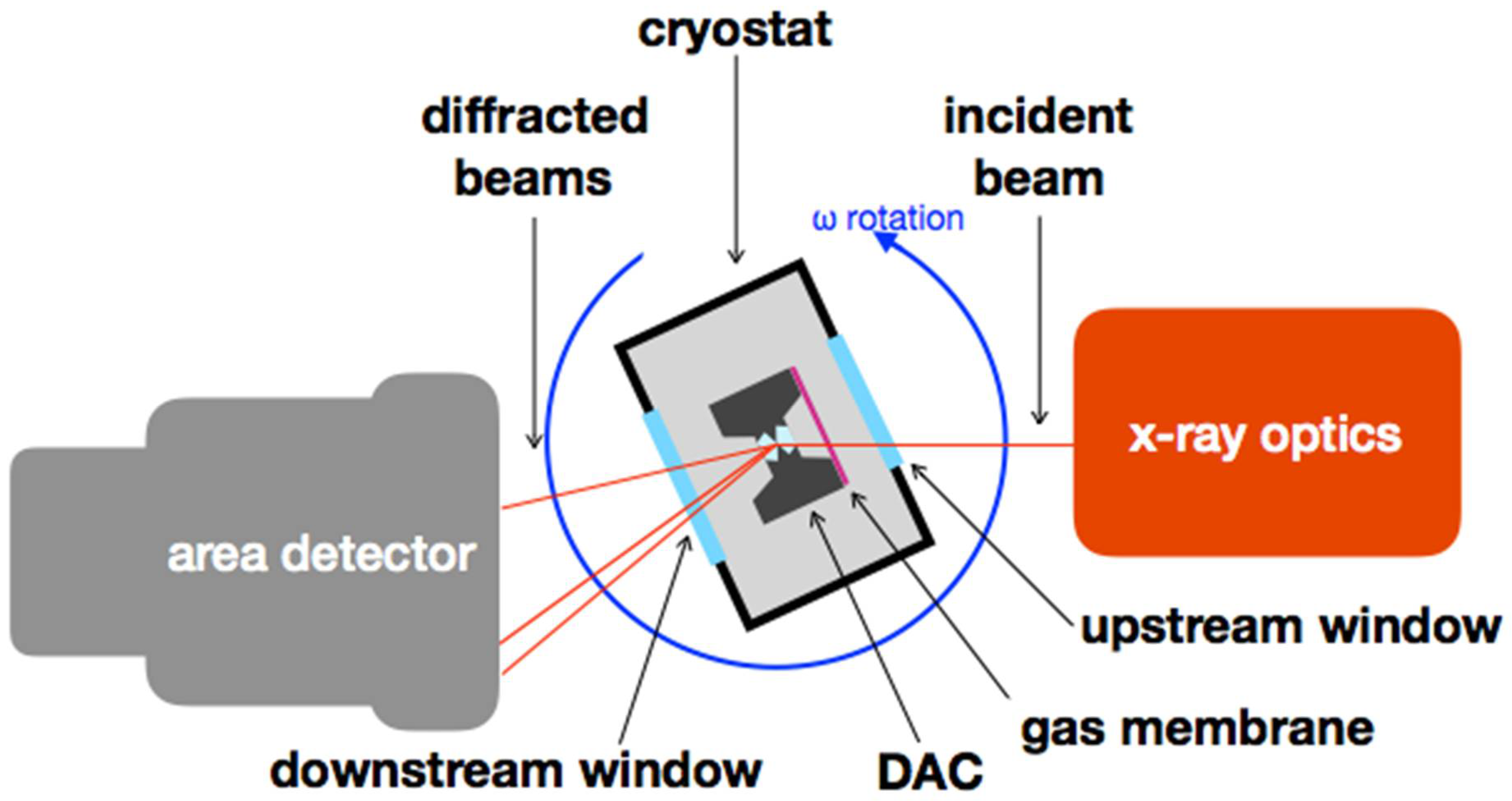
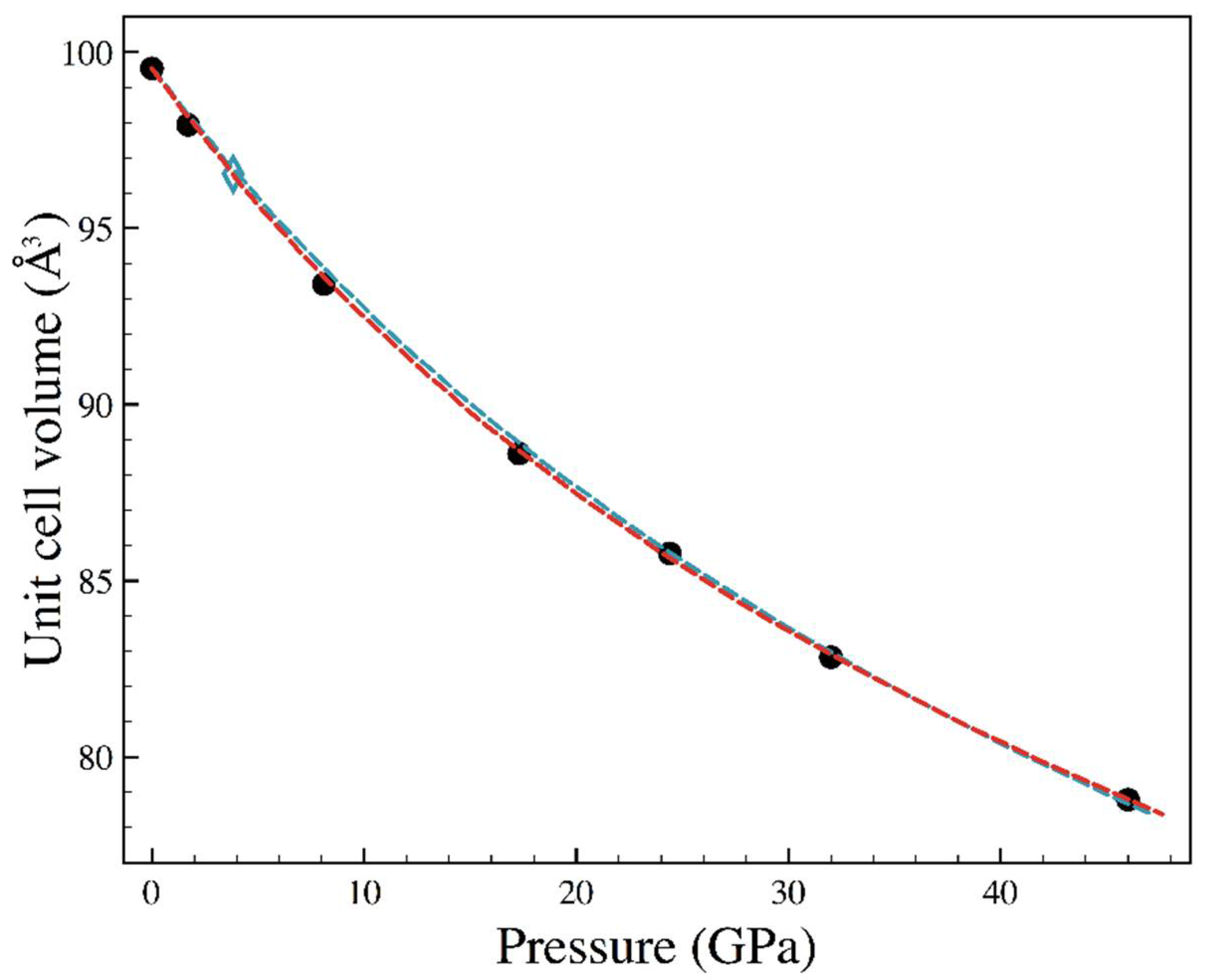
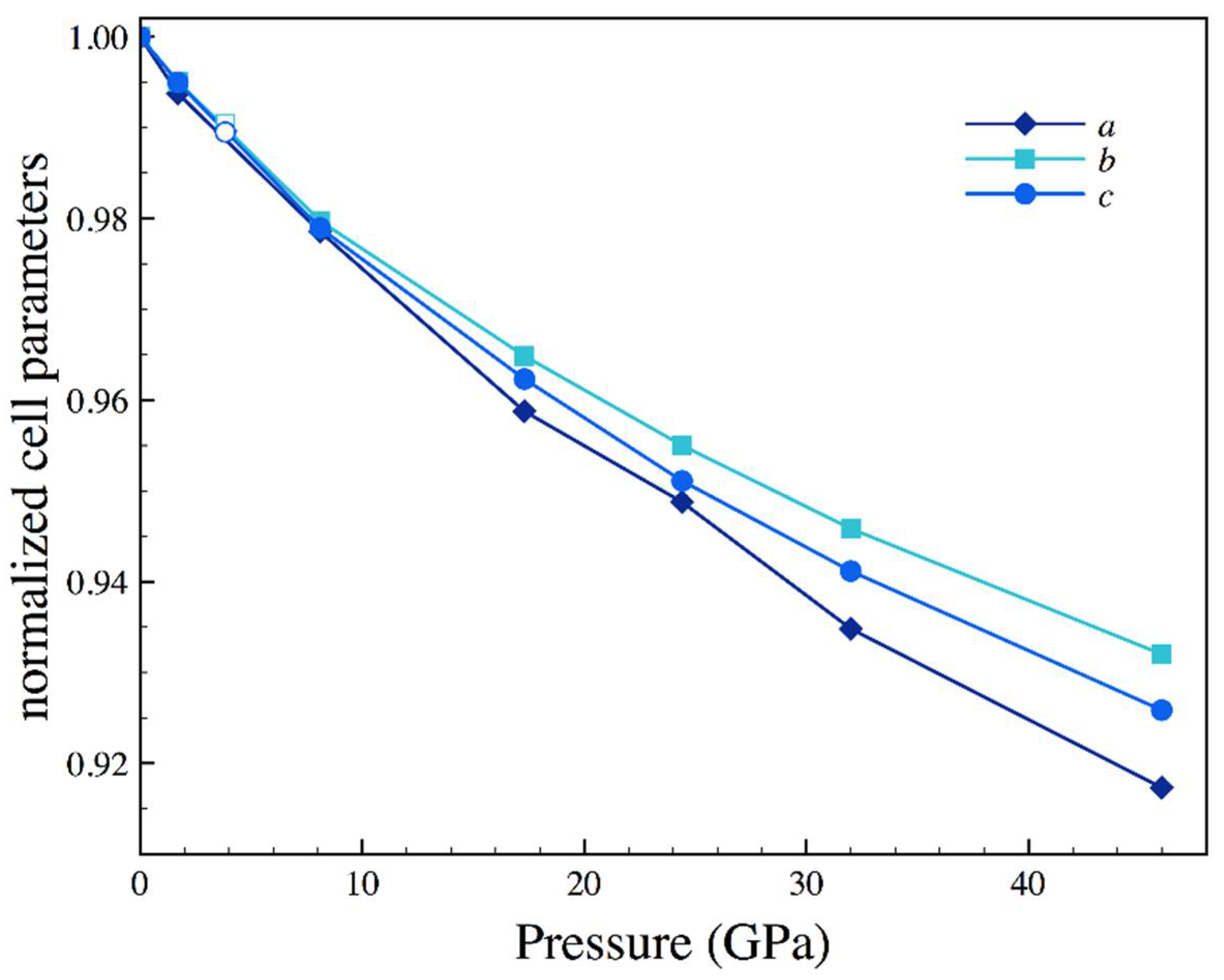
| Sample | Nall, Nind | a (Å) | b (Å) | c (Å) | Req, R1 (%) | x (Se) | y (Se) | Ueq-Fe (Å2) | Ueq-Se (Å2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. [23] | 4.8002(4) | 5.7823(5) | 3.5834(4) | 0.2127(6) | 0.3701(5) | ||||
| Ref. [24] | 4.804(2) | 5.784(3) | 3.586(2) | 0.2134(2) | 0.3690(1) | ||||
| RRUFF (a) | 4.795(3) | 5.777(4) | 3.584(1) | ||||||
| Ref. [2] | 4.8031(6) | 5.7849(2) | 3.5840(4) | 0.2127(2) | 0.3691(7) | ||||
| Measurement in the DAC | |||||||||
| DAC | 204, 98 | 4.801(3) | 5.787(2) | 3.5859(7) | 12, 4.9 | 0.213593) | 0.3692(2) | 0.0095(5) | 0.0099(5) |
| Measurement in the DAC and cryostat | |||||||||
| C1 (b) | 205, 82 | 4.804(4) | 5.781(3) | 3.5814(7) | 8.4, 4.4 | 0.2133(3) | 0.3692(1) | 0.0056(5) | 0.0059(4) |
| C2 (c) | 253,103 | 4.8016(9) | 5.777(1) | 3.5850(8) | 9.6, 5.4 | 0.2137(2) | 0.36921(13) | 0.0090(5) | 0.0090(4) |
| C3 (b) | 214,94 | 4.799(1) | 5.785(2) | 3.5820(4) | 33, 12 | 0.2130(7) | 0.3699(3) | 0.0067(12) | 0.0086(10) |
| P (GPa) | a (Å) | b (Å) | c (Å) | x (Se) | y (Se) | Ueq-Fe (Å2) | Ueq-Se (Å2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.7 | 4.771(2) | 5.756(1) | 3.5663(6) | 0.2129(4) | 0.36884(13) | 0.0079(6) | 0.0083(5) |
| 3.83 (a) | 4.751(2) | 5.729(2) | 3.5467(11) | 0.2125(60 | 0.3687(7) | 0.014(2) | 0.013(2) |
| 8.1 | 4.698(3) | 5.667(2) | 3.5088(7) | 0.2123(6) | 0.3688(2) | 0.0083(8) | 0.0090(7) |
| 17.3 | 4.603(3) | 5.581(2) | 3.4492(9) | 0.2123(3) | 0.36854(9) | 0.0085(5) | 0.0088(5) |
| 24.4 | 4.555(2) | 5.524(12) | 3.4090(5) | 0.2114(4) | 0.3683(2) | 0.0066(9) | 0.0057(7) |
| 32 | 4.488(4) | 5.471(3) | 3.3734(11) | 0.2111(6) | 0.3676(2) | 0.0063(13) | 0.0064(12) |
| 46 | 4.404(3) | 5.391(2) | 3.3185(9) | 0.2103(4) | 0.36689(13) | 0.0066(9) | 0.0070(8) |
| T (K) | P (GPa) | a (Å) | b (Å) | c (Å) | x (Se) | y (Se) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 198.2 | 10−4 | 4.7885 | 5.7782 | 3.5821 | 0.2148(4) | 0.3692(2) |
| 148.4 | 10−4 | 4.7893 | 5.7775 | 3.5795 | 0.2135(2) | 0.3691(2) |
| 50.4 | 10−4 | 4.7834 | 5.7767 | 3.5789 | 0.2138(3) | 0.3694(2) |
| 197 | 3.68 | 4.751(2) | 5.723(2) | 3.5501(11) | 0.2131(7) | 0.3699(6) |
| 116 | 3.64 | 4.7446(11) | 5.772(2) | 3.5512(8) | 0.2130(6) | 0.3695(7) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lavina, B.; Downs, R.T.; Sinogeikin, S. The Structure of Ferroselite, FeSe2, at Pressures up to 46 GPa and Temperatures down to 50 K: A Single-Crystal Micro-Diffraction Analysis. Crystals 2018, 8, 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8070289
Lavina B, Downs RT, Sinogeikin S. The Structure of Ferroselite, FeSe2, at Pressures up to 46 GPa and Temperatures down to 50 K: A Single-Crystal Micro-Diffraction Analysis. Crystals. 2018; 8(7):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8070289
Chicago/Turabian StyleLavina, Barbara, Robert T. Downs, and Stanislav Sinogeikin. 2018. "The Structure of Ferroselite, FeSe2, at Pressures up to 46 GPa and Temperatures down to 50 K: A Single-Crystal Micro-Diffraction Analysis" Crystals 8, no. 7: 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8070289
APA StyleLavina, B., Downs, R. T., & Sinogeikin, S. (2018). The Structure of Ferroselite, FeSe2, at Pressures up to 46 GPa and Temperatures down to 50 K: A Single-Crystal Micro-Diffraction Analysis. Crystals, 8(7), 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8070289





