Abstract
In this work, we report the synthesis of a monoclinic hydroxyapatite [Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2] (hereafter called HA) prepared by the sol-gel method assisted by ultrasound radiation at room temperature. The characterization of both the monoclinic and the hexagonal phases were performed by powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) and using synchrotron radiation (SR). The measurement of the piezoelectricity was performed by piezoresponse force microscopy (PFM). The synthesis produced a mixture of monoclinic and hexagonal hydroxyapatite (HA). We also discuss the importance of stabilizing the monoclinic phase at room temperature with ultrasound irradiation. The existence of the monoclinic phase has important advantages in terms of showing piezoelectric properties for applications in the new medical rehabilitation therapies. Rietveld refinement of the PXRD data from SR indicated the monoclinic phase to be of about 81%. Finally, piezoelectric force microscopy was used to distinguish the phases of hydroxyapatite by measuring the average piezoelectric coefficient deff = 10.8 pm/V.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, the development and synthesis of advanced and functional materials for biomedical applications is one of the leading challenges in materials science [1,2,3,4]. Significant progress has recently been made in surgical reconstruction [5,6] and the use of prostheses to treat the loss or failure of an organ or bone tissue [7,8]. We know that natural bone is made of 65 wt% carbonate hydroxyapatite (HA), 20 to 30 wt% organic matrix and 10% water [7]. The synthetic (HA) has chemical and mechanical properties like the inorganic component in the rigid matrix of bone [9,10]. Both crystallographic and chemical studies have shown that synthetic HA is likely to naturally occur in inorganic components found in the bone matrix and teeth. Because of this close similarity, there has been an extensive research effort to employ synthetic HA as a bone substitute and/or replacement in several biomedical applications [11,12].
The HA can usually be found in two crystallographic forms, the hexagonal phase having the P63/m space group with unit cell parameters a = b = 9.432 Å, c = 6.881 Å, and the monoclinic phase, with the space group P21/b and a = 9.421 Å, b = 2 Å, c = 6.881 Å, β = 120° as unit cell parameters [10]. However, it has been reported that powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) structural results at room temperature can be better explained considering the existence of two monoclinic phases: the crystal class 2/m (centrosymmetric) and the polar crystal class 2 (non-centrosymmetric) [13].
It has been shown that the orientation of the OH groups is fundamental to determine the final structure in HA. This hydroxyl ion channel runs parallel to the c-axis; when the OH groups lie along the direction of the OH channels the hexagonal phase is usually present, whereasthe OH groupsoriented in a preferential direction of the screw axes have non-centrosymmetric structures described by the monoclinic phase;as we already know, one symmetry condition for piezoelectricity to be found in a crystal is the existence of a non-centrosymmetric structure [14].
Although the structural differences between monoclinic and hexagonal HA are very small, they are sufficient to exert a substantial impact on some of their physicochemical properties [9,10,11]. The novel medical rehabilitation therapies of bones require smart biomaterials, particularly the piezoelectric ones because they are mechanical–electrical transductors. Figure 1 shows the unit cells of both phases of HA, as an arrangement of PO4 tetrahedral units bound by Ca ions [11].
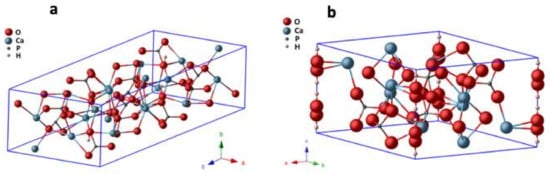
Figure 1.
(a) Monoclinic and (b) hexagonal unit cell of HA at 298 K and 673 K, respectively, according to the results obtained by powder X-ray diffraction by using synchrotron radiation [1].
Although we have used different methods to synthesize the HA, we still have encountered several difficulties in obtaining only one phase. However, HA is usually synthesized at high temperatures (around 1000 °C), obtaining the hexagonal phase [9,10]. Nonetheless, the sol-gel-assisted ultrasound method allows us to control the stoichiometry, crystallinity and purity of the obtained sample. This method was used to synthesize the monoclinic phase of HA at low temperature. In general, the sol-gel method is the common way to prepare ceramics, composites and mixed doped materials [15,16].
The observation of piezoelectric properties in the monoclinic phase of the HA suggests that the piezoelectric effect plays an important physiological role in bone growth, bone remodeling and fracture healing [17,18]. Through piezo response force microscopy (PFM), we were able to measure the local mechanical deformation of the sample in response to an electric field applied by a conductive tip, which was the way to obtain an effective piezoelectric coefficient (deff) of the HA. PFM is a determining technique to understand the contribution of organic materials at nanoscopic scale from the disordered structure of the piezoelectric materials [10,19,20].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
The HA powders were obtained using the sol-gel method assisted by ultrasonic irradiation based on the methodology of a recently reported publication [21]. Calcium nitrate [Ca(NO3)2·4H2O] (99.99%, JT Baker, Phillipsburg, NJ, USA) and ammonium dibasic phosphate [(NH4)2HPO4] (99.99%, JT Baker, USA) were used as the starting reagents. Ca(NO3)2·4H2O (10g) and (NH4)2HPO4 (2.3 g) were dissolved in solutions with Trizma base solution (0.1 M) to obtain 50 mL volumetric mixtures. The solution of (NH4)2HPO4 was stabilized at pH 9 with NH4OH and then adding Ca(NO3)2·4H2O every 30 min at an interval of 15 s each with a magnetic stirring bar. When the mixture was completed, we placed the sample under pulsed irradiation over 1 h at intervals of 25 s. The product of the synthesis (HA) was subsequently washed with deionized water several times in order to eliminate the extra product from the reaction. The resulting sample was then heated in air using a glass crystallizer at 200 °C inside a muffle (Cole Parmer, Vernon Hills, IL, USA) over 2 h until the classic xerogel was obtained. An ultrasonic processor from Sonics & Materials Inc., (Newton, CT, USA) was used with a disposable tapered microtip (3 mm) and operated at 500 W and 20 kHz.
2.2. Characterization
2.2.1. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) characterization was initially carried out on a Panalytical Empyrean diffractometer (2015, Panalytical, Almelo, The Netherlands) operating at 45 kV/40 mA and using Cu Kα radiation. The diffraction patterns were obtained ranging from 5° to 90° (2θ) degrees, with a step size 0.017° and scan step time 293.3 s. The sample holder rotates to prevent preferred orientation effects.
Synchrotron X-ray powder diffraction (SXRPD) analyses were performed using the Huber Kappa Goniometer installed at the beamline XRD-1 at Elettra Synchrotron, Basovizza, Italy. The experimental set up consisted of a bending magnet in the light source, a double crystal monochromator Si (111), a focusing mirror of Pt-coating, and a detector Dectris Pilatus 2 M (DECTRIS Ltd., Baden-Daettwil, Switzerland). A monochromatized 0.7 Å X-ray beam was utilized with the sampler rotating 180° to prevent orientation effects. Rietveld refinement of the XRPD pattern was carried out using X’PertHighScore Plus 2.2.2® (version 4.7, 2017, Malvern Panalytical Ltd., Almelo, The Netherlands) [22]. Rietveld program on HighScore suite modeled the background by Chebyshev function and the shape of the peaks were studied using the pseudo-Voigt algorithm. Refinement was performed until close fit between the observed and the calculated patterns. The crystal Structure of phases was plotted using Crystal Maker software® (10.2.2, 2018, Crystal Maker Software Ltd., Wales, UK).
2.2.2. Piezoresponse Force Microscopy (PFM)
Atomic force microscopy (2016, AFM Park systems Park XE7, Albany, NY, USA) performed with a lock-in amplifier SR865A from Stanford Research, controlled by a LABVIEW® program was used (LabViewer2018, National Instruments, Austin, TX, USA). Pt-coated Silicon AFM tip was also used for the experiment. The AFM was switched to contact mode for piezoelectric characterization along the whole experiment. In the resonant PFM mode, an AFM conductive tip got in contact with the sample under a constant pressure force. Then a potential difference between the tip and the substrate was applied by an AC voltage at the tip-sample contact resonant frequency, causing deformation in the surface of the sample due to the converse piezoelectric effect.
The spring constant of the cantilever was 0.26 N/m. The sample analyzed was a powder tablet of HA compressed by two tons of pressure, with diameter 10 mm and 2 mm thickness. A lead zirconate titanate (PZT) sample was used as a calibration reference for the PFM. The deff was measured by varying the AC input, sweeping the voltage from zero to 2 V, with steps of 0.1 V at a fixed point in the sample, acquiring the corresponding PFM resonant peak. The piezoresponse signal of the probe was deconvoluted in the lock-in amplifier. The response of the signal was plotted with the LABVIEW Program.
The PFM images were performed using the PinPoint method. This method allowed us to measure soft and fragile surfaces of the samples without deforming the surface. This technique is based on positioning and measuring pixel by pixel the force-distance curves, at the same time an AC voltage is applied, and the PFM measurements are carried out during the contact following the experimental method suggested by Kalinin et al. [23]. The procedure was performed in 256 × 256 pixel boxes. To each of the pixels we applied a 1 V of AC voltage and a frequency of 200 kHz. This strategy allowed us to measure and to obtain the topography, borders and ferroelectric domains of the HA.
3. Results
3.1. Structure
Concerning the structure, Figure 2a,b shows the XRD diffractograms of the PDF files for the monoclinic and the hexagonal phases respectively.
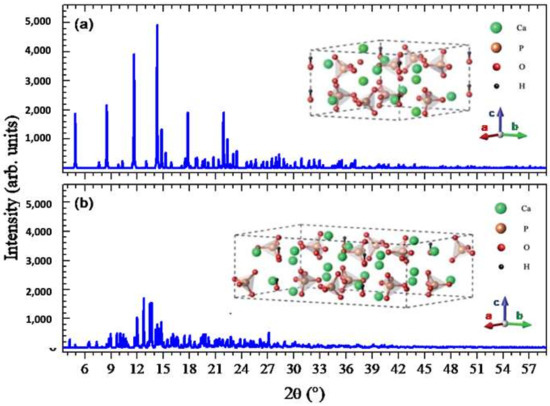
Figure 2.
Calculated powder diffraction pattern using X-ray wavelength of 0.7 Å. (a) Hexagonal phase (space group176, P63/m) and (b) monoclinic phase (space group 14, P21/b). Crystallographic information for (a,b) are respectively from References [24,25]. Structural models are shown in the insets.
The Rietveld refinement analyses and quantification of the phases of HA samples wereperformed using the HighScore Suite program. The refined crystallographic parameters of hexagonal and monoclinic are in good agreement with the references; the results are shown in Table 1. The indexes (hkl) shown in Figure 3 correspond to the X-ray powder diffraction file (PDF+4) card number 04-016-1185 (a = 9.4214(8) Å, b = 2 Å, c = 6.8814(7) Å, and γ = 120°), ICCD PDF4+ #04-007-5086 (a = b = 9.432 Å, c = 6.881 Å), for monoclinic and hexagonal phases respectively. The quantification of phases by the Rietveld method clearly shows that the powder sample analyzed is a mixture of monoclinic and hexagonal phases. The difference in the percentages of phases obtained between copper and synchrotron radiation is due to the radiation source and the high-resolution detector used.

Table 1.
Rietveld refinement and phase quantification of HA.
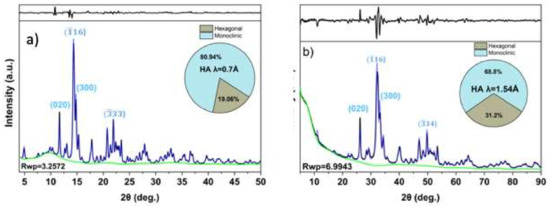
Figure 3.
(a) Room temperature XRD pattern of HA powder sample collected with λ = 0.7 Å (synchrotron radiation); (b) Cu Kα (λ = 1.54 Å) patterns. In case of the SR data, there is a better signal to noise ratio and a larger reciprocal space coverage which permits more reliable phase fraction analysis from a Rietveld refinement analysis.
According to the bibliography mentioned above [10], the peaks corresponding to the monoclinic and hexagonal phases based on the diffractogram are not clearly assigned. Through the use of synchrotron X-ray (SXRPD) and Rietveld refinement we revealed three deconvolved peaks around θ = 9.8, of which two correspond to the monoclinic phase (100) at 2θ = 9.873 and monoclinic (002) at 2θ = 9.856 and one corresponds to the hexagonal phase at 2θ = 9.785; peaks have not been assigned in previous publications.
3.2. Local Piezoelectric Properties
In recent years, resonant PFM has become the widely used technique for the characterization of local piezo-ferroelectric properties in several materials. However, some PFM artifacts can affect the signal obtained during the PFM measurements. There are different sources of these artifacts, including electrostatic forces and electrostriction [26,27]. Some strategies have been developed in order to identify and avoid these artifacts in PFM. One of these strategies was reported by Yuan et al. [28]. This consisted of comparing the first and second harmonic to obtain the electrostriction signal and the piezoelectric contributions. In order to obtain quality PFM measurements, we required the first harmonic to be higher than the second. Measures of the first and second harmonic are shown in Figure 4. Here we can see that the first harmonic is certainly higher than the second, confirming, therefore, that the signal measured was due to the piezoelectric properties of hydroxyapatite. Nonetheless, according to Reference [29], the difference in the phases for piezo-ferroelectric materials needs to be approximately 90°. These measurements agree with the literature recently published [29].
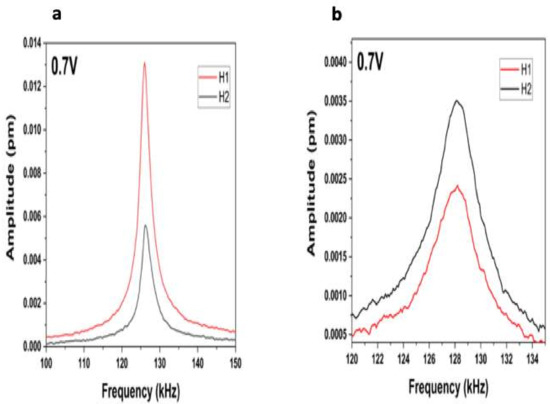
Figure 4.
Comparative response of the first and second harmonic for the sweep of frequencies with a voltage of 0.7 V for (a) Monoclinic HAP and (b) Hexagonal HAP.
Synthetic apatites obtained at low temperatures display a number of characteristics including non-stoichiometry. This fact makes an assessment of stable ionic configuration difficult. Apatites found in bone are piezoelectric, although true apatites with space group P63/m are not [30]. In order to prove this assumption, we prepared a hexagonal hydroxyapatite in the same conditions as those used for the monoclinic synthesis, but the temperature used for this synthesis was 1300 Celsius to guarantee just the hexagonal phase. This hexagonal hydroxyapatite was analyzed by piezoresponse force microscopy to be compared with the monoclinic phase, which is piezoelectric. The monoclinic (Figure 4a) is five times higher in amplitude for the first harmonic values than the hexagonal hydroxyapatite (Figure 4b). The most important point is that the first harmonic for the hexagonal phase is lower than the second one demonstrating therefore that the hexagonal phase is not piezoelectric, which is in agreement with Reference [26]. The change in the polarization plane is determined by the phase domain difference of 90°, whose rotation is due to the polarization vector. A more general study is observed in Figure 5, where the first and second harmonic versus the Vac is shown. It is clear that for low Vac values, the first harmonic is higher than the second. In contrast, for above 1 Vac the inverse behavior was obtained. Additionally, the phase of the first and second harmonic versus the Vac was compared, see Figure 6 (the difference of 90° is evident between the two harmonics [29]). Based on all these results and on the experimental PFM measurements, clear piezoelectric properties were demonstrated for the hydroxyapatite sample.
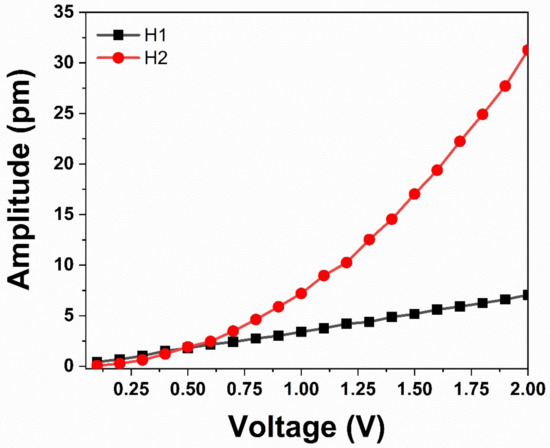
Figure 5.
Values for the first and second harmonic of the PFM cantilever over the surface of HA.
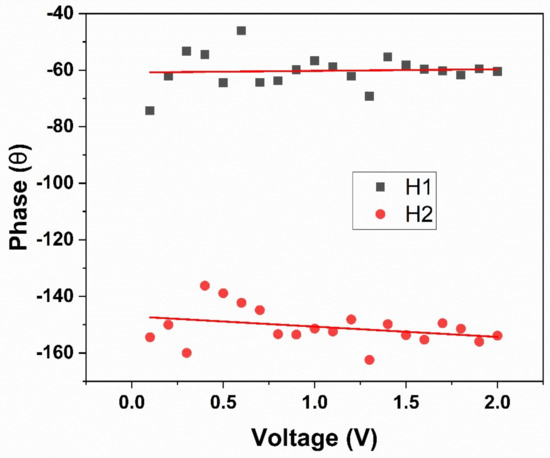
Figure 6.
Corresponding phase values for the voltage sweeps of the first and second harmonics of the PFM tip, where the difference of 90 degrees between the two phases can be seen.
However, the comparison of the first and second harmonic dependson the VAC applied, as shown in Figure 5. For this reason, we performed another test to ascertain the ferroelectricity in the hydroxyapatite sample. Figure 6 also shows the comparison of the first and second harmonic phase. According to Reference [31], a difference of 90 degrees confirms the existence of piezo-ferroelectric systems samples. However, the difference for non-ferroelectric samples is yet to be found. Additionally, some domains and domain walls were obtained by out-plane resonance piezoresponse force microscopy. Figure 7 shows the dependence of the maximum height of the amplitude with respect to the applied Vac voltage. The adjustment of this straight line can be standardized with the PZT, which allows to calculate the average value of deff in the pellet of HA by sweeps of voltage and amplitude. Additionally, some domains and domain walls were obtained by out-plane pinpoint resonance piezoresponse for microscopy. Figure 8 shows the topography of the powder pellet compressed up to 2T metric pressure. An isometric view is usually obtained when measuring with the Pinpoint method, thus showing a rather large roughness due to the size of the grains. Figure 9 shows the domains of the surface of the HA comparing two images in contrasting colors, where the borders of the domains can be seen in the left image while clear domains are observed in the PFM phase.
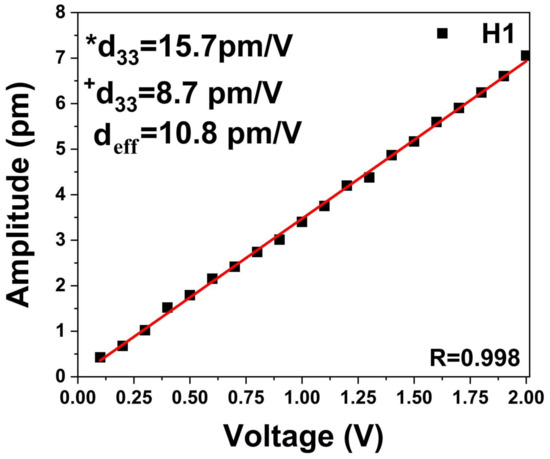
Figure 7.
Representative voltage dependence of the amplitude of HA for H1.
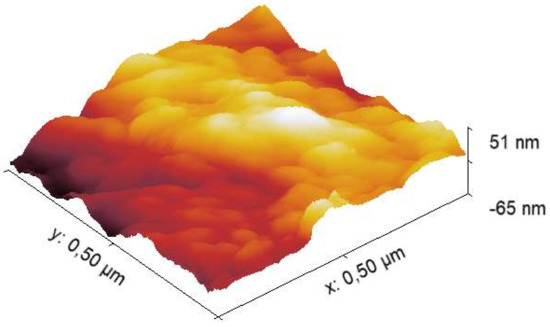
Figure 8.
Topography of the Hydroxyapatite obtained by Pinpoint method.Due to the soft sample, a setpoint of 30 nN–40 nN was used in order to appreciate the shape of the grains on the surface.
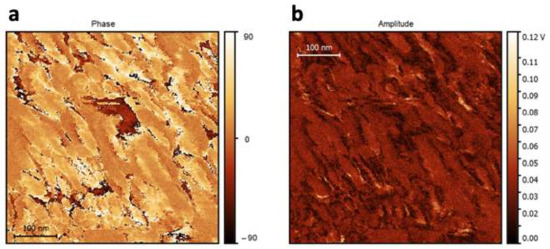
Figure 9.
(a) The PFM phase and (b) the PFM amplitude of the material.
There are different methods to synthesize hydroxyapatites. For instance, Bouyer et al. [32] have synthesized nanometer size hydroxyapatites crystals prepared by a wet chemical precipitation method at different temperatures. By using this method, they took into account the effect of different synthesis parameters on the morphology such as the phase and the rheological properties of the colloidal HA suspensions.
A recent contribution based on modeling using crystallographic data by Uskokovic shows the importance of the hydroxyl ion channel, which runs directly through the center of the basal plane of the hexagonal lattice parallel to the c-axis. This arrangement of the hydroxyl channel seems to be responsible for the extraordinary characteristics of the hydroxyapatites [11]; it does not explain the piezoelectricity effect, but it describes in detail the structure of hydroxyapatites. The hexagonal space group P63/m is centrosymmetric but is not a piezoelectric group as stated by Cockbain [30]. Our results based on experimental data using the piezoresponse in the atomic force microscopy have proved our assumption along this contribution.
4. Conclusions
A high percentage of the monoclinic phase of HA was obtained by means of a sol-gel method assisted by ultrasonic irradiation method. The characterization by synchrotron light showed a percentage of monoclinic phase of 80.94% with an Rwp = 3.5, in comparison with the Cu-Kα data. Thanks to synchrotron radiation we were able to differentiate the peak corresponding to the monoclinic phase from the peak corresponding to the hexagonal phase, a thing that would have been very difficult to do otherwise.
The use of PFM measurements allowed us to calculate the average piezoelectric coefficient value deff = 10.8 pm/V, which agrees with the theoretical (d33 = 15.7 pm/V) and the experimental (d33 = 8.7 pm/V) values reported in the literature [20]. Nonetheless, in the sample, we observed a difference of 90° in the phase signals corresponding to piezo-ferroelectric behavior. This fact confirms that the piezoelectric phase present in the sample is the monoclinic phase of HA. The pinpoint technique is a reliable technique to measure soft materials and to obtain high quality PFM images of domains and domain borders without using additional components from those that are already measured in the contact mode.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.E.M and A.M.; methodology, R.P.-S.; software, J.J.G.-A; validation, R.P.-S., and J.J.G.-A. and M.E.M.; formal analysis, A.M., M.E.M. and B.J.; investigation, R.P.-S., B.J. and J.J.G.-A; resources, ELETTRA SYNCHROTRON.; writing—original draft preparation, R.P.-S.; writing—review and editing, A.M. and M.E.M.
Acknowledgments
One of the authors (RP-S) thanks to CONACYT scholarship for PhD studies registration CVU. 131200. MEM acknowledges CONACYT project No 256788. B.J. acknowledges the IISc-ICTP fellowship from IISc Bangalore and ICTP Trieste. All authors thanks to Antonia Sánchez-Marín for the English revision and grammar corrections of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tamai, N.; Myoui, A.; Tomita, T.; Nakase, T.; Tanaka, J.; Ochi, T.; Yoshikawa, H. Novel hydroxyapatite ceramics with an interconnective porous structure exhibit superior osteoconduction in vivo. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 59, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucholz, R.W.; Carlton, A.; Holmes, R.E. Hydroxyapatite and Tricalcium Phosphate Bone-Graft Substitutes. Orthoped. Clin. N. Am. 1987, 18, 323–334. [Google Scholar]
- Bucholz, R.W.; Carlton, A.; Holmes, R. Interporous Hydroxyapatite as a Bone-Graft Substitute in Tibial Plateau Fractures. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1989, 240, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.A.; Simske, S.J.; Nunes, C.R.; Wolford, L.M. Long-term bone ingrowth and residual microhardness of porous block hydroxyapatite implants in humans. J. Oral Maxil. Surg. 1998, 56, 1297–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohgushi, H.; Goldberg, V.M.; Caplan, A.I. Repair of Bone Defects with Marrow-Cells and Porous Ceramic–Experiments in Rats. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1989, 60, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, A.; Araki, N.; Shinto, Y.; Yoshikawa, H.; Kurisaki, E.; Ono, K. The Use of Calcium Hydroxyapatite Ceramic in Bone-Tumor Surgery. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1990, 72, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heise, U.; Osborn, J.F.; Duwe, F. Hydroxyapatite Ceramic as a Bone Substitute. Int. Orthop. 1990, 14, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.R.; Passi, D.; Singh, P.; Bhuibhar, A. Ceramic and non-ceramic hydroxyapatite as a bone graft material: A brief review. Irish J. Med. Sci. 2015, 184, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlovskii, V.P.; Komlev, V.S.; Barinov, S.M. Hydroxyapatite and hydroxyapatite-based ceramics. Inorg. Mater. 2002, 38, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.B.; Liu, X.Y. Hydroxyapatite: Hexagonal or Monoclinic? Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 2991–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskokovic, V. The role of hydroxyl channel in defining selected physicochemical peculiarities exhibited by hydroxyapatite. Rsc Adv. 2015, 5, 36614–36633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashima, M.; Kubo, N.; Omoto, K.; Fujimori, H.; Fujii, K.; Ohoyama, K. Diffusion Path and Conduction Mechanism of Protons in Hydroxyapatite. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 5180–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverty, D.; Tofail, S.A.M.; Stanton, K.T.; McMonagle, J.B. Structure and stability of hydroxyapatite: Density functional calculation and Rietveld analysis. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 094103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nye, J.F. Physical Properties of Crystals; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Robles-Aguila, M.J.; Mendoza, M.E.; Davila-Jimenez, M.M.; Bentrup, U.; Elizalde-Gonzalez, M.P. Influence of Ni doping on the structural, optical and textural properties of TiO2 nanocrystals prepared via an ultrasound assisted sol-gel method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Agrawal, D.K.; Roy, D.M.; Roy, R. Fabrication of Porous Hydroxyapatite Ceramics by Microwave Processing. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukada, E.; Yasuda, I. On the Piezoelectric Effect of Bone. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1957, 12, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halperin, C.; Mutchnik, S.; Agronin, A.; Molotskii, M.; Urenski, P.; Salai, M.; Rosenman, G. Piezoelectric effect in human bones studied in nanometer scale. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystrov, V.S. Piezoelectricity in the Ordered Monoclinic Hydroxyapatite. Ferroelectrics 2015, 475, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, A.A.; Wojtas, M.; Lang, S.B.; Kholkin, A.L.; Tofail, S.A.M. Piezoelectricity in Poled Hydroxyapatite Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 2867–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Aguila, M.J.; Reyes-Avendano, J.A.; Mendoza, M.E. Structural analysis of metal-doped (Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) calcium hydroxyapatite synthetized by a sol-gel microwave-assisted method. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 12705–12709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, T.; Sadki, M.; Bron, E.; Konig, U.; Nenert, G. The HighScore suite. Powder Diffr. 2014, 29, S13–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, A.S.; Polyakov, V.V.; Bykov, V.A. Hybrid mode piezoresponse force microscopy for compositional electromechanical study of biopiezoelectrics. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 917, 042018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.M.; Elliot, J.C.; Dowker, S.E.P. Rietveld refinement of the crystallographic structure of human dental enamel apatites. Am. Mineral. 1999, 84, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikoma, T.; Yamazaki, A.; Nakamura, S.; Akao, M. Preparation and structure refinement of monoclinic hydroxyapatite. J. Solid State Chem. 1999, 144, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.N.; Ou, Y.; Ma, F.Y.; Li, J.Y. Mechanisms of electromechanical coupling in strain based scanning probe microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, R. Electrochemical strain microscopy of silica glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 66804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Chow, M.J.; Chen, Q.N.; Li, J.Y. Biological Ferroelectricity Uncovered in Aortic Walls by Piezoresponse Force Microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 078103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharb, N.B.; Trolier-McKinstry, S.; Damjanovic, D. Piezoelectric nonlinearity in ferroelectric thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 044107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockbain, A.G. The crystal chemistry of apatites. Miner. Mag. 1968, 36, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.M.; Okatan, M.B.; Paranthaman, M.P.; Jesse, S.; Noh, T.W.; Kalinin, S.V. Second harmonic detection in the electrochemical strain microscopy of Ag-ion conducting glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 193106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyer, E.; Gitzhofer, F.; Boulos, M.I. Morphological study of hydroxyapatite nanocrystals suspension. J. Mat. Sci. Mater. Med. 2000, 11, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).