Structural, Electronic, Magnetic, Mechanic and Thermodynamic Properties of the Inverse Heusler Alloy Ti2NiIn Under Pressure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Computational Details
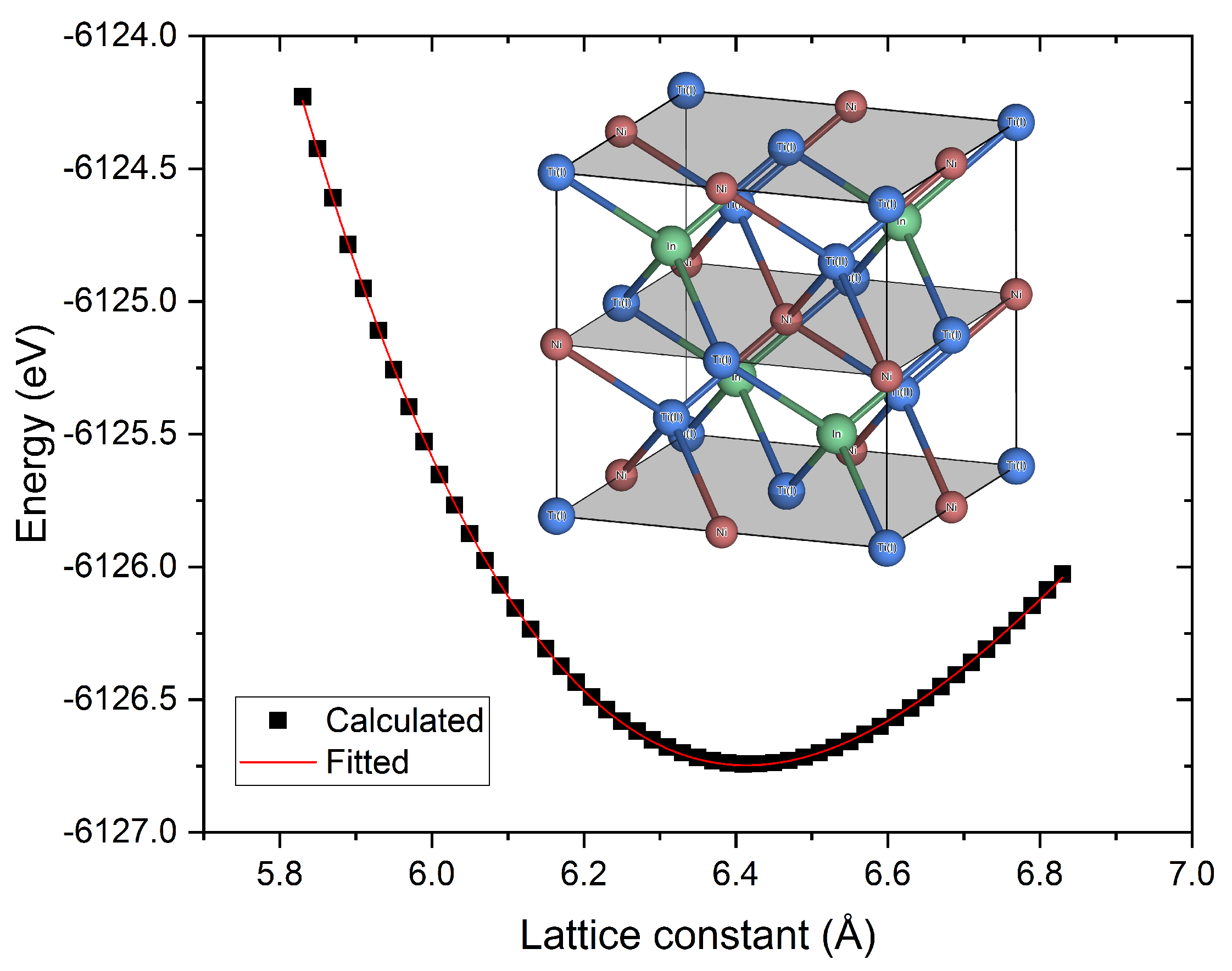
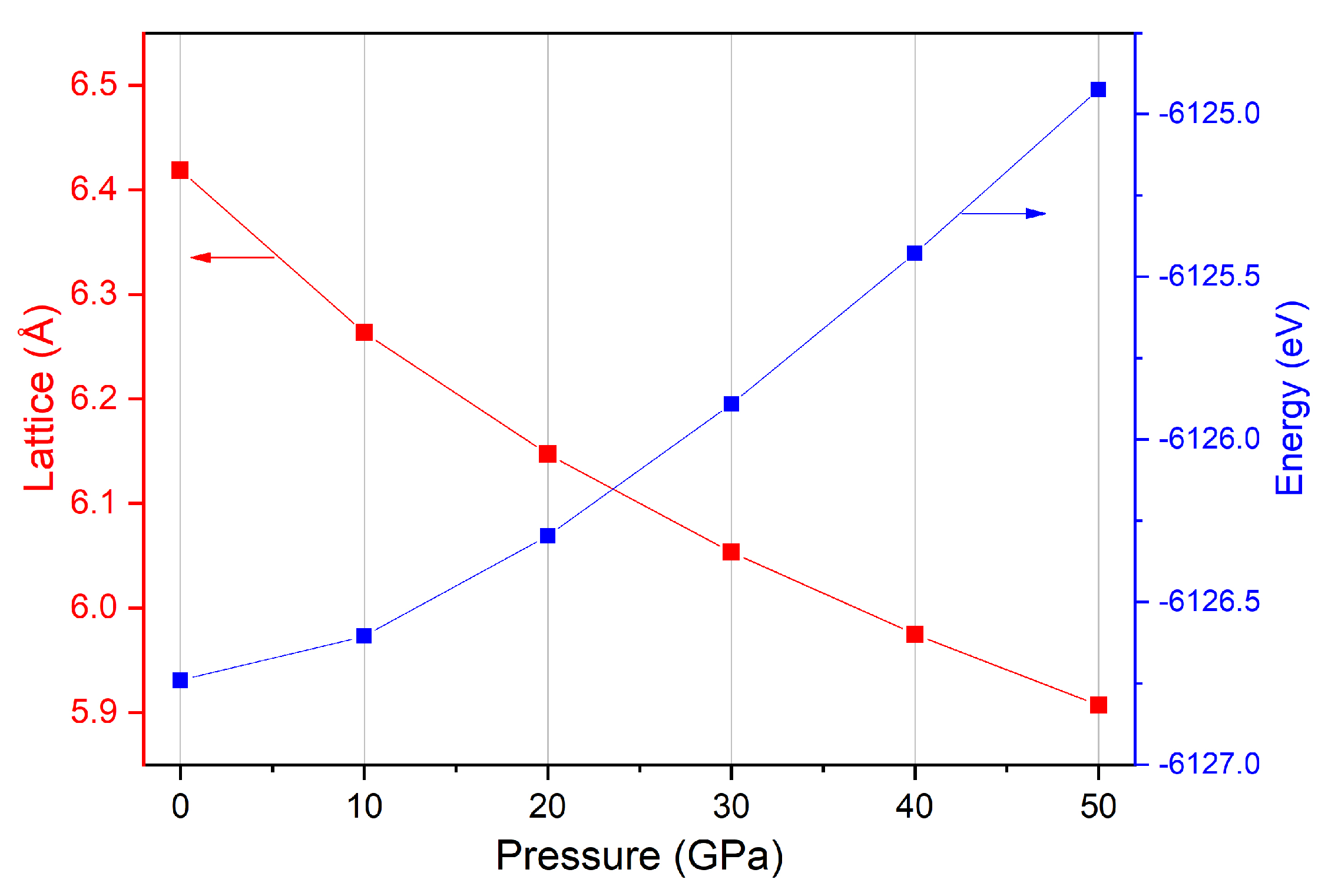
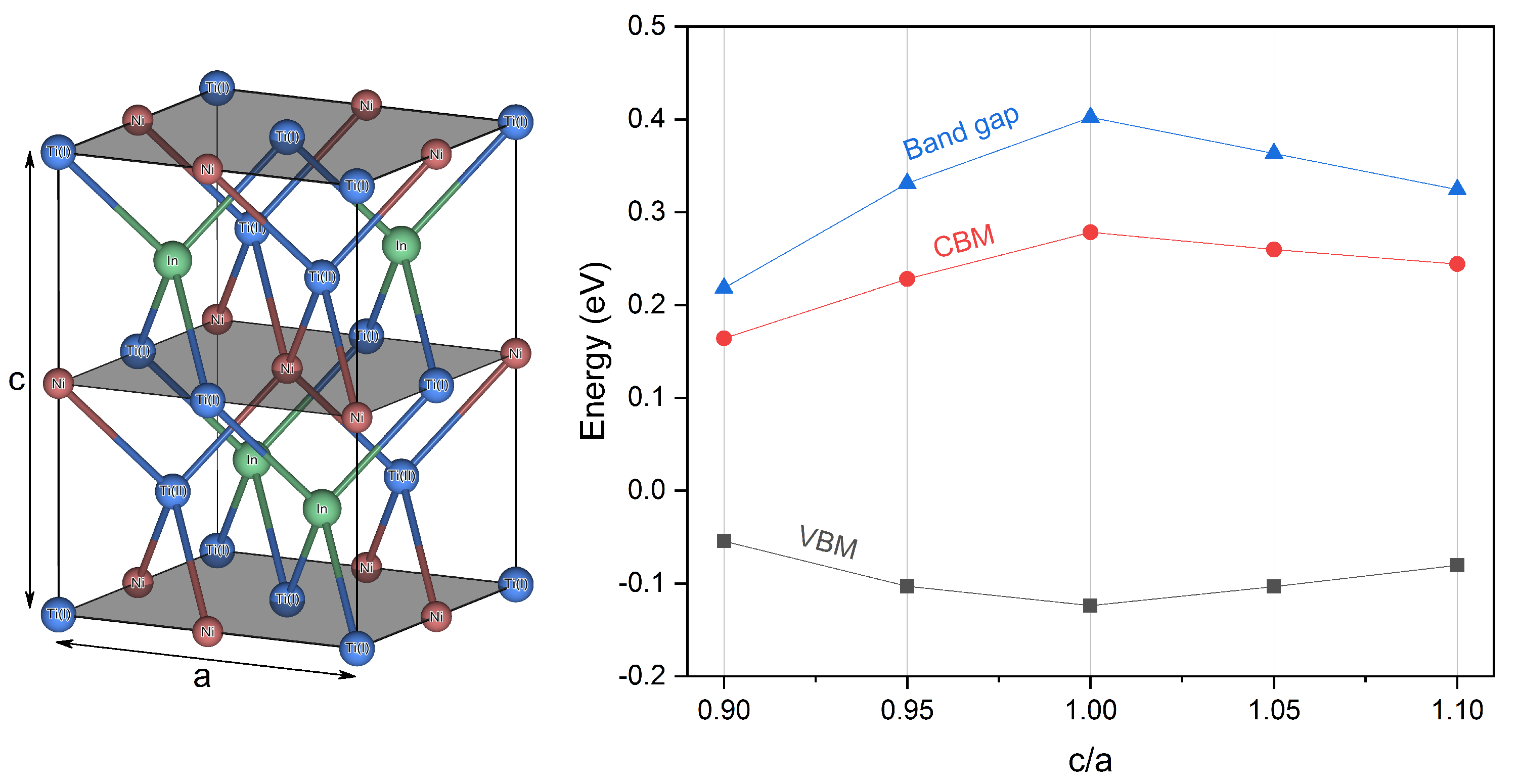
2.1. Crystal Structure and Equilibrium Lattice
2.2. Electronic and Magnetic Properties
2.3. Mechanical Properties
2.4. Thermodynamic Properties
3. Results and Discussion
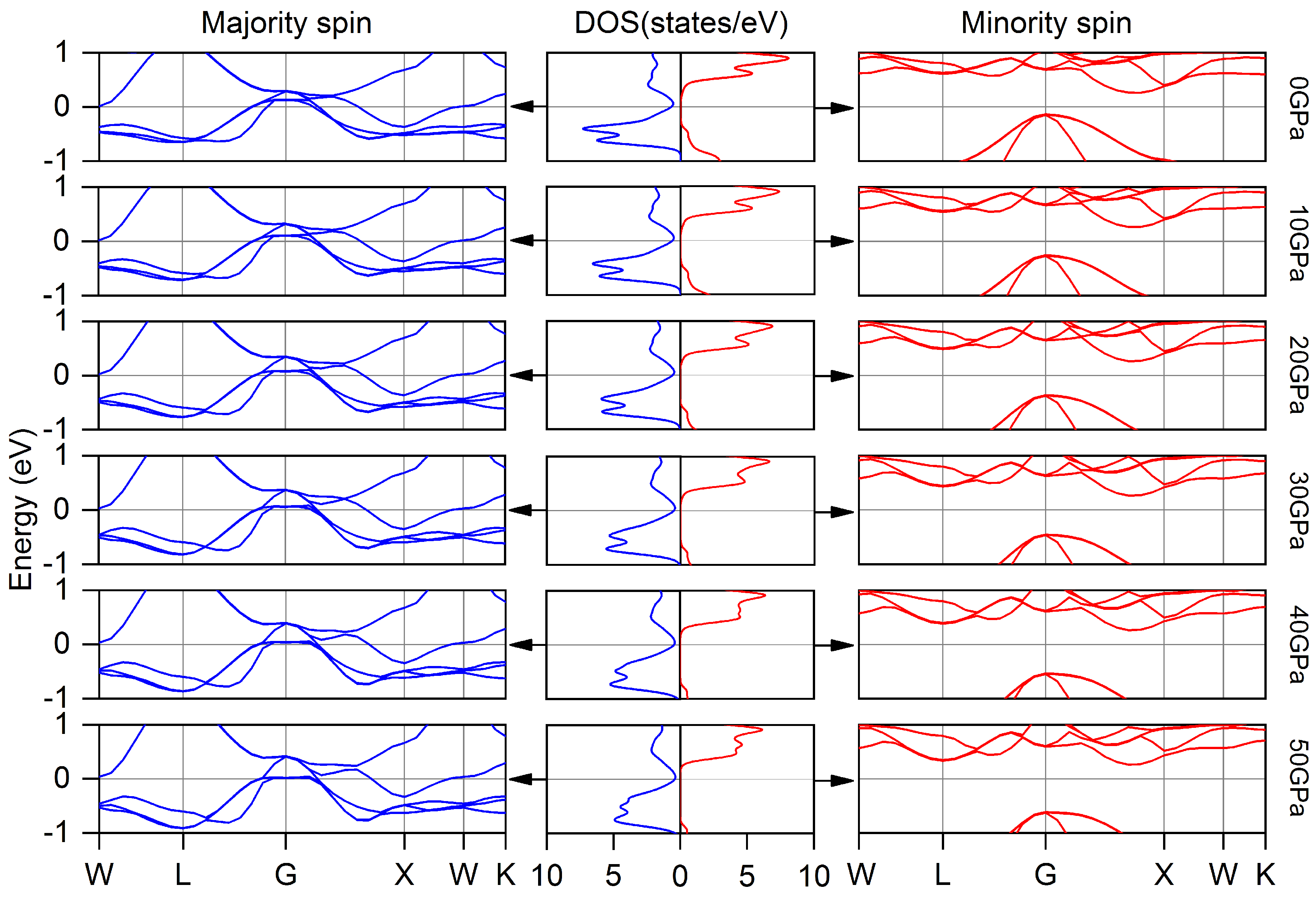
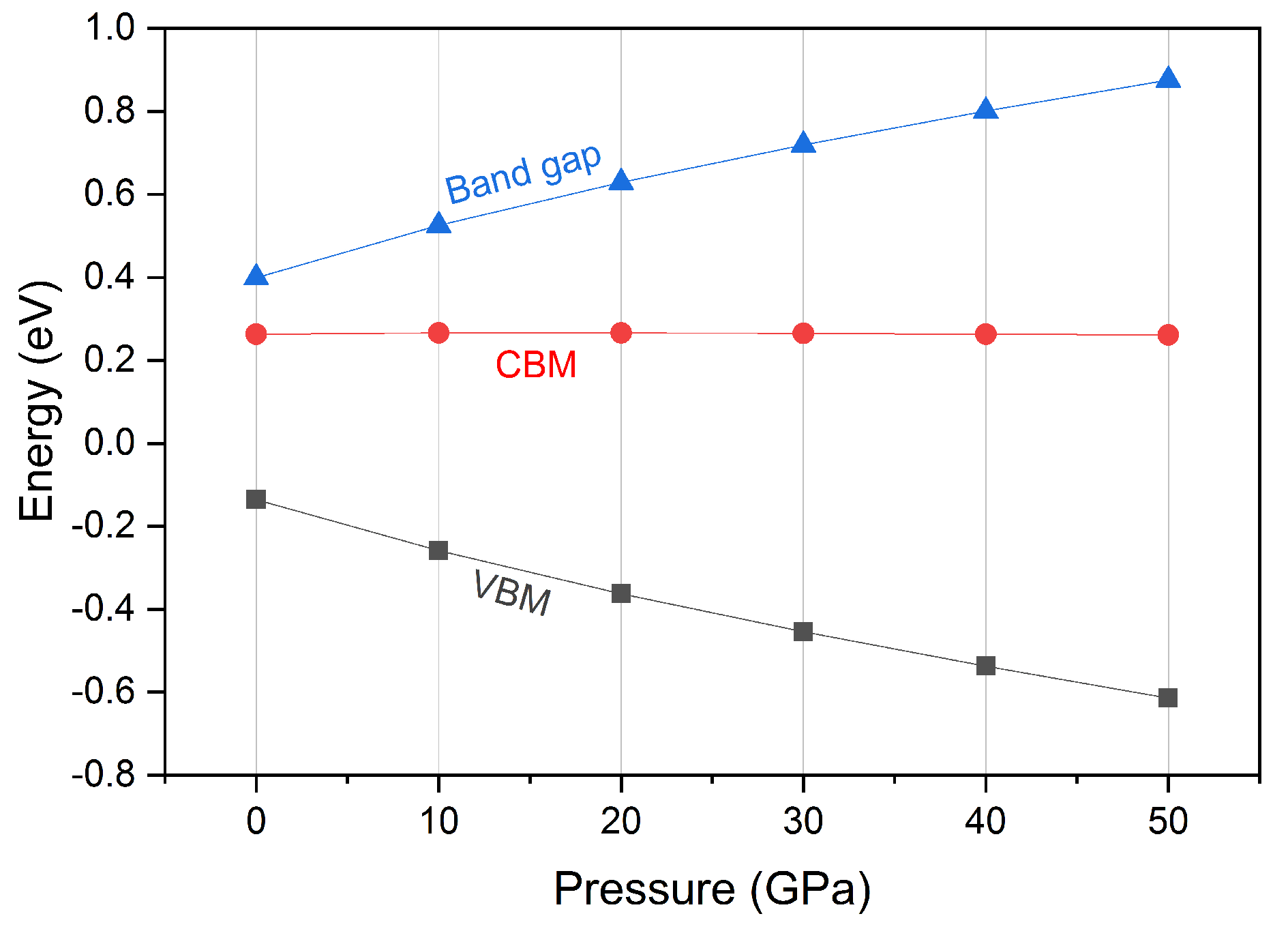
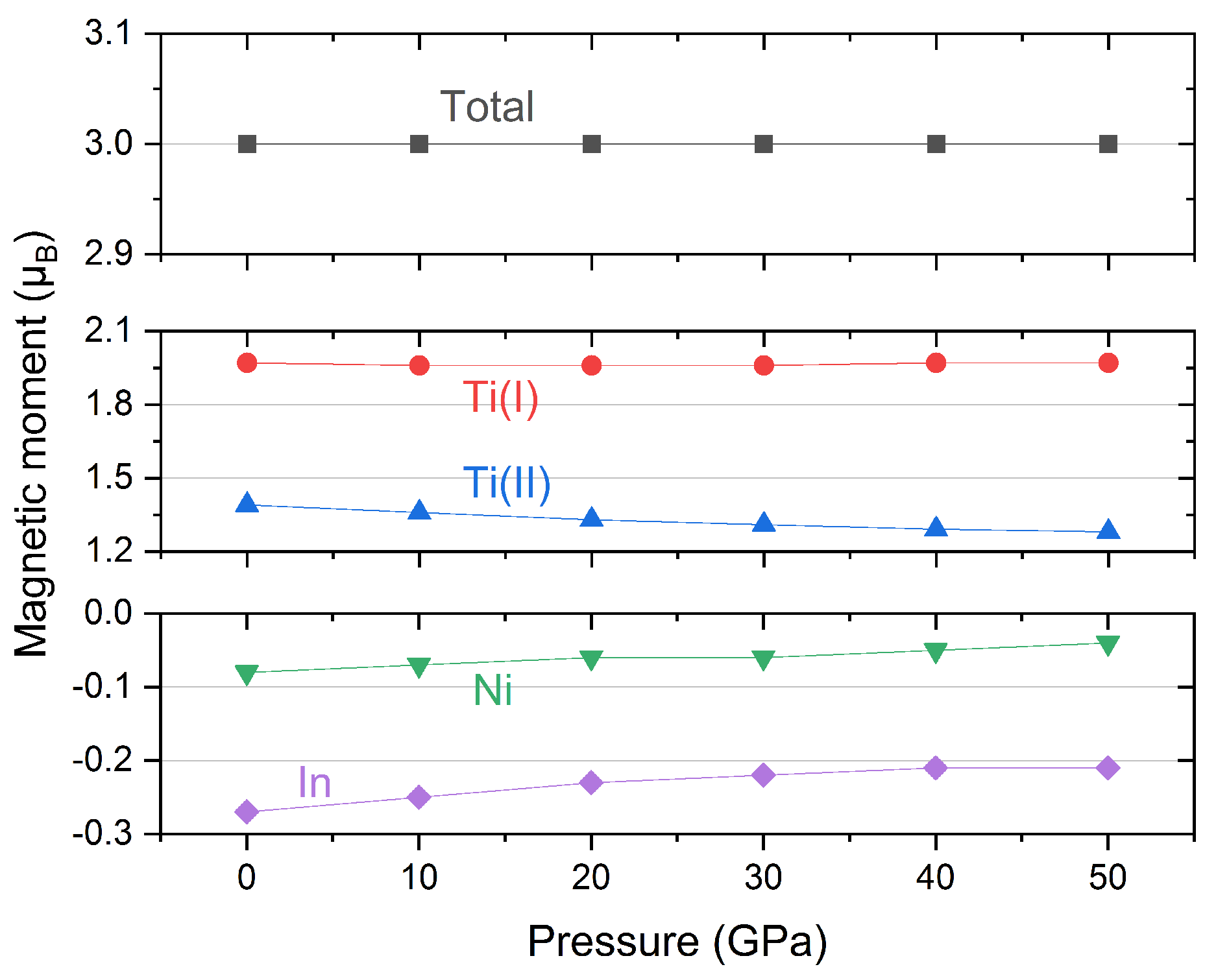
3.1. Electronic, Magnetic and Half-Metallic Behaviors
3.2. Mechanic Properties
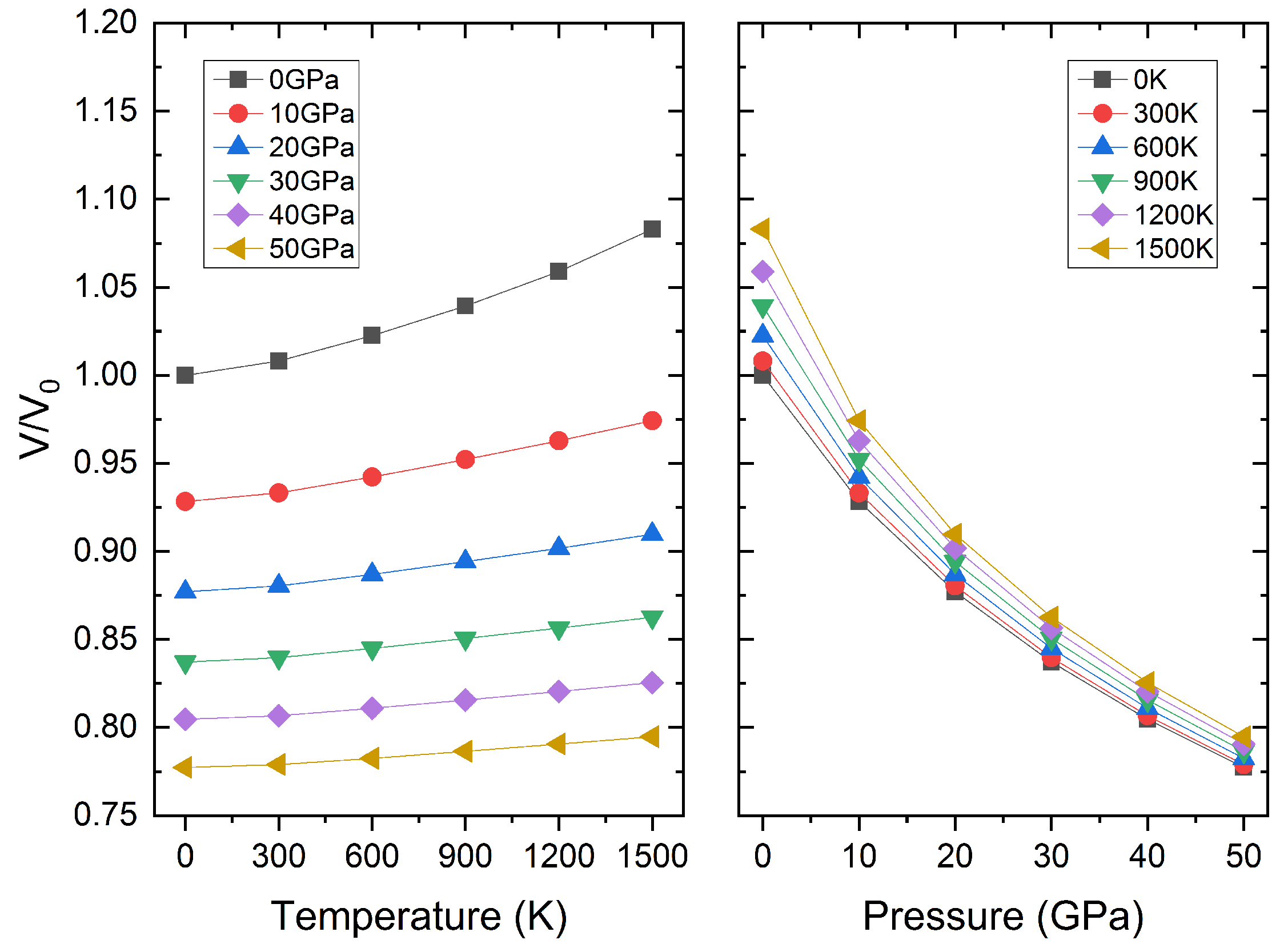
3.3. Thermodynamic Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Žutić, I.; Fabian, J.; Das Sarma, S. Spintronics: Fundamentals and applications. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2004, 76, 323–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, R.A.; Mueller, F.M.; van Engen, P.G.; Buschow, K.H.J. New Class of Materials: Half-Metallic Ferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983, 50, 2024–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leuken, H.; de Groot, R.A. Half-Metallic Antiferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 1171–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.Y.; Hu, L.; Yao, K.L.; Luo, B.; Liu, N. Large half-metallic gaps in the quaternary Heusler alloys CoFeCrZ (Z=Al, Si, Ga, Ge): A first-principles study. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 551, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, T.; Khenata, R.; Yang, T.; Wang, X. Electronic, Magnetic, Half-Metallic, and Mechanical Properties of a New Equiatomic Quaternary Heusler Compound YRhTiGe: A First-Principles Study. Materials 2018, 11, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alijani, V.; Ouardi, S.; Fecher, G.H.; Winterlik, J.; Naghavi, S.S.; Kozina, X.; Stryganyuk, G.; Felser, C.; Ikenaga, E.; Yamashita, Y.; et al. Electronic, structural, and magnetic properties of the half-metallic ferromagnetic quaternary Heusler compounds CoFeMnZ (Z=Al, Ga, Si, Ge). Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 224416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainsla, L.; Mallick, A.I.; Raja, M.M.; Nigam, A.K.; Varaprasad, B.S.D.C.S.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Alam, A.; Suresh, K.G.; Hono, K. Spin gapless semiconducting behavior in equiatomic quaternary CoFeMnSi Heusler alloy. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 91, 104408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Khachai, H.; Khenata, R.; Yuan, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Bouhemadou, A.; Hao, L.; Dai, X.; Guo, R.; et al. Structural, electronic, magnetic, half-metallic, mechanical, and thermodynamic properties of the quaternary Heusler compound FeCrRuSi: A first-principles study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bainsla, L.; Suresh, K.G. Equiatomic quaternary Heusler alloys: A material perspective for spintronic applications. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2016, 3, 031101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainsla, L.; Mallick, A.I.; Coelho, A.A.; Nigam, A.K.; Varaprasad, B.S.D.C.S.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Alam, A.; Suresh, K.G.; Hono, K. High spin polarization and spin splitting in equiatomic quaternary CoFeCrAl Heusler alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 394, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, T.; Yuan, H.; Chen, H. Structural stability, half-metallicity and magnetism of the CoFeMnSi/GaAs(001) interface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 346, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurmehl, S.; Fecher, G.H.; Kandpal, H.C.; Ksenofontov, V.; Felser, C.; Lin, H.J. Investigation of Co2FeSi: The Heusler compound with highest Curie temperature and magnetic moment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 032503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gofryk, K.; Kaczorowski, D.; Plackowski, T.; Leithe-Jasper, A.; Grin, Y. Magnetic and transport properties of rare-earth-based half-Heusler phases RPdBi: Prospective systems for topological quantum phenomena. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 035208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.K.; Suresh, K.G.; Nigam, A.K. Anomalous effects of repeated martensitic transitions on the transport, magnetic and thermal properties in Ni–Co–Mn–Sb Heusler alloy. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 3304–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.T.; Cui, Y.T.; Liu, X.F.; Liu, G.D. Electronic structures and magnetism in the Li2AgSb-type Heusler alloys, Zr2CoZ (Z=Al, Ga, In, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, Sb): A first-principles study. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 394, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiker A, S.; Gao, G.; Yao, K. Half-metallicity and magnetism of Heusler alloys Co2HfZ (Z=Al, Ga, Ge, Sn). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 441, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akriche, A.; Bouafia, H.; Hiadsi, S.; Abidri, B.; Sahli, B.; Elchikh, M.; Timaoui, M.A.; Djebour, B. First-principles study of mechanical, exchange interactions and the robustness in Co2MnSi full Heusler compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 422, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jin, Y. A spin-gapless semiconductor of inverse Heusler Ti2CrSi alloy: First-principles prediction. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 385, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.P.; Deng, J.B.; Mao, G.Y.; Chu, S.B.; Hu, X.R. Half-metallic properties for the Ti2YZ (Y = Fe, Co, Ni, Z = Al, Ga, In) Heusler alloys: A first-principles study. Intermetallics 2012, 29, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Jin, Y. Band-gap and Slater–Pauling rule in half-metallic Ti2-based Heusler alloys: A first-principles study. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 3099–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birsan, A.; Palade, P.; Kuncser, V. Half-metallic state and magnetic properties versus the lattice constant in Ti2CoSn Heusler compound: An ab initio study. Solid State Commun. 2012, 152, 2147–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.L.; Zhang, J.M.; Xu, K.W. Magnetic properties and origin of the half-metallicity of Ti2MnZ (Z = Al, Ga, In, Si, Ge, Sn) Heusler alloys with the Hg2CuTi-type structure. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 349, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Hao, L.; Khenata, R.; Wang, X. Strain Conditions for the Inverse Heusler Type Fully Compensated Spin-Gapless Semiconductor Ti2MnAl: A First-Principles Study. Materials 2018, 11, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.Y.; Dai, X.F.; Wang, L.Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, X.T.; Li, P.P.; Cui, Y.T.; Liu, G.D. Ti2MnZ (Z = Al, Ga, In) compounds: Nearly spin gapless semiconductors. AIP Adv. 2014, 4, 047113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Muechler, L.; Manna, K.; Zhang, Y.; Koepernik, K.; Car, R.; van den Brink, J.; Felser, C.; Sun, Y. Prediction of a magnetic Weyl semimetal without spin-orbit coupling and strong anomalous Hall effect in the Heusler compensated ferrimagnet Ti2MnAl. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 97, 060406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Tang, C.; Wang, S.; He, W. Half-metallic full-Heusler compound Ti2NiAl: A first-principles study. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 5187–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Wang, S.J. A New Ti-Based Half-Metallic Compound: A First-Principles Study. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 320, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudali, A.; Zemouli, M.; Saadaoui, F.; Khodja, M.D. Structural, Elastic, Electronic, and Magnetic Properties of the Full-Heusler Compounds Ti2NiX (X= Al, Ga, and In). J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 2017, 30, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.P.; Zhang, Y.L.; Sun, X.W.; Song, T.; Guo, P. The electronic and magnetic properties of defects on half-metallic Ti2NiIn alloy. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 233, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, M.C.; Teter, M.P.; Allan, D.C.; Arias, T.A.; Joannopoulos, J.D. Iterative minimization techniques for ab initio total-energy calculations: Molecular dynamics and conjugate gradients. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1992, 64, 1045–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, M.D.; Philip, J.D.L.; Probert, M.J.; Pickard, C.J.; Hasnip, P.J.; Clark, S.J.; Payne, M.C. First-principles simulation: Ideas, illustrations and the CASTEP code. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Yu, X.; Zeng, X.; Ye, Y.; Wu, D.; Gou, Q. Ab initio calculations of the mechanical and acoustic properties of Ti2-based Heusler alloys under pressures. Eur. Phys. J. B 2018, 91, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.P.; Chu, Y.D.; Sun, X.W.; Deng, J.B. First-principles study on stability, electronic and thermodynamic properties of Ti2CoIn and Ti2NiIn. Eur. Phys. J. B 2013, 86, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfrommer, B.G.; Côté, M.; Louie, S.G.; Cohen, M.L. Relaxation of Crystals with the Quasi-Newton Method. J. Comput. Phys. 1997, 131, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Yip, S.; Phillpot, S.; Wolf, D. Mechanical instabilities of homogeneous crystals. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 52, 12627–12635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin’ko, G.V.; Smirnov, N.A. Ab initio calculations of elastic constants and thermodynamic properties of bcc, fcc, and hcp Al crystals under pressure. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 6989. [Google Scholar]
- Yip, S.; Li, J.; Tang, M.; Wang, J. Mechanistic aspects and atomic-level consequences of elastic instabilities in homogeneous crystals. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 317, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R. The Elastic Behaviour of a Crystalline Aggregate. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. A 1952, 65, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.J.; Zhao, E.J.; Xiang, H.P.; Hao, X.F.; Liu, X.J.; Meng, J. Crystal structures and elastic properties of superhard IrN2 and IrN3 from first principles. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 054115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherid, S.; Benstaali, W.; Abbad, A.; Bentata, S.; Lantri, T.; Abbar, B. Theoretical prediction of half metallic ferromagnetic full-Heusler alloys Cs2CrGe. Solid State Commun. 2017, 260, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.A.; Francisco, E.; Luaña, V. GIBBS: Isothermal-isobaric thermodynamics of solids from energy curves using a quasi-harmonic Debye model. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2004, 158, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-de-la Roza, A.; Abbasi-Pérez, D.; Luaña, V. Gibbs2: A new version of the quasiharmonic model code. II. Models for solid-state thermodynamics, features and implementation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2011, 182, 2232–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-de-la Roza, A.; Luaña, V. Gibbs2: A new version of the quasi-harmonic model code. I. Robust treatment of the static data. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2011, 182, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

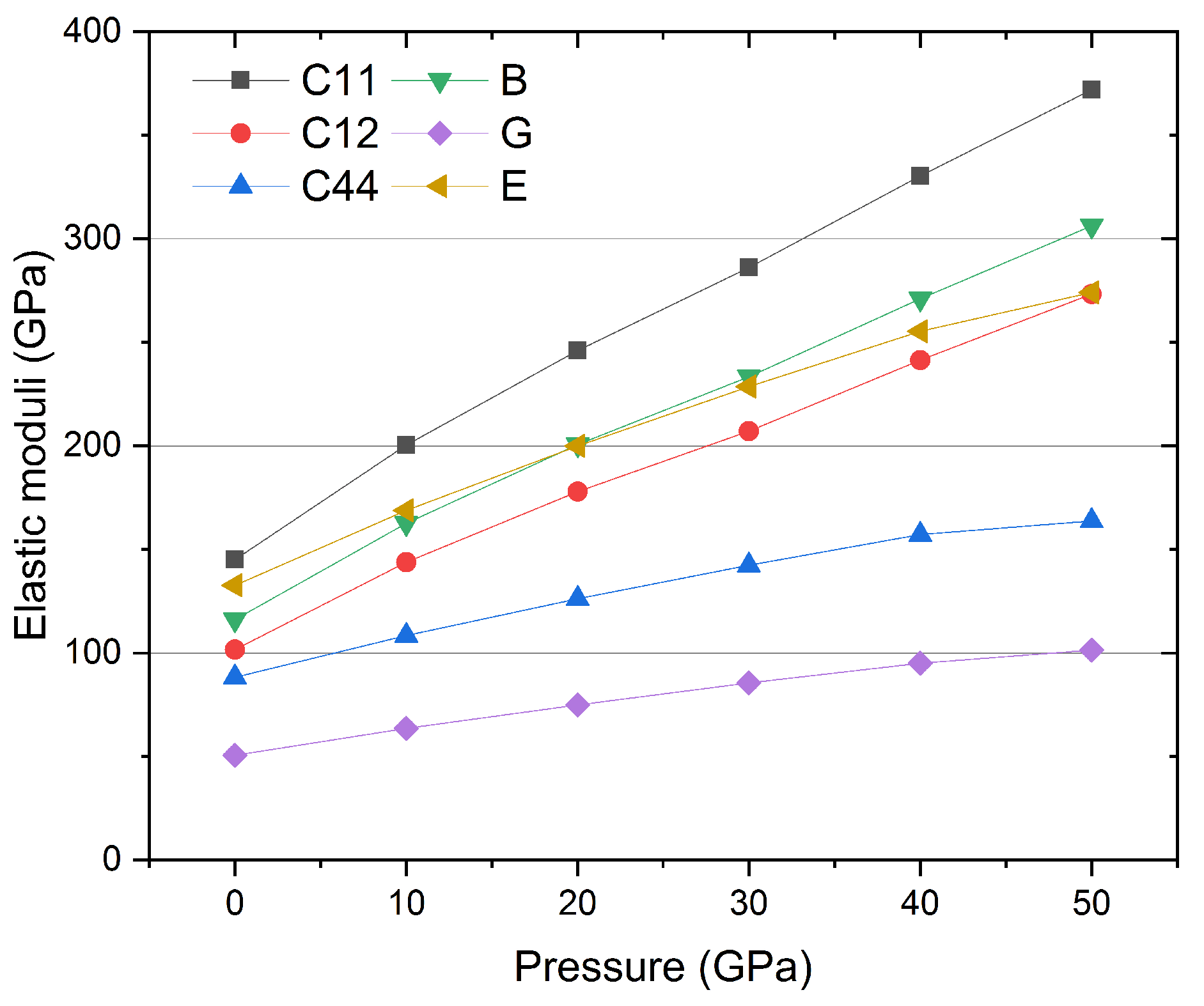
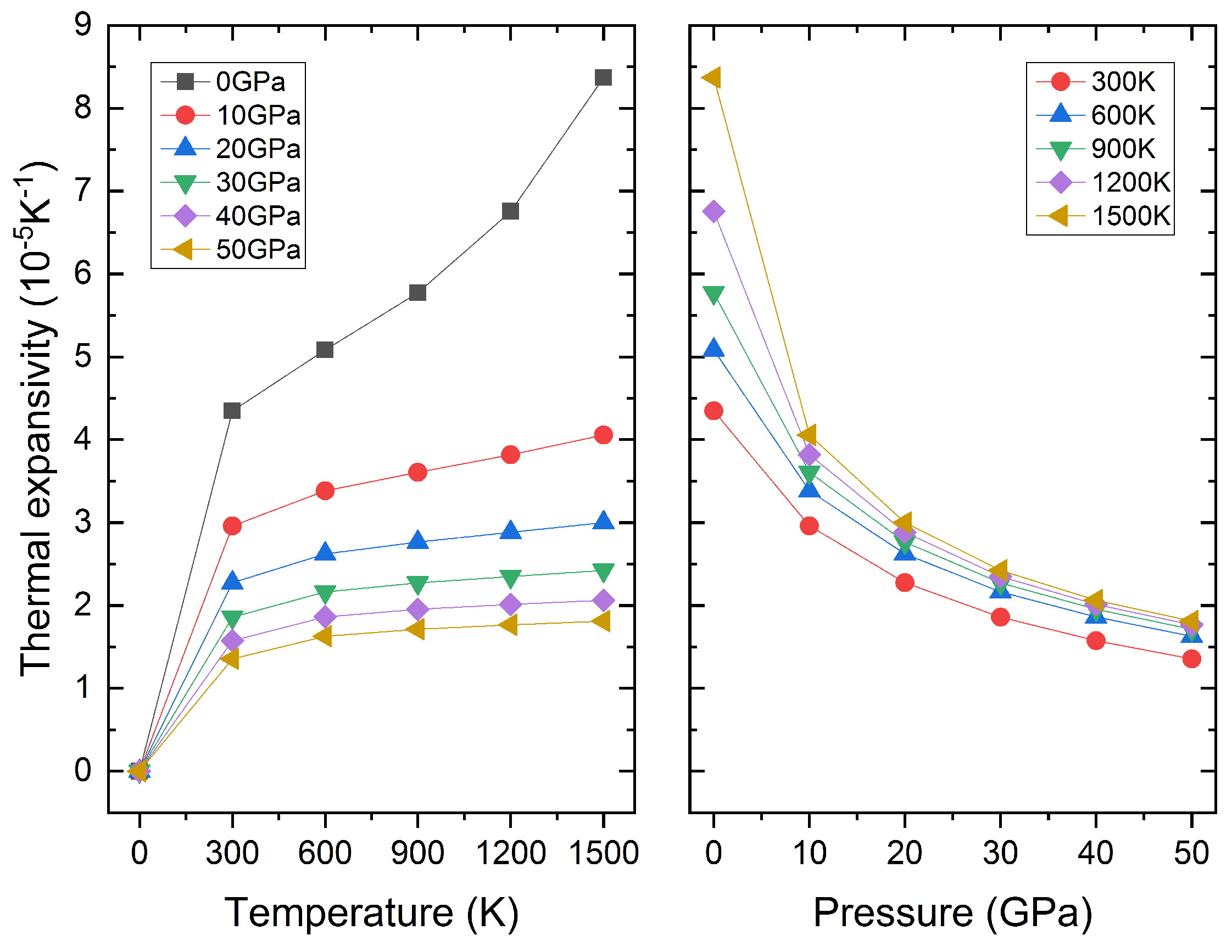
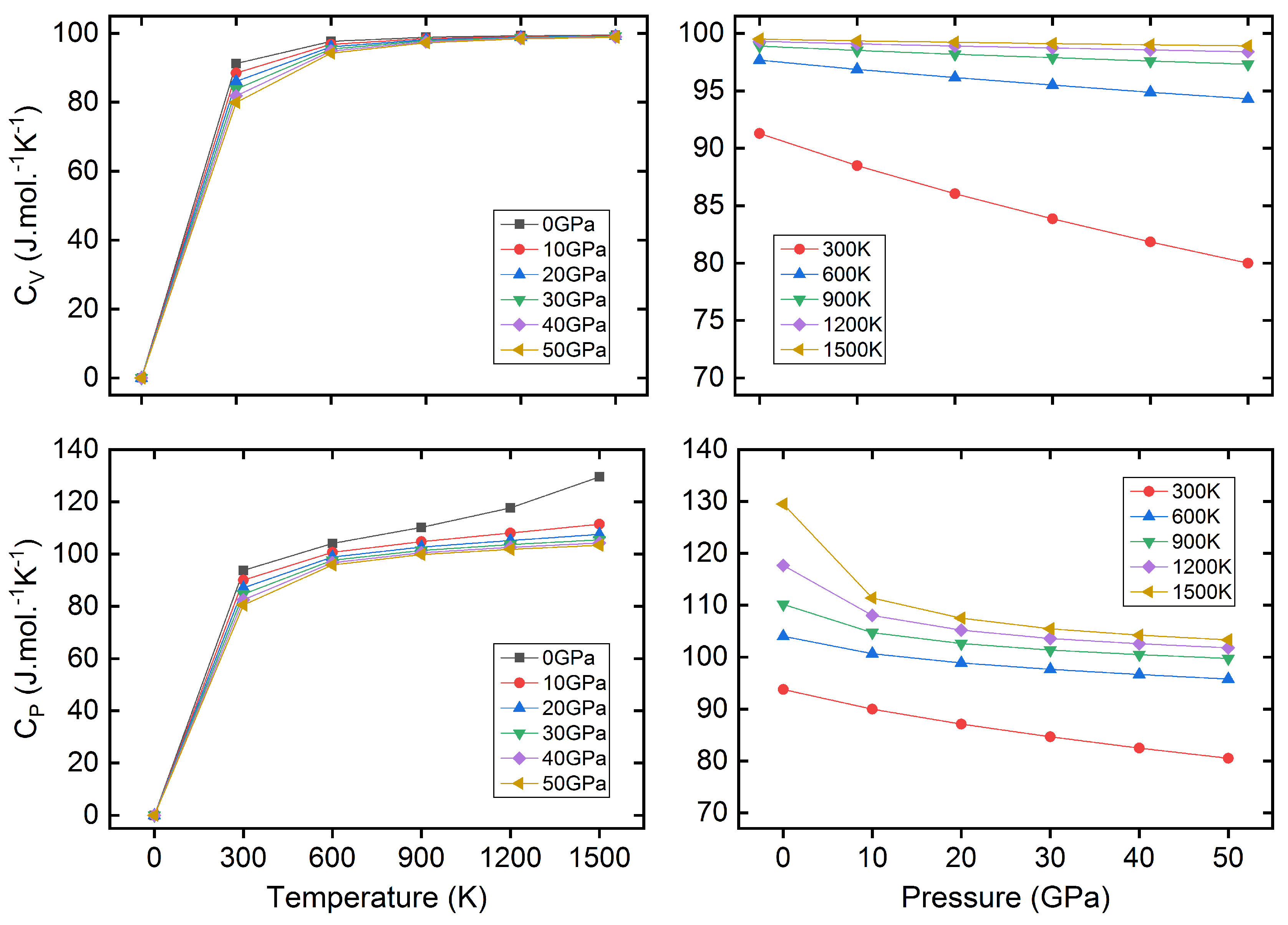

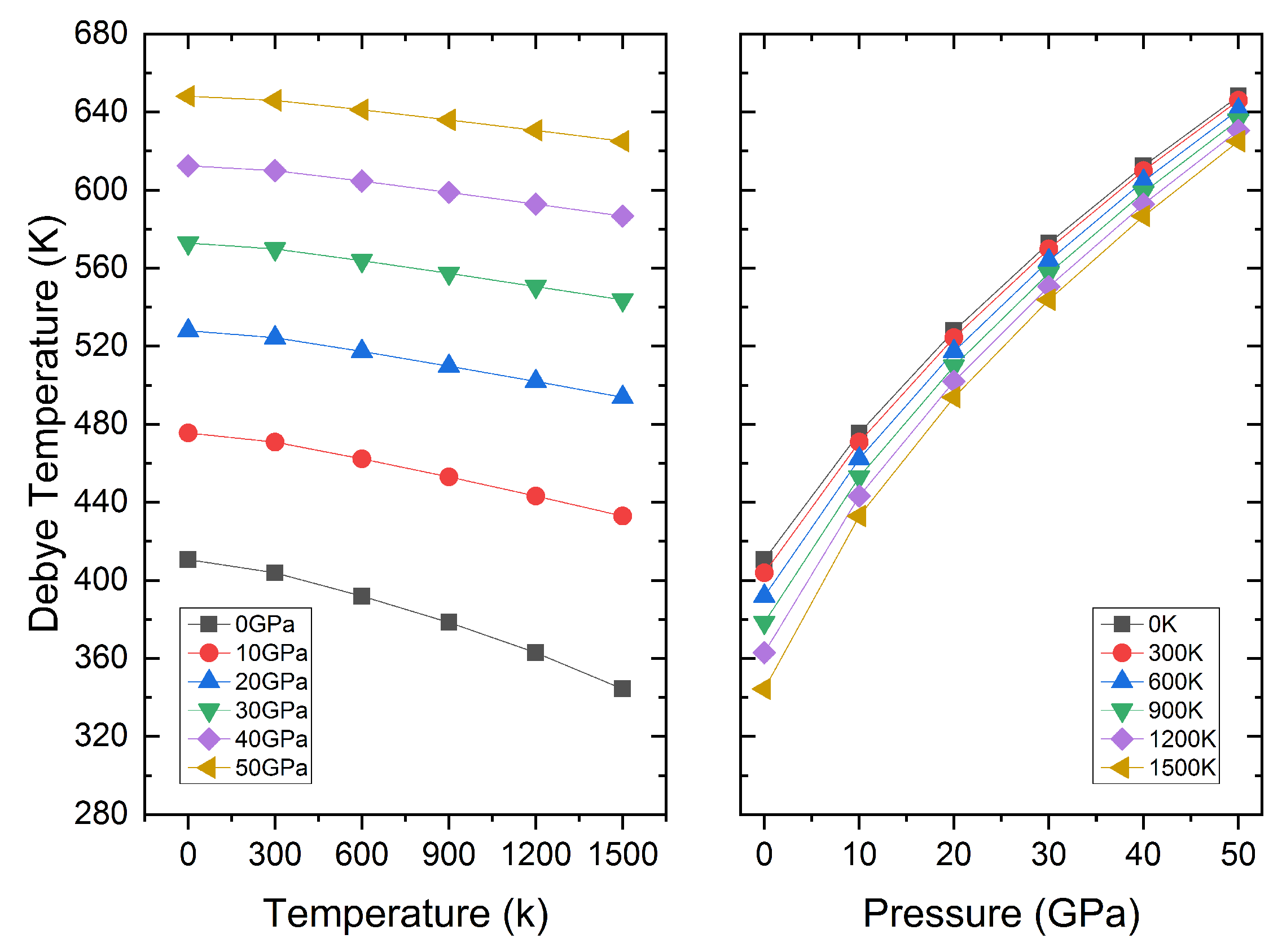
| P | C11 | C12 | C44 | B | G | E | B/G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (GPa) | (GPa) | (GPa) | (GPa) | (GPa) | (GPa) | (GPa) | |
| 0 | 145.06 | 101.66 | 88.24 | 116.13 | 50.63 | 132.61 | 2.29 |
| 10 | 200.41 | 143.84 | 108.47 | 162.70 | 63.61 | 168.83 | 2.56 |
| 20 | 246.02 | 177.93 | 126.21 | 200.63 | 74.97 | 199.99 | 2.68 |
| 30 | 286.15 | 207.09 | 142.41 | 233.44 | 85.52 | 228.64 | 2.73 |
| 40 | 330.37 | 241.47 | 157.26 | 271.10 | 95.09 | 255.40 | 2.85 |
| 50 | 372.05 | 273.39 | 163.73 | 306.28 | 101.45 | 274.09 | 3.02 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, T.; Cao, J.; Wang, X. Structural, Electronic, Magnetic, Mechanic and Thermodynamic Properties of the Inverse Heusler Alloy Ti2NiIn Under Pressure. Crystals 2018, 8, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8110429
Yang T, Cao J, Wang X. Structural, Electronic, Magnetic, Mechanic and Thermodynamic Properties of the Inverse Heusler Alloy Ti2NiIn Under Pressure. Crystals. 2018; 8(11):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8110429
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Tie, Jieting Cao, and Xiaotian Wang. 2018. "Structural, Electronic, Magnetic, Mechanic and Thermodynamic Properties of the Inverse Heusler Alloy Ti2NiIn Under Pressure" Crystals 8, no. 11: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8110429
APA StyleYang, T., Cao, J., & Wang, X. (2018). Structural, Electronic, Magnetic, Mechanic and Thermodynamic Properties of the Inverse Heusler Alloy Ti2NiIn Under Pressure. Crystals, 8(11), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8110429






