Propylene-Selective Thin Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Membranes on Ceramic Tubes by Microwave Seeding and Solvothermal Secondary Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carne, A.; Carbonell, C.; Imaz, I.; Maspoch, D. Nanoscale metal-organic materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhah, O.; Liu, J.; Fischer, R.A.; Woll, C. MOF thin films: Existing and future applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1081–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodenas, T.; Luz, I.; Prieto, G.; Seoane, B.; Miro, H.; Corma, A.; Kapteijn, F.; Xamena, F.X.L.I.; Gascon, J. Metal-organic framework nanosheets in polymer composite materials for gas separation. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Xue, M.; Zhu, G. Metal-organic framework membranes: From synthesis to separation application. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6116–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Cote, A.P.; Furukawa, H.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Colossal cages in zeolitic imidazolate frameworks as selective carbon dioxide reservoirs. Nature 2008, 453, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, W.; Doonan, C.J.; Furukawa, H.; Banerjee, R.; Yaghi, O.M. Crystals as molecules: Postsynthesis covalent functionalization of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12626–12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.S.; Ni, Z.; Cote, A.P.; Choi, J.Y.; Huang, R.D.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Chae, H.K.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Exceptional chemical and thermal stability of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. PNAS 2006, 103, 10186–10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, H.; Cote, A.P.; Furukawa, H.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Zeolite a imidazolate frameworks. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravanchi, M.T.; Kaghazchi, T.; Kargari, A. Application of membrane separation processes in petrochemical industry: A review. Desalination 2009, 235, 199–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, R.B. Olefin/paraffin separation technology: A review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1993, 32, 2208–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bux, H.; Liang, F.; Li, Y.; Cravillon, J.; Wiebcke, M.; Caro, J.R. Zeolitic imidazolate framework membrane with molecular sieving properties by microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16000–16001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.C.; Li, T.; Lestari, G.; Lai, Z.P. Effective separation of propylene/propane binary mixtures by zif-8 membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 390, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramu, G.; Lee, M.; Jeong, H.-K. Effects of zinc salts on the microstructure and performance of zeolitic-imidazolate framework zif-8 membranes for propylene/propane separation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 259, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.T.; Jeong, H.K.; Lee, A.S.; An, H.S.; Lee, J.S. Heteroepitaxially grown zeolitic imidazolate framework membranes with unprecedented propylene/propane separation performances. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 12304–12311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.T.; Jeong, H.K. Highly propylene-selective supported zeolite-imidazolate framework (zif-8) membranes synthesized by rapid microwave-assisted seeding and secondary growth. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3854–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Kwon, H.T.; Jeong, H.K. Defect-dependent stability of highly propylene-selective zeolitic-imidazolate framework zif-8 membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, D.; Yi, Z.; Cao, R. Bimetallic alloy nanocrystals encapsulated in zif-8 for synergistic catalysis of ethylene oxidative degradation. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 10115–10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, M.C.; Varela-Guerrero, V.; Barnett, G.V.; Jeong, H.K. Synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework films and membranes with controlled microstructures. Langmuir 2010, 26, 14636–14641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.S.; Bux, H.; Feldhoff, A.; Li, G.L.; Yang, W.S.; Caro, J. Controllable synthesis of metal–organic frameworks: From mof nanorods to oriented mof membranes. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3322–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.S.; Liang, F.Y.; Bux, H.; Feldhoff, A.; Yang, W.S.; Caro, J. Molecular sieve membrane: Supported metal–organic framework with high hydrogen selectivity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 122, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Lai, Z. Sharp separation of c2/c3 hydrocarbon mixtures by zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (zif-8) membranes synthesized in aqueous solutions. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10275–10277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.; Kwon, H.T.; Tran, V.; Sachdeva, S.; Jeong, H.-K. One step in situ synthesis of supported zeolitic imidazolate framework zif-8 membranes: Role of sodium formate. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 165, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yao, J.; Chen, R.; He, L.; Wang, K.; Wang, H. Infiltration of precursors into a porous alumina support for zif-8 membrane synthesis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 168, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.T.; Jeong, H.-K.; Lee, A.S.; An, H.S.; Lee, T.; Jang, E.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, J. Defect-induced ripening of zeolitic-imidazolate framework zif-8 and its implication to vapor-phase membrane synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11669–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bissett, H.; Zah, J.; Krieg, H.M. Manufacture and optimization of tubular ceramic membrane supports. Powder Technol. 2008, 181, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesheuvel, P.M.; Breedveld, V.; Higler, A.P.; Verweij, H. Graded membrane supports produced by centrifugal casting of a slightly polydisperse suspension. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 3517–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina, M.; Arruebo, M.; Felipe, M.; Fleta, F.; Bernal, M.; Coronas, J.; Menendez, M.; Santamaria, J. A semi-continuous method for the synthesis of naa zeolite membranes on tubular supports. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 244, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W.; Low, B.T. Gas separation membrane materials: A perspective. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 6999–7013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlacher, T.; Wessling, M. Gas–gas separation by membranes. In Progress in Filtration and Separation; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 557–584. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, N.; Yoshimune, M.; Negishi, H.; Haraya, K.; Hara, S.; Yamaguchi, T. Diffusive separation of propylene/propane with zif-8 membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 450, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, N.; Yoshimune, M.; Negishi, H.; Haraya, K.; Hara, S.; Yamaguchi, T. Effect of temperature on synthesis of zif-8 membranes for propylene/propane separation by counter diffusion method. J. Jpn. Pet. Inst. 2015, 58, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Okubo, K.; Kida, K.; Sugita, M.; Takewaki, T. Grain size control of zif-8 membranes by seeding-free aqueous synthesis and their performances in propylene/propane separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 544, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, T.; Shen, H.; Ji, S.; Li, J.R.; Zhang, R. Ceramic tubular mof hybrid membrane fabricated through in situ layer-by-layer self-assembly for nanofiltration. AlChE J. 2016, 62, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Bai, J.; Yin, H.; Yuan, B.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Duan, C. Deposition of chemically modified α-al 2 o 3 particles for high performance zif-8 membrane on a macroporous tube. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5977–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Lively, R.P.; Zhang, C.; Koros, W.J.; Chance, R.R. Investigating the intrinsic ethanol/water separation capability of zif-8: An adsorption and diffusion study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 7214–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Kong, L.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Han, W.; Yeung, K.L.; Zhu, W.; Yang, W. New membrane architecture with high performance: Zif-8 membrane supported on vertically aligned zno nanorods for gas permeation and separation. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 1975–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, C.; Wang, N.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.-R. Self-modified fabrication of inner skin zif-8 tubular membranes by a counter diffusion assisted secondary growth method. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 33007–33012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, M.; Meng, B.; Tan, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, S. Formation of continuous and highly permeable zif-8 membranes on porous alumina and zinc oxide hollow fibers. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 13448–13451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Yao, J.; Wang, K.; He, L.; Webley, P.A.; Chen, C.-S.; Wang, H. Preparation of zif-8 membranes supported on ceramic hollow fibers from a concentrated synthesis gel. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 385, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.J.; Brunelli, N.A.; Eum, K.; Rashidi, F.; Johnson, J.; Koros, W.J.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. Interfacial microfluidic processing of metal-organic framework hollow fiber membranes. Science 2014, 345, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eum, K.; Rownaghi, A.; Choi, D.; Bhave, R.R.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. Fluidic processing of high-performance zif-8 membranes on polymeric hollow fibers: Mechanistic insights and microstructure control. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 5011–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eum, K.; Ma, C.; Rownaghi, A.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. Zif-8 membranes via interfacial microfluidic processing in polymeric hollow fibers: Efficient propylene separation at elevated pressures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 25337–25342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.J.; Johnson, J.; Lydon, M.E.; Koros, W.J.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. Continuous polycrystalline zeolitic imidazolate framework-90 membranes on polymeric hollow fibers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10615–10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Hamid, M.R.A.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Jeong, H.-K. Ultrathin zeolitic-imidazolate framework zif-8 membranes on polymeric hollow fibers for propylene/propane separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 559, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Sutrisna, P.D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, V. Formation of ultrathin, continuous metal–organic framework membranes on flexible polymer substrates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3947–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Su, P.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wang, F.; Ou, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, E. Ultrathin metal–organic framework membrane production by gel–vapour deposition. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacho-Bailo, F.; Catalan-Aguirre, S.; Etxeberria-Benavides, M.; Karvan, O.; Sebastian, V.; Tellez, C.; Coronas, J. Metal-organic framework membranes on the inner-side of a polymeric hollow fiber by microfluidic synthesis. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 476, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, A.M.; Wickramanayake, W.; Dahe, G.; Sekizkardes, A.; Bank, T.L.; Hopkinson, D.P.; Venna, S.R. Continuous flow processing of zif-8 membranes on polymeric porous hollow fiber supports for CO2 capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 5678–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswal, B.P.; Bhaskar, A.; Banerjee, R.; Kharul, U.K. Selective interfacial synthesis of metal–organic frameworks on a polybenzimidazole hollow fiber membrane for gas separation. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 7291–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, B.; Lai, Z. Synthesis of ceramic hollow fiber supported zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (zif-8) membranes with high hydrogen permeability. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 421, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Larbot, A.; Hu, X. Elaboration and characterization of tubular macroporous ceramic support for membranes from kaolin and dolomite. J. Porous Mater. 2010, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Dou, W.; Caro, J.r. Steam-stable zeolitic imidazolate framework zif-90 membrane with hydrogen selectivity through covalent functionalization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15562–15564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venna, S.R.; Carreon, M.A. Highly permeable zeolite imidazolate framework-8 membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 132, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, N.; Yoshimune, M.; Negishi, H.; Haraya, K.; Hara, S.; Yamaguchi, T. Zif-8 membranes prepared at miscible and immiscible liquid–liquid interfaces. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 206, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Shimada, T.; Fujita, K.; Miyake, Y.; Kida, K.; Yogo, K.; Denayer, J.F.; Sugita, M.; Takewaki, T. Seeding-free aqueous synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 membranes: How to trigger preferential heterogeneous nucleation and membrane growth in aqueous rapid reaction solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 472, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colling, C.W.; Huff, G.A., Jr.; Bartels, J.V. Processes Using Solid Perm-Selective Membranes in Multiple Groups for Simultaneous Recovery of Specified Products from a Fluid Mixture. U.S. Patent US20040004040A1, 1 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Soukup, K.; Schneider, P.; Šolcová, O. Comparison of wicke–kallenbach and graham’s diffusion cells for obtaining transport characteristics of porous solids. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
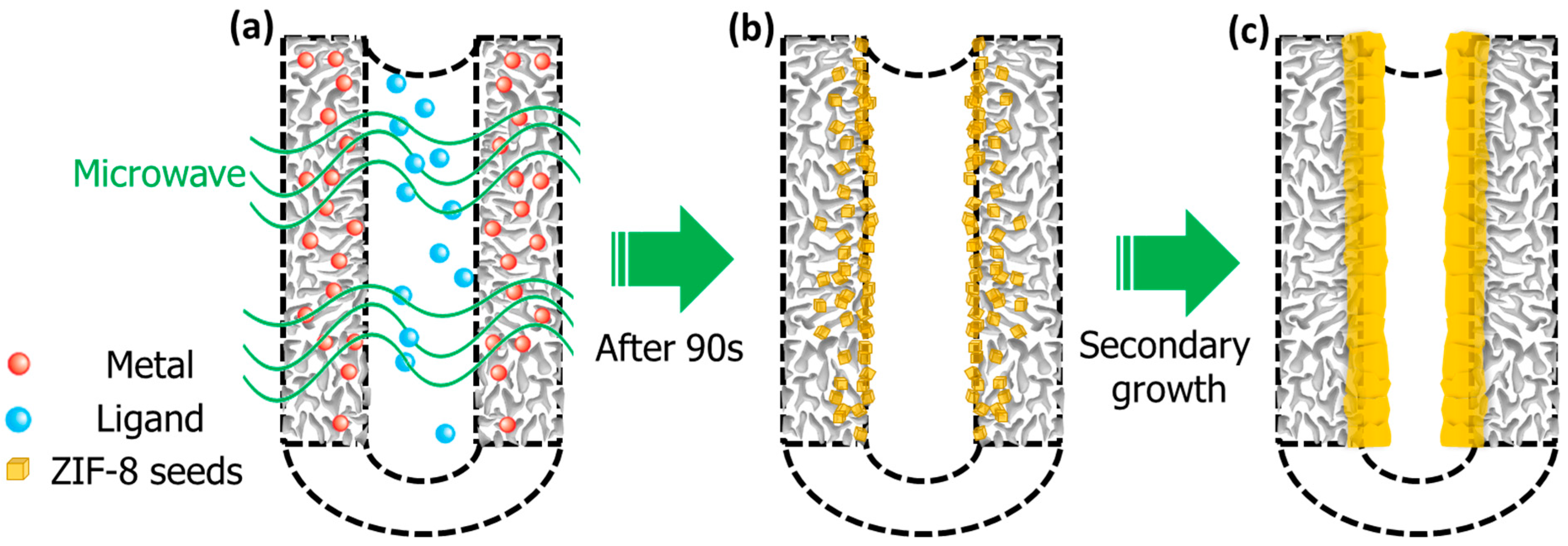


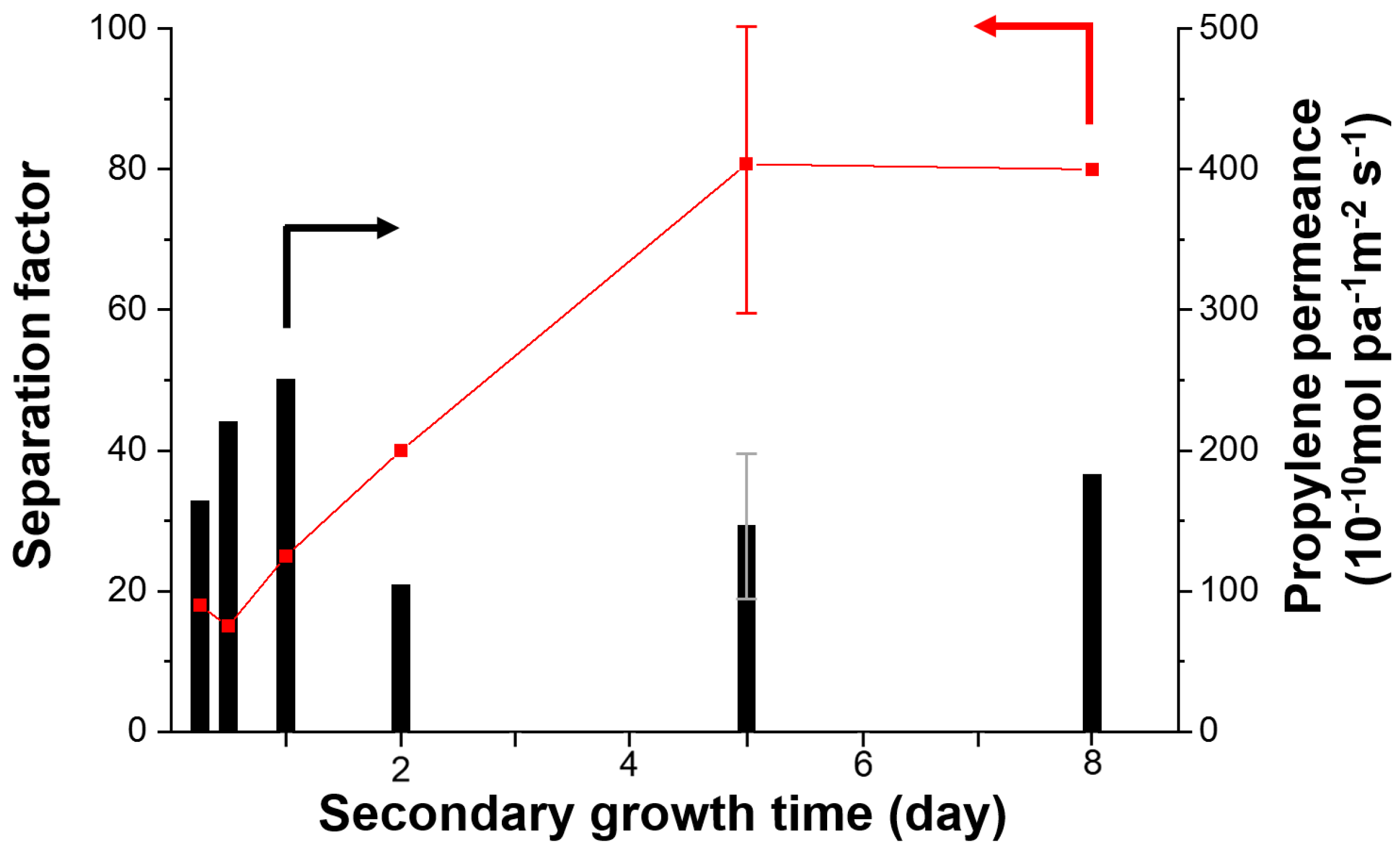

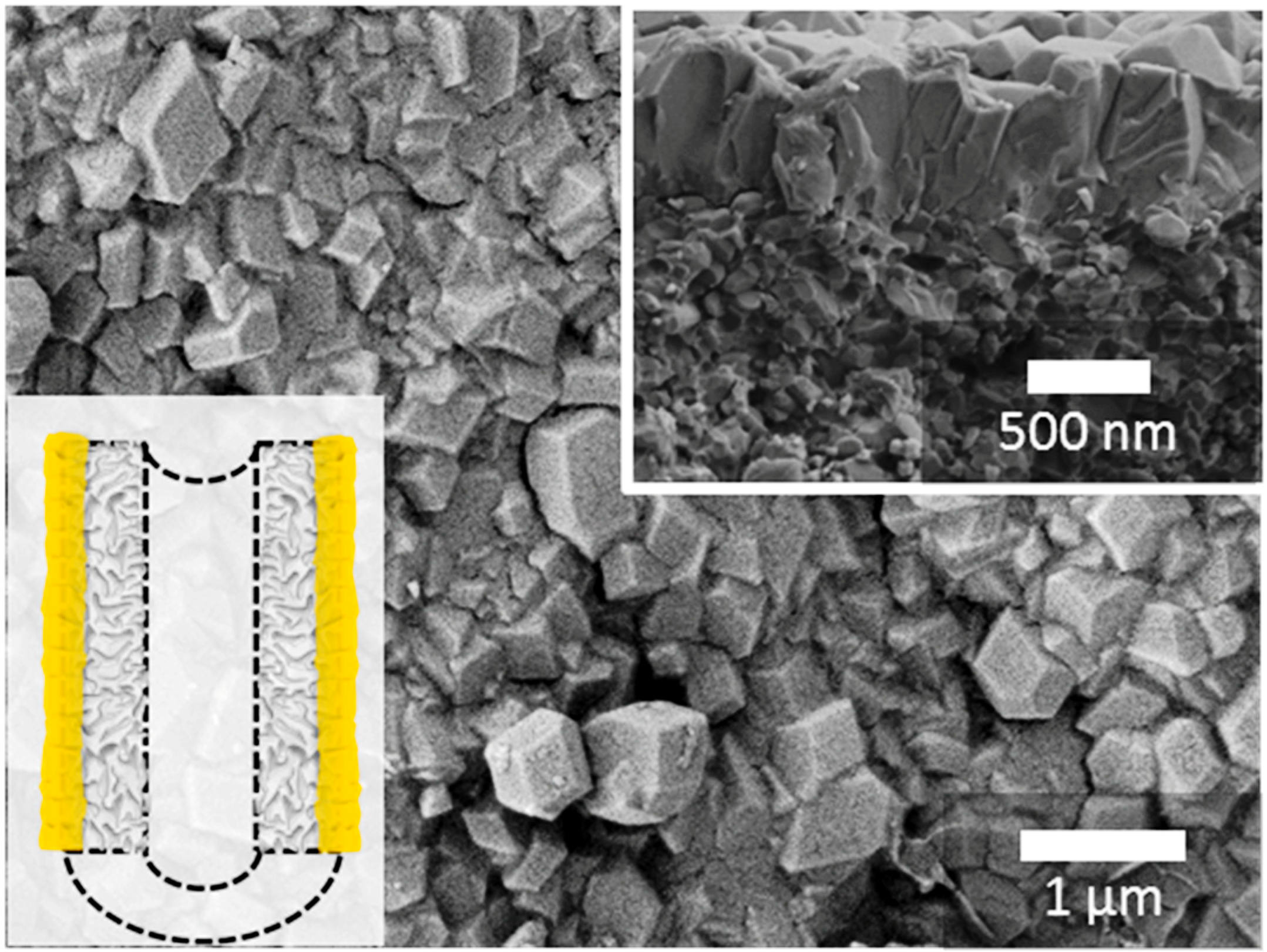
| Year | Group | Permeance (×10−10 mol s−1 Pa−1 m−2) | Permeabilit Barrer | SF | Thickness (μm) | Membrane Position | Method | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymeric hollow fibers | 2014 | Nair | 135 | 355 | 12 | 8.8 | Internal | Interfacial fluidic processing | [39] |
| 2015 | 220 | 460 | 65 | 7 | Internal | Interfacial fluidic processing | [40] | ||
| 2015 | 150 | 355 | 180 | 8 | Internal | Interfacial fluidic | [41] | ||
| 2017 | Li & Zhang | 215400 | 109 | 70 | 0.017 | External | Gel-vapor deposition | [46] | |
| 2018 | Jeong | 185 | 44 | 46 | 0.8 | Internal | Microwave seeding and secondary growth | [44] | |
| Ceramic capillary tubes | 2014 | Yamaguchi | 25 | 597 | 59 | 80 | External | Counter-diffusion | [29] |
| 2015 | 220 | 2628 | 10 | 40 | External | Counter-diffusion with interface control by two immiscible solvents | [31] | ||
| 2015 | 120 | 1075 | 7.2 | 30 | External | Counter-diffusion with interface control by two immiscible solvents | [30] | ||
| Ceramic tubes | 2017 | Tanaka | 100 | 30 | 36 | 1 | Internal | Surface modification with (3-Aminopropyl)triethoxysilate (APTES) | [32] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Yu, C.; Jeong, H.-K. Propylene-Selective Thin Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Membranes on Ceramic Tubes by Microwave Seeding and Solvothermal Secondary Growth. Crystals 2018, 8, 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8100373
Sun J, Yu C, Jeong H-K. Propylene-Selective Thin Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Membranes on Ceramic Tubes by Microwave Seeding and Solvothermal Secondary Growth. Crystals. 2018; 8(10):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8100373
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jingze, Chen Yu, and Hae-Kwon Jeong. 2018. "Propylene-Selective Thin Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Membranes on Ceramic Tubes by Microwave Seeding and Solvothermal Secondary Growth" Crystals 8, no. 10: 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8100373
APA StyleSun, J., Yu, C., & Jeong, H.-K. (2018). Propylene-Selective Thin Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Membranes on Ceramic Tubes by Microwave Seeding and Solvothermal Secondary Growth. Crystals, 8(10), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8100373




