Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Magnetic Properties of Amidate and Carboxylate Dimers of Ruthenium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis
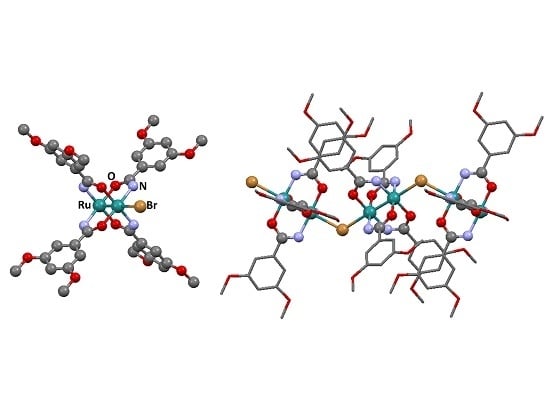
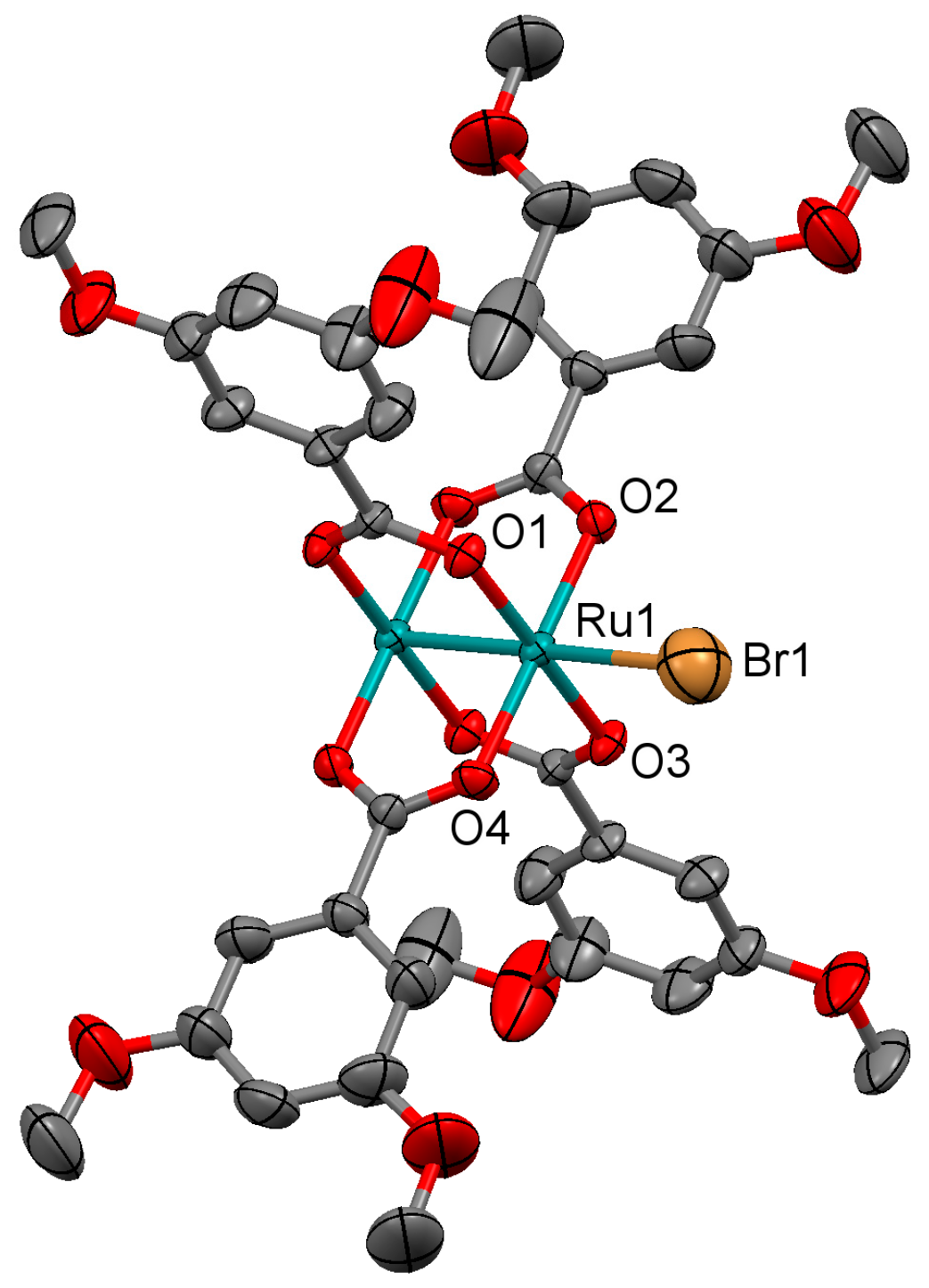
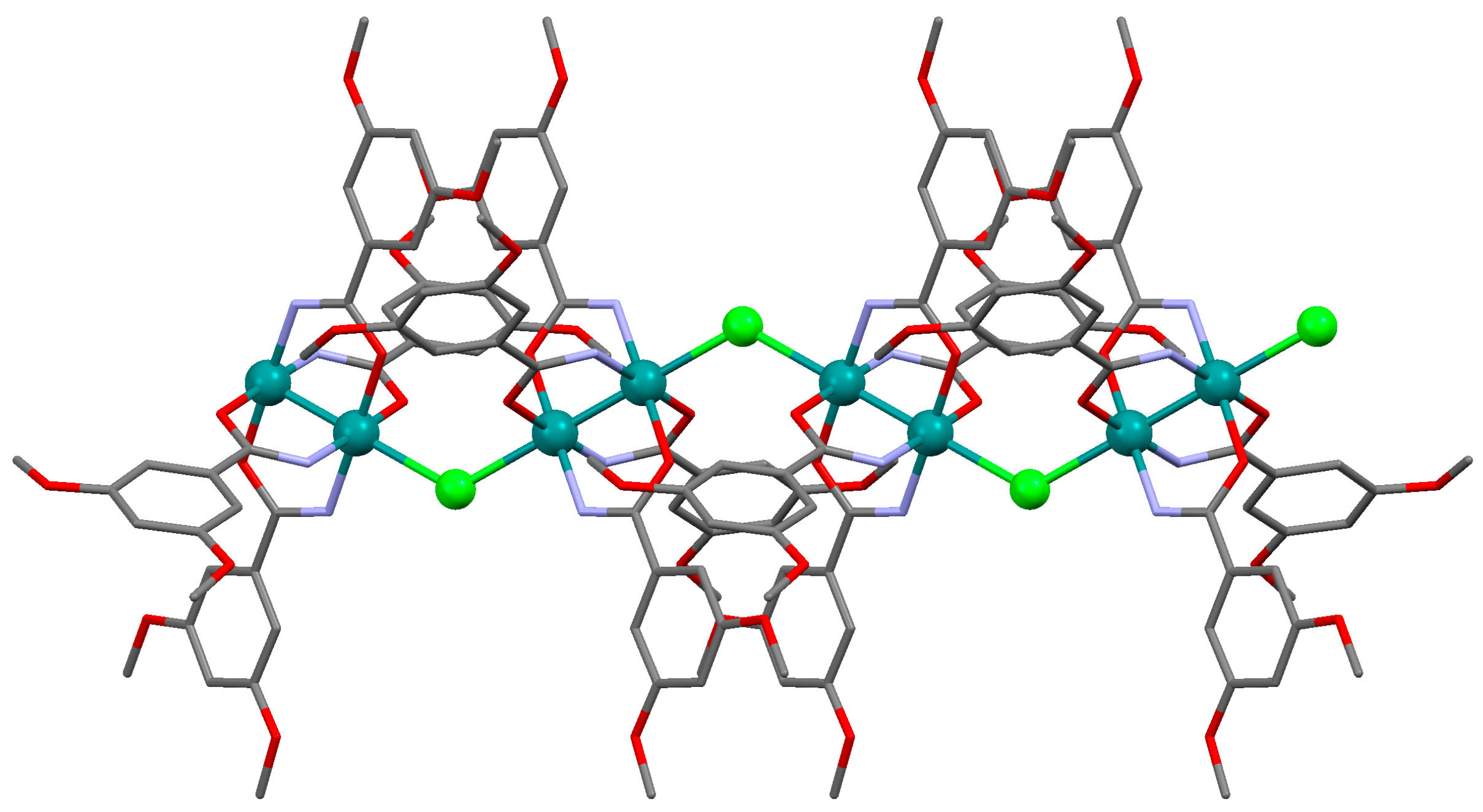
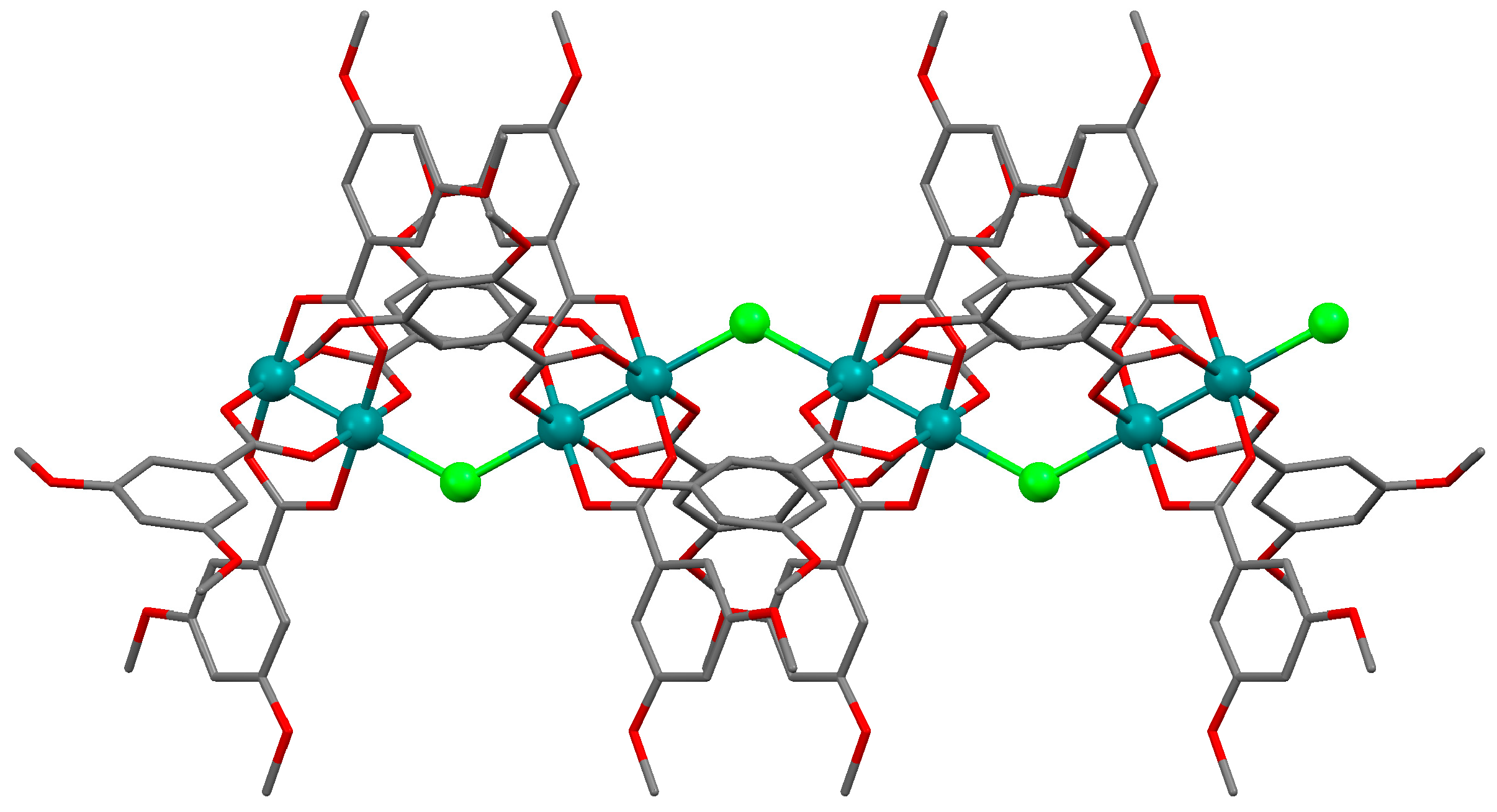
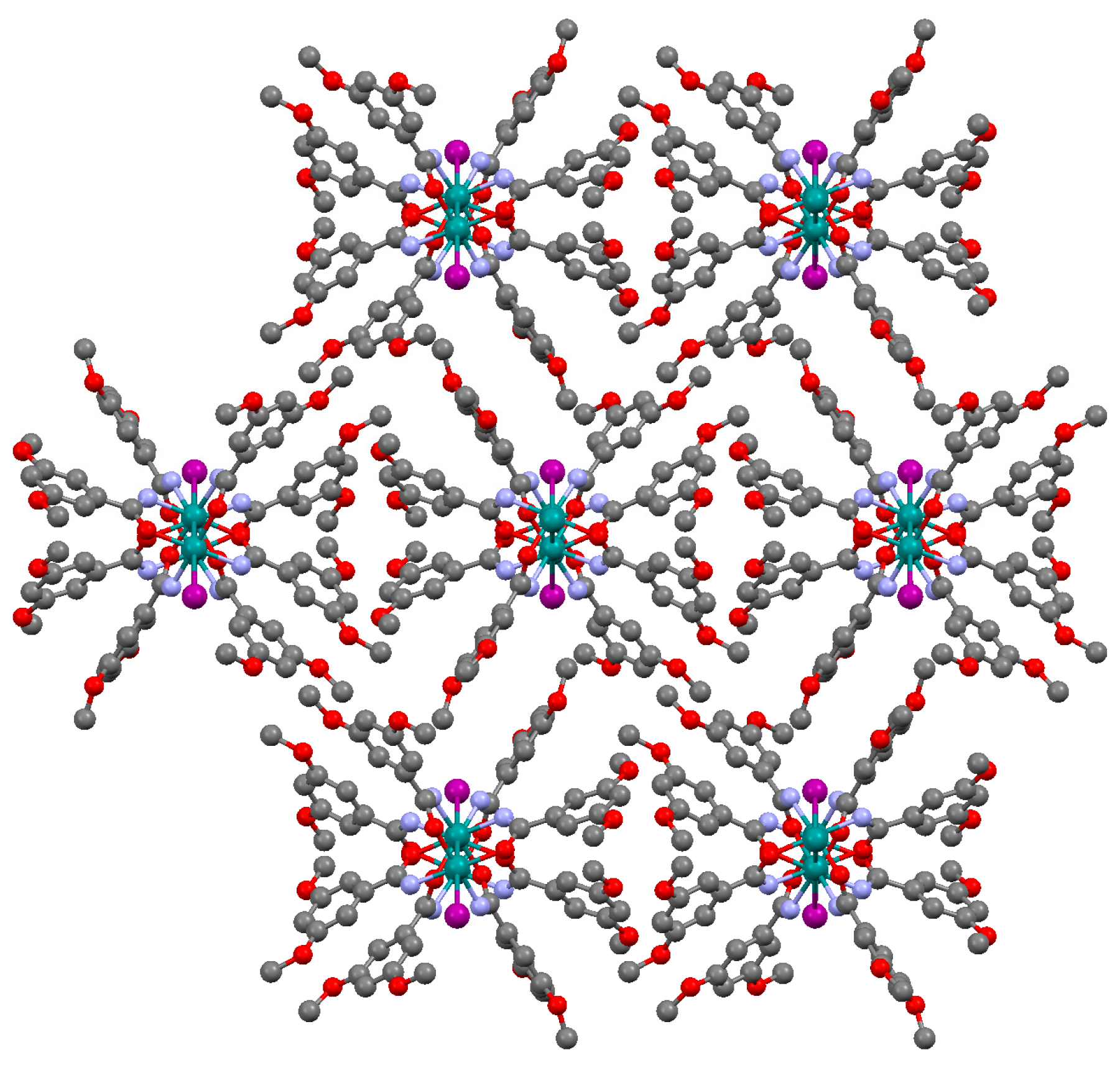
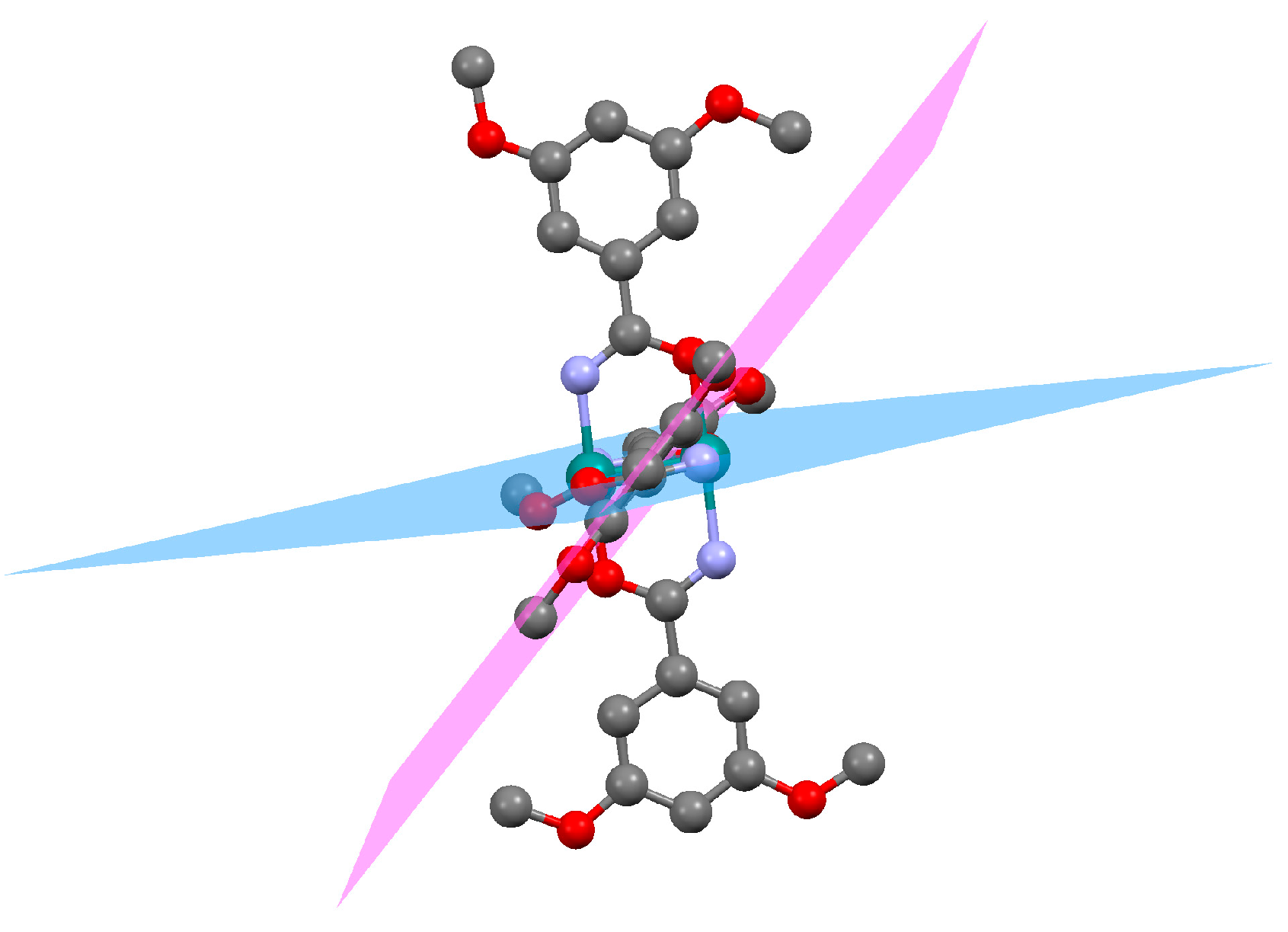
2.2. Crystal Structures
2.3. Spectroscopic Properties
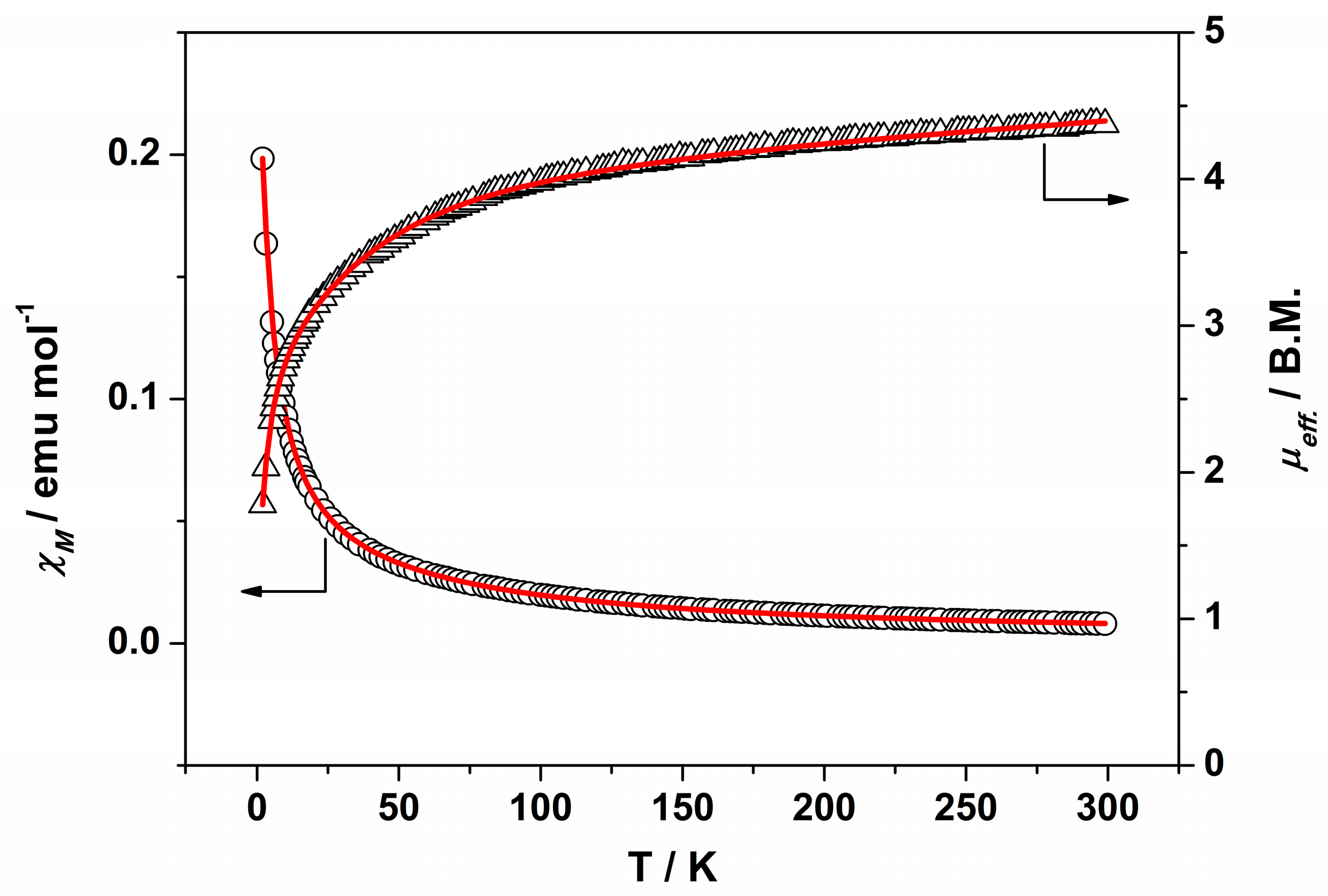
2.4. Magnetic Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Aspects
3.2. Synthesis of Complexes
3.2.1. Synthesis of [Ru2Cl(µ-NHOCC6H3-3,5-(OMe)2)4]n (1)
3.2.2. Synthesis of [Ru2Br(µ-NHOCC6H3-3,5-(OMe)2)4]n (2)
3.2.3. Synthesis of [Ru2I(µ-NHOCC6H3-3,5-(OMe)2)4]n (3)
3.2.4. Synthesis of [Ru2Cl(µ-O2CC6H3-3,5-(OMe)2)4]n (4)
3.2.5. Synthesis of [Ru2Br(µ-O2CC6H3-3,5-(OMe)2)4]n (5)
3.2.6. Synthesis of [Ru2I(µ-O2CC6H3-3,5-(OMe)2)4]n (6)
3.3. Crystal Structure Determination
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cotton, F.A.; Murillo, C.A.; Walton, R.A. Multiple Bonds between Metal Atoms, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 377–430. [Google Scholar]
- Aquino, M.A.S. Recent developments in the synthesis and properties of diruthenium tetracarboxylates. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 1025–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikuriya, M.; Yoshioka, D.; Handa, M. Magnetic interactions in one-, two-, and three-dimensional assemblies of dinuclear ruthenium carboxylates. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 2194–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Chakravarty, A.R. Synthesis and Physico-Chemical Properties of Diruthenium(III,II) Tetra-aryl Carboxylato Compounds. Polyhedron 1988, 7, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barral, M.C.; Jiménez-Aparicio, R.; Rial, C.; Royer, E.C.; Saucedo, M.J.; Urbanos, F.A. Synthesis and Characterization of new Carboxylate Dimers of Ruthenium. Polyhedron 1990, 9, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinski, T.; Chang, D.; Feldmann, F.N.; Bear, J.L.; Kadish, K.M. Electrochemical Studies of a Novel Ruthenium(II,III) Dimer, Ru2(HNOCCF3)4Cl. Inorg. Chem. 1983, 22, 3225–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, M.Y.; Feldmann, F.N.; Lin, X.Q.; Bear, J.L.; Kadish, K.M. Electrochemical Generation of New Dinuclear Ruthenium Acetamidate Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1984, 23, 2373–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, A.R.; Cotton, F.A.; Tocher, D.A. Structure of a Diruthenum(II,III) Complex with Benzamidate Bridging Ligands. Polyhedron 1985, 4, 1957–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, A.R.; Cotton, F.A. Synthesis and Structure of a Binuclear ruthenium 4-Chlorobenzamidato Complex. Polyhedron 1985, 4, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryde, K.; Tocher, D.A. The Electra-oxidation of the Binuclear Ruthenium(II/III) Tetraamidate Complex, Ru2(Me3CCONH)4Cl. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1986, 118, L49–L51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barral, M.C.; Jiménez-Aparicio, R.; Monge, A.; Priego, J.L.; Royer, E.C.; Ruíz-Valero, C.; Urbanos, F.A. Tert-butylbenzamidatediruthenium(II,III) Compounds. Crystal Structure of [Ru2(μ-HNOCC6H4-p-CMe3)4(OPPh3)2]BF4. Polyhedron 1993, 12, 2947–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barral, M.C.; de la Fuente, I.; Jiménez-Aparicio, R.; Priego, J.L.; Torres, M.R.; Urbanos, F.A. Synthesis of diruthenium(II,III) amidate compounds. Crystal structure of [Ru2(μ-HNOCC4H3S)4(thf)2]SbF6·0.5cyclohexane. Polyhedron 2001, 20, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, L.; Cao, Z.; Fanwick, P.E.; Ren, T. Diruthenium(II,III) tetramidates as a new class of oxygenation catalysts. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.D.; Powell, G.L. Microwave-assisted synthesis of dimolybdenum tetracarboxylates and a decanuclear osmium cluster. J. Organomet. Chem. 2008, 693, 1712–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, S.; Jiménez-Aparicio, R.; Perles, J.; Priego, J.L.; Urbanos, F.A. First microwave synthesis of multiple metal-metal bond paddlewheel compounds. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 965–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, S.; Jiménez-Aparicio, R.; Perles, J.; Priego, J.L.; Saguar, S.; Urbanos, F.A. Microwave methods for the synthesis of paddlewheel diruthenium compounds with N,N-donor ligands. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 1885–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, P.; González-Prieto, R.; Jiménez-Aparicio, R.; Perles, J.; Priego, J.L.; Torres, M.R. Comparative study of different methods for the preparation of tetraamidato and tetracarboxylatodiruthenium compounds. Structural and magnetic characterization. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 11866–11874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Martínez, P.; Gómez-García, C.J.; González-Prieto, R.; Jiménez-Aparicio, R.; Priego, J.L.; Torres, M.R. Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of one-dimensional tetraamidatodiruthenium compounds. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 3227–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Ren, T.; Valente, E.J.; Zubkowski, J.D.; Smith, E.T. Continuous Spectroscopy and Redox Tuning of Dinuclear Compounds: Chlorotetrakis(μ-N,N′-diarylformamidinato)diruthenium(II,III). Chem. Lett. 1997, 26, 753–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarella, G.N.; Cotton, F.A.; Murillo, C.A.; Ventura, K.; Villagrán, D.; Wang, X. Manipulating Magnetism: Ru25+ Paddlewheels Devoid of Axial Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 9580–9589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-Z.; Fanwick, P.E.; Ren, T. Peripheral Functionalization of Diruthenium Compounds via Heck Reactions. Organometallics 2007, 26, 4115–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.-L.; Ren, T. Suzuki Coupling at the Periphery of Diruthenium Coordination and Organometallic Compounds. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 10449–10456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bear, J.L.; Han, B.; Huang, S.; Kadish, K.M. Effect of Axial Ligands on the Oxidation State, Structure, and Electronic Configuration of Diruthenium Complexes. Synthesis and Characterization of Ru2(dpf)4Cl, Ru2(dpf)4(C≡CC6H5), Ru2(dpf)4(C≡CC6H5)2, and Ru2(dpf)4(CN)2 (dpf = N,N’-Diphenylformamidinate). Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiak, C. A critical account on π–π stacking in metal complexes with aromatic nitrogen-containing ligands. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2000, 21, 3885–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskowski, V.M.; Loehr, T.M.; Gray, H.B. Electronic and Vibrational Spectra of Ru2(carboxylate)4+ Complexes. Characterization of a High-Spin Metal-Metal Ground State. Inorg. Chem. 1987, 26, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskowski, V.M.; Gray, H.B. Electronic Spectra of Ru2(carboxylate)4+ Complexes. Higher Energy Electronic Excited States. Inorg. Chem. 1988, 27, 2501–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, G.J.; Renzoni, G.E.; Case, D.A. Electronic Structure of Ru2(O2CR)4+ and Rh2(O2CR)4+ Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1979, 101, 5256–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, C.J. Magnetochemistry-Advances in Theory and Experimentation. Prog. Inorg. Chem. 1982, 29, 203–283. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Aparicio, R.; Urbanos, F.A.; Arrieta, J.M. Magnetic Properties of Diruthenium(II,III) Carboxylate Compounds with Large Zero-Field Splitting and Strong Antiferromagnetic Coupling. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-Z.; Cotton, F.A.; Dalal, N.S.; Murillo, C.A.; Ramsey, C.M.; Ren, T.; Wang, X. Proof of Large Positive Zero-Field Splitting in a Ru25+ Paddlewheel. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12691–12696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estiú, G.; Cukiernik, F.D.; Maldivi, P.; Poizat, O. Electronic, Magnetic, and Spectroscopic Properties of Binuclear Diruthenium Tetracarboxylates: A Theoretical and Experimental Study. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 38, 3030–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.W.; Spencer, A.; Wilkinson, G. Carboxylato-triphenylphosphine Complexes of Ruthenium, Cationic Triphenylphosphine Complexes derived from them, and their Behaviour as Homogeneous Hydrogenation Catalysts for Alkenes. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1973, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaida, M.; Nomura, T.; Ishimori, T. Syntheses of formato-, acetato-, benezoato-, and chloro-substituted acetatoruthenium complexes, and their properties. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1972, 45, 2143–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Prieto, R. Compuestos Dinucleares de Rutenio: Propiedades, Tipos de Ordenamiento y Aplicaciones Como Materiales Moleculares. Ph.D. Thesis, University Complutense of Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Siemens. SMART, SAINT and SHELXTL; Siemens Analytical X-ray Instruments Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mercury, C.S.D.; Bruno, I.J.; Chisholm, J.A.; Edgington, P.R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Rodriguez-Monge, R.; Taylor, L.; Van de Streek, J.; Wood, P.A. Mercury CSD 2.0—New features for the visualization and investigation of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2008, 41, 466–470. [Google Scholar]


| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance (Å) | |||||
| Ru1-Ru1 | 2.2931(6) | 2.2922(12) | - | 2.2848(10) | 2.2891(17) |
| Ru1-Ru2 | - | - | 2.2979(10) | - | - |
| Ru1-X | 2.5875(6) | 2.6909(9) | 2.8623(10) | 2.5631(11) | 2.6027(19) |
| Ru2-X | - | - | 2.8699(10) | - | - |
| Ru1 O1 | 2.035(3) | 2.038(6) | 2.053(6) | 2.019(4) | 2.016(7) |
| Ru1 O2 | 2.040(3) | 2.029(6) | 2.040(7) | 2.013(4) | 2.004(8) |
| Ru1-O3 | - | - | 2.045(6) | 2.027(4) | 2.031(7) |
| Ru1-O4 | - | - | 2.042(7) | 2.022(4) | 2.028(8) |
| Ru1-N1 | 2.047(3) | 2.023(6) | 2.033(6) | - | - |
| Ru1-N2 | 2.030(3) | 2.024(6) | 2.024(7) | - | - |
| Ru2-N3 | - | - | 2.013(6) | - | - |
| Ru2-N4 | - | - | 2.031(8) | - | - |
| Angles (o) | |||||
| Ru1-X-Ru1 | 124.51(5) | 119.24(5) | - | 124.89(8) | 123.45(15) |
| Ru1-X-Ru2 | - | - | 101.84(3) | - | - |
| Ru1-Ru1-X | 179.47(2) | 178.29(5) | - | 176.70(3) | 176.60(7) |
| Ru1-Ru2-X | - | - | 171.97(4) | - | - |
| Ru2-Ru1-X | - | - | 175.71(4) | - | - |
| Torsion angles (o) | |||||
| O1-Ru1-Ru1-N1 | −0.76 | −0.13 | −2.61/−1.44 a | - | - |
| O2-Ru1-Ru1-N2 | −0.19 | +0.99 | −1.97/−3.02 b | - | - |
| O1-Ru1-Ru1-O4 | - | - | - | −0.68 | - |
| O2-Ru1-Ru1-O3 | - | - | - | −0.99 | - |
| O1-Ru1-Ru1-O3 | - | - | - | - | −0.76 |
| O2-Ru1-Ru1-O4 | - | - | - | - | −0.59 |
| θ angle/° | 12.05 | 10.37 | 6.74 | 9.41 | 8.92 |
| 24.18 | 21.39 | 43.56 | 19.03 | 18.71 |
| Compound | Amide-I/Amide-II (cm−1) | ν(COO−)a (cm−1) | ν(COO−)s (cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1483, 1452, 1420 | - | - |
| 2 | 1483, 1451, 1420 | - | - |
| 3 | 1482, 1453, 1417 | - | - |
| 4 | - | 1448 | 1381 |
| 5 | - | 1449 | 1383 |
| 6 | 1449 | 1380 |
| Compound | σ(axial ligand) → σ*(Ru2) | π(RuO/N,Ru2) → π*(Ru2) | δ(Ru2) → δ*(Ru2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 338 | 473 | 995 |
| 2 | 343 | 467 | 999 |
| 3 | 324 | a | 1002 |
| 4 | 321 | 482 | 1153 |
| 5 | 322 | 494 | 1137 |
| 6 | 346 | 500 | 1100 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g | 2.12 | 2.15 | 2.14 | 2.11 | 2.25 | 2.34 |
| D (cm−1) | 49.43 | 49.43 | 58.89 | 49.47 | 58.84 | 58.87 |
| zJ (cm−1) | −2.05 | −0.95 | −3.62 | −1.74 | −2.29 | −1.79 |
| TIP (cm3·mol−1) | 1.3 × 10−3 | 4.1 × 10−4 | 1.9 × 10−7 | 1.3 × 10−4 | 7.4 × 10−4 | 7.7 × 10−4 |
| P (%) | 0.02 | 6.8 × 10−5 | 0.04 | 4.1 × 10−5 | 0.03 | 0.01 |
| a σ2 | 1.1 × 10−5 | 2.9 × 10−5 | 4.5 × 10−5 | 4.0 × 10−5 | 4.8 × 10−5 | 2.6 × 10−5 |
| Compound | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Empirical formula | C36 H40 Cl N4 O12 Ru2 | C36 H40 Br N4 O12 Ru2 | C36 H40 I N4 O12 Ru2 |
| Formula weight | 958.31 | 1002.77 | 1049.76 |
| Temperature | 293(2) K | 293(2) K | 293(2) K |
| Wavelength | 0.71073 Å | 0.71073 Å | 0.71073 Å |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Monoclinic | Orthorhombic |
| Space group | C2/c | C2/c | Pbca |
| a | 23.6020(5) Å | 23.6552(16) Å | 24.9352(11) Å |
| b | 12.9621(2) Å | 12.9492(9) Å | 12.7509(5) Å |
| c | 13.2114(3) Å | 13.3075(9) Å | 27.8809(15) Å |
| α | 90° | 90° | 90° |
| β | 111.009(2)° | 111.0620(10)° | 90° |
| γ | 90° | 90° | 90° |
| Volume | 3773.10(13) Å3 | 3804.0(4) Å3 | 8864.7(7) Å3 |
| Z | 4 | 4 | 8 |
| Density | 1.687 Mg/m3 | 1.751 Mg/m3 | 1.573 Mg/m3 |
| Absorption coefficient | 0.940 mm−1 | 1.912 mm−1 | 1.436 mm−1 |
| F(000) | 1940 | 2012 | 4168 |
| Crystal size | 0.45 × 0.18 × 0.13 mm3 | 0.23 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm3 | 0.39 × 0.12 × 0.05 mm3 |
| Theta range for data collection | 2.67° to 26.00° | 1.82° to 26.00° | 3.28° to 25.01° |
| Index ranges | −9 ≤ h ≤ 25 | −29 ≤ h ≤ 29 | −29 ≤ h ≤ 21 |
| −15 ≤ k ≤ 15 | −14 ≤ k ≤ 15 | −11 ≤ k ≤ 15 | |
| −16 ≤ l ≤ 15 | −16 ≤ l ≤ 16 | −33 ≤ l ≤ 25 | |
| Reflections collected | 14838 | 15382 | 26230 |
| Independent reflections | 3710 [R(int) = 0.0250] | 3707 [R(int) = 0.0444] | 7798 [R(int) = 0.0585] |
| Completeness to theta | 99.9% | 99.0% | 99.8% |
| Absorption correction | None | None | Semi-empirical from equivalents |
| Refinement method | Full-matrix least squares on F2 | Full-matrix least squares on F2 | Full-matrix least squares on F2 |
| Data/restrains/parameters | 3710/4/234 | 3707/8/189 | 7798/1/490 |
| Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.057 | 0.997 | 0.998 |
| Final R indices [I > 2sigma(I)] | R1 = 0.0382 | R1 = 0.0547 | R1 = 0.0757 |
| wR2 = 0.1059 | wR2 = 0.1447 | wR2 = 0.2118 | |
| R indices (all data) | R1 = 0.0464 | R1 = 0.0974 | R1 = 0.1280 |
| wR2 = 0.1106 | wR2 = 0.1897 | wR2 = 0.2394 | |
| Largest diff. peak and hole | 1.485 and −1.254 e Å−3 | 1.286 and −0.715 e Å−3 | 1.431 and −1.129 e Å−3 |
| Compound | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|
| Empirical formula | C36 H36 Cl O16 Ru2 | C36 H36 Br O16 Ru2 |
| Formula weight | 962.24 | 1006.70 |
| Temperature | 293(2) K | 293(2) K |
| Wavelength | 0.71073 Å | 0.71073 Å |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Monoclinic |
| Space group | C2/c | C2/c |
| a | 23.187(3) Å | 23.277(3) Å |
| b | 12.8452(18) Å | 12.8620(14) Å |
| c | 13.1625(19) Å | 13.2455(14) Å |
| α | 90° | 90° |
| β | 110.379(2)° | 110.633(2)° |
| γ | 90° | 90° |
| Volume | 3675.0(9) Å3 | 3711.2(7) Å3 |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| Density | 1.739 Mg/m3 | 1.802 Mg/m3 |
| Absorption coefficient | 0.970 mm−1 | 1.966 mm−1 |
| F(000) | 1940 | 2012 |
| Crystal size | 0.44 × 0.07 × 0.05 mm3 | 0.44 × 0.09 × 0.07 mm3 |
| Theta range for data collection | 1.84° to 25.00° | 1.84° to 25.00° |
| Index ranges | −27 ≤ h ≤ 27 | −27 ≤ h ≤ 27 |
| −13 ≤ k ≤ 15 | −15 ≤ k ≤ 12 | |
| −15 ≤ l ≤ 15 | −15 ≤ l ≤ 15 | |
| Reflections collected | 13717 | 13572 |
| Independent reflections | 3228 [R(int) = 0.0543] | 3232 [R(int) = 0.0549] |
| Completeness to theta | 99.4% | 98.4% |
| Absorption correction | None | None |
| Refinement method | Full-matrix least squares on F2 | Full-matrix least squares on F2 |
| Data/restrains/parameters | 3228/0/209 | 3232/0/225 |
| Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 0.998 | 0.999 |
| Final R indices [I>2sigma(I)] | R1 = 0.0527 | R1 = 0.0781 |
| wR2 = 0.1476 | wR2 = 0.2316 | |
| R indices (all data) | R1 = 0.0658 | R1 = 0.1080 |
| wR2 = 0.1564 | wR2 = 0.2562 | |
| Largest diff. peak and hole | 1.255 and −1.301 e Å−3 | 1.427 and −4.062 e Å−3 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delgado-Martínez, P.; Freire, C.; González-Prieto, R.; Jiménez-Aparicio, R.; Priego, J.L.; Torres, M.R. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Magnetic Properties of Amidate and Carboxylate Dimers of Ruthenium. Crystals 2017, 7, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst7070192
Delgado-Martínez P, Freire C, González-Prieto R, Jiménez-Aparicio R, Priego JL, Torres MR. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Magnetic Properties of Amidate and Carboxylate Dimers of Ruthenium. Crystals. 2017; 7(7):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst7070192
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelgado-Martínez, Patricia, Carlos Freire, Rodrigo González-Prieto, Reyes Jiménez-Aparicio, José L. Priego, and M. Rosario Torres. 2017. "Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Magnetic Properties of Amidate and Carboxylate Dimers of Ruthenium" Crystals 7, no. 7: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst7070192
APA StyleDelgado-Martínez, P., Freire, C., González-Prieto, R., Jiménez-Aparicio, R., Priego, J. L., & Torres, M. R. (2017). Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Magnetic Properties of Amidate and Carboxylate Dimers of Ruthenium. Crystals, 7(7), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst7070192