The Hydrogen Bonded Structures of Two 5-Bromobarbituric Acids and Analysis of Unequal C5–X and C5–X′ Bond Lengths (X = X′ = F, Cl, Br or Me) in 5,5-Disubstituted Barbituric Acids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
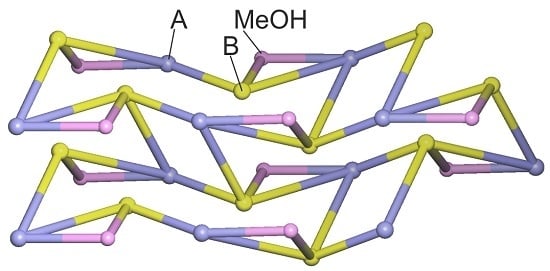
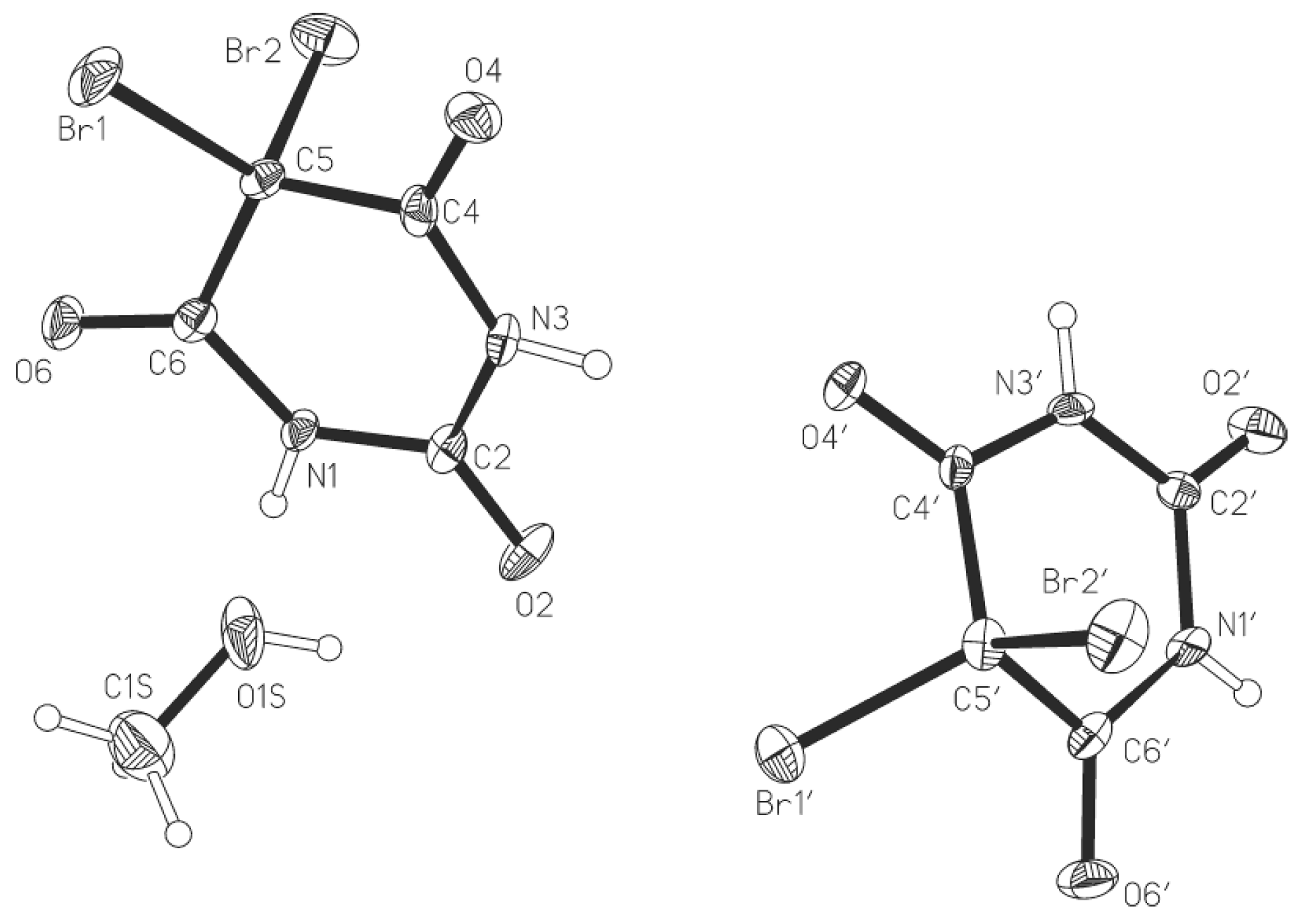
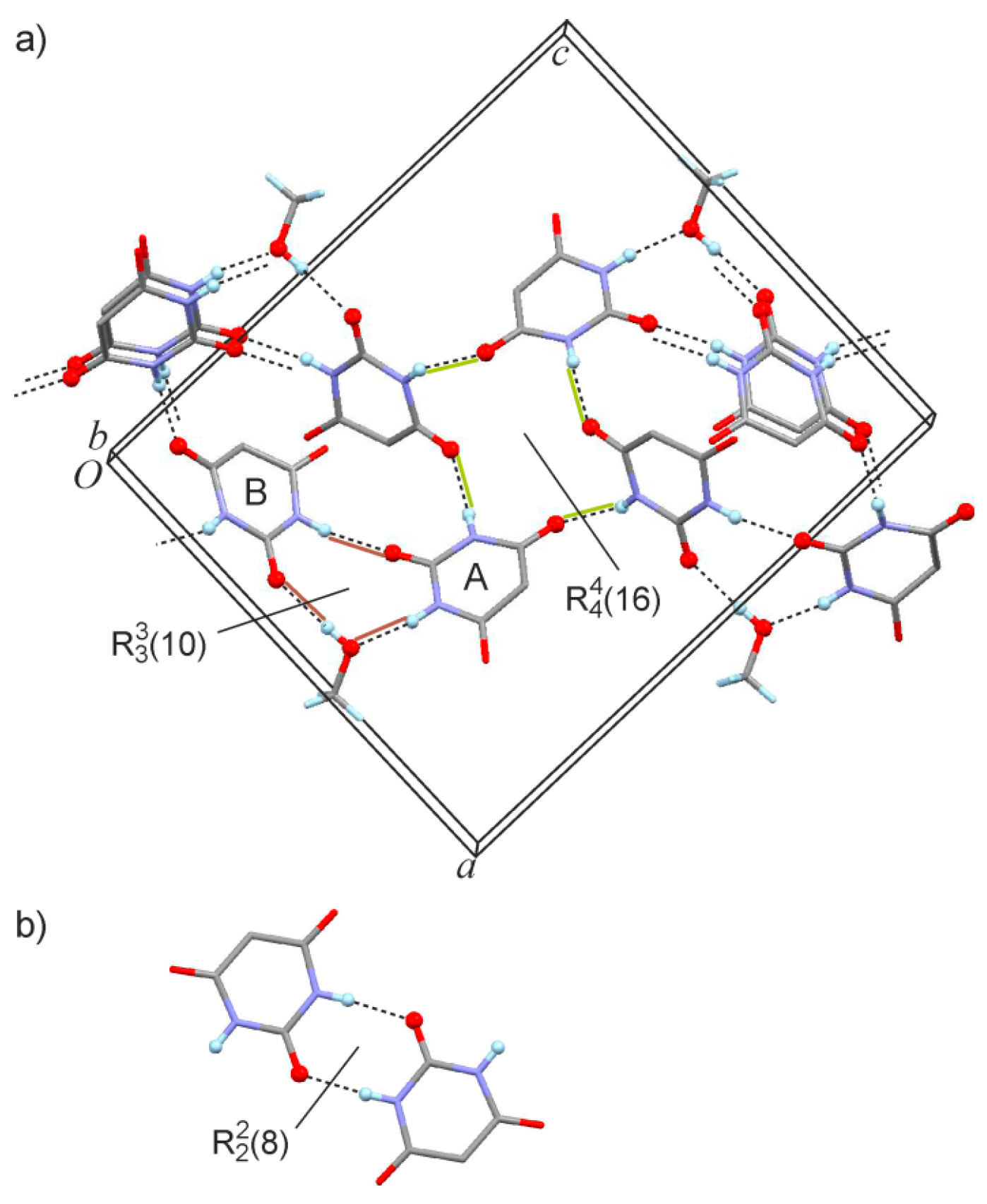
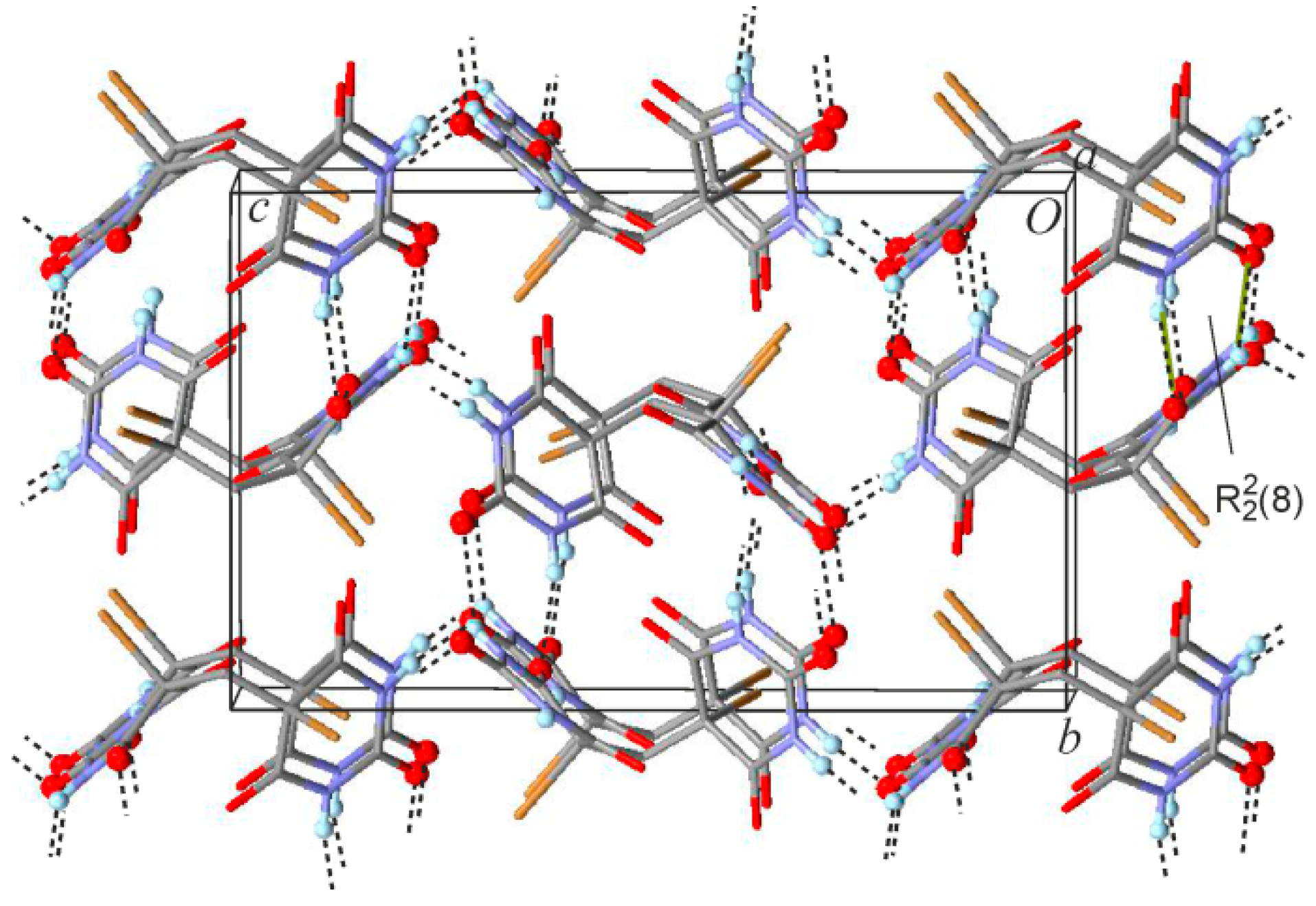
2.1. Crystal Structure of 5,5-Dibromobarbituric Acid Hemisolvate (1MH)
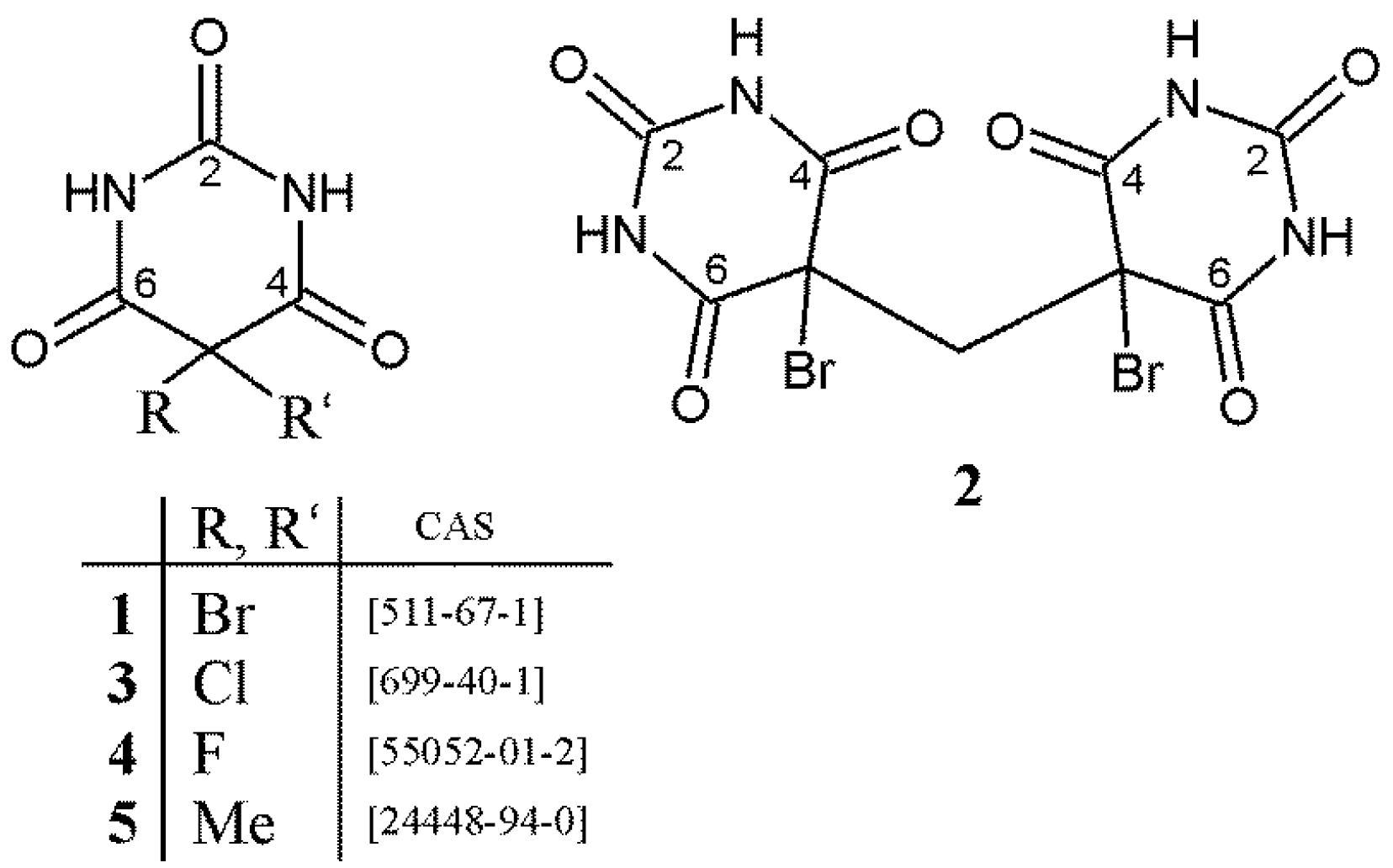
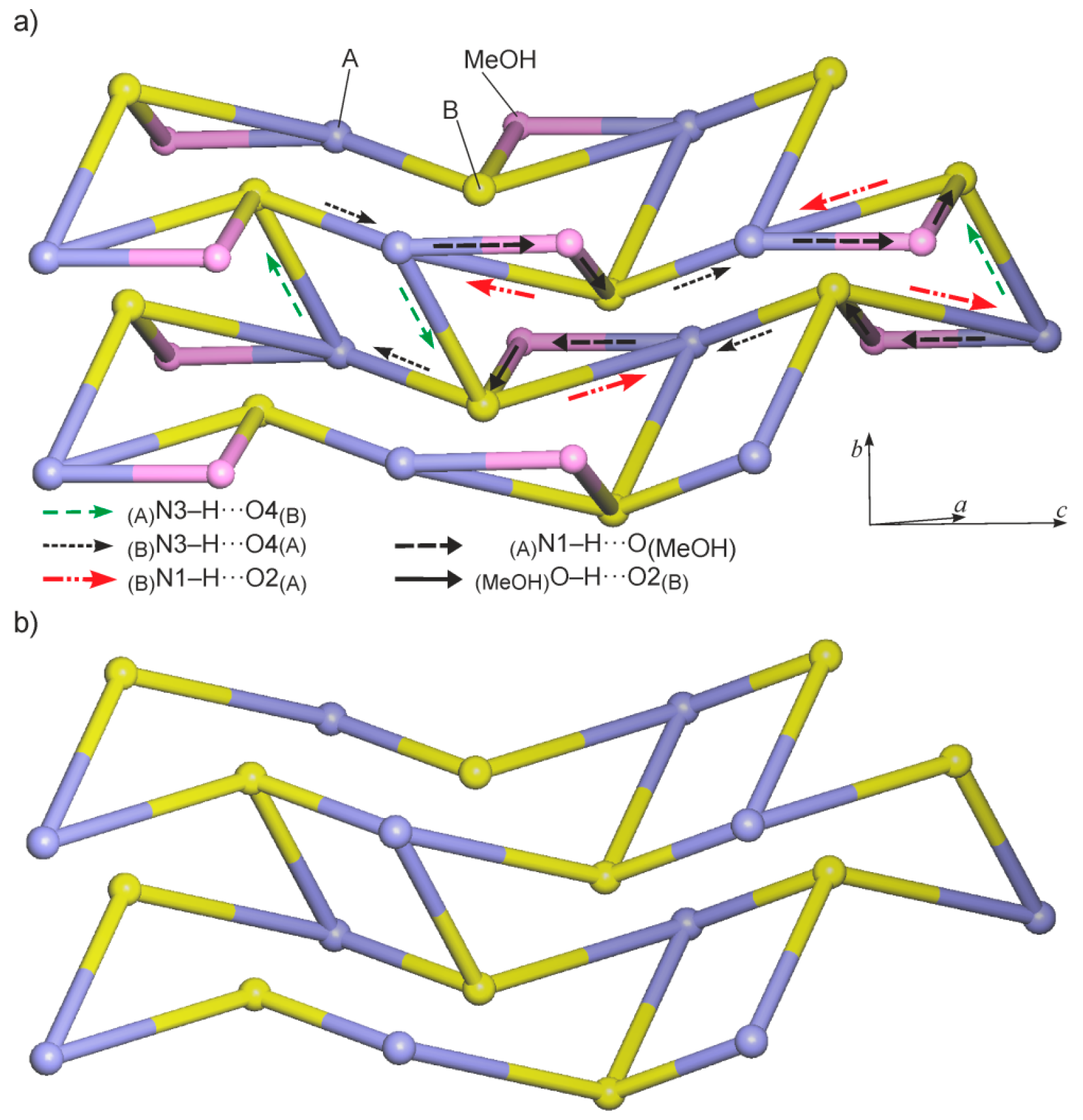
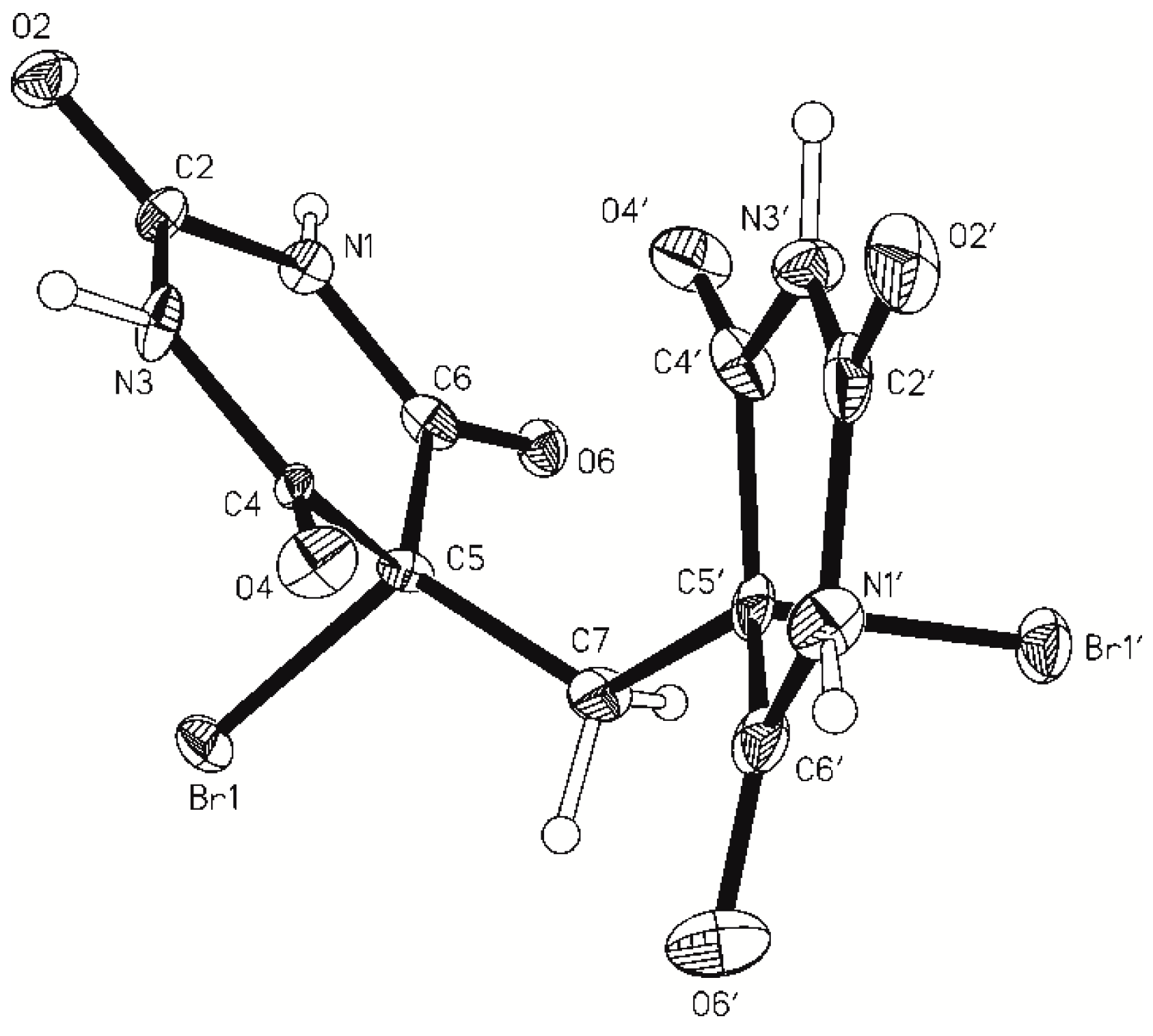
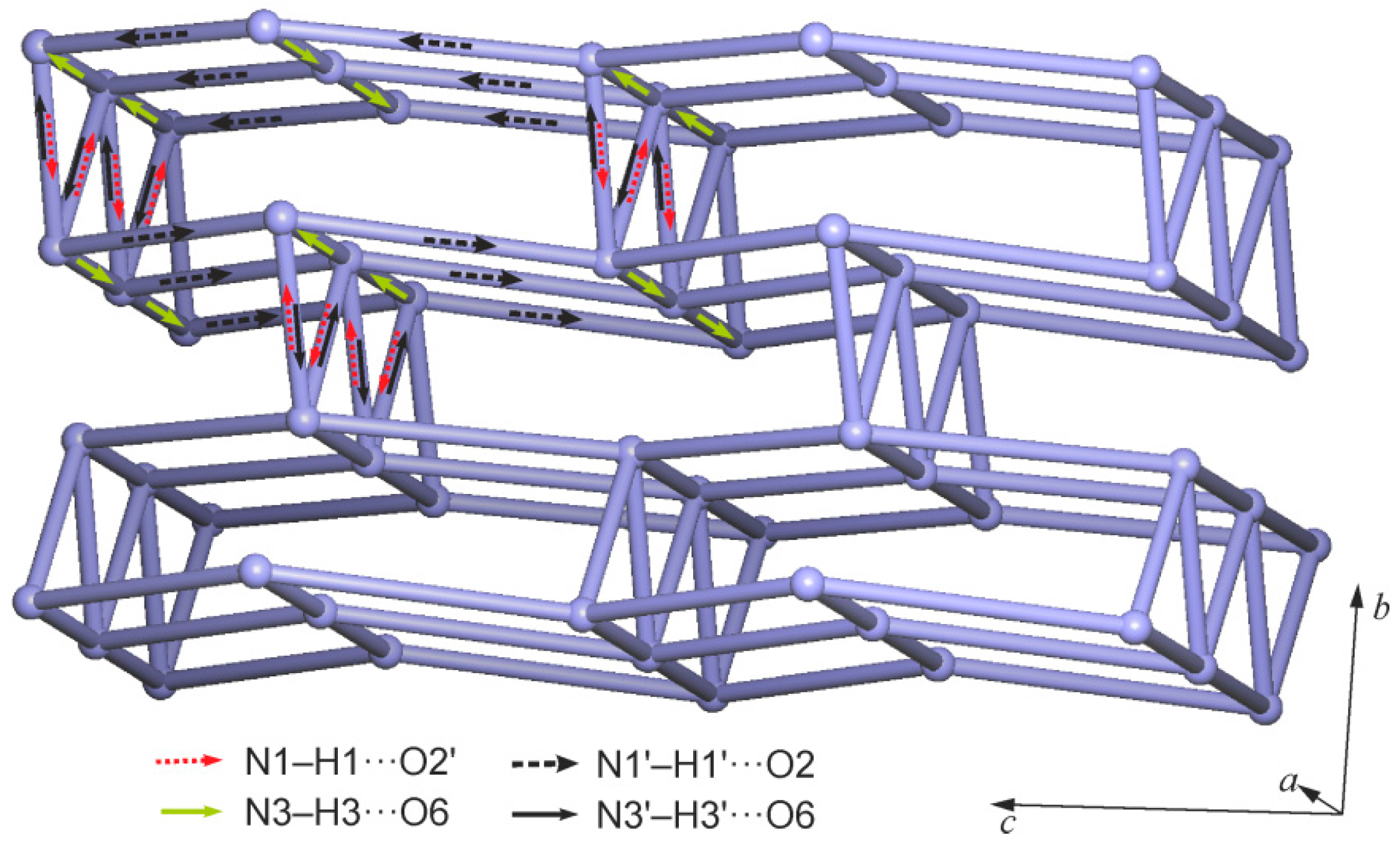
2.2. Crystal Structure of 5,5'-Methanediylbis(5-bromobarbituric acid)(2)
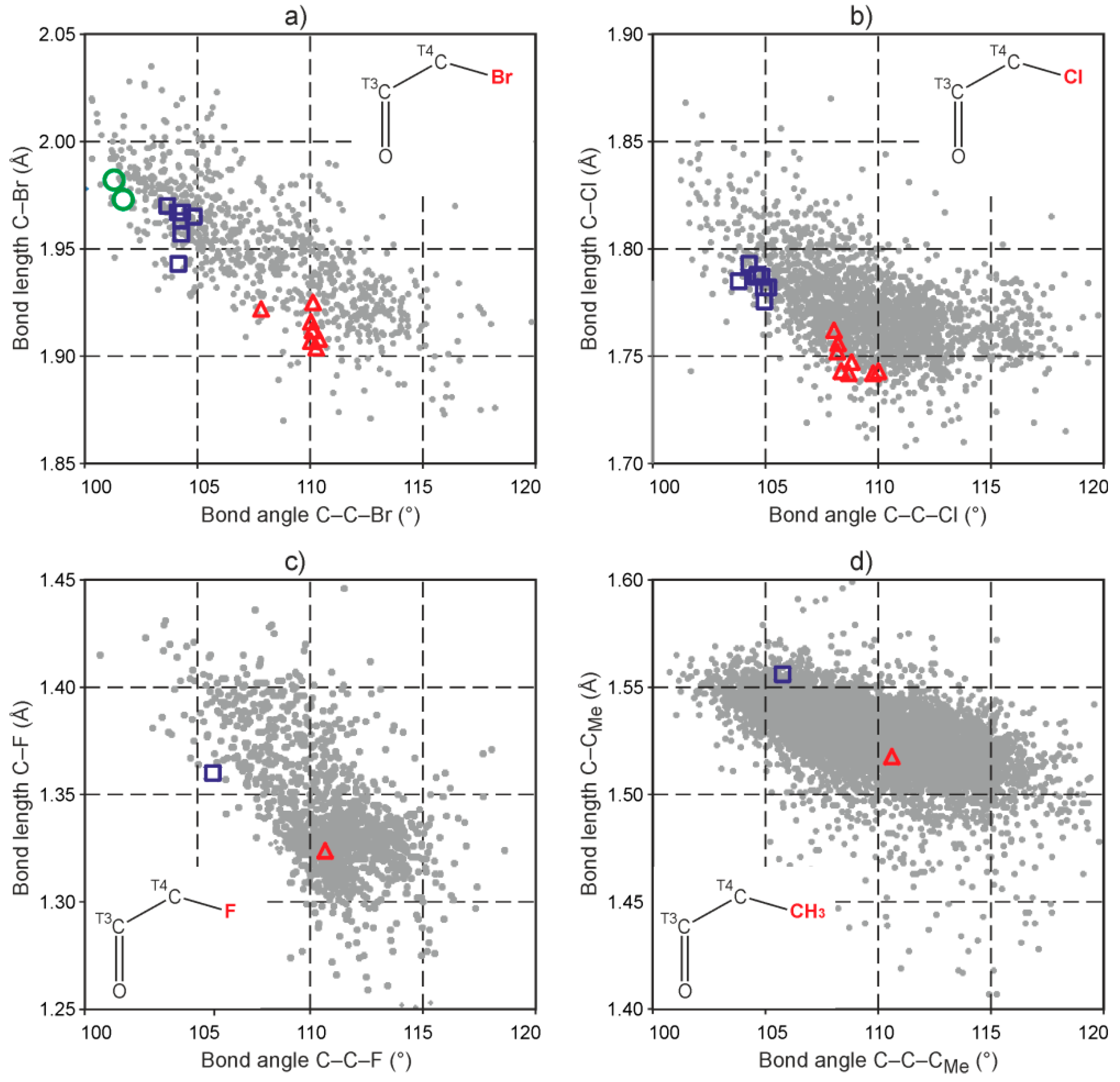
2.3. Analysis of C5–X and C5–X′ Bond Lengths (X = X′ = F, Cl, Br, Me) in 5,5-Disubstituted Barbituric Acids
2.4. Geometry Optimization of 5,5-Disubstituted Barbituric Acid Analogues (X = X′ = F, Cl, Br, Me)
2.5. Correlation between Bond Parameters
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Preparation of Crystal Forms
3.2. Single-Crystal X-ray Structure Analyses
3.3. Analysis of Crystal Data
3.4. Computational Modelling
3.5. SCDS-PIXEL Calculation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brandstätter-Kuhnert, M.; Aepkers, M. Molecular compounds, crystalline solid solutions, and new cases of polymorphism in barbiturates. I. Microchim. Acta 1962, 50, 1041–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandstätter-Kuhnert, M.; Aepkers, M. Molecular compounds, crystalline solid solutions, and new cases of polymorphism in barbiturates. II. Microchim. Acta 1962, 50, 1055–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandstätter-Kuhnert, M.; Aepkers, M. Molecular compounds, crystalline solid solutions, and new cases of polymorphism in barbiturates. III. Microchim. Acta 1963, 51, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnert-Brandstätter, M.; Vlachopoulos, A. Molecular compounds, crystalline solid solutions, and new cases of polymorphism in barbiturates. IV. Microchim. Acta 1967, 55, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zencirci, N.; Gelbrich, T.; Kahlenberg, V.; Griesser, U.J. Crystallization of metastable polymorphs of phenobarbital by isomorphic seeding. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 3444–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Gelbrich, T.; Kahlenberg, V.; Griesser, U.J. Supramolecular constructs and thermodynamic stability of four polymorphs and a co-crystal of pentobarbital (nembutal). CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 2494–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zencirci, N.; Griesser, U.J.; Gelbrich, T.; Kahlenberg, V.; Jetti, R.K.R.; Apperley, D.C.; Harris, R.K. New solvates of an old drug compound (phenobarbital): Structure and stability. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 3267–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelbrich, T.; Meischberger, I.; Griesser, U.J. Two polymorphs of 5-cyclohexyl-5-ethylbarbituric acid and their packing relationships with other barbiturates. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C-Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelbrich, T.; Braun, D.E.; Griesser, U.J. Specific energy contributions from competing hydrogen-bonded structures in six polymorphs of phenobarbital. Chem. Cent. J. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groth, P. Chemische Krystallographie. Dritter Teil. Aliphatische und Hydroaromatische Kohlenstoffverbindungen; Verlag von Wilhelm Engelmann: Leipzig, Germany, 1910; p. 579. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Gelbrich, T.; Rossi, D.; Häfele, C.A.; Griesser, U.J. Barbiturates with hydrogen-bonded layer and framework structures. CrystEngComm 2011, 13, 5502–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbrich, T.; Rossi, D.; Griesser, U.J. Tetragonal polymorph of 5,5-dichlorobarbituric acid. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E-Struct. Rep. Online 2012, 68, o235–o236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.P. Polymorphism of phenobarbitone: The crystal structure of 5-ethyl-5-phenylbarbituric acid monohydrate. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B-Struct. Sci. 1973, 29, 1572–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.M.; Desiraju, G.R. 5,5-Dibenzylbarbituric acid monohydrate. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E-Struct. Rep. Online 2007, 63, o771–o772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbrich, T.; Rossi, D.; Griesser, U.J. Butallylonal 1,4-dioxane hemisolvate. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E-Struct. Rep. Online 2010, 66, o2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi Kiran, B.; Suchetan, P.A.; Amar, H.; Vijayakumar, G.R. Crystal structure of 5,5-bis(4-methylbenzyl)pyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione monohydrate. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E-Struct. Commun. 2015, 71, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremer, D.; Pople, J.A. General definition of ring puckering coordinates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 1354–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etter, M.C.; MacDonald, J.C.; Bernstein, J. Graph-set analysis of hydrogen-bond patterns in organic crystals. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B-Struct. Sci. 1990, 46, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, J.; Davis, R.E.; Shimoni, L.; Chang, N.-L. Patterns in hydrogen bonding: Functionality and graph set analysis in crystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1995, 34, 1555–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baburin, I.A.; Blatov, V.A. Three-dimensional hydrogen-bonded frameworks in organic crystals: A topological study. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B-Struct. Sci. 2007, 63, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hursthouse, M.B.; Hughes, D.S.; Gelbrich, T.; Threlfall, T.L. Describing hydrogen-bonded structures; topology graphs, nodal symbols and connectivity tables, exemplified by five polymorphs of each of sulfathiazole and sulfapyridine. Chem. Cent. J. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Keeffe, M.; Peskov, M.A.; Ramsden, S.J.; Yaghi, O.M. The reticular chemistry structure resource (RCSR) database of, and symbols for, crystal nets. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondi, A. Van der waals volumes and radii. J. Phys. Chem. 1964, 68, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunitz, J.D.; Gavezzotti, A. Molecular recognition in organic crystals: Directed intermolecular bonds or nonlocalized bonding? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 1766–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavezzotti, A. Molecular Aggregation: Structure Analysis and Molecular Simulation of Crystals and Liquids; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gavezzotti, A. Calculation of lattice energies of organic crystals: The PIXEL integration method in comparison with more traditional methods. Z. Kristallogr. 2005, 220, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavezzotti, A. Quantitative ranking of crystal packing modes by systematic calculations on potential energies and vibrational amplitudes of molecular dimers. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2005, 1, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Groom, C.R.; Allen, F.H. The Cambridge Structural Database in retrospect and prospect. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DesMarteau, D.D.; Pennington, W.T.; Resnati, G. Fluorinated barbituric acid derivatives. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C-Cryst. Struct. Commun. 1994, 50, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, M.V.; Notario, R.; Foces-Foces, C.; Temprado, M.; Ros, F.; Emel’yanenko, V.N.; Verevkin, S.P. Experimental and computational thermochemical study and solid-phase structure of 5,5-dimethylbarbituric acid. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 3583–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornblum, N.; Smiley, R.A.; Blackwood, R.K.; Iffland, D.C. The mechanism of the reaction of silver nitrite with alkyl halides. The contrasting reactions of silver and alkali metal salts with alkyl halides. The alkylation of ambident anions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 6269–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.J.; Mason, S.F. The Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds: The Pyrimidines, 99th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Grundke, G.; Keese, W.; Rimpler, M. 5,5-Dibrombarbitursäure, ein neues Reagenz zur Bromierung von gesättigten und α,β-ungesättigten Carbonylverbindungen. Chem. Berichte 1985, 118, 4288–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gysling, H.; Schwarzenbach, G. Metallindikatoren II. Beziehungen zwischen Struktur und Komplexbildungsvermögen bei Verwandten des Murexids. Helv. Chim. Acta 1949, 32, 1484–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilzadeh, M.; Pesyan, N.N.; Rezaee, F.; Rastgar, S.; Hosseini, Y.; Sahin, E. New one-pot synthesis of spiro[furo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-6,5′-pyrimidine]pentaones and their sulfur analogues. Mol. Divers. 2011, 15, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ara, T.; Khan, K.Z. Synthesis of some derivatives of dimedone, γ-pyrone and barbituric acid. J. Pharm. Res. (Mohali, India) 2014, 8, 786–790. [Google Scholar]
- Oxford Diffraction Ltd. Crysalis CCD and CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction Ltd.: Abingdon, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SADABS. Version 2007/7; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A-Fundam. Crystallogr. 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C-Cryst. Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D-Biol. Crystallogr. 2009, 65, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatov, V.A. Multipurpose crystallochemical analysis with the program package TOPOS. IUCr Compcomm Newsl. 2006, 7, 4–38. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gavezzotti, A. OPiX: A Computer Program Package for the Calculation of Intermolecular Interactions and Crystal Energies; University of Milan: Milano, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Khamitova, D.R.; Blatov, V.A.; Carlucci, L.; Ciani, G.; Proserpio, D.M. Local and global topology of two-dimensional structural groups. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A-Fundam. Crystallogr. 2009, 65, s306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | 1MH | 2 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moiety formula | 2(C4H2Br2N2O3)·CH4O | C9H6Br2N4O6 | C6H8N2O3 |
| Formula mass | 603.83 | 426.00 | 156.14 |
| Crystal system | monoclinic | orthorhombic | triclinic |
| Space group | P21/n | P212121 | P |
| Z | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| a/Å | 14.6451(4) | 6.8347(3) | 5.6667(7) |
| b/Å | 6.73660(16) | 10.6206(5) | 6.4172(7) |
| c/Å | 17.1159(4) | 17.0982(9) | 10.5800(8) |
| α/° | 90 | 90 | 84.429(8) |
| β/° | 90.238(2) | 90 | 81.341(8) |
| γ/° | 90 | 90 | 64.916(12) |
| Unit cell volume/Å3 | 1688.61(7) | 1241.13(10) | 344.24(7) |
| Temperature/K | 173 | 173 | 173 |
| No. of reflections measured | 5387 | 9500 | 2223 |
| No. of independent reflections | 3388 | 2256 | 1329 |
| Rint | 0.0277 | 0.1130 | 0.0268 |
| No. of parameters | 238 | 202 | 117 |
| Absolute structure parameter (Flack) | - | 0.014(18) | - |
| Final R1 value (I > 2σ(I)) | 0.0310 | 0.0477 | 0.0331 |
| Final wR(F2) value (all data) | 0.0620 | 0.1220 | 0.0821 |
| Type | D–H···A | d(D–H)/Å | d(H···A)/Å | d(D···A)/Å | ∠(DHA)/° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A→MeOH | N1–H1···O1S | 0.855(10) | 1.881(15) | 2.721(4) | 167(5) |
| A→B | N3–H3···O4′ | 0.862(10) | 2.071(15) | 2.910(4) | 164(3) |
| B→A | N1′–H1′···O2 i | 0.851(10) | 1.974(13) | 2.814(4) | 169(4) |
| B→A | N3′–H3′ ···O4 ii | 0.850(10) | 2.162(19) | 2.942(4) | 152(3) |
| MeOH→B | O1S–H1S··· O2′ iii | 0.838(10) | 1.97(2) | 2.757(4) | 157(5) |
| # | Type | D–H···A | d(D–H)/Å | d(H···A)/Å | d(D···A)/Å | ∠(DHA)/° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | A→B | N1–H1···O2′ i | 0.863(14) | 2.34(7) | 3.085(11) | 144(10) |
| b | A→A | N3–H3···O6 ii | 0.861(14) | 2.13(5) | 2.929(10) | 153(10) |
| c | B→A | N1′–H1′···O2 iii | 0.861(14) | 2.12(5) | 2.933(11) | 158(10) |
| d | B→A | N3′–H3′···O6 iv | 0.859(14) | 2.05(4) | 2.871(10) | 161(11) |
| Structure | CSD Refcode | Reference | X, X′ | Mol. | Ring Conformationa | Q (Å) | dC5–X (Å) | dC5–X′ (Å) | ∆d (Å)b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1MH | - | this work | Br | A | E | 0.201(4) | 1.907(4) | 1.963(4) | 0.056(5) |
| B | E | 0.196(4) | 1.912(4) | 1.967(3) | 0.055(5) | ||||
| 1a | UXIZAD | [11] | Br | A | E | 0.217(9) | 1.916(8) | 1.943(8) | 0.027(11) |
| B | E | 0.091(9) | 1.922(8) | 1.957(8) | 0.035(11) | ||||
| C | E→HC | 0.232(9) | 1.925(9) | 1.967(9) | 0.042(12) | ||||
| 1b | UXIZAD01 | [11] | Br | A | E→C | 0.184(6) | 1.904(6) | 1.970(5) | 0.066(8) |
| B | E→SB | 0.246(6) | 1.908(5) | 1.965(5) | 0.057(7) | ||||
| 3a | UXIYOQ | [11] | Cl | A | E→SB | 0.146(4) | 1.762(3) | 1.782(3) | 0.020(5) |
| B | E→SB | 0.154(4) | 1.743(3) | 1.787(3) | 0.044(5) | ||||
| C | E→SB | 0.143(4) | 1.756(3) | 1.782(3) | 0.026(4) | ||||
| D | E→SB | 0.156(4) | 1.742(3) | 1.788(3) | 0.046(5) | ||||
| 3b | UXIYOQ01 | [11] | Cl | A | E→HC | 0.220(2) | 1.742(2) | 1.7849(19) | 0.043(3) |
| B | E | 0.112(2) | 1.7521(18) | 1.7755(18) | 0.023(3) | ||||
| C | E→HC | 0.256(2) | 1.743(2) | 1.793(2) | 0.050(3) | ||||
| 3c | UXIYOQ02 | [12] | Cl | - | SB→E | 0.136(3) | 1.7472(18) | 1.7868(18) | 0.040(3) |
| 4 | HEKTIA | [29] | F | - | E | 0.173 | 1.324(6) | 1.359(7) | 0.035(9) |
| 5 (173 K) | - | this work | Me | - | E | 0.201(2) | 1.518(2)c | 1.5586(18)c | 0.041(3) |
| 5 (293 K) | NUXTAC | [30] | Me | - | E | 0.200 | 1.532(3)c | 1.562(3)c | 0.030(4) |
| Compound (X, X′) | Level of Theory | Ring Conformation a | Q (Å) | dC5–X (Å) | dC5–X′ (Å) | ∆d (Å) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (Br) | PBE0/6-31G(d,p) | E | 0.252 | 1.902 | 1.967 | 0.064 |
| PBE0/aug-cc-pVTz | E | 0.174 | 1.909 | 1.959 | 0.050 | |
| MP2/6-31G(d,p) | E | 0.288 | 1.919 | 1.976 | 0.057 | |
| 3 (Cl) | PBE0/6-31G(d,p) | E | 0.245 | 1.748 | 1.800 | 0.052 |
| PBE0/aug-cc-pVTz | E | 0.203 | 1.744 | 1.794 | 0.050 | |
| MP2/6-31G(d,p) | E | 0.274 | 1.745 | 1.797 | 0.051 | |
| 4 (F) | PBE0/6-31G(d,p) | E | 0.251 | 1.331 | 1.363 | 0.032 |
| PBE0/aug-cc-pVTz | E | 0.210 | 1.327 | 1.360 | 0.033 | |
| MP2/6-31G(d,p) | E | 0.233 | 1.344 | 1.378 | 0.033 | |
| 5 (Me) | PBE0/6-31G(d,p) | nearly planar | - | 1.535 | 1.541 | 0.006 |
| PBE0/aug-cc-pVTz | nearly planar | - | 1.531 | 1.539 | 0.008 | |
| MP2/6-31G(d,p) | E | 0.197 | 1.522 | 1.543 | 0.021 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gelbrich, T.; Braun, D.E.; Oberparleiter, S.; Schottenberger, H.; Griesser, U.J. The Hydrogen Bonded Structures of Two 5-Bromobarbituric Acids and Analysis of Unequal C5–X and C5–X′ Bond Lengths (X = X′ = F, Cl, Br or Me) in 5,5-Disubstituted Barbituric Acids. Crystals 2016, 6, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst6040047
Gelbrich T, Braun DE, Oberparleiter S, Schottenberger H, Griesser UJ. The Hydrogen Bonded Structures of Two 5-Bromobarbituric Acids and Analysis of Unequal C5–X and C5–X′ Bond Lengths (X = X′ = F, Cl, Br or Me) in 5,5-Disubstituted Barbituric Acids. Crystals. 2016; 6(4):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst6040047
Chicago/Turabian StyleGelbrich, Thomas, Doris E. Braun, Stefan Oberparleiter, Herwig Schottenberger, and Ulrich J. Griesser. 2016. "The Hydrogen Bonded Structures of Two 5-Bromobarbituric Acids and Analysis of Unequal C5–X and C5–X′ Bond Lengths (X = X′ = F, Cl, Br or Me) in 5,5-Disubstituted Barbituric Acids" Crystals 6, no. 4: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst6040047
APA StyleGelbrich, T., Braun, D. E., Oberparleiter, S., Schottenberger, H., & Griesser, U. J. (2016). The Hydrogen Bonded Structures of Two 5-Bromobarbituric Acids and Analysis of Unequal C5–X and C5–X′ Bond Lengths (X = X′ = F, Cl, Br or Me) in 5,5-Disubstituted Barbituric Acids. Crystals, 6(4), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst6040047