Betaine Chloride-Betaine Tetrachloridoferrate(III)—An Ionic Liquid Related Crystal Structure Governed by the Pearson Concept
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
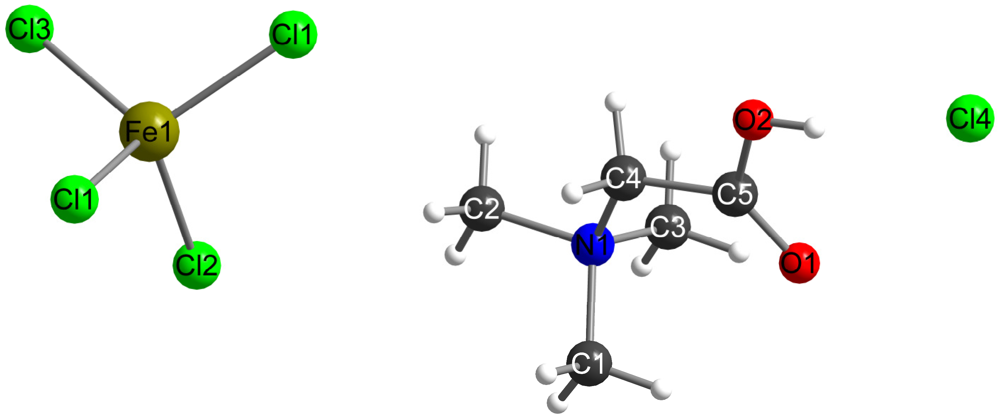
| formula | C10H24N2O2FeCl5 |
| molar mass | 469.41 |
| crystal system | orthorhombic |
| space group | Pbcm (No. 57) |
| a (Å) | 6.2717(13) |
| b (Å) | 12.841(3) |
| c (Å) | 25.693(5) |
| α = β = γ | 90° |
| volume (Å Å 3) | 2069.2(8) |
| ρ | 1.507 |
| Z | 4 |
| T (K) | 170 |
| F (000) | 964 |
| μ (mm−1) | 1.388 |
| reflections | 11322 |
| unique | 1680 |
| Rint | 0.1013 |
| R1 | 0.0393 |
| wR2 | 0.0752 |
| Goof | 0.80 |
| Fe1-Cl1 (2x) | 2.187(1) Å |
| Fe1-Cl2 | 2.186(2) Å |
| Fe1-Cl3 | 2.207(2) Å |
| Cl1-Fe1-Cl1 | 112.85(6) ° |
| Cl1-Fe1-Cl2 (2x) | 108.36(7) ° |
| Cl1-Fe1-Cl3 (2x) | 108.90(7) ° |
| Cl2-Fe1-Cl3 | 109.43(8) ° |
| C1-N1 | 1.508(7) Å |
| C2-N1 | 1.500(6) Å |
| C3-N1 | 1.499(6) Å |
| N1-C4 | 1.497(6) Å |
| C4-C5 | 1.493(7) Å |
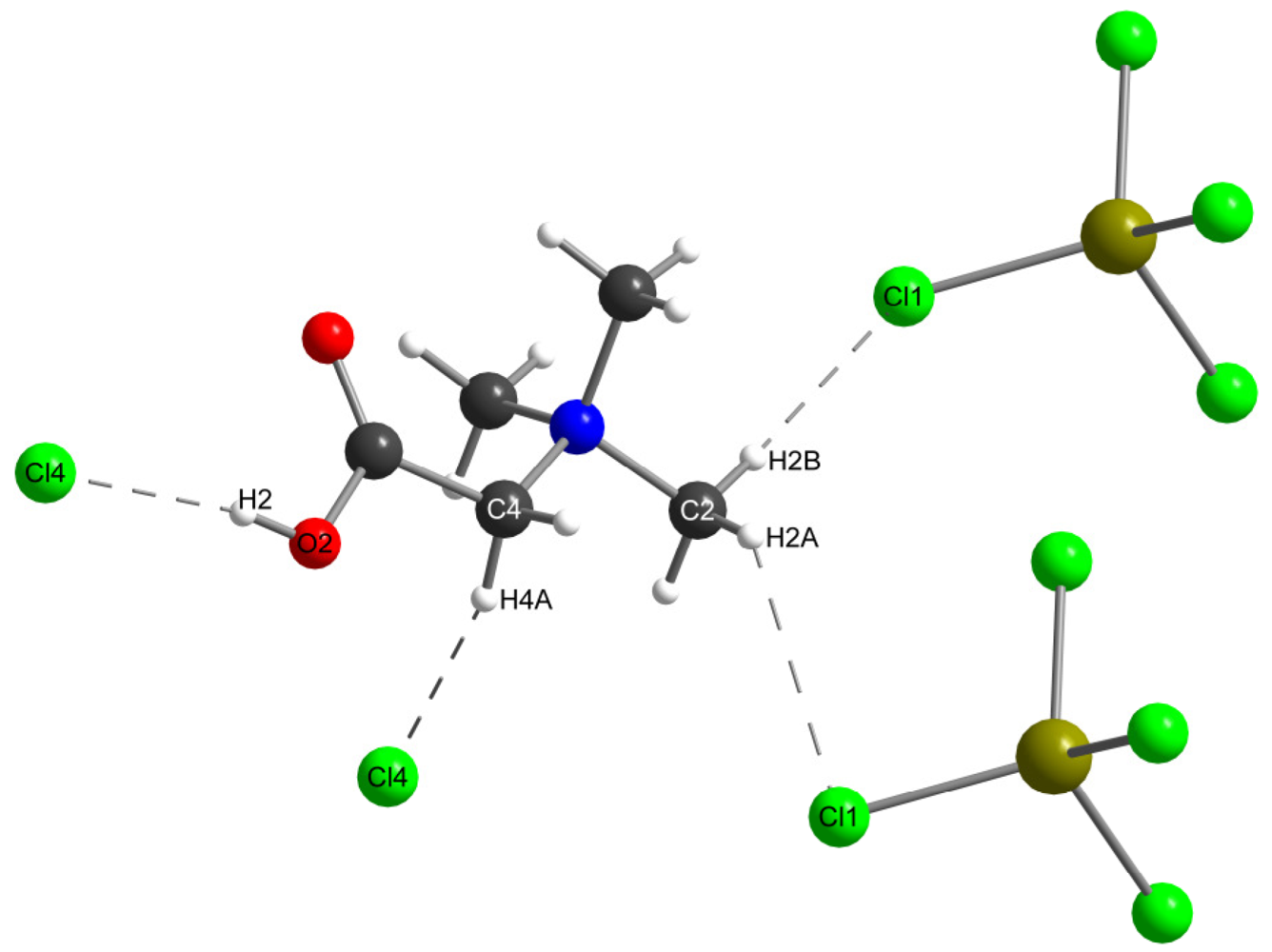
| d(donor-acceptor) | d(H-acceptor) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C2-Cl1 | 3.585(6) Å | H2A-Cl1 | 2.949(1) Å |
| C2-Cl1 | 3.650(6) Å | H2B-Cl1 | 2.692(1) Å |
| C4-Cl4 | 3.535(5) Å | H4A-Cl4 | 2.1909(5) Å |
| O2-Cl4 | 3.000(4) Å | H2-Cl4 | 2.6188(5) Å |
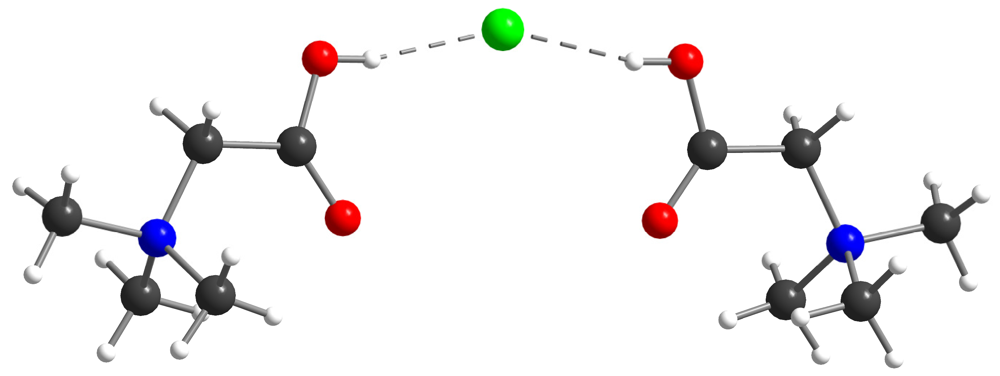
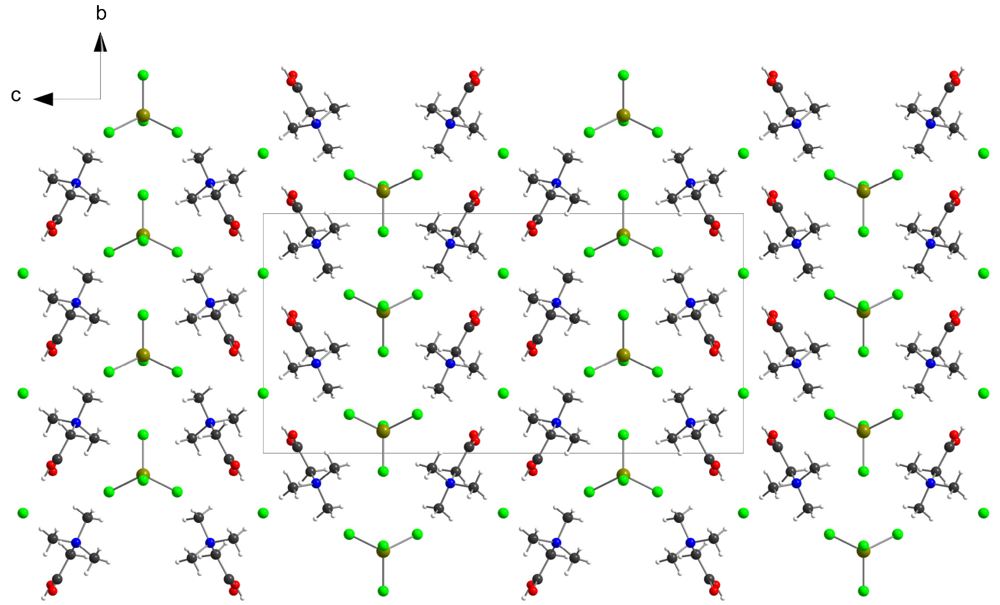
3. Experimental Section
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Nyyssölä, A.; Kerovuo, J.; Kaukinen, P.; von Weymarn, N.; Reinikainen, T. Extreme Halophiles Synthesize Betaine from Glycine by Methylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 22196–22201. [Google Scholar]
- 2. Calas, M.; Cordina, G.; Bompart, J.; Bari, M.B.; Jei, T.; Ancelin, M.L.; Vial, H. Antimalarial Activity of Molecules Interfering with Plasmodium Falciparum Phospholipid Metabolism. Structure-Activity Relationship Analysis. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 3557–3566. [Google Scholar]
- Katsh, S.; Keighley, G. Comparative Activities of Certain Quaternary Ammonium Compounds as Assayed by the Isolated Auricle Technique. Am. J. Physiol. 1953, 174, 431–435. [Google Scholar]
- Brieskorn, C.H.; Herrig, H. Eigenschaften der Betainester einiger Sterine und pentacyclischer Triterpene. Fette Seifen Anstrichm. 1959, 61, 1077–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nockemann, P.; Thijs, B.; Pittois, S.; Thoen, J.; Glorieux, C.; Van Hecke, K.; Van Meervelt, L.; Kirchner, B.; Binnemans, K. Task-Specific Ionic Liquid for Solubilizing Metal Oxides. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 20978–20992. [Google Scholar]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Keim, W. Ionic liquids—new “solutions” for transition metal catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 112, 3772–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, P.M.; Turanjanin, J.; Yoshizawa-Fujita, M.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Scott, J.L. Exploring an Anti-Crystal Engineering Approach to the Preparation of Pharmaceutically Active Ionic Liquids. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoimenovski, J.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Bica, K.; Rogers, R.D. Crystalline vs. Ionic Liquid Salt Forms of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients: A Position Paper. Pharmaceut. Res. 2010, 27, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, S.; Wendler, K.; Delle Site, L.; Kirchner, B. Depolarization of water in protic ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 15083–15093. [Google Scholar]
- Henschel, D.; Moers, O.; Wijaya, K.; Wirth, A.; Blaschette, A.; Jones, P.G. Schwache Wasserstoffbrücken mit aktivierten Methyldonoren: Kristallstrukturen von Cholinium-, Betainium- und Dimethyl[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]ammonium-dimesylamid. Z. Naturforsch. 2002, 57b, 534–546. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, R.G. Hard and Soft Acids and Bases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 3533–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowiak, T.; Durcanska, E.; Ondrejkovicova, I.; Ondrejovic, G. Structure of methyltriphenyl-phosphonium tetrachloroferrate(III). Acta Crystallogr. 1986, C42, 1331–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, R.R.; Gregory, N.W. The crystal structure of sodium tetrachloroferrate(III). J. Phys. Chem. 1965, 69, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, G. Chlorometallate(III) mit Barytstruktur: CsFeCl4 und CsAlCl4. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1977, 436, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerisier, J.; Guillot, C.; Palvadeau, P.; Rouxel, J. Characterization and study of physical properties and ionic conductivity of alkali metal tetrachloroferrates(1-) (alkali metal = lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium). Eur. J. Solid State Inorg. Chem. 1988, 25, 35–52. [Google Scholar]
- Baecker, T.; Breunig, O.; Valldor, M.; Merz, K.; Vasylyeva, V.; Mudring, A.-V. In-Situ Crystal Growth and Properties of the Magnetic Ionic Liquid [C2mim][FeCl4]. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 2564–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, J.; Drozd, M.; Glowiak, T.; Sledz, M.; Ratajczak, H. Crystal structure, phase transitions and vibrational spectra of bis(betaine)nitrate. J. Mol. Struct. 1995, 372, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.S.; Templeton, D.H.; Zalkin, A. Solid state structure and chemistry of the choline halides and their analogues. Redetermination of the betaine hydrochloride structure, [(CH3)3NCH2COOH]+Cl−. Acta Crystallogr. 1970, B26, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, T. The Hydrogen Bond in the Solid State. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 48–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- X-RED, Stoe & Cie: Darmstadt, Germany, 2002.
- X-Shape, Stoe & Cie: Darmstadt, Germany; 2002.
- Sheldrick, W.S. SHELXS-97; Universität Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- International Table for Crystallography; Prince, E. (Ed.) Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume C.
- Diamond Ver. 3.2, Crystal Impact GbR: Bonn, Germany, 2010.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bäcker, T.; Mudring, A.-V. Betaine Chloride-Betaine Tetrachloridoferrate(III)—An Ionic Liquid Related Crystal Structure Governed by the Pearson Concept. Crystals 2012, 2, 110-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst2010110
Bäcker T, Mudring A-V. Betaine Chloride-Betaine Tetrachloridoferrate(III)—An Ionic Liquid Related Crystal Structure Governed by the Pearson Concept. Crystals. 2012; 2(1):110-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst2010110
Chicago/Turabian StyleBäcker, Tobias, and Anja-Verena Mudring. 2012. "Betaine Chloride-Betaine Tetrachloridoferrate(III)—An Ionic Liquid Related Crystal Structure Governed by the Pearson Concept" Crystals 2, no. 1: 110-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst2010110
APA StyleBäcker, T., & Mudring, A.-V. (2012). Betaine Chloride-Betaine Tetrachloridoferrate(III)—An Ionic Liquid Related Crystal Structure Governed by the Pearson Concept. Crystals, 2(1), 110-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst2010110




