Impact of Calcination Temperature on the Properties and Photocatalytic Efficiency of Cd0.6Mg0.2Cu0.2Fe2O4 Spinel Ferrites Synthesized via the Sol–Gel Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Photocatalytic Test
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural and Morphological Analyses
3.1.1. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.1.2. Morphology Study (SEM)
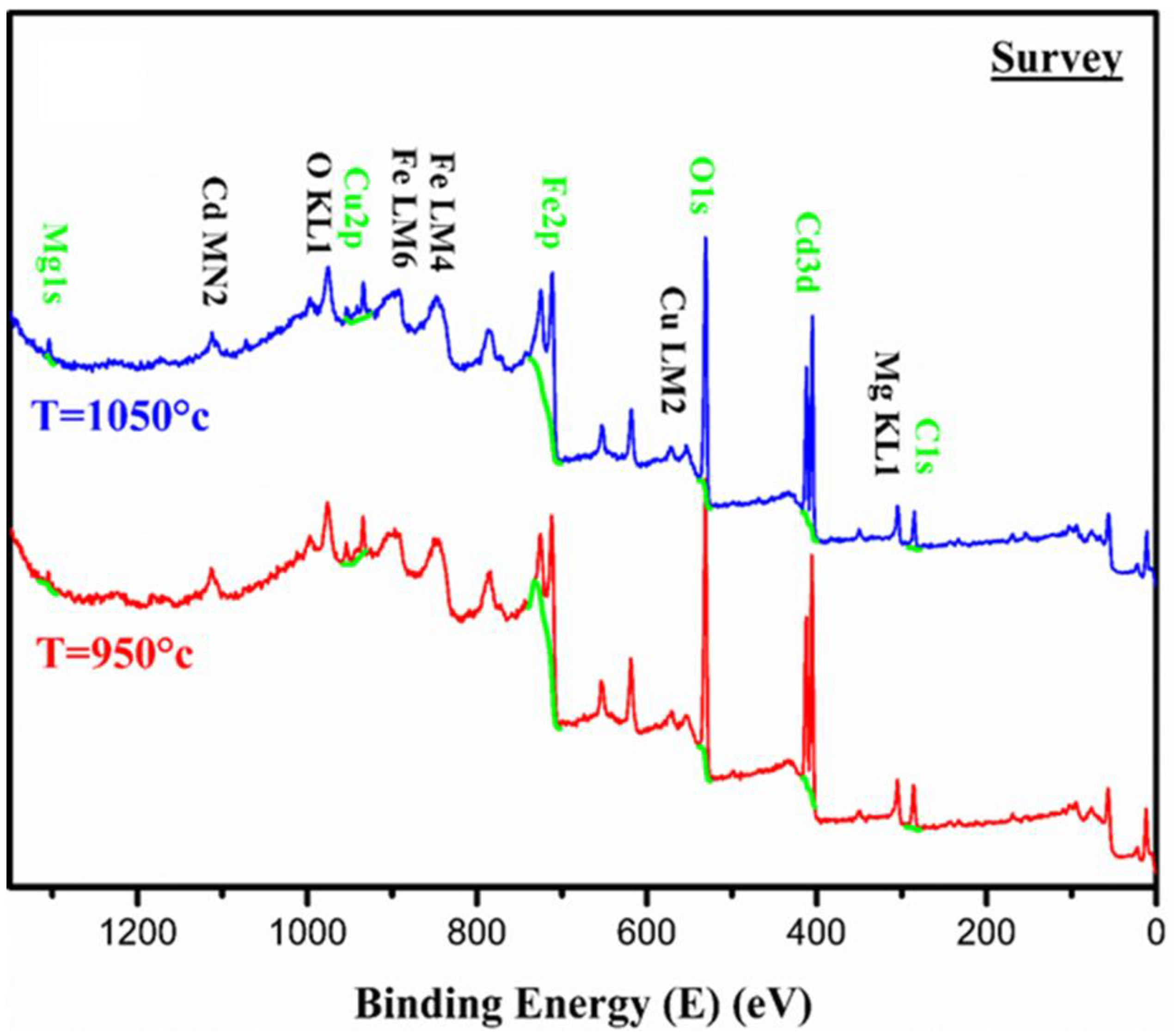
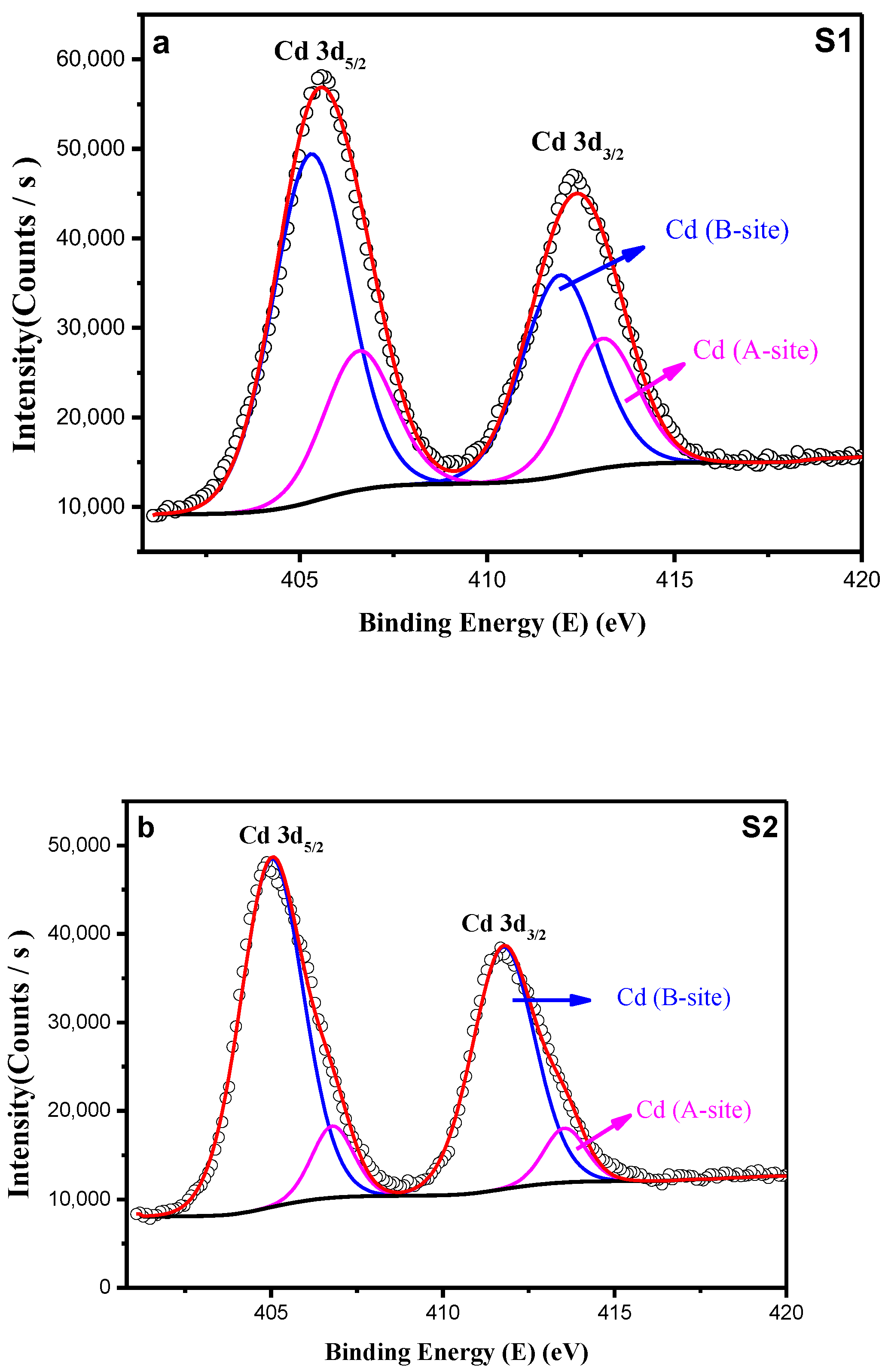
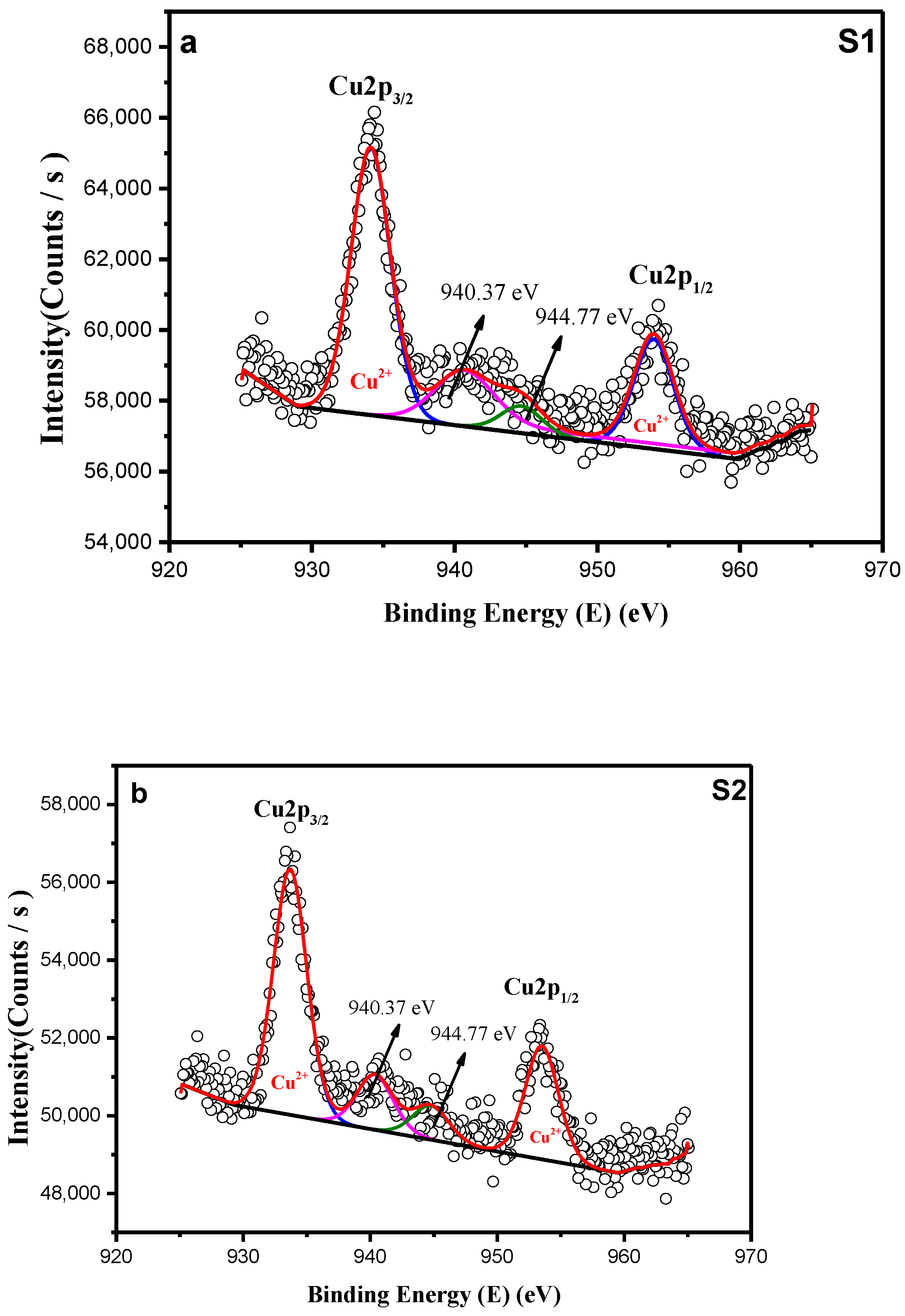
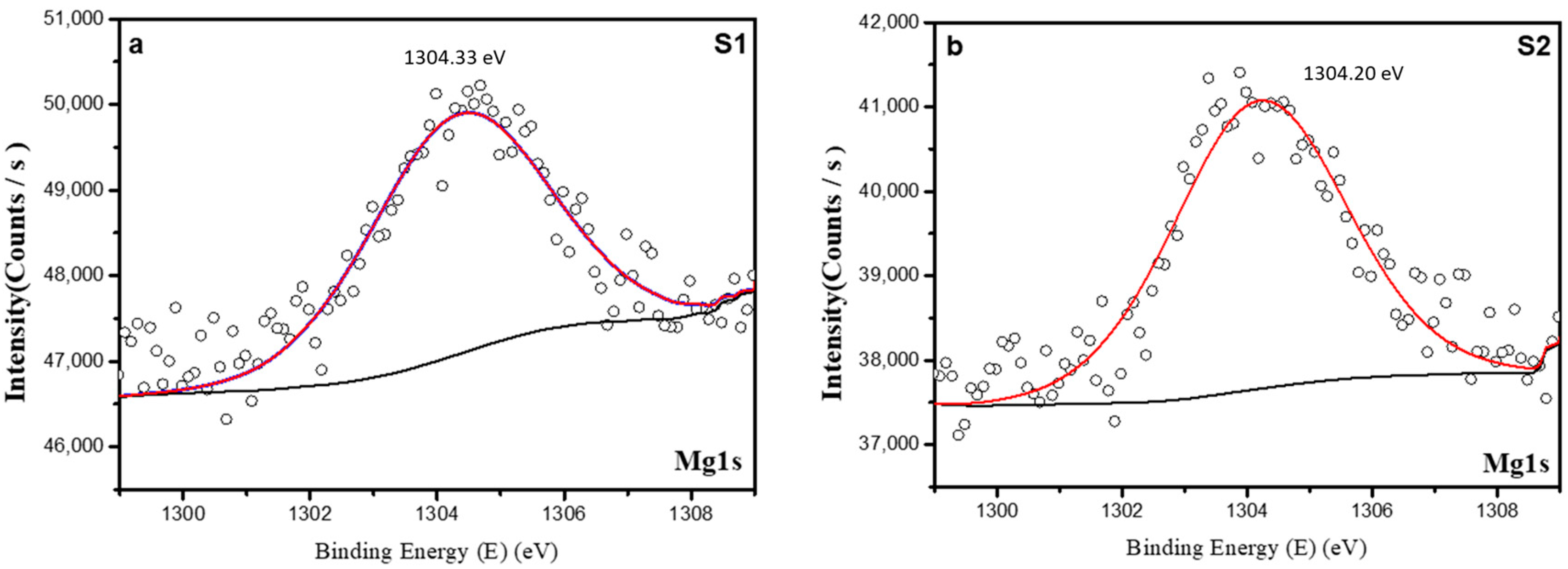
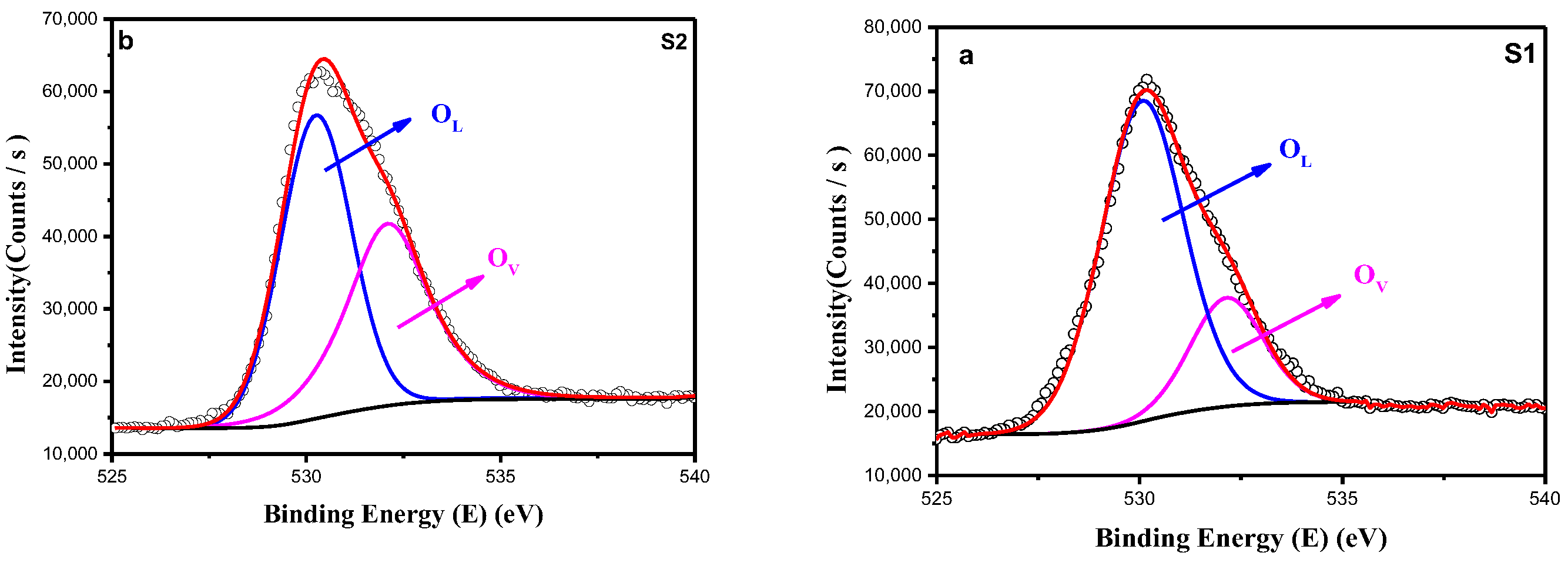
3.1.3. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
3.2. Optical Band Gap Study
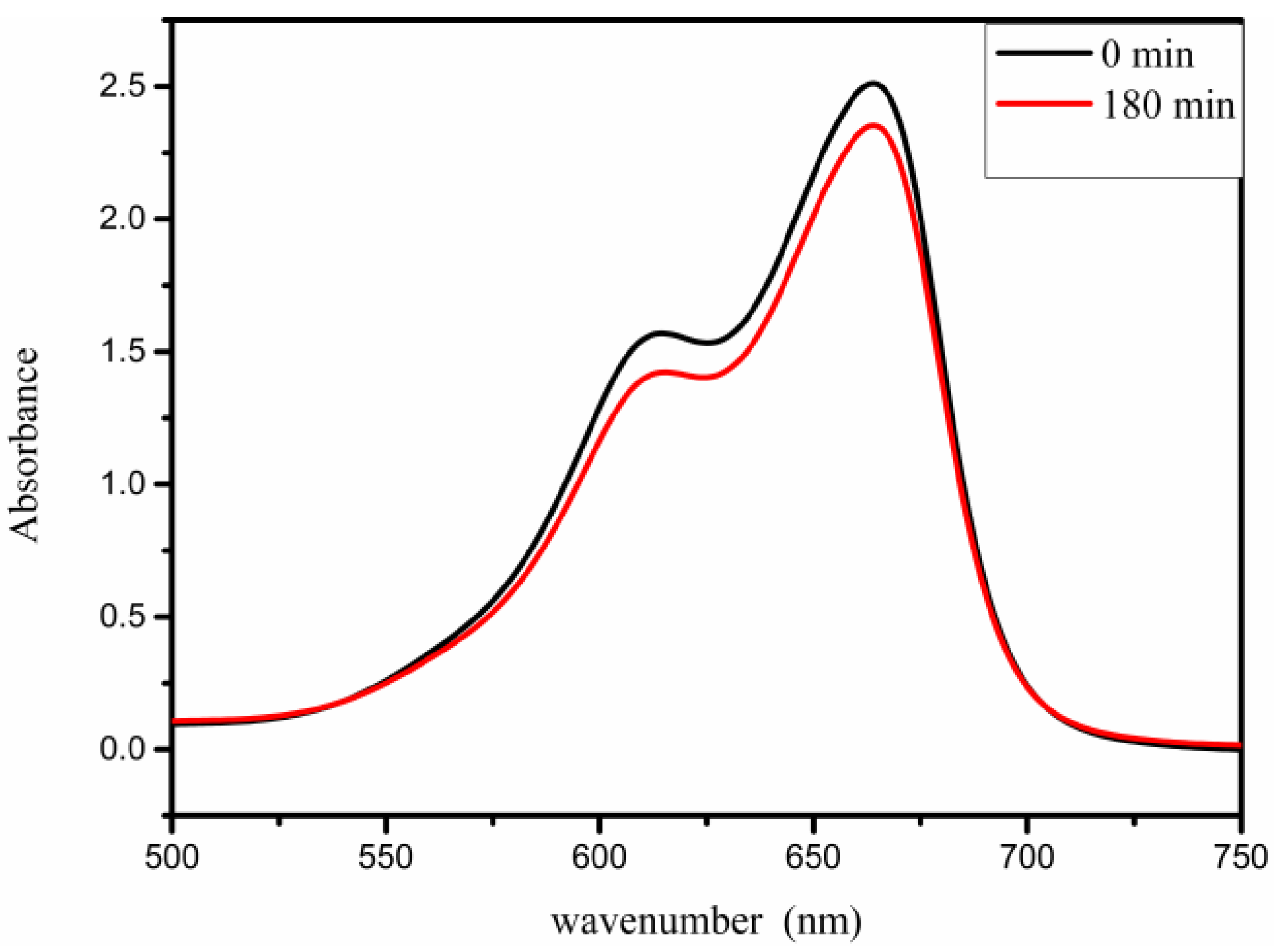
3.3. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Blue (MB) Dye
3.3.1. Photodegradation Mechanism
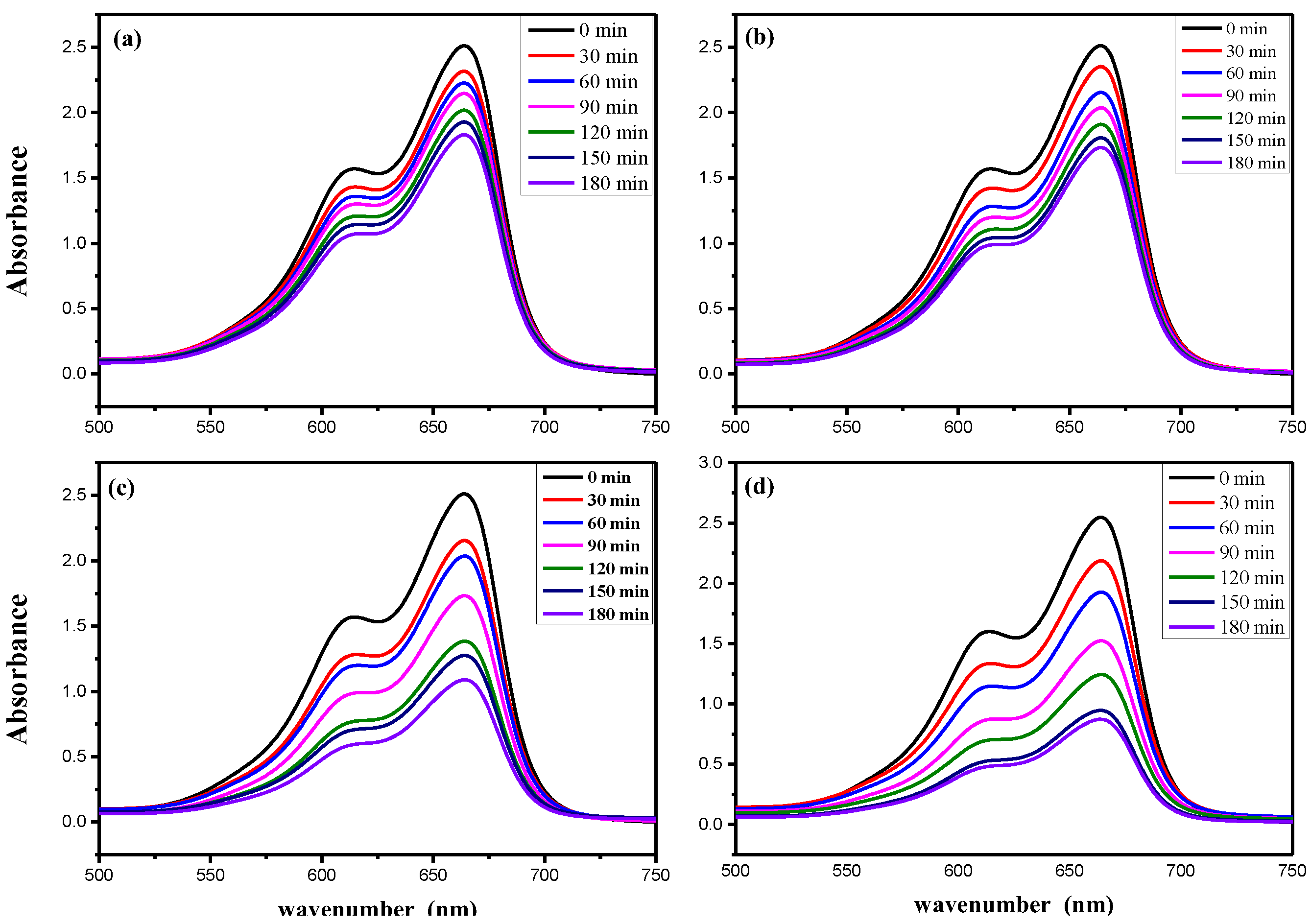
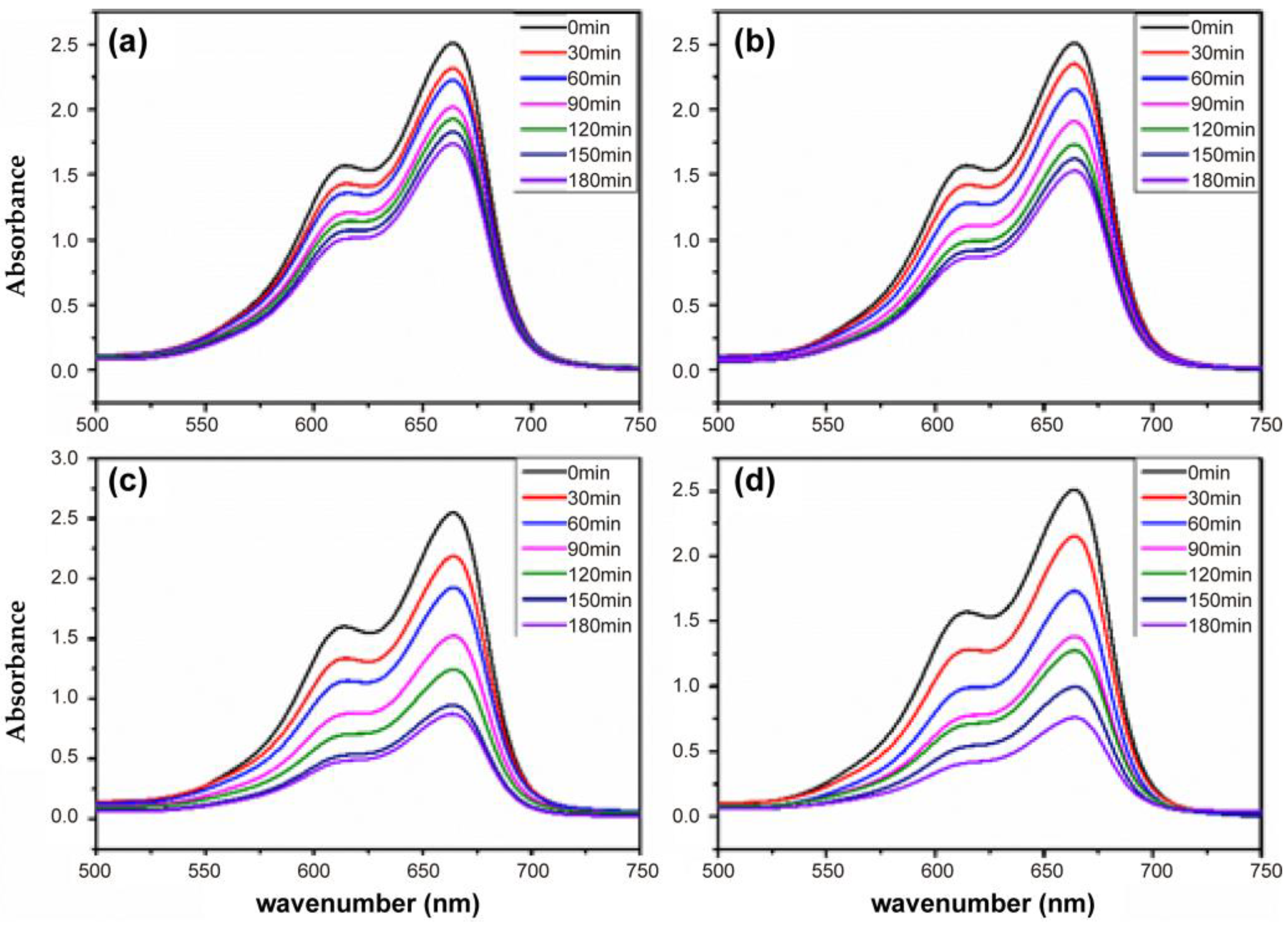
3.3.2. Effect of Irradiation Time
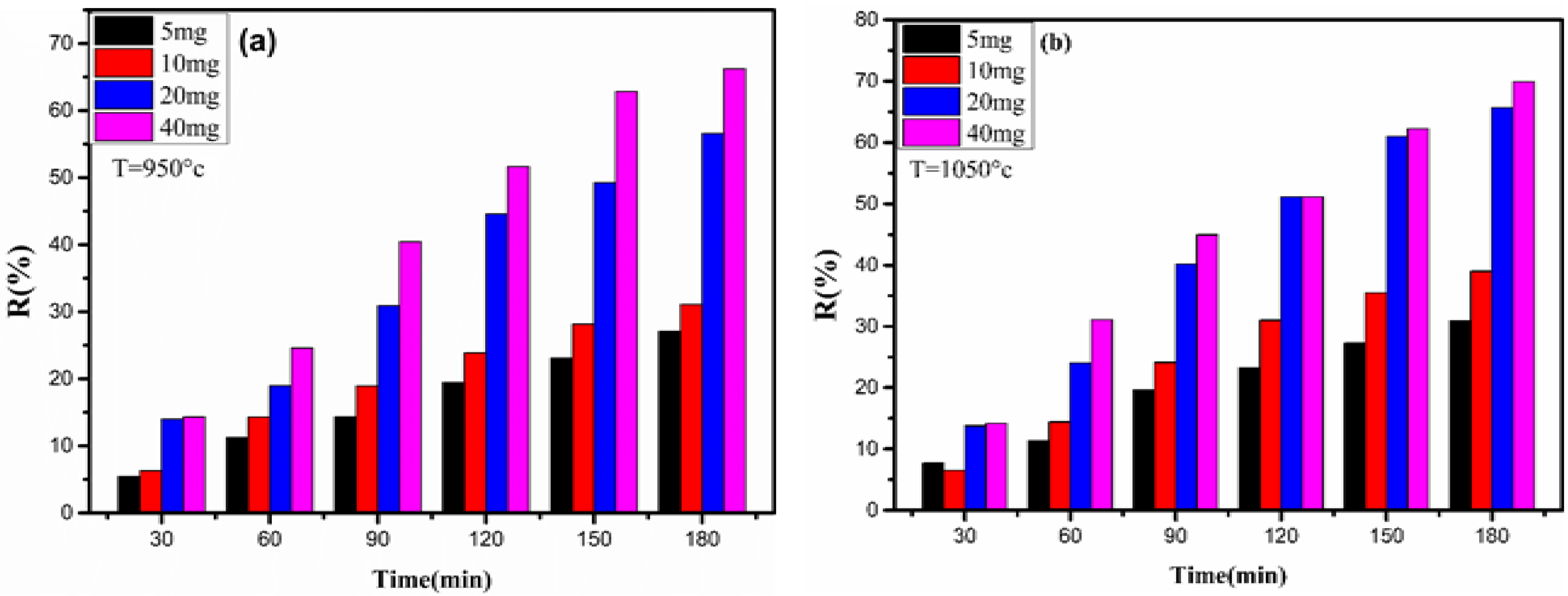
3.3.3. Effect of Catalyst Content
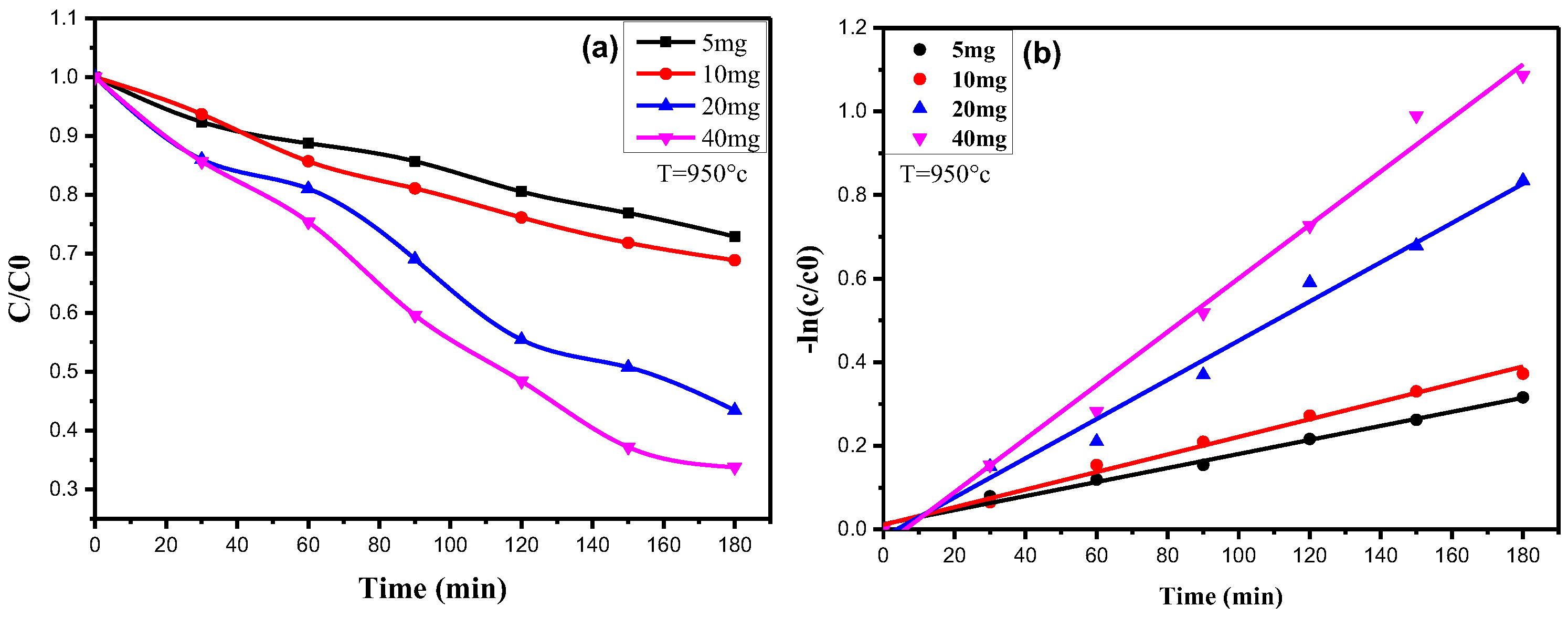
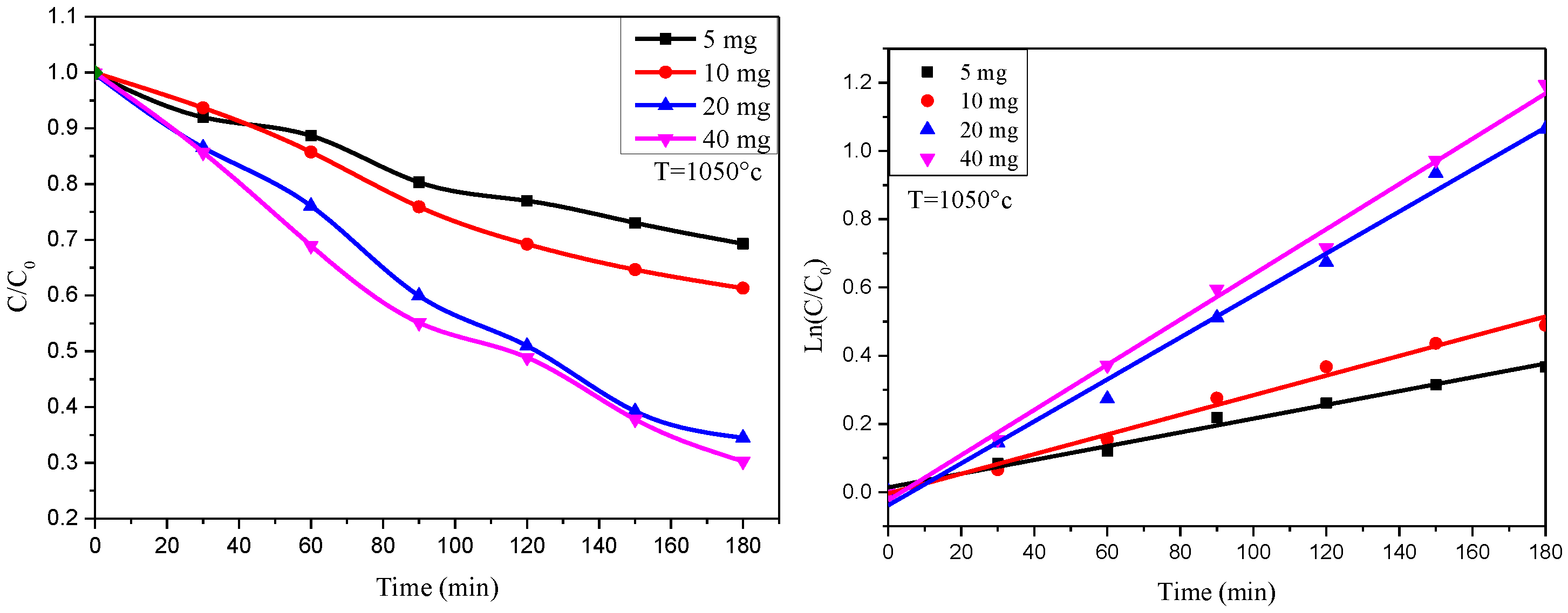
3.3.4. Kinetic Analysis of Methylene Blue Degradation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naresh, U.; Kumar, R.J.; Naidu, K.C.B. Optical, magnetic and ferroelectric properties of Ba0.2Cu0.8−xLaxFe2O4 (x = 0.2–0.6) nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 7515–7523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naresh, U.; Kumar, R.J.; Naidu, K.C.B. Hydrothermal synthesis of barium copper ferrite nanoparticles: Nanofiber formation, optical, and magnetic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 236, 121807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.; Masoudpanah, S.; Mirkazemi, S.; Aliyan, N. PVA assisted coprecipitation synthesis and characterization of MgFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 6263–6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, N.R.; Prakash, M.; Naresh, U.; Kumar, N.S.; Sarmash, T.S.; Subbarao, T.; Kumar, R.J.; Kumar, G.R.; Naidu, K.C.B. Review on magnetocaloric effect and materials. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2018, 31, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, J.; Mathew, M.J. Structural, optical and magnetic studies of CuFe2O4, MgFe2O4 and ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by hydrothermal/solvothermal method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 451, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüders, U.; Barthelemy, A.; Bibes, M.; Bouzehouane, K.; Fusil, S.; Jacquet, E.; Contour, J.-P.; Bobo, J.-F.; Fontcuberta, J.; Fert, A. NiFe2O4: A versatile spinel material brings new opportunities for spintronics. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 1733–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonkumwong, J.; Ananta, S.; Jantaratana, P.; Phumying, S.; Maensiri, S.; Srisombat, L. Phase formation, morphology and magnetic properties of MgFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by hydrothermal technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 381, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.; Yuan, C.; Yin, J.; Cao, D.; Wang, G. MgFe2O4 nanoparticles as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 109, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, M.; Tondo, C.; Capsoni, D.; Mozzati, M.C.; Albini, B.; Galinetto, P. Superparamagnetic ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles: The effect of Ca and Gd doping. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 204, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkov, V.I.; Tolstoy, V.P.; Semenov, V.G. Synthesis of phase-pure superparamagnetic nanoparticles of ZnFe2O4 via thermal decomposition of zinc-iron layered double hydroxysulphate. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 813, 152179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.-C.; Wang, Z.-L.; Yi, M.-Z.; Ran, L.-P. Fabrication and magnetic transformation from paramagnetic to ferrimagnetic of ZnFe2O4 hollow spheres. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghazzawy, E.H. Effect of heat treatment on structural, magnetic, elastic and optical properties of the co-precipitated Co0.4Sr0.6Fe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 497, 166017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Nadeem, K.; Anis-ur-Rehman, M.; Mumtaz, M.; Naeem, S.; Letofsky-Papst, I.J.C.I. Structural and magnetic properties of ZnMg-ferrite nanoparticles prepared using the co-precipitation method. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 5235–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qin, F.; Chen, D.; Shen, H.; Wang, H.; Xing, D.; Phan, M.-H.; Sun, J. Combined current-modulation annealing induced enhancement of giant magnetoimpedance effect of Co-rich amorphous microwires. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 17A326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarío, E.; Herrasti, P.; Morales, M.P.; Menéndez, N. Synthesis and characterization of CoFe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles obtained by an electrochemical method. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 355708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Jauhar, S.; Kumar, V.; Singh, J.; Singhal, S. Synthesis of zinc substituted cobalt ferrites via reverse micelle technique involving in situ template formation: A study on their structural, magnetic, optical and catalytic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 156, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavender, A.T.; Jadhav, K.M. Dielectric properties of Al-substituted Co ferrite nanoparticles. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2009, 32, 575–578. [Google Scholar]
- Harrabi, D.; Hcini, S.; Dhahri, J.; Hamdaoui, N.; Charguia, R.; Bouazizi, M.L.; Mansouri, S. Structural, Magnetic, and Dielectric Properties for Mg0.6Co0.2Cu0.2FeCrO4 Spinel Ferrites Prepared Under Different Calcination Temperatures. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2023, 36, 1549–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S.; Vo, D.V.N. Critical review on hazardous pollutants in water environment: Occurrence, monitoring, fate, removal technologies and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkaczyk, A.; Mitrowska, K.; Posyniak, A. Synthetic organic dyes as contaminants of the aquatic environment and their implications for ecosystems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Karthikeyan, S.; Lee, A.F. g-C3N4-based nanomaterials for visible light-driven photocatalysis. Catalysts 2018, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettcher, S.W.; Mallouk, T.E.; Osterloh, F.E. Themed issue on water splitting and photocatalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 2764–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardood, S.T.; Moradnia, F.; Forootan, R.; Abbassi, R.; Jalalifar, S.; Ramazani, A.; Sillanpää, M. Facile green synthesis, characterization and visible light photocatalytic activity of MgFe2O4@ CoCr2O4 magnetic nanocomposite. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2022, 423, 113621. [Google Scholar]
- Moradnia, F.; Fardood, S.T.; Ramazani, A.; Min, B.-K.; Joo, S.W.; Varma, R.S. Magnetic Mg0.5Zn0.5FeMnO4 nanoparticles: Green sol-gel synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oller, I.; Malato, S.; Sánchez Pérez, J.A. Combination of advanced oxidation processes and biological treatments for wastewater decontamination—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4141–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.A.; Jingsong, G.; Ping, L.Z.; Ya, P.Y.; Al-Rekabi, W.S. Review on LandWll leachate treatments. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2009, 5, 534–545. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.H.S.; Wu, T.Y.; Juan, J.C.; Teh, C.Y. Recent developments of metal oxide semiconductors as photocatalysts in advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for treatment of dye waste-water. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2011, 86, 1130–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi Fardood, S.; Moradnia, F.; Heidarzadeh, S.; Naghipour, A. Green synthesis, characterization, photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of copper oxide nanoparticles of copper oxide nanoparticles. Nanochem. Res. 2023, 8, 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zheng, G.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y. Photocatalytic and luminescent properties of SrMoO4 phosphors prepared via hydrothermal method with different stirring speeds. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreishi, S.M. Facile synthesis and characterization of CaWO4 nanoparticles using a new Schiff base as capping agent: Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 14833–14838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Makhlouf, C.; Bouzidi, S.; Gassoumi, A.; Selmi, A.; Hcini, F.; Hcini, S.; Gassoumi, M. Experimental study of electrical and dielectric properties of Cu0.6Mg0.2Co0.2FeCrO4 spinel ferrite. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2024, 110, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouki, N.; Hcini, S.; Aldawas, R.; Boudard, M. Structural, Infrared, Magnetic, and Electrical Properties of Ni0.6Cd0.2Cu0.2Fe2O4 Ferrites Synthesized Using Sol-Gel Method Under Different Sintering Temperatures. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2019, 32, 2209–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ben Makhlouf, C.; Bouazizi, M.L.; Hcini, S.; ben Bacha, H.; HajTaieb, L.; Gassoumi, M. Detailed Structural Study, Optical, and Dielectric Properties of Co0.4Ni0.3Zn0.3Fe2O4 Ferrite and Its Potential Applications for Optoelectronic and Electronic Devices. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2025, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Chu, Y. General Route to the Fabrication of ZnS and M-Doped (M = Cd2+, Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, and Eu3+) ZnS Nanoclews and a Study of Their Properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 2010, 2504–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakil, M.; Inayat, U.; Khalid, N.R.; Tanveer, M.; Gillani SS, A.; Tariq, N.H.; Shah, A.; Mahmood, A.; Dahshan, A. Enhanced structural, optical, and photocatalytic activities of Cd–Co doped Zn ferrites for degrading methyl orange dye under irradiation by visible light. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2022, 161, 110419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanveer, M.; Nisa, I.; Nabi, G.; Shakil, M.; Khalid, S.; Qadeer, M. Enhanced structural, optical, and photocatalytic activity of novel Cd–Zn co-doped Mg0.25 Fe1.75O4 for degradation of RhB dye under visible light irradiation. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 15451–15461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.K.; Ghaffari, Y.; Kim, S.; Bae, J.; Kim, K.S.; Saifuddin, M. Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants over MFe2O4 (M = Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) nanoparticles at neutral pH. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaramahalingam, A.; Lawrence, J.B. Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of MgFe2O4 synthesized with addition of copper. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Nano-Met. Chem. 2012, 42, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, T.M.; Kuhn, S.; Amsha, A.A.; Hejazy, N.K.; Hempelmann, R. Comprehensive study of the impact of Mg2+ doping on optical, structural, and magnetic properties of copper nanoferrites. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2020, 33, 3065–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, A.; Priya, R.S.; Chaudhary, P.; Kumar, E.R.; Indumathi, T.; Srinivas, C.; Yadav, B.C.; Sastry, D.L. Natural fuel assisted synthesis of Mg–Cu ferrite nanoparticles: Evaluation of structural, dielectric, magnetic and humidity sensing properties. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 4874–4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jdidi, A.R.; Rhimi, N.; Hcini, F.; Hcini, S.; Bouzidi, S.; Khirouni, K.; Gassoumi, M. Enhancing dielectric properties of CuFe2O4 spinel ferrites through Mg, Co, and Cr doping: A sol-gel synthesis approach. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2024, 034103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; Li, F.; Li, L. Enhanced photocatalytic performance of spinel ferrite (MFe2O4, M = Zn, Mn, Co, Fe, Ni) catalysts: The correlation between morphology–microstructure and photogenerated charge efficiency. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, V.A.F.; Bernadsha, S.B.; Mahendiran, M.; Lawrence, K.L.; Madhavan, J.; Raj MV, A.; Prathap, S. Impact of calcination temperature on structural, optical, and magnetic properties of spinel CuFe2O4 for enhancing photocatalytic activity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 6574–6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, R.N.; Vijayasri, G. Study of microstructure and semiconductor to metallic conductivity transition in solid state sintered Li0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4−δ spinel ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 223701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.B.; Bhojya Naik, H.S.; Nagaraju, G.; Shiralgi, Y. Sugarcane juice facilitated eco-friendly synthesis of solar light active CdFe2O4 nanoparticles and its photocatalytic application. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Kameli, P.; Ranjbar, M.; Salamati, H. The effect of sintering temperature on evolution of structural and magnetic properties of nanostructured Ni0.3Zn0.7Fe2O4 ferrite. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.; Hankare, P.; Garadkar, K.; Sasikala, R. Effect of sintering temperature on structural, magnetic properties of lithium chromium ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 523, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherca, D.; Pui, A.; Cornei, N.; Cojocariu, A.; Nica, V.; Caltun, O. Synthesis, characterization and magnetic properties of MFe2O4 (M = Co, Mg, Mn, Ni) nanoparticles using ricin oil as capping agent. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 3906–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Afify, H.; El Zawawia, I.; Azab, A. Novel structural and magnetic properties of Mg doped copper nanoferrites prepared by conventional and wet methods. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, A.; Jafari, E. Effects of sintering atmosphere and temperature on structural and magnetic properties of Ni-Cu-Zn ferrite nano-particles: Magnetic enhancement by a reducing atmosphere. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 422, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, M.; Rahman, M.L.; Ahmed, M.F.; Biswas, B.; Sharmin, N. Calcination effect on structural, morphological and magnetic properties of nano-sized CoFe2O4 developed by a simple co-precipitation technique. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 264, 124442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippong, T.; Cadar, O.; Levei, E.A.; Deac, I.G.; Goga, F.; Borodi, G.; Barbu-Tudoran, L. Influence of polyol structure and molecular weight on the shape and properties of Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles obtained by sol-gel synthesis. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 7458–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippong, T.; Cadar, O.; Levei, E.A.; Deac, I.G. Microstructure, porosity and magnetic properties of Zn0.5Co0.5Fe2O4/SiO2 nanocomposites prepared by sol-gel method using different polyols. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 498, 166168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.C.; Harris, S.J.; Jutson, J.A.; Dyke, J.M. A study of a number of mixed transition metal oxide spinels using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1989, 37, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.C.; Hallam, K.R. Characterisation of the spinels MxCo1−xFe2O4 (M = Mn, Fe or Ni) using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1996, 93, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Tan, J.; Zhou, K.; Garcia-Meza, J.V.; Song, S.; Xia, L. Yeast-derived biochar to load CoFe2O4: Degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride by heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, W.; Yang, Z.; Strasser, P.; Yang, R. A CoFe2O4/graphene nanohybrid as an efficient bi-functional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution. J. Power Sources 2014, 250, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, N.; Tougaard, S.; Yubero, F. Determination of the Cu 2p primary excitation spectra for Cu, Cu2O and CuO. Surf. Sci. 2014, 620, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuler, M.R.; Benbow, R.L.; Hurych, Z. Resonant photo-and Auger emission at the 3p threshold of Cu, Cu2O, and CuO. Phys. Rev. B 1982, 26, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.S.G.; Govardhanan, B.; Aabel, P.; Ashok, M.; Kumar, M.S. Effect of oxygen partial pressure on the tuning of copper oxide thin films by reactive sputtering for solar light driven photocatalysis. Sol. Energy 2019, 187, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlKhoori, A.A.; Polychronopoulou, K.; Belabbes, A.; Abi Jaoude, M.; Vega, L.F.; Sebastian, V.; Hinder, S.; Baker, M.A.; Zedan, A.F. Cu, Sm co-doping effect on the CO oxidation activity of CeO2. A combined experimental and density functional study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 521, 146305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Handoko, A.D.; Du, Y.; Xi, S.; Yeo, B.S. In Situ Raman Spectroscopy of Copper and Copper Oxide Surfaces during Electrochemical Oxygen Evolution Reaction: Identification of CuIII Oxides as Catalytically Active Species. ACS Catal. 2016, 64, 2473–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajlani, Y.; Placido, F.; Barlow, A.; Chu, H.O.; Song, S.; Rahman, S.U.; De Bold, R.; Gibson, D. Characterisation of Cu2O, Cu4O3, and CuO mixed phase thin films produced by microwave-activated reactive sputtering. Vacuum 2017, 144, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallel, W.; Bouattour, S.; Ferreira, L.V.; do Rego, A.B. Synthesis, XPS and luminescence (investigations) of Li+ and/or Y3+ doped nanosized titanium oxide. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 114, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessergenev, V.G.; Pereira RJ, F.; Mateus, M.C.; Khmelinskii, I.V.; Vasconcelos, D.A. 379 R. Nicula, E. Burkela, AM Botelho do Rego, AI Saprykin. Thin Solid Films 2006, 503, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Naeem, M.; Hasanain, S.K.; Kobayashi, M.; Ishida, Y.; Fujimori, A.; Buzby, S.; Shah, S.I. Effect of reducing atmosphere on the magnetism of Zn1−xCoxO (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.10) nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitran, G.; Chen, S.; Seo, D.K. Role of oxygen vacancies and Mn4+/Mn3+ ratio in oxidation and dry reforming over cobalt-manganese spinel oxides. Mol. Catal. 2020, 483, 110704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souifi, K.; Rejaiba, O.; Amorri, O.; Nasri, M.; Alzahrani, B.; Bouazizi, M.L.; Khirouni, K.; Khelifi, J. Detailed Investigation of Structural, Morphology, Magnetic, Electical and Optical Properties of the Half-Doped Perovsikte Nd0.5Ba0.5FeO3. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2022, 32, 4515–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raddaoui, G.; Rejaiba, O.; Nasri, M.; Khirouni, K.; Alzahrani, B.; Bouazizi, M.L.; Khelifi, J. Investigation studies of structural, electrical, dielectric, and optical of DyTi0.5Mn0.5O3 multiferroic for optoelectronics applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 21890–21912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagandeep Singh, K.; Lark, B.S.; Sahota, H.S. Attenuation measurements in solutions of some carbohydrates. Nucl. Sci. Eng. 2000, 134, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaid, S.M.H.; Al-Asbahi, B.A.; Ghaithan, H.M.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Al Dwayyan, A.S. Optical and structural properties of CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots/PFO polymer composite thin films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 563, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, A.A.; Mansour, A.M.; Turky, G.M. Structural, Magnetic, and Dielectric properties of Sr4Fe6O13 ferrite prepared of small crystallites. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, P.; Sharma, R.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, P. Structural and optical properties of Mn0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nano ferrites: Effect of sintering temperature. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 193, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Hammad, A.B.; Mansour, A.M.; Elhelali, T.M.; El Nahrawy, A.M. Sol-Gel/Gel Casting Nanoarchitectonics of Hybrid Fe2O3–ZnO/PS-PEG Nanocomposites and Their Optomagnetic Properties. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2023, 33, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Bakar, S.; Soltani, N.; Yunus, W.M.M.; Saion, E.; Bahrami, A. Structural and paramagnetic behavior of spinel NiCr2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by thermal treatment method: Effect of calcination temperature. Solid State Commun. 2014, 192, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman; Chahal, S.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P. Zn Doped α-Fe2O3: An Efficient Material for UV Driven Photocatalysis and Electrical Conductivity. Crystal 2020, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, S.; Tian, Z.; Hu, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Duan, G.; Yang, W.; Jiang, S. Enhanced visible light photocatalytic efficiency of La-doped ZnO nanofibers via electrospinning-calcination technology. Adv. Powder Mater. 2022, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, H.; Khan, M.; Mohuddin, B.; Iqbal, T. Solution-phase growth of tin oxide (SnO2) nanostructures: Structural, optical and photocatalytic properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2020, 258, 114568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Bhatti, H.N.; Younis, S.; Rehmat, S.; Alwadai, N.; Almuqrin, A.H.; Iqbal, M. Graphene oxide nanocomposite with CuSe and photocatalytic removal of methyl green dye under visible light irradiation. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2021, 113, 108254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann, D.; Mendive, C.; Bahnemann, D. TiO2 for water treatment: Parameters affecting the kinetics and mechanisms of photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 99, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahar, D.; Taneja, S.; Bisht, S.; Kesarwani, S.; Thakur, P.; Thakur, A.; Sharma, P.B. Photocatalytic activity of cobalt substituted zinc ferrite for the degradation of methylene blue dye under visible light irradiation. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 851, 156878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocarlan, R.-G.; Seftel, E.M.; Mertens, M.; Pui, A.; Mazaj, M.; Tusar, N.N.; Cool, P. Novel magnetic nanocomposites containing quaternary ferrites systems Co0.5Zn0.25M0.25Fe2O4(M = Ni, Cu, Mn, Mg) and TiO2-anatase phase as photocatalysts for wastewater remediation under solar light irradiation, Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2018, 230, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Pu, X.; Du, K.; Yu, Y.M.; Shim, J.J.; Cai, P.; Kim, S.I.; Seo, H.J. Combustion synthesis of magnetic Ag/NiFe2O4 composites with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 137, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, N.; Karim, K.M.R.; Abdullah, H.; Khan, M.R. Synthesis of titania doped copper ferrite photocatalyst and its photoactivity towards methylene blue degradation under visible light irradiation. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2019, 14, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmapriya, G.; Manikandan, A.; Krishnasamy, V.; Jaganathan, S.K.; Antony, S.A. Spinel NixZn1−xFe2O4 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0) nano-photocatalysts: Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1119, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathubala, G.; Manikandan, A.; Antony, S.A.; Ramar, P. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye and magneto-optical studies of magnetically recyclable spinel NixMn1−xFe2O4 (x = 0.0–1.0) nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1113, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nahrawy, A.M.; Abou Hammad, A.B.; Bakr, A.M.; Shaheen, T.I.; Mansour, A.M. Sol–gel synthesis and physical characterization of high impact polystyrene nanocomposites based on Fe2O3 doped with ZnO. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
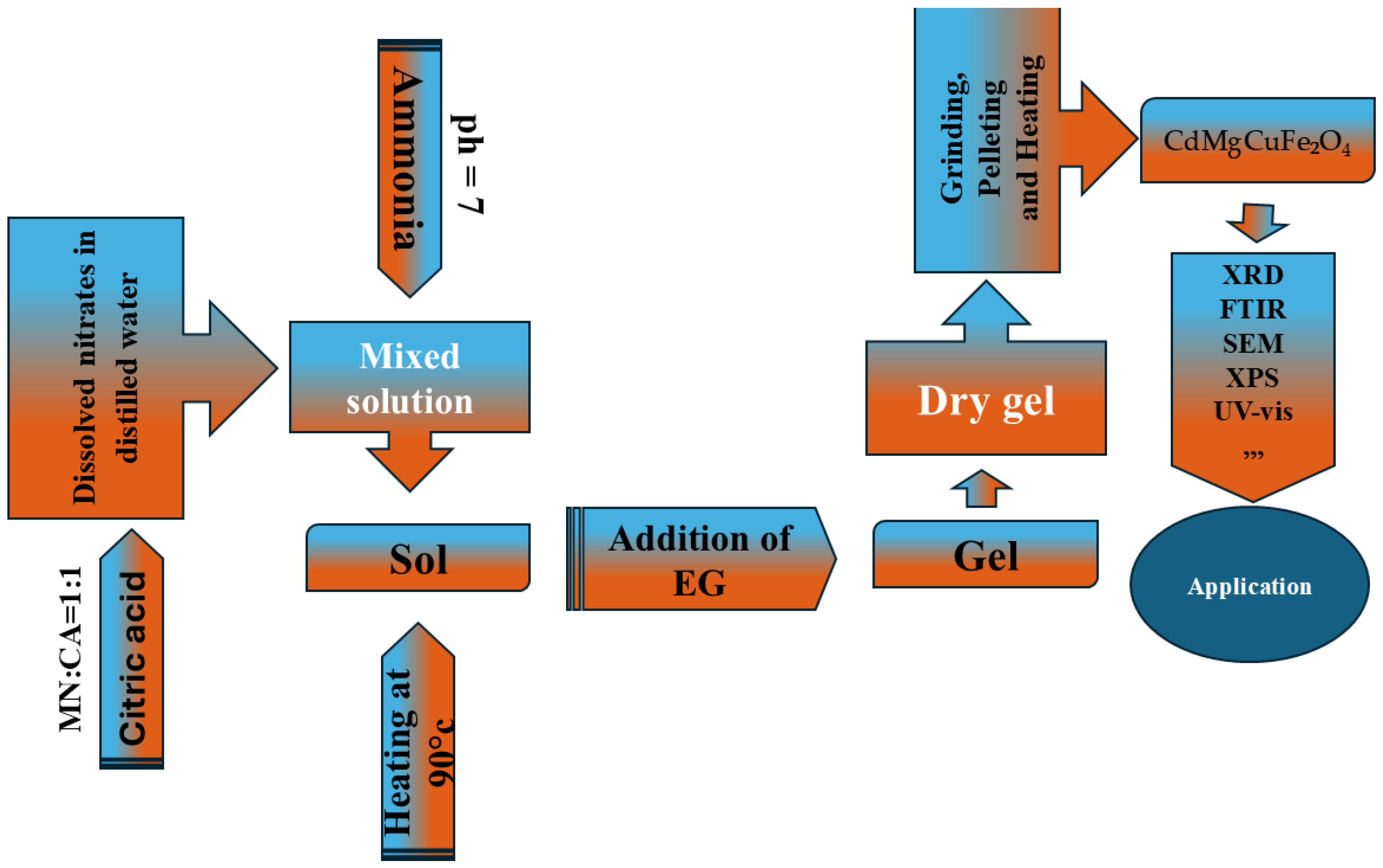
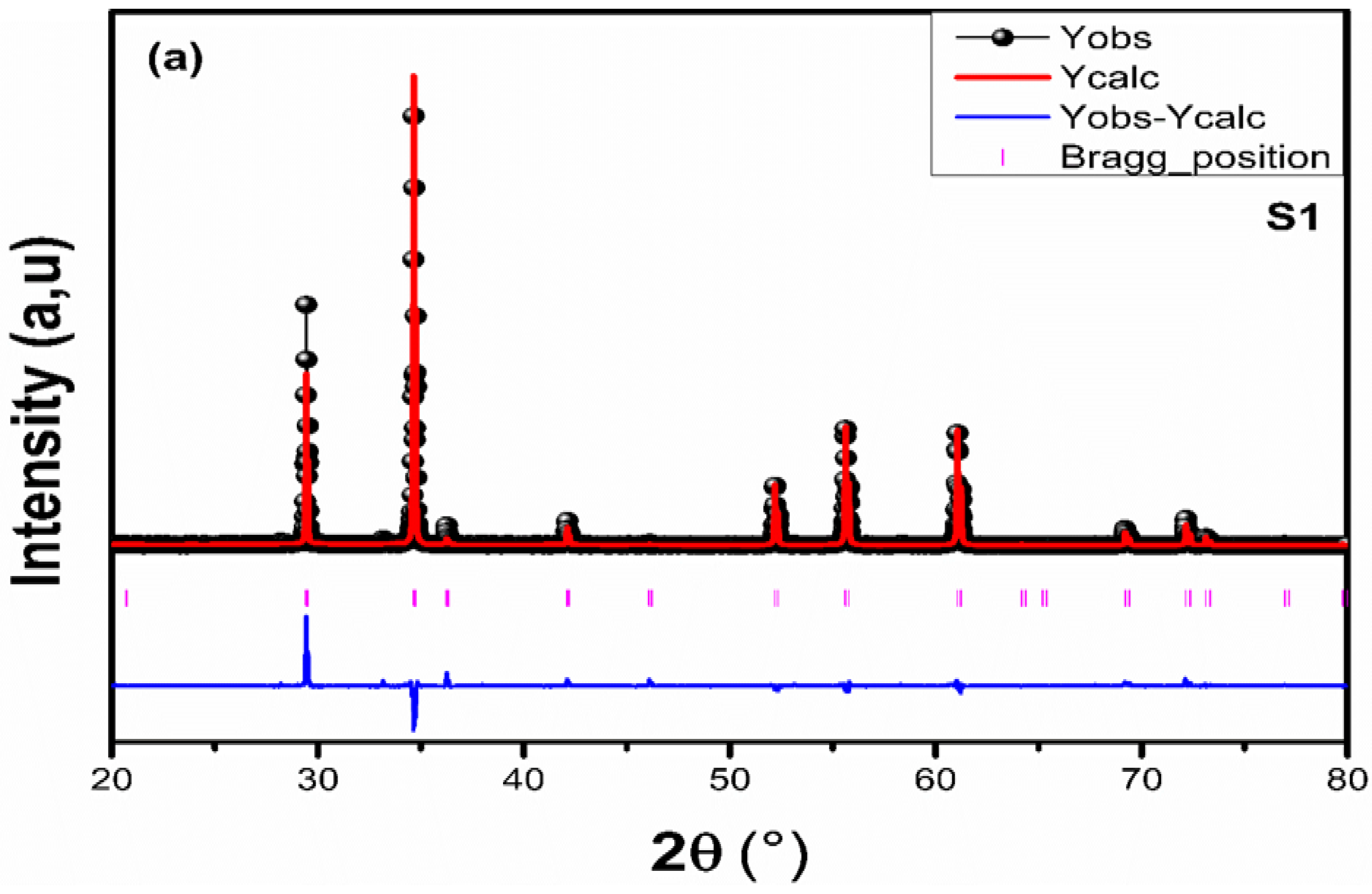
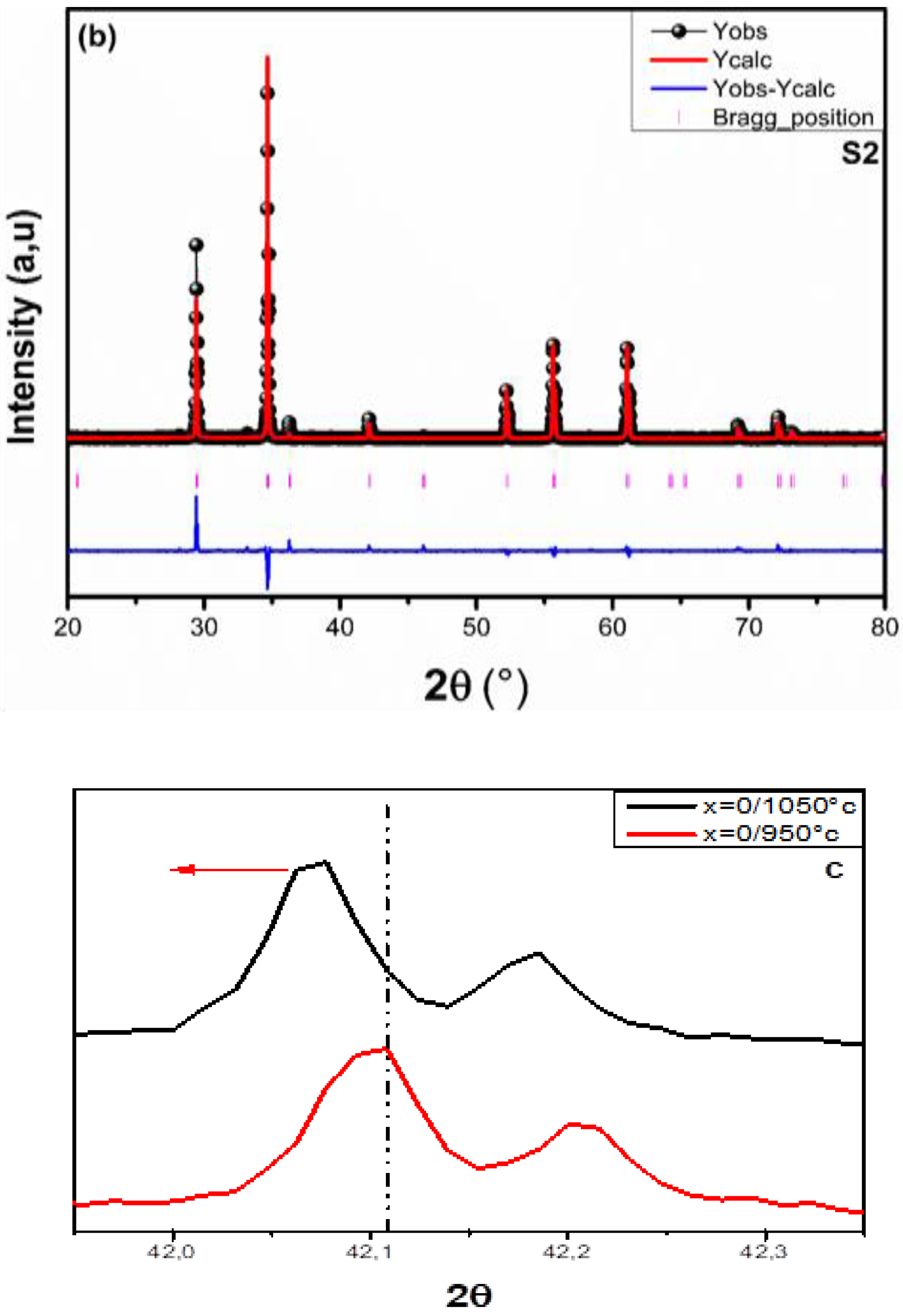
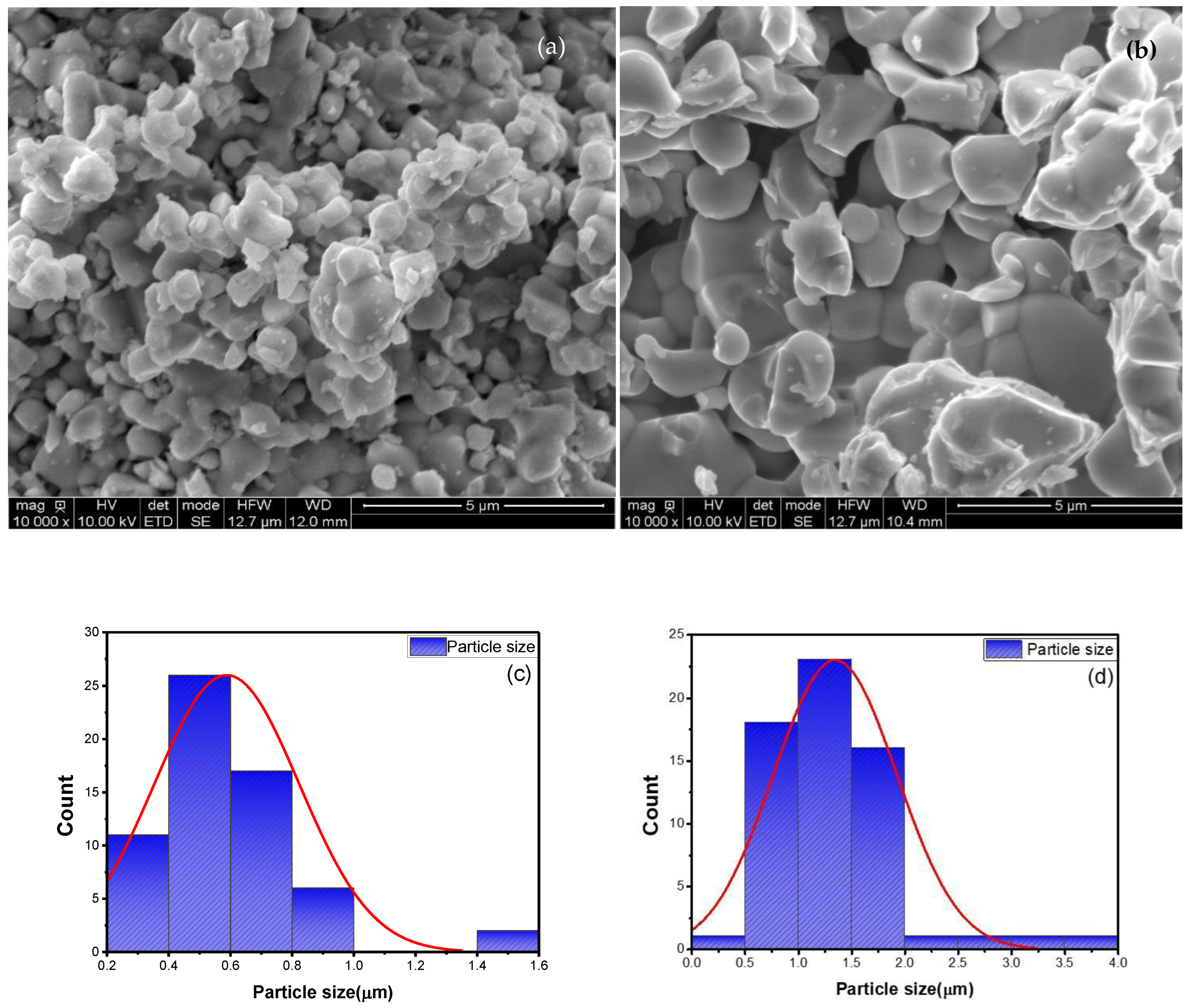


| Sample | Cd0.6 Mg0.2 Cu0.2Fe2O4 T = 950 °C (S1) | Cd0.6 Mg0.2 Cu0.2Fe2O4 T = 1050 °C (S2) |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal system | Cubic | Cubic |
| Space group | F d-3 m | F d-3 m |
| Lattice parameters | ||
| a (Å) | 8.5776 (±0.000098) | 8.5849 (±0.000096) |
| Cell volume V (Å3) | ||
| dx (g cm−3) | 5.4882 | 5.4749 |
| DXRD (nm) | 12.14 | 13.05 |
| R-factors | ||
| Rp (%) | 13.5 | 13.0 |
| Rwp (%) | 17.4 | 16.9 |
| Rexp (%) | 15.98 | 10.49 |
| Bragg R-factor | 13.0 | 13.0 |
| Rf-factor | 9.58 | 9.84 |
| Χ2 | 2.71 | 2.58 |
| DSch | nm | nm |
| S1 | S2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elements | BE (eV) | Atomic % | BE (eV) | Atomic % |
| O1s | 531.11 | 65.59 | 530.96 | 60.55 |
| Fe2p | 711.73 | 21.00 | 711.49 | 27.76 |
| Cd3d | 405.76 | 8.06 | 405.24 | 6.19 |
| Cu2p | 934.21 | 2.89 | 933.84 | 2.77 |
| Mg1s | 1304.45 | 2.46 | 1303.96 | 2.73 |
| Fe2p | S1 | S2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE (eV) | Atomic% | BE (eV) | Atomic% | |
| Fe3+ (B-site) | 711.36 | 70.30 | 711.39 | 81.67 |
| Fe3+ (A-site) | 714.89 | 29.70 | 715.04 | 18.33 |
| satellite | 719.83 | -- | 719.11 | -- |
| Cd3d | S1 | S2 | ||
| Cd2+ (B-site) | 406.58 | 26.88 | 406.79 | 12.14 |
| Cd2+ (A-site) | 405.29 | 73.12 | 405.02 | 87.86 |
| O1s | S1 | S2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE (eV) | Atomic % | BE (eV) | Atomic% | |
| Ol | 529.97 | 77.01 | 530.25 | 57.09 |
| Ov | 532.05 | 22.99 | 532.10 | 42.91 |
| Chemical Name | Methylene Blue (Methylthioninium Chloride) |
|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C16H18ClN3S |
| Molar mass | 319.85 g/mol |
| Appearance | Blue crystalline powder |
| Water solubility | Soluble (35 g/L at 25 °C) |
| Melting point | 100–110 °C (decomposition) |
| Main applications | Dye, antiseptic agent, photosensitizer |
| Maximum absorption wavelength (λmax) | 664 nm (in water) |
| pKa | 3.8 |
| Toxicity | Moderately toxic if ingested or inhaled |
| M-Fe2O4 | Pollutant/s | Contact Time (min) | Light Source | Removal Capacity % | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnFe2O4 | MB | 60 | Vis | 64 | [77,78] |
| Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 | MB | 60 | Vis | 77 | [78] |
| Co0.5Zn0.25N0.25Fe2O4–TiO2 | MB | 80 | UV–vis | 12.66 | [79] |
| Ag/NiFe2O4 | MB | 120 | Vis | 80 | [80,81] |
| CuFe2O4@TiO2 | MB | 180 | Vis | 40 | [80] |
| S1 | MB | 180 | UV | 56.57 | This work |
| S2 | MB | 180 | UV | 69.84 | This work |
| Ni0.6Zn0.4Fe2O | MB | 200 | UV | 60 | [81,82,83] |
| MnFe2O4 | MB | 300 | UV | 84 | [82,83,84,85,86] |
| NiFe2O4 | MB | 300 | UV | 94 | [82] |
| m (mg) | S1 | S2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K (min−1) | R2 | K (min−1) | R2 | |
| 5 | 0.0010 (±6.623 × 10−5) | 0.9872 | 0.0021 (±6.2423 × 10−5) | 0.9858 |
| 10 | 0.0021 (±8.7839 × 10−5) | 0.9953 | 0.0029 (±5.0023 × 10−5) | 0.9954 |
| 20 | 0.0047 (±2.4101 × 10−5) | 0.9670 | 0.0061 (±1.6333 × 10−5) | 0.9672 |
| 40 | 0.0064 (±2.9936 × 10−5) | 0.9352 | 0.0066 (±5.6003 × 10−5) | 0.9372 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jdidi, A.R.; Nouira, W.; Selmi, A.; Drissi, N.; Aissa, M.; Hcini, S.; Gassoumi, M. Impact of Calcination Temperature on the Properties and Photocatalytic Efficiency of Cd0.6Mg0.2Cu0.2Fe2O4 Spinel Ferrites Synthesized via the Sol–Gel Method. Crystals 2025, 15, 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15050457
Jdidi AR, Nouira W, Selmi A, Drissi N, Aissa M, Hcini S, Gassoumi M. Impact of Calcination Temperature on the Properties and Photocatalytic Efficiency of Cd0.6Mg0.2Cu0.2Fe2O4 Spinel Ferrites Synthesized via the Sol–Gel Method. Crystals. 2025; 15(5):457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15050457
Chicago/Turabian StyleJdidi, Abd Raouf, Wided Nouira, Ahmed Selmi, Nidhal Drissi, Mohamed Aissa, Sobhi Hcini, and Malek Gassoumi. 2025. "Impact of Calcination Temperature on the Properties and Photocatalytic Efficiency of Cd0.6Mg0.2Cu0.2Fe2O4 Spinel Ferrites Synthesized via the Sol–Gel Method" Crystals 15, no. 5: 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15050457
APA StyleJdidi, A. R., Nouira, W., Selmi, A., Drissi, N., Aissa, M., Hcini, S., & Gassoumi, M. (2025). Impact of Calcination Temperature on the Properties and Photocatalytic Efficiency of Cd0.6Mg0.2Cu0.2Fe2O4 Spinel Ferrites Synthesized via the Sol–Gel Method. Crystals, 15(5), 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15050457




