Particle Size Grading Strategy for Enhanced Performance of Lithium Iron Phosphate Cathode Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Material Synthesis
2.2. Materials Characterization
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
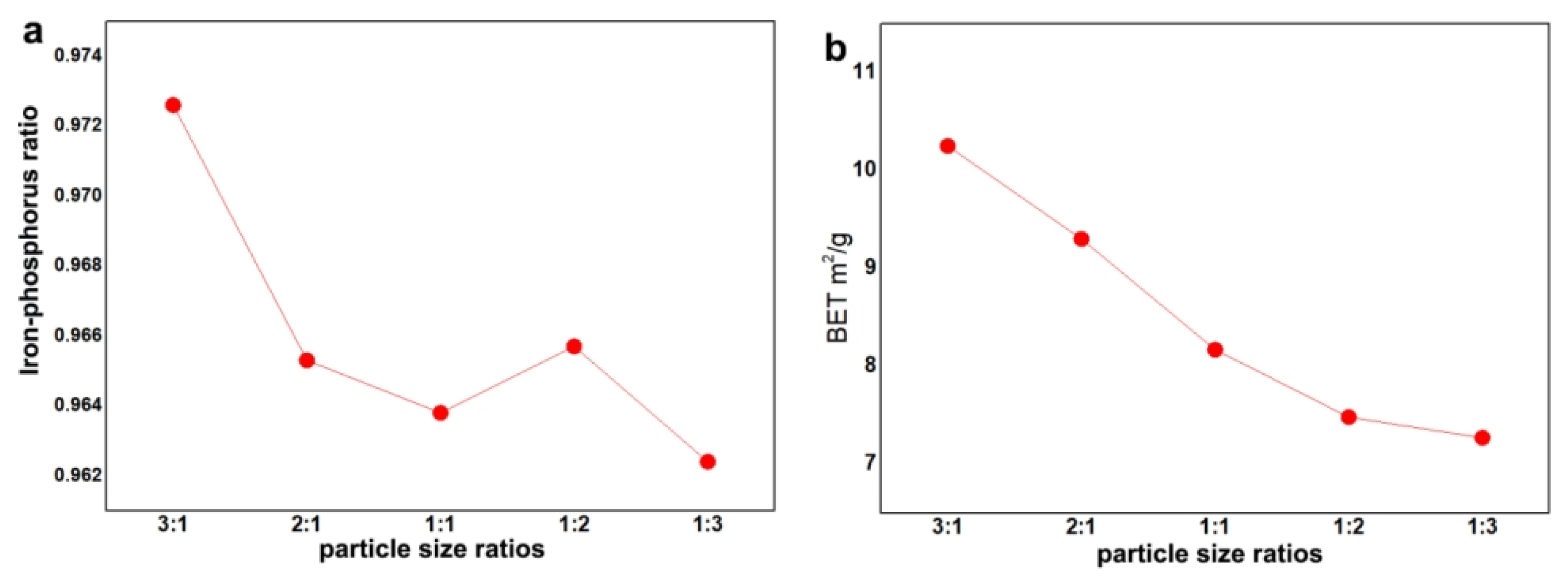
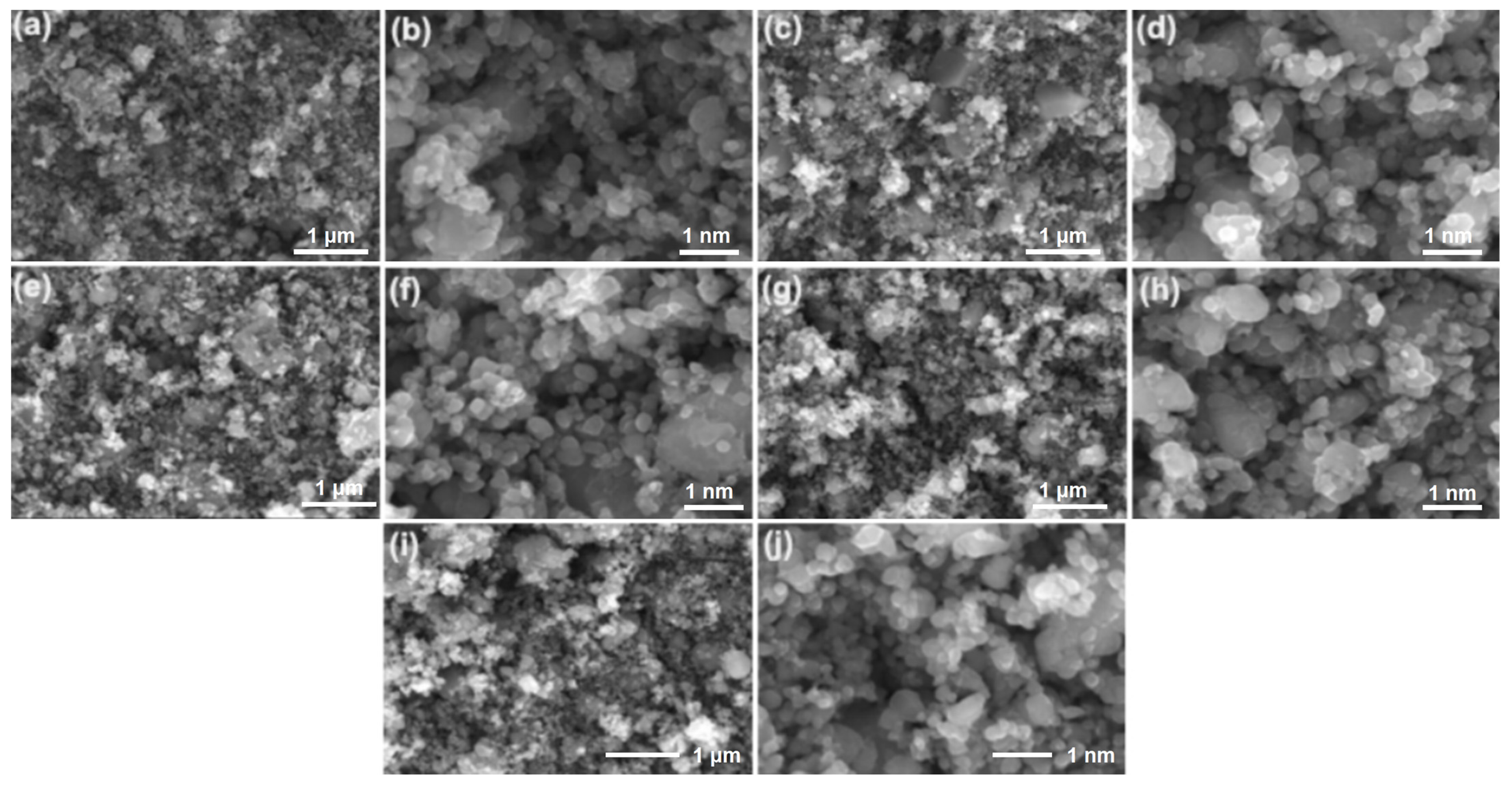
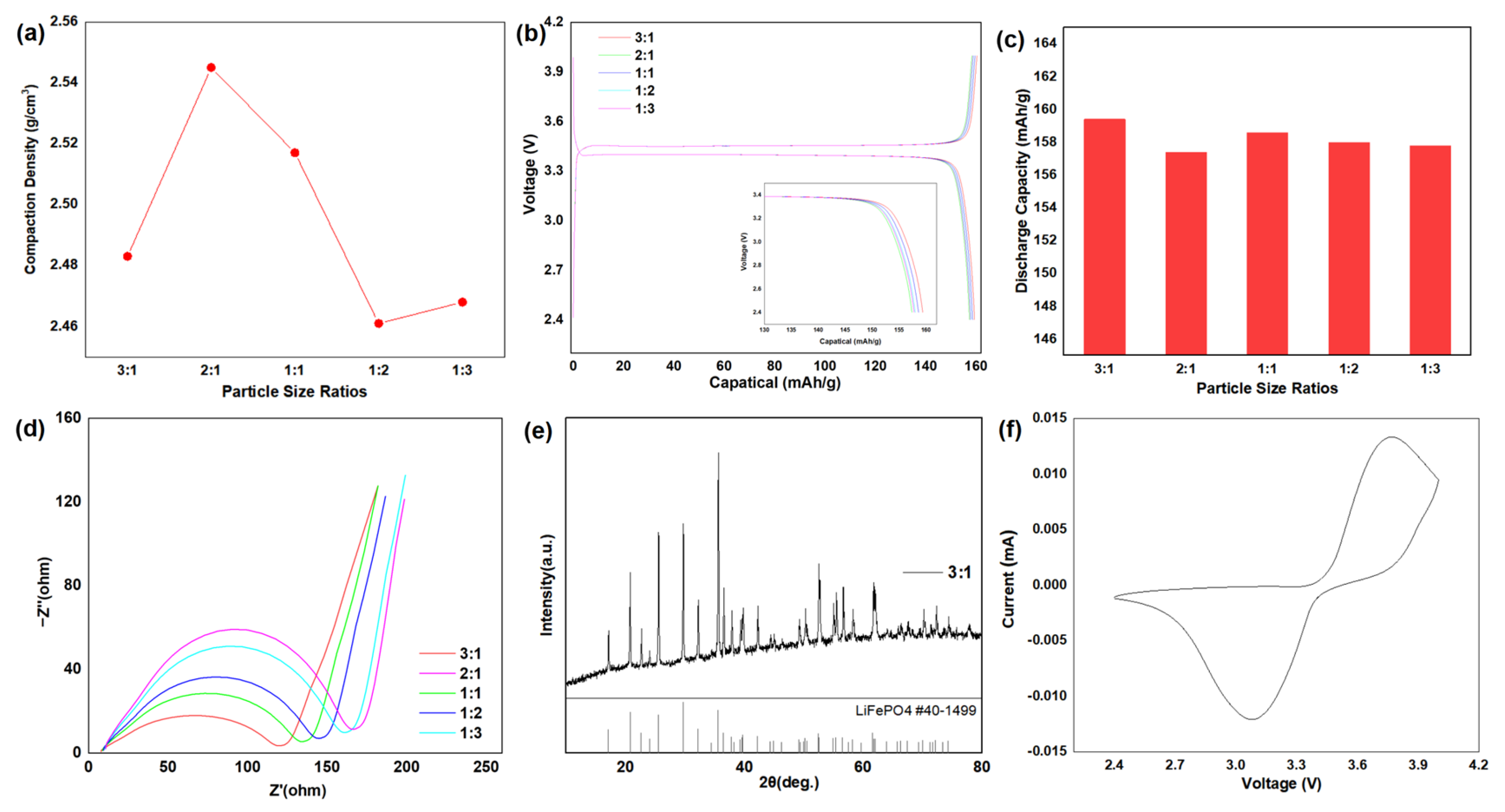
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Shao, Z.; Ru, H. Influence of carbon sources on LiFePO4/C composites synthesized by the high-temperature high-energy ball milling method. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 6979–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Shen, W.; Yao, Y. Preparation of Nanoscale Iron (III) Phosphate by Using FerroPhosphorus as Raw Material. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 252, 022032. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.-G.; Liu, T.; Wang, C.-Y. Thermally modulated lithium iron phosphate batteries for mass-market electric vehicles. Nat. Energy 2021, 6, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.-J.; Li, X.; Lu, S.-G. Crystallinity dependence of electrochemical properties for LiFePO4. Rare Met. 2014, 34, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S.; Sang, M.; Jia, J.; Yang, M.; Li, X.; Yang, S. Biological phytic acid guided formation of monodisperse large-sized carbon@LiFePO4/graphene composite microspheres for high-performance lithium-ion battery cathodes. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Huang, Y.; Gu, H.; Deng, C.; Han, X.; Feng, X.; Zheng, Y. Turning waste into wealth: A systematic review on echelon utilization and material recycling of retired lithium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 40, 96–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shentu, H.; Xiang, B.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Dong, T.; Gao, J.; Xia, Y. A fast and efficient method for selective extraction of lithium from spent lithium iron phosphate battery. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, P. The Foreseeable Future of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: Advanced Upcycling for Toxic Electrolyte, Cathode, and Anode from Environmental and Technological Perspectives. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 13270–13291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, M.; Song, L.; Jin, Y. A Highly Efficient Additive for Direct Reactivation of Waste LiFePO4 with Practical Electrochemical Performance. Energy Fuel 2024, 38, 6518–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, J.; Qiu, B.; Chen, X.; Zhou, F.; Li, X.; Gao, S.; Wang, D.; et al. Fast ammonium sulfate salt assisted roasting for selectively recycling degraded LiFePO4 cathode. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 435, 140428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Neiber, R.R.; Park, J.; Ali Soomro, R.; Greene, G.W.; Ali Mazari, S.; Young Seo, H.; Hong Lee, J.; Shon, M.; Wook Chang, D.; et al. Recent progress in sustainable recycling of LiFePO4-type lithium-ion batteries: Strategies for highly selective lithium recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, F.-S.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Zhang, C.-C. An environmentally friendly process for selective recovery of lithium and simultaneous synthesis of LiFe5O8 from spent LiFePO4 battery by mechanochemical. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 396, 136504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, M.; Dang, C.; Meng, K.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, G.; Zhu, M. Recycling of LiFePO4 cathode materials: From laboratory scale to industrial production. Mater. Today 2024, 73, 130–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Kong, W. Numerical and experimental study on thermal behavior of prismatic lithium-ion battery for large-capacity energy storage. J. Energy Storage 2024, 83, 110620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Lu, Y.-Y.; Jiang, H.; Huang, Y.-Q.; Xu, M.-X.; Lu, Q. Recovery of Electrode Materials from a Spent Lithium-Ion Battery through a Pyrolysis-Coupled Mechanical Milling Method. Energy Fuel 2024, 38, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Hu, J.; Hu, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, W.; Yang, Y.; Zou, G.; Hou, H.; Ji, X. Redox-Mediated Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Coupled with Low-Energy Consumption Hydrogen Production. ACS Energy Lett. 2024, 9, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qiao, J.; Sun, K.; Wang, Z. Balancing particle properties for practical lithium-ion batteries. Particuology 2022, 61, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, C.; Qiu, B.; Chen, G.; Shang, Y.; Liu, Z. Revealing Li-ion diffusion kinetic limitations in micron-sized Li-rich layered oxides. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 53, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, W.; He, L. LiMn2O4 submicronization: Shorten Li+ diffusion pathway for enhancing electrochemical lithium extraction and cycle performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 359, 130394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, D.H. Enhancing electrode wettability in lithium-ion battery via particle-size ratio control. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 22, 100976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Wei, W.; He, G. Optimizing the particle-size distribution and tap density of LiFePO4/C composites containing excess lithium. Ionics 2018, 25, 2035–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wen, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, H.; Liang, G. Facile synthesis and electrochemical properties of high tap density LiFePO4/C. Ionics 2019, 25, 4589–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; He, W. Control and influence of morphology, particle size and structure of LiFePO4 on its properties. Solid State Ion. 2024, 410, 116535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, W.; Duan, Y.; Cui, S.; Song, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Lin, Y.; Pan, F. Single-Particle Performances and Properties of LiFePO4 Nanocrystals for Li-Ion Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 7, 1601894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, E.R.; Eldesoky, A.; Liu, Y.; Lei, M.; Yang, X.; Hebecker, H.; Luscombe, A.; Johnson, M.B.; Dahn, J.R. The Effect of LiFePO4 Particle Size and Surface Area on the Performance of LiFePO4/Graphite Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 050524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, K.; Liu, W.; Chen, T.; Liu, K. Particle Size Grading Strategy for Enhanced Performance of Lithium Iron Phosphate Cathode Materials. Crystals 2025, 15, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040308
Li P, Wang Y, Zhu L, Zhang K, Liu W, Chen T, Liu K. Particle Size Grading Strategy for Enhanced Performance of Lithium Iron Phosphate Cathode Materials. Crystals. 2025; 15(4):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040308
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Puliang, Yang Wang, Liying Zhu, Kun Zhang, Weifang Liu, Tao Chen, and Kaiyu Liu. 2025. "Particle Size Grading Strategy for Enhanced Performance of Lithium Iron Phosphate Cathode Materials" Crystals 15, no. 4: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040308
APA StyleLi, P., Wang, Y., Zhu, L., Zhang, K., Liu, W., Chen, T., & Liu, K. (2025). Particle Size Grading Strategy for Enhanced Performance of Lithium Iron Phosphate Cathode Materials. Crystals, 15(4), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040308




