The Stirring Effect on the Crystal Morphology of p-Acetamidobenzoic Acid Solution Crystallization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Crystallization Experiments
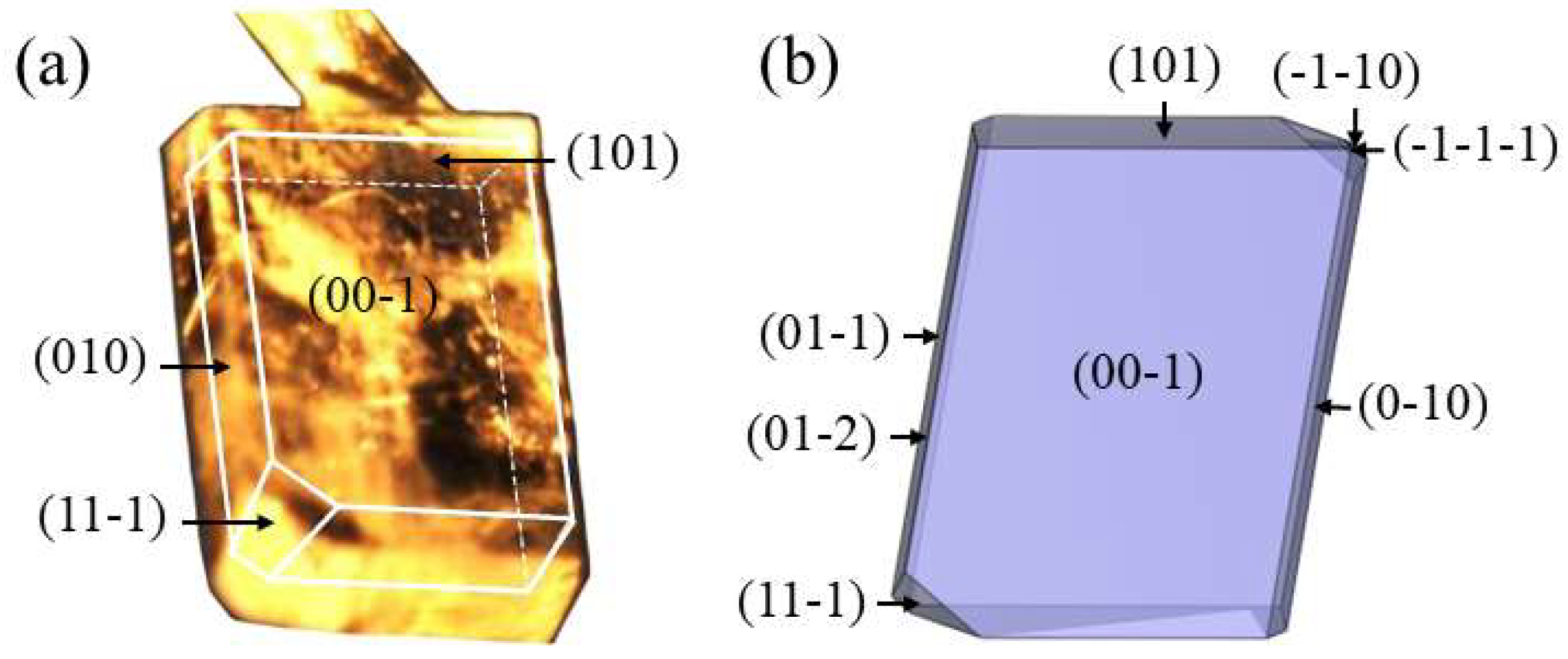
2.3. Single-Crystal Structure Analysis and Crystal Face Indexing
2.4. Crystal Morphology Analysis
2.5. Crystal Aspect Ratio Measurement
2.6. Crystal Size Measurement
2.7. Molecular Simulation
3. CFD Numerical Simulations
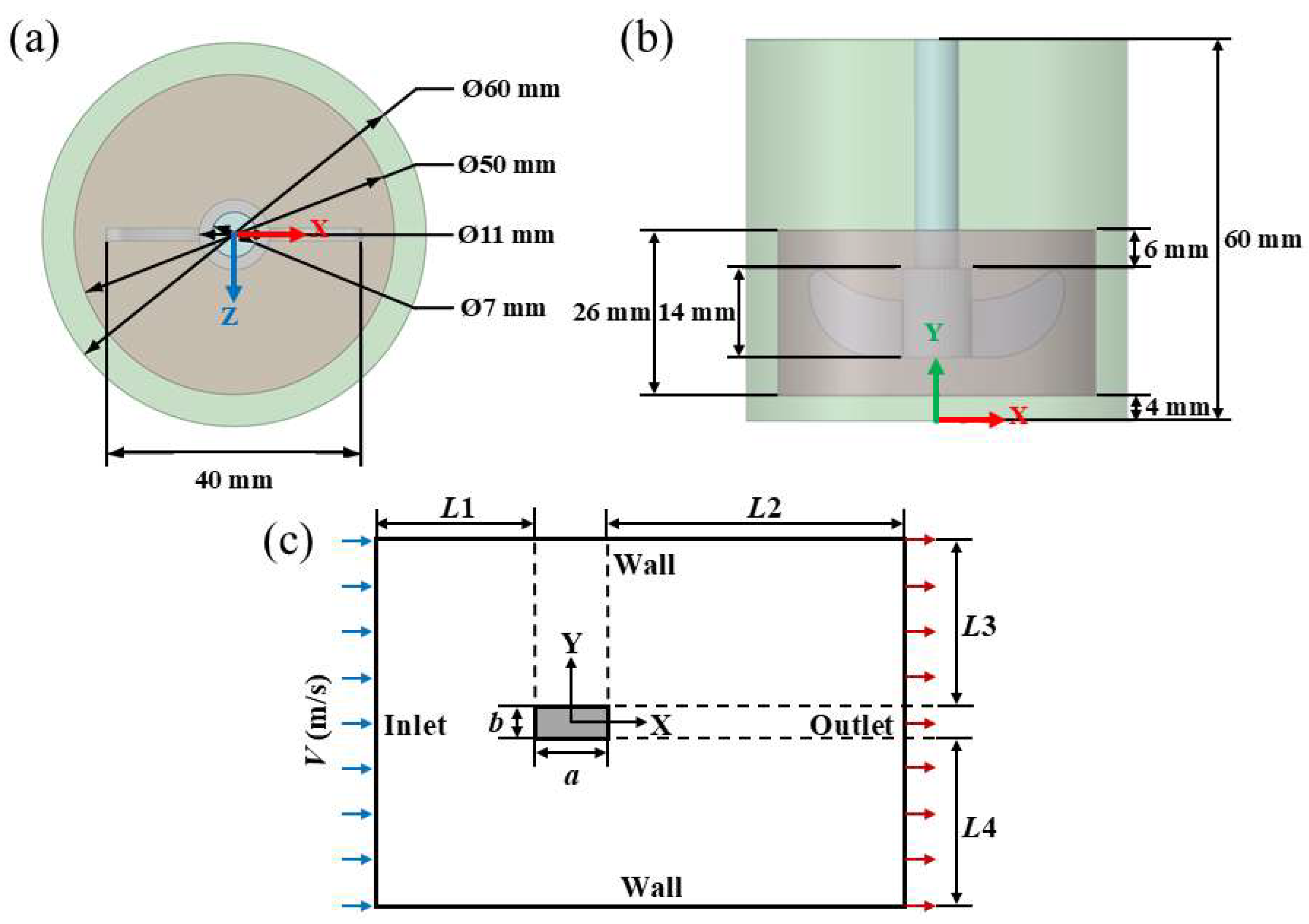
3.1. Physical Model
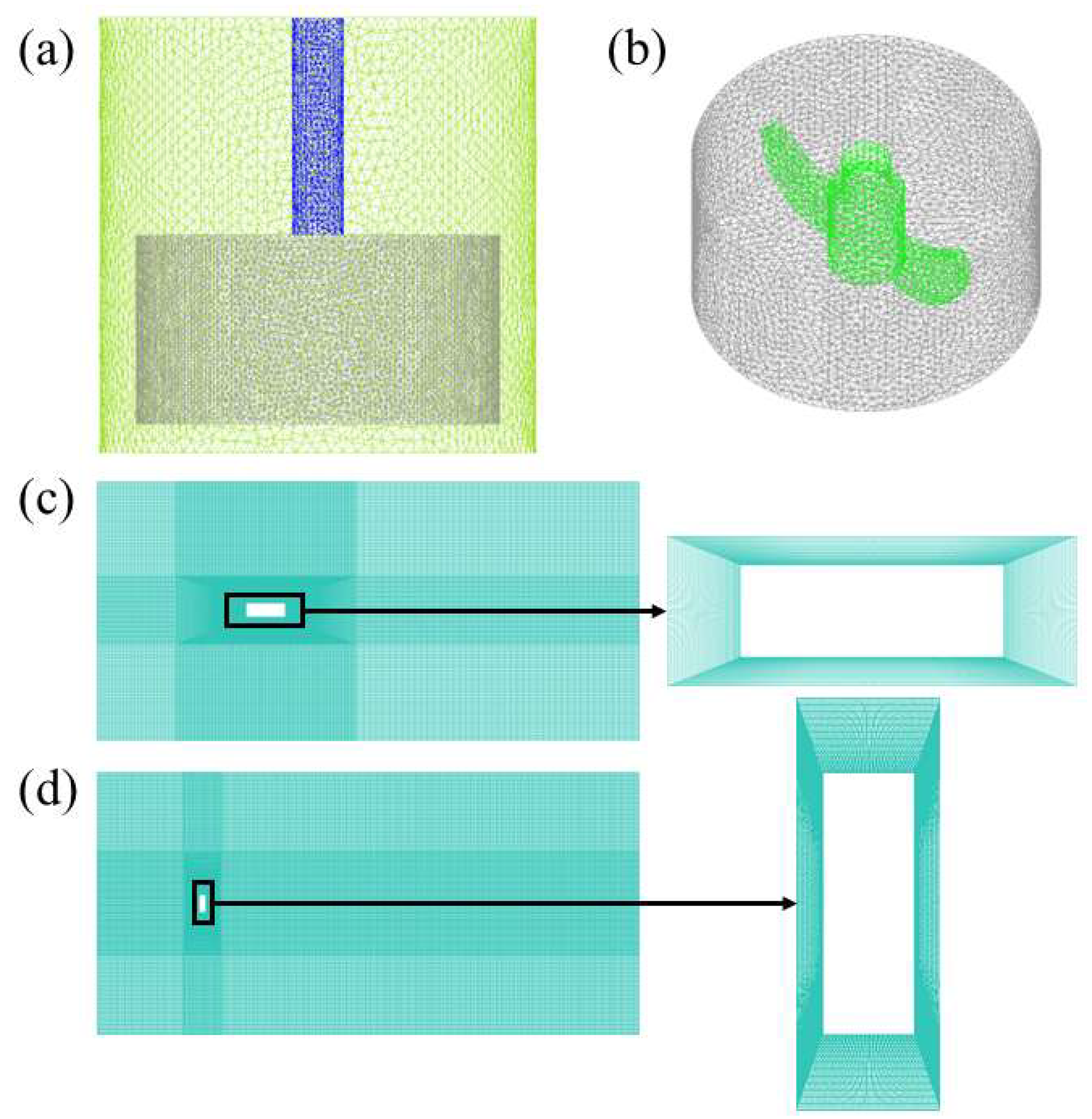
3.2. Grid Generation for the Models
3.3. Numerical Simulation Settings
3.3.1. Physical Parameters
3.3.2. Boundary Conditions
3.3.3. Simulation Methods
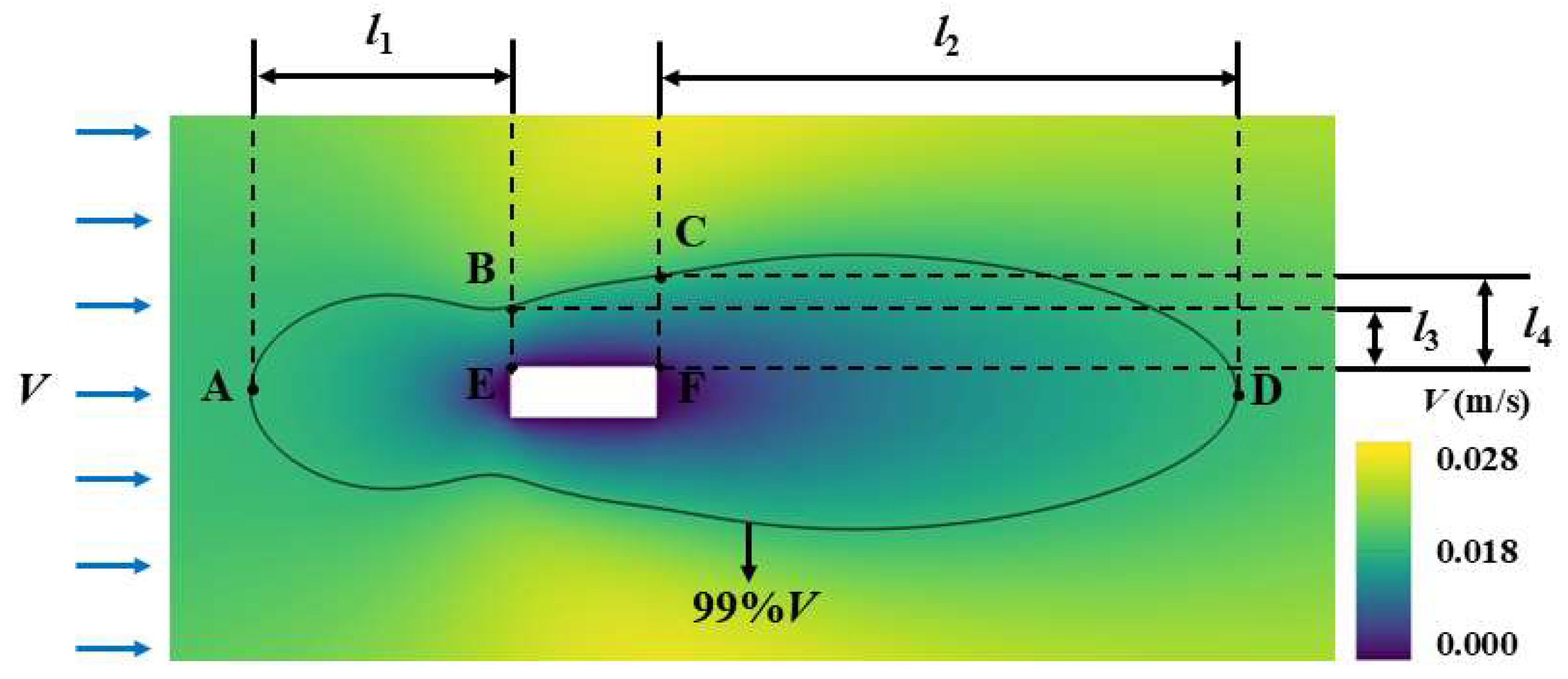
3.4. Calculation Method of Boundary Layer Thickness
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Crystal Face Indexing and Crystal Habit Simulation
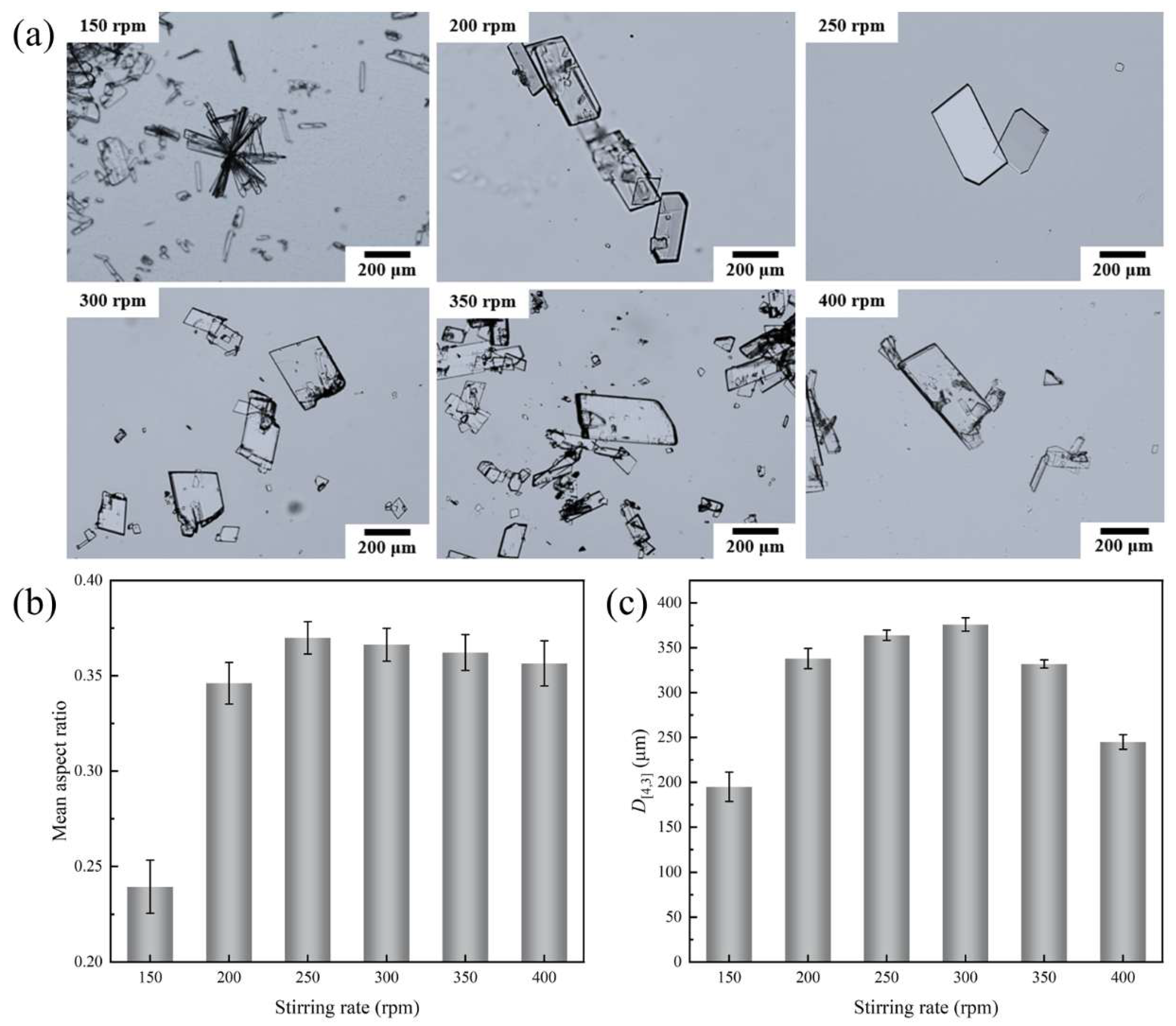
4.2. Stirring Effect on Crystal Morphology
4.3. Reasons for the Stirring Effect on Crystal Morphology
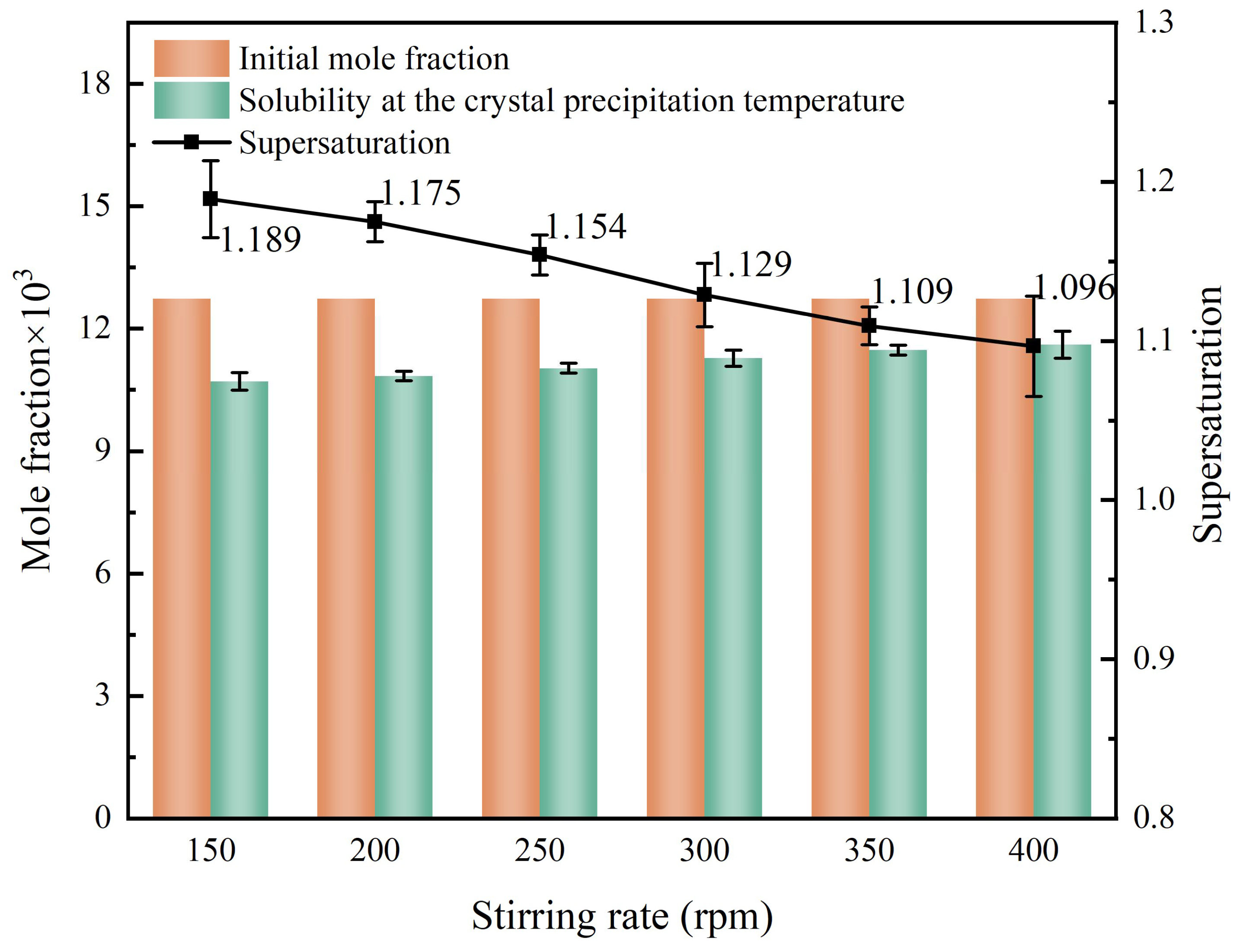
4.3.1. Stirring Effect on Crystal Nucleation and Growth
4.3.2. Stirring Effect on Crystal Boundary
4.3.3. Stirring Effect on Crystal Fragmentation
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The p-AABA crystal belong to the triclinic crystal system with the space group of P-1 and are plate-like rectangles. MS results show that solute molecules have a stronger adsorption ability to the {101} face than to the {010} face, and the theoretical growth rate of the {101} face is higher than that of the {010} face.
- (2)
- At low stirring rates, crystals have a small aspect ratio and tend to aggregate, while high rates can prevent aggregation, but cause fragmentation. As the rate increases, both the crystal aspect ratio and crystal size first increase and then decrease, while the PSD generally tends to broaden.
- (3)
- In a static growth environment, the growth rates of the {101} and {010} faces show a good exponential function relationship with supersaturation. At the same supersaturation, the growth rate of the {101} face is greater. Without stirring, theoretically, the smaller the supersaturation, the larger the crystal aspect ratio.
- (4)
- Stirring rate influences nucleation supersaturation, thereby affecting nucleation rate and nucleus size. At a low stirring rate, high supersaturation at the nucleation moment promotes crystal aggregation. As the rate increases, the supersaturation at the nucleation moment decreases, and the relative growth rates of the {101} and {010} faces change, leading to different crystal aspect ratios.
- (5)
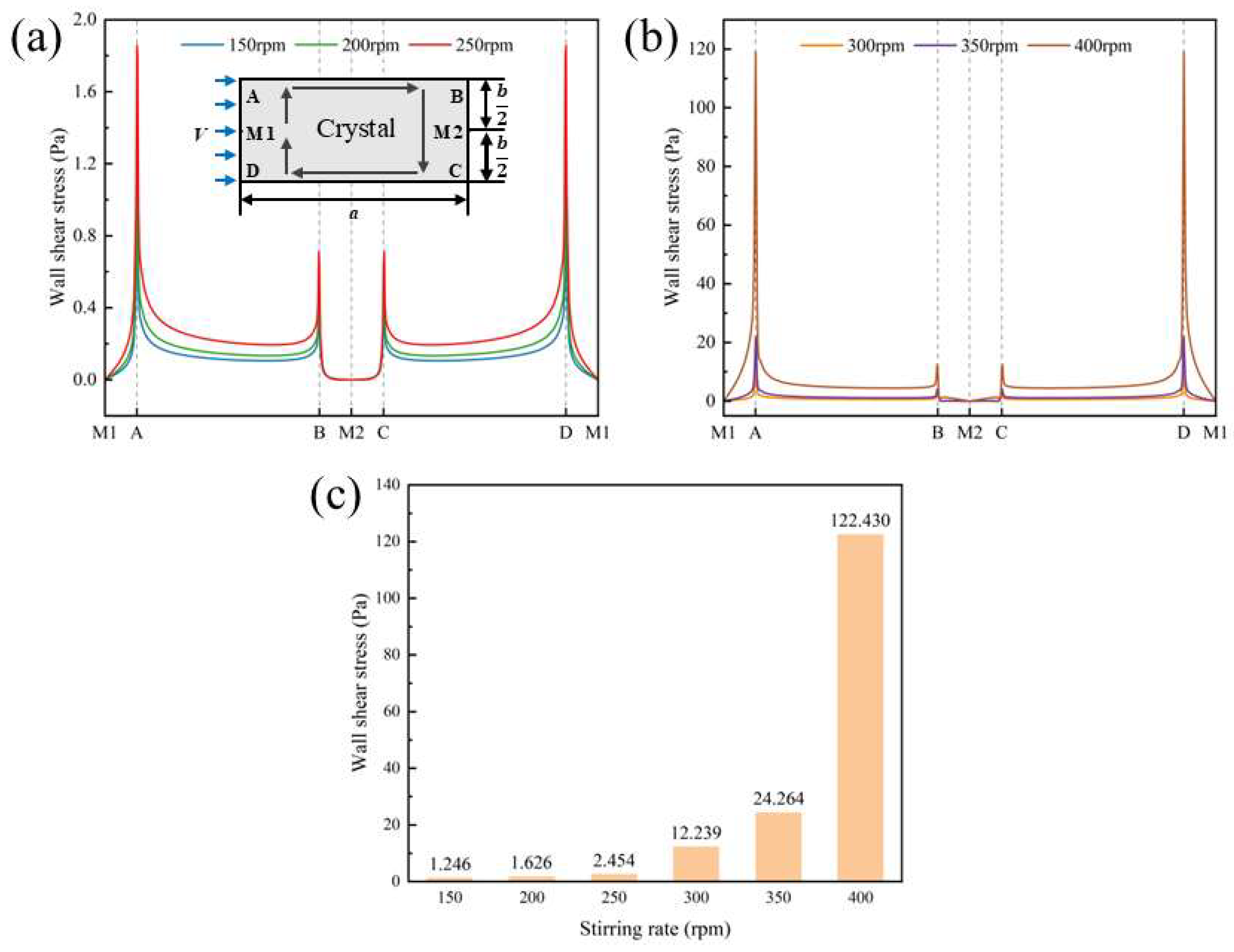
- By analyzing the impact force, shear stress, and rotational moment acting on the crystals, it is found that the flow resistance of rectangular crystals in a stirred flow field is minimized when the short side faces the flow.
- (6)
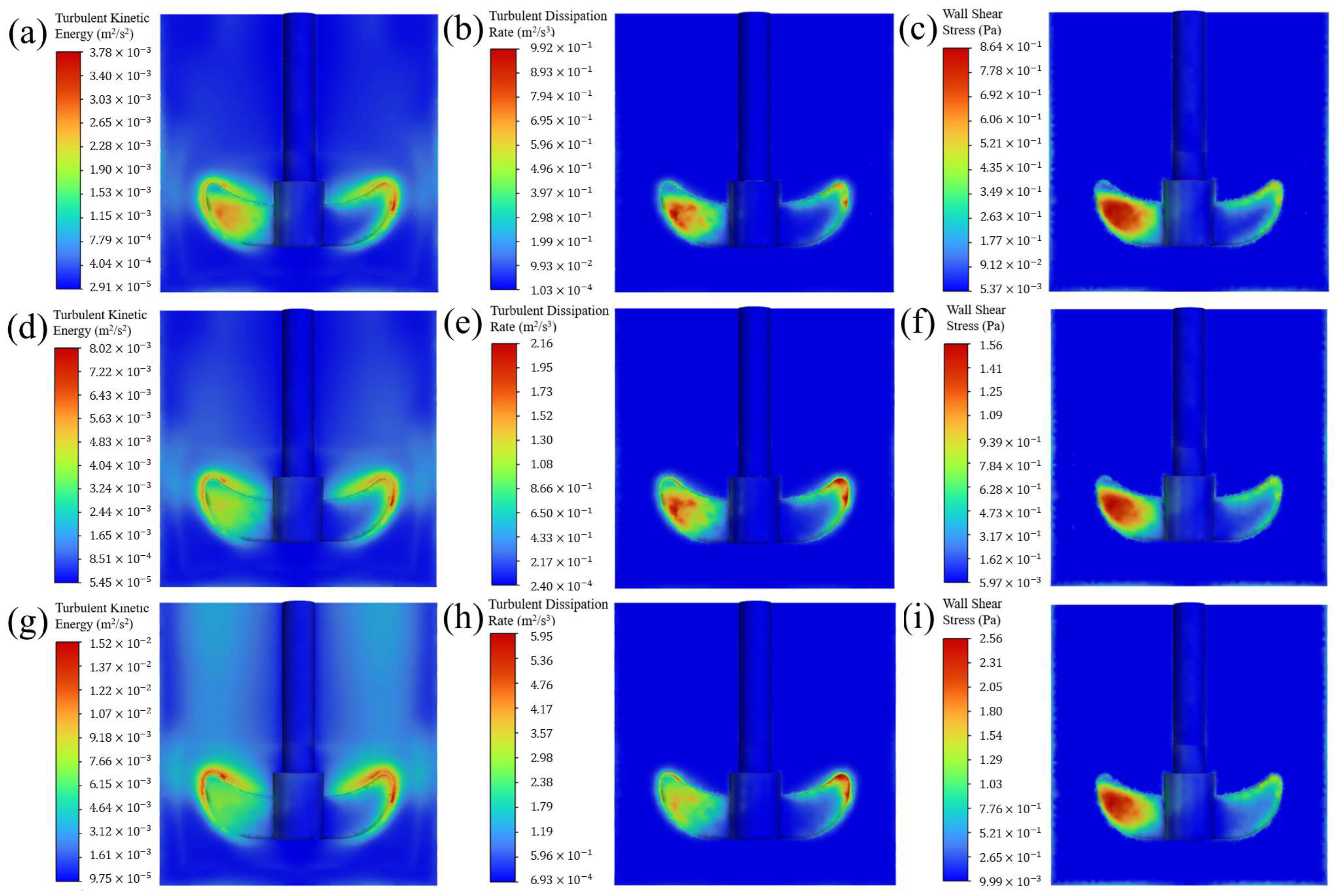
- CFD simulations demonstrate that the stirring rate affects the mass-transfer boundary layer thickness and shear stresses at the {101} and {010} faces, ultimately influencing the aspect ratio of p-AABA crystals. A high stirring rate increases turbulent kinetic energy, turbulent dissipation rate, and shear stress in the paddle region. Meanwhile, it also significantly increases shear stress at the corner points of the {101} face, leading to obvious fragmentation of p-AABA crystals. As a result, the average size of the crystals decreases under high-rate stirring.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Kwak, J.H.; Karande, P.; Farmanesh, S.; Rimer, J.D. A high-throughput assay for screening modifiers of calcium oxalate crystallization. AIChE J. 2016, 62, 3538–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapwijk, A.R.; Simone, E.; Nagy, Z.K.; Wilson, C.C. Tuning crystal morphology of succinic acid using a polymer additive. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 4349–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.Y.; Li, E.H.; Zhang, L.; Du, J.; Meng, Q.W. Crystallization solvent design based on a new quantitative prediction model of crystal morphology. AIChE J. 2022, 68, e17499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.J.; Chow, P.S.; Tan, R.B.H. Strong additive-surface interaction leads to the unusual revival of growth at solvent-poisoned faces of DL-Alanine crystal. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 5555–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, C.J.; Ni, X.W. Probing into nucleation mechanisms of cooling crystallization of sodium chlorate in a stirred tank crystallizer and an oscillatory baffled crystallizer. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 2525–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.P.; White, G.; Wilkinson, D.; Ford, L.J.; Roberts, K.J.; Wood, W.M.L. Examination of the process scale dependence of L-Glutamic Acid batch crystallized from supersaturated aqueous solutions in relation to reactor hydrodynamics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, S.Z.M.; Camacho, D.M.; Ma, C.Y.; Mahmud, T. Effect of crystallization conditions on the metastable zone width and nucleation kinetics of p-Aminobenzoic Acid in ethanol. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2020, 43, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Z.; Fan, H.A.; Lin, G.B.; Fang, Z.C.; Yang, W.L.; Li, M.; Wang, J.H.; Lu, X.Y.; Li, B.L.; Wu, K.J.; et al. Multi-objective optimization of radially stirred tank based on CFD and machine learning. AIChE J. 2024, 70, e18324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.T.; Li, B.B.; Jia, S.Z.; Chen, M.Y.; Gao, Z.G.; Gong, J.B. Taylor vortex-based protein crystal nucleation enhancement and growth evaluation in batchwise and slug flow crystallizers. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 193, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Rasmuson, A.C. Influence of agitation and fluid shear on primary nucleation in solution. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 4385–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmidt, L.E.V.; Shmidt, J. Mechanism of crystallization in agitated solutions. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1985, 36, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, G.Y.; Huang, B.F.; Dai, M.; Shi, Z.; Wen, Z.J.; Li, W.J.; Luo, L.B.; Yang, L.J. Optimization of ammonium sulfate crystallization under ammonium nitrate based on response surface method. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2022, 58, 2200246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, C.T.; Wen, T.; Zhou, Y.N.; Ouyang, J.B. Designing spherical particles of arbidol hydrochloride via spherical crystallization: Preparation and characterization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 5249–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Tilbury, C.J.; Kim, S.H.; Doherty, M.F. A design aid for crystal growth engineering. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 82, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.M. Application of computational fluid dynamics in industrial crystallization. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1064, 012057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offiler, C.A.; Fonte, C.P.; Kras, W.; Neoptolemou, P.; Davey, R.J.; Vetter, T.; Cruz-Cabeza, A.J. Complex growth of benzamide form I: Effect of additives, solution flow, and surface rugosity. Cryst. Growth Des. 2022, 22, 6248–6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.Y.; Zhang, D.J.; Xu, S.J.; Yu, B.; Zhang, K.K.; Rohani, S.; Gong, J.B. Effect of mixing on the particle size distribution of paracetamol continuous cooling crystallization products using a computational fluid dynamics-population balance equation simulation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 2851–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.; Norouzi, H.R.; Sahlodin, A.M. Computational fluid dynamics simulation of a jet crystallizer for continuous crystallization of lovastatin. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, L.F.I.; de Souza, J.A.; Braatz, R.D.; da Rosa, C.A. Coupling of the population balance equation into a two-phase model for the simulation of combined cooling and antisolvent crystallization using OpenFOAM. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2019, 123, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.K.; Sobolev, Y.I.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Grzybowski, B.A. Enhancing crystal growth using polyelectrolyte solutions and shear flow. Nature 2020, 579, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Liu, X.C.; Zhang, C.K.; Wang, S.M.; Wen, J. CFD-PBE simulation of para-Xylene crystallization behavior and process amplification under different operating conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 14657–14670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janbon, S.L.M.; Parsons, A.R.; Gavi, E.; Reynolds, G.K. Effects of scale, equipment, and operation on agglomeration during a reactive crystallization. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2019, 23, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ji, X.T.; Cheng, X.W.; Li, D.N.; Wang, T.; Huang, X.; Wang, N.; Yin, Q.X.; Hao, H.X. Effect of the solvent on the morphology of sulfamerazine crystals and its molecular mechanism. CrystEngComm 2022, 24, 5497–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnay, J.D.; Harker, D. A new law of crystal morphology extending the law of Bravais. Am. Mineral. 1937, 22, 463. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, P.; Perdok, W.G. On the relations between structure and morphology of crystals. Acta Crystallogr. 1955, 8, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, P.; Bennema, P. The attachment energy as a habit controlling factor: I theoretical considerations. J. Cryst. Growth 1980, 49, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, R.B.; Pencheva, K.; Ramachandran, V.; Roberts, K.J. Application of grid-based molecular methods for modeling solvent-dependent crystal growth morphology: Aspirin crystallized from aqueous ethanolic solution. Cryst. Growth Des. 2007, 7, 1571–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Shang, Z.R.; Wang, K.; Han, J.H.; Wu, S.G. Solubility measurement, correlation and computational analysis of p-Acetamidobenzoic acid in 12 pure solvents. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2021, 159, 106478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Fan, J.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, W.G. Synthesis, crystal structures, and photoluminescence of lanthanide coordination polymers with 4-Acetamidobenzoate. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2011, 637, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Fan, J.; Zhang, W.G. Studies of radii-dependent lanthanide coordination behavior with 4-Acetamidobenzoate and 1,10-Phenanthroline. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2009, 635, 2333–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathwar, V.R.; Thakur, T.S.; Row, T.N.G.; Desiraju, G.R. Transferability of Multipole Charge Density Parameters for Supramolecular Synthons: A New Tool for Quantitative Crystal Engineering. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, Z.K.; Wang, L.Y.; Lin, J.W.; Gao, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.B.; Cao, Y.T.; Gong, J.B.; Han, D.D. Non-negligible modulation role of the solvent in the asymmetric growth of α-Resorcinol. Cryst. Growth Des. 2022, 22, 6240–6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.J.; Zhang, G.L. Principles of Chemical Engineering-Ehemical Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer, 3rd ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 152–153. [Google Scholar]
- Szilágyi, B.; Lakatos, B.G. Model-based analysis of stirred cooling crystallizer of high aspect ratio crystals with linear and nonlinear breakage. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2017, 98, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.Y.; Shen, Y.Q.; Ma, Y.L.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.P.; Yang, M.H.; Xu, M.L.; Tian, Y.Q. Nucleation, growth, and aggregation kinetics of KCI produced by stirred crystallization. Appl. Phys. A 2023, 129, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, M.; Frawley, P.J. Secondary nucleation from nuclei breeding and its quantitative link with fluid shear stress in mixing: A potential approach for precise scale-up in industrial crystallization. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2019, 23, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, A.U.; Bridgwater, J. Attrition of particulate solids under shear. Powder Technol. 1994, 80, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilbury, C.J.; Green, D.A.; Marshall, W.J.; Doherty, M.F. Predicting the effect of solvent on the crystal habit of small organic molecules. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 2590–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwal, K. A novel self-consistent Nyvlt-like equation for metastable zone width determined by the polythermal method. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2009, 44, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.R.; Zhou, R.F.; Yin, H.; Yuan, S.F. Study on the nucleation kinetics of DL-methionine based on the metastable zone width of unseeded batch crystallization. J. Cryst. Growth 2023, 601, 126941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullin, J.W. Crystallization, 4th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: England, UK, 2001; pp. 181–215. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.F.; Wang, J.F.; Jin, Y. A novel theoretical breakup kernel function for bubbles/droplets in a turbulent flow. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 4629–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.J.; Zhao, L.H.; Andersson, H.I.; Deng, J.Q. Three-dimensional Voronoi analysis of preferential concentration of spheroidal particles in wall turbulence. Phys. Fluids 2018, 30, 063304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Deepak, F.L. In situ kinetic observations on crystal nucleation and growth. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 16911–16982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan-Kharicha, M.; Kharicha, A.; Zaidat, K.; Reiss, G.; Essl, W.; Goodwin, F.; Wu, M.H.; Ludwig, A.; Mugrauer, C. Hydrodynamically driven facet kinetics in crystal growth. J. Cryst. Growth 2022, 584, 126557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jousse, F.; Jongen, T.; Agterof, W. A method to dynamically estimate the diffusion boundary layer from local velocity conditions in laminar flows. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2005, 48, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radel, B.; Gleiss, M.; Nirschl, H. Crystal breakage due to combined normal and shear loading. Crystals 2022, 12, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capellades, G.; Joshi, P.U.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Mealy, M.J.; Christensen, T.V.; Kiil, S. Characterization of a multistage continuous MSMPR crystallization process assisted by image analysis of elongated crystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 6455–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| solution density | 817 | kg·m−3 |
| solution viscosity | 0.0009 | kg·(m·s)−1 |
| p-AABA size | 0.1 | mm |
| p-AABA density | 1327 | kg·m−3 |
| p-AABA molar mass | 179.17 | kg·kmol−1 |
| p-AABA particle volume fraction in solution | 2.19 | % |
| Stirring Rate/rpm | Liquid Velocity/(m·s−1) | δ1/mm | δ2/mm | Average Shear Stress on the {101} Face/Pa | Average Shear Stress on the {010} Face/Pa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 1.822 × 10−2 | 2.145 | 1.393 × 10−1 | 5.707 × 10−2 | 1.460 × 10−1 |
| 200 | 2.210 × 10−2 | 2.593 | 1.281 × 10−1 | 7.331 × 10−2 | 1.859 × 10−1 |
| 250 | 2.958 × 10−2 | 2.888 | 1.119 × 10−1 | 1.114 × 10−1 | 2.714 × 10−1 |
| 300 | 6.681 × 10−2 | 3.346 | 6.225 × 10−2 | 5.240 × 10−1 | 8.962 × 10−1 |
| 350 | 1.050 × 10−1 | 3.828 | 4.807 × 10−2 | 1.149 | 1.632 |
| 400 | 3.062 × 10−1 | 4.697 | 2.934 × 10−2 | 6.346 | 6.270 |
| Stirring Rate/rpm | {101} Face Facing the Flow | {010} Face Facing the Flow | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impact Force/N | Shear Stress/Pa | Rotational Moment/(N·m) | Impact Force/N | Shear Stress/Pa | Rotational Moment/(N·m) | |
| 150 | 2.891 × 10−5 | 1.630 × 10−1 | 2.818 × 10−13 | 4.649 × 10−5 | 2.121 × 10−1 | 7.628 × 10−9 |
| 250 | 5.613 × 10−5 | 2.922 × 10−1 | 7.310 × 10−13 | 9.477 × 10−5 | 3.679 × 10−1 | 1.483 × 10−8 |
| 350 | 3.742 × 10−4 | 1.414 | 2.761 × 10−12 | 7.353 × 10−4 | 1.585 | 1.042 × 10−7 |
| Stirring Rate/rpm | k/(m2·s−2) | ε/(m2·s−3) | WSS/Pa |
|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 4.819 × 10−4 | 5.507 × 10−3 | 1.011 × 10−3 |
| 200 | 7.982 × 10−4 | 1.116 × 10−2 | 1.370 × 10−3 |
| 250 | 1.181 × 10−3 | 1.930 × 10−2 | 1.711 × 10−3 |
| 300 | 1.610 × 10−3 | 3.003 × 10−2 | 2.053 × 10−3 |
| 350 | 2.121 × 10−3 | 4.428 × 10−2 | 2.421 × 10−3 |
| 400 | 2.697 × 10−3 | 6.281 × 10−2 | 2.869 × 10−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, R.; Wang, F.; Jing, D.; Liu, Y.; Bao, Y. The Stirring Effect on the Crystal Morphology of p-Acetamidobenzoic Acid Solution Crystallization. Crystals 2025, 15, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15030284
Dong R, Wang F, Jing D, Liu Y, Bao Y. The Stirring Effect on the Crystal Morphology of p-Acetamidobenzoic Acid Solution Crystallization. Crystals. 2025; 15(3):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15030284
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Rui, Fan Wang, Dingding Jing, Yong Liu, and Ying Bao. 2025. "The Stirring Effect on the Crystal Morphology of p-Acetamidobenzoic Acid Solution Crystallization" Crystals 15, no. 3: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15030284
APA StyleDong, R., Wang, F., Jing, D., Liu, Y., & Bao, Y. (2025). The Stirring Effect on the Crystal Morphology of p-Acetamidobenzoic Acid Solution Crystallization. Crystals, 15(3), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15030284




