A Review of Near-Infrared Reflective Nanopigments: Aesthetic and Cooling Properties
Abstract
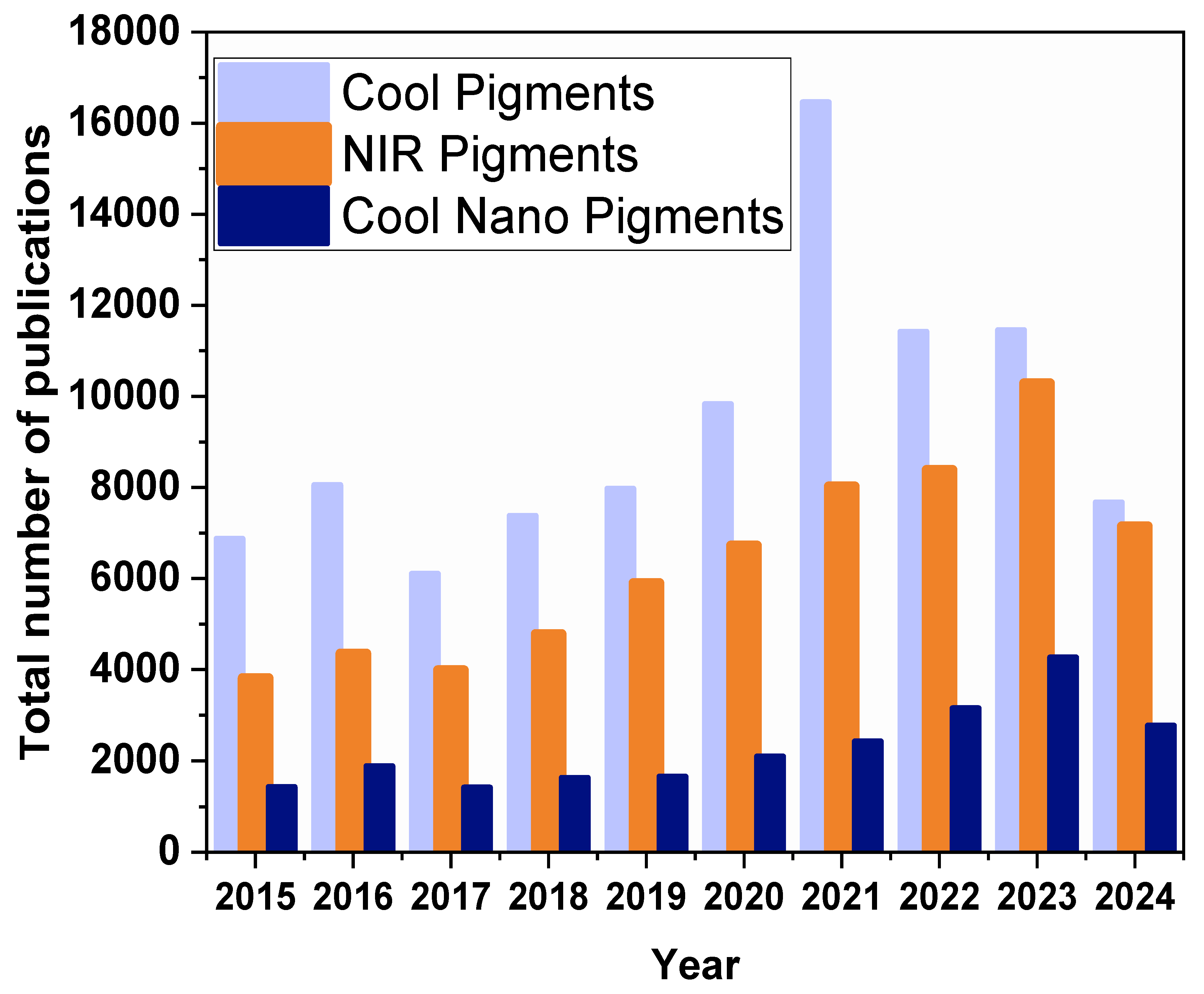
1. Introduction
2. Basic Concepts
2.1. NIR Reflectance Materials
2.1.1. Transition Metals
2.1.2. Inorganic Materials
2.1.3. Organic Materials
2.1.4. Natural Materials
2.1.5. Applications of NIR Materials
2.2. Pigments
2.3. Factors Affecting Infrared Reflectivity of Pigments
2.3.1. Pigment Selection
2.3.2. Dispersion
2.3.3. Blending Pigments
2.3.4. Opacity
2.3.5. Contamination
2.3.6. Particle Size
3. Developmental Status and Limitation of Cool Pigments
4. Cool-Colored Nanopigments
4.1. Figure of Merit for Cool-Colored Pigments
4.2. Application and Impact of Cool-Colored Nanopigments
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Optimization parameter of pigmented coatings. | |
| Reflectance ability over the NIR region from 700 to 2500 nm. | |
| Reflectance ability over the visible region. | |
| η(λ) | Standardized luminous efficiency based on the photopic conditions of the CIE #1931 model |
| Spectral reflection (Wm−2) that was measured in the lab. | |
| Solar spectral irradiance (Wm−2nm−1) that was measured in the lab. | |
| Color lightness coordinate. | |
| color coordinates for green and blue ranges for red and yellow colors, respectively. | |
| Hue of color space. | |
| Chroma or saturation of color space. | |
| CIE color coordinates of the chromaticity. | |
| Brightness parameter. | |
| Normalized color coordinates of the chromaticity. | |
| Normalization factor. | |
| , | Color coordinates of the chromaticity. |
References
- Song, J.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Z.; Pan, M.; Tian, F.; Li, X.; Ye, M.; Deng, X. Durable radiative cooling against environmental aging. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuruzzaman, M. Urban Heat Island: Causes, Effects and Mitigation Measures—A Review. Int. J. Environ. Monit. Anal. 2015, 3, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousse, Y.S. Mitigating the Urban Heat Island Effect with an Intensive Green Roof During Summer in Reading, UK. Ph.D. Thesis, Reading University, Reading, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Masson, V. Urban surface modeling and the meso-scale impact of cities. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2006, 84, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarsini, R.; Hien, W.N.; Wai David, C.K. Microclimatic modeling of the urban thermal environment of Singapore to mitigate urban heat island. Sol. Energy 2008, 82, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synnefa, A.; Karlessi, T.; Gaitani, N.; Santamouris, M.; Asimakopoulos, D.; Papakatsikas, C. Experimental testing of cool colored thin layer asphalt and estimation of its potential to improve the urban microclimate. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centre, U.C.C. The Heat Is On, A World of Climate Promises Not Yet Delivered. DEW/2388/NA. 1 March 2021. Available online: https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/video/world-climate-promises-not-yet-delivered (accessed on 18 February 2025).
- Akbari, H.; Cartalis, C.; Kolokotsa, D.; Muscio, A.; Pisello, A.L.; Rossi, F.; Santamouris, M.; Synnefa, A.; Wong, N.H.; Zinzi, M. Local climate change and urban heat island mitigation techniques—The state of the art. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2016, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgal, F.P.; Buratti, C.; Kalaiselvam, S.; Granqvist, C.-G.; Ivano, V. Nano and Biotech Based Materials for Energy Building Efficiency; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; p. 485. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari, H.; Damon Matthews, H.; Seto, D. The long-term effect of increasing the albedo of urban areas. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 024004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolokotroni, M.; Gowreesunker, B.L.; Giridharan, R. Cool roof technology in London: An experimental and modelling study. Energy Build. 2013, 67, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, C.; Zinzi, M. Impact of a cool roof application on the energy and comfort performance in an existing non-residential building. A Sicilian case study. Energy Build. 2013, 67, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farha, A.H.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Mansour, S.A. Ga-Doped ZnO Nanostructured Powder for Cool-Nanopigment in Environment Applications. Materials 2020, 13, 5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, C.; Muscio, A.; Siligardi, C.; Manfredini, T. Design of a cool color glaze for solar reflective tile application. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 11106–11116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, V.; Kennedy, J.V.; Futter, J.; Manning, J. A Review of Near Infrared Reflectance Properties of Metal Oxide Nanostructures; GNS Science: Lower Hutt, New Zealand, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.-Q.; Mei, S.-G.; Byon, Y.-J.; Wang, J.-L.; Zhang, G. Highly Solar Radiation Reflective Cr2O3–3TiO2 Orange Nanopigment Prepared by a Polymer-Pyrolysis Method. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, J.; Sun, X. Environment-friendly pigments based on praseodymium and terbium doped La2Ce2O7 with high near-infrared reflectance: Synthesis and characterization. Dye. Pigment. 2017, 147, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Chen, Y.; Lin, H. Facile fabrication of cool yellow pigment with enhanced NIR reflectance by tailoring oxygen defects and its application in energy-saving building. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 10756–10764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thekaekara, M.P. Solar Energy Monitor in Space (SEMIS). In Proceedings of the Symposium on Solar Radiation Measurements and Instrumentation, Rockville, MD, USA, 13–15 November 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Thekaekara, M. Solar irradiance: Total and spectral and its possible variations. Appl. Opt. 1976, 15, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.; Joshy, D.; Narendranath, S.B.; Periyat, P. Recent advances in infrared reflective inorganic pigments. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 194, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, H.; Berdahl, P.; Levinson, R.; Wiel, S.; Miller, B.; Desjarlais, A. Cool color roofing materials. In California Energy Commission PIER Program; Heat Island Group, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jeevanandam, P.; Mulukutla, R.S.; Phillips, M.; Chaudhuri, S.; Erickson, L.; Klabunde, K. Near Infrared Reflectance Properties of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 1912–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitran, M.; Murray, W. Infrared, Visible, and Ultraviolet Radiation. In Patty’s Toxicology; Bingham, E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 249–314. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, C.; Bamola, P.; Singh, B.; Sharma, H. Chapter 2—Infrared radiation and materials interaction: Active, passive, transparent, and opaque coatings. In Energy Saving Coating Materials; Dalapati, G.K., Sharma, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 33–56. [Google Scholar]
- Pisello, A.L. State of the art on the development of cool coatings for buildings and cities. Sol. Energy 2017, 144, 660–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y. Study and Development of Near-Infrared Reflective and Absorptive Materials for Energy Saving Application. Ph.D. Thesis, Reading University, Reading, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, S.A.; Eldafatry, I.; Elsad, R.A.; Farag, E.M. Nanosized amorphous and nanocrystalline titania doped by Cr as novel, efficient, and cost-effective cool-colored nanopigments. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 33089–33098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gallais, L. A theoretical investigation of the laser damage threshold of metal multi-dielectric mirrors for high power ultrashort applications. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 14698–14711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mara, J.; Bodnár, A.-E.; Trif, L.; Telegdi, J. Development of Effective Infrared Reflective Coatings. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.K.; Zhou, K.; Kim, S.-K.; Manjarrez, A.; Hoque, M.J.; Seong, T.-Y.; Cai, L. Visibly Transparent and Infrared Reflective Coatings for Personal Thermal Management and Thermal Camouflage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2201432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, T.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y. Preparation of high near-infrared reflectance mica/(Ni, Sb)-co-doped rutile yellow composite pigment via mechanochemical pretreatment and sintering. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 6015–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M.; Yun, G. Recent development and research priorities on cool and super cool materials to mitigate urban heat island. Renew. Energy 2020, 161, 792–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyquist, R.A.; Kagel, R.O. Handbook of Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic Compounds and Organic Salts: Infrared Spectra of Inorganic Compounds; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Kure-Chu, S.-Z.; Ogasawara, T.; Yashiro, H.; Ye, R.; Hosokai, T.; Uchidate, M.; Suziki, E.; Naito, T. Multilayered Sn/Ag3Sn electroplating on Cu alloys for high reliable electronic/electric materials. Trans. Jpn. Inst. Electron. Packag. 2014, 7, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tony, M.A.; Mansour, S.A. Synthesis of nanosized amorphous and nanocrystalline TiO2 for photochemical oxidation of methomyl insecticide in aqueous media. Water Environ. J. 2020, 34, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilokur, M.; Gentle, A.; Arnold, M.; Cortie, M.; Smith, G. Optical properties of refractory TiN, AlN and (Ti, Al) N coatings. In Micro+ Nano Materials, Devices, and Systems; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; pp. 536–548. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.G.; Birau, M.; Yu, G.; Yu, H.; Qi, Y.H.; Desjardins, P.; Meng, X.S.; Gao, J.; et al. Near-infrared absorbing organic materials. Pure Appl. Chem. 2004, 76, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, W.; Song, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, M.; Hu, X. Thiophene-Fused-Heteroaromatic Diones as Promising NIR Reflectors for Radiative Cooling. Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 6397–6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Bhattacharya, S.; Henry, D. Interpreting the near-infrared reflectance of a series of perylene pigments. Dye. Pigment. 2013, 99, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X. Hybrid Solar Reflective Coatings Based on Colloidal and Solvothermal Synthesis; National University of Singapore: Singapore, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, G.; Wang, Z.Y. Near-Infrared Organic Compounds and Emerging Applications. Chem.—Asian J. 2010, 5, 1006–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, H.; Loonen, R.C.G.M.; Hensen, J.L.M.; Debije, M.G.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. Electrically switchable polymer stabilised broadband infrared reflectors and their potential as smart windows for energy saving in buildings. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.K.; Nishkam, A.; Kasturiya, N. Camouflage in the Non-Visible Region. J. Ind. Text. 2001, 31, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendiganavale, A.; Malshe, V. Infrared Reflective Inorganic Pigments. Recent Pat. Chem. Eng. 2010, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkallas, F.H.; Elshokrofy, K.M.; Mansour, S.A. Structural and Diffuse Reflectance Study of Cr-Doped ZnO Nanorod-Pigments Prepared via Facile Thermal Decomposition Technique. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2019, 29, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsth, D.F.L.; Primo, J.d.O.; Anaissi, F.J.; Umek, P.; Bittencourt, C. Sustainable Near-Infrared Reflective Blue Pigments: Recycled Aluminum from Can Seals for Cobalt Aluminates in Cool Coatings. Colorants 2024, 3, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Mochizuki, S.; Nagato, Y.; Morimoto, T.; Masui, T. Synthesis of High Near-Infrared Reflective Black Pigment Based on YMn2O5. Colorants 2023, 2, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklar, L.R.; Almutawa, F.; Lim, H.W.; Hamzavi, I. Effects of ultraviolet radiation, visible light, and infrared radiation on erythema and pigmentation: A review. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2013, 12, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farha, A.H.; Al Naim, A.F.; Mansour, S.A. Cost-Effective and Efficient Cool Nanopigments Based on Oleic-Acid-Surface-Modified ZnO Nanostructured. Materials 2023, 16, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Chen, W. Insights into the Intrinsic Factors Affecting the NIR Reflectance Based on Rylene Diimide Molecules. Materials 2021, 14, 5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malshe, V.C.; Bendiganavale, A.K. Infrared reflective inorganic pigments. Recent Pat. Chem. Eng. 2008, 1, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Pei, W.; Li, G. Experimental study of optical and cooling performances of CuO and TiO2 near-infrared reflective blending coatings. Sol. Energy 2021, 225, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagorio, M. Why Do Marbles Become Paler on Grinding? Reflectance, Spectroscopy, Color, and Particle Size. J. Chem. Educ. 2004, 81, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, D.R. Basics of Paint Technology (Part 1). Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 51, 162. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari, H. Measured energy savings from the application of reflective roofs in two small non-residential buildings. Energy 2003, 28, 953–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M.; Synnefa, A.; Kolokotsa, D.; Dimitriou, V.; Apostolakis, K. Passive cooling of the built environment—Use of innovative reflective materials to fight heat islands and decrease cooling needs. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2008, 3, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, K.M.; Ismail, M.; Rahman, A.M.A. Passive cooling techniques through reflective and radiative roofs in tropical houses in Southeast Asia: A literature review. Front. Archit. Res. 2014, 3, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Carlson, J.; Golden, J.; Bryan, H. An integrated empirical and modeling methodology for analyzing solar reflective roof technologies on commercial buildings. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.A.; Farha, A.H.; Tahoun, B.A.; Elsad, R.A. Novel magnetic polyaniline nanocomposites based on as-synthesized and surface modified Co-doped ZnO diluted magnetic oxide (DMO) nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 265, 115032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkallas, F.H.; Al-Rebdi, T.A.; Mansour, S.A. Structural and diffuse reflectance investigation of dysprosium-doped TiO2 nanopowder synthesized by sonochemical hydrolysis technique. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2021, 603, 412664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkallas, F.; Elshokrofy, K.M.; Mansour, S. Structural and diffuse reflectance characterization of cobalt-doped titanium dioxide nanostructured powder prepared via facile sonochemical hydrolysis technique. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2019, 9, 184798041984780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, B.; Chen, J.; Sun, X. Novel Bi3+ doped and Bi3+/Tb3+ co-doped LaYO3 pigments with high near-infrared reflectances. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 762, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Tang, M.; Quan, R.; Chai, Z. Synthesis of solar heat-reflective ZnTiO3 pigments with novel roof cooling effect. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 15768–15771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Han, A.; Ye, M.; Chen, X.; Yuan, L. The influence of Mn/N-codoping on the thermal performance of ZnAl2O4 as high near-infrared reflective inorganic pigment. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 696, 1329–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Han, A.; Ye, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, L.; Yang, J. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of novel yellow pigments based on V5+ doped BiPO4 with high near-infrared reflectance. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 19690–19700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baneshi, M.; Maruyama, S.; Komiya, A. The Effects of Using Some Common White Pigments on Thermal and Aesthetic Performances of Pigmented Coatings. J. Therm. Sci. Technol. 2009, 4, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baneshi, M.; Maruyama, S.; Nakai, H.; Komiya, A. A new approach to optimizing pigmented coatings considering both thermal and aesthetic effects. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2009, 110, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, R.; Berdahl, P.; Akbari, H.; Miller, W.; Joedicke, I.; Reilly, J.; Suzuki, Y.; Vondran, M. Methods of creating solar-reflective nonwhite surfaces and their application to residential roofing materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2007, 91, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbert, R. Paint Technology Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; p. 240. [Google Scholar]
- Baneshi, M.; Gonome, H.; Komiya, A.; Maruyama, S. The effect of particles size distribution on aesthetic and thermal performances of polydisperse TiO2 pigmented coatings: Comparison between numerical and experimental results. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2012, 113, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolvaj, L.; Persze, L.; Lang, E. Correlation between Hue Angle and lightness of wood species grown in Hungary. Wood Res. 2013, 58, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Baneshi, M.; Maruyama, S.; Komiya, A. Comparison between aesthetic and thermal performances of copper oxide and titanium dioxide nano-particulate coatings. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2011, 112, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Cole, J.B.; Yatagai, T. Colour characterization of a Morpho butterfly wing-scale using a high accuracy nonstandard finite-difference time-domain method. Micron 2007, 38, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariane, M.; Jennifer, V.; Kamil, K.; David, S.; Jose, M.; Bill, C.; Zachary, V.T.; Jolina, K.; Linus, N.; Portia, L.; et al. Cool Pavement Pilot Program; City of Phoenix: Phoenix, AZ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ashghal Completes the Works of Cool Pavement Paint. Available online: https://www.ashghal.gov.qa/en/MediaHub/News/Pages/Ashghal-completes-the-works-of-cool-pavement-paint.aspx (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Nejad, F.M.; Baghshahi, S.; Bakhtiari, L. Advantages of Nano Pigments Over Micro Pigments in Obtaining Larger Spectra of Colours in CMYK System. Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc. 2011, 70, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, D.Y. Effect of pigmentation on organic coating characteristics. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 50, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Choi, H.; Kwon, S.-J.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.; Chung, C.; Lee, J. Development of High-Contrast CRT Based on Nano Pigment Screen Technique. In Sid Symposium Digest of Technical Papers; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2005; Volume 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| White Pigment | Structure | Synthesization Technique | NIR Reflectance % | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO | Hexagonal, Wurtzite | Thermal decomposition | 80.47 | [50] |
| Oleic-acid-treated ZnO | Hexagonal, Wurtzite | Thermal decomposition | 84.75 | [50] |
| ZnO | Hexagonal, Wurtzite | Thermal decomposition | 64.8 | [46] |
| ZnO | Hexagonal, Wurtzite | Modified polymer pyrolysis with γ-irradiation | 88 | [13] |
| ZnO | Hexagonal, Wurtzite | Arc discharge | 14 to 54 | [15] |
| TiO2 | Tetragonal, Anatase | Hydrolysis process | 79.53 | [28] |
| TiO2 | Tetragonal, Rutile + Anatase | Hydrolysis process | 94.72 | [32] |
| TiO2 | Amorphous | Hydrolysis process | 88.14 | [61] |
| TiO2 | Rutile | Polymer pyrolysis | 87 | [16] |
| La2Ce2O7 | Fluorite type | Sol–gel | 95.95 | [17] |
| LaYO3 | Fluorite type | Sol–gel | 92 | [63] |
| ZnTiO3 | Perovskite | Solid state | 95 | [64] |
| ZnAl2O4 | Spinel | Solid state | 85 | [65] |
| BiPO4 | Monoclinic | Hydrothermal | 80 | [66] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mansour, S.A.; Farha, A.H. A Review of Near-Infrared Reflective Nanopigments: Aesthetic and Cooling Properties. Crystals 2025, 15, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15030271
Mansour SA, Farha AH. A Review of Near-Infrared Reflective Nanopigments: Aesthetic and Cooling Properties. Crystals. 2025; 15(3):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15030271
Chicago/Turabian StyleMansour, Shehab A., and Ashraf H. Farha. 2025. "A Review of Near-Infrared Reflective Nanopigments: Aesthetic and Cooling Properties" Crystals 15, no. 3: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15030271
APA StyleMansour, S. A., & Farha, A. H. (2025). A Review of Near-Infrared Reflective Nanopigments: Aesthetic and Cooling Properties. Crystals, 15(3), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15030271






