Chromaticity Study of Yellow HTHP Lab-Grown Diamonds Based on Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results
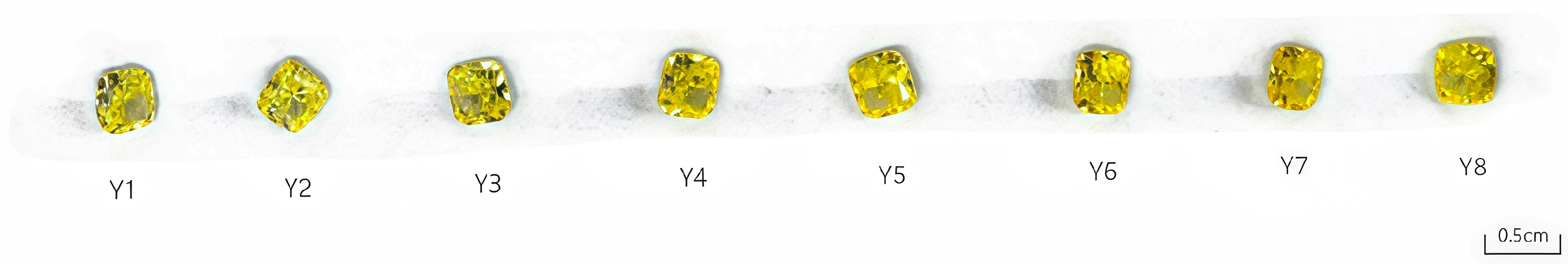
3.1. Gemological and Defect Characteristics
3.2. Colorimetric Characteristics
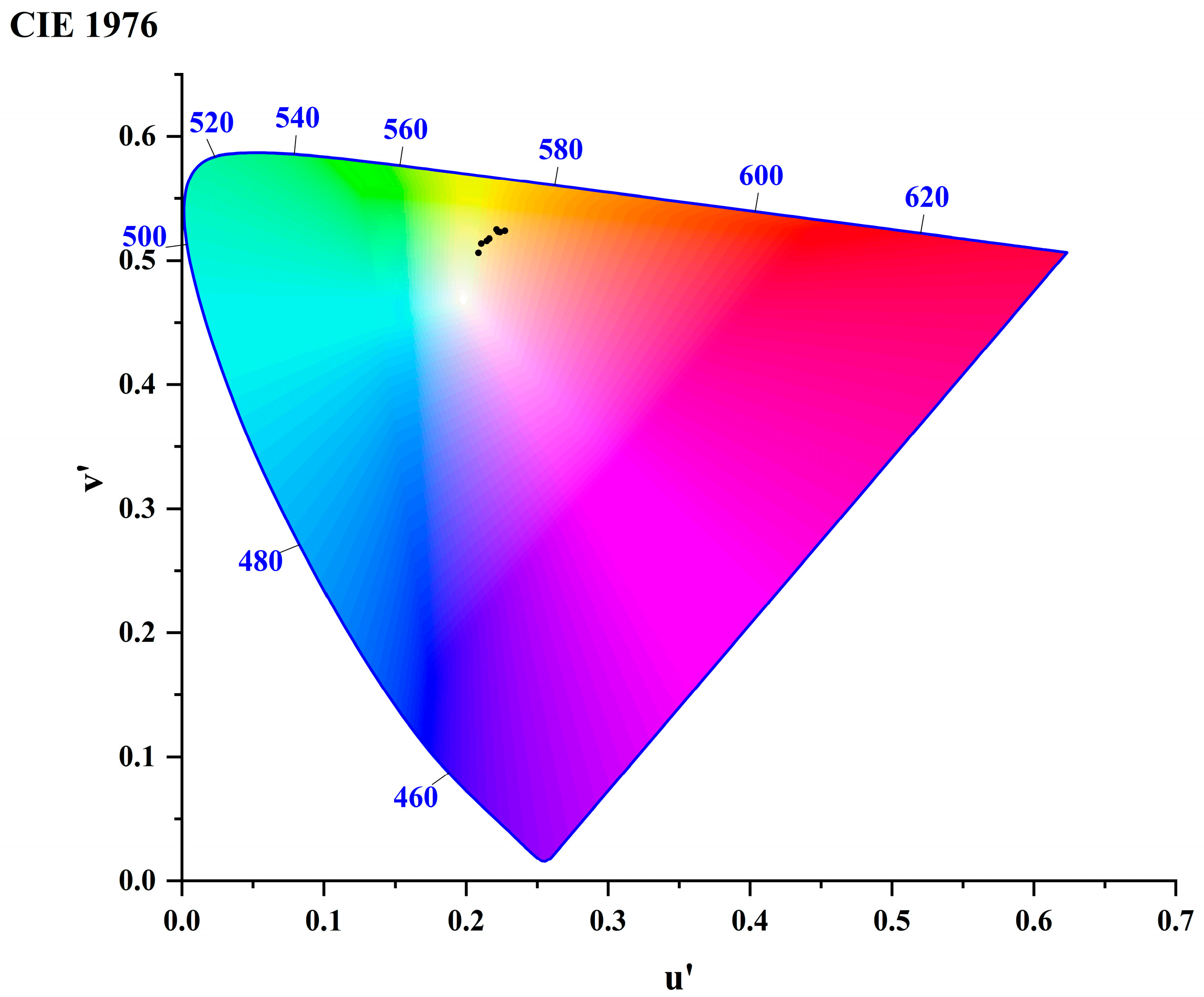
3.2.1. Colorimetric Parameters
3.2.2. Hue Angle h and Yellowness Index YI E313
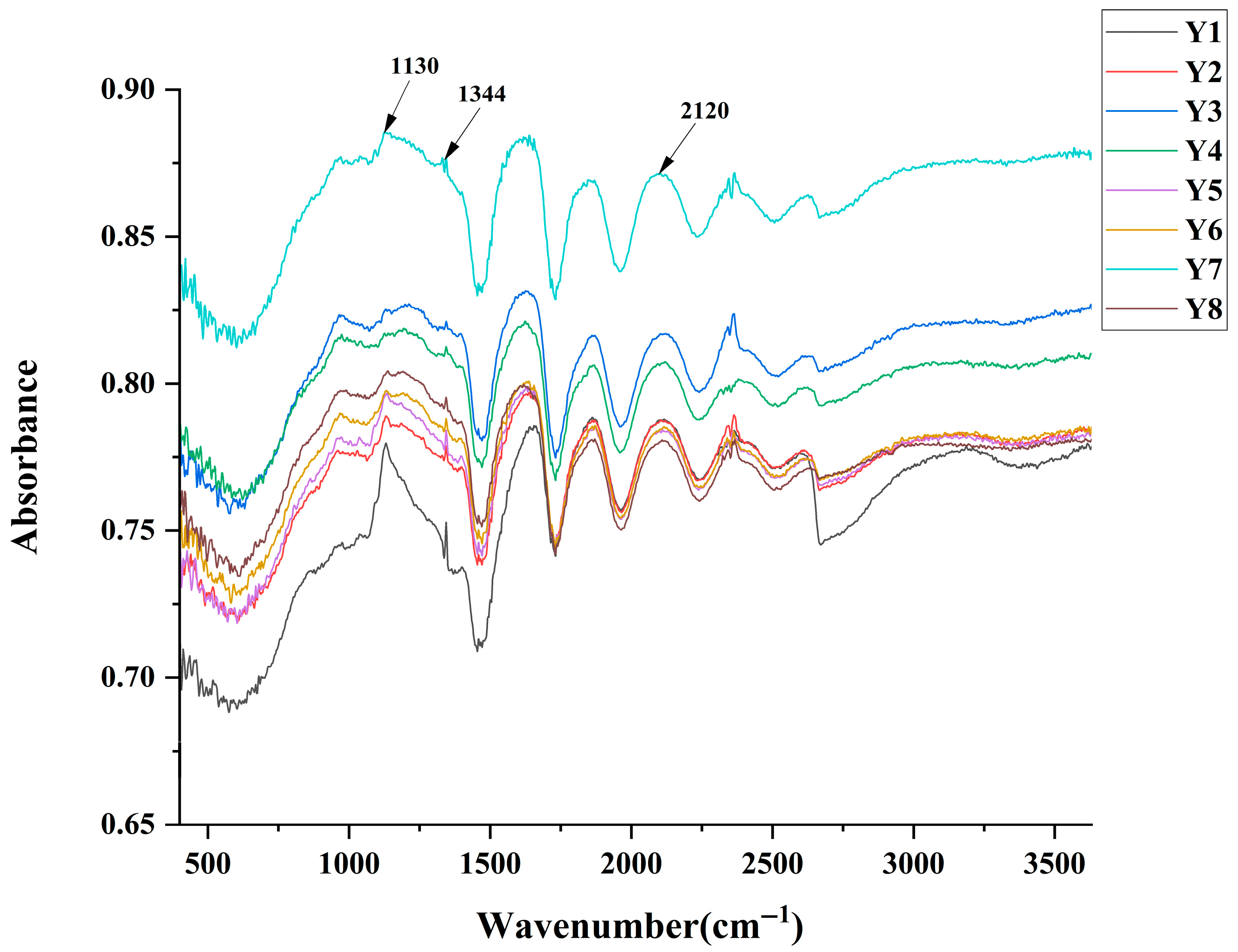
3.3. Infrared Spectra Testing
3.4. Raman Spectra Testing
4. Discussion
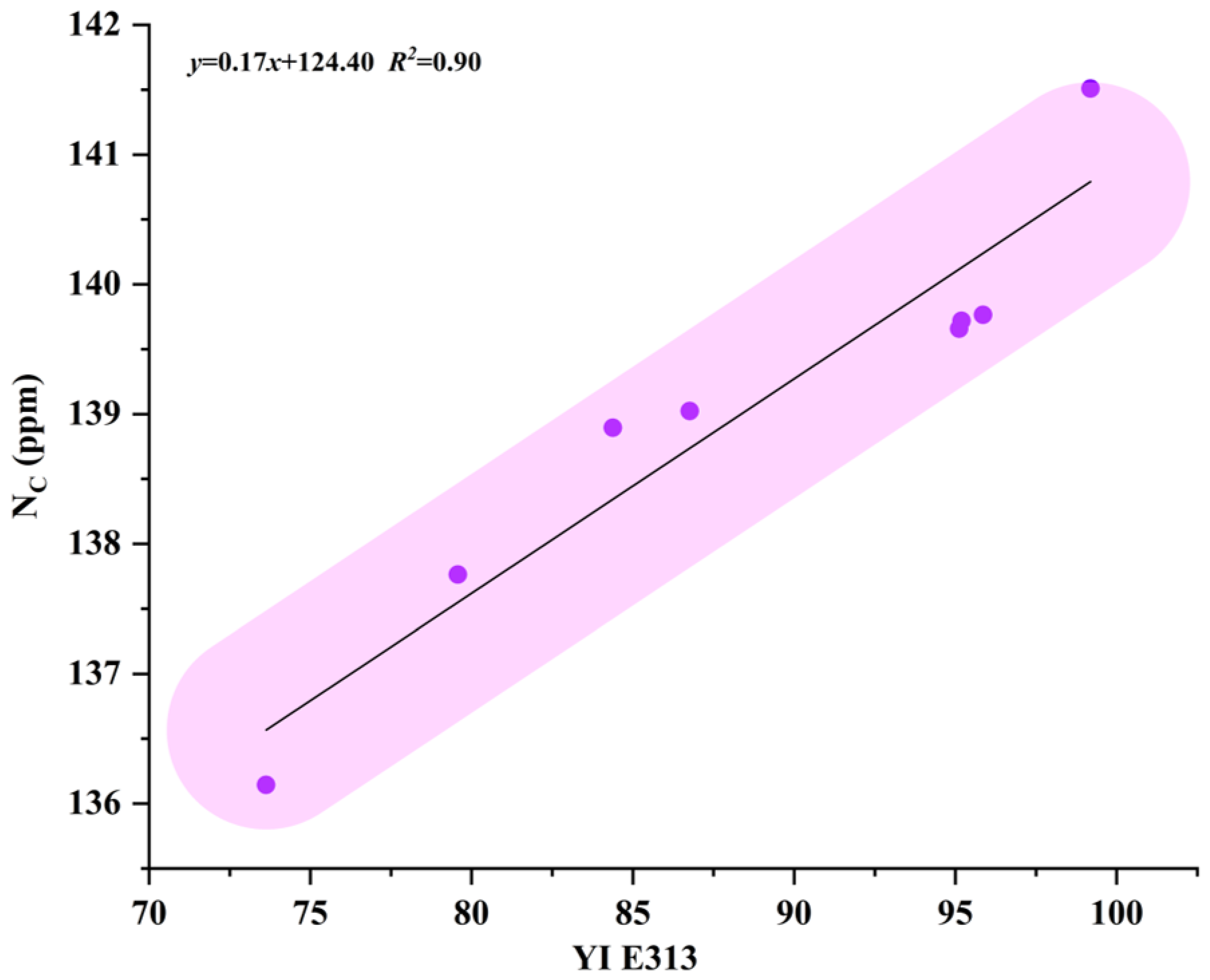
4.1. Yellowness Index YI E313 and Nitrogen Content NC Discussion
4.2. Yellowness Index YI E313 and FWHM Discussion
4.3. Yellowness Index YI E313 and Concentration Ratio R Discussion
4.4. Color Classification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, B.L. Systematic Gemology, 2nd ed.; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 131–143. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.F.; Peng, M.S.; Chen, W.X. Spectral Study of Transition Metal Ions in Colored Diamond. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2004, 24, 769–774. [Google Scholar]
- Green, B.L.; Collins, A.T.; Breeding, C.M. Diamond Spectroscopy, defect centers, color, and treatments. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2022, 88, 637–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.Q.; Zhang, C.H.; An, Q.Y. Research on the Chromogenic Mechanism of Natural, Synthetic, and Processed Blue Diamonds. Shandong Ind. Technol. 2018, 19, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, E.M.; Shirey, S.B.; Richardson, S.H.; Nestola, F.; Bullock, E.S.; Wang, J.; Wang, W. Blue boron-bearing diamonds from Earth’s lower mantle. Nature 2018, 560, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.L.; Elina, M.; Matthew, F.H.; Sally, E.M.; Christopher, M.B. Spectroscopic characterization of rare natural pink diamonds with yellow color zones. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2024, 148, 111428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taryn, L.M.; Sally, E.M.; Christopher, M.B.; Daniel, J.; Elina, M. Spectroscopy of green fluorescence rims on rough pink diamonds from Argyle mine. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2025, 153, 112079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.F.; Zhu, X.X.; Zhao, X.Y.; Ye, H. Discussion on the Identification of an Irradiated Green type IIa Diamond. China Gems Jades. 2020, 158, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.J.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Zhao, B.W.; Zeng, C.G.; Xiang, C.J. Difference of lattice radiation damage and spectroscopic characterization in natural and artificial radiation green diamonds. J. Gems Gemol. 2022, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.J.; Yuan, X.Q.; Tian, L.G.; Yuan, Z.Z. Evolution and colouration of lattice defects in diamonds at high pressure and high temperature. J. Gems Gemol. 2001, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi, M.; Karasawa, S.; Ohya, S.; Togashi, F. Dislocation of epitaxial CVD diamond and the characterization by Raman spectroscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1992, 60–61, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wotherspoon, A.; Steeds, J.W.; Catmull, B.; Butler, J. Photoluminescence and positron annihilation measurements of nitrogen doped CVD diamond. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2003, 12, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.L.; Gao, X.X.; Liu, Y.M.; Lu, R. The anisotropy of photoluminescence of gemstones and materials: In Cr-bearing ruby and chrysoberyl. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2024, 56, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, M.; Sally, E.M.; James, E.S. Naturally Colored Yellow and Orange Gem Diamonds: The Nitrogen Factor. J. Gems Gemol. 2022, 56, 194–219. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; He, X.M.; Xie, T.Q. Exploration of the Color Formation and Color Modification Mechanism of High temperature and high pressure Synthesis of Yellow Diamond. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2014, 33, 120–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.F.; Ding, T.; Li, H.H.; Zhu, X.X. Identification characteristic of HPHT-Treated yellow type Ib CVD synthetic diamond. J. Gems Gemol. 2021, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.; Goss, J.P.; Briddon, P.R. Acceptor level of nitrogen in diamond and the 270-nm absorption band. Philos. Mag. B 2009, 80, 033205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainschwang, T.; Fritsch, E.; Notari, F.; Rondeau, B. A new defect center in type Ib diamond inducing one phonon infrared absorption: The Y center. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2012, 21, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massi, L.; Fritsch, E.; Collins, A.T.; Hainschwang, T.; Notari, F. The “amber centres” and their relation to the brown colour. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2005, 14, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.-M.; Jia, X.-P.; Qin, J.-M.; Sun, S.-S.; Zhou, Z.-X.; Fang, C.; Ma, H.-A. Characterization of typical infrared characteristic peaks of hydrogen in nitrogen hydrogen co doped diamond. Acta Phys. Sin. 2014, 63, 048101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F. Color centers in minerals: Taking diamond nitrogen centers as an example. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2021, 41, 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.H.; Tang, P.; Zhu, W.F.; Gao, B.; Li, Y.J. Spectral characteristics of yellow diamonds synthesized under high pressure and high temperature and natural pure Ib type yellow diamonds. J. Gems Gemol. 2021, 23, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.M.; Teng, Y.J.; Tan, H.L.; Zu, E.D. Study on Fresh water Cultured White Pearls from Anhui Province Based on Chromaticity and Raman Spectra. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2022, 42, 1504–1507. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.Y.; He, X.M.; Lin, C.L.; Jin, X.Y.; Pan, Y.M. Identification of Beihong Agate and Nanhong Agate from China Based on Chromaticity and Raman Spectra. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2019, 39, 2153–2159. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E313-20; Standard Practice for Calculating Yellowness and Whiteness Indices from Instrumentally Measured Color Coordinates. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Zhang, Y.F. Cultivation of High Nitrogen Content Gemstone Diamond. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kuganathan, N.; Chroneos, A.; Grimes, R.W. Vacancy defects in nitrogen doped diamond. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2023, 655, 414769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, N.R.; Jonathan, P.G.; Ben, L.G. Nitrogen in Diamond. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 5745–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchakarla, L.S.; Subrahmanyam, K.S.; Saha, S.K. Synthesis, Structure and Properties of Boron and Nitrogen Doped Graphene. ACS Nano. 2009, 3, 4726–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Chen, M.H.; Wu, G.; Gong, N.N. Study on the evaluation of the crystal quality of diamonds. J. Synth. Cryst. 2014, 43, 559–564. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, S.R.; Kiflawi, I.; Woods, G.S. The correlation between absorption and the A defect concentration in diamond. Philos. Mag. B 1994, 69, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.R.; Kiflawi, I.; Woods, G.S. Infrared absorption by the B aggregate in diamond. Philos. Mag. B 1995, 72, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiflawi, I.; Mayer, A.E.; Spear, P.M.; VanWyk, J.A.; Woods, G.S. Infrared absorption by the single nitrogen and A defect centers in diamond. Philos. Mag. B 1994, 69, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.H.; Bi, N.; Gong, C.S. Study on synthesis and Raman spectra of boron and nitrogen doped diamond single crystals. J. Synth. Cryst. 2016, 45, 1477–1481. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.T. Current status and prospect of defect in gemmology. J. Miner. Petrol. 2025, 45, 86–105. [Google Scholar]



| Type | The Form of N Atoms | The Characteristics of Color | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type I (Consist of N) | Type Ia | Type IaA | Two N atoms | Colorless to Yellow | The type of most natural diamonds |
| Type IaB | Three to Nine N atoms | ||||
| Type Ib | One N atom | Colorless to Yellow/Brown | The type of most lab-grown diamonds | ||
| Type II(No N) | Type IIa | No N atom or w(N) < 0.001% | Colorless to Brown/Pinkish Red | Because of the lattice dislocation of the C atom | |
| Type IIb | Litte B | Blue | Can be conductive | ||
| Sample Number | L* | a* | b* | h | YI E313 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | 72.30 | 3.78 | 37.04 | 1.47 | 73.63 |
| Y2 | 81.30 | 4.21 | 45.69 | 1.48 | 79.57 |
| Y3 | 73.97 | 5.35 | 44.98 | 1.45 | 84.38 |
| Y4 | 74.24 | 5.77 | 46.79 | 1.45 | 86.76 |
| Y5 | 73.79 | 7.76 | 52.30 | 1.42 | 95.12 |
| Y6 | 79.18 | 7.45 | 56.25 | 1.44 | 95.19 |
| Y7 | 72.07 | 7.82 | 51.78 | 1.42 | 95.86 |
| Y8 | 74.60 | 10.12 | 54.50 | 1.39 | 99.19 |
| Sample Number | YI E313 | NC (ppm) |
|---|---|---|
| Y1 | 73.63 | 136.14 |
| Y2 | 79.57 | 137.76 |
| Y3 | 84.38 | 138.89 |
| Y4 | 86.76 | 139.02 |
| Y5 | 95.12 | 139.66 |
| Y6 | 95.19 | 139.72 |
| Y7 | 95.86 | 139.77 |
| Y8 | 99.19 | 141.51 |
| Sample Number | FWHM | NC (ppm) | YI E313 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | 7.08 | 136.14 | 73.63 |
| Y2 | 9.16 | 137.76 | 79.57 |
| Y3 | 7.95 | 138.89 | 84.38 |
| Y4 | 7.00 | 139.02 | 86.76 |
| Y5 | 2.18 | 139.66 | 95.12 |
| Y6 | 5.55 | 139.72 | 95.19 |
| Y7 | 5.57 | 139.77 | 95.86 |
| Y8 | 5.51 | 141.51 | 99.19 |
| Sample Number | NV0 Peak Intensity | NV− Peak Intensity | R | NC (ppm) | YI E313 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | 0.0034 | 0.0015 | 0.309 | 136.14 | 73.63 |
| Y2 | 0.0120 | 0.0126 | 0.513 | 137.76 | 79.57 |
| Y3 | 0.0150 | 0.0192 | 0.561 | 138.89 | 84.38 |
| Y4 | 0.0186 | 0.0377 | 0.670 | 139.02 | 86.76 |
| Y5 | 0.0153 | 0.0323 | 0.678 | 139.66 | 95.12 |
| Y6 | 0.0096 | 0.0379 | 0.798 | 139.72 | 95.19 |
| Y7 | 0.0232 | 0.0834 | 0.783 | 139.77 | 95.86 |
| Y8 | 0.0210 | 0.0859 | 0.804 | 141.51 | 99.19 |
| Hue | h | YI E313 | NC (ppm) | R | Sample Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light | 1.47–1.48 | 70–80 | 136–138 | 0.31–0.51 | Y1–Y2 |
| Intense | 1.45–1.46 | 80–90 | 138–139 | 0.52–0.67 | Y3–Y4 |
| Deep | 1.39–1.44 | 90–100 | 139–141 | 0.68–0.80 | Y5–Y8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, B.; Yang, S.; Zu, E. Chromaticity Study of Yellow HTHP Lab-Grown Diamonds Based on Spectroscopy. Crystals 2025, 15, 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110942
Peng Z, Sun Y, Xie M, Zhang Z, Meng B, Yang S, Zu E. Chromaticity Study of Yellow HTHP Lab-Grown Diamonds Based on Spectroscopy. Crystals. 2025; 15(11):942. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110942
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Zhuchun, Yicong Sun, Mingming Xie, Zheng Zhang, Bin Meng, Siqi Yang, and Endong Zu. 2025. "Chromaticity Study of Yellow HTHP Lab-Grown Diamonds Based on Spectroscopy" Crystals 15, no. 11: 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110942
APA StylePeng, Z., Sun, Y., Xie, M., Zhang, Z., Meng, B., Yang, S., & Zu, E. (2025). Chromaticity Study of Yellow HTHP Lab-Grown Diamonds Based on Spectroscopy. Crystals, 15(11), 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110942






