Effect of Y on the Microstructures and Heat-Resistant Property of ZL109 Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
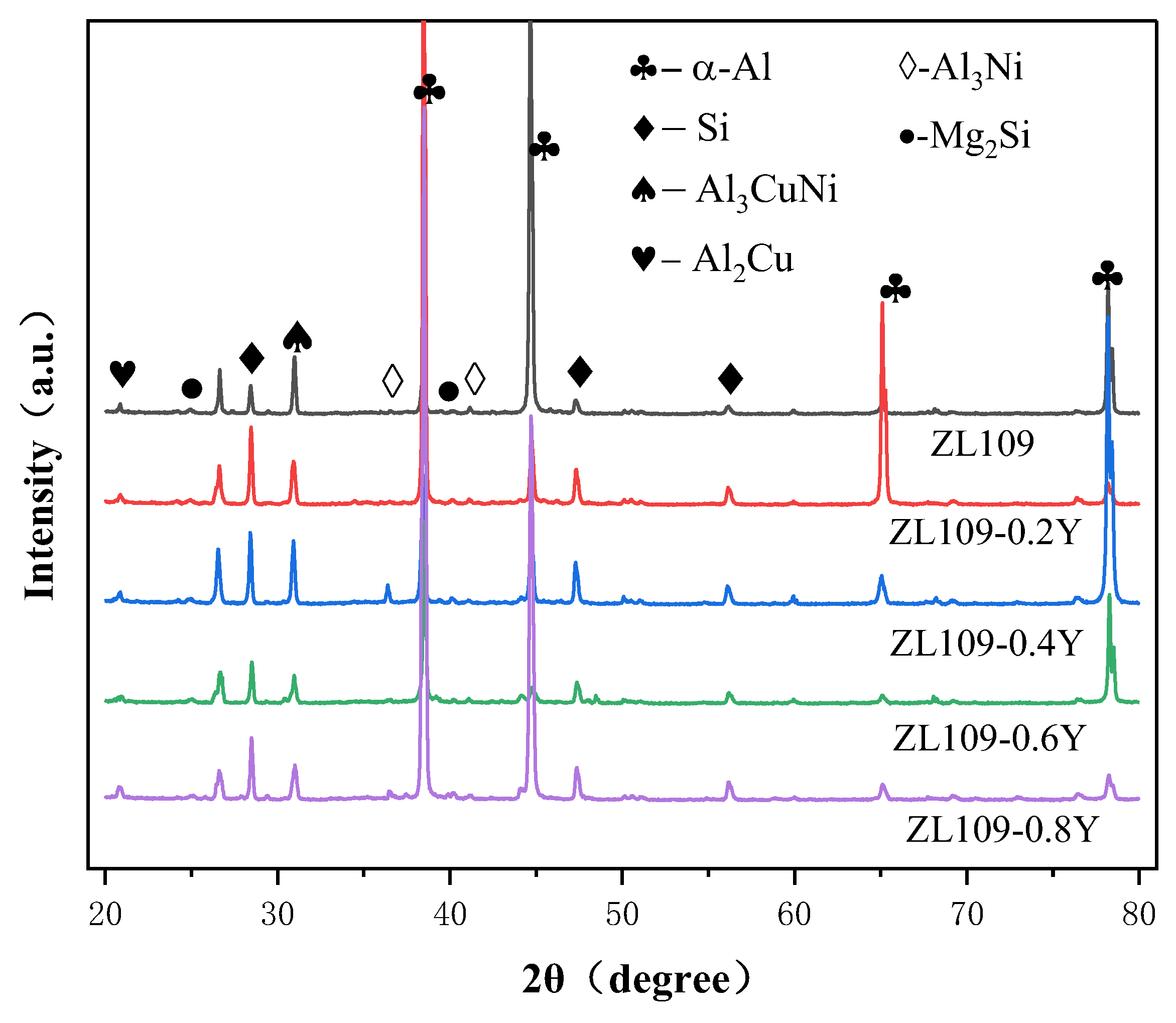
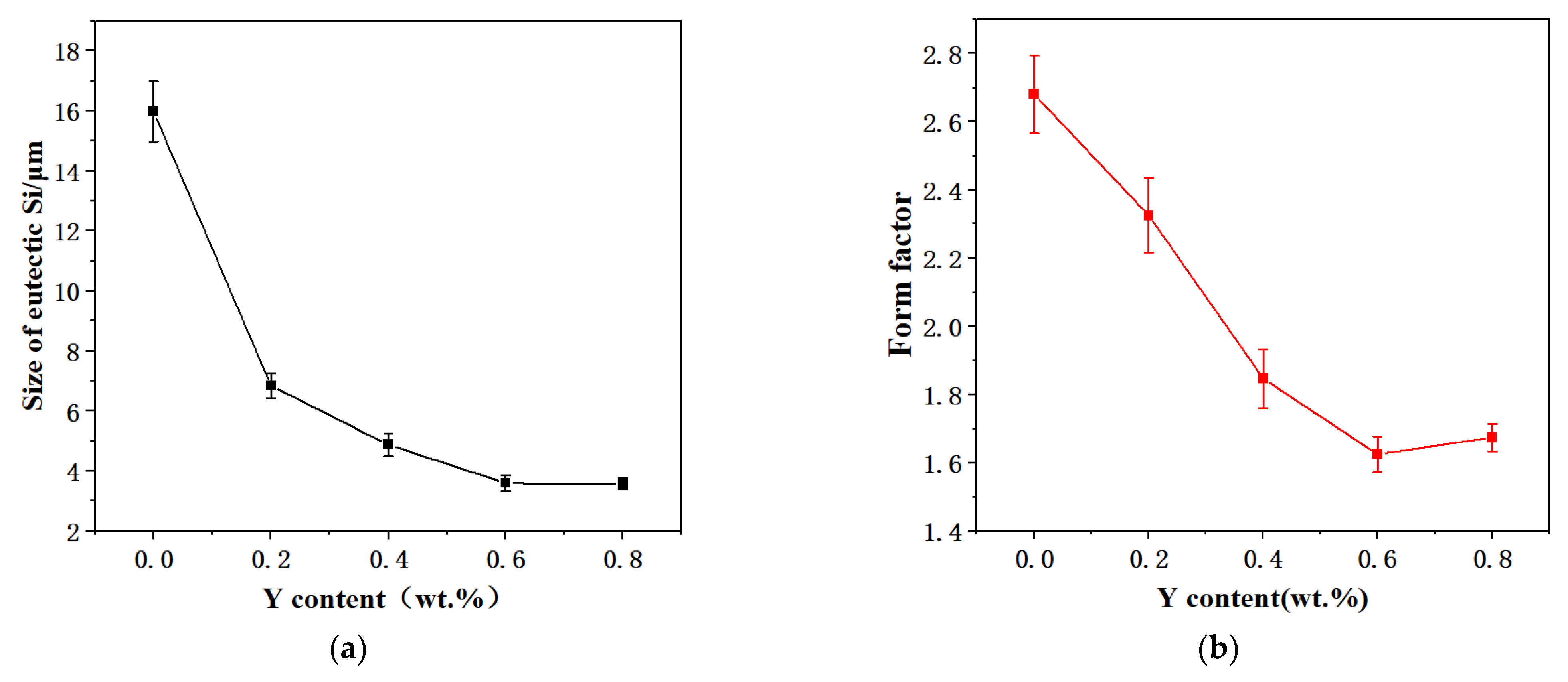
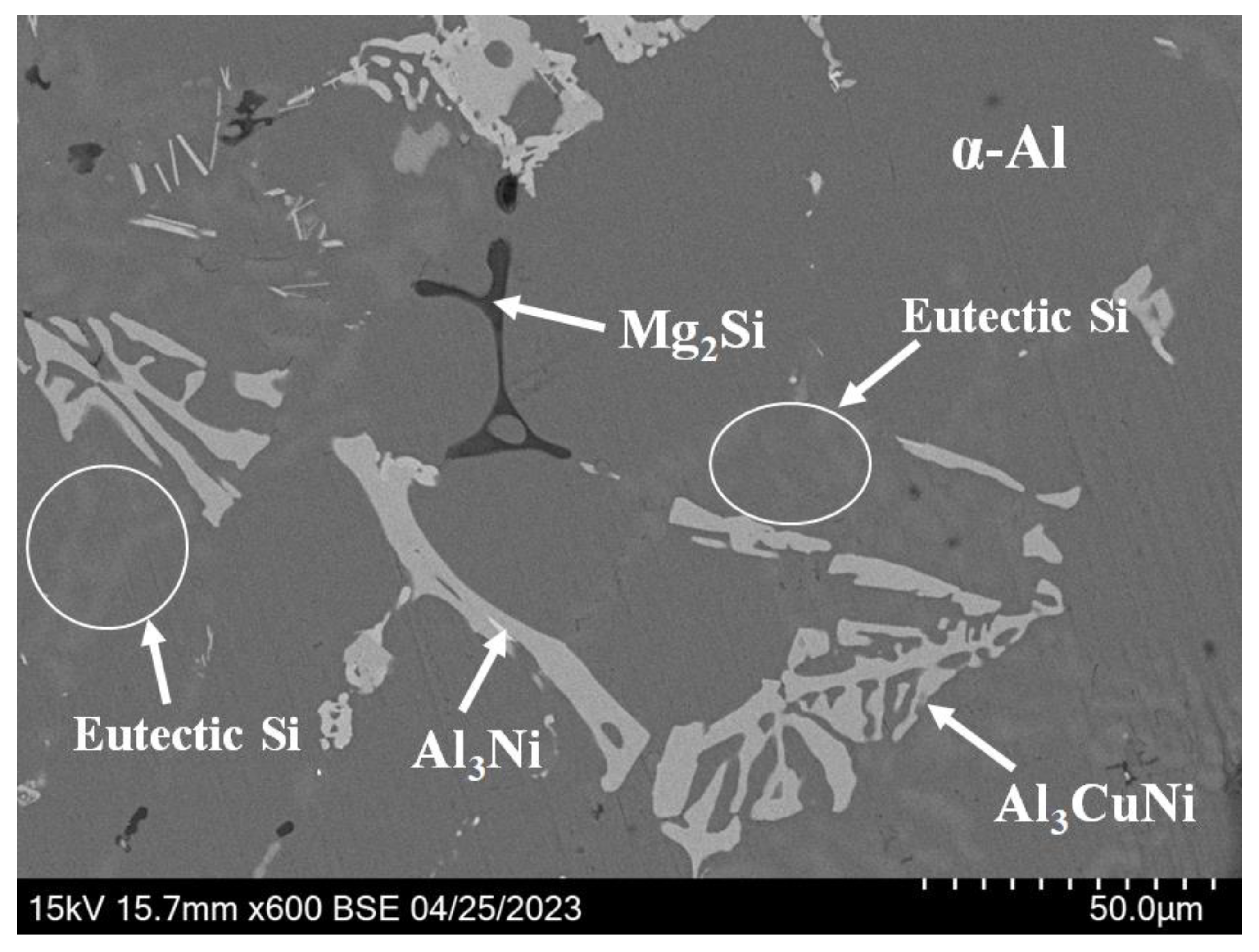
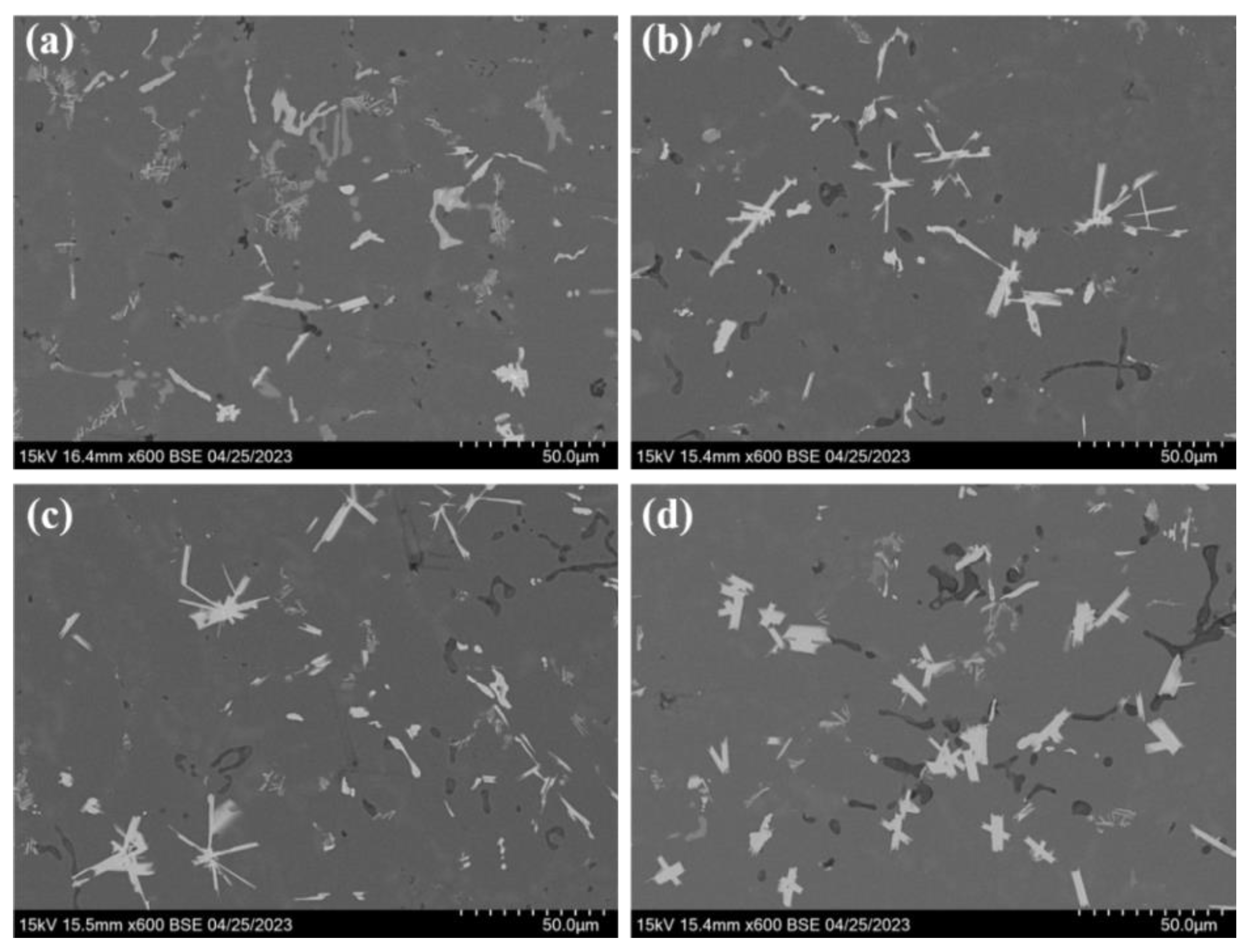
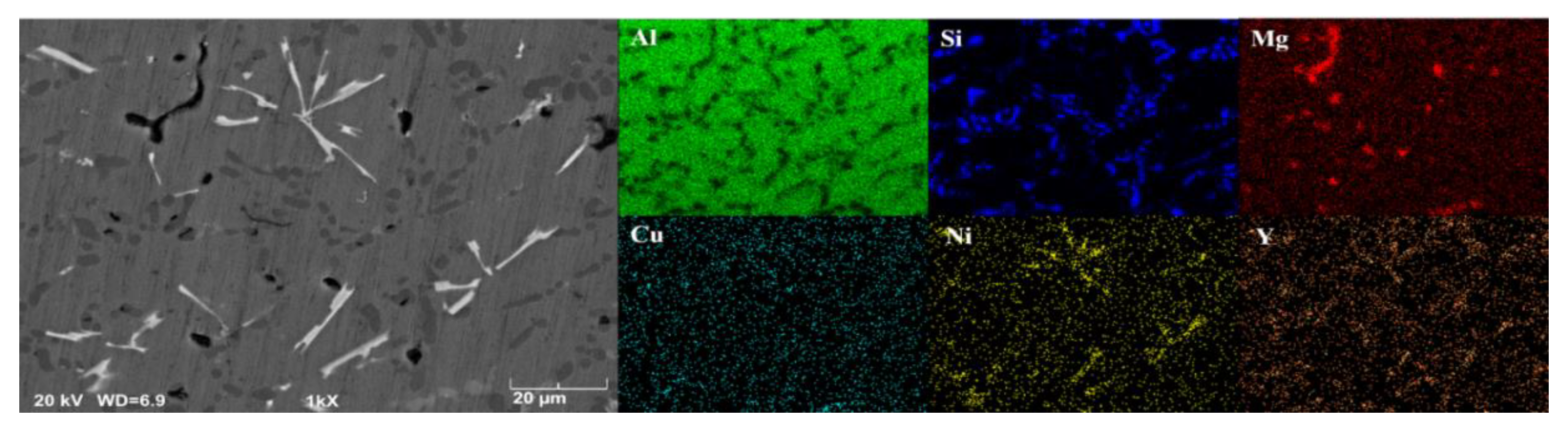
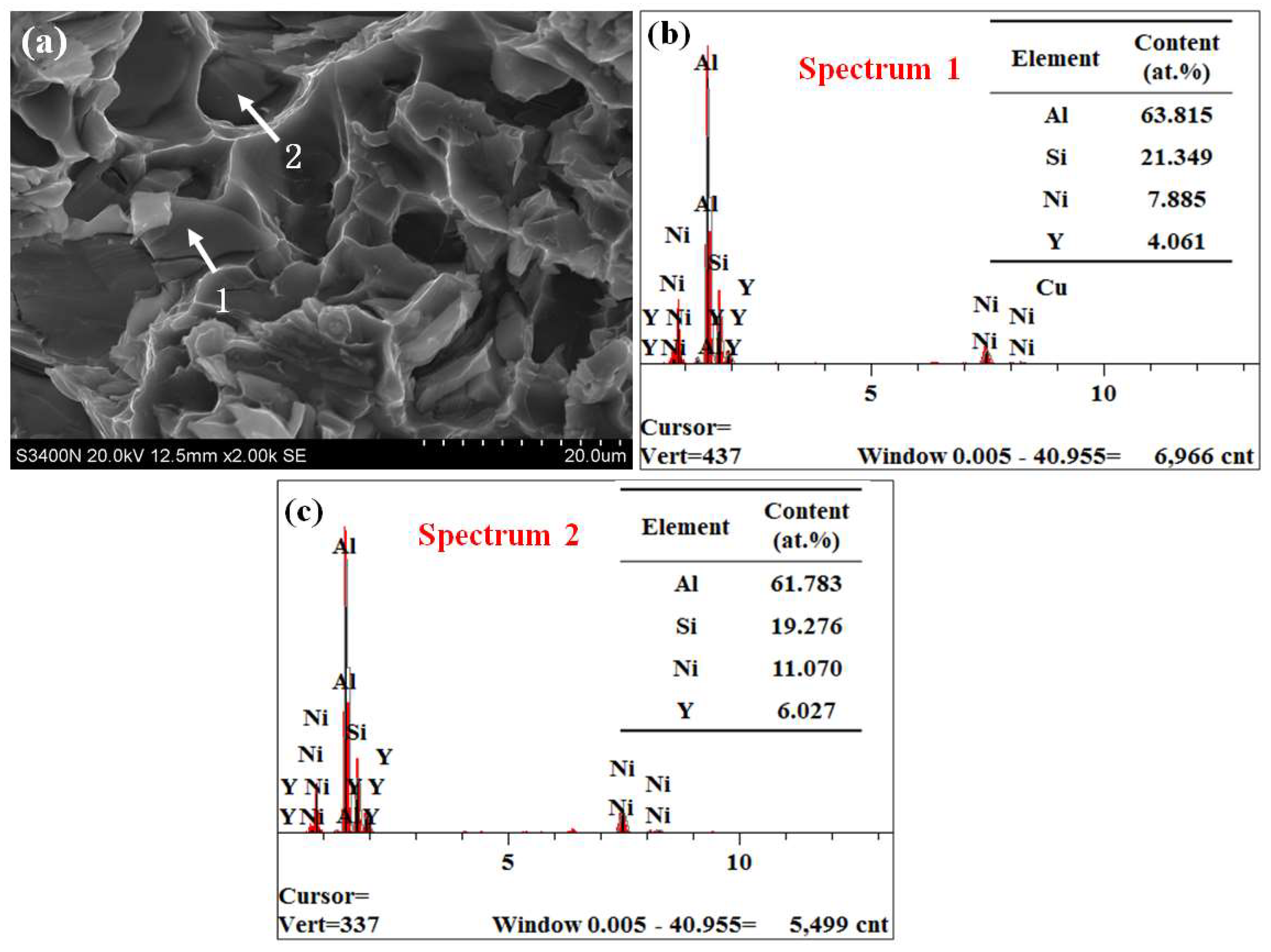
3.1. Microstructure of Alloys
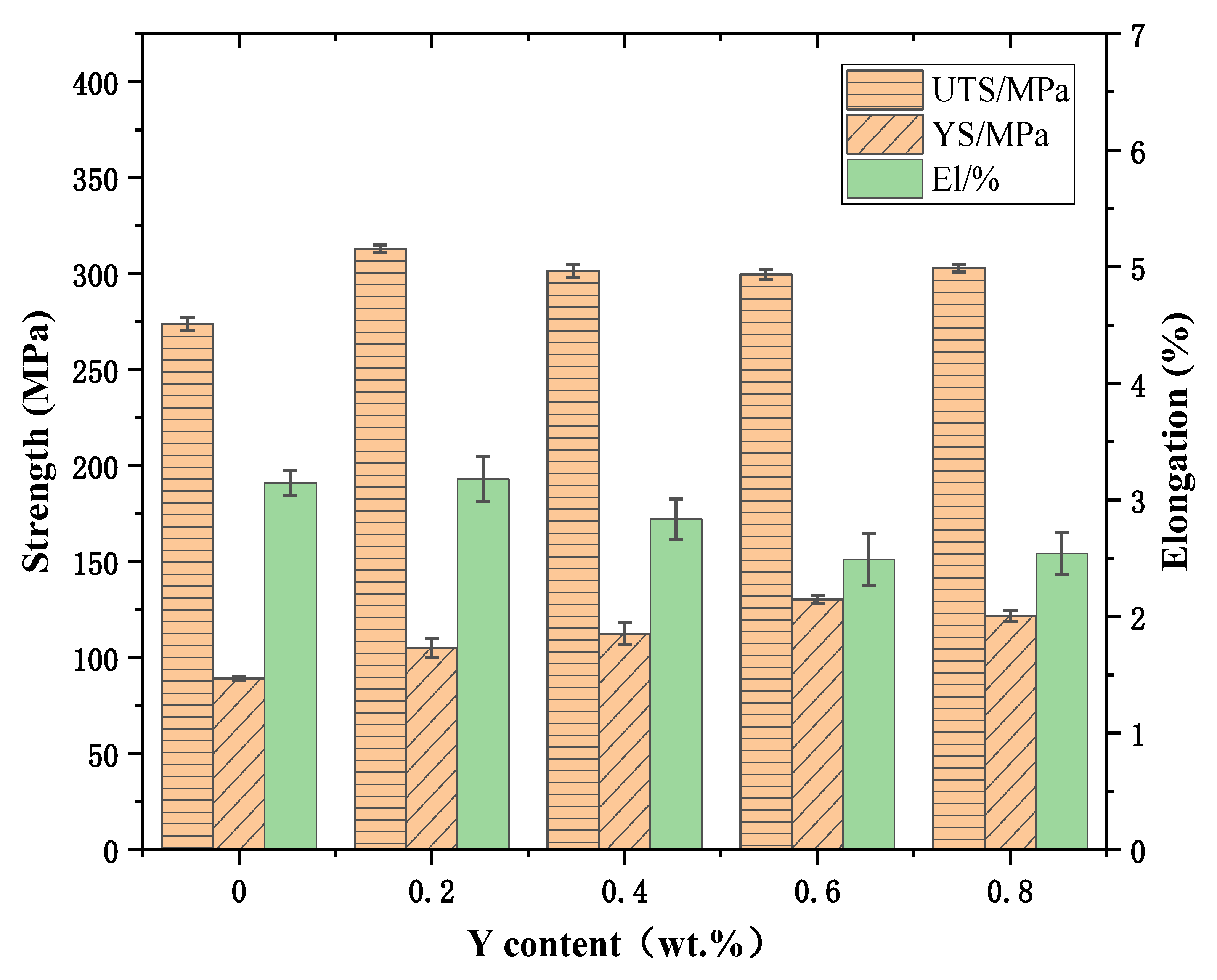
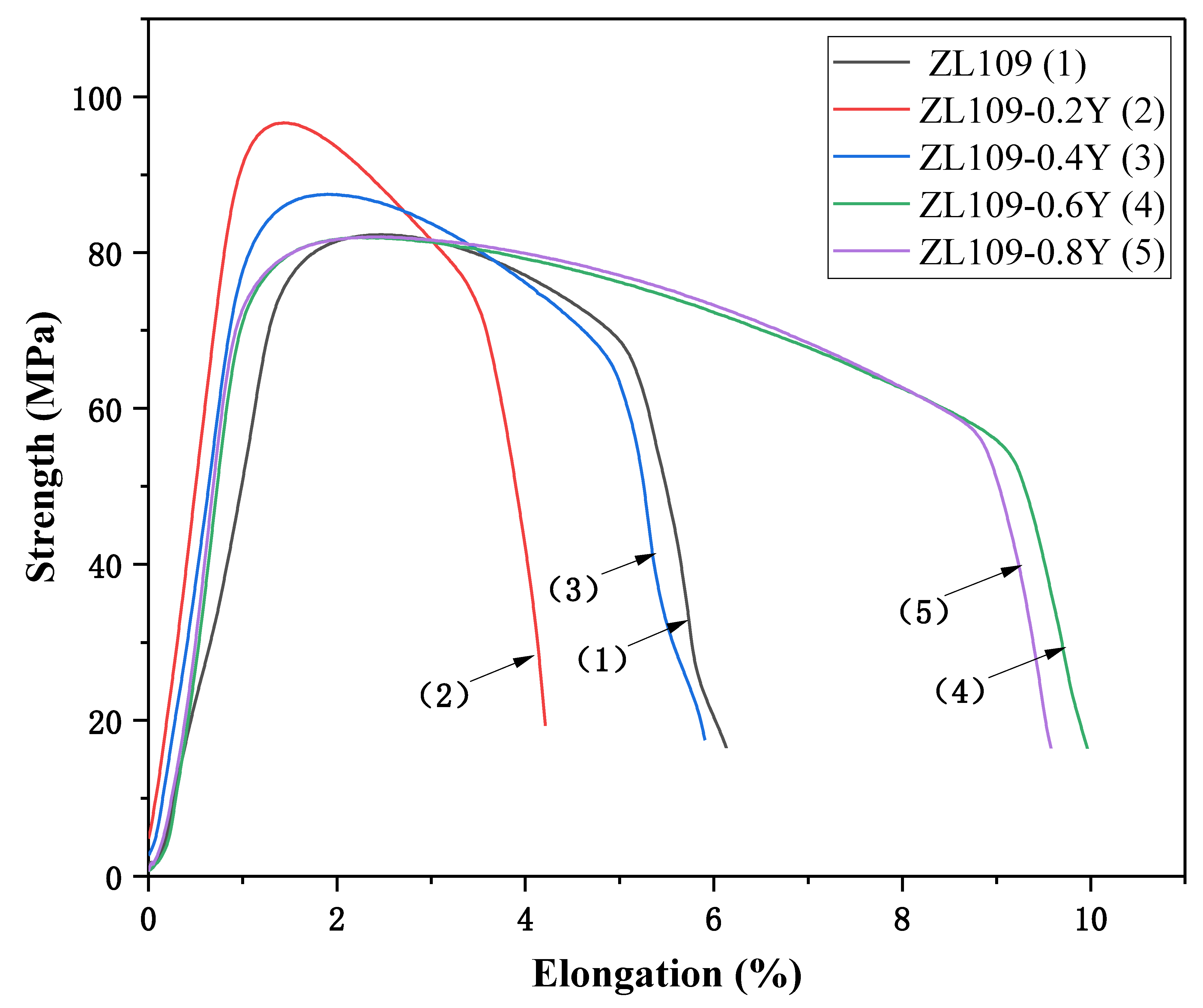
3.2. Tensile Properties of Alloys
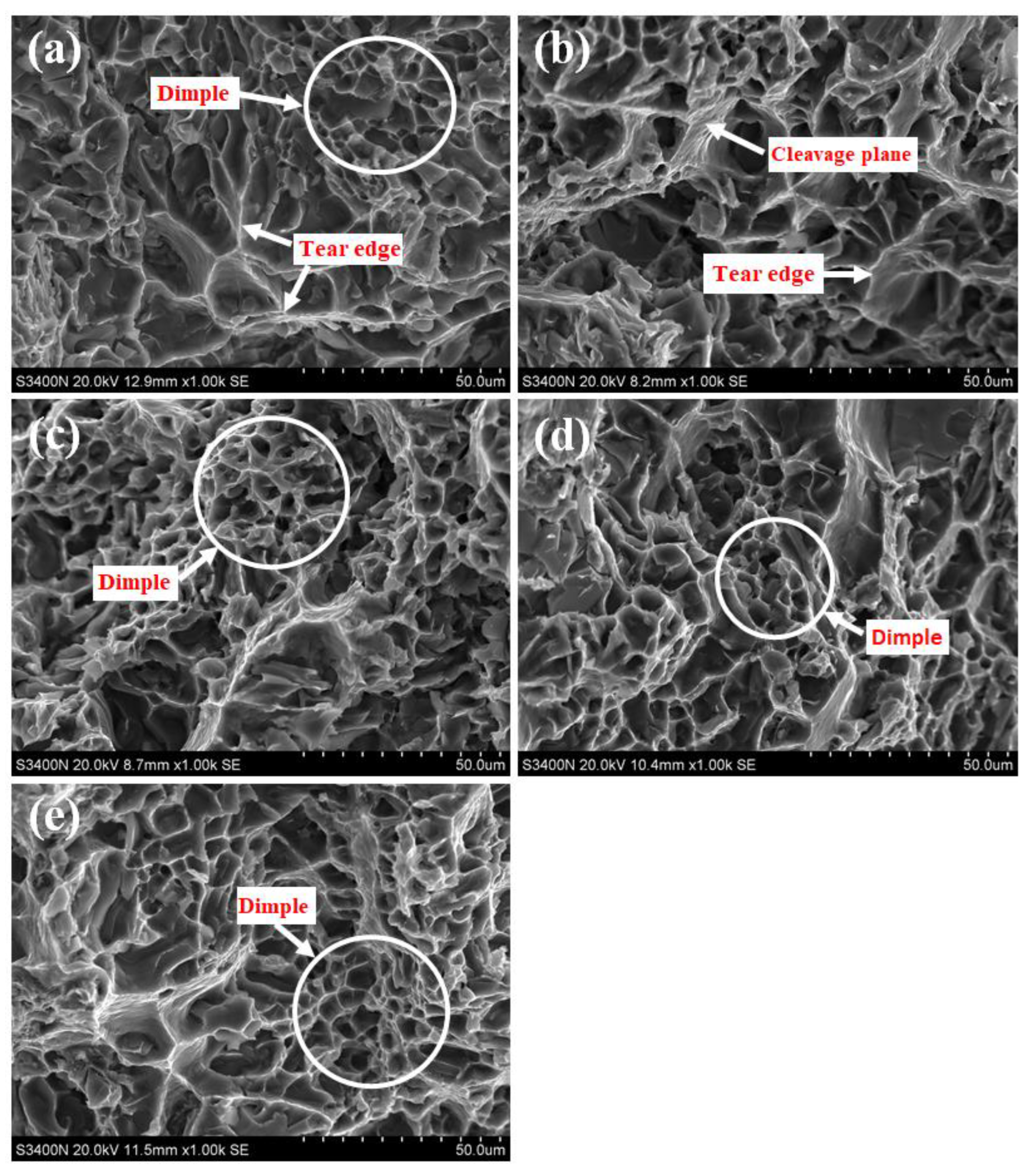
3.3. Test Results and Analysis of Tensile Properties of Alloys at High Temperature
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The strengthening phases of the ZL109-xY alloy include the eutectic Si phase, the Al3Ni phase, the Al3CuNi phase, the Al2Si2Y phase, the Mg2Si phase, and a small amount of the Al2Cu phase; moreover, the Al3Ni phase and the Al2Si2Y phase always exist simultaneously.
- (2)
- The tensile strength of the ZL109-xY alloy at room temperature and at high temperature increases first and then decreases with the increase in the Y content. When the Y content is 0.2 wt.%, the tensile strength of the alloy at room temperature is 313.08 MPa, which is 14.4% higher than that of the ZL109 alloy, and the comprehensive tensile property is better. The tensile strength and the yield strength of the ZL109-0.2Y alloy at high temperature are the highest, which are increased by 17.4% and 18.9%, respectively, compared with the ZL109 alloy. Therefore, the ZL109-0.2Y alloy has the better comprehensive mechanical properties.
- (3)
- The strengthening phase Al2Si2Y is formed by adding the Y element to the ZL109 alloy, which can inhibit dislocation and grain boundary movement. The α-Al dendrites are obviously refined and tend to become fine isometric crystals. The size of the eutectic Si decreases, and its shape is modified. The morphology and size of high temperature strengthening phases, such as Al3CuNi, are optimized. The tensile properties of the alloy are improved at both room temperature and high temperature. However, with the addition of the Y element, the Al2Si2Y phase increases, and coarsening results in decreasing the strength of the alloy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, T.X. Research Progress and Prospect of Casting Heat-resistant Aluminum Alloy. Mater. Rev. 2022, 36, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.S.; Li, A.M.; Sui, Q.P. Microstructure and High Temperature Creep Properties of ZrB2/Al-12Si Composites Prepared by in-situ Reaction Method. Mater. Rev. 2019, 12–19, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Shyam, A.; Bahl, S. Heat-resistant aluminium alloys. Nat. Mater. 2023, 22, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manasijevic, S.; Radisa, R.; Markovic, S.; Acimovic-Pavlovic, Z.; Raic, K. Thermal Analysis and Microscopic Characterization of the Piston Alloy AlSi13Cu4Ni2Mg. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H. Progress of Application of Aluminum Alloy in automobile. Automot. Ind. Res. 2003, 3, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, Y.D.; Wang, Q.D. Application Research and Development of cast Heat-resistant Aluminum Alloy in Engine. Mater. Rev. 2015, 29, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, D.S.; Wang, H.X.; Zheng, L.Q.; Dong, G.J. Research Progress of casting, Quick-setting and Additive Heat-resistant Aluminum Alloys. Chin. J. Non-Ferr. Met. 2022, 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ram, S.C.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Chakrabarty, I. Microstructures and High Temperature Mechanical Properties of A356-Mg2Si Functionally Graded Composites in as-cast and Artificially aged (T6) Conditions. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 805, 454–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Ye, B.; Feng, J.; Zhang, H.; Kong, X.; Jiang, H. Effect of ε-Al3Ni Phase on Mechanical Properties of Al-Si-Cu-Mg-Ni Alloys at Elevated Temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 772, 138794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhao, D.; Liu, X. Effect of Existing Form of Alloying Elements on the Microhardness of Al-Si-Cu-Ni-Mg Piston Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 528, 5723–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jia, L.; Wang, W.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, H. Effects of Ni Content on Microstructure and Wear Behavior of Al-13Si-3Cu-1Mg-xNi-0.6Fe-0.6Mn Alloys. Wear 2022, 500, 204365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Manojit, G.; Gyan, S. On the Role of Precipitates in Controlling Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ag and Sn Added 7075 Alloys During Artificial Ageing. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 738, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Liu, X.F.; Zhao, D.G.; Zhang, G.H. Effects of Trace Mn Addition on the Elevated Temperature Tensile Strength and Microstructure of a Low-Iron Al–Si Piston Alloy. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 2146–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, N.; Cui, X.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Lu, K. On the Microstructures and Properties of a Zr-modified Al-Si-Cu-Mg alloy at Intermediate Temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 178328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadi, D.; Rao, A.P.; Mahfoud, M. Influence of Scandium on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of A319 Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 527, 6123–6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, A.M.; Qin, X.D.; Yang, H.L.; Cheng, P. Effect of La on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Al-5.4Cu-0.7Mg-0.6Ag Alloys. Materials 2024, 17, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Li, A.M.; Rao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zuo, T.; Hu, Y. Effect of Rare Earth Y and Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of 6016 Aluminum Alloy. Mater. Rev. 2002, 36, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, Y.; Pei, R.; Feng, X.; Xia, T.; Liu, D. Effect of Scandium Addition on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of as-cast Al-5%Cu alloys. Vacuum 2020, 177, 109385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; Li, B.Q.; Zhu, Y.Q. Modification of multi-component Al-Si Castingpiston Alloys by Adding of Rare Earth Yttrium. Microsc. Microanal. 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.R.; Yan, Z.J.; Xiong, W.; Yan, L. Study on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of ZL107 Alloy Added with Yttrium. J. Rare Earths 2013, 31, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.Y.; Chen, Z.Q.; Hu, W.X. Effect of La and Y on Microstructure of Refined A356 Aluminum Alloy. Rare Earth 2020, 41, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wang, H.W.; Jie, J.C.; Wei, Z.J. Effects of Yttrium and Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Al–7.5Si–0.5Mg Alloy. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogita, K.; Yasuda, H.; Yoshiya, M. The role of trace element segregation in the eutectic modification of hypoeutectic Al-Si alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 489, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.D.; Wang, Q.D.; Wang, G.L.; Liu, T. Effects of Sr Content on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Cast Al–12Si–4Cu–2Ni–0.8 Mg Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 622, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Chen, W.; Liu, L. Effect of Trace Yttrium Addition on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Recycled Al–7Si–0.3Mg–1.0Fe Casting Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 666, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.X.; Li, Y.D.; Liu, W.J.; Yang, H.K.; Cao, Y.J.; Bi, G.L. Effect of La and Sc Co-Addition on the Mechanical Properties and Thermal Conductivity of As-Cast Al-4.8% Cu Alloys. Metals 2021, 11, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.F.; Lei, Y.S.; Yan, H.; Xu, X.; He, J. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of A356 Alloy with Yttrium Addition Processed by Hot Extrusion. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.H.; Song, M.; Chen, K.H.; Huang, B.Y. Effect of Rare Earth Yb Additionon Mechanical Properties of Al–5.3Cu–0.8Mg–0·6Ag Alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2007, 23, 1156–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Chaudhari, G.P.; Qian, M. Grain Refinement of Binary Al-Si, Al-Cu and Al-Ni Alloys by Ultrasonication. J. Mater. Proces. Technol. 2017, 249, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Villanova, J.; Lhuissier, P.; Salvo, L. In Situ Nanotomography Study of Creep Cavitiesin Al-3.6-Cu Alloy. Acta Mater. 2019, 166, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Ye, B.; Zuo, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Ding, W. Bonding of Aluminum Alloys in Compound Casting. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 4636–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhong, S.Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Ma, N.; Wang, H. Effect of Cr Content and heat-treatment on the High Temperature Strength of Eutectic Al–Si Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 647, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
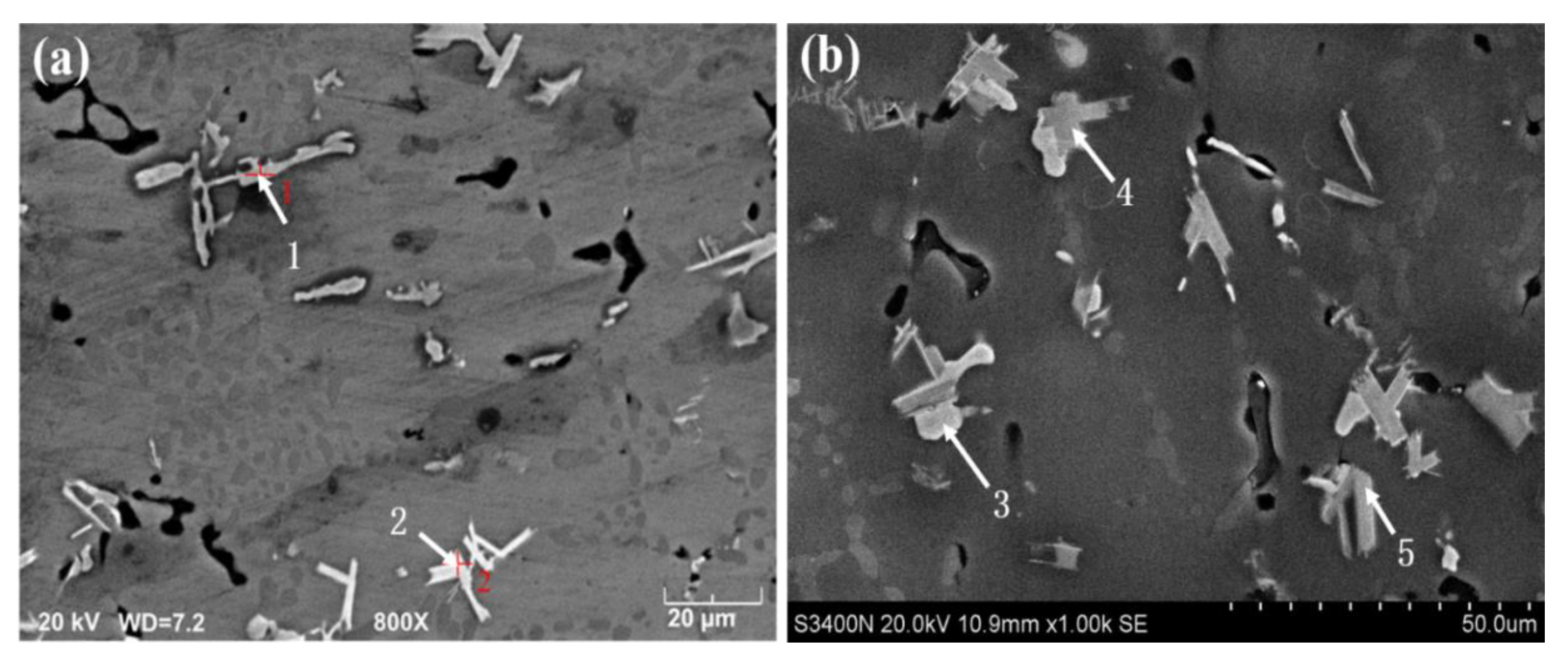



| Alloy | Si | Cu | Mg | Ni | Y | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y-free | 12 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 0 | Bal. |
| 2Y | 12 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 0.2 | Bal. |
| 4Y | 12 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 0.4 | Bal. |
| 6Y | 12 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 0.6 | Bal. |
| 8Y | 12 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 0.8 | Bal. |
| Alloy | Si | Cu | Mg | Ni | Y | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y-free | 12.13 | 1.18 | 1.22 | 1.21 | 0 | Bal. |
| 2Y | 12.25 | 1.21 | 1.19 | 1.22 | 0.21 | Bal. |
| 4Y | 11.98 | 1.23 | 1.23 | 1.18 | 0.37 | Bal. |
| 6Y | 11.93 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.23 | 0.59 | Bal. |
| 8Y | 12.07 | 1.23 | 1.18 | 1.18 | 0.78 | Bal. |
| Spot | Al | Cu | Ni | Si | Mg | Y | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 45.681 | 23.222 | 27.369 | 2.010 | 0.869 | 0.264 | Al3CuNi |
| 2 | 41.491 | 1.395 | 20.179 | 15.538 | 1.079 | 17.468 | Al3Ni, Al2Si2Y |
| 3 | 70.728 | 13.289 | 14.543 | 0.000 | 1.440 | 0.000 | Al3CuNi |
| 4 | 52.130 | 0.505 | 8.710 | 24.521 | 2.338 | 11.796 | Al3Ni, Al2Si3Y |
| 5 | 50.528 | 0.424 | 7.787 | 26.346 | 2.112 | 12.802 | Al2Si2Y |
| Y (wt.%) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 273.73 | 89.14 | 3.15 |
| 0.2 | 313.08 | 105 | 3.18 |
| 0.4 | 301.43 | 112.56 | 2.84 |
| 0.6 | 299.52 | 130.3 | 2.49 |
| 0.8 | 302.91 | 121.63 | 2.54 |
| Y (wt.%) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 82.3 | 78.71 | 5.21 |
| 0.2 | 96.65 | 93.62 | 3.66 |
| 0.4 | 87.48 | 81.34 | 5.14 |
| 0.6 | 81.94 | 75.77 | 8.76 |
| 0.8 | 82 | 77.1 | 8.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, X.; Li, A.; Li, X. Effect of Y on the Microstructures and Heat-Resistant Property of ZL109 Alloys. Crystals 2025, 15, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15010075
Qin X, Li A, Li X. Effect of Y on the Microstructures and Heat-Resistant Property of ZL109 Alloys. Crystals. 2025; 15(1):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15010075
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Xiangdu, Anmin Li, and Xiang Li. 2025. "Effect of Y on the Microstructures and Heat-Resistant Property of ZL109 Alloys" Crystals 15, no. 1: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15010075
APA StyleQin, X., Li, A., & Li, X. (2025). Effect of Y on the Microstructures and Heat-Resistant Property of ZL109 Alloys. Crystals, 15(1), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15010075





