Self-Consistent Explanation of the Untwist Alignment of Ferroelectric Nematic Liquid Crystals with Decreasing Cell Thickness and Deviation of the Surface Easy Axis Experimented upon Using the Brewster Angle Reflection Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
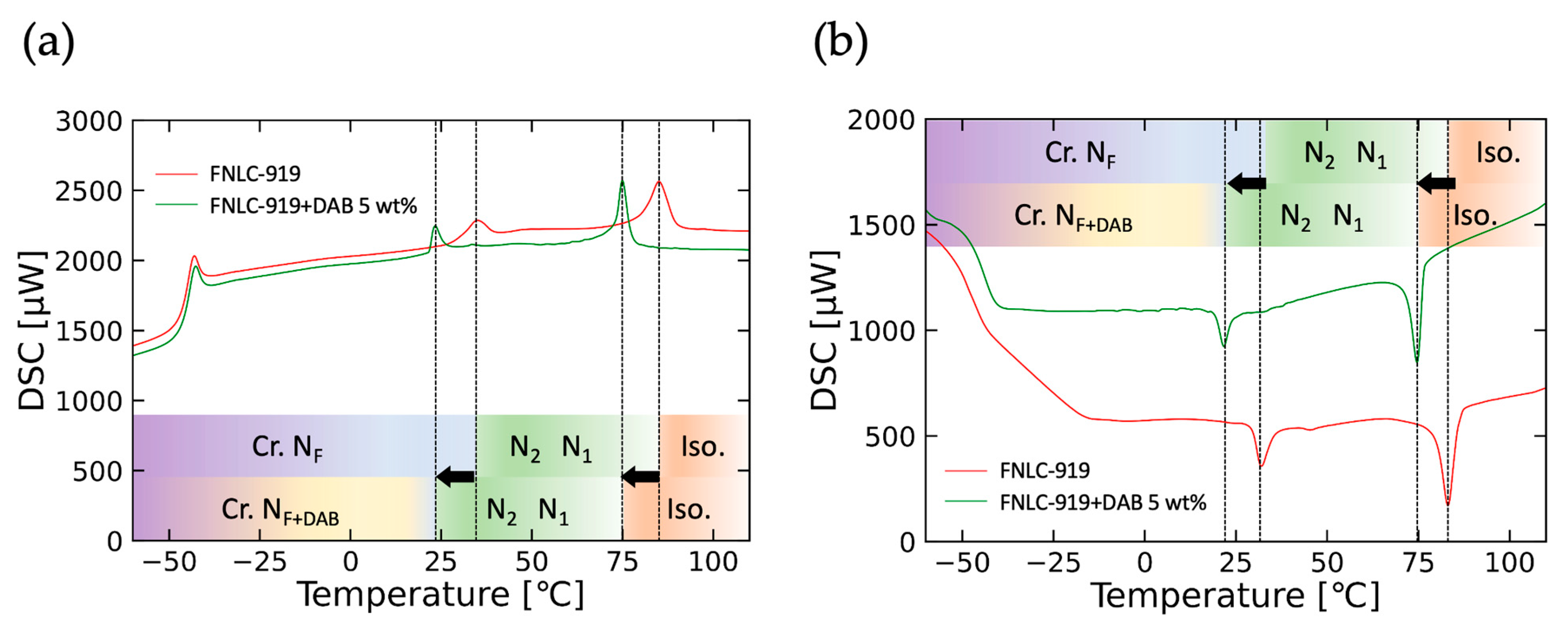
2.1. FNLC Substance and Sample Cell Praparation
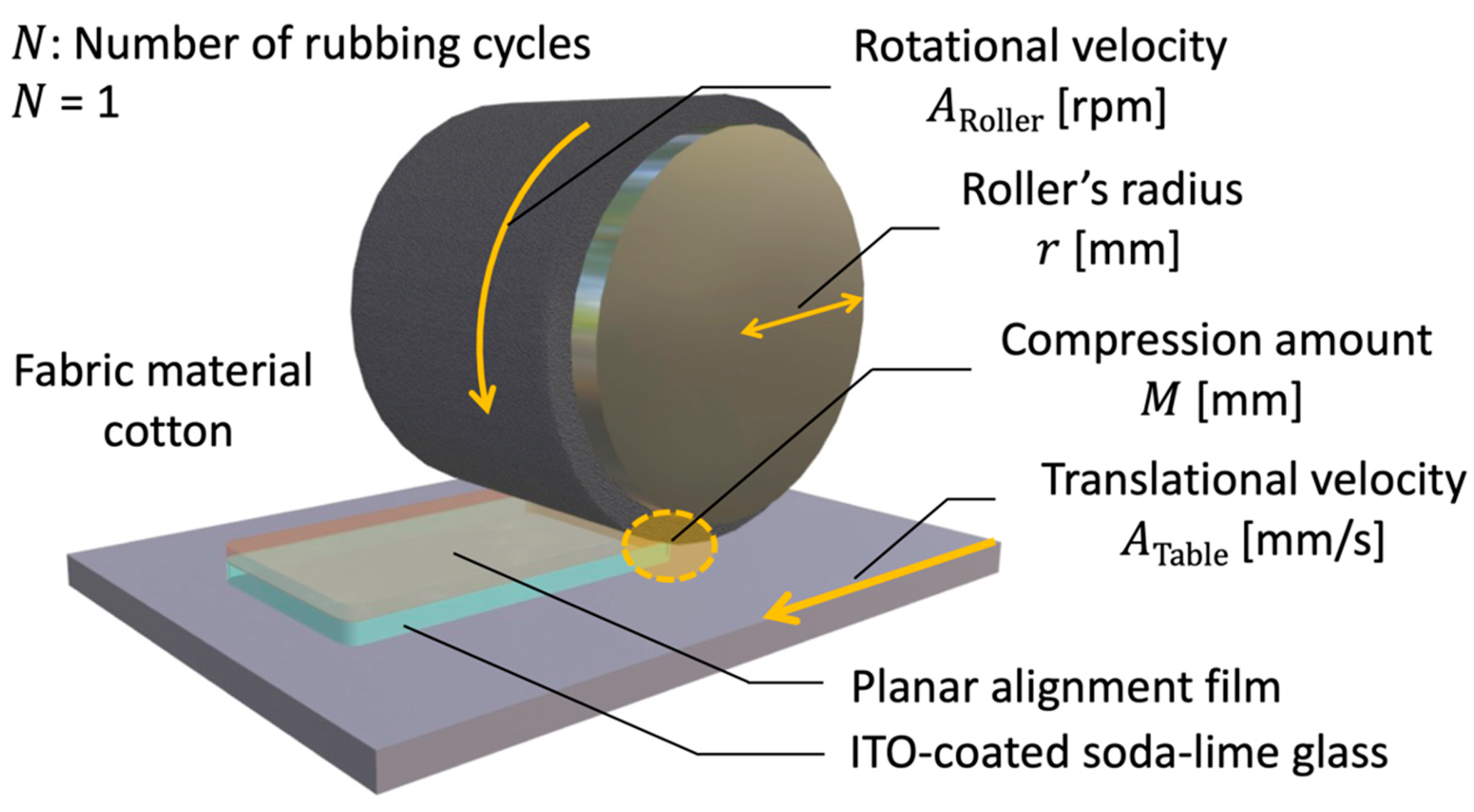
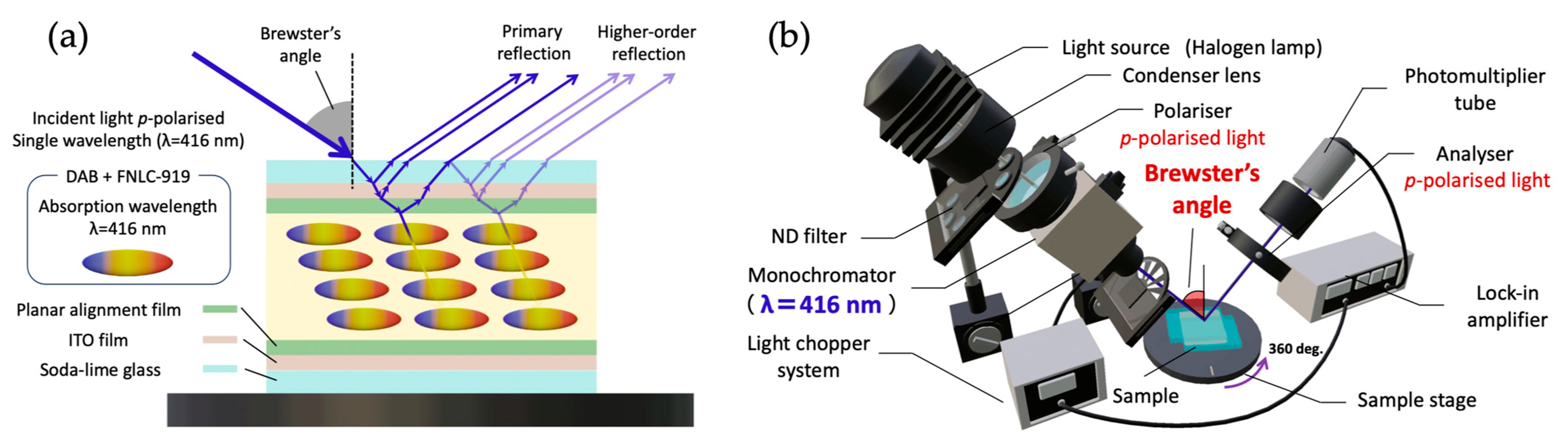
2.2. Brewster Angle Reflection (BAR) Method
3. Consideration for Twist Unwind Based on the Torque Balance Equation
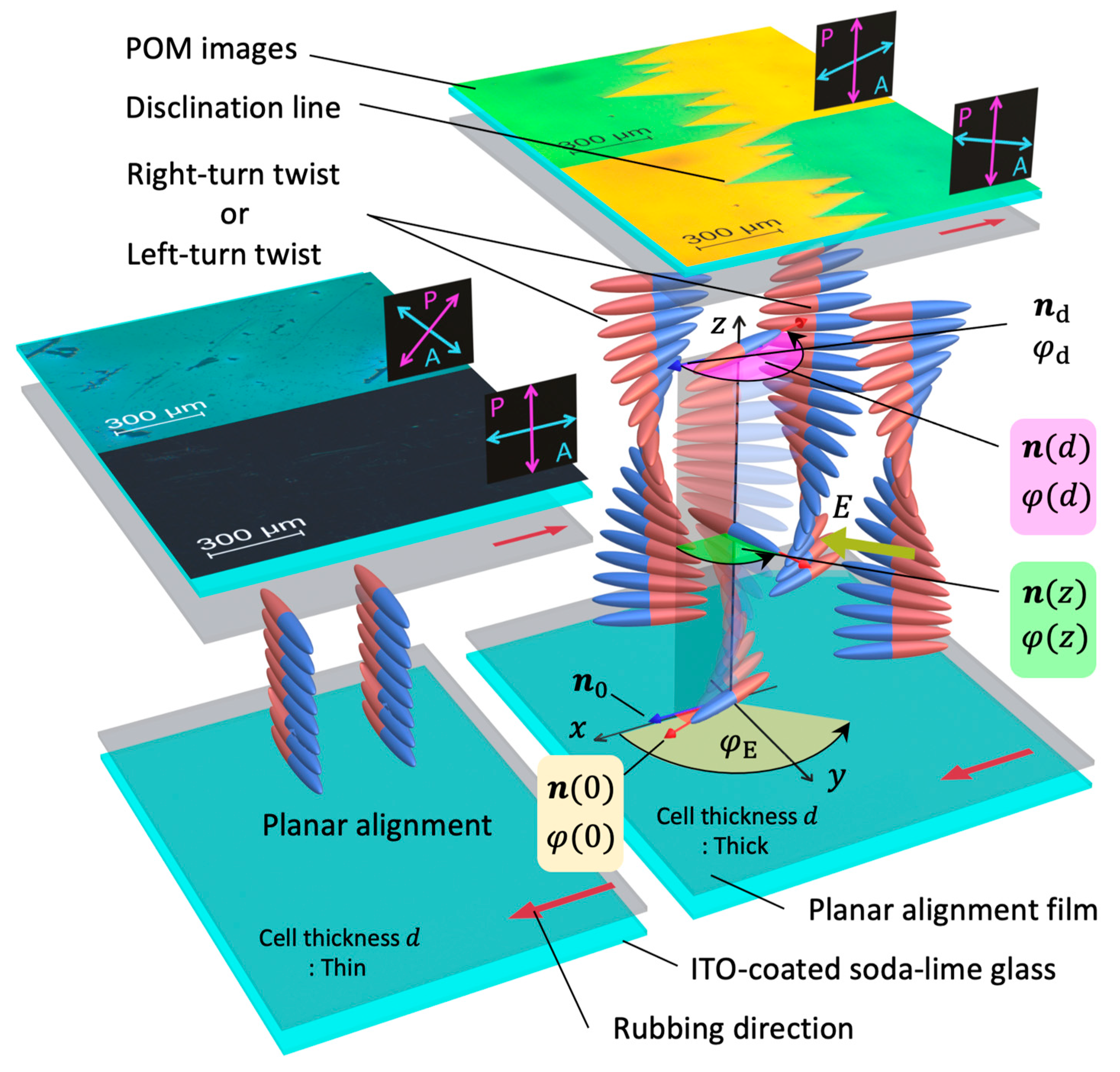
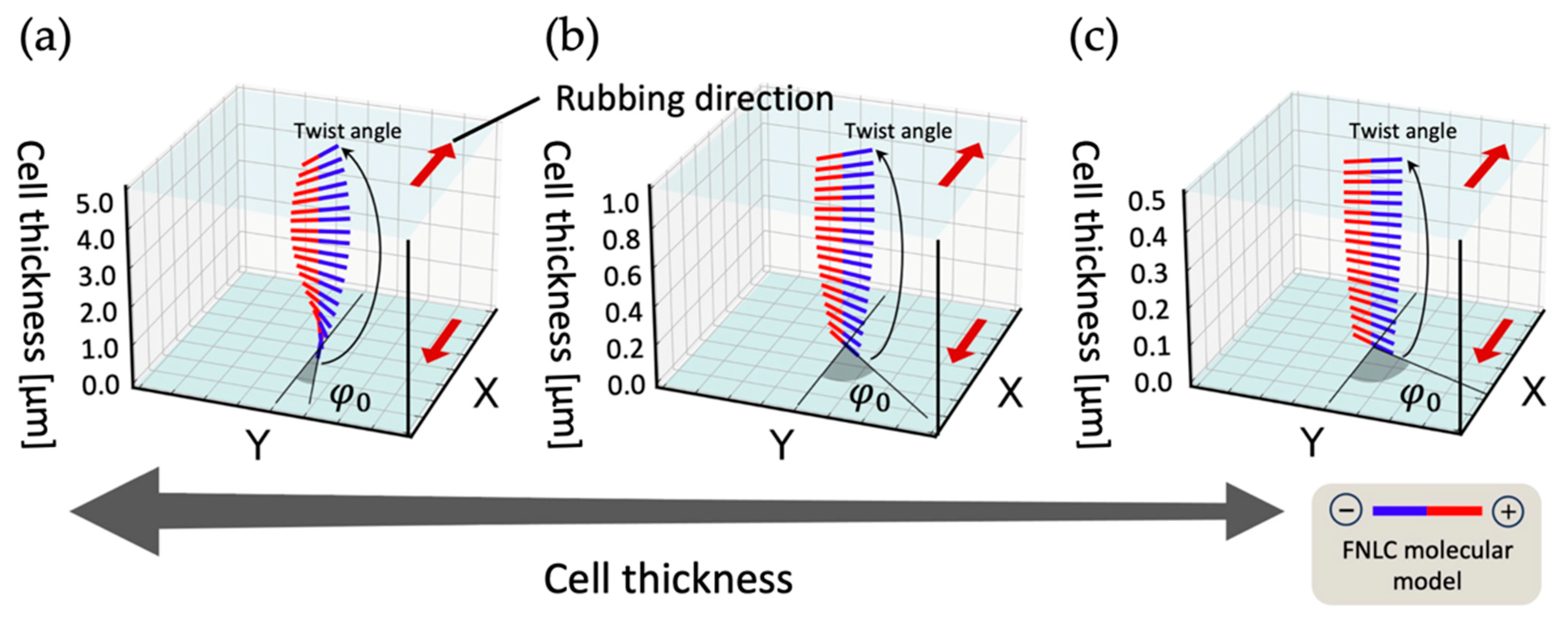
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
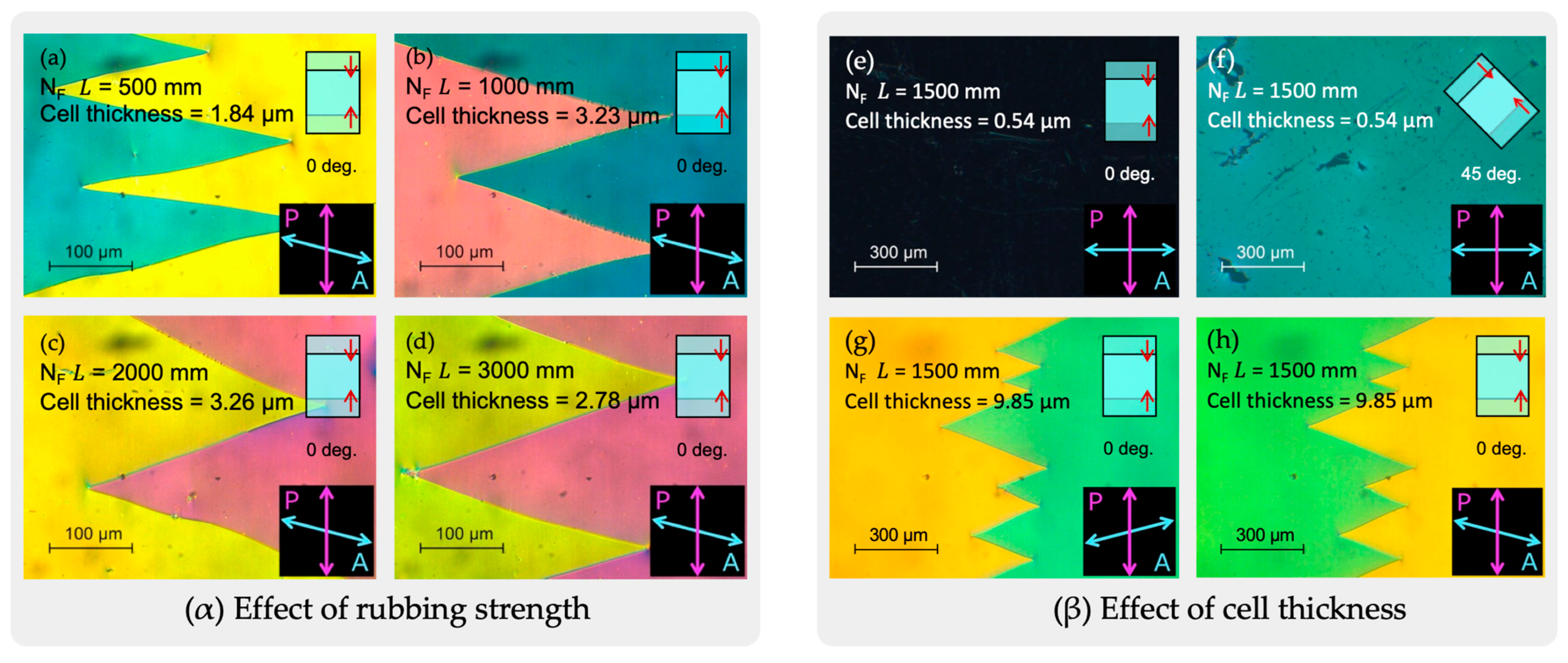
4.1. Rubbing Strength and Polar Alignment Structure
4.2. Director near the Alignment Surface (Easy Axis)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Born, M. Über anisotrope Flüssigkeiten. Versuch einer Theorie der flüssigen Kristalle und des elektrischen Kerr-Effekts in Flüssigkeiten. Sitzungsber. Preuss. Akad. Wiss. 1916, 30, 614–650. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Korblova, E.; Dong, D.; Wei, X.; Shao, R.; Radzihovsky, L.; Glaser, M.A.; Maclennan, J.E.; Bedrov, D.; Walba, D.M.; et al. First-principles experimental demonstration of ferroelectricity in a thermotropic nematic liquid crystal: Polar domains and striking electro-optics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14021–14031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Shiroshita, K.; Higuchi, H.; Okumura, Y.; Haseba, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Sago, K.; Kikuchi, H. A Fluid Liquid-Crystal Material with Highly Polar Order. Adv. Mat. 2017, 29, 1702354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandle, R.J.; Cowling, S.J.; Goodby, J.W. Rational Design of Rod-Like Liquid Crystals Exhibiting Two Nematic Phases. Chem. A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 14554–14562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandle, R.J.; Cowling, S.J.; Goodby, J.W. A nematic to nematic transformation exhibited by a rod-like liquid crystal. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 11429–11435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Nishikawa, H.; Kougo, J.; Zhou, J.; Dai, S.; Tang, W.; Zhao, X.; Hisai, Y.; Huang, M.; Aya, S. Development of ferroelectric nematic fluids with giant-ε dielectricity and nonlinear optical properties. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastián, N.; Čopič, M.; Mertelj, A. Ferroelectric nematic liquid-crystalline phases. Phys. Rev. E 2022, 106, 021001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavrentovich, O.D. Ferroelectric nematic liquid crystal, a century in waiting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14629–14631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, K.; Haputhantrige, N.; Md Sakhawat, H.H.; Md Mostafa; Adaka, A.; Mann, E.K.; Lavrentovich, O.D.; Jákli, A. Electrically Tunable Polymer Stabilized Chiral Ferroelectric Nematic Liquid Crystal Microlenses. Adv. Opt. Mat. 2023, 11, 2302500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máthé, M.T.; Perera, K.; Buka, Á.; Salamon, P.; Jákli, A. Fluid Ferroelectric Filaments. Adv. Sci. 2023, 2305950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máthé, M.T.; Himel, M.S.H.; Adaka, A.; Gleeson, J.T.; Sprunt, S.; Salamon, P.; Jákli, A. Liquid Piezoelectric Materials: Linear Electromechanical Effect in Fluid Ferroelectric Nematic Liquid Crystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 2314158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Cruickshank, E.; Storey, J.M.D.; Imrie, C.T.; Pociecha, D.; Majewska, M.; Makal, A.; Gorecka, E. Multiple Polar and Non-polar Nematic Phases. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2021, 22, 2493–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastián, N.; Mandle, R.J.; Petelin, A.; Eremin, A.; Mertelj, A. Electrooptics of mm-scale polar domains in the ferroelectric nematic phase. Liq. Cryst. 2021, 48, 2055–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caimi, F.; Nava, G.; Barboza, R.; Clark, N.A.; Korblova, E.; Walba, D.M.; Bellini, T.; Lucchetti, L. Surface alignment of ferroelectric nematic liquid crystals. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 8130–8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Korblova, E.; Glaser, M.A.; Maclennan, J.E.; Walba, D.M.; Clark, N.A. Polar in-plane surface orientation of a ferroelectric nematic liquid crystal: Polar monodomains and twisted state electro-optics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2104092118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basnet, B.; Rajabi, M.; Wang, H.; Kumari, P.; Thapa, K.; Paul, S.; Lavrentovich, M.O.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Soliton walls paired by polar surface interactions in a ferroelectric nematic liquid crystal. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-H. Alignment properties of a ferroelectric nematic liquid crystal on the rubbed substrates. Soft Matter 2023, 19, 2446–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudquist, P. Revealing the polar nature of a ferroelectric nematic by means of circular alignment. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zou, Y.; Tang, W.; Li, J.; Huang, M.; Aya, S. Spontaneous electric-polarization topology in confined ferroelectric nematics. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Basnet, B.; Wang, H.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Ferroelectric nematic liquids with conics. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerwall, S.T. Ferroelectric and Antiferroelectric Liquid Crystals; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1999; pp. 241–262. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, N.A.; Lagerwall, S.T. Submicrosecond bistable electro-optic switching in liquid crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1980, 36, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastián, N.; Lovšin, M.; Berteloot, B.; Osterman, N.; Petelin, A.; Mandle, R.J.; Aya, S.; Huang, M.; Neyts, K.; Mertelj, A. Polarization patterning in ferroelectric nematic liquids via flexoelectric coupling. Nature Commun. 2023, 14, 3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akahane, T.; Kaneko, H.; Kimura, M. Novel Method of Measuring Surface Torsional Anchoring Strength of Nematic Liquid Crystals. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 35, 4434–4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okutani, S.; Kimura, M.; Akahane, T.; Toriumi, H.; Tadokoro, T.; Akao, K. Investigation of Interfacial Liquid Crystal Orientation by Reflection Ellipsometry. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1999, 329, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T.; Hirano, M.; Sakai, H. Director orientation of a ferroelectric liquid crystal on substrates with rubbing treatment: The effect of surface anchoring strength. Liq. Cryst. 1989, 5, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Sato, K.; Uchida, T. Relationship between Rubbing Strength and Surface Anchoring of Nematic Liquid Crystal. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 31, L579–L581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Lu, C.; Ye, Y.-C. Effects of Mechanical Rubbing on Surface Tension of Polyimide Thin Films. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 1651–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Goda, K.; Kimura, M.; Akahane, T. Relationship between rubbing-induced anisotropy and surface azimuthal anchoring energy of nematic liquid crystals. J. SID 2013, 21, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryasova, N.; Reznikov, Y. Liquid crystal alignment at macroscopically isotropic polymer surfaces: Effect of an isotropic-nematic phase transition. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 94, 032702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Máthé, M.T.; Buka, Á.; Jákli, A.; Salamon, P. Ferroelectric nematic liquid crystal thermomotor. Phys. Rev. E 2022, 105, L052701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palto, S.P.; Geivandov, A.R.; Barnik, M.I.; Blinov, L.M. The New Role of Alignment Layers in Bistable Switching of Ferroelectric Liquid Crystals. Numerical Simulation and Experimental Results. Ferroelectrics 2004, 310, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselev, A.D.; Chigrinov, V.G.; Pozhidaev, E.P. Switching Dynamics of Surface Stabilized Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal Cells: Effects of Anchoring Energy Asymmetry. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75, 61706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Pan, W.; Luo, B.; Zhang, W.; Zou, X. Improved Equivalent Circuit Model for V-Shaped, Thresholdless Switching Ferroelectric Liquid Crystals. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.D.; Shampine, L.F. A collocation method for boundary value problems. Numer. Math. 1972, 19, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abe, S.; Shibata, Y.; Kimura, M.; Akahane, T. Self-Consistent Explanation of the Untwist Alignment of Ferroelectric Nematic Liquid Crystals with Decreasing Cell Thickness and Deviation of the Surface Easy Axis Experimented upon Using the Brewster Angle Reflection Method. Crystals 2024, 14, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14020157
Abe S, Shibata Y, Kimura M, Akahane T. Self-Consistent Explanation of the Untwist Alignment of Ferroelectric Nematic Liquid Crystals with Decreasing Cell Thickness and Deviation of the Surface Easy Axis Experimented upon Using the Brewster Angle Reflection Method. Crystals. 2024; 14(2):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14020157
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbe, Sakunosuke, Yosei Shibata, Munehiro Kimura, and Tadashi Akahane. 2024. "Self-Consistent Explanation of the Untwist Alignment of Ferroelectric Nematic Liquid Crystals with Decreasing Cell Thickness and Deviation of the Surface Easy Axis Experimented upon Using the Brewster Angle Reflection Method" Crystals 14, no. 2: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14020157
APA StyleAbe, S., Shibata, Y., Kimura, M., & Akahane, T. (2024). Self-Consistent Explanation of the Untwist Alignment of Ferroelectric Nematic Liquid Crystals with Decreasing Cell Thickness and Deviation of the Surface Easy Axis Experimented upon Using the Brewster Angle Reflection Method. Crystals, 14(2), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14020157






