Mechanical Properties and Mineral Characteristics of Multi-Source Coal-Based Solid Waste Filling Materials under Different Proportioning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Raw Materials and Experimental Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.1.1. Coal-Based Solid Waste
- Desulfurized gypsum (DG)
- Fly ash (FA)
- Coal gangue (CG)
2.1.2. Portland Cement (PC)
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Mix Proportions
2.2.2. Preparation and Curing
2.2.3. Mechanical Properties
- Compressive strength
- Consistency and setting time
2.2.4. Micro-Morphological Testing
- XRD analysis
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. Macro Experimental Analyses
3.1.1. Compressive Strength Analysis
- Effect of Portland cement on compressive strength
- Effect of DG dosage on compressive strength
- Effect of FA dosage on compressive strength
- Effect of both DG and FA on compressive strength
3.1.2. Hydration and Setting
- Setting time of PC specimen
- Effect of DG dosage on setting time
- Effect of FA dosage on setting time
- Effect of both DG and FA on hydration reaction
3.2. Micro Experiment Analysis
XRD Analysis
- XRD analysis of raw materials
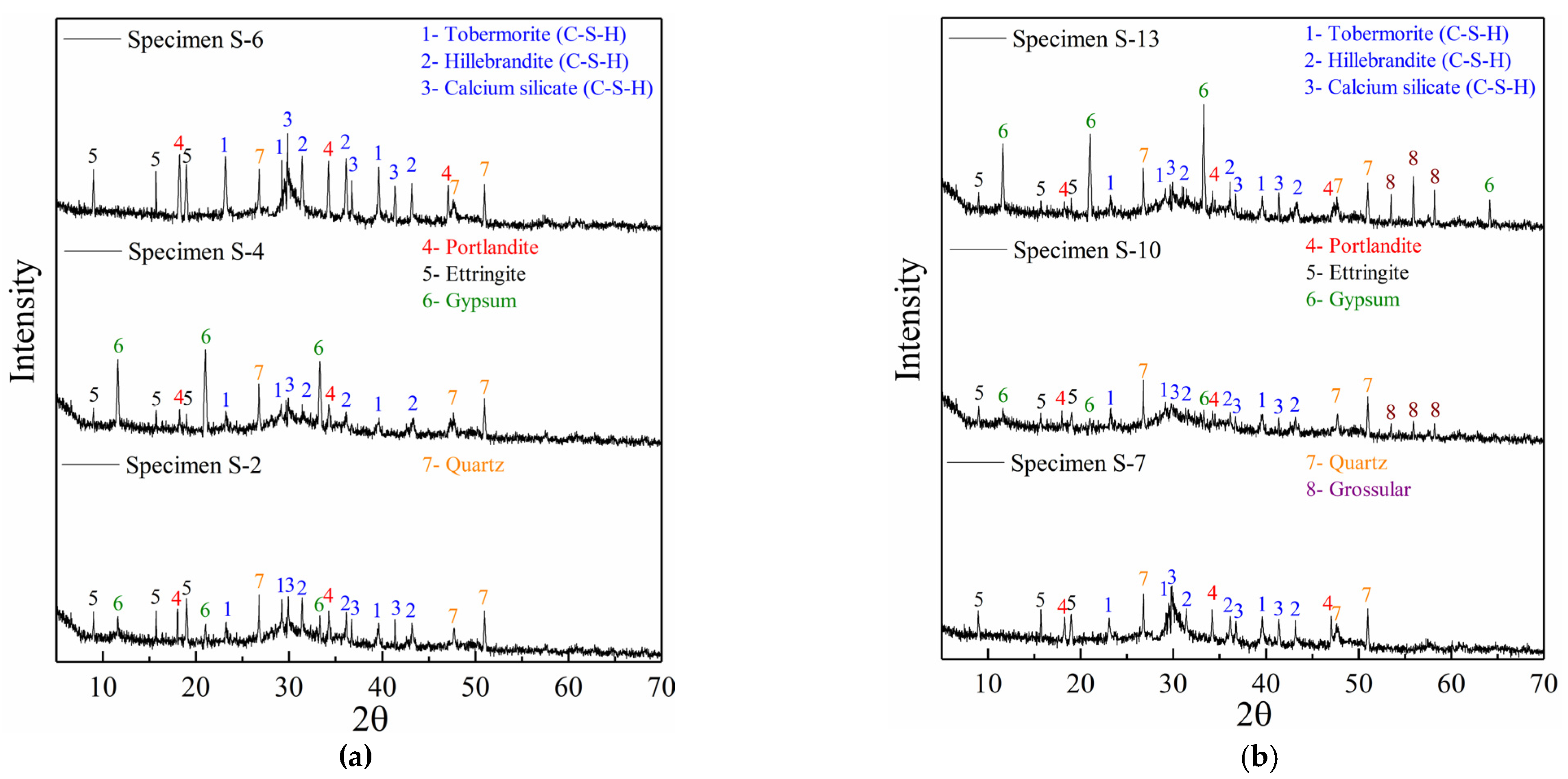
- XRD analysis of DG-incorporated pastes
- XRD analysis of FA-incorporated pastes
- XRD analysis of pastes containing both DG and FA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, K.; Zhao, X.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, J. Development overview of paste backfill technology in China’s coal mines: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 67957–67969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, G.; Qi, T.; Guo, Y.; Du, X. Evaluation of static segregation of cemented gangue-fly ash backfill material using electrical resistivity method. Measurement 2020, 154, 107483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Gao, X.; Feng, G.; Bai, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wang, H.; Du, X. Effect of biomass power plant ash on fresh properties of cemented coal gangue backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 340, 127853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Yang, K.; Sun, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zuo, L.; Feng, Y.; Qian, R.; Qi, Y.; Ji, Y.; et al. Influence of NaOH content on the alkali conversion mechanism in MSWI bottom ash alkali-activated mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 248, 118582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wang, H. Experimental investigation on some performance of rubber fiber modified cemented paste backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 271, 121586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shi, X.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Z.; Huang, P. Determination of mechanical, flowability, and microstructural properties of cemented tailings backfill containing rice straw. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Qi, T.Y.; Feng, G.R.; Wen, X.Z.; Wang, Z.H.; Shi, X.D.; Du, X.J. Effect of partial substitution of corn straw fly ash for fly ash as supplementary cementitious material on the mechanical properties of cemented coal gangue backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 280, 122553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, X.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; Wei, M.; Ke, Y.; Luo, Z. Mechanical properties of cemented tailings backfill containing alkalized rice straw of various lengths. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, B.; Li, M.; Jin, L.; Gong, J. The Effect of Slag on the Mechanical Properties of Coralline-Activated Materials and the Formation and Transformation of Mineral Crystals. Crystals 2022, 12, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Zhu, W.; Yan, B.; Guan, K.; Du, J. Influence of binder content on temperature and internal strain evolution of early age cemented tailings backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 189, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Luan, X.; Cheng, K.; Guan, X.; Yang, M.; Xiao, Z. Study on the modification effect and mechanism of tailings powder on coal gangue-based mining cementitious filling material. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 46038–46057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Qi, T.; Gao, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z. Influence of the use of corn straw fibers to connect the interfacial transition zone with the mechanical properties of cemented coal gangue backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yang, K.; He, X.; Zhang, J.; Hu, G. Experimental Study on the Optimization of Coal-Based Solid Waste Filling Slurry Ratio Based on the Response Surface Method. Materials 2022, 15, 5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, G. Experimental study of microorganism-induced calcium carbonate precipitation to solidify coal gangue as backfill materials: Mechanical properties and microstructure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 45774–45782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Cheng, K.; Zhang, R.; Gao, Y.; Guan, X. Study on the influence mechanism of activated coal gangue powder on the properties of filling body. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Li, D.; Cui, Y.; Feng, J.; Gao, Q.; Lu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J. Compressive Strength Enhancement in Early Age Acid Activated Mortars: Mechanical Properties and Analysis. Crystals 2022, 12, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, D.; Wang, B. Effect of Sodium Hydroxide, Liquid Sodium Silicate, Calcium Hydroxide, and Slag on the Mechanical Properties and Mineral Crystal Structure Evolution of Polymer Materials. Crystals 2021, 11, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z. Road base materials prepared by multi-industrial solid wastes in China: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 373, 130860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.K.; Poater, A. Review on the Use of Heavy Metal Deposits from Water Treatment Waste towards Catalytic Chemical Syntheses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Huang, G.; Wang, B.; Cui, Y.; Chang, B.; Yin, Q.; Ge, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Feng, J. Mechanical Properties and Coagulation Characteristics of Flue Gas Desulfurization Gypsum-Based Polymer Materials. Polymers 2022, 14, 4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T1596-2017; Fly Ash Used for Cement and Concrete. AQSIQ: Beijing, China, 2017.
- GB/T 175-2020; Common Portland Cement. AQSIQ: Beijing, China, 2020.
- GB/T 50107-2010; Standard for Evaluation of Concrete Compressive Strength. AQSIQ: Beijing, China, 2010.
- GB/T 1346-2011; Test Methods for Water Requirement of Normal Consistency, Setting Time and Soundness of the Portland Cement. AQSIQ: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Li, F.; Pang, Z. Investigation of hydraulic-mechanical properties of paste backfill containing coal gangue-fly ash and its application in an underground coal mine. Energies 2017, 10, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, T.; Feng, G.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y. Effects of fine gangue on strength, resistivity, and microscopic properties of cemented coal gangue backfill for coal mining. Shock. Vib. 2015, 2015, 752678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, Q.-J.; Sun, W.; Guan, C.-P.; Yu, W.-J.; Zhu, X.-N.; Khoso, S.A.; Wang, P.; Peng, W.-Q. Promotion of conversion activity of flue gas desulfurization gypsum into α-hemihydrate gypsum by calcination-hydration treatment. J. Cent. South Univ. 2019, 26, 3213–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, Y.; Tang, J.; Yang, L. Effect of Flue Gas Desulfurization Gypsum on the Properties of Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement Blended with Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag. Materials 2021, 14, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, W.; Jiao, F.; Qin, W.; Yang, C. Production and resource utilization of flue gas desulfurized gypsum in China—A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Li, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, N.; Chu, H. Utilization of flue gas desulfurization gypsum as an activation agent for high-volume slag concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 205, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sithole, T.; Mashifana, T.; Mahlangu, D.; Tchadjie, L. Physical, Chemical and Geotechnical Characterization of Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization Gypsum and Its Potential Application as Building Materials. Buildings 2021, 11, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X. Influence of Calcined Flue Gas Desulfurization Gypsum and Calcium Aluminate on the Strength and AFt Evolution of Fly Ash Blended Concrete under Steam Curing. Materials 2021, 14, 7171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, S.; Yang, X.; Gao, W.; Li, B.; Gao, X.; Huang, W.; Tan, H.; Lei, Y. Study on performance and function mechanisms of whisker modified flue gas desulfurization (FGD) gypsum. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 301, 124341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; He, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J. Hydration heat of slag or fly ash in the composite binder at different temperatures. Thermochim. Acta 2017, 655, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Zhao, Q.; Shi, X. Quantification of the reaction degree of fly ash in blended cement systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 167, 107121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Alrefaei, Y.; Dai, J.-G. Influence of coal fly ash on the early performance enhancement and formation mechanisms of silico-aluminophosphate geopolymer. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 127, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, H.; Li, L. A review: The comparison between alkali-activated slag (Si + Ca) and metakaolin (Si + Al) cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nied, D.; Enemark-Rasmussen, K.; L’Hopital, E.; Skibsted, J.; Lothenbach, B. Properties of magnesium silicate hydrates (M-S-H). Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 79, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanton, S.W.; Heath, T.G.; Clacher, A. Leaching behaviour of low Ca:Si ratio CaO–SiO2–H2O systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 88, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillahua, M.C.; Moura, F.J. Technical feasibility for use of FGD gypsum as an additive setting time retarder for Portland cement. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2018, 7, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Zhang, S.; Banthia, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Interpreting the early-age reaction process of alkali-activated slag by using combined embedded ultrasonic measurement, thermal analysis, XRD, FTIR and SEM. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 186, 107840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Yuan, L.; Ji, Y.; Liu, B.; Xu, Z. Cooperative action and compatibility between Portland cement and MSWI bottom ash alkali-activated double gel system materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Ji, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, B. Effect of activated silica on polymerization mechanism and strength development of MSWI bottom ash alkali-activated mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


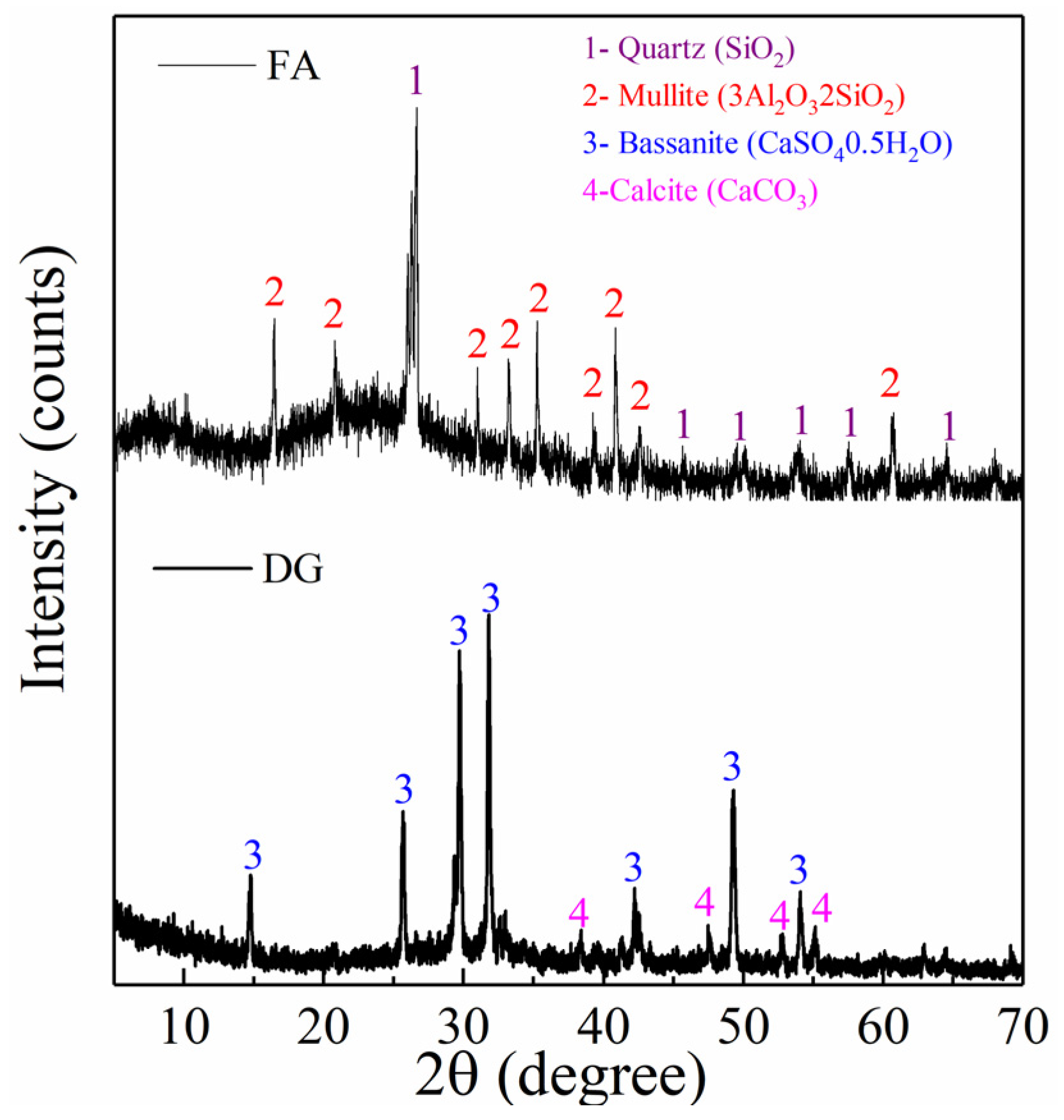
| Raw Material | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | Na2O | K2O | SO3 | Others | Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DG | 4.36 | 1.65 | 0.89 | 32.45 | 1.24 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 39.32 | 0.82 | 18.52 |
| FA | 55.24 | 31.35 | 4.85 | 2.07 | 1.13 | 0.84 | 0.25 | - | 1.82 | 1.73 |
| CG | 59.26 | 20.25 | 5.37 | 1.94 | 1.05 | 0.25 | 2.37 | - | 0.36 | 8.33 |
| PC | 22.97 | 8.89 | 3.78 | 56.34 | 2.43 | 0.34 | 1.48 | - | 1.18 | 1.85 |
| PC | DG | FA | Water | Liquid–Solid Ratio | CG Fine Aggregate | CG Coarse Aggregate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-1 | 300 | 0 | 0 | 180 | 0.6 | 600 | 1200 |
| S-2 | 240 | 60 | 0 | 180 | 0.6 | 600 | 1200 |
| S-3 | 180 | 120 | 0 | 180 | 0.6 | 600 | 1200 |
| S-4 | 120 | 180 | 0 | 180 | 0.6 | 600 | 1200 |
| S-5 | 60 | 240 | 0 | 180 | 0.6 | 600 | 1200 |
| S-6 | 240 | 0 | 60 | 180 | 0.6 | 600 | 1200 |
| S-7 | 180 | 0 | 120 | 180 | 0.6 | 600 | 1200 |
| S-8 | 120 | 0 | 180 | 180 | 0.6 | 600 | 1200 |
| S-9 | 60 | 0 | 240 | 180 | 0.6 | 600 | 1200 |
| S-10 | 240 | 30 | 30 | 180 | 0.6 | 600 | 1200 |
| S-11 | 180 | 60 | 60 | 180 | 0.6 | 600 | 1200 |
| S-12 | 120 | 120 | 60 | 180 | 0.6 | 600 | 1200 |
| S-13 | 60 | 180 | 60 | 180 | 0.6 | 600 | 1200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, G.; Zheng, X.; Gao, M.; Chen, Q.; Qiao, Z.; Xie, T.; Deng, M.; Wei, Q. Mechanical Properties and Mineral Characteristics of Multi-Source Coal-Based Solid Waste Filling Materials under Different Proportioning. Crystals 2023, 13, 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13070997
Huang G, Zheng X, Gao M, Chen Q, Qiao Z, Xie T, Deng M, Wei Q. Mechanical Properties and Mineral Characteristics of Multi-Source Coal-Based Solid Waste Filling Materials under Different Proportioning. Crystals. 2023; 13(7):997. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13070997
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Guodong, Xiaojun Zheng, Miao Gao, Qi Chen, Zheng Qiao, Tianbao Xie, Mengyao Deng, and Qing Wei. 2023. "Mechanical Properties and Mineral Characteristics of Multi-Source Coal-Based Solid Waste Filling Materials under Different Proportioning" Crystals 13, no. 7: 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13070997
APA StyleHuang, G., Zheng, X., Gao, M., Chen, Q., Qiao, Z., Xie, T., Deng, M., & Wei, Q. (2023). Mechanical Properties and Mineral Characteristics of Multi-Source Coal-Based Solid Waste Filling Materials under Different Proportioning. Crystals, 13(7), 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13070997






