Synthesis, Structural and Magnetic Characterization of Superparamagnetic Ni0.3Zn0.7Cr2−xFexO4 Oxides Obtained by Sol-Gel Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation Method
2.2. Measurements and Characterizations
3. Results
3.1. Structural Analyses
3.2. Mössbauer Spectrometry
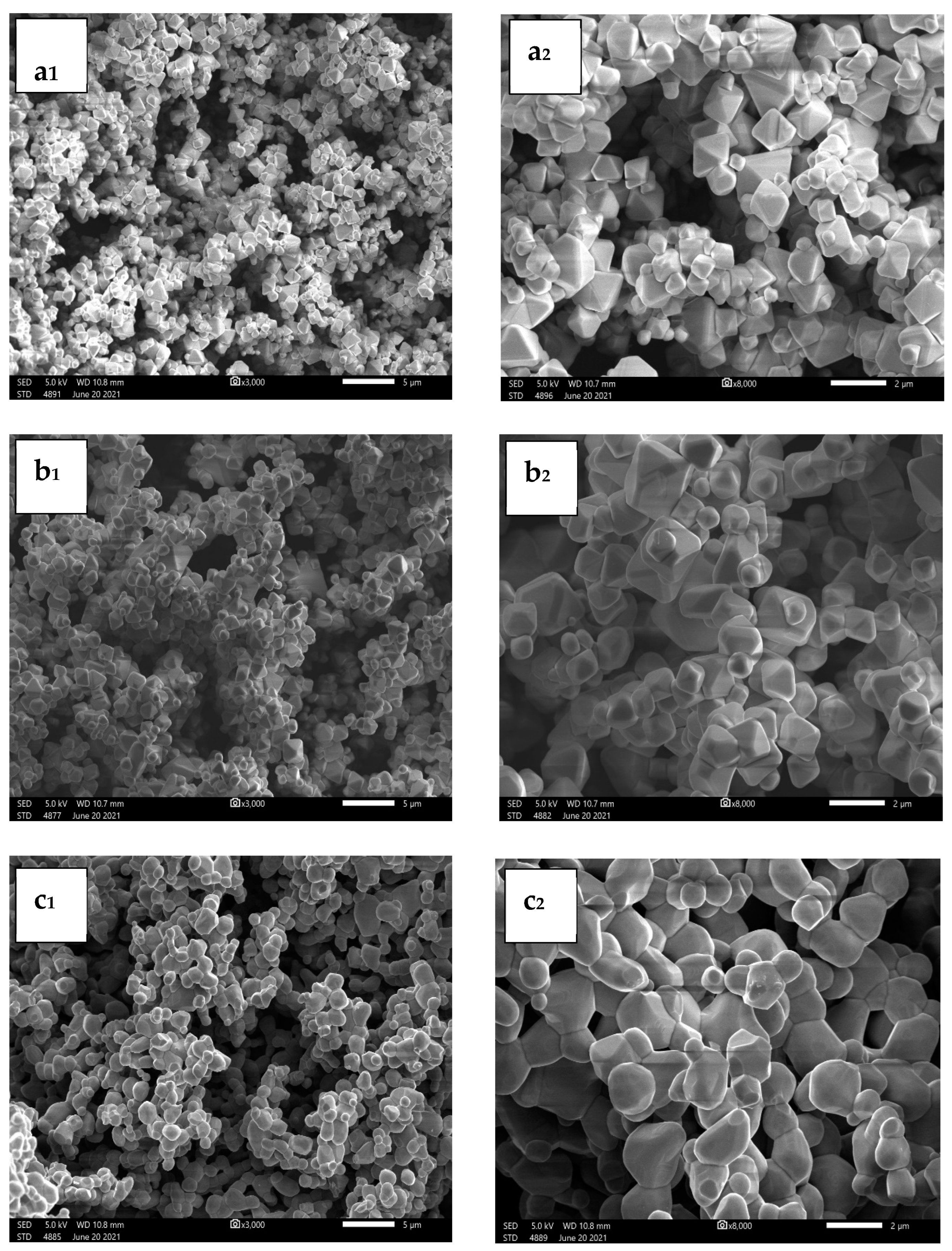
3.3. Morphological Study
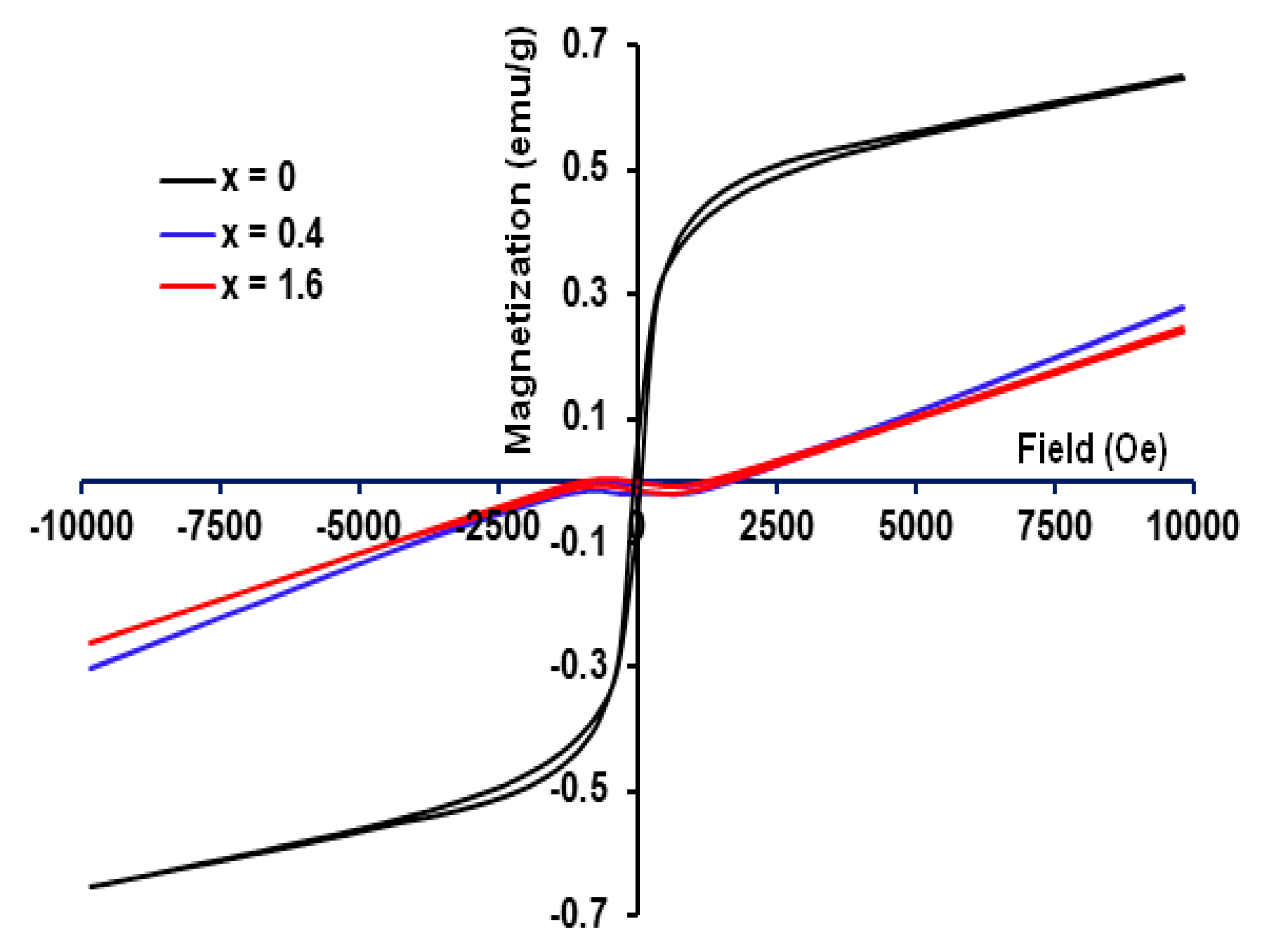
3.4. Magnetic Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandal, K.; Mandal, S.P.; Agudo, P.; Pal, M. A study of nanocrystalline (Mn–Zn) ferrite in SiO2 matrix. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2001, 182, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shen, L.; Zhao, L. Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Li0.5Fe2.1Cr0.4O4 ferrite. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 2455–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Li, M.; Wang, L. A study of the photovoltage properties of nanocrystalline LiFe5O8. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1997, 48, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.M.H.E.; Alsobhi, B.O.; Almeshal, A. Structural, elastic, thermodynamic, electronic, magnetic, thermoelectric and optical investigation of chromate spinels TCr2O4 [T = V2+, Mn2+, Fe2+] for optoelectronic applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 294, 127041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z.J. Size-dependent superparamagnetic properties of MgFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanocrystallites. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 73, 3156–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, J. Magnetic properties of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles produced by a low-temperature solid-state reaction method. J. Magn. Magn. Mat. 2007, 309, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zeng, H.; Robinson, D.B.; Raoux, S.; Rice, P.M.; Wang, S.X.; Li, G. Preparation and Reversible Phase Transfer of CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyeon, T.; Chung, Y.; Park, J.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, Y.W.; Park, B.H. Monodisperse MFe2O4 (M = Fe, Co, Mn) Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.K.; Bid, S.; Gateshki, M.; Petkov, V. Microstructure characterization and cation distribution of nanocrystalline magnesium ferrite prepared by ball milling. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 93, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepelak, V.; Becker, K.D. Mössbauer studies in the mechanochemistry of spinel ferrites. J. Mater. Synth. Process 2000, 8, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Dubenko, I.; Edorh, D.D.; Ali, N. Size-induced variations in structural and magnetic properties of double exchange La0.8Sr0.2MnO3−δ nano-ferromagnet. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 96, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHenry, M.E.; Laughlin, D.E. Nano-scale materials development for future magnetic applications. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.; Abdul Khadar, M. VSM and Mössbauer study of nanostructured hematite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, R.H.; Berkowitz, A.E.; McNiff, E.J.; Foner, S. Surface Spin Disorder in NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnasamy, C.N.; Narayanasamy, A.; Ponpandian, N.; Justin Joseyphus, R.; Jayadevan, B.; Tohji, K.; Chattopadhyay, K. Grain size effect on the Néel temperature and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline NiFe2O4 spinel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 238, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Ding, J. Strong unidirectional anisotropy in mechanically alloyed spinel ferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Nunes, A.C.; Majkrzak, C.F.; Berkowitz, A.E. Polarized neutron study of the magnetization density distribution within a CoFe2O4 colloidal particle II. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1995, 145, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.A.; Harris, V.G.; Hamdeh, H.H.; Ho, J.C. Large zinc cation occupancy of octahedral sites in mechanically activated zinc ferrite powders. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 76, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Z.; Goya, G.F.; Rechenberg, H.R. Magnetic properties of nanostructured CuFe2O4. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1999, 11, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, T. Economics of ceramic magnet. Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 1994, 73, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Seyyed Ebrahimi, S.A.; Azadmanjiri, J. Evaluation of NiFe2O4 ferrite nanocrystalline powder synthesized by a sol–gel auto-combustion method. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2007, 353, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, M.M.; Fouad, O.A. Synthesis and characterization of nano-sized nickel ferrites from fly ash for catalytic oxidation of CO. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 94, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, S.L. Microstructure and properties of ferrites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1958, 41, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C. Behavior of ferro-or ferrimagnetic very fine particles. J. Appl. Phys. 1961, 32, S233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, R.J.; Kingery, W.D. Nickel ferrite thin films: Microstructures and magnetic properties. J. Appl. Phys. 1967, 38, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, A.; Priyadharsini, P.; Chandrasekaran, G. Production of single phase nano size NiFe2O4 particles using sol–gel auto combustion route by optimizing the preparation conditions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 112, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathani, H.; Misra, R.D.K. Surface effects on the magnetic behavior of nanocrystalline nickel ferrites and nickel ferrite-polymer nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2004, 113, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.; John, A.M.; Nair, S.S.; Joy, P.A.; Anantharaman, M.R. Finite size effects on the structural and magnetic properties of sol–gel synthesized NiFe2O4 powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 302, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xianghui, H.; Zhenhua, C. A study of nanocrystalline NiFe2O4 in a silica matrix. Mater. Res. Bull. 2005, 40, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbala, S.; Nathani, H.; Koizol, K.; Misra, R.D.K. Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Ni-Zn, Zn-Mn, Ni-Mn ferrites synthesized by reverse micelle technique. J. Phys. B 2004, 348, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saafan, S.A.; Meaz, T.M.; El-Ghazzawy, E.H.; El Nimr, M.K.; Ayad, M.M.; Bakr, M. A.C. and D.C. conductivity of NiZn ferrite nanoparticles in wet and dry conditions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 2369–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, S.; Chandra, K. Cation distribution and magnetic properties in chromium-substituted nickel ferrites prepared using aerosol route. J. Solid State Chem. 2007, 180, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, C.Y.; Liu, K.S.; Lin, T.F.; Lin, I.N. Microwave sintering of NiCuZn ferrites and multilayer chip inductors. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2000, 209, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aphesteguy, J.C.; Damiani, A.; DiGiovanni, D.; Jacobo, S.E. Microwave-absorbing characteristics of epoxy resin composite containing nanoparticles of NiZn- and NiCuZn-ferrite. J. Phys. B 2009, 404, 2713–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustace, D.A.; Docherty, F.T.; McComb, D.W.; Craven, A.J. ELNES as a Probe of Magnetic Order in Mixed Oxides. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2006, 26, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijo, A.K. Magnetic and structural properties of CoCrxFe2−xO4 spinels prepared by solution self-combustion method. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 2288–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghasudha, M.; Ravinder, D.; Veerasomaiah, P. FTIR Studies and Dielectric Properties of Cr Substituted Cobalt Nano Ferrites Synthesized by Citrate-Gel Method. Nanosci. Nanotech. 2013, 3, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijo, A.K.; Dimple, P.D.; Roy, M.; Sudheesh, V.D. Magnetic and dielectric properties of NiCrFeO4 prepared by solution self-combustion method. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 94, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, H.M. A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 1969, 2, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teillet, J.; Varret, F. MOSFIT Program, Université du Maine, Le Mans, France. unpublished.
- Chakrabarti, M.; Sanyal, D.; Chakrabarti, A. Preparation of Zn(1−x)CdxFe2O4 (x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7 and 1.0) ferrite samples and their characterization by Mössbauer and positron annihilation techniques. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patange, S.M.; Shirsath, S.E.; Jadhav, S.S.; Jadhav, K.M. Cation distribution study of nanocrystalline NiFe2−xCrxO4 ferrite by XRD, magnetization and Mössbauer spectroscopy. Phys. Status Solidi A 2012, 209, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gismelseed, A.M.; Yousif, A.A. Mössbauer study of chromium-substituted nickel ferrites. Phys. B 2005, 370, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.S.; Ahmed, F.; Koo, B.H. Enhanced relative cooling power of Ni1−xZnxFe2O4 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.7) ferrites. Acta Mater. 2014, 71, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, M.A.; Nath, S.K.; Sikder, S.S.; Maria, K.H. Cation distribution and electromagnetic properties of spinel type Ni–Cd ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2013, 74, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohar, K.S.; Patange, S.M.; Mane, M.L.; Shirsath, S.E. Cation distribution investigation and characterizations of Ni1−xCdxFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by citrate gel process. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1032, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, K.A.; Al Rawas, A.D.; Gismelssed, A.M.; Al Jamel, A.; Al Ani, S.K.; Shongwe, M.S.; Al Riyami, K.O.; Al Alawi, S.R. Influence of Cr substitution on Debye-Waller factor and related structural parameters of ZnFe2−xCrxO4 spinels. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 701, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta crystallographica section A: Crystal physics, diffraction, theoretical and general crystallography. Acta Cryst. 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hcini, S.; Kouki, N.; Omri, A.; Dhahri, A.; Bouazizi, M.L. Effect of sintering temperature on structural, magnetic, magnetocaloric and critical behaviors of Ni-Cd-Zn ferrites prepared using sol-gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 464, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouki, N.; Hcini, S.; Boudard, M.; Aldawas, R.; Dhahri, A. Microstructural analysis, magnetic properties, magnetocaloric effect, and critical behaviors of Ni0.6Cd0.2Cu0.2Fe2O4 ferrites prepared using the sol–gel method under different sintering temperatures. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 1990–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Kotnala, R.K.; Shah, J.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A.; Dhiman, P.; Singh, M. Cation distribution: A key to ascertain the magnetic interactions in a cobalt substituted Mg–Mn nanoferrite matrix. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 16669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Thakur, P.; Kumar, M.; Thakur, J.N.; Negi, N.S.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, V. Improvement in magnetic behaviour of cobalt doped magnesium zinc nano-ferrites via co-precipitation route. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 684, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhadhbi, M.; Khitouni, M.; Azabou, M.; Kolsi, A. Characterization of Al and Fe nanosized powders synthesized by high energy mechanical milling. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khitouni, M.; Kolsi, A.W.; Njah, N. The effect of boron additions on the disordering and crystallite refinement of Ni3Al powders during mechanical milling. Ann. Chim. Sci. Mat. 2003, 28, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, D.; Singh, F.; Das, R. X-ray diffraction analysis by Williamson-Hall, Halder-Wagner and size-strain plot methods of CdSe nanoparticles- a comparative study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 122021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.K.; Hall, W.H. X-ray line broadening from filed aluminum and wolfram. Acta Metall. 1953, 1, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, H.P.; Alexander, L.E. X-ray Diffraction Procedure for Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Bindu, P.; Thomas, S. Estimation of lattice strain in ZnO nanoparticles: X-ray peak profile analysis. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2014, 8, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenari, H.M.; Seibel, C.; Hauschild, D.; Reinert, F.; Abdollahian, H. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, X-ray line analysis, and chemical composition study. Mater. Res. 2016, 19, 1319–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mote, V.; Prakash, R.; Kumar, V. X-ray analysis of α-Al2O3 particles by Williamson–Hall methods. Mater. Focus 2016, 5, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.H. X-ray line broadening in metals. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. 1949, 62, 741–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hcini, S.; Boudard, M.; Zemni, S.; Oumezzine, M. Critical behavior of Nd0.67Ba0.33Mn1−xFexO3 (x = 0 and 0.02) manganites. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 2042–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie-Pelecky, D.L.; Rieke, R.D. Magnetic properties of nanostructured materials. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 1770–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, R.H. Magnetic Nanoparticle. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadharsini, P.; Pradeep, A.; Rao, P.S.; Chandrasekaran, G. Structural, spectroscopic and magnetic study of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 116, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, K.; Karim, S.; Mumtaz, A.; Hasanain, S.K.; Liu, J.; Duan, J.L. Synthesis and magnetic characterization of nickel ferrite nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 1838–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
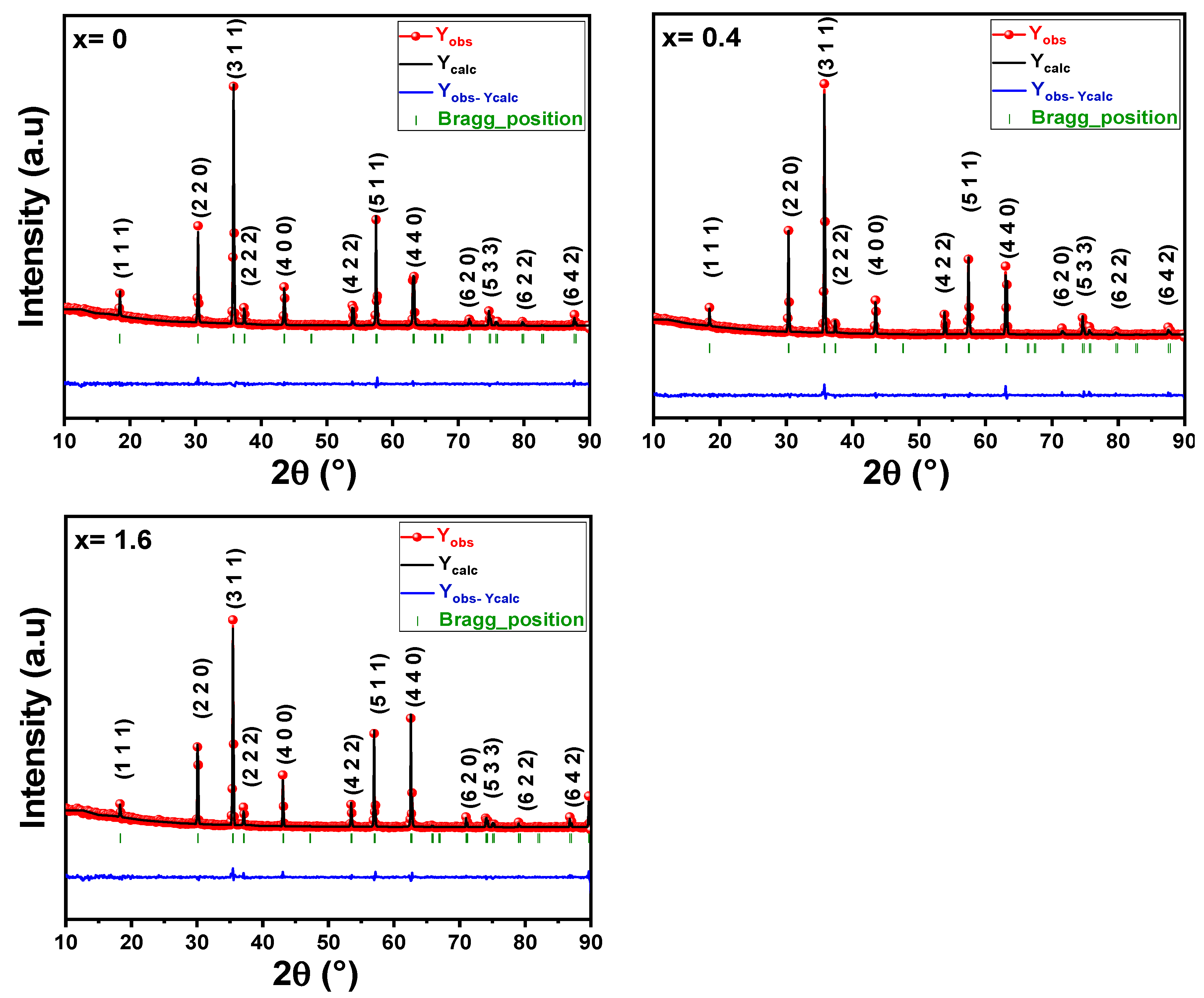


| Fe Content | x = 0 | x = 0.4 | x = 1.6 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space group | ||||||
| Cell parameters | Lattice constant a (Å) | 8.3242 (5) | 8.3329 (5) | 8.3906 (5) | ||
| Cell volume V (Å3) | 476.80 (6) | 578.62 (6) | 590.71 (6) | |||
| Atoms | Zn/Cr/Fe | Wyckoff positions | 4c | 4c | 4c | |
| Site symmetry | −43 m | −43 m | −43 m | |||
| Atomic positions | x = y = z | 1/8 | 1/8 | 1/8 | ||
| Occupancy factors | ||||||
| Biso (Å2) | 2.2 (4) | 1.9 (5) | 1.98 (4) | |||
| Ni/Fe/Cr | Wyckoff positions | 16d | 16d | 16d | ||
| Site symmetry | −3 m | −3 m | −3 m | |||
| Atomic positions | x = y = z | ½ | ½ | 1/2 | ||
| Occupancy factors | ||||||
| Biso (Å2) | 2.4 (4) | 1.5 (5) | 1.8 (3) | |||
| O | Wyckoff positions | 32e | 32e | 32e | ||
| Site symmetry | 3 m | 3 m | 3 m | |||
| Atomic positions | x = y= z | 0.2582 (1) | 0.2572 (2) | 0.2558(2) | ||
| Occupancy factors | ||||||
| Biso (Å2) | 2.1 (5) | 1.2 (8) | 2.8 (7) | |||
| Structural parameters | RA (Å) | 1.920 (1) | 1.905 (2) | 1.904 (2) | ||
| RB (Å) | 2.015 (1) | 2.027 (2) | 2.049 (2) | |||
| θA-O-B (°) | 122.5 (4) | 122.9 (7) | 123.3 (7) | |||
| θB-O-B (°) | 93.8 (4) | 93.2 (7) | 92.8 (7) | |||
| Dc (nm) | 156 | 163 | 172 | |||
| Agreement factors | Rp (%) | 6.29 | 6.73 | 7.45 | ||
| Rwp (%) | 8.32 | 9.15 | 9.59 | |||
| RF (%) | 4.26 | 5.01 | 8.06 | |||
| χ2 (%) | 1.20 | 1.43 | 1.51 | |||
| xFe | Composition | Cation Distribution | D (nm) ±2 | a (Å) ±0.0005 | Ms (emu/g) | Hc (Oe) ±5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Ni0.3Zn0.7Cr2O4 | 156 | 8.3242 | 0.46 | 316 | |
| 0.4 | Ni0.3Zn0.7Cr1.6Fe0.4O4 | 163 | 8.3329 | -- | … | |
| 1.6 | Ni0.3Zn0.7Cr0.4Fe1.6O4 | 172 | 8.3906 | ----- | … |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mallah, A.; Al-Thuwayb, F.; Khitouni, M.; Alsawi, A.; Suñol, J.-J.; Greneche, J.-M.; Almoneef, M.M. Synthesis, Structural and Magnetic Characterization of Superparamagnetic Ni0.3Zn0.7Cr2−xFexO4 Oxides Obtained by Sol-Gel Method. Crystals 2023, 13, 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13060894
Mallah A, Al-Thuwayb F, Khitouni M, Alsawi A, Suñol J-J, Greneche J-M, Almoneef MM. Synthesis, Structural and Magnetic Characterization of Superparamagnetic Ni0.3Zn0.7Cr2−xFexO4 Oxides Obtained by Sol-Gel Method. Crystals. 2023; 13(6):894. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13060894
Chicago/Turabian StyleMallah, Abdulrahman, Fatimah Al-Thuwayb, Mohamed Khitouni, Abdulrahman Alsawi, Joan-Josep Suñol, Jean-Marc Greneche, and Maha M. Almoneef. 2023. "Synthesis, Structural and Magnetic Characterization of Superparamagnetic Ni0.3Zn0.7Cr2−xFexO4 Oxides Obtained by Sol-Gel Method" Crystals 13, no. 6: 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13060894
APA StyleMallah, A., Al-Thuwayb, F., Khitouni, M., Alsawi, A., Suñol, J.-J., Greneche, J.-M., & Almoneef, M. M. (2023). Synthesis, Structural and Magnetic Characterization of Superparamagnetic Ni0.3Zn0.7Cr2−xFexO4 Oxides Obtained by Sol-Gel Method. Crystals, 13(6), 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13060894








