Frequency Magnetically Tunable Terahertz Perfect Absorber Based on Graphene and Silica Layered Dielectric
Abstract
1. Introduction
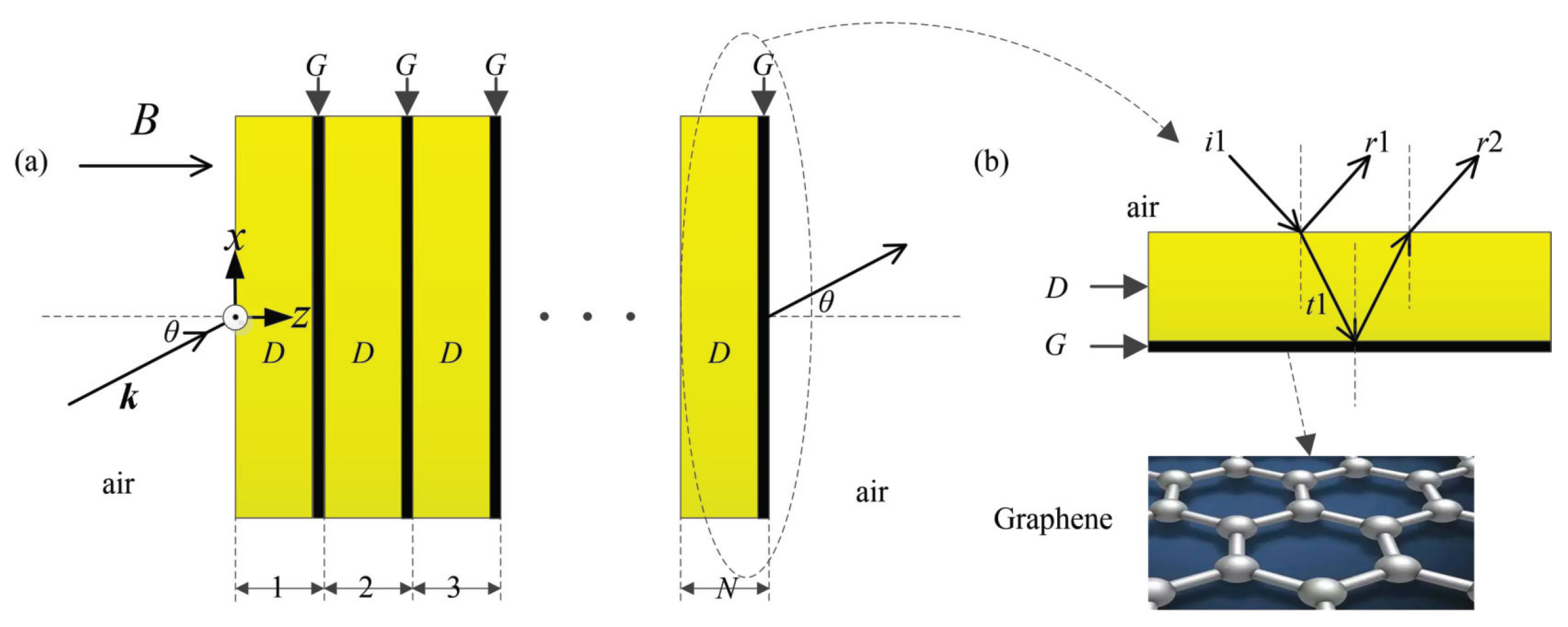
2. Model and Method
2.1. Absorber and Magnetized Graphene Models
2.2. Research Methods
3. Results and Discussion
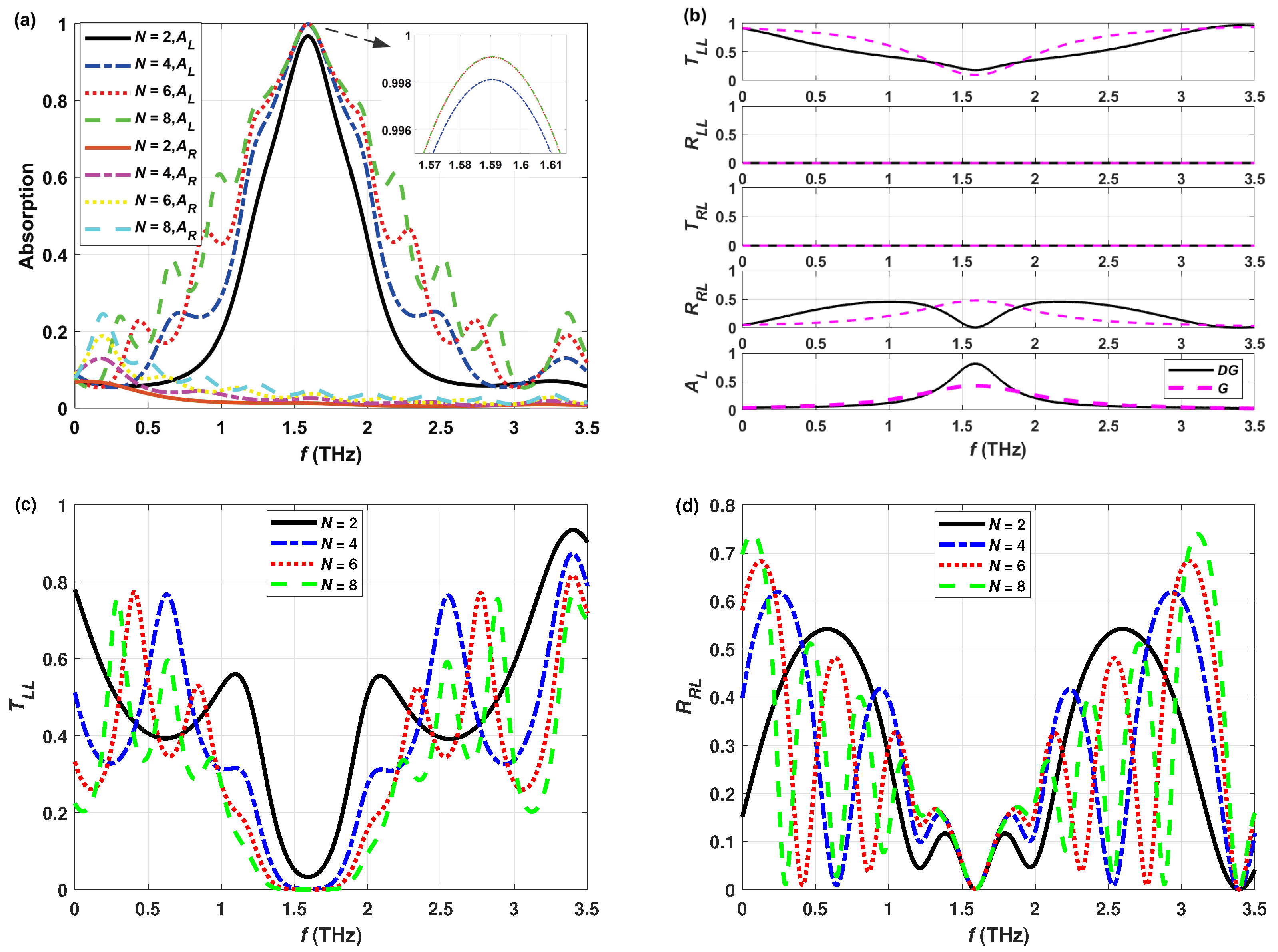
3.1. Absorption for Various Period Numbers N
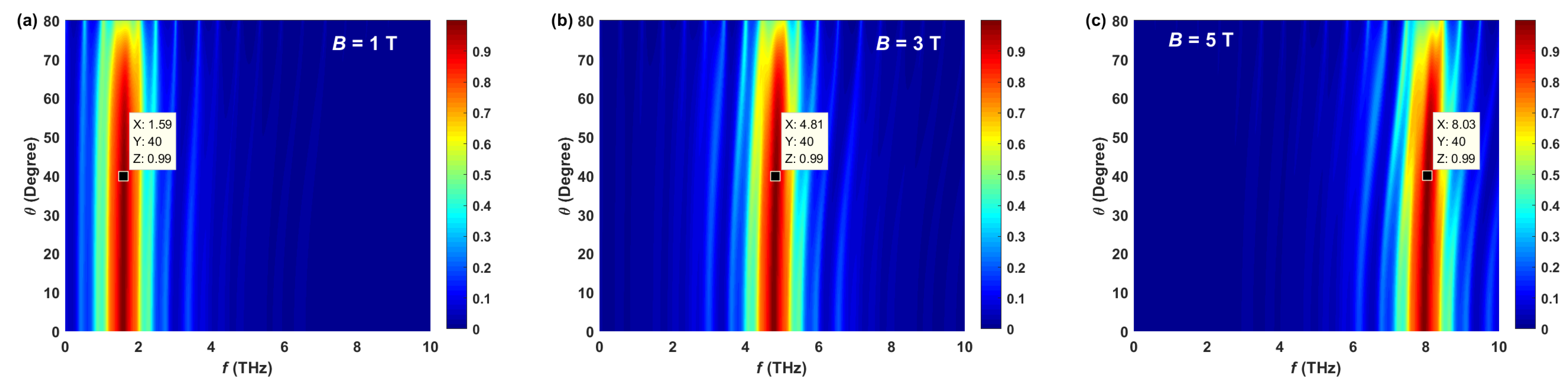
3.2. Frequency Tuning with Various SBMFs B
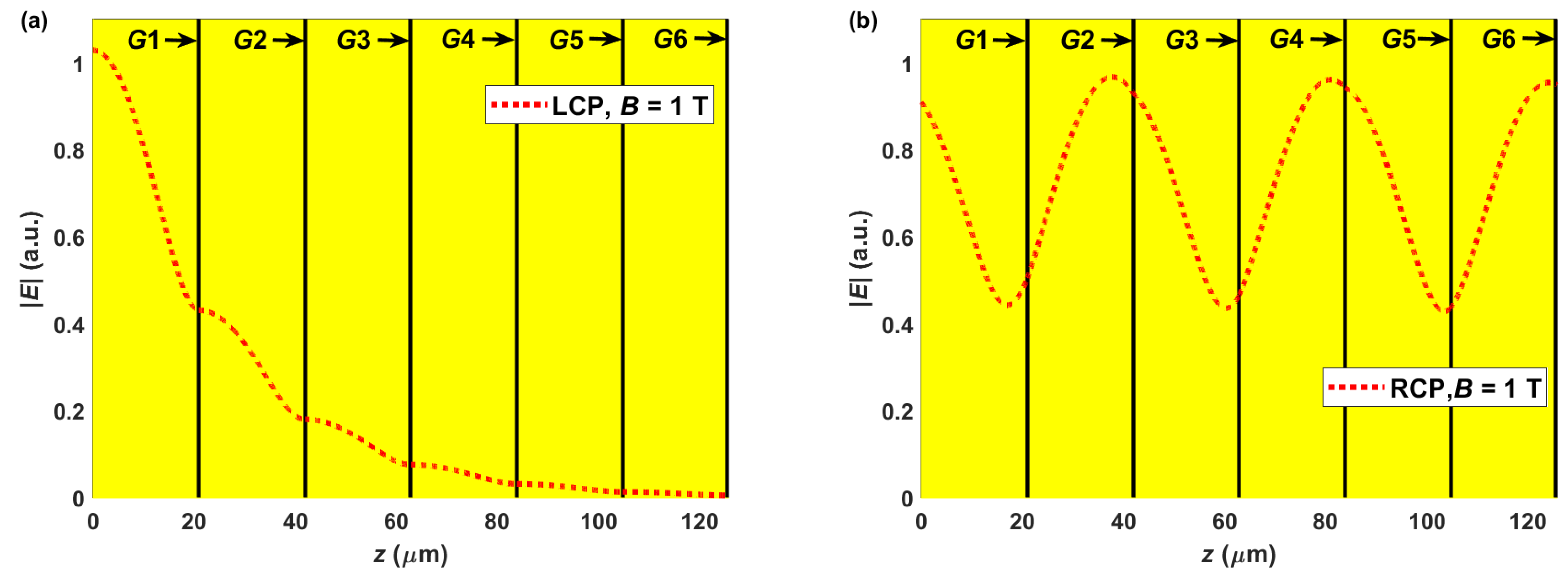
3.3. Influence of Incident Angle on Magnetic Tuning
3.4. Influence of the Nonmagnetic Dielectric Loss
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tse, W.K.; Qiao, Z.; Yao, Y.; MacDonald, A.; Niu, Q. Quantum anomalous Hall effect in single-layer and bilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 155447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Cen, C.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Z.; Ye, X.; Yi, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yi, Y.; et al. Tunable dual-band perfect absorber consisting of periodic cross-cross monolayer graphene arrays. Results Phys. 2019, 13, 102217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorenko, A.N.; Polini, M.; Novoselov, K. Graphene plasmonics. Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, P.; Garcia-Pomar, J.L.; Hoh, M.; Reinhard, B.; Brodyanski, A.; Rahm, M. Spectrally wide-band terahertz wave modulator based on optically tuned graphene. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9118–9124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, L. Tunable terahertz dual-band band-stop filter based on surface magnetoplasmons in graphene sheet array. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 132, 106484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, W.; Deng, S.; Liu, H.; Teng, C.; Deng, H.; Yang, H.; Xu, R.; Yin, J.; Yu, L.; et al. Wide-range frequency tunable absorber based on cross-groove metamaterials and graphene-sheet. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 255102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, Z.A.; Al-Dossari, M.; Zohny, E.I.; Aly, A.H. Refractive index sensor using Fibonacci sequence of gyroidal graphene and porous silicon based on Tamm plasmon polariton. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2023, 55, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, Z.A.; Singh, M.R.; Aly, A.H. Tamm resonance excited by different metals/graphene. Photonics Nanostruc. 2022, 49, 100995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, Z.A.; Aly, A.H. Gyroidal graphene/porous silicon array for exciting optical Tamm state as optical sensor. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, Z.A.; Sharma, A.; Aly, A.H. Gyroidal graphene for exciting tamm plasmon polariton as refractive index sensor: Theoretical study. Opt. Mater. 2021, 122, 111684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divdel, H.; Taghipour-Farshi, H.; Saghai, H.R.; Jahani, M.A.T.G. Thermally switchable terahertz metasurface absorber composed of H-fractal and enabled by phase-change material of vanadium dioxide. Frequenz 2022, 76, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.; Khonina, S.; Kazanskiy, N.; Piramidowicz, R. Hybrid metasurface perfect absorbers for temperature and biosensing applications. Opt. Mater. 2022, 123, 111906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.; Jeong, H.; Kim, Y.K.; Lim, S.; Baek, C.W. Design and Fabrication of Millimeter-Wave Frequency-Tunable Metamaterial Absorber Using MEMS Cantilever Actuators. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, R.; Baqir, M.; Iftikhar, A.; Naqvi, S.; Mughal, M.; Ali, M. Polarization-controllable and angle-insensitive multiband Yagi-Uda-shaped metamaterial absorber in the microwave regime. Opt. Mater. Express 2022, 12, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jornet, J.M.; Akyildiz, I.F. Channel modeling and capacity analysis for electromagnetic wireless nanonetworks in the terahertz band. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 2011, 10, 3211–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppens, F.H.; Chang, D.E.; García de Abajo, F.J. Graphene plasmonics: A platform for strong light–matter interactions. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3370–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, A.; Namdar, A.; Abdi-Ghaleh, R. Magnetically tunable enhanced absorption of circularly polarized light in graphene-based 1D photonic crystals. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 5914–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wang, F.; Huang, S.; Xie, Z.; Li, L.; Han, X.; Chen, H.; Zhou, H. Coherent perfect absorber with independently tunable frequency based on multilayer graphene. Opt. Commun. 2019, 446, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Chen, J.; Cen, C.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, Y.; Ye, X.; Xiao, S.; Luo, W.; Wu, P. Tunable graphene-based plasmonic perfect metamaterial absorber in the THz region. Micromachines 2019, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Ding, J.; Wang, X.; Yi, Z. Tunable multi-band terahertz absorber based on composite graphene structures with square ring and Jerusalem cross. Results Phys. 2021, 25, 104233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi-Razani, A.; Rezaei, P. Multiband polarization insensitive and tunable terahertz metamaterial perfect absorber based on the heterogeneous structure of graphene. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2022, 54, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Liu, F.; Ren, G.J.; Su, F.; Li, D.; Yao, J.Q. A broadband metamaterial absorber based on multi-layer graphene in the terahertz region. Opt. Commun. 2018, 417, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zeng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.H. Frequency-reconfigurable wide-angle terahertz absorbers using single-and double-layer decussate graphene ribbon arrays. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Shi, X.; Lu, Y.; Hu, F.; Zong, R.; Li, G. Dynamically tunable triple-band terahertz perfect absorber based on graphene metasurface. Superlattices Microstruct. 2021, 150, 106797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, N.; Sun, S.; Dong, H.; Dong, S.; He, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L. Hybridization-induced broadband terahertz wave absorption with graphene metasurfaces. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 11728–11736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Lakhtakia, A.; Jain, P.K. Graphene pixel-based polarization-insensitive metasurface for almost perfect and wideband terahertz absorption. JOSA B 2019, 36, F84–F88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.K.; Shi, X.Z.; Mo, J.J.; Fang, Y.T.; Chen, X.L.; Liu, S.B. Tunable multichannel absorber composed of graphene and doped periodic structures. Opt. Commun. 2017, 383, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; You, Q.; Guo, J.; Dai, X.; Xiang, Y. Tunable and multichannel terahertz perfect absorber due to Tamm surface plasmons with graphene. Photonics Res. 2017, 5, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.A.; Deng, Z.; Hong, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, P.; Li, G. Double-mode absorption in double-defect photonic crystal with one graphene multilayer. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2020, 52, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, X.; Li, Q. Graphene-Based Magnetically Tunable Broadband Terahertz Absorber. IEEE Photonics J. 2021, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, G.; Zhou, X.; Shen, H.; Wang, Q.; Zha, Y. Tunable graphene-based terahertz absorber via an external magnetic field. Opt. Mater. Express 2020, 10, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, A.; Nayak, C.; Bezerra, C.G.; Costa, C.H.; Pinheiro, F.A. Tunable terahertz absorption in Si/SiO2-graphene multilayers: Disorder and magneto-optical effects. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 11034–11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Entezar, S.R.; Habil, M.K. Nonreciprocal optical isolation via graphene based photonic crystals. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 449, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, P.; Nayak, C. Multimode absorption in single-layer graphene: Disordered photonics and magneto-optic effect. Opt. Mater. 2022, 126, 112172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crassee, I.; Levallois, J.; Walter, A.L.; Ostler, M.; Bostwick, A.; Rotenberg, E.; Seyller, T.; Van Der Marel, D.; Kuzmenko, A.B. Giant Faraday rotation in single-and multilayer graphene. Nat. Phys. 2011, 7, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, F.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H. Atomically thin nonreciprocal optical isolation. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berreman, D.W. Optics in stratified and anisotropic media: 4× 4-matrix formulation. Josa 1972, 62, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, I.; Adrián Reyes, J.; Avendaño, C.G. Electrically controlled optical bandgap in a twisted photonic liquid crystal. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 113510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habil, M.K.; Entezar, S.R. Polarization conversion and phase modulation of terahertz electromagnetic waves via graphene-dielectric structure. Phys. Scr. 2019, 95, 015503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.C.; Wu, C.J.; Chang, S.J. Terahertz temperature-dependent defect mode in a semiconductor-dielectric photonic crystal. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 093110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, M.; Nolte, D.D. Optical contrast and clarity of graphene on an arbitrary substrate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 081102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, P.J. Magnetic circular dichroism. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1974, 25, 201–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qu, Y.; Du, K.; Bai, S.; Tian, J.; Pan, M.; Ye, H.; Qiu, M.; Li, Q. Broadband optical absorption based on single-sized metal-dielectric-metal plasmonic nanostructures with high-ε′′ metals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 101101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, A.; Entezar, S.R. Optical properties of one-dimensional photonic crystals containing graphene sheets. Phys. B 2013, 431, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.T.; Oh, S.S.; Kim, H.D.; Park, H.S.; Hess, O.; Min, B.; Zhang, S. Electrical access to critical coupling of circularly polarized waves in graphene chiral metamaterials. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Liu, C. Complex band structures of 1D anisotropic graphene photonic crystal. Photonics Res. 2017, 5, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J. Frequency Magnetically Tunable Terahertz Perfect Absorber Based on Graphene and Silica Layered Dielectric. Crystals 2023, 13, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13040553
Wei Z, Jiang Y, Wang J. Frequency Magnetically Tunable Terahertz Perfect Absorber Based on Graphene and Silica Layered Dielectric. Crystals. 2023; 13(4):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13040553
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Zhenyan, Yannan Jiang, and Jiao Wang. 2023. "Frequency Magnetically Tunable Terahertz Perfect Absorber Based on Graphene and Silica Layered Dielectric" Crystals 13, no. 4: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13040553
APA StyleWei, Z., Jiang, Y., & Wang, J. (2023). Frequency Magnetically Tunable Terahertz Perfect Absorber Based on Graphene and Silica Layered Dielectric. Crystals, 13(4), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13040553






