Effect of Process Parameters on Arc Shape, Macroscopic Features, and Microhardness in Pulsed GMA–Additive Manufacturing
Abstract
1. Introduction
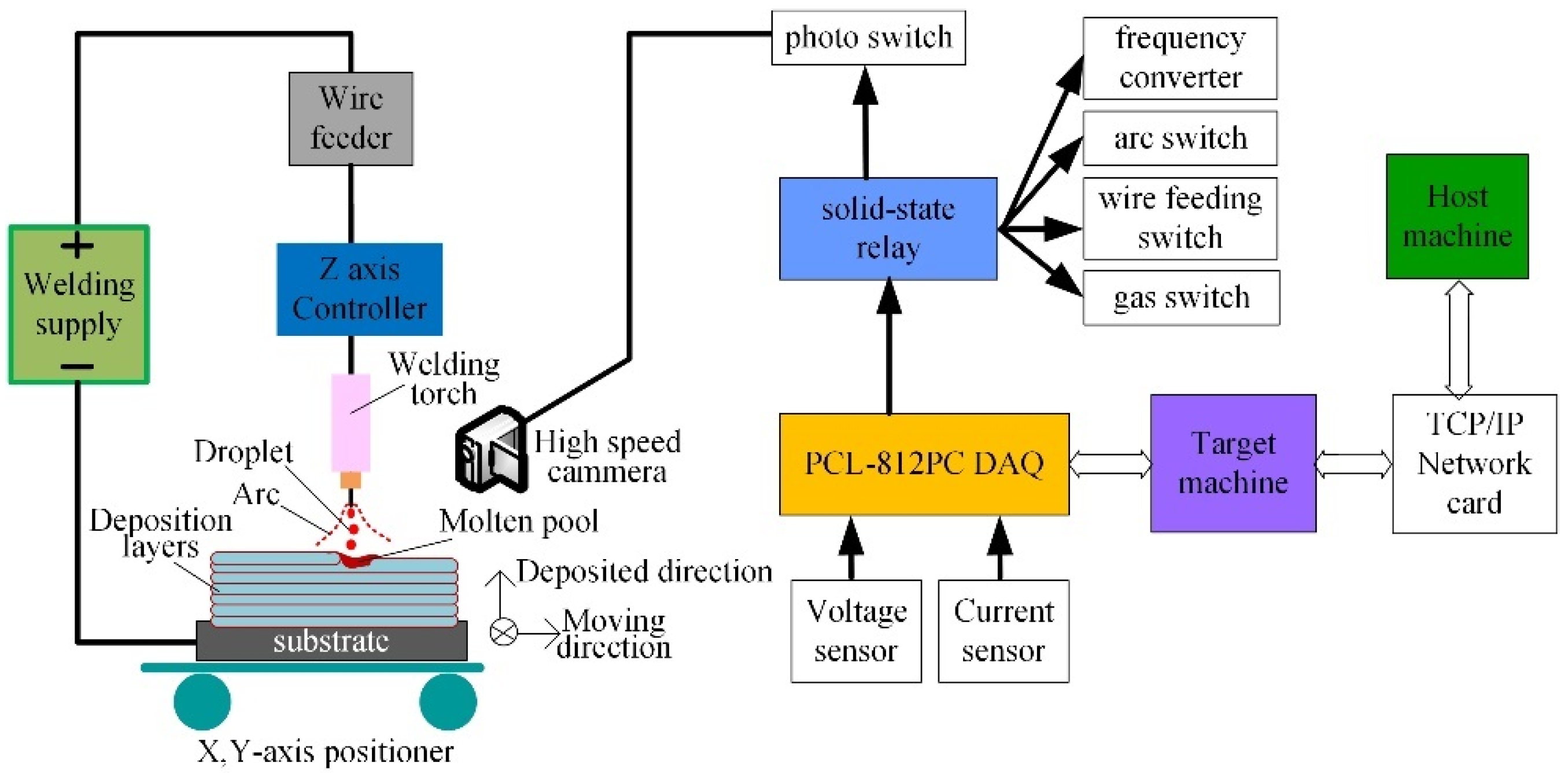
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
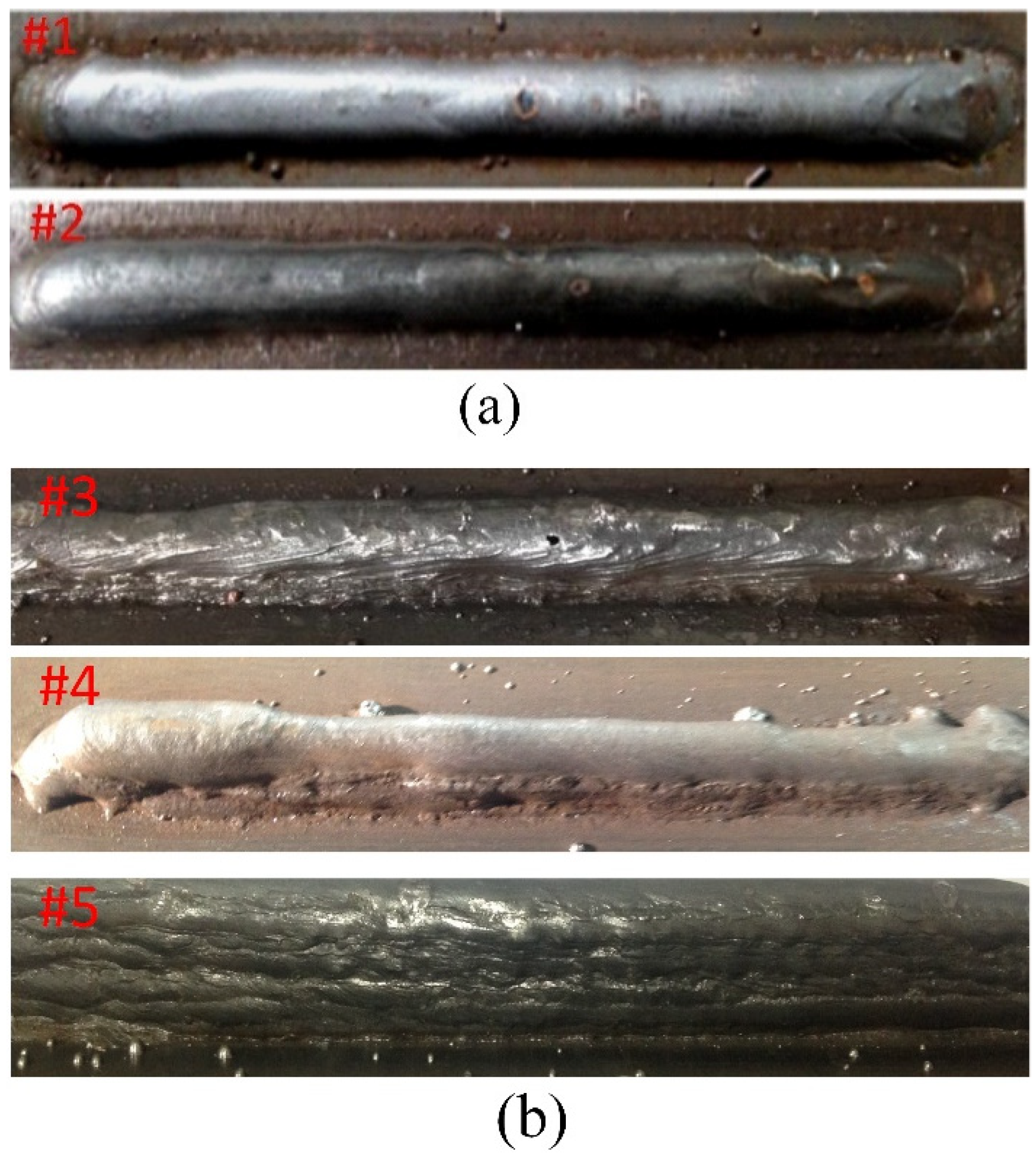
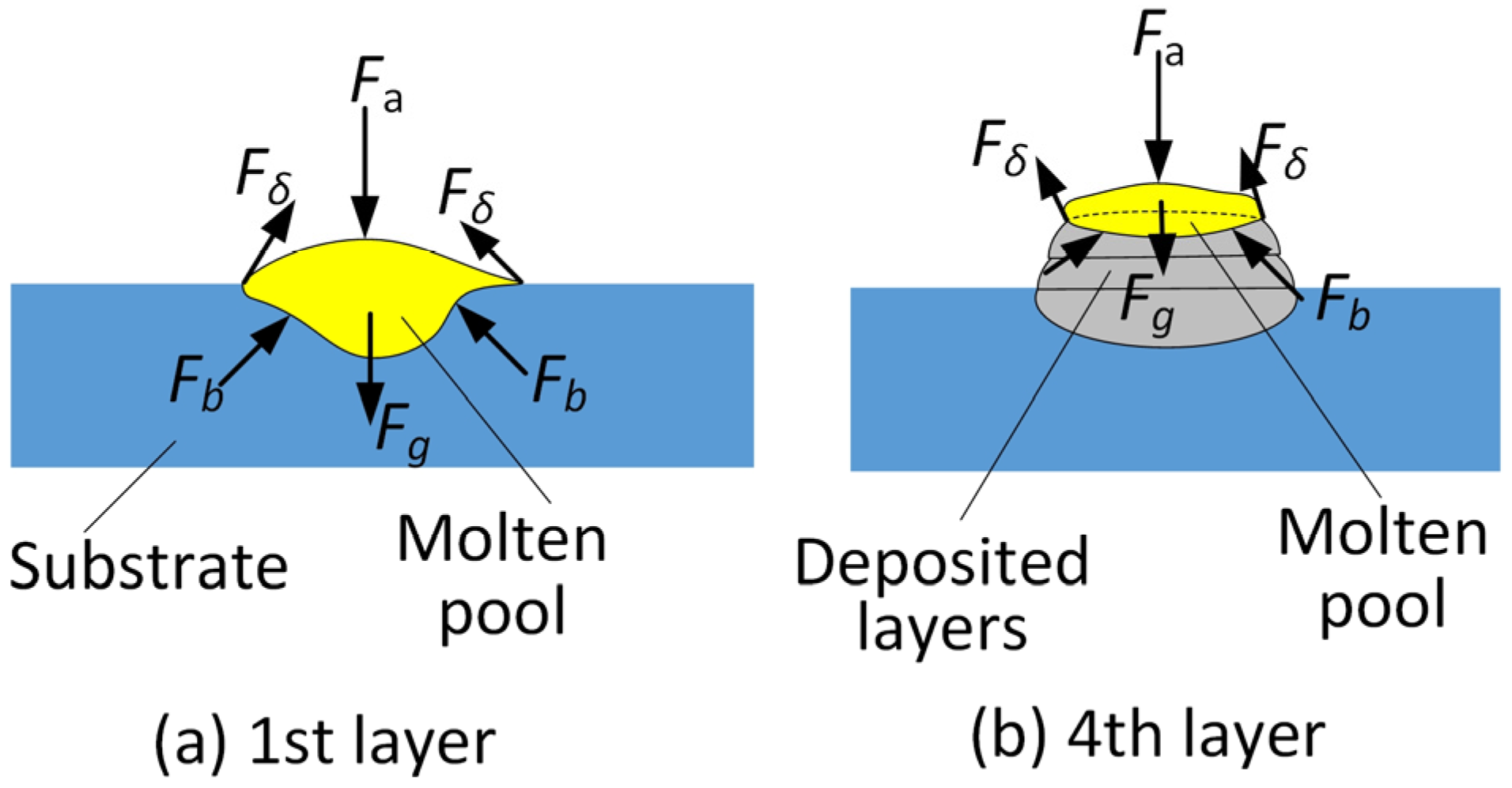
3.1. Deposition Morphology
3.2. Arc Characteristics and Droplet Transfer Behavior in the GMA–AM Process
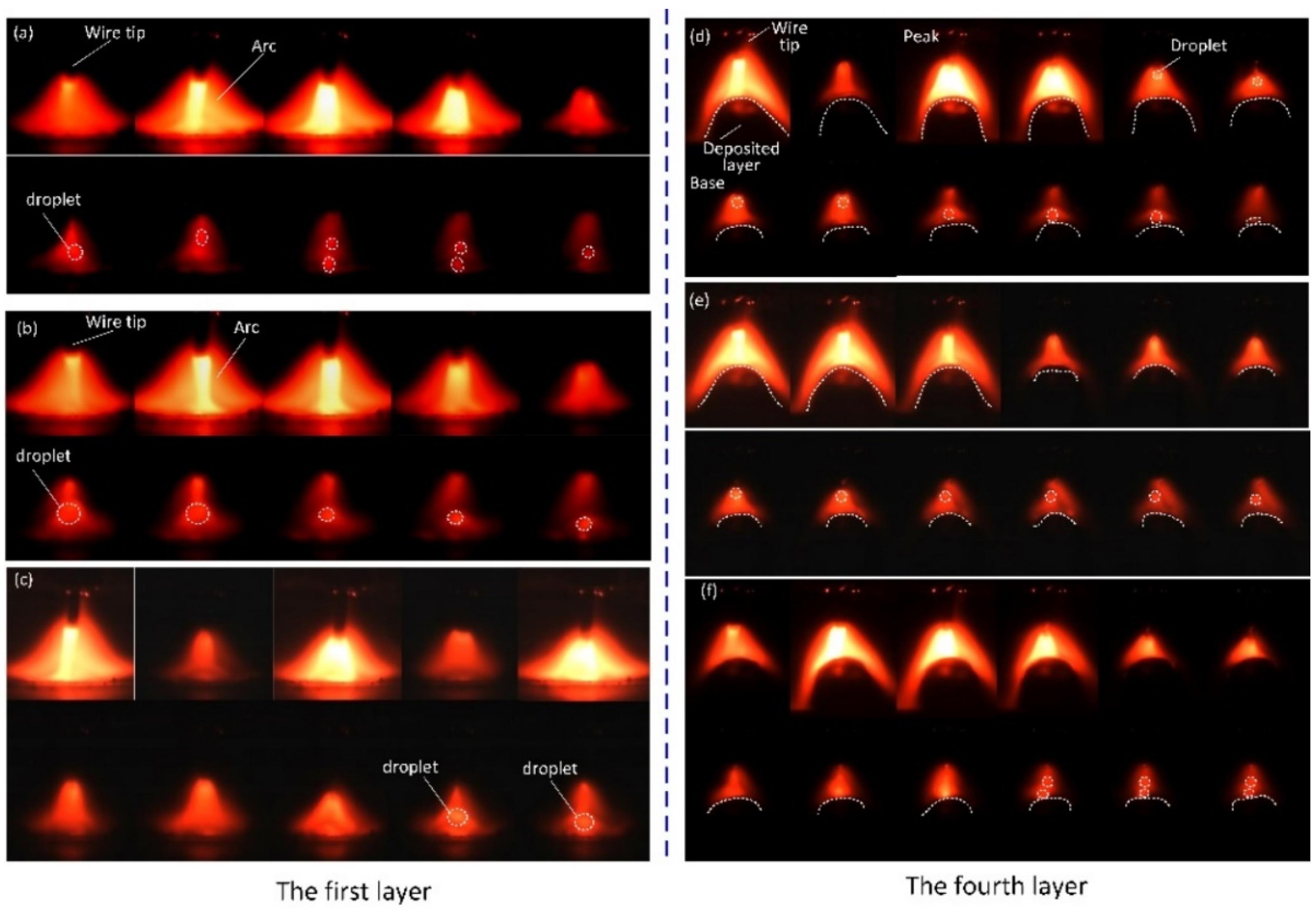
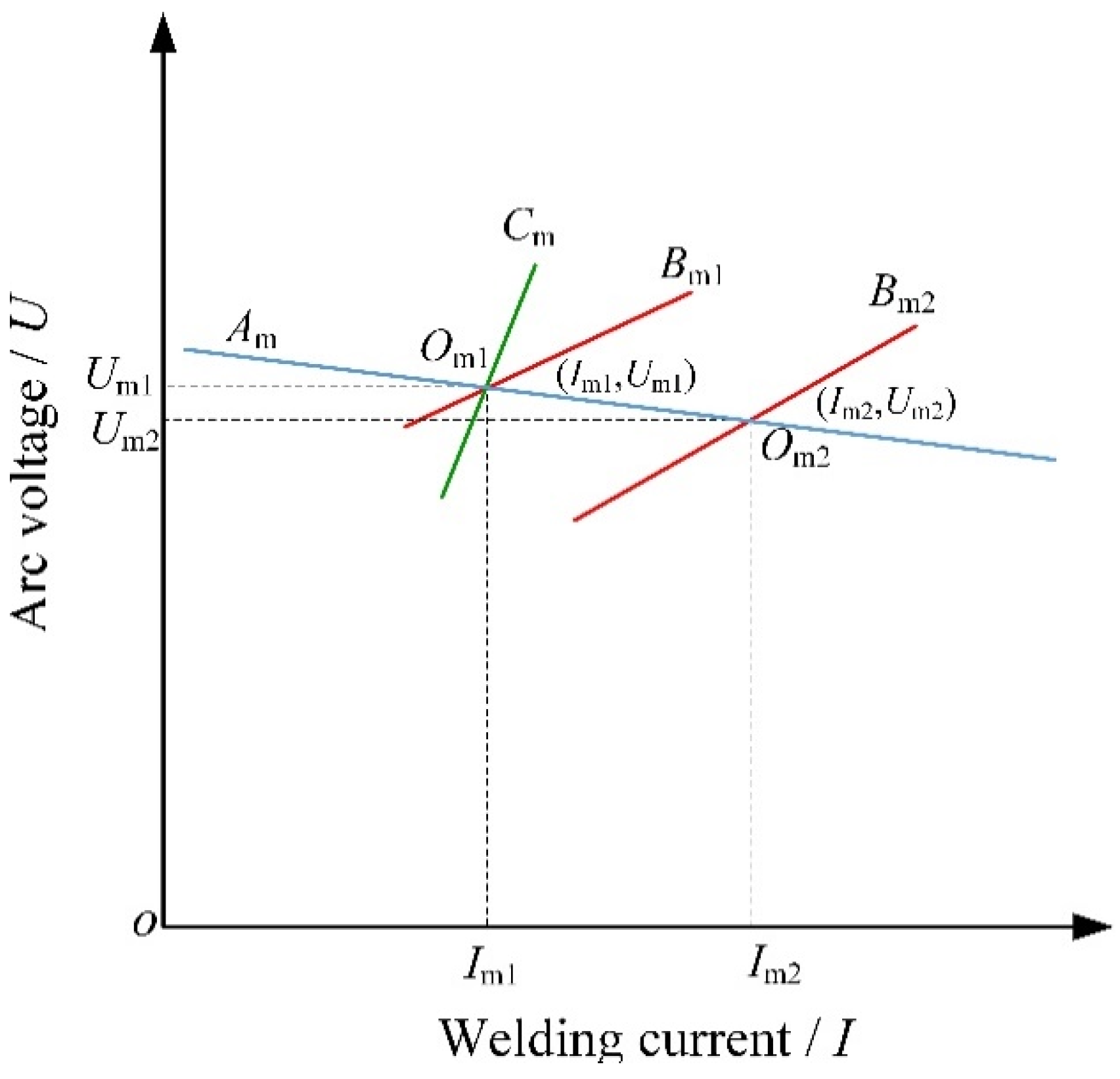
3.2.1. DC GMA–AM Process
3.2.2. PC GMAW–AM Process
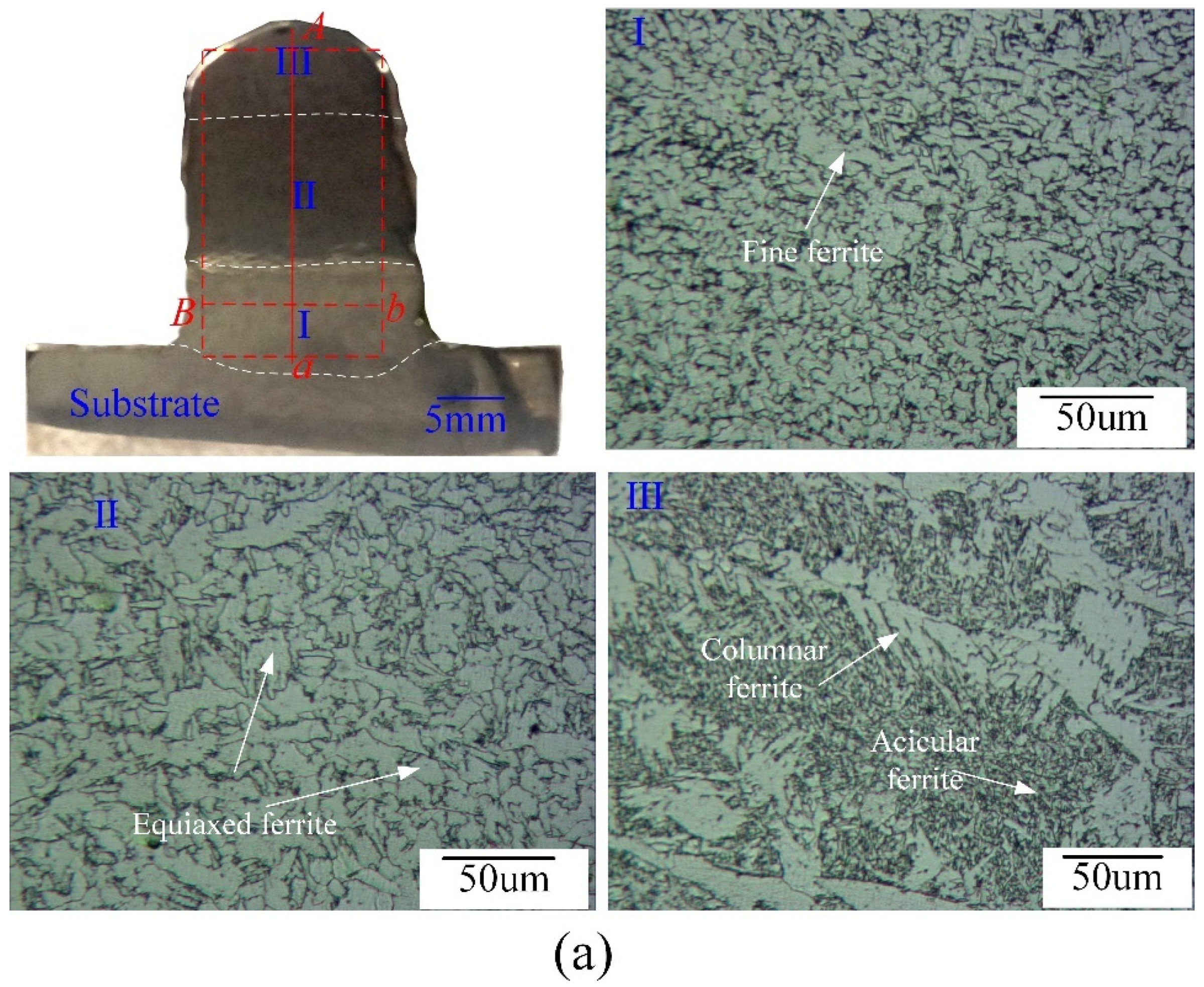
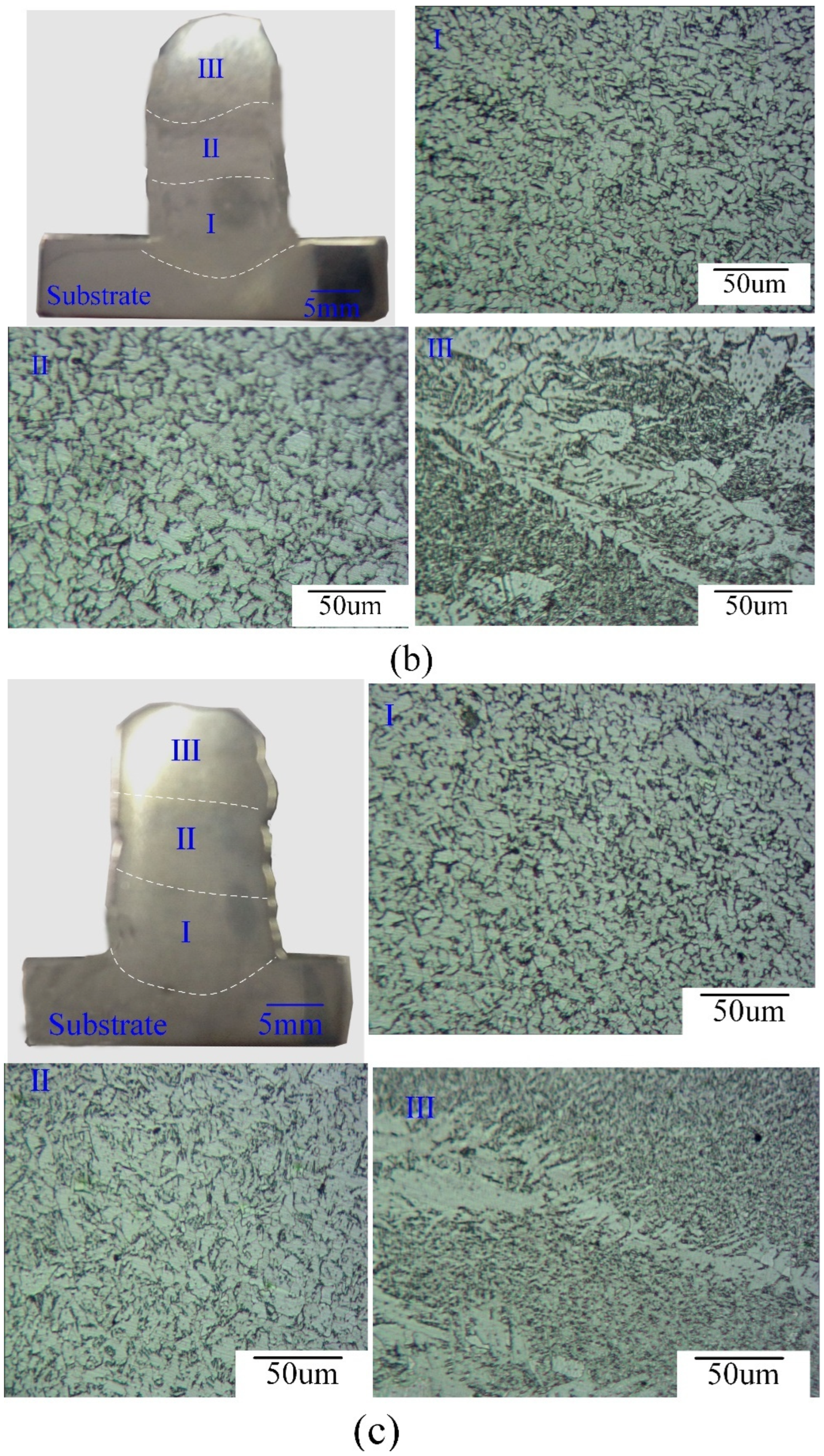
3.3. Microstructure and Microhardness of the Deposited Layers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Müller, J.; Grabowski, M.; Müller, C.; Hensel, J.; Unglaub, J.; Thiele, K. Design and parameter identification of wire and arc additively manufactured (WAAM) steel bars for use in construction. Metals 2019, 12, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Riddle, M.; Graziano, D.; Warren, J.; Das, S.; Nimbalkar, S. Energy and emissions saving potential of additive manufacturing: The case of lightweight aircraft components. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, G.; Montevecchi, C. Feature based three axes computer aided manufacturing software for wire arc additive manufacturing dedicated to thin walled components. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezovi, N.; Topi, A. Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM)—A New Advance in Manufacturing; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2019; pp. 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Giganto, S.; Martínez-Pellitero, S.; Barreiro, J.; Zapico, P. Influence of 17-4 PH stainless steel powder recycling on properties of SLM additive manufactured parts. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 16, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirish, M.; Rajendra, R. Suitability of metal additive manufacturing processes for part topology optimization-a comparative study. Mater. Today 2020, 27, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.; Schlienger, E. Practical consideration sand capabilities for laser assisted direct metal deposition. Mater. Des. 2000, 21, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Elangovan, S.; Mohanraj, R.; Narayanan, V. Significance of continuous wave and pulsed wave laser in direct metal deposition. Mater. Today 2021, 46, 8086–8096. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Pang, S.; Chen, B.; Suo, H.; Zhou, J. A three-dimensional transient model for heat transfer and fluid flow of weld pool during electron beam freeform fabrication of Ti-6-Al-4-V alloy. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 2014, 78, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, A.; Miriyev, A.; Sridharan, N.; Han, T.; Tuval, E.; Babu, S.S.; Frage, N. Ultrasonic additive manufacturing of steel: Method, post-processing treatments and properties. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 256, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Cui, Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, C. Exploring the inclined angle limit of fabricating unsupported rods structures by pulse hot-wire arc additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 295, 117160–117170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henckell, P.; Gierth, M.; Ali, Y.; Reimann, J.; Bergmann, J. Reduction of energy input in wire arc additive manufacturing with gas metal arc welding. Materials 2020, 13, 2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. A review of aluminum alloy fabricated by different processes of wire arc additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. 2021, 27, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, W.; Knapp, G.; Mukherjee, T.; Wei, Y.; Debroy, T. An improved heat transfer and fluid flow model of wire-arc additive manufacturing. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 2021, 167, 120835–120845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Alkahari, M.; Rosli, N.; Hasan, R.; Ramli, F. Review of wire arc additive manufacturing for 3d metal printing. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2019, 13, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, A.; Aldalur, E.; Veiga, F.; Artaza, T.; Lamikiz, A. Wire arc additive manufacturing of an aeronautic fitting with different metal alloys: From the design to the part. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 64, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andric, Z.; Labudovic, M.; Kovacevic, R. Effect of heat sink on microstructure of three-dimensional parts built by welding-based deposition. Int. J. Mach. Tool Manuf. 2004, 44, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baufeld, B.; Biest, O.; Gault, R. Microstructure of Ti-6Al-4V specimens produced by shaped metal deposition. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2009, 100, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baufeld, B.; Biest, O.; Gault, R. Manufacturing Ti-6Al-4V components by shaped metal deposition: Microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2001, 26, 012001–012011. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, J.D.; Dickens, P.M.; Wykes, C.M. Rapid prototyping of metal parts by three-dimensional welding. Part I J. Eng. Manuf. 1998, 212, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Chen, Y.; Li, P. Weld deposition-based rapid prototyping: A preliminary study. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 135, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.A.; Park, S.; Choi, D. 3D welding and milling: Part I–a direct approach for freeform fabrication of metallic prototypes. Int. J. Mach. Tool Manuf. 2005, 45, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanjara, P.; Brochu, M.; Jahazi, M. Electron beam free forming of stainless steel using solid wire feed. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 2278–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zhang, G.J.; Gao, H.M. Modeling of bead section profile and overlapping beads with experimental validation for robotic GMAW-based rapid manufacturing. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2012, 29, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xiong, J.; Lei, Y. Investigation on thermal stress evolution induced by wire and arc additive manufacturing for circular thin-walled parts. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 40, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Liu, Y.; Yin, Z. Passive vision measurement for robust reconstruction of molten pool in wire and arc additive manufacturing. Measurement 2020, 153, 107407–107414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, T.P.; Szanto, M.; Gilad, I.; Shai, I. Coupled arc and droplet model of GMAW. Sci. Technol. Weld. Joi. 2005, 10, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Fan, D.; Huang, J.; Tashiro, S.; Tanaka, M. Numerical study on arc-droplet coupled behavior in magnetic field controlled GMAW process. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 115202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwig, D.D.; Dierksheide, J.E.; Yapp, D.; Blackman, S. Arc behavior and melting rate in the VP-GMAW process. Weld. J. 2006, 85, 52–62. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, R.A.; Dos Santos, E.B.F.; Assunção, P.D.C.; Braga, E.M.; Gerlich, A.P. Cold wire gas metal arc welding: Droplet transfer and geometry. Weld. J. 2019, 98, 135S–149S. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, P.; Xue, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Chen, T.; Ji, S. Effects of arc length adjustment on weld bead formation and droplet transfer in pulsed GMAW based on datum current time. Metals 2020, 10, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, M.; Fan, D. Arc characteristics and metal transfer behavior in narrow gap gas metal arc welding process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 245, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Wire and arc additive manufacturing of metal components: A review of recent research developments. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 111, 2315–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QueguineurG, A.; RückertF, C.; Hascot, Y. Evaluation of wire arc additive manufacturing for large-sized components in naval applications. Weld. World 2018, 62, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, P.; Xue, S.; Wang, J.; Tao, Y.; Chen, W. Comparative Study of Droplet Transfer Modes on Appearance, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties of Weld during Pulsed GMAW. Metals 2020, 10, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Li, Y.; Li, R. Influences of process parameters on surface roughness of multi-layer single-pass thin-walled parts in GMAW-based additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 252, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldalur, E.; Veiga, F.; Suarez, A. High deposition wire arc additive manufacturing of mild steel: Strategies and heat input effect on microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 58, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldalur, E.; Veiga, F.; Suárez, A. Analysis of the Wall Geometry with Different Strategies for High Deposition Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing of Mild Steel. Metals 2020, 10, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wei, Y.; Long, J. Modeling and simulation of heat transfer, fluid flow and geometry morphology in GMAW-based wire arc additive manufacturing. Weld. World 2021, 65, 1571–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Luo, Y.; Han, J. Energy characteristics of droplet transfer in wire-arc additive manufacturing based on the analysis of arc signals. Measurement 2019, 134, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingül, Z. Instability phenomena in the gas—Metal arc welding self-regulation process. Part I Mech. Eng. J. Eng. 2002, 216, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Xiong, J.; Li, R. Effect of inter layer idle time on thermal behavior for multi-layer single-pass thin-walled parts in GMAW-based additive manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 1355–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.; Souza, L.J.; De Araújo, D.M.; De Araújo, D.B. Concept and validation of an active cooling technique to mitigate heat accumulation in WAAM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 107, 2513–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, F.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, H. Effect of in-process active cooling on forming quality and efficiency of tandem GMAW–based additive manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 101, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Akshay, J.; Yash, J.; Henriette, S.; Tonya, W. Concurrent geometry-and material-based process identification and optimization for robotic CMT-based wire arc additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. 2020, 194, 108841–108856. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.X.; Miao, J.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Li, C.T.; Fang, K.W. Microstructure and properties of ER50-6 steel fabricated by wire arc additive manufacturing. Scanning 2021, 2021, 7846116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Wang, L.S.; Tang, Z.M.; Yu, S.W.; Bu, Z.X.; Hu, X.; Cheng, Y.H. Effect of Trajectory Curvature on the Microstructure and Properties of Surfacing Wall Formed with the Process of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. Coatings 2019, 9, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Elements | C | Mn | Si | S | P | Cu | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q235 | 0.17 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.035 | 0.015 | / | Bal. |
| ER50-6 | 0.06–0.15 | 1.40–1.85 | 0.80–1.15 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.50 | Bal. |
| No | Voltage (V) | Wire Feed Speed (cm/s) | Moving Speed (cm/s) | Wire Extension (mm) | Heat Input (J/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 32~34 | 10.58 | 5.33 | 12 | ~1114 |
| #2 | 28~30 | 10.58 | 5.33 | 12 | ~1013 |
| No | Peak Current (A) | Base Current (A) | Pulse Frequency (Hz) | Duty Ratio (%) | Moving Speed (cm/s) | Heat Input (J/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #3 | 420 | 100 | 100 | 20 | 5.33 | ~923 |
| #4 | 580 | 5.33 | ~1103 | |||
| #5 | 500 | 5.33 | ~1013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; He, G.; Gu, Y.; Shi, Y. Effect of Process Parameters on Arc Shape, Macroscopic Features, and Microhardness in Pulsed GMA–Additive Manufacturing. Crystals 2023, 13, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030546
Zhang G, He G, Gu Y, Shi Y. Effect of Process Parameters on Arc Shape, Macroscopic Features, and Microhardness in Pulsed GMA–Additive Manufacturing. Crystals. 2023; 13(3):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030546
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Gang, Guanyu He, Yufen Gu, and Yu Shi. 2023. "Effect of Process Parameters on Arc Shape, Macroscopic Features, and Microhardness in Pulsed GMA–Additive Manufacturing" Crystals 13, no. 3: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030546
APA StyleZhang, G., He, G., Gu, Y., & Shi, Y. (2023). Effect of Process Parameters on Arc Shape, Macroscopic Features, and Microhardness in Pulsed GMA–Additive Manufacturing. Crystals, 13(3), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13030546






