Two Cd(II)-Based MOFs Constructed from Tris(3′-F-4′-carboxybiphenyl)amine: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Luminescence Sensing towards Nitrophenols and Acetylacetone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of MOFs
2.3. X-ray Structure Determination
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Description
3.1.1. Crystal Structure of CdMOF-1
3.1.2. Crystal Structure of CdMOF-2
3.2. Stability of CdMOF-1 and CdMOF-2
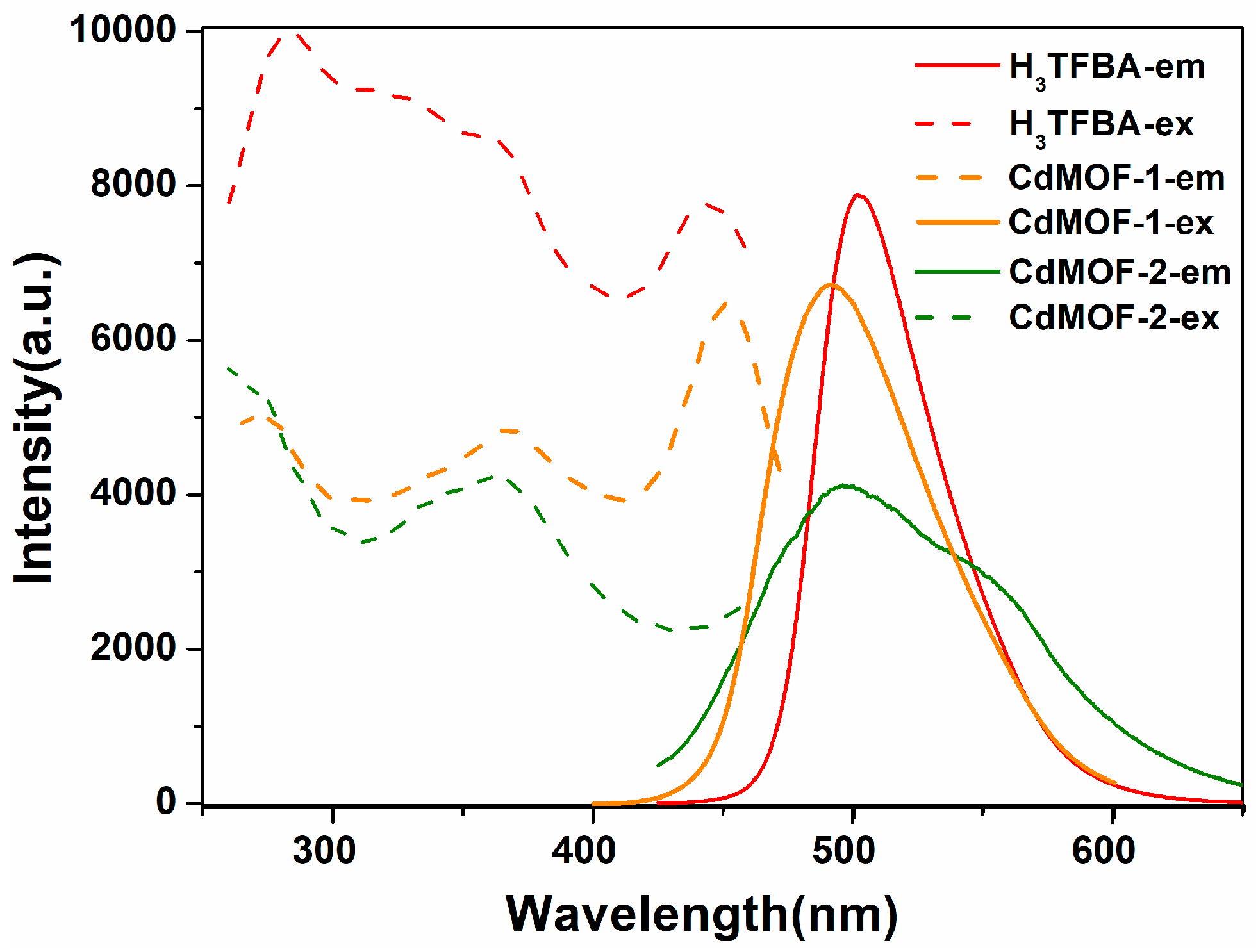
3.3. Solid-State Photoluminescent Spectra
3.4. Sensing of Nitrobenzene Explosive
3.5. Luminescence Sensing Properties for Organic Molecules
3.6. Sensing Mechanism for Detecting TNP/PNP and Solvent Molecules
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zang, Z.S.; Xu, Y.M.; Lau, A.T.Y. Molecular and pathophysiological aspects of metal ion uptake by the zinc transporter ZIP8. Toxicol. Res. 2016, 5, 987–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bilge, S.; Dogan-Topal, B.; Yücel, A.; Sınağ, A.; Ozkan, S.A. Recent advances in flower-like nanomaterials: Synthesis, characterization, and advantages in gas sensing applications. Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 153, 116638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Ren, G.J.; Li, M.L.; Yang, W.T.; Pan, Q.H. Selective Detection of Aromatic Nitrophenols by a Metal–Organic Framework-Based Fluorescent Sensor. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 6308–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Ren, S.; Xia, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J. An ultra-stable Cd coordination polymer based on double-chelated ligand for efficient dual-response of TNP and MnO4−. Sens. Actuators B 2020, 317, 128230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Mandal, S.K. Understanding the effect of an amino group on the selective and ultrafast detection of TNP in water using fluorescent organic probes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 3288–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, M.A.; Nawar, N.; Radwan, F.M.; Hosny, N.M. Spectral characterization, optical band gap calculations and DNA binding of some binuclear Schiff-base metal complexes derived from 2-amino-ethanoic acid and acetylacetone. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1080, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, G.A.; Hipolito, M.G.; Fruti, M.A.; Tellez, S.C.; Martinez, R.M.; Arias, M.P.C.; Alejandre, E.Z.; Falcony, C. Synthesis and fabrication of Y2O3:Tb3+ and Y2O3:Eu3+ thin films for electroluminescent applications: Optical and structural characteristics. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 149, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zastrow, M.L.; Radford, R.J.; Chyan, W.; Anderson, C.T.; Zhan, D.; Loas, A.; Tzounopoulos, T.; Lippard, S.J. Reaction-Based Probes for Imaging Mobile Zinc in Live Cells and Tissues. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, X.M.; Fan, X.Y.; Hao, P.Y.; Wang, W.M.; Zhao, B. A stable zinc–organic framework with luminescence detection of acetylacetone in aqueous solution. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, B.M.; Ryan, M.C. Indenylmetal Catalysis in Organic Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2862–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Séby, F.; Charles, S.; Gagean, M.; Garraud, H.; Donard, O.F.X. Chromium speciation by hyphenation of high-performance liquid chromatography to inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry-study of the influence of interfering ions. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2003, 18, 1386–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Singh, A.K.; Jain, A.K. Electrochemical sensors for the determination of Zn2+ ions based on pendant armed macrocyclic ligand. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 5386–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprara, S.; Laglera, L.M.; Monticelli, D. Ultrasensitive and Fast Voltammetric Determination of Iron in Seawater by Atmospheric Oxygen Catalysis in 500 μL Samples. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6357–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmakar, A.; Hazra, S.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Urea and thiourea based coordination polymers and metal-organic frameworks: Synthesis, structure and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 453, 214314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoedel, A.; Li, M.; Li, D.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Structures of Metal-Organic Frameworks with Rod Secondary Building Units. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12466–12535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Astruc, D. State of the Art and Prospects in Metal–Organic Framework (MOF)-Based and MOF-Derived Nanocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 1438–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, A.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Hazra, S.; Guedes da Silva, M.F.C.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Metal–Organic Frameworks with Pyridyl-Based Isophthalic Acid and Their Catalytic Applications in Microwave Assisted Peroxidative Oxidation of Alcohols and Henry Reaction. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 1837–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islamoglu, T.; Chen, Z.; Wasson, M.C.; Buru, C.T.; Kirlikovali, K.O.; Afrin, U.; Mian, M.R.; Farha, O.K. Metal–Organic Frameworks against Toxic Chemicals. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8130–8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Dou, Y.; Xie, L.H.; Rutledge, W.; Li, J.R.; Zhou, H.C. Zr-based metal–organic frameworks: Design, synthesis, structure, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2327–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Dutta, S.; More, Y.D.; Fajal, S.; Ghosh, S.K. Post-synthetically modified metal–organic frameworks for sensing and capture of water pollutants. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 17832–17850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Han, J.J.; Cuan, J.; Zhou, Y. Responsive luminescent MOF materials for advanced anticounterfeiting. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 134170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.T.; Li, H.T.; Huang, H.N.; Cao, X.H.; Chen, X.D.; Cao, D.P. Porous organic polymers as a platform for sensing applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 2031–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.N.; Huang, K.; Li, X.L.; Han, D.F.; Qiu, Q.; Jing, L.H.; Qin, D.B. Tetra(4-imidazoylphenyl)ethylene based metal-organic frameworks for highly selective detection of TNP and Fe3+. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 280, 120993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.L.; Liu, S.J.; Tian, X.M.; Zheng, T.F.; Cao, C.; Niu, C.Y.; Chen, Y.Q.; Chen, J.L.; Huang, H.P.; Wen, H.R. ZnII-Based Metal–Organic Framework with a Rare tcj Topology as a Turn-On Fluorescent Sensor for Acetylacetone. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 3578–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.E.; Wang, Y.H.; Yan, H.; Lu, J.; Liu, H.T.; Li, Y.W.; Wang, S.N.; Li, D.C.; Dou, J.M.; Yang, L.; et al. A Multiresponsive Luminescent Sensitivities of a 3D Cd-CP with Visual Turn-on and Ratiometric Sensing toward Al3+ and Cr3+ as Well as Turn-off Sensing toward Fe3+. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 3828–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, R.; Bhowmick, R.; Ghosh, P.; Biswas, S.; Koner, S. Selective luminescent sensing of metal ions and nitroaromatics over a porous mixed-linker cadmium(ii) based metal–organic framework. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 8523–8533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.S.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Liao, R.B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Qiao, R.; Liu, Z.D. A Photoluminescent Cd(II) Coordination Polymer with Potential Active Sites Exhibiting Multiresponsive Fluorescence Sensing for Trace Amounts of NACs and Fe3+ and Al3+ Ions. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 4945–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tian, J.F.; Yu, H.H.; Fan, M.Y.; Li, X.; Liu, F.B.; Sun, J.; Su, Z.M. Controllable Synthesis of Metal–Organic Frameworks Based on Anthracene Ligands for High-Sensitivity Fluorescence Sensing of Fe3+, Cr2O72–, and TNP. Cryst. Growth Des. 2022, 22, 2954–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yao, S.L.; Zheng, T.F.; Xu, H.; Li, J.Y.; Peng, Y.; Chen, J.L.; Liu, S.J.; Wen, H.R. Turn-on and blue-shift fluorescence sensor toward l-histidine based on stable CdII metal–organic framework with tetranuclear cluster units. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 5983–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.T.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, L.N.; Wu, Y.L.; Cai, W.; Tang, P.F.; Su, X.L.; Zhang, W.Y.; Wang, Y.Y. Luminescent metal-organic frameworks constructed by a V-shaped pentacarboxylic acid ligand as bifunctional chemosensors for Fe3+ and Cr2O72−. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 309, 122988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Zhang, R.F.; Wang, Y.X.; Ma, X.X.; Guo, Q.; Du, X.M.; Li, L.L.; Wang, Y.L. Water-stable Cd(II) metal-organic framework as multi-responsive luminescent sensor for CrO42−, Cr2O72− ions and picric acid as well as its mixed matrix membranes. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 311, 123119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Zhang, R.F.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Li, L.L.; Ma, C.L. Multi-responsive luminescent probes for Fe3+, Cr2O72− and acetylacetone with Cd-MOF based on tris(3′-F-4′-carboxybiphenyl)amine and trans-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethene. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 307, 122820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXTL V6.1 Software Reference Manual; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.H.; Yao, S.L.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Zheng, T.F.; Liu, S.J.; Chen, J.L.; Wen, H.R. A novel CdII-based metal–organic framework as a multi-responsive luminescent sensor for Fe3+, MnO4−, Cr2O72−, salicylaldehyde and ethylenediamine detection with high selectivity and sensitivity. CrystEngComm 2021, 23, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spek, A.L. Single-crystal structure validation with the program PLATON. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, P.; Xie, Q.; Ma, Q.Q.; Meng, Y.H.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X.J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. Cadmium(II)–Triazole Framework as a Luminescent Probe for Ca2+ and Cyano Complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 10459–10474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.W.; Yang, S.H.; Cao, M.; Li, L.K.; Du, C.X.; Zang, S.Q. Rational Design of Three Two-Fold Interpenetrated Metal–Organic Frameworks: Luminescent Zn/Cd-Metal–Organic Frameworks for Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol and Nitrofurazone in the Aqueous Phase. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 7173–7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Han, Y.F.; Zheng, Z.B.; Wang, C.A.; Nie, K.; Li, J.K.; Zhang, R.F.; Ru, J.; Ma, C.L. A luminescent Zn-MOF constructed from l-aspartic acid and 4, 4-bipyridine: Selectively and sensitively detect Fe3+ and 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol (TNP) in aqueous solution. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 295, 121887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Wu, J.J.; Tang, G.D.; Feng, J.Y.; Luo, F.M.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C. Multiresponsive water-stable luminescent Cd coordination polymer for detection of TNP and Cu2+. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 272, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yao, Z.; Ye, Y.; Chen, L.; Lin, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, S. Robustness, Selective Gas Separation, and Nitrobenzene Sensing on Two Isomers of Cadmium Metal–Organic Frameworks Containing Various Metal–O–Metal Chains. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 12961–12968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Qin, L.; Chen, J.X.; Zheng, H.G. H-Bonding Interactions Induced Two Isostructural Cd(II) Metal–Organic Frameworks Showing Different Selective Detection of Nitroaromatic Explosives. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 10999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, L. The detection of selectivity and sensitivity towards TNP by a new Zn(II)-coordination polymer as luminescent sensor in aqueous solution. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2022, 266, 120419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.M.; Yao, S.L.; Qiu, C.Q.; Zheng, T.F.; Chen, Y.Q.; Huang, H.P.; Chen, J.L.; Liu, S.J.; Wen, H.R. Turn-On Luminescent Sensor toward Fe3+, Cr3+, and Al3+ Based on a Co(II) Metal–Organic Framework with Open Functional Sites. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 2803–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.L.; Xiong, Y.C.; Tian, X.M.; Liu, S.J.; Xu, H.; Zheng, T.F.; Chen, J.L.; Wen, H.R. A multifunctional benzothiadiazole-based fluorescence sensor for Al3+, Cr3+ and Fe3+. CrystEngComm 2021, 23, 1898–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.Y.; Yu, H.H.; Fu, P.; Su, Z.M.; Li, X.; Hu, X.L.; Gao, F.W.; Pan, Q.Q. Luminescent Cd(II) metal-organic frameworks with anthracene nitrogen-containing organic ligands as novel multifunctional chemosensors for the detection of picric acid, pesticides, and ferric ions. Dyes Pigm. 2021, 185, 108834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, Z.Y.; Xu, S.S.; Li, D.D.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, W.; Zhou, H.P.; Wu, J.Y.; Tian, Y.P. Fluorescent metal–organic frameworks based on mixed organic ligands: New candidates for highly sensitive detection of TNP. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 1900–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Dai, R.D.; Li, B.J.; Hang, T.X.; Xie, J.X.; Lu, J.; Zhu, X.D. Fluorescent Metal–Organic Framework Constructed from Semi-rigid Ligand for the Sensitive Sensing of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarkar, S.S.; Joarder, B.; Chaudhari, A.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ghosh, S.K. Highly Selective Detection of Nitro Explosives by a Luminescent Metal–Organic Framework. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.F.; Chen, H.H.; Xia, Z.Q.; Ren, C.T.; Han, J.; Sun, W.J.; Wei, W.; Xie, G.; Chen, S.P. A Robust TbIII-MOF for Ultrasensitive Detection of Trinitrophenol: Matched Channel Dimensions and Strong Host−Guest Interactions. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 8198–8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Identification Code | CdMOF-1 | CdMOF-2 |
|---|---|---|
| formula | C117H71Cd4F9N3O22 | C49H29CdF3N3O6 |
| Mr | 2491.36 | 925.15 |
| crystal system | monoclinic | monoclinic |
| space group | C2 | C2/c |
| a, Å | 35.739(3) | 42.050(4) |
| b, Å | 21.5187(19) | 11.5480(11) |
| c, Å | 22.094(2) | 21.7211(19) |
| α, deg | 90 | 90 |
| β, deg | 123.367(5) | 119.215(5) |
| γ, deg | 90 | 90 |
| V, Å3 | 14,191(2) | 9205.9(15) |
| Z | 4 | 8 |
| ρcalcd, g cm–3 | 1.166 | 1.335 |
| T/K | 298(2) | 293(2) |
| μ, mm–1 | 0.658 | 0.535 |
| F(000) | 4972 | 3736 |
| data/restraints/parameters | 23,248/4361/1400 | 8047/1177/560 |
| GOF (F2) | 0.825 | 1.044 |
| R1a,wR2b (I > 2σ(I)) | 0.0834, 0.1769 | 0.1265, 0.2976 |
| R1a, wR2b (all data) | 0.2077, 0.2281 | 0.1795, 0.3354 |
| R1a = Σ||Fo| − |Fc||/Σ|Fo|. wR2b = [Σw(Fo2 − Fc2)2/Σw(Fo2)2]1/2 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ru, J.; Shi, Y.; Guo, Q.; Hu, B.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, C. Two Cd(II)-Based MOFs Constructed from Tris(3′-F-4′-carboxybiphenyl)amine: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Luminescence Sensing towards Nitrophenols and Acetylacetone. Crystals 2022, 12, 1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121708
Ru J, Shi Y, Guo Q, Hu B, Li L, Wang Y, Ma C. Two Cd(II)-Based MOFs Constructed from Tris(3′-F-4′-carboxybiphenyl)amine: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Luminescence Sensing towards Nitrophenols and Acetylacetone. Crystals. 2022; 12(12):1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121708
Chicago/Turabian StyleRu, Jing, Yixuan Shi, Qiang Guo, Boxuan Hu, Leilei Li, Yanlan Wang, and Chunlin Ma. 2022. "Two Cd(II)-Based MOFs Constructed from Tris(3′-F-4′-carboxybiphenyl)amine: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Luminescence Sensing towards Nitrophenols and Acetylacetone" Crystals 12, no. 12: 1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121708
APA StyleRu, J., Shi, Y., Guo, Q., Hu, B., Li, L., Wang, Y., & Ma, C. (2022). Two Cd(II)-Based MOFs Constructed from Tris(3′-F-4′-carboxybiphenyl)amine: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Luminescence Sensing towards Nitrophenols and Acetylacetone. Crystals, 12(12), 1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121708






