Fabrication of Ti-Alloy Powder/Solid Composite with Uniaxial Anisotropy by Introducing Unidirectional Honeycomb Structure via Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Densities and Microstructures of Specimens
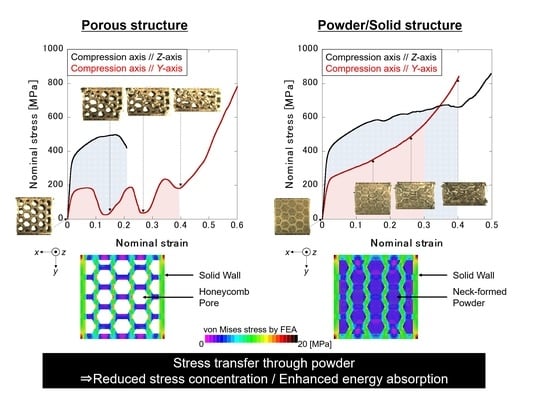
3.2. Deformation Behaviors and Mechanical Properties of the Products
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Powder/Solid Structuring on the Anisotropy Deformation Behavior of Porous Specimens with Unidirectional Honeycomb Pores
4.2. Influence of Honeycomb Pore Introduction and Powder/Solid Structuring on Anisotropy of Mechanical Properties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiner, S.; Traub, W. Bone structure from ångstroms to microns. FASEB J. 1992, 6, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Kaibara, K.; Tabata, Y.; Nagata, N.; Enomoto, S.; Marukawa, E.; Umakoshi, Y. Unique alignment and texture of biological apatite crystallites in typical calcified tissues analyzed by micro-beam X-ray diffractometer system. Bone 2002, 31, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimoto, T.; Kawahara, K.; Matsugaki, A.; Kamioka, H.; Nakano, T. Quantitative evaluation of osteocyte morphology and bone anisotropic extracellular matrix in rat femur. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huiskes, R.; Weinans, H.; van Rietbergen, B. The relationship between stress shielding and bone resorption around total hip stems and the effects of flexible materials. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1992, 274, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyama, Y.; Miura, T.; Ishimoto, T.; Itaya, T.; Niinomi, M.; Nakano, T. Bone loss and reduced bone quality of the human femur after total hip arthroplasty under stress-shielding effects by titanium-based implant. Mater. Trans. 2012, 53, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Dong, E.; Li, D.; Dong, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L. Anisotropy characteristics of microstructures for bone substitutes and porous implants with application of additive manufacturing in orthopaedic. Mater. Des. 2020, 191, 108608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimoto, T.; Hagihara, K.; Hisamoto, K.; Sun, S.-H.; Nakano, T. Crystallographic texture control of beta-type Ti–15Mo–5Zr–3Al alloy by selective laser melting for the development of novel implants with a biocompatible low Young’s modulus. Scr. Mater. 2017, 132, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeo, N.; Fukuda, H.; Matsugaki, A.; Inoue, T.; Serizawa, A.; Matsuzaka, T.; Ishimoto, T.; Ozasa, R.; Gokcekaya, O.; Nakano, T. 3D puzzle in cube pattern for anisotropic/isotropic mechanical control of structure fabricated by metal additive manufacturing. Crystals 2021, 11, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickels, L. AM and aerospace: An ideal combination. Met. Powder Rep. 2015, 70, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zou, J.; Li, S.; Jamshidi, P.; Abena, A.; Forsey, A.; Moat, R.J.; Essa, K.; Wang, M.; Zhou, K.; et al. Additive manufacturing of bio–inspired multi–scale hierarchically strengthened lattice structures. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2021, 167, 103764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeo, N.; Ishimoto, T.; Nakano, T. Novel powder/solid composites possessing low Young’s modulus and tunable energy absorption capacity, fabricated by electron beam melting, for biomedical applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 639, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soro, N.; Saintier, N.; Merzeau, J.; Veidt, M.; Dargusch, M.S. Quasi-static and fatigue properties of graded Ti–6Al–4V lattices produced by Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF). Addit. Manuf. 2021, 37, 101653. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Ling, M.; Nai, S.; Ding, J.; Wei, J. Electron beam melted heterogeneously porous micro lattices for metallic bone applications: Design and investigations of boundary and edge effects. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101566. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Ding, S.; Wen, C. Additive manufacturing technology for porous metal implant applications and triple minimal surface structures: A review. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobbert, F.S.L.; Lietaert, K.; Eftekhari, A.A.; Pouran, B.; Ahmadi, S.M.; Weinans, H.; Zadpoor, A.A. Additively manufactured metallic porous biomaterials based on minimal surfaces: A unique combination of topological, mechanical, and mass transport properties. Acta Biomater. 2017, 53, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Li, X.; Luo, S.; Ling, M.; Nai, S.; Ding, J.; Wei, J. Additively manufactured heterogeneously porous metallic bone with biostructural functions and bone-like mechanical properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 62, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugino, A.; Ohtsuki, C.; Tsuru, K.; Hayakawa, S.; Nakano, T.; Okazaki, Y.; Osaka, A. Effect of spatial design and thermal oxidation on apatite formation on Ti-15Zr-4Ta-4Nb alloy. Acta Biomater. 2008, 5, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsugaki, A.; Aramoto, G.; Nakano, T. The alignment of MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts on steps of slip traces introduced by dislocation motion. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7327–7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, Y.; Matsugaki, A.; Kawahara, K.; Ninomiya, T.; Sawada, H.; Nakano, T. Unique arrangement of bone matrix orthogonal to osteoblast alignment controlled by Tspan11-mediated focal adhesion assembly. Biomaterials 2019, 209, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Sin, W.J.; Nai, M.L.S.; Wei, J. Effects of processing parameters on surface roughness of additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V via electron beam melting. Materials 2017, 10, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsugaki, A.; Aramoto, G.; Ninomiya, T.; Sawada, H.; Hata, S.; Nakano, T. Abnormal arrangement of a collagen/apatite extracellular matrix orthogonal to osteoblast alignment is constructed by a nanoscale periodic surface structure. Biomaterials 2015, 37, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Fujitani, W.; Ishimoto, T.; Lee, J.W.; Ikeo, N.; Fukuda, H.; Kuramoto, K. Formation of new bone with preferentially oriented biological apatite crystals using a novel cylindrical implant containing anisotropic open pores fabricated by the electron beam melting (EBM) method. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nakano, T.; Kan, T.; Ishimoto, T.; Ohashi, Y.; Fujitani, W.; Umakoshi, Y.; Hattori, T.; Higuchi, Y.; Tane, M.; Nakajima, H. Evaluation of bone quality near metallic implants with and without lotus-type pores for optimal biomaterial design. Mater. Trans. 2006, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeo, N.; Ishimoto, T.; Serizawa, A.; Nakano, T. Control of mechanical properties of three-dimensional Ti–6Al–4V products fabricated by electron beam melting with unidirectional elongated pores. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 2014, 45, 4293–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.J.; Ashby, M.F. Cellular Solids—Structure and Properties, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zeng, X. Controlling the tensile and fatigue properties of selective laser melted Ti–6Al–4V alloy by post treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 857, 157552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaghmandfard, R.; Chalasani, D.; Odeshi, A.; Mohammadi, M. Activated slip and twin systems in electron beam melted Ti-6Al-4V subjected to elevated and high strain rate dynamic deformations. Mater. Charact. 2021, 172, 110866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Vijayan, S.; Nandwana, P.; Jinschek, J.R. The effect of beam scan strategies on microstructural variations in Ti–6Al–4V fabricated by electron beam powder bed fusion. Mater. Des. 2020, 196, 109165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bermani, S.; Blackmore, M.; Zhang, W.; Todd, I. The origin of microstructural diversity, texture, and mechanical properties in electron beam melted Ti6Al4V. Metal. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 41, 3422–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Jiang, F.; Sun, X.; Chen, Z.; Tian, C.; Zhao, H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V fabricated by electron beam melting. Crystals 2020, 10, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, L.; Yang, P.; Fang, J.; Li, W. Energy absorption of additively manufactured functionally bi-graded thickness honeycombs subjected to axial loads. Thin-Walled Struct. 2019, 164, 107810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lee, P.D.; Singh, R.; Wu, G.; Lindley, T.C. Micro-CT characterization of structural features and deformation behavior of fly ash/aluminum syntactic foam. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 3003–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Q.; Patil, D.; Le, T.; Eppley, T.; Salti, Z.; Goss, D.; Grishin, A.; Bhate, D. An examination of the low strain rate sensitivity of additively manufactured polymer, composite and metallic honeycomb structures. Materials 2019, 12, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowski, P.; Płatek, P.; Antolak-Dudka, A.; Sarzyński, M.; Kucewicz, M.; Durejko, T.; Małachowski, J.; Janiszewski, J.; Czujko, T. Deformation of honeycomb cellular structures manufactured with Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS) technology under quasi-static loading: Experimental testing and simulation. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 25, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyongmaneerat, Y. Mechanical properties of partially sintered materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 452–453, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tan, Y.H.; Wang, P.; Su, X.; Jean, H.; Herng, T.S.; Ding, J. Metallic microlattice and epoxy interpenetrating phase composites: Experimental and simulation studies on superior mechanical properties and their mechanisms. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 135, 105934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeo, N.; Ishimoto, T.; Hiramoto, N.; Fukuda, H.; Ogisu, H.; Araki, Y.; Nakano, T. Solid/powder clad Ti-6Al-4V alloy with low Young’s modulus and high toughness fabricated by electron beam melting. Mater. Trans. 2015, 56, 755–758. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, T.; Ishimoto, T. Powder-based additive manufacturing for development of tailor-made implants for orthopedic applications. KONA 2015, 32, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilton, M.; Lewis, G.S.; Wee, H.B.; Armstrong, A.; Hast, M.W.; Manogharan, G. Additive manufacturing of fracture fixation implants: Design, material characterization, biomechanical modeling and experimentation. Addit. Manufact. 2020, 33, 101137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Compressive Axis | Porous Specimen | Composite Specimen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z-Direction | Y-Direction | Z-Direction | Y-Direction | |
| Young’s modulus [GPa] | 41.9 ± 9.3 | 28.9 ± 1.1 | 50.5 ± 3.9 | 38.1 ± 2.9 |
| 0.2% Proof stress [MPa] | 326 ± 8 | 120 ± 13 | 368 ± 13 | 210 ± 20 |
| Plateau stress [MPa] | - | - | 629 ± 12 | 455 ± 26 |
| Densification strain | - | - | 0.40 ± 0.02 | 0.29 ± 0.00 |
| Toughness [MPa] | 85.8 ± 6.2 | 16.0 ± 1.8 | 231 ± 8 | 101 ± 12 |
| Specific energy absorption [J/g] | 19.4 ± 1.4 | 3.6 ± 0.4 | 52.1 ± 1.8 | 22.8 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ikeo, N.; Matsumi, T.; Ishimoto, T.; Ozasa, R.; Matsugaki, A.; Matsuzaka, T.; Gokcekaya, O.; Takigawa, Y.; Nakano, T. Fabrication of Ti-Alloy Powder/Solid Composite with Uniaxial Anisotropy by Introducing Unidirectional Honeycomb Structure via Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion. Crystals 2021, 11, 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091074
Ikeo N, Matsumi T, Ishimoto T, Ozasa R, Matsugaki A, Matsuzaka T, Gokcekaya O, Takigawa Y, Nakano T. Fabrication of Ti-Alloy Powder/Solid Composite with Uniaxial Anisotropy by Introducing Unidirectional Honeycomb Structure via Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion. Crystals. 2021; 11(9):1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091074
Chicago/Turabian StyleIkeo, Naoko, Tatsuya Matsumi, Takuya Ishimoto, Ryosuke Ozasa, Aira Matsugaki, Tadaaki Matsuzaka, Ozkan Gokcekaya, Yorinobu Takigawa, and Takayoshi Nakano. 2021. "Fabrication of Ti-Alloy Powder/Solid Composite with Uniaxial Anisotropy by Introducing Unidirectional Honeycomb Structure via Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion" Crystals 11, no. 9: 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091074
APA StyleIkeo, N., Matsumi, T., Ishimoto, T., Ozasa, R., Matsugaki, A., Matsuzaka, T., Gokcekaya, O., Takigawa, Y., & Nakano, T. (2021). Fabrication of Ti-Alloy Powder/Solid Composite with Uniaxial Anisotropy by Introducing Unidirectional Honeycomb Structure via Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion. Crystals, 11(9), 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091074