Self-Assembly of an Equimolar Mixture of Liquid Crystals and Magnetic Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Simulation Details
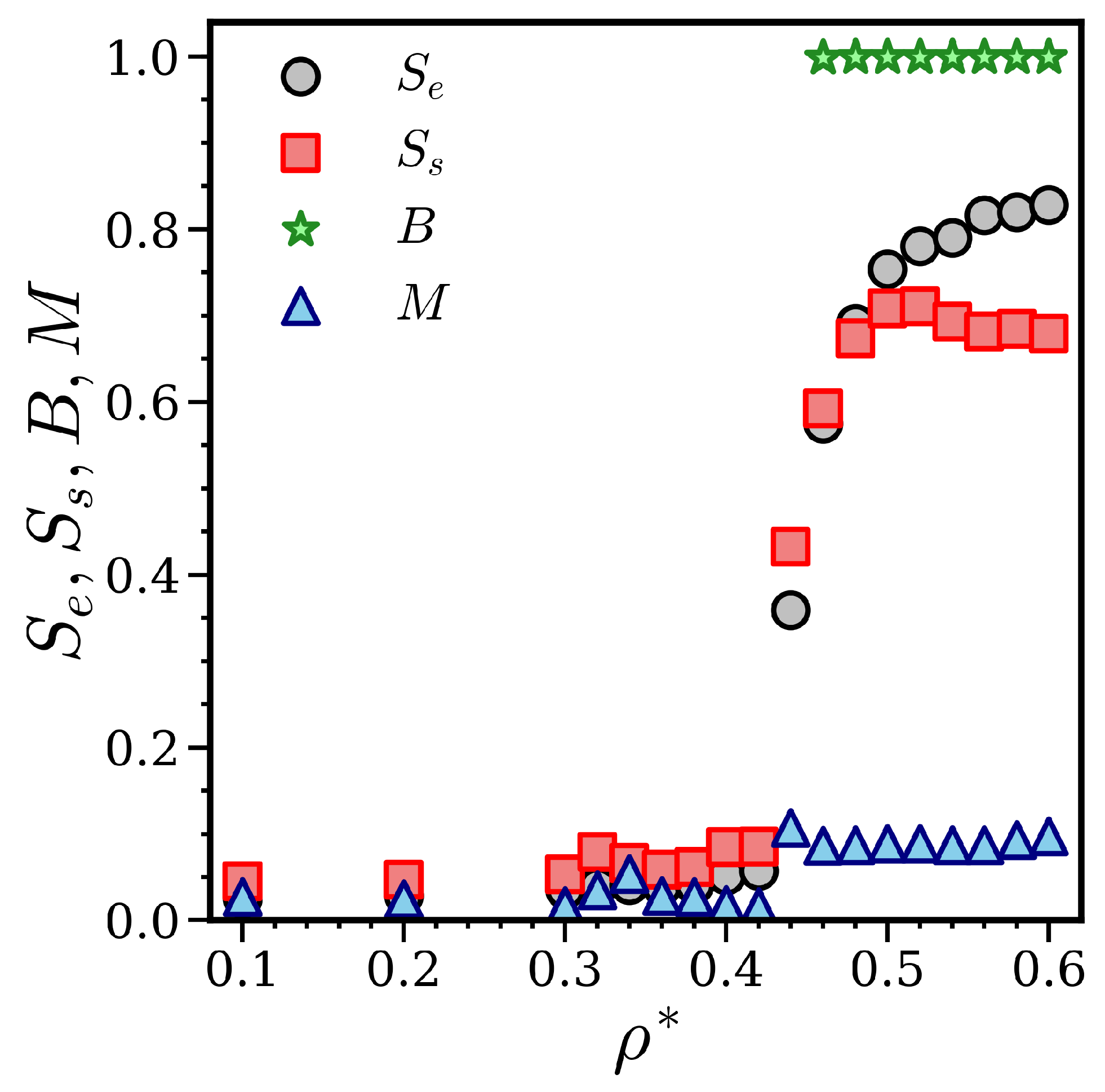
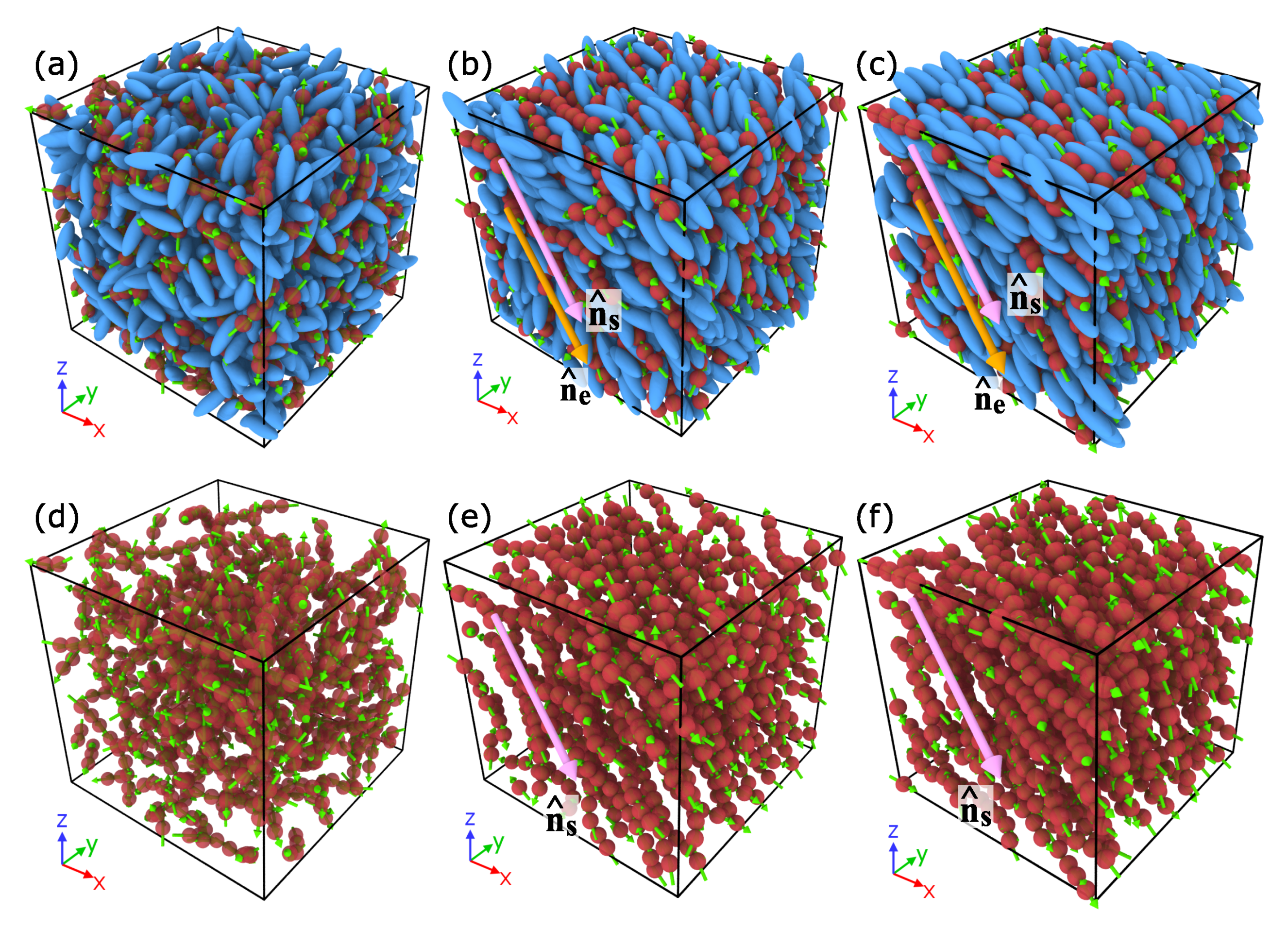
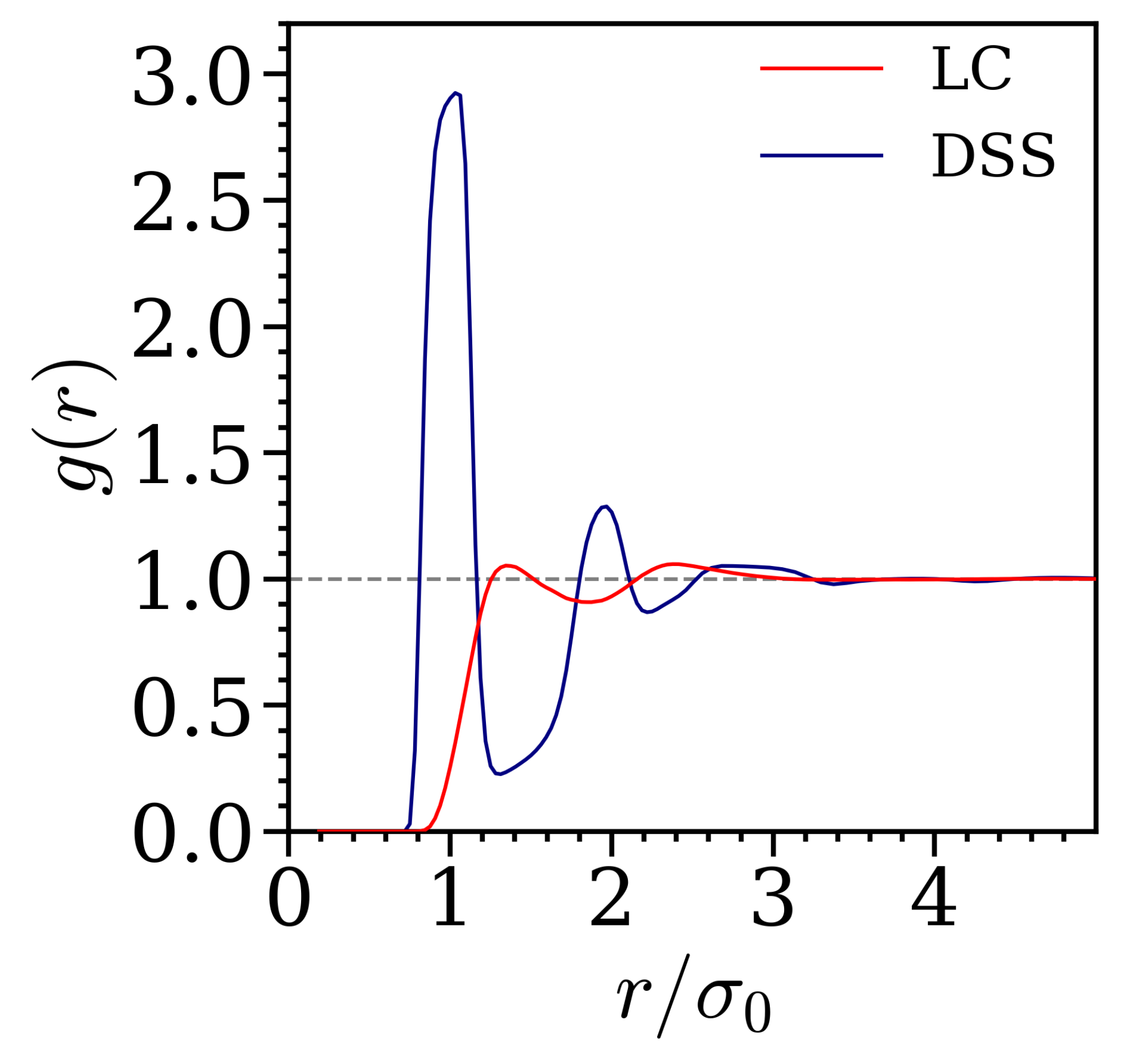
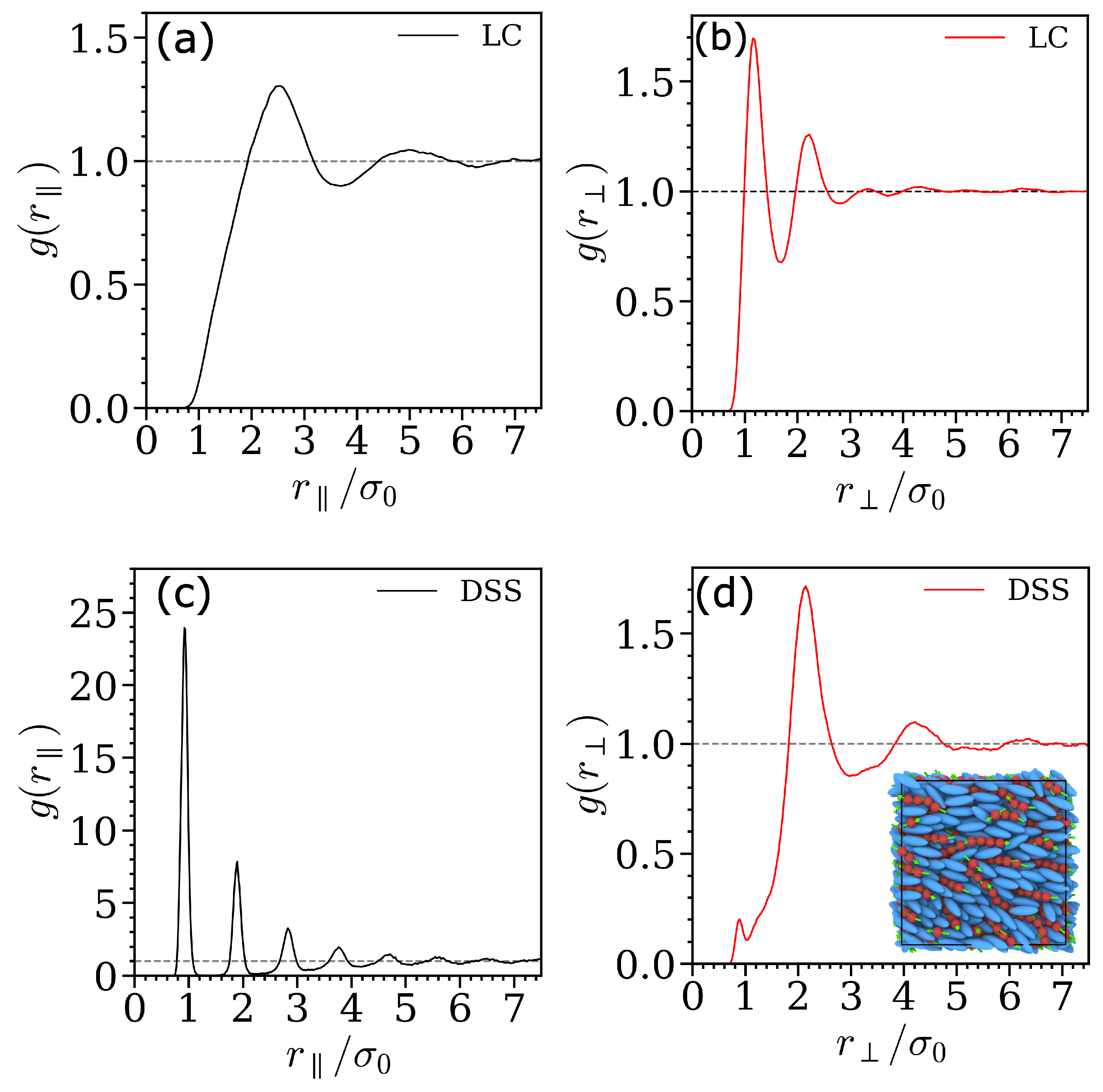
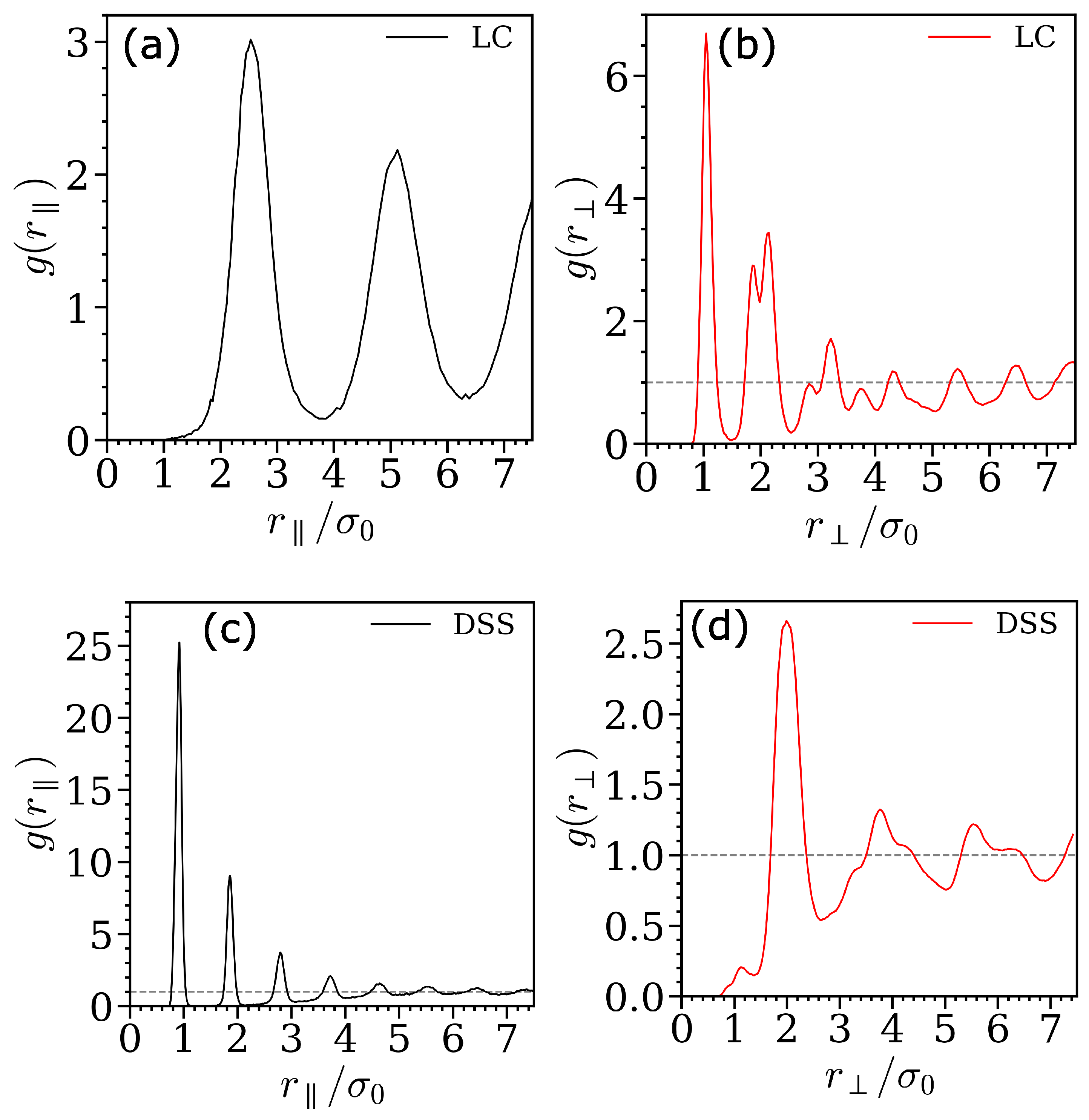
3. Results
4. Discussion
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lagerwall, J.P.F.; Scalia, G. A new era for liquid crystal research: Applications of liquid crystals in soft matter nano-, bio- and microtechnology. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisoyi, H.K.; Kumar, S. Liquid-crystal nanoscience: An emerging avenue of soft self-assembly. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanc, C.; Coursault, D.; Lacaze, E. Ordering nano-and microparticles assemblies with liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. Rev. 2013, 1, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, C.; Neto, A.M.F. Ferrofluids: Properties and applications. Braz. J. Phys. 2015, 35, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, I.; Yoshida, S.; Kelly, T.; Pitcher, W. Liquid crystal–ferrofluid emulsions. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 6021–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Gennes, P.; Brochard, F. Theory of magnetic suspensions in liquid crystals. J. Phys. 1970, 31, 691. [Google Scholar]
- Liebert, L.; Martinet, A. Coupling between nematic lyomesophases and ferrofluids. J. Phys. Lett. 1979, 40, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rault, J.; Cladis, P.; Burger, J. Ferronematics. Phys. Lett. A 1970, 32, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Chiang, S. The magnetic-field-induced birefringence of the mixtures of the chiral molecules and the ferronematic liquid crystals. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1987, 144, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, C. Magnetic platelets in a nematic liquid crystal. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1976, 36, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapp, S.H. Dipolar fluids under external perturbations. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, R525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, I.; Heberle, M.; Osipov, M.; Giesselmann, F. Ordering of ferromagnetic nanoparticles in nematic liquid crystals. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 4636–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lapointe, C.P.; Mason, T.G.; Smalyukh, I.I. Shape-controlled colloidal interactions in nematic liquid crystals. Science 2009, 326, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Ackerman, P.J.; Lubensky, T.C.; Smalyukh, I.I. Biaxial ferromagnetic liquid crystal colloids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10479–10484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neto, A.M.F.; Saba, M.M.F. Determination of the minimum concentration of ferrofluid required to orient nematic liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. A 1986, 34, 3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.H.; Amer, N.M. Observation of macroscopic collective behavior and new texture in magnetically doped liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983, 51, 2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopčanský, P.; Tomašovičová, N.; Koneracká, M.; Závišová, V.; Timko, M.; Džarová, A.; Šprincová, A.; Éber, N.; Fodor-Csorba, K.; Tóth-Katona, T.; et al. Structural changes in the 6CHBT liquid crystal doped with spherical, rodlike, and chainlike magnetic particles. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 78, 011702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berejnov, V.; Bacri, J.C.; Cabuil, V.; Perzynski, R.; Raikher, Y. Lyotropic ferronematics: Magnetic orientational transition in the discotic phase. Europhys. Lett. 1998, 41, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podoliak, N.; Buchnev, O.; Buluy, O.; D’Alessandro, G.; Kaczmarek, M.; Reznikov, Y.; Sluckin, T. Macroscopic optical effects in low concentration ferronematics. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buluy, O.; Nepijko, S.; Reshetnyak, V.; Ouskova, E.; Zadorozhnii, V.; Leonhardt, A.; Ritschel, M.; Schönhense, G.; Reznikov, Y. Magnetic sensitivity of a dispersion of aggregated ferromagnetic carbon nanotubes in liquid crystals. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kredentser, S.; Buluy, O.; Davidson, P.; Dozov, I.; Malynych, S.; Reshetnyak, V.; Slyusarenko, K.; Reznikov, Y. Strong orientational coupling in two-component suspensions of rod-like nanoparticles. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertelj, A.; Lisjak, D.; Drofenik, M.; Čopič, M. Ferromagnetism in suspensions of magnetic platelets in liquid crystal. Nature 2013, 504, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arantes, F.; Odenbach, S. The magnetoviscous effect of micellar solutions doped with water based ferrofluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 390, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertelj, A.; Osterman, N.; Lisjak, D.; Čopič, M. Magneto-optic and converse magnetoelectric effects in a ferromagnetic liquid crystal. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 9065–9072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertelj, A.; Lisjak, D. Ferromagnetic nematic liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. Rev. 2017, 5, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, A.; Banerjee, V.; Puri, S. Slaved coarsening in ferronematics. EPL Europhys. Lett. 2020, 128, 66001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, A.; Banerjee, V.; Puri, S. Domain growth in ferronematics: Slaved coarsening, emergent morphologies and growth laws. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 2659–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burylov, S.I.; Raikher, Y.L. Macroscopic properties of ferronematics caused by orientational interactions on the particle surfaces. II. Behavior of real ferronematics in external fields. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1995, 258, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryskin, A.B.; Pleiner, H.; Müller, H.W. Hydrodynamic instabilities in ferronematics. Eur. Phys. J. E 2003, 11, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarkova, E.; Pleiner, H.; Müller, H.W.; Brand, H.R. Macroscopic dynamics of ferronematics. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisht, K.; Banerjee, V.; Milewski, P.; Majumdar, A. Magnetic nanoparticles in a nematic channel: A one-dimensional study. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 100, 012703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisht, K.; Wang, Y.; Banerjee, V.; Majumdar, A. Tailored morphologies in two-dimensional ferronematic wells. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 101, 022706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peroukidis, S.D.; Klapp, S.H.L. Spontaneous ordering of magnetic particles in liquid crystals: From chains to biaxial lamellae. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 92, 010501(R). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peroukidis, S.D.; Lichtner, K.; Klapp, S.H.L. Tunable structures of mixtures of magnetic particles in liquid-crystalline matrices. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peroukidis, S.D.; Klapp, S.H.L. Orientational order and translational dynamics of magnetic particle assemblies in liquid crystals. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrivastav, G.P.; Klapp, S.H. Anomalous transport of magnetic colloids in a liquid crystal–magnetic colloid mixture. Soft matter 2019, 15, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siboni, N.H.; Shrivastav, G.P.; Peroukidis, S.D.; Klapp, S.H. Structure and rheology of soft hybrid systems of magnetic nanoparticles in liquid-crystalline matrices: Results from particle-resolved computer simulations. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, K.; Eremin, A.; Stannarius, R.; Peroukidis, S.D.; Klapp, S.H.L.; Klein, S. Colloidal suspensions of rodlike nanocrystals and magnetic spheres under an external magnetic stimulus: Experiment and molecular dynamics simulation. Langmuir 2016, 32, 5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroukidis, S.D.; Klapp, S.H.; Vanakaras, A.G. Field-induced anti-nematic and biaxial ordering in binary mixtures of discotic mesogens and spherical magnetic nanoparticles. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 10667–10675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorkunov, M.V.; Osipov, M.A. Mean-field theory of a nematic liquid crystal doped with anisotropic nanoparticles. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 4348–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, M.A.; Gorkunov, M.V. Molecular theory of phase separation in nematic liquid crystals doped with spherical nanoparticles. ChemPhysChem 2014, 15, 1496–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, M.; Luckhurst, G. Computer simulation of liquid crystal phases formed by Gay-Berne mesogens. In Liquid Crystals I; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 65–137. [Google Scholar]
- Gay, J.; Berne, B. Modification of the overlap potential to mimic a linear site–site potential. J. Chem. Phys. 1981, 74, 3316–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.M.; Petersen, M.K.; Plimpton, S.J.; Grest, G.S. Liquid crystal nanodroplets in solution. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 044901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, R.; Costantini, A.; Muccioli, L.; Orlandi, S.; Zannoni, C. A computer simulation study of the formation of liquid crystal nanodroplets from a homogeneous solution. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 044905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Everaers, R.; Ejtehadi, M. Interaction potentials for soft and hard ellipsoids. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 67, 041710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, D.; Patey, G.N. Orientational order in simple dipolar liquids: Computer simulation of a ferroelectric nematic phase. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morenao-Razo, J.A.; Díaz-Herrera, E.; Klapp, S.H.L. Computer simulations of strongly interacting dipolar systems: Performance of a truncated Ewald sum. Mol. Phys. 2006, 104, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Holm, C.; Müller, H.W. Molecular dynamics study on the equilibrium magnetization properties and structure of ferrofluids. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 66, 021405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comp. Phys. 1995, 117, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrivastav, G.P.; Siboni, N.H.; Klapp, S.H. Steady-state rheology and structure of soft hybrid mixtures of liquid crystals and magnetic nanoparticles. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 2516–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoen, M.; In, S.H.L.K. Reviews of Computational Chemistry; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 24. [Google Scholar]
- Sreekumari, A.; Ilg, P. Slow relaxation in structure-forming ferrofluids. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 88, 042315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.; Tildesley, D. Computer Simulation of Liquids; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Andrienko, D. Introduction to liquid crystals. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 267, 520–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennes, P.G.; Prost, J. The Physics of Liquid Crystals; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1993; Volume 83. [Google Scholar]
- Cuetos, A.; Galindo, A.; Jackson, G. Thermotropic biaxial liquid crystalline phases in a mixture of attractive uniaxial rod and disk particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 237802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Patey, G.N. Ferroelectric liquid-crystal and solid phases formed by strongly interacting dipolar soft spheres. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 46, 7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stukowski, A. Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO–the Open Visualization Tool. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 18, 015012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, J.J.; Levesque, D. Ferroelectric phases of dipolar hard spheres. Phys. Rev. E 1993, 48, 3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañeda-Guzmán, E.; Moreno-Razo, J.; Díaz-Herrera, E.; Sambriski, E. Molecular aspect ratio and anchoring strength effects in a confined Gay–Berne liquid crystal. Mol. Phys. 2014, 112, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siboni, N.H.; Shrivastav, G.P.; Klapp, S.H. Non-monotonic response of a sheared magnetic liquid crystal to a continuously increasing external field. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 024505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shrivastav, G.P. Self-Assembly of an Equimolar Mixture of Liquid Crystals and Magnetic Nanoparticles. Crystals 2021, 11, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070834
Shrivastav GP. Self-Assembly of an Equimolar Mixture of Liquid Crystals and Magnetic Nanoparticles. Crystals. 2021; 11(7):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070834
Chicago/Turabian StyleShrivastav, Gaurav P. 2021. "Self-Assembly of an Equimolar Mixture of Liquid Crystals and Magnetic Nanoparticles" Crystals 11, no. 7: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070834
APA StyleShrivastav, G. P. (2021). Self-Assembly of an Equimolar Mixture of Liquid Crystals and Magnetic Nanoparticles. Crystals, 11(7), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070834





