Abstract
We report optimized crystal growth conditions for the quarternary compound AgCrPS by chemical vapor transport. Compositional and structural characterization of the obtained crystals were carried out by means of energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and powder X-ray diffraction. AgCrPS is structurally closely related to the PS family, which contains several compounds that are under investigation as 2D magnets. As-grown crystals exhibit a plate-like, layered morphology as well as a hexagonal habitus. AgCrPS crystallizes in monoclinic symmetry in the space group (No. 13). The successful growth of large high-quality single crystals paves the way for further investigations of low dimensional magnetism and its anisotropies in the future and may further allow for the manufacturing of few-layer (or even monolayer) samples by exfoliation.
1. Introduction
Among the magnetic quasi-two-dimensional materials that have recently moved in the focus of (quasi-)two-dimensional (2D) materials research [1,2,3], the PS class of layered materials offers a plenitude of isostructural compounds with different magnetic properties depending on M [4,5]. Thus, PS allows to investigate fundamental aspects of low dimensional magnetism and several members may be promising for future applications, e.g., complementing non-magnetic (quasi-)2D materials in heterostructures or in spintronic devices [6,7]. Furthermore, future applications in the field of catalysis are conceivable due to the structural similarity to the non-magnetic 2D materials such as graphene or the transition metal dichalcogenide compounds for which such applications are already discussed [8,9,10].
Regarding the crystal structure, the PS family consists of van der Waals layered compounds which share a honeycomb network of and, most prominently, a dominantly covalent anion located in the voids of the honeycomb [4,5]. In the bulk, such layers are stacked on top of each other only interacting via weak van der Waals forces. Consequently, these compounds can be easily exfoliated potentially down to a single layer [11,12].
Several isovalent substitution series of by another (e.g., (MnFe)PS [13], (MnNi)PS [14], (FeNi)PS [15,16] and (ZnNi)PS [4]) are reported to exhibit solid solution behavior and, thus, imply a random distribution of the substituents on the honeycomb network, as illustrated in Figure 1a. Beyond isovalent substitution, Colombet et al. [17,18,19,20] demonstrated that a substitution of by also yields several stable compounds. In contrast to the isovalent substitution series however, and do not randomly occupy the M positions in the lattice but order either in an alternating or in a zig-zag stripe-like arrangement on the honeycomb, as illustrated in Figure 1b,c, respectively. The former arrangement is attributed to a minimization of repulsive Coloumb interactions (i.e., charge ordering). The latter is observed for compounds for which and have notably different sizes and, thus, is dominantly driven by a minimization of lattice distortion and steric effects [4,17].
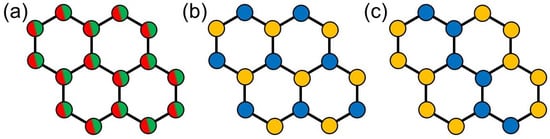
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the different arrangements of M and on the honeycomb lattice of PS. (a) Random distribution for PS. (b) Alternating/triangular arrangement and (c) zig-zag stripe like arrangement for PS.
With being a magnetic ion (e.g., V or Cr) and being non-magnetic (e.g., Cu or Ag), the magnetic sublattices formed in PS extend the magnetic structures of the usually magnetically hexagonal PS compounds by an alternating/triangular and a zig-zag stripe-like magnetic arrangement [4,17,19]. The stripe-like magnetic structure is especially notable, as each stripe of magnetic ions is well isolated from the adjacent magnetic stripes by a stripe of non-magnetic ions. Although the corresponding compound still has a (quasi-)2D layered crystal structure, the magnetic structure can be expected to exhibit 1D magnetic characteristics. Indeed, several indications for such low dimensional magnetism are reported for PS with and [19,21], making it an interesting compound for further studies.
However, until now only details on the synthesis of AgCrPS via solid state synthesis are reported (although Mutka et al. [21] mention CVT grown crystals, they do not report any further details or conditions regarding the crystal growth) [19]. Although small crystals in the m scale could be obtained by solid state synthesis, which allowed for a structural solution based on single crystal X-ray diffraction, significantly larger crystals are needed for detailed investigations of the physical properties including anisotropies.
As a crystal growth method of choice, for macroscopic AgCrPS single crystals, the chemical vapor transport (CVT) technique is suitable due to the contained volatile elements such as S and P. Phosphorus and sulfur are both volatile and readily evaporate at elevated temperatures. The generation of volatile intermediate transition metal species for the vapor transport using so-called transport agents is well established [22]. CVT is the crystal growth technique of choice for virtually all ternary PS compounds [4,5]. For example, Taylor et al. [23] and Nitsche et al. [24] report the successful crystal growth of PS with by CVT using either chlorine or iodine as transport agent and we present the crystal growth of mixed transition metal phosphorus sulfides of the substitution series (FeNi)PS [16] and (MnNi)PS [14] by the same technique with iodine as agent. To determine a suitable temperature gradient for the CVT growth of the quarternary compound AgCrPS, several growth experiments with different temperature profiles were conducted. The temperature profile, which is reported hereafter, resulted in the best crystal size and quality as well as regarding impurity contributions and opens up access to macroscopic AgCrPS single crystals. In addition to the crystal growth of AgCrPS, we also present a comprehensive compositional and structural characterization of the obtained crystals.
2. Materials and Methods
The elemental educts for the crystal growth of AgCrPS, as listed in Table 1, were obtained from Alfa Aesar and kept in an argon filled glove box for storage and handling.

Table 1.
Elemental educts used for the CVT growth of AgCrPS.
The crystals obtained from the CVT crystal growth experiments were thoroughly characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) regarding their morphology and topography using a secondary electron (SE) detector and regarding chemical homogeneity via the chemical contrast obtained from a back scattered electron (BSE) detector. For this, a ZEISS EVO MA 10 scanning electron microscope was used. The chemical composition of the crystals was investigated by energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), which was measured in the same SEM device with an accelerating voltage of 30 kV for the electron beam and using an energy dispersive X-ray analyzer.
The crystal structure of the obtained crystals was investigated by powder X-ray diffraction (pXRD), which was measured on a STOE STADI laboratory diffractometer in transmission geometry with Cu-K radiation from a curved Ge(111) single crystal monochromator and detected by a MYTHEN 1K 12.5-linear position sensitive detector manufactured by DECTRIS. The pXRD patterns were initially analyzed by pattern matching using the HighScore Plus program suite [25]. After the crystallographic phase was identified, a structural refinement of the crystal structure model was performed based on our experimental patterns using the Rietveld method in Jana2006 [26].
3. Crystal Growth via Chemical Vapor Transport
All procedures for the preparation were performed in a glove box under argon atmosphere. The elemental educts silver, chromium, red phosphorus and sulfur were weighed out in a molar ratio of Ag:Cr:P:S = 1:1:2:6 and homogenized in an agate mortar. 0.5 g of reaction mixture were loaded in a quartz ampule (6 mm inner diameter, 2 mm wall thickness) together with approx. 50 mg of the transport agent iodine. Immediately prior to use, the ampule was cleaned by washing with distilled water, rinsing with isopropanol and, subsequently, baking out at 800 C for at least 12 h in an electric tube furnace. This is done to avoid contamination of the reaction volume with (adsorbed) water. The filled ampule was then transferred to a vacuum pump and evacuated to a residual pressure of bar. To suppress the unintended sublimation of the transport agent during evacuation, the end of the ampule containing the material was cooled with a small Dewar flask filled with liquid nitrogen. After reaching the desired internal pressure, the valve to the vacuum pump was closed, the cooling was stopped and the ampule was sealed under static pressure at a length of approximately 12 cm.
The ampule was carefully placed in a two-zone tube furnace in such a way that the reaction mixture was only at one side of the ampule which is referred to as the charge region. As illustrated in Figure 2a, the furnace was initially heated homogeneously to 750 C at 100 C/h. The charge region was kept at this temperature for 274.5 h while the other side of the ampule, which is the sink region (see Figure 2b), was initially heated up to 800 C at 100 C/h, dwelled at this temperature for 24 h and then cooled back to 750 C at 1 C/h. An inverse transport gradient is formed, i.e., transport from sink to charge, to clean the sink region of particles which stuck to the walls of the quartz ampule during the previous preparation steps. This ensures improved nucleation conditions in the following step. Then the sink region was cooled to 690 C at 0.5 C/h to gradually form the thermal transport gradient resulting in a controlled nucleation. With a final gradient of 750 C (charge) to 690 C (sink), the ampule was dwelled for 100 h. After this period of time, the charge region was cooled to the sink temperature in 1 h before both regions were furnace cooled (i.e., the heating elements were turned off) to room temperature.
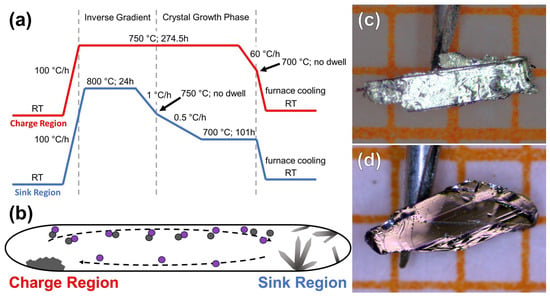
Figure 2.
(a) Graphical illustrations of the temperature profile for the CVT growth of AgCrPS and (b) schematic drawing of an ampule during CVT. Arrows indicate the mass flow of the volatile transport species (top) and the flow of the released transport agent back to the charge (bottom). (c,d): As-grown crystals of AgCrPS. A orange square in the background corresponds to for scale.
Shiny plate-like crystals of AgCrPS in the size of approximately were obtained. As example, as-grown single crystals are shown in Figure 2c,d. These crystals exhibit a layered morphology and are easily exfoliated, which is typical for bulk crystals of (quasi-)2D materials.
As shown in Figure 3a, some as-grown crystals exhibit small spherical particles (likely solidified droplets) of a secondary phase (bright) and pieces of a second secondary phase (dark). As the secondary phases are found only on the surface, exfoliating the crystals is sufficient to remove the secondary phases and results in crystals with clean surfaces, as illustrated in Figure 3b.
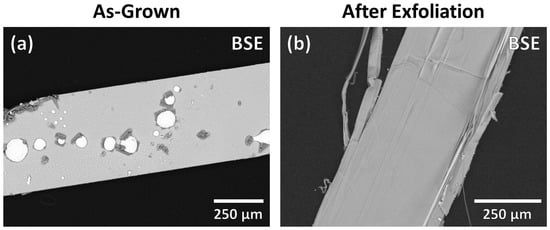
Figure 3.
SEM image with chemical contrast (BSE detector) of (a) an as-grown crystal of AgCrPS with superficial impurities and (b) a piece of the same crystal after exfoliation with a clean surface.
4. Crystal Morphology and Compositional Analysis
The topographical SE image of a AgCrPS crystal in Figure 4a exhibits a flat crystal surface and sharp edges. The terrace close to the upper edge of the crystal is a typical feature of layered systems. Furthermore, on the upper edge of the crystal, some steps can be seen, which form 120 angles, indicative of a hexagonal crystal habitus. The SE image with BSE detector in in Figure 4b shows an overall homogeneous contrast over the surface of the crystal demonstrating that it is chemically homogeneous. At some small areas, a change in contrast is observed. In comparison with the SEM image in SE mode, these spots can be clearly attributed to impurity particles on top of the crystal and not to any region of intergrowth with a secondary phase.
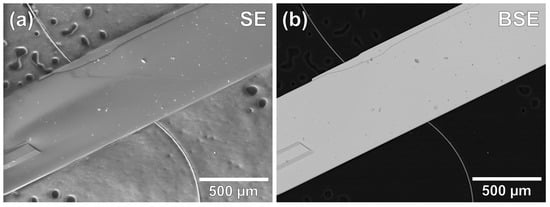
Figure 4.
SEM image of a AgCrPS crystal with topographical contrast (SE mode) in (a) and chemical contrast (BSE mode) in (b).
By EDX measurements on multiple spots on several crystals, the mean elemental composition of the crystals was obtained as AgCrPS. This composition is in ideal agreement with the expected composition of AgCrPS and the small standard deviations (given in parentheses) indicate a homogeneous elemental distribution and composition.
5. Structural Analysis
The pXRD pattern obtained from exfoliated AgCrPS crystals, as shown in Figure 5a, was indexed in the space group (No. 13), in agreement with the literature [19]. No additional reflection were observed demonstrating the intrinsic phase purity of our crystals.
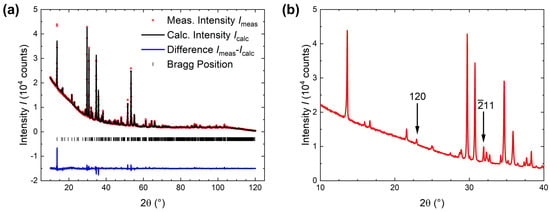
Figure 5.
(a) pXRD pattern from powdered AgCrPS crystals compared to the calculated pattern based on the refined crystal structure model. (b) Zoomed-in view on the low angle regime (10–40). The marked reflections are expected to be systematically absent assuming a crystal structure in the space group of instead of .
The space group, which is typically observed for compounds of the PS family [23,27], including PS compounds of isovalent substitution series (e.g., MnFePS [13], MnNiPS [14] and FeNiPS [16]), can be ruled out. Assuming a monoclinic unit cell, several observed reflections correspond to Laue indices that are systematically absent for C centering, as they violate the reflection condition : . Examples are the reflections at corresponding to 120 and at corresponding to , as shown in Figure 5b.
This implies that Ag and Cr indeed arrange as zig-zag stripes in AgCrPS and do not just randomly occupy the corners of the structural honeycomb network, as it is the case for isovalent substitutions. While the former scenario breaks the mirror symmetry of the space group of the FePS aristotype [28], which results in a space group, the latter scenario would not. Furthermore, a space group, as reported, e.g., for CuCrPS [17] with a triangular arrangement of the two transition element cations, can be ruled out based on the same considerations.
Starting from the crystal structure model proposed by Colombet et al. [19], a refined crystal structure model is obtained using the Rietveld method which is sufficient to describe our experimental pattern with good agreement, as shown in Figure 5a. The obtained lattice parameter and reliability factors are summarized in Table 2 (top) and the refined structural model is given in the same table on the bottom and is illustrated in Figure 6. The strongest disagreement between model and experiment is observed for the high intensity 001 reflection at . As this reflection corresponds to the stacking of layers, it is most prominently affected by any kind of disorder or defects influencing the stacking. Due to the weak structural interaction between layers, which are only based on weak van der Waals forces, the PS compounds are prone to stacking faults and twinning between layers. In the presence of such defects, the shape of the corresponding 001 reflection is altered, which may be a reason for the observed deviation between the experiment and the model without defects.

Table 2.
Top: Summary of experimental parameters of the pXRD experiment on AgCrPS, extracted lattice parameters and reliability factors of the structural model obtained by the Rietveld method. Bottom: Refined crystal structure model of AgCrPS and isotropic displacement parameters with standard deviations given in parentheses. All sites were treated as fully occupied.
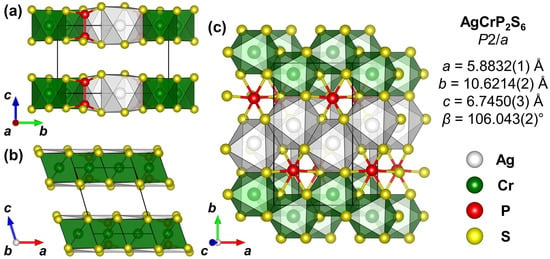
Figure 6.
Refined crystal structure model of AgCrPS after Rietveld refinement. View along a in (a), along b in (b) and along in (c). The CrS and AgS coordination environments are shown in the color of the respective central atom.
Additionally, the experimental pattern exhibits significantly altered reflection intensities compared to an initial model, which are attributed to a strongly preferred orientation of the crystallites in the investigated sample. Due to the layered structure with only weak van der Waals interactions between layers, the powder particles obtained from grinding AgCrPS crystals are plate-like and tend to lie flat on the sample holder. Thus, reflections with a dominant l component (e.g., 001) exhibit higher intensities than expected for spherical crystallites in transmission geometry. To adjust for this effect in the model, the method proposed by March [29] and extended by Dollase [30] was used. However, the preferred orientation in AgCrPS is strongly pronounced, such that it might be beyond the limit of what the semi-empirical March-Dollase model is capable of describing accurately. This may furthermore contribute to the deviation between model and experiment around the 001 reflection.
The refined crystal structure model for AgCrPS shows that the Ag–S bonds are notably longer than the Cr–S bonds, as expected based on the difference between the size of the transition element cations (e.g., ionic radii for octahedral coordination: Å and Å [31]). These different bond lengths result in a distortion of the structure compared to the aristotype FePS, which can be clearly observed, e.g., in Figure 6a. In detail, the CrS coordination environment remains antiprismatic (i.e., close to octahedral with a slight trigonal elongation along ) with the faces above and below the shared plane of the transition elements being parallel to each other. However, the AgS coordination environment as well as for the PS environment are distorted in such a way that the faces above and below the transition element plane are not parallel to each other. In the view along the direction in Figure 6c, this distortion manifests in Ag and P being shifted off-center in their respective sulfur coordination environments away from the closest Cr positions. Meanwhile, Cr is located exactly in the center of the CrS unit. The observation that the CrS unit is closer to an ideal octahedral coordination environment than the AgS unit can be understood considering the local charge density (i.e., ionic size and charge). Cr is small and highly charged and, thus, interacts with the surrounding S atoms stronger than the comparable large and less charged Ag. Another notable structural aspect is the strong distortion of the [PS] units that demonstrates how flexible this covalent complex anion is. This complex anion is a common and characteristic building unit in the PS family and its flexibility may indicate that several more compounds of the general formula PS are stable but have not been synthesized yet.
6. Summary and Conclusions
We report optimized crystal growth conditions for the quarternary compound AgCrPS via Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT). A temperature profile adapted from the CVT growth of ternary PS compounds is sufficient to yield crystals of the target AgCrPS phase in the mm-size. On some crystals, traces of a superficial impurity phase is found which could be readily removed by exfoliation.
The as-grown crystals exhibit a plate-like, layered morphology as well as a hexagonal habitus and have the expected composition of AgCrPS based on EDX spectroscopy. The pXRD pattern is indexed in the space group in agreement with the literature [19]. The space group, on which the zig-zag type arrangement of M and is based on, can be well distinguished from, e.g., the and space groups due to reflections that are systematically absent for C centering. Starting from the model of Colombet et al. [19], a refined structural model is obtained using the Rietveld method. This model contains a notable distortion of the AgS and PS coordination environments, while the CrS units remain antiprismatic with a slight trigonal distortion.
The zig-zag stripe-like arrangement in AgCrPS and the alternating arrangement of M and , which is reported, e.g., for CuCrPS, are promising to yield interesting magnetic and electronic structures. While only few such quarternary phosphorus sulfide compounds have been synthesized until now, many more combinations of a 1+-ion and a 3+-ion can be expected to form analogous compounds. Furthermore, the fundamental idea of replacing by may be adoptable to the closely related structures such as, (Si,Ge)Te compounds.
The single crystals of AgCrPS that were obtained using the presented growth conditions allow for studies of the low dimensional magnetic interactions including the magnetic anisotropy of this compound in the future, which may lead to a better fundamental understanding of low dimensional magnetism. Furthermore, the van der Waals layered structure makes exfoliation easily possible and, thus, our successful growth of single crystals paves the way for further manufacturing of few-layer or even monolayer samples of AgCrPS.
Author Contributions
Investigation, S.S., Y.S., S.A.; data curation, S.S., Y.S.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S., S.A.; writing—review and editing, S.S., S.A.; supervision, B.B., S.A.; funding acquisition, B.B., S.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) via Grant No. DFG A.S 523\4-1. S.S. acknowledges financial support from GRK-1621 graduate academy of the DFG. B.B. acknowledges financial support from the DFG through SFB 1143 (project-id 247310070). Y.S acknowledge the support of BMBF through UKRATOP (BMBF). S.A., B.B. and S.S. thank DFG for financial support in the frame of the joint DFG-RSF project-id 405940956.
Data Availability Statement
The refined crystal structure model and the powder X-ray diffraction dataset of AgCrPS presented in this study are openly available in the Crystallography Open Database (COD), COD ID: 3000295 under https://www.crystallography.net/cod/3000295.html.
Acknowledgments
The publication of this article was funded by the Open Access Fund of the Leibniz Association.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Single crystals of AgCrPS are available from the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| 2D | Two-dimensional |
| CVT | Chemical vapor transport |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| SE | Secondary electron |
| BSE | Back-scattered electron |
| EDX | Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| pXRD | Powder X-ray diffraction |
References
- 2D magnetism gets hot. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 269. [CrossRef]
- Gibertini, M.; Koperski, M.; Morpurgo, A.F.; Novoselov, K.S. Magnetic 2D materials and heterostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarth, N. Magnetism in flatland. Nature 2017, 546, 216–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brec, R. Review on Structural and Chemical Properties of Transition Metal Phosphorus Trisulfides MPS3. In Intercalation in Layered Materials; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 93–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susner, M.A.; Chyasnavichyus, M.; McGuire, M.A.; Ganesh, P.; Maksymovych, P. Metal Thio- and Selenophosphates as Multifunctional van der Waals Layered Materials. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1602852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, D.; Seyler, K.L.; Linpeng, X.; Cheng, R.; Sivadas, N.; Huang, B.; Schmidgall, E.; Taniguchi, T.; Watanabe, K.; McGuire, M.A.; et al. Van der Waals engineering of ferromagnetic semiconductor heterostructures for spin and valleytronics. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1603113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.; Tu, M.W.Y.; Carnahan, C.; Cai, X.; Taniguchi, T.; Watanabe, K.; McGuire, M.A.; Cobden, D.H.; Xiao, D.; Yao, W.; et al. Voltage Control of a van der Waals Spin-Filter Magnetic Tunnel Junction. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Cha, J.J.; Wang, H.; Lee, H.R.; Cui, Y. First-row transition metal dichalcogenide catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, S.; Karuppannan, M.; Vinothkannan, M.; Ramachandran, K.; Kwon, O.J.; Yoo, D.J. Ultrafine Pt Nanoparticles Stabilized by MoS2/N-Doped Reduced Graphene Oxide as a Durable Electrocatalyst for Alcohol Oxidation and Oxygen Reduction Reactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 12504–12515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Shin, W.I.; Chen, H.; Lee, S.M.; Manickam, S.; Hanson, S.; Zhao, H.; Lester, E.; Wu, T.; Pang, C.H. A recent trend: Application of graphene in catalysis. Carbon Lett. 2020, 31, 177–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.U.; Lee, S.; Ryoo, J.H.; Kang, S.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, P.; Park, C.H.; Park, J.G.; Cheong, H. Ising-Type Magnetic Ordering in Atomically Thin FePS3. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 7433–7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lim, S.Y.; Lee, J.U.; Lee, S.; Kim, T.Y.; Park, K.; Jeon, G.S.; Park, C.H.; Park, J.G.; Cheong, H. Suppression of magnetic ordering in XXZ-type antiferromagnetic monolayer NiPS3. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masubuchi, T.; Hoya, H.; Watanabe, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Ban, S.; Ohkubo, N.; Takase, K.; Takano, Y. Phase diagram, magnetic properties and specific heat of Mn1-xFexPS3. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 460, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemerliuk, Y.; Wolter, A.U.B.; Cao, G.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Büchner, B.; Aswartham, S. Tuning magnetic and transport properties in (Mn1-xNix)2P2S6 Single crystals. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.11579. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, R.R.; Raychaudhuri, A.K. Magnetic Studies of a Mixed Antiferromagnetic System Fe1-xNixPS3. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1992, 53, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selter, S.; Shemerliuk, Y.; Sturza, M.I.; Wolter, A.U.B.; Büchner, B.; Aswartham, S. Crystal Growth and Anisotropic Magnetic Properties of Quasi-2D (Fe1-xNix)2P2S6. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.00066. [Google Scholar]
- Colombet, P.; Leblanc, A.; Danot, M.; Rouxel, J. Structural aspects and magnetic properties of the lamellar compound Cu0.50Cr0.50PS3. J. Solid State Chem. 1982, 41, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouili, Z.; Leblanc, A.; Colombet, P. Crystal structure of a new lamellar compound. J. Solid State Chem. 1987, 66, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombet, P.; Leblanc, A.; Danot, M.; Rouxel, J. Coordinance inhabituelle de l’argent dans un sufur lamellaire a sous-reseau magnetique 1D: Le compose Ag0.5Cr0.5PS3. Nouv. J. Chim. 1983, 7, 333–338. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Colombet, P.; Ouvrard, G.; Brec, R. A new chain compound of vanadium (III): Structure, metal ordering, and magnetic properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 1986, 21, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutka, H.; Payen, C.; Molinié, P. One-Dimensional Heisenberg Antiferromagnet with Spin S = 3/2. Experiments on AgCrP2S6. Europhys. Lett. (EPL) 1993, 21, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnewies, M.; Glaum, R.; Schmidt, M.; Schmidt, P. Chemical Vapor Transport Reactions; Walter de Gruyter GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, B.E.; Steger, J.; Wold, A. Preparation and properties of some transition metal phosphorus trisulfide compounds. J. Solid State Chem. 1973, 7, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, R.; Wild, P. Crystal growth of metal-phosphorus-sulfur compounds by vapor transport. Mater. Res. Bull. 1970, 5, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, T.; Sadki, M.; Bron, E.; König, U.; Nénert, G. The HighScore suite. Powder Diffr. 2014, 29, S13–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petříček, V.; Dušek, M.; Palatinus, L. Crystallographic Computing System JANA2006: General features. Z. Krist.-Cryst. Mater. 2014, 229, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brec, R.; Ouvrard, G.; Louisy, A.; Rouxel, J. Proprietes Structurales de Phases MIIPX3 (X = S, Se). Ann. Chim. 1980, 5, 499–512. [Google Scholar]
- Klingen, W.; Eulenberger, G.; Hahn, H. Über Hexachalkogeno-hypodiphosphate vom Typ M2P2X6. Die Naturwissenschaften 1970, 57, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, A. Mathematische Theorie der Regelung nach der Korngestalt bei affiner Deformation. Z. Krist.-Cryst. Mater. 1932, 81, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollase, W.A. Correction of intensities for preferred orientation in powder diffractometry: Application of the March model. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1986, 19, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised Effective Ionic Radii and Systematic Studies of Interatomic Distances in Halides and Chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).