A Switchable Cholesteric Phase Grating with a Low Operating Voltage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cell Fabrication
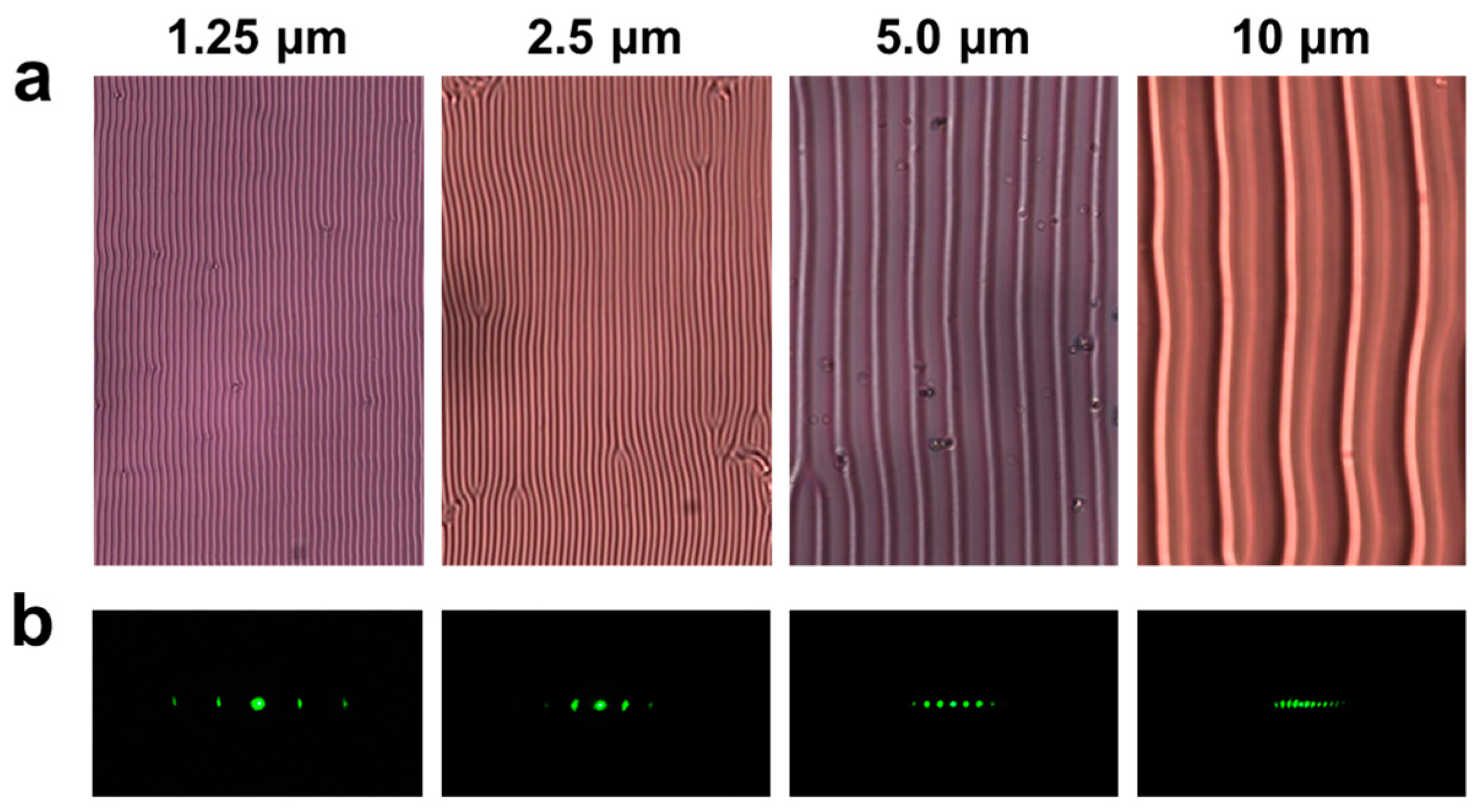
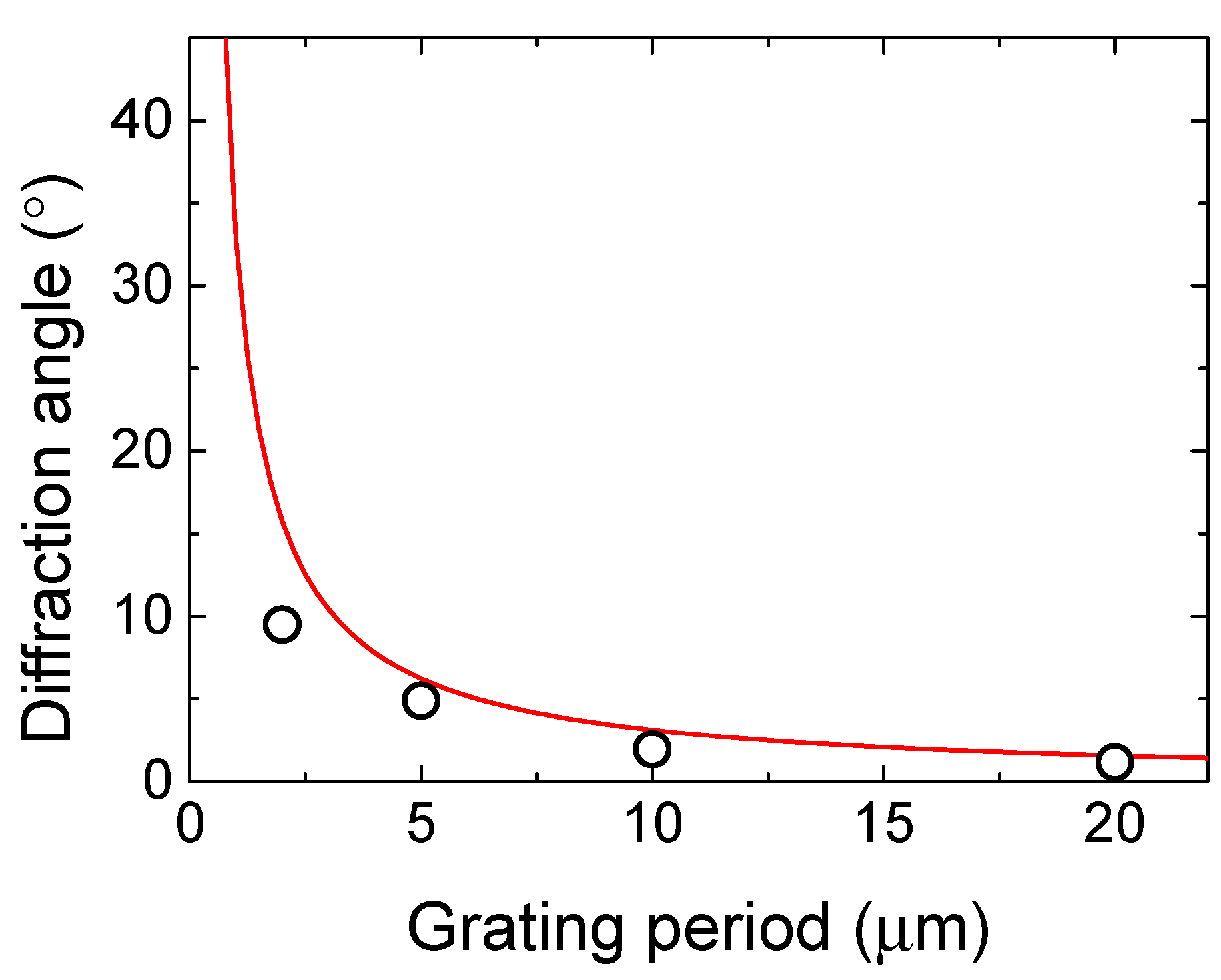
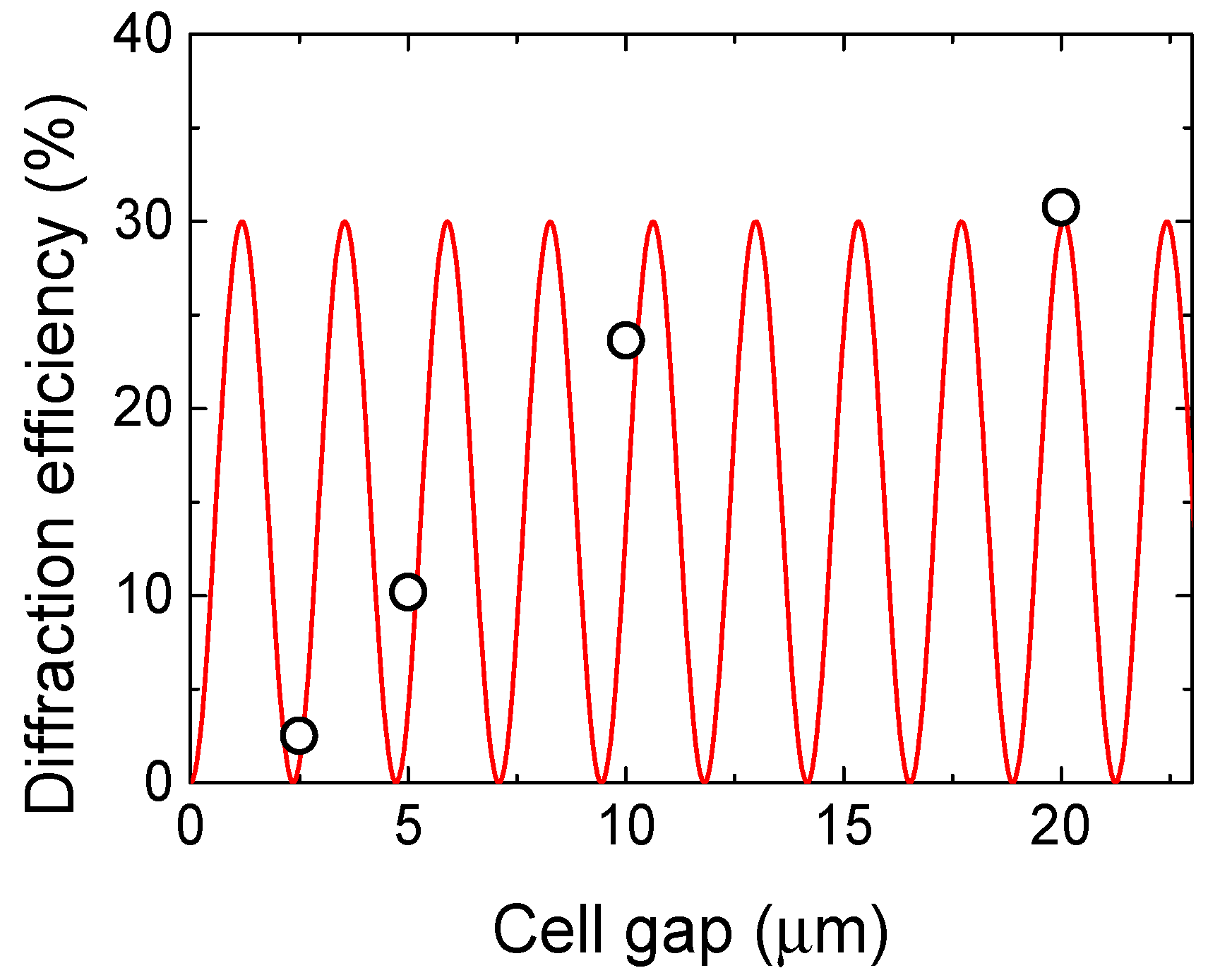
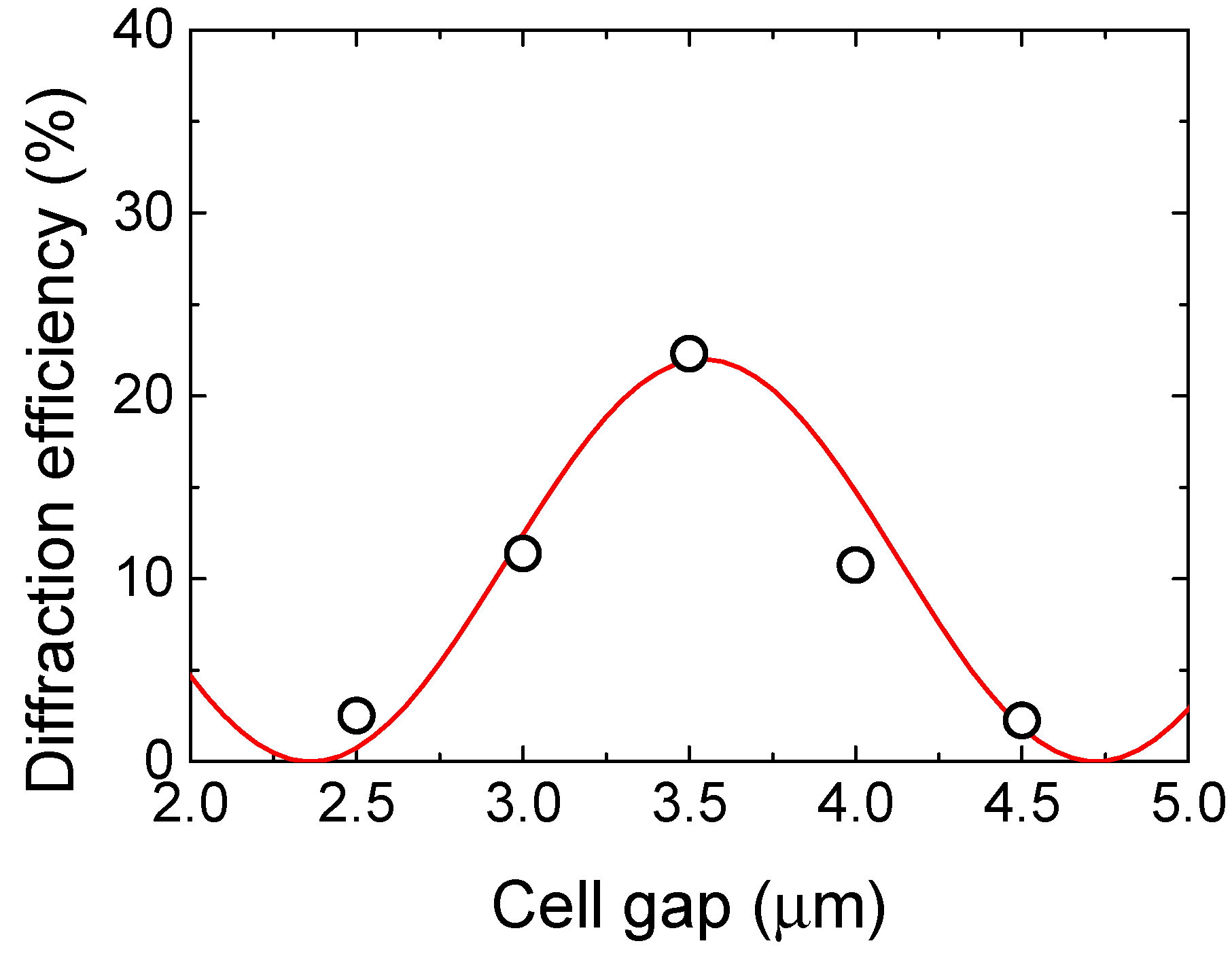
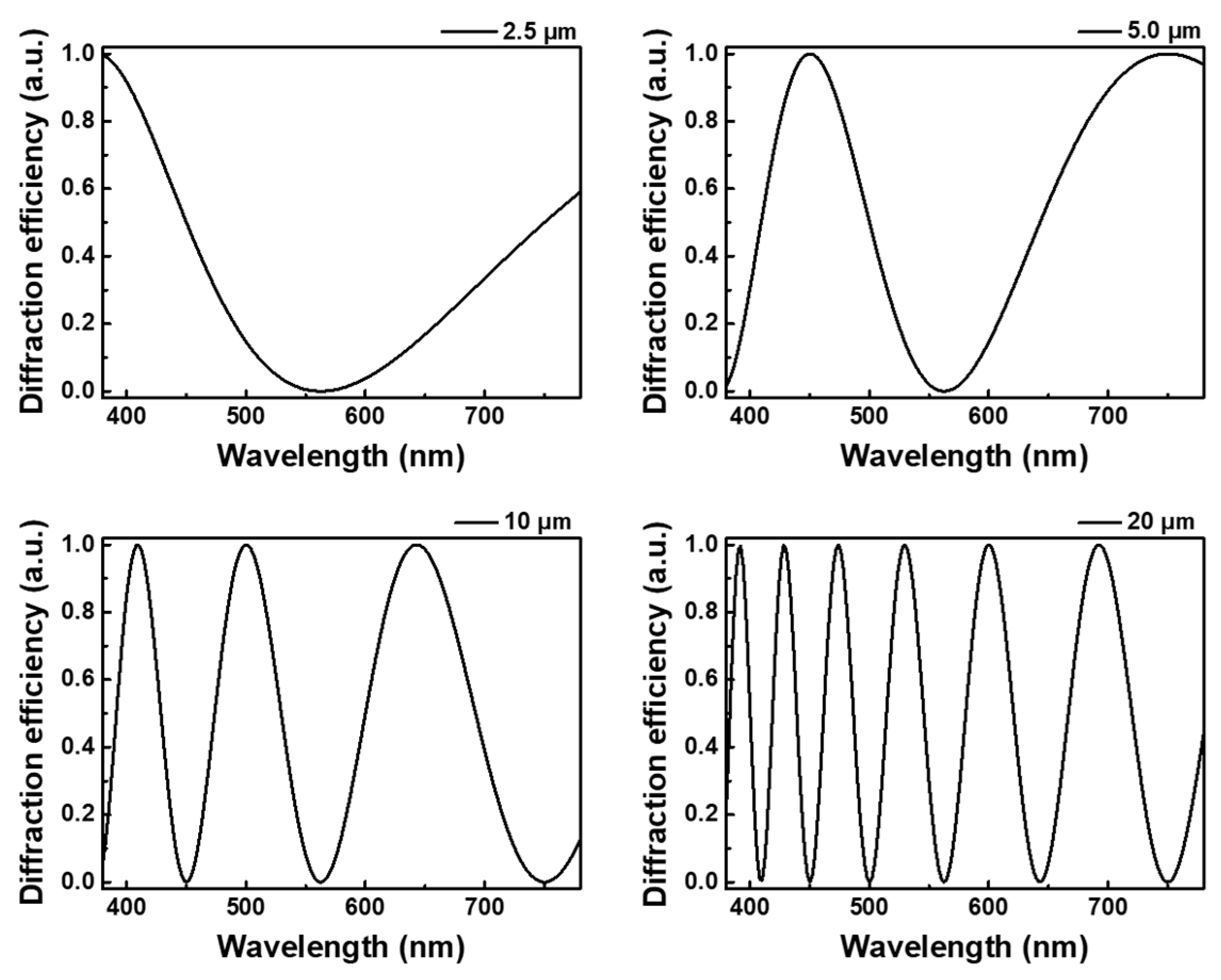
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shang, X.; Meeus, L.; Cuypers, D.; Smet, H.D. Fast switching cholesteric liquid crystal optical beam deflector with polarization independence. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Jin, H.-J.; Park, K.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, J.C.; Yoon, T.-H. Long-pitch cholesteric liquid crystal cell for switchable achromatic reflection. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 16745–16750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kang, S.-W.; Lee, S.-H. Advanced bistable cholesteric light shutter with dual frequency nematic liquid crystal. Opt. Mater. Express 2012, 2, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.-H.; Huh, J.-W.; Kim, K.-H.; Yoon, T.-H. Light shutter using dichroic-dye-doped long-pitch cholesteric liquid crystals. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 29332–29337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J.-W.; Yu, B.-H.; Heo, J.; Yoon, T.-H. Double-layered light shutter using long-pitch cholesteric liquid crystal cells. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 3792–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-W.; Baek, J.-M.; Heo, J.; Yoon, T.-H. Dye-doped cholesteric liquid crystal light shutter with a polymer-dispersed liquid crystal film. Dye. Pigment. 2016, 134, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-W.; Kim, S.-H.; Yoon, T.-H. Thermal control of transmission property by phase transition in cholesteric liquid crystals. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 6520–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Munos, A.; Palffy-Muhoray, P.; Taheri, B. Lasing in a three-dimensional photonic crystal of the liquid crystal blue phase II. Nat. Mater. 2002, 1, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, V.I.; Zhang, Z.-Q.; Genacka, A.Z. Lasing in chiral photonic structures. Prog. Quantum. Electron. 2003, 27, 369–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, H.; Morris, S. Liquid-crystal lasers. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Varanytsia, A.; Minkowski, F.; Paterson, D.A.; Storey, J.M.D.; Imrie, C.T.; Lavrentovich, O.D.; Palffy-Muhoray, P. Electrically tunable laser based on oblique heliconical cholesteric liquid crystal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12925–12928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryabchun, A.; Bobrovsky, A. Cholesteric liquid crystal materials for tunable diffractive optics. Adv Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 1800335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.; Folcia, C.L.; Etxebarria, J. Upgrading the performance of cholesteric liquid crystal lasers: Improvement margins and limitations. Materials 2018, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subacius, D.; Shiyanovskii, S.V.; Bos, P.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Cholesteric gratings with field-controlled period. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 71, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subacius, D.; Bos, P.J.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Switchable diffractive cholesteric gratings. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 71, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.N.; Chien, L.C.; Sprunt, S. Polymer-stabilized diffraction gratings from cholesteric liquid crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 72, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ryabchun, A.; Bobrovsky, A.; Stumpe, J.; Shibaev, V. Rotatable diffraction gratings based on cholesteric liquid crystals with phototunable helix pitch. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2015, 3, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demus, D.; Goodby, J.W.; Gray, G.W.; Spiess, H.W.; Vill, V. Handbook of Liquid Crystals; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, Y.; Moritake, H. Formation of a defect-free uniform lying helix in a thick cholesteric liquid crystal cell. Appl. Phys. Express 2015, 8, 071701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudquist, P.; Komitov, L.; Lagerwall, S.T. Volume-stabilized ULH structure for the flexoelectro-optic effect and the phase-shift effect in cholesterics. Liq. Cryst. 1998, 24, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komitov, L. Alignment of cholesteric liquid crystals using periodic anchoring. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, G.; Salter, P.; Elston, S.J.; Raynes, P.; Sio, L.D.; Ferjani, S.; Strangi, G.; Umeton, C.; Bartolino, R. Short pitch cholesteric electro-optical device based on periodic polymer structures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 011102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Shi, L.; Chien, L.-C. Fast flexoelectric switching in a cholesteric liquid crystal cell with surface-localized polymer network. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 195102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cladis, P.E.; Kléman, M. The cholesteric domain texture. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1972, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, P.; Baudry, J.; Pirkl, S. Static and dynamic properties of cholesteric fingers in electric field. Phys. Rep. 2000, 337, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvozdovskyy, I.; Yaroshchuk, O.; Serbina, M.; Yamaguchi, R. Photoinduced helical inversion in cholesteric liquid crystal cells with homeotropic anchoring. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-W.; Baek, J.-M.; Kim, S.-H.; Yoon, T.-H. Optical and electrical switching of cholesteric liquid crystals containing azo dye. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 19497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-W.; Kim, S.-H.; Baek, J.-M.; Yoon, T.-H. Optical and thermal switching of liquid crystals for self-shading windows. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2018, 2, 1700164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, G.; Komitov, L. Periodic anchoring condition for alignment of a short pitch cholesteric liquid crystal in uniform lying helix texture. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 113503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobashi, J.; Mohri, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Ozaki, M. Circularly-polarized, large-angle reflective deflectors based on periodically patterned cholesteric liquid crystals. Opt. Data Process. Storage 2017, 3, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-Y.; Huang, B.-Y.; Kang, C.-C.; Kuo, C.-T. Diffraction and polarization properties of electrically–tunable nematic liquid crystal grating. Polymers 2020, 12, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sohn, H.-J.; Oh, S.-W.; Choi, Y.; Ji, S.-M.; Yoon, T.-H. A Switchable Cholesteric Phase Grating with a Low Operating Voltage. Crystals 2021, 11, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11020100
Sohn H-J, Oh S-W, Choi Y, Ji S-M, Yoon T-H. A Switchable Cholesteric Phase Grating with a Low Operating Voltage. Crystals. 2021; 11(2):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11020100
Chicago/Turabian StyleSohn, Ho-Jin, Seung-Won Oh, Yeongyu Choi, Seong-Min Ji, and Tae-Hoon Yoon. 2021. "A Switchable Cholesteric Phase Grating with a Low Operating Voltage" Crystals 11, no. 2: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11020100
APA StyleSohn, H.-J., Oh, S.-W., Choi, Y., Ji, S.-M., & Yoon, T.-H. (2021). A Switchable Cholesteric Phase Grating with a Low Operating Voltage. Crystals, 11(2), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11020100




