Microdiamonds in Alkalic Dolerites from the North China Craton: FTIR and C Isotopic Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Background and Samples
3. Analytical Method
3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.2. Carbon Isotopic Composition
4. Analysis Result
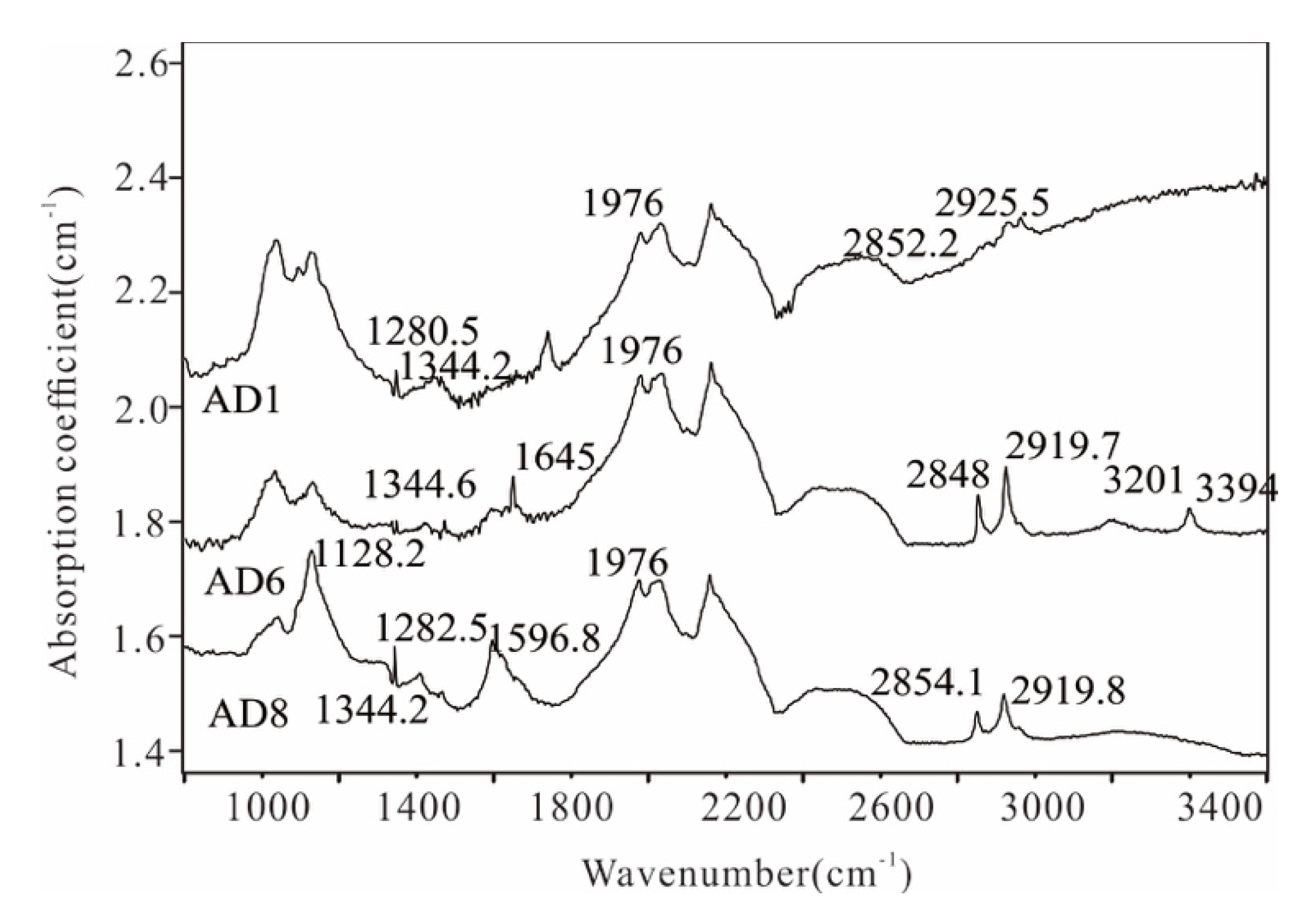
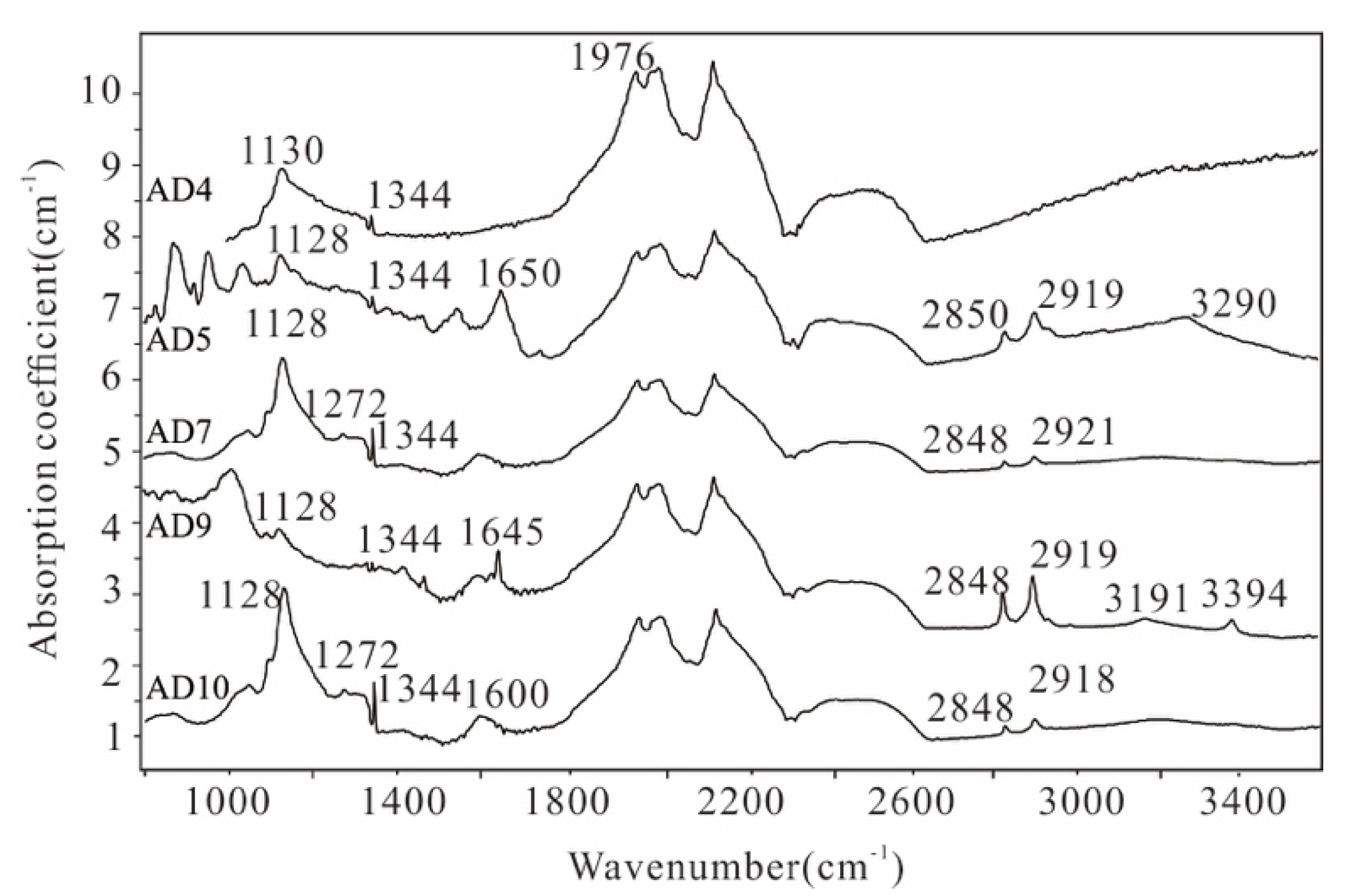
4.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
4.2. C Isotope
5. Discussion
5.1. FTIR Spectra of AD Microdiamonds
5.1.1. C-C Absorption Lines
5.1.2. C-N Absorption Lines
5.1.3. H2O and C-H Absorption Line
5.1.4. Y-Centre
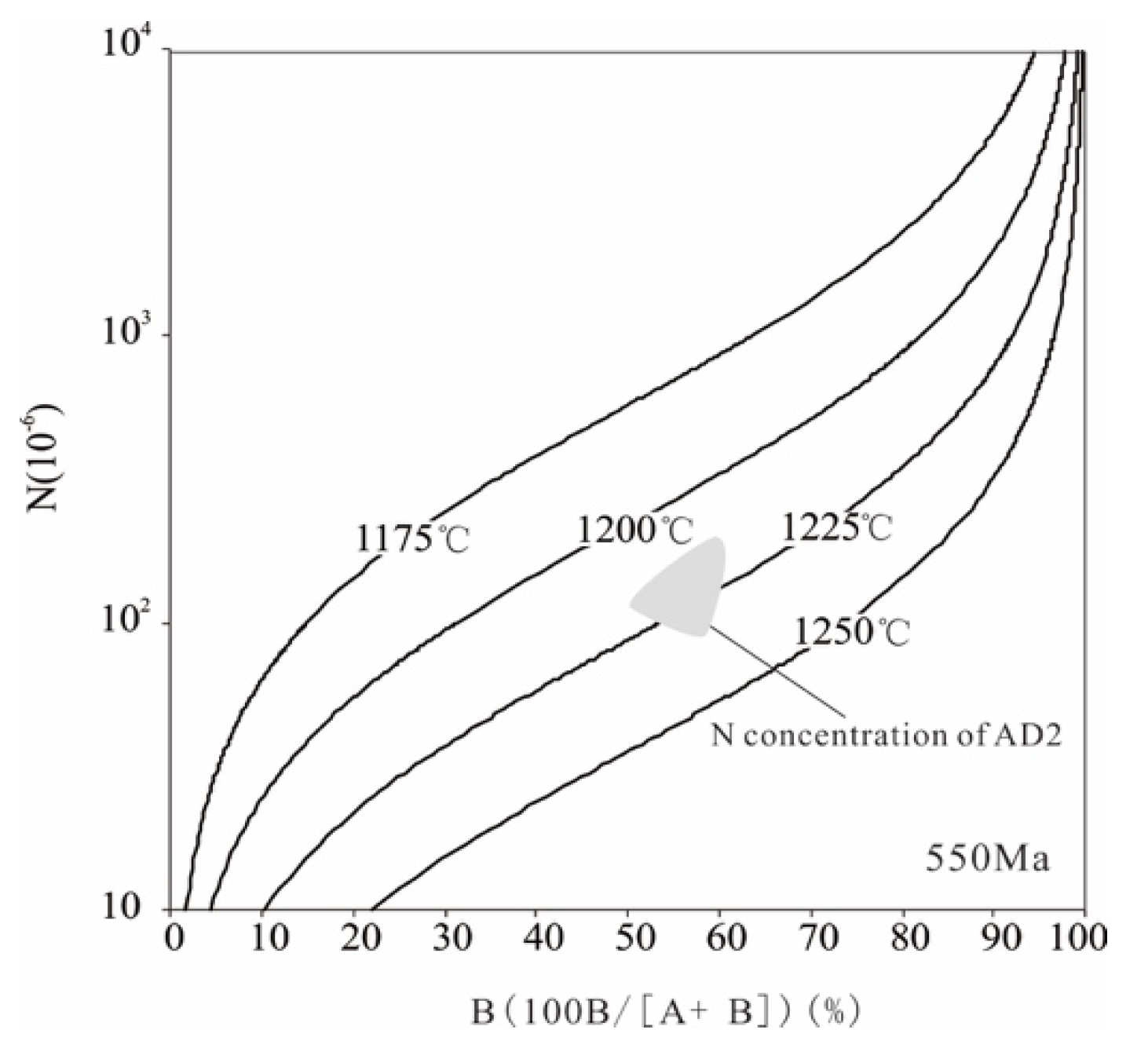
5.2. Modelling of Mantle Residence Time
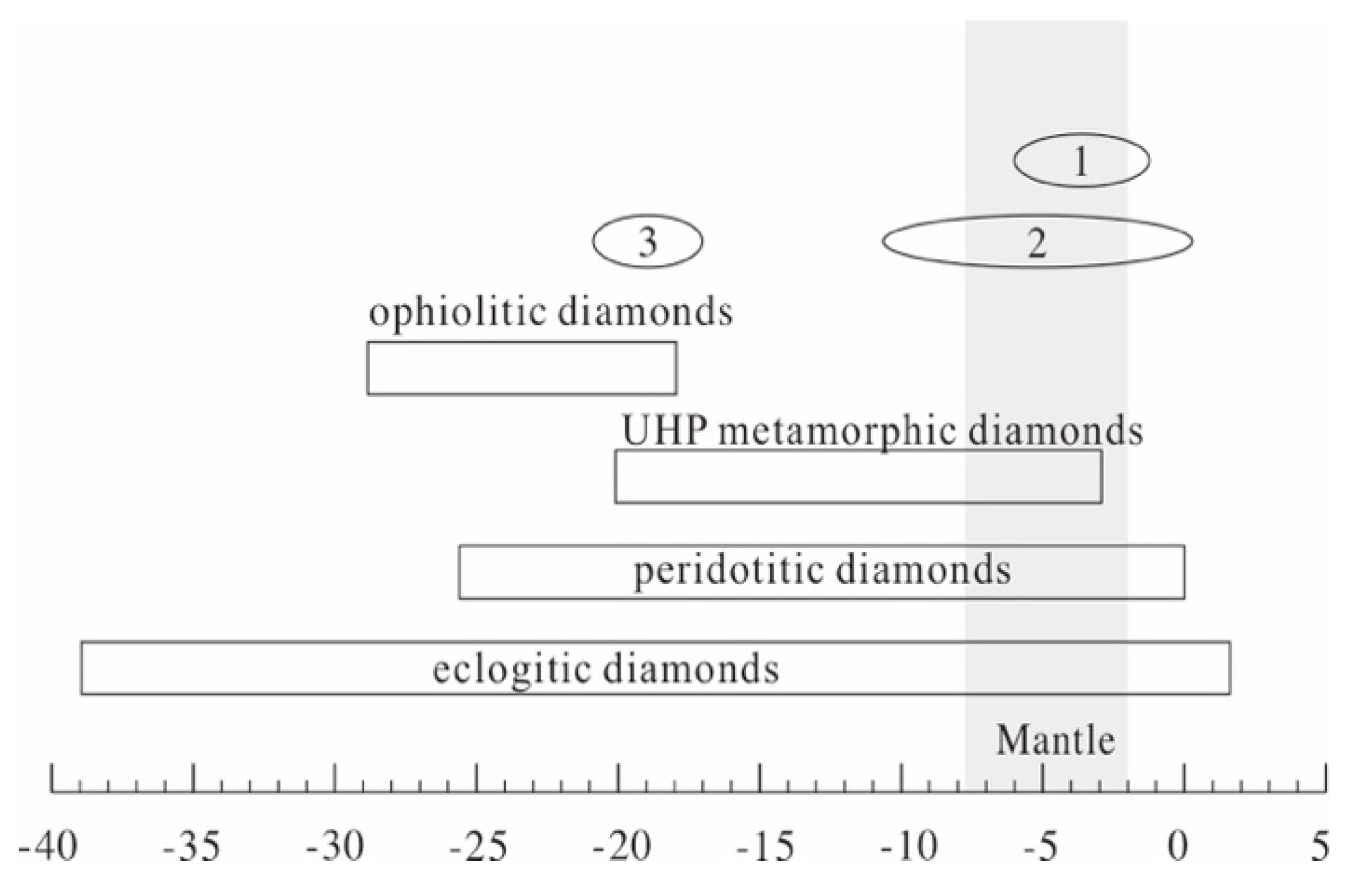
5.3. C Isotope
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, P. Actively explore a new type diamond primary deposit. Manag. Geol. Sci. Technol. 1998, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P. New knowledge of some important questions about diamond deposit genesis. Hunan Geol. 1998, 17, 204–210. [Google Scholar]
- Tappert, R.; Tappert, M.C. The Morphology of Diamonds. In Diamonds in Nature; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; GmbH & Co. K: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Tappert, R.; Tappert, M.C. The Origin of Diamonds. In Diamonds in Nature; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; GmbH & Co. K: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, K. Diamond Pipeline; SNL Metals Economics Group: Halifax, NS, Canada, 2014; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fedortchouk, Y.; McIsaac, E. Surface Dissolution Features on Kimberlitic Chromites as Indicators of Magmatic Fluid and Diamond Quality. In Proceedings of the 10th International Kimberlite Conference, Bangalore, India, 5–11 February 2012; pp. 297–308. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison, M.T. In Diamond Exploration and Regional Prospectivity of the Northern Territory of Australia. In Proceedings of the 10th International Kimberlite Conference, Bangalore, India, 5–11 February 2012; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2013; pp. 257–280. [Google Scholar]
- Kogarko, L.N.; Ryabchikov, I.D. Diamond potential versus oxygen regime of carbonatites. Petrology 2013, 21, 316–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, Y. Microdiamonds in ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks. Elements 2005, 1, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, Z.; Dobrzhinetskaya, L.F.; Green, H.W.; Pei, X.; Shi, R.; Wu, C.; Wooden, J.L.; Zhang, J.; Wan, Y. Discovery of metamorphic diamonds in central China: An indication of a >4000-km-long zone of deep subduction resulting from multiple continental collisions. Terra Nova 2003, 15, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huss, G.R. Meteoritic nanodiamonds: Messengers from the stars. Elements 2005, 1, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappert, R.; Foden, J.; Stachel, T.; Muehlenbachs, K. Deep mantle diamonds from South Australia: A record of Pacific subduction at the Gondwanan margin. Geology 2009, 37, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Ba, D.; Rong, H.; Zhang, Z. Diamonds recovered from peridotite of the Purang ophiolite in the Yarlung-Zangbo suture of Tibet: A proposal for a new type of diamond occurrence. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 27, 3171–3178. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Bai, W.; Zhang, Z.; Rong, H. Features of diamond in ophiolite. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 2113–2124. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X. A preliminary study of FT-IR on the diamonds from the Luobusa chromitites of Tibet and the eclogite of CCSD-MH, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2013, 029, 1861–1866. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wu, W.; Lian, D.; Rui, H. Peridotites, chromitites and diamonds in ophiolites. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Z.; Cao, Z.; Xiao, S.; Li, S.; Li, C.; Chen, L.; Fan, F. Neoproterozoic basic magmatism in the north of Anhui Province: Evidence from whole-rock geochemistry and U-Pb geochronology of Diabase in Langan area. Geol. China 2018, 45, 351–366. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Cai, Y.; Dong, Z.; Ma, Y.; Fan, F.; Chen, L.; Li, C.; Yang, D. Investigation on Mineral Characteristic of Diamond and Geochemical Characteristic of its host in the Langan Area, Anhui Province. J. Gems Gemmol. 2015, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, D.; Yang, J. Ophiolite-Hosted Diamond: A New Window for Probing Carbon Cycling in the Deep Mantle. Engineering 2019, 5, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yang, X.; Kang, C. Understanding of the present study of the diamond at domestic and overseas. East China Geol. 2017, 38, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, K.; Gu, H.; Hou, Z.; Tian, Y.; Wu, W.; et al. Initiation of the North China Craton destruction: Constraints from the diamond-bearing alkaline basalts from Lan’gan, China. Gondwana Res. 2020, 80, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Simakov, S.K.; Moe, K.; Scribano, V.; Lian, D.; Wu, W. Comment on “Comparison of enigmatic diamonds from the Tolbachik arc volcano (Kamchatka) and Tibetan ophiolites: Assessing the role of contamination by synthetic materials” by Litasov et al. 2019. Gondwana Res. 2020, 79, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, D.; Yang, J.; Wiedenbeck, M.; Dilek, Y.; Rocholl, A.; Wu, W. Carbon and nitrogen isotope, and mineral inclusion studies on the diamonds from the Pozanti–Karsanti chromitite, Turkey. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2018, 173, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, D.; Griffin, W.L.; Yang, J.; Gain, S.; Stern, R.A.; Huang, J.; Jacob, D.E.; Xu, X.; Stokes, A.J.; O’Reilly, S.Y. Diamonds in ophiolites: Contamination or a new diamond growth environment? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2015, 430, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Xu, M.; Shi, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Kang, C.; Cao, Z.; Dong, Z.; Ma, Y. Mineral chemistry characteristics of clinopyroxene and ilmenite in basite of Langan area, northern Anhui Province. Geol. Bull. China 2019, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Kang, C.; Yang, X.; Cao, Z.; Dong, Z.; Ma, Y.; Shi, J. Mineral chemistry characteristics of garnets in diamondiferous basite of Langan area, Anhui Province. Geol. Bull. China 2019, 38, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, F.; Cai, Y. Characteristic of alkali-basic rock type diamond ore’s Remote Sensing in the Langan area, Anhui province. J. Gems Gemmol. 2016, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Z.; Zhou, S. Geochemical features of the olivine-gabbros and its relationship with diamond-forming in the Langan area, Anhui province. Resour. Surv. Environ. 2014, 35, 245–253. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, J. Study of magnetic anomaly features and its implications for diamond exploration in the Langan-Chualan area, Suzhou City. Geol. Anhui 2013, 23, 123–125. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Q. Study on the Geochemistry of the Diamondiferous Olivine Basalt and Magma Evolution in Bailushan area, Xuzhou. China Geol. 2020. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20200507.1415.004.html (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Yang, J.; Dobrzhinetskaya, L.; Bai, W.; Fang, Q.; Robinson, P.T.; Zhang, J.; Green, H.W. Diamond and coesite-bearing chromitites from the Luobusa ophiolite, Tibet. Geology 2007, 35, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Y. Emplacement age and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic characteristics of the diamondiferous kimberlites from the eastern North China Craton. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Qiu, Z.; Lu, T.; Richard, S.; Thomas, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ke, J.; Peng, S.; Qin, S. Variations in carbon isotopic composition in the subcontinental lithospheric mantle beneath the Yangtze and North China Cratons: Evidence from in-situ analysis of diamonds using SIMS. China Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.; Wilde, S.A.; Cawood, P.A.; Lu, L. Thermal evolution of two textural types of mafic granulites in the North China craton: Evidence for both mantle plume and collisional tectonics. Geol. Mag. 1999, 136, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Zheng, J.; Chen, M. Discussion on Formation Condition of Diamonds. Earth Sci. Front. 1998, 5, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, M.Y.; Stachel, T.; Breeding, C.M.; Stern, R.A. Yellow diamonds with colourless cores—Evidence for episodic diamond growth beneath Chidliak and the Ekati Mine, Canada. Miner. Petrol. 2020, 114, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, D.; O’Neill, C.J.; Grant, K.J.; Griffin, W.L.; Pearson, N.J.; O’Reilly, S.Y. μ-FTIR mapping: Distribution of impurities in different types of diamond growth. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2012, 29, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, L.; Pearson, D.G.; Stachel, T. Diamond isotope compositions indicate altered igneous oceanic crust dominates deep carbon recycling. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2019, 516, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, D.; Weiss, Y.; Smit, K.V.; Loudin, L.; Nestola, F. In DiaMap: New applications for processing IR spectra of fluid-rich diamonds and mapping diamonds containing isolated nitrogen (Type Ib) and boron (Type IIb). In Proceedings of the 11th International Kimberlite Conference, Gaborone, Botswana, 18–22 September 2017; Spring: Gaborone, Botswana, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hainschwang, T.; Fritsch, E.; Notari, F.; Rondeau, B. A new defect center in type Ib diamond inducing one phonon infrared absorption: The Y center. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2012, 21, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.Y.; Breeding, C.M.; Stachel, T.; Stern, R.A. Spectroscopic features of natural and HPHT-treated yellow diamonds. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020, 101, 107642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liggins, S. Identification of point defects in treated single crystal diamond. Ph.D Thesis, University of Warwick, Coventry, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Lu, T.; Chen, H.; Chen, B.; Peng, S.; Wei, R.; Li, L. Micro-FTIR Mapping Tracer for the Heterogeneity Growth of Nitrogen Impurities in Natural Diamond from Three Localities in China. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2012, 32, 2070–2074. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, G. Decomposing the IR absorption spectra of diamonds. Nature 1981, 290, 40–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, G. The A nitrogen aggregate in diamond-its symmetry and possible structure. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1976, 9, L537–L542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, F. A Mineralogical and Isotope Study of Macrodiamonds from the Helam Mine. Honors Thesis, Queens University, Belfast, South Africa, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Mc Kenna, N.; Gurney, J.J.; Klump, J.; Davidson, J.M. Aspects of Diamond Mineralisation and Distribution at the Helam Mine, South Africa. Lithos 2004, 77, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.M.; Griffin, W.L.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Doyle, B.J. Mineral inclusions and geochemical characteristics of microdiamonds from the DO27, A154, A21, A418, DO18, DD17 and Ranch Lake kimberlites at Lac de Gras, Slave Craton, Canada. Lithos 2004, 77, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartigny, P. Mantle-related carbonados? Geochemical insights from diamonds from the Dachine komatiite (French Guiana). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 296, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, K.V.; Shirey, S.B.; Richardson, S.H.; le Roex, A.P.; Gurney, J.J. Re–Os isotopic composition of peridotitic sulphide inclusions in diamonds from Ellendale, Australia: Age constraints on Kimberley cratonic lithosphere. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 3292–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.B.; Walter, M.J.; Bulanova, G.P.; Mikhail, S.; Burnham, A.D.; Gobbo, L.; Kohn, S.C. Diamonds from Dachine, French Guiana: A unique record of Early Proterozoic subduction. Lithos 2016, 265, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timmerman, S.; Koornneef, J.M.; Chinn, I.L.; Davies, G.R. Dated eclogitic diamond growth zones reveal variable recycling of crustal carbon through time. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 463, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, K.; De Floriani, L. Diamond Hierarchies of Arbitrary Dimension. Comput. Graph. Forum 2009, 28, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiss, Y.; Kessel, R.; Griffin, W.L.; Kiflawi, I.; Klein-BenDavid, O.; Bell, D.R.; Harris, J.W.; Navon, O. A new model for the evolution of diamond-forming fluids: Evidence from microinclusion-bearing diamonds from Kankan, Guinea. Lithos 2009, 112, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.P.; Evans, T. Aggregation of Nitrogen in Diamond, Including Platelet Formation. Math. Phys. Sci. 1981, 375, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, C.D.; Davey, S.T. One-phonon infrared absorption in diamond. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1984, 17, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Di, J.; Lu, F.; Zheng, J. Agate-like Structure and Heterogeneities of Nitrogen and Hydrogen Impurities of Diamond in Mengyin, China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2006, 80, 1197–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Lu, F.; Di, J.; Zheng, J. Cathodoluminescence and Infrared Spectroscopy of Wafangdian Diamond in Liaoning Province. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2000, 45, 1424–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, D.; O Neill, C.; Grant, K.; Griffin, W.; O Reilly, S.; Pearson, N.; Stern, R.; Stachel, T. Platelet development in cuboid diamonds: Insights from micro-FTIR mapping. Mineral. Petrol. 2012, 164, 1011–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirey, S.B.; Cartigny, P.; Frost, D.J.; Keshav, S.; Nestola, F.; Nimis, P.; Pearson, D.G.; Sobolev, N.V.; Walter, M.J. Diamonds and the geology of mantle carbon. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2013, 75, 355–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palot, M.; Cartigny, P.; Harris, J.W.; Kaminsky, F.V.; Stachel, T. Evidence for deep mantle convection and primordial heterogeneity from nitrogen and carbon stable isotopes in diamond. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 357, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartigny, P. Stable isotopes and the origin of diamond. Elements 2005, 1, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample No. | Color | Shape | Surface Character |
|---|---|---|---|
| AD1 | yellow | cubo-octahedral | Shallow depressions |
| AD2 | Light yellow | Rounded Dodecahedra | Stacked growth layers, plastic deformation lines, terraces, elongate hillocks |
| AD3 | colorless | fragment | Stacked growth layers, |
| AD4 | yellow | cubo-octahedral | Stacked growth layers, |
| AD5 | yellow | cubo-octahedral | Stacked growth layers, |
| AD6 | yellow | cubo-octahedral | Shallow depressions, abrasion, scratch mark |
| AD7 | yellow | cubo-octahedral | |
| AD8 | yellow | cubo-octahedral | |
| AD9 | yellow | cubo-octahedral | |
| AD10 | yellow | cubo-octahedral |
| Sample No. | Major Peak (cm−1) | Type of C-N | Type | N Concentration (10−6) | N total (10−6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AD1 | 1280, 1344, 1976, 2852.2, 2925 | A, C | IaA/Ib | 143.0 (C centre) | 143.0 |
| AD2 | 1172, 1288, 1361, 1650, 1976, 1851, 2919 | A, B’, B | IaAB | 60.9 (A centre), 134.2 (B centre) | 195.1 |
| AD3 | 1650, 1976, 2850, 2919 | A | Ia | 4.5 (A centre) | 4.5 |
| AD4 | 1130, 1344, 1976 | C | Ib | 10.7 (C centre) | 10.7 |
| AD5 | 1128, 1344, 1650, 1976, 2850, 2919, 3290 | C | Ib | 76.9 (C centre) | 76.9 |
| AD5 | 1130, 1284, 1344.6, 1645, 1976.7, 2848, 2919.7, 3201, 3394 | A, C | IaA/Ib | 23.6 (C centre) | 23.6 |
| AD7 | 1128, 1272, 1344, 1976, 2848, 2921 | C | Ib | 393.5 (C centre) | 393.5 |
| AD8 | 1128, 1282, 1344, 1596, 1976, 2854, 2919 | A, C | IaA/Ib | 240.9 (C centre) | 240.9 |
| AD9 | 1344, 1645, 1976, 2848, 2919, 3191, 3394 | C | Ib | 137.0 (C centre) | 137.0 |
| AD10 | 1128, 1272, 1344, 1600, 1976, 2848, 2917 | C | Ib | 503.5 (C centre) | 503.5 |
| Sample ID | δ13C (‰) |
|---|---|
| AD5 | −20.2 |
| AD6 | −19.1 |
| AD7 | −18.6 |
| AD8 | −20.5 |
| AD9 | −21.1 |
| AD10 | −20.6 |
| Location | NA/ppm | NB/ppm | NT (×10−6) | Modelling Age/Ga |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (~1282 cm−1) | NB(~1175 cm−1) | |||
| 01 | 41.590 | 56.615 | 98.205 | 1.29 |
| 02 | 58.767 | 71.982 | 130.750 | 0.87 |
| 03 | 56.229 | 59.316 | 115.545 | 0.85 |
| 04 | 74.587 | 109.528 | 184.115 | 0.74 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Y.; Cao, Z.; Liu, F.; Li, K.; Li, L.; Yang, J. Microdiamonds in Alkalic Dolerites from the North China Craton: FTIR and C Isotopic Characteristics. Crystals 2021, 11, 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111325
Cai Y, Cao Z, Liu F, Li K, Li L, Yang J. Microdiamonds in Alkalic Dolerites from the North China Craton: FTIR and C Isotopic Characteristics. Crystals. 2021; 11(11):1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111325
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Yitao, Zhengqi Cao, Fei Liu, Kan Li, Long Li, and Jingsui Yang. 2021. "Microdiamonds in Alkalic Dolerites from the North China Craton: FTIR and C Isotopic Characteristics" Crystals 11, no. 11: 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111325
APA StyleCai, Y., Cao, Z., Liu, F., Li, K., Li, L., & Yang, J. (2021). Microdiamonds in Alkalic Dolerites from the North China Craton: FTIR and C Isotopic Characteristics. Crystals, 11(11), 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111325








