Discovery of Disulfane (H2S2) in Fluid Inclusions in Rubies from Yuanjiang, China, and Its Implications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
5. Discussion
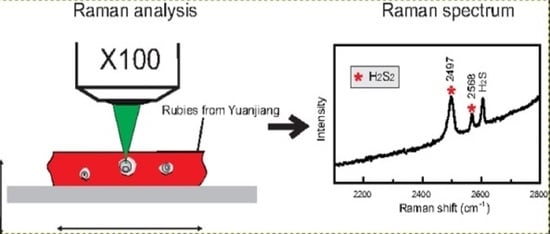
5.1. Identification of Disulfane
5.2. Origin of Sulfane in Yuanjiang Rubies
5.3. Favorable Geological Condition for the Generation of Sulfanes
5.4. Implication for Thermochemical Stability of Sulfanes
5.5. Geochemical Implications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frezzotti, M.L.; Tecce, F.; Casagli, A. Raman spectroscopy for fluid inclusion analysis. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 112, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, G.; Dubessy, J.; Banks, D.; Hoàng Quang, V.; Lhomme, T.; Pironon, J.; Garnier, V.; Phan Trong, T.; Pham Van, L.; Ohnenstetter, D.; et al. CO2–H2S–COS–S8–AlO (OH)-bearing fluid inclusions in ruby from marble-hosted deposits in Luc Yen area, North Vietnam. Chem. Geol. 2003, 194, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steudel, R. Inorganic Polysulfanes H2Sn with n > 1. In Elemental Sulfur und Sulfur–Rich Compounds II; Steudel, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 99–125. [Google Scholar]
- Hurai, V.; Černušák, I.; Randive, K. Raman spectroscopic study of polysulfanes (H2Sn) in natural fluid inclusions. Chem. Geol. 2019, 508, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, G.; Dubessy, J.; Banks, D.A.; Lhomme, T.; Ohnenstetter, D. Fluid inclusions in ruby from Asian marble deposits: Genetic implications. Eur. J. Mineral. 2015, 27, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapponnier, P.; Lacassin, R.; Leloup, P.H.; Schärer, U.; Zhong, D.L.; Wu, H.W.; Liu, X.H.; Ji, S.C.; Zhang, L.S.; Zhong, J.Y. The Ailao Shan/Red River metamorphic belt: Tertiary left-lateral shear between Indochina and South China. Nature 1990, 343, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leloup, P.H.; Lacassin, R.; Tapponnier, P.; Schärer, U.; Zhong, D.L.; Liu, X.H.; Zhang, L.S.; Ji, S.C.; Trinh, P.T. The Ailao Shan-Red river shear zone (Yunnan, China), tertiary transform boundary of Indochina. Tectonophysics 1995, 251, 3–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leloup, P.H.; Harrison, T.M.; Ryerson, F.J.; Chen, W.J.; Li, Q.; Tapponnier, P.; Lacassin, R. Structural, petrological and thermal evolution of a Tertiary ductile strike-slip shear zone, Diancang Shan, Yunnan. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 6715–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.S.; Schärer, U. Age and origin of magmatism along the Cenozoic Red River shear belt, China. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1999, 134, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.Q.; Ni, P.; Zhou, J.G.; Shui, T.; Pan, J.Y.; Fan, M.S.; Yang, Y.L. Fluid inclusion and titanite U-Pb age constraints on the Yuanjiang ruby mineralization in the Ailao Shan-Red River metamorphic belt, Southwest China. Can. Mineral. 2021. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Leloup, P.H.; Kienast, J.R. High-temperature metamorphism in a major strike-slip shear zone: The Ailao Shan-Red River, People’s Republic of China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1993, 118, 213–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloke, P.L. The geologic role of polysulfides—Part II: The solubility of acanthite and covellite in sodium polysulfide solutions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1963, 27, 1299–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Migdisov, A.A.; Bychkov, A.Y. The behaviour of metals and sulphur during the formation of hydrothermal mercury-antimony-arsenic mineralization, Uzon caldera, Kamchatka, Russia. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1998, 84, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migdisov, A.A.; Suleimenov, O.M.; Alekhin, Y.V. Experimental study of polysulfane stability in gaseous hydrogen sulfide. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 2627–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, V.; Giuliani, G.; Ohnenstetter, D.; Fallick, A.E.; Dubessy, J.; Banks, D.; Hoàng Quang, V.; Lhomme, T.; Maluski, H.; Pêcher, A.; et al. Marble-hosted ruby deposits from Central and Southeast Asia: Towards a new genetic model. Ore Geol. Rev. 2008, 34, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapponnier, P.; Xu, Z.Q.; Roger, F.; Meyer, B.; Arnaud, N.; Wittlinger, G.; Yang, J.S. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau. Science 2001, 294, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunnan Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. The Census Report of Ruby Deposit from Xiaoyangjie Township, Yuanjiang County, Yunnan Province, 1992; Yunnan Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources: Yuxi, China, 1992.
- Wang, J.H.; Yin, A.; Harrison, T.M.; Grove, M.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Xie, G.H. A tectonic model for Cenozoic igneous activities in the eastern Indo–Asian collision zone. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 188, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, G.; Hoàng Quang, V.; Phan Trong, T.; France-Lanord, C.; Coget, P. Carbon isotopes study on graphite and coexisting calcite-graphite pairs in marbles from the Luc Yen and Yen Bai districts, North of Vietnam. Bull. Liaison SFMC 1999, 11, 80–82. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.Q.; Ni, P.; Shui, T.; Pan, J.Y.; Fan, M.S.; Yang, Y.L.; Chi, Z.; Ding, J.Y. Trace element geochemistry and mineral inclusions constraints on the petrogenesis of the marble-hosted ruby deposit from Yuanjiang, China. Can. Mineral. 2021, 59, 381–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzikowski, T.J.; Cempírek, J.; Groat, L.A.; Dipple, G.M.; Giuliani, G. Origin of gem corundum in calcite marble: The Revelstoke occurrence in the Canadian Cordillera of British Columbia. Lithos 2014, 198, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Pan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Mucci, A. The solubility of Pt and Pd sulfides and Au in bisulfide solutions. Miner. Depos. 1994, 29, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Inclusion Types | Occurrence Description | Fluid Components | Solids |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Oriented clusters throughout the host or small clusters in the core of the host, sometimes occurred as isolated or clusters within colored growth zonation | CO2–H2S–COS–S8–H2S2–CH4 | Diaspore, gibbsite, dawsonite, rutile, and arsenopyrite |
| Pseudo-secondary | In intragranular fractures that do not traverse into the rim of the host | CO2–H2S–COS–S8–H2S2–CH4 | Diaspore, arsenopyrite, and pyrite |
| Secondary | In sealed fractures present in planar arrays that traversedThe growth zone of crystals | CO2–H2S–COS–S8–CH4 | Diaspore |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, W.; Ni, P.; Zhou, J.; Shui, T.; Ding, J.; Zhu, R.; Cai, Y.; Fan, M. Discovery of Disulfane (H2S2) in Fluid Inclusions in Rubies from Yuanjiang, China, and Its Implications. Crystals 2021, 11, 1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111305
Huang W, Ni P, Zhou J, Shui T, Ding J, Zhu R, Cai Y, Fan M. Discovery of Disulfane (H2S2) in Fluid Inclusions in Rubies from Yuanjiang, China, and Its Implications. Crystals. 2021; 11(11):1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111305
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Wenqing, Pei Ni, Jungui Zhou, Ting Shui, Junying Ding, Renzhi Zhu, Yitao Cai, and Mingsen Fan. 2021. "Discovery of Disulfane (H2S2) in Fluid Inclusions in Rubies from Yuanjiang, China, and Its Implications" Crystals 11, no. 11: 1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111305
APA StyleHuang, W., Ni, P., Zhou, J., Shui, T., Ding, J., Zhu, R., Cai, Y., & Fan, M. (2021). Discovery of Disulfane (H2S2) in Fluid Inclusions in Rubies from Yuanjiang, China, and Its Implications. Crystals, 11(11), 1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111305