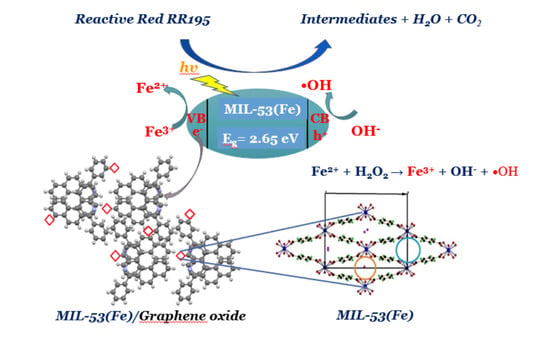
Design of Metal-Organic Polymers MIL-53(M3+): Preparation and Characterization of MIL-53(Fe) and Graphene Oxide Composite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- -
- M(OH)(BDC)2− x(H2BDC)≡MIL-53(M3+) (as) c M=Al, Cr—structure (phase) I;
- -
- M(OH)(BDC)2− ≡ MIL-53(M3+) (ht) c M=Al, Cr—structure (phase) II;
- -
- M(OH)(BDC)2− xH2O≡MIL-53(M3+) (lt) c M=Al, Cr—structure (phase) III;
- -
- M(OH)(BDC)2−≡MIL-53(M3+) (ht) c M=Ga, Fe—structure (phase) IV;
- -
- M(OH)(BDC)2− x(H2O)≡MIL-53(M3+) (lt) c M=Ga, Fe—structure (phase) V (superstructure to structure III).
- -
- M(OH)(BDC)2− ≡ MIL-53(M3+) (int) c M=Fe—structure (phase) VI.


2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of MIL-53 (Fe) and MIL-53 (Fe)/GO
2.3. Material Characterization
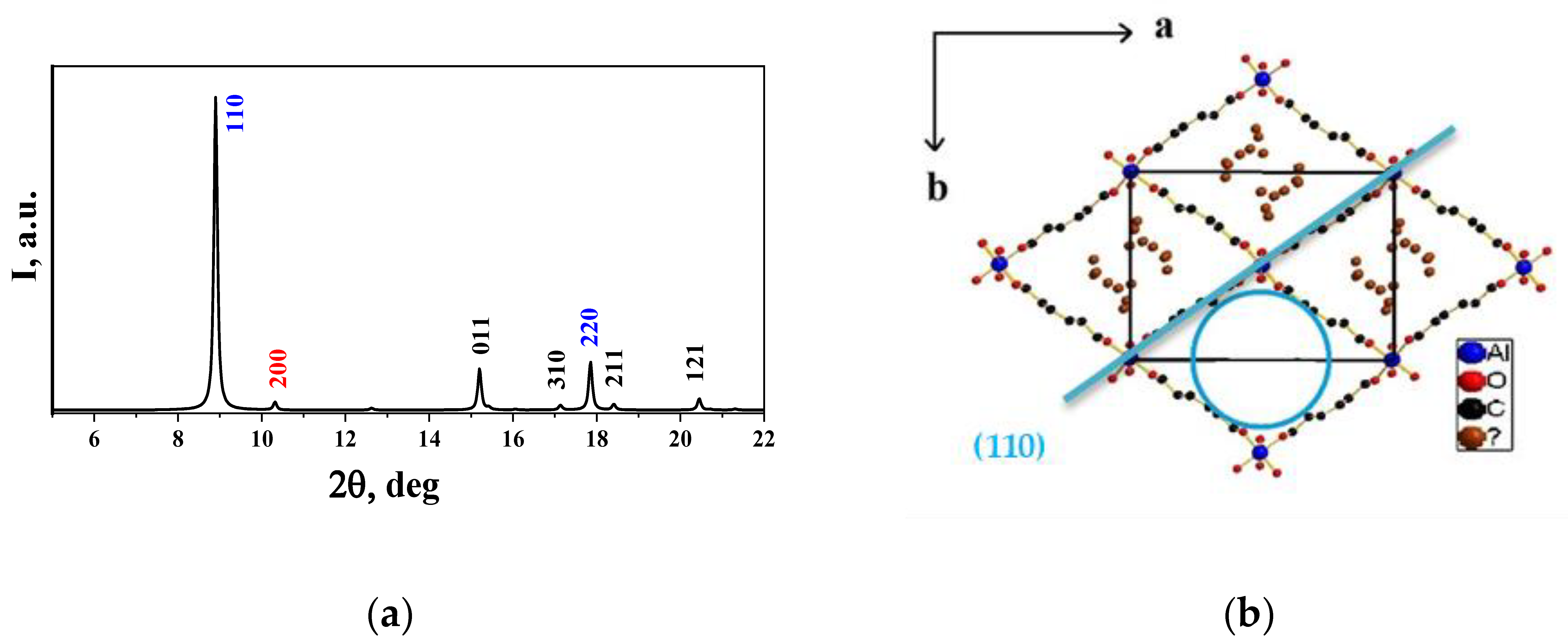
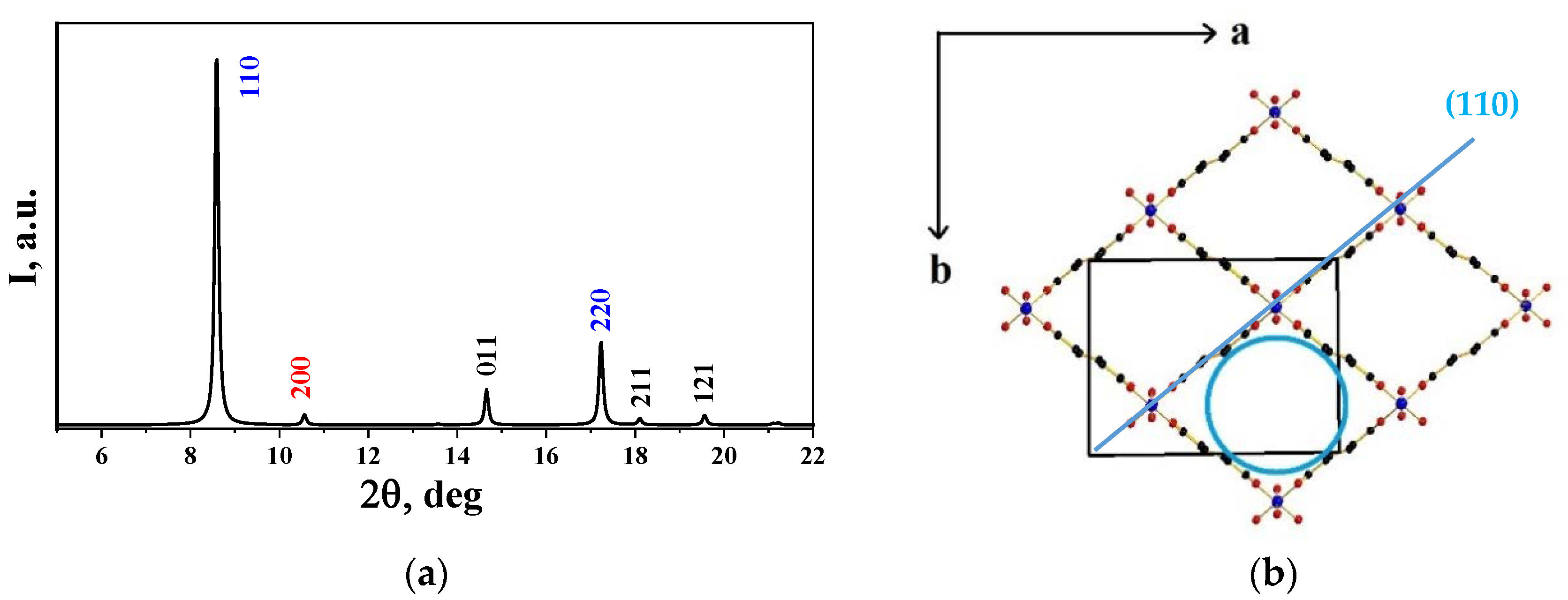
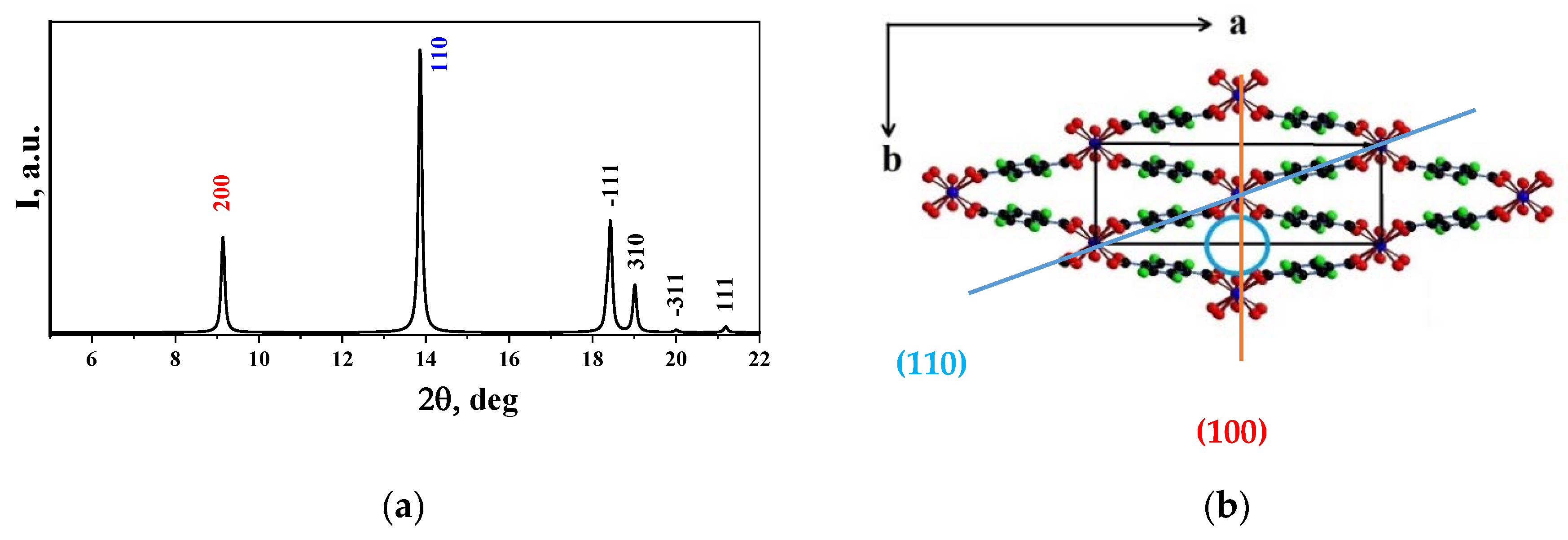
2.3.1. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)
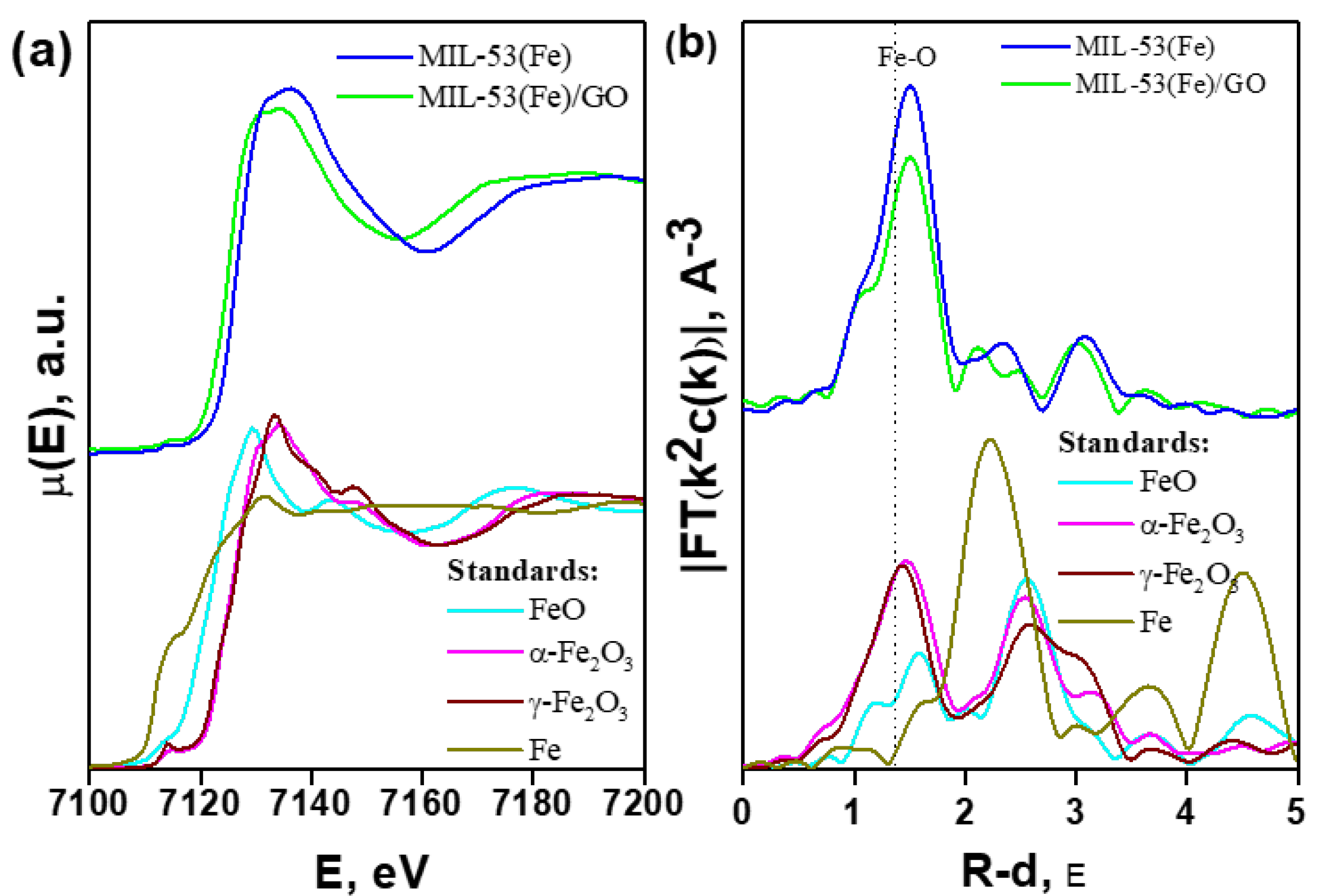
2.3.2. X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy (XAS)
2.3.3. X-ray Photoelectron Spectra (XPS)
2.4. Testing of Photocatalytic Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.2. X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy (XAS)
3.3. X-ray Photoelectron Spectra (XPS)
3.4. Photocatalytic Properties
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Ben-Mansour, R.; Habib, M.A. An efficient CO2 adsorptive storage using MOF-5 and MOF-177. Appl. Energy 2018, 210, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almáši, M.; Zeleňák, V.; Palotai, P.; Beňová, E.; Zeleňáková, A. Metal-organic framework MOF-76(Nd): Synthesis, characterization, and study of hydrogen storage and humidity sensing. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2018, 93, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Du, X.D.; Li, J.; Guo, X.X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J. Photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction in metal-organic frameworks: A mini-review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 193, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaka, S.; Kumar, R.; Deep, A.; Kurade, M.B.; Ji, S.W.; Jeon, B.H. Performance of metal–organic frameworks for the adsorptive removal of potentially toxic elements in a water system: A critical review. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 380, 330–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmicheva, G.M. Some Aspects of the Applied Crystallochemistry; MIREA: Moscow, Russia, 2016; p. 286. [Google Scholar]
- Kravchenko, G.V.; Podbelsky, V.V.; Kuz’micheva, G.M. Certificate of State Registration of Computer Software. Russia No. 2020667596, August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Serre, C.; Millange, F.; Thouvenot, C.; Noguè, M.; Marsolier, G.; Louër, D.; Férey, G. Very large breathing effect in the first nanoporous chromium(III)-based solids: MIL-53 or CrIII(OH)·{O2C−C6H4−CO2}·{HO2C−C6H4−CO2H}x·H2Oy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 13519–13526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiseau, T.; Serre, C.; Huguenard, C.; Fink, G.; Taulelle, F.; Henry, M.; Bataille, T.; Férey, G. A rationale for the large breathing of the porous aluminum terephthalate (MIL-53) upon hydration. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millange, F.; Guillou, N.; Walton, R.I.; Grenèche, J.M.; Margiolaki, I.; Férey, G. Effect of the nature of the metal on the breathing steps in MOFs with dynamic frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2008, 39, 4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkringer, C.; Loiseau, T.; Guillou, N.; Férey, G.; Elkaïm, E.; Vimont, A. XRD and IR structural investigations of a particular breathing effect in the MOF-type gallium terephthalate MIL-53(Ga). Dalton Trans. 2009, 12, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Урусoв, В.С. Теoретическая Кристаллoхимия М; МГУ: Ulitsa Kolmogorova, Moscow, Russia, 1987; p. 272. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Cryst. Phys. Diffr. Theor. Gen. Crystallogr. 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclerc, H.; Devic, T.; Devautour-Vinot, S.; Bazin, P.; Audebrand, N.; Férey, G.; Daturi, M.; Vimont, A.; Clet, G. Influence of the oxidation state of the metal center on the flexibility and adsorption properties of a porous metal organic framework: MIL-47(V). J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 19828–19840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowat, J.P.S.; Miller, S.R.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Seymour, V.R.; Ashbrook, S.E.; Wright, P.A. Isoreticular chemistry of scandium analogues of the multicomponent metal–organic framework MIL-142. CrystEngComm 2011, 142, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chaplais, G.; Xue, M.; Qiu, S.; Patarin, J.; Simon-Masseron, A.; Chen, H. New functionalized MIL-53(In) solids: Syntheses, characterization, sorption, and structural flexibility. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breeze, M.I.; Clet, G.; Campo, B.C.; Vimont, A.; Daturi, M.; Grenèche, J.-M.; Dent, A.J.; Millange, F.; Walton, R.I. Isomorphous substitution in a flexible metal–organic framework: Mixed-metal, mixed-valent MIL-53 type materials. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 8171–8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouar, F.; Devic, T.; Chevreau, H.; Guillou, N.; Gibson, E.; Clet, G.; Daturi, M.; Vimont, A.; Grenèche, J.M.; Breeze, M.I.; et al. Tuning the breathing behaviour of MIL-53 by cation mixing. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendt, M.; Jee, B.; Stock, N.; Ahnfeldt, T.; Hartmann, M.; Himsl, D.; Pöppl, A. Structural phase transitions and thermal hysteresis in the metal−organic framework compound MIL-53 as studied by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 19443–19451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchii, D.Y.; Olivos-Suarez, A.I.; Szécsényi, Á.; Li, G.; Nasalevich, M.A.; Dugulan, I.A.; Crespo, P.S.; Hensen, E.J.M.; Veber, S.L.; Fedin, M.V.; et al. Isolated fe sites in metal organic frameworks catalyze the direct conversion of methane to methanol. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 5542–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bignami, G.P.M.; Davis, Z.H.; Dawson, D.M.; Morris, S.A.; Russell, S.E.; McKay, D.; Parke, R.E.; Iuga, D.; Morris, R.E.; Ashbrook, S.E. Cost-effective 17O enrichment and NMR spectroscopy of mixed-metal terephthalate metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozachuk, O.; Meilikhov, M.; Yusenko, K.; Schneemann, A.; Jee, B.; Kuttatheyil, A.V.; Bertmer, M.; Sternemann, C.; Pöppl, A.; Fischer, R.A. A solid-solution approach to mixed-metal metal–organic frameworks–detailed characterization of local structures, defects and breathing behaviour of Al/V frameworks. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 26, 4546–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaeva, V.I.; Vedenyapina, M.; Kulayshin, S.; Lobova, A.; Chernyshev, V.V.; Kapustin, G.I.; Tkachenko, O.P.; Vergun, V.V.; Arkhipov, D.A.; Nissenbaum, V.D.; et al. Adsorption of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in an aqueous medium on nanoscale MIL-53(Al) type materials. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 15091–15104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescouet, T.; Kockrick, E.; Bergeret, G.; Pera-Titus, M.; Aguado, S.; Farrusseng, D. Homogeneity of flexible metal–organic frameworks containing mixed linkers. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 10287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubnova, R.S.; Filatov, S.K. High-Temperature borate crystal chemistry. Z. Für Krist. 2013, 228, 395–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, A.A. Growth of copolymer chains and mixed crystals: Statistics of trials and errors. Usp. Fiz. Nauk. 1970, 13, 111–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtukenberg, A.G.; Punin, Y.O.; Frank-Kamenetskaya, O.V. The kinetic ordering and growth dissymmetrisation in crystalline solid solutions. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2016, 75, 1083–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.A.; Le, G.H.; Dao, C.D.; Dang, L.Q.; Nguyen, K.T.; Nguyen, Q.K.; Lee, G.D. Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption using novel MIL-53(Fe) as a highly efficient adsorbent. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 5261–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, T.V.; Linh, T.T.; Giang, H.L.; Quang, K.N.; Tan, M.V.; Tuan, A.V. Synthesis and application of novel Fe-MIL-53/GO nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of reactive dye from aqueous solution. Vietnam. J. Chem. 2019, 57, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, G.H.; Ngo, Q.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, Q.K.; Quan, T.T.T.; Vu, L.D.; Vu, T.A. High catalytic activity of phenol photodegradation from aqueous solution with Novel Fe-Fe3O4-GO nanocomposite. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 4225–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetogorov, R.D.; Dorovatovskii, P.V.; Lazarenko, V.A. Belok/XSA Diffraction beamline for studying crystalline samples at kurchatov synchrotron radiation source. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2020, 55, 1900184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petříček, V.; Dušek, M.; Palatinus, L. Crystallographic computing system JANA2006: General features. Z. Kristallogr 2014, 229, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyshov, A.A.; Veligzhanin, A.A.; Zubavichus, Y.V. X-ray structural studies of the Pd–In–Ru system using synchrotron radiation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 2009, 603, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, B.; Newville, M. Data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2005, 12, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walton, J.; Wincott, P.; Fairley, N.; Carrick, A. Peak Fitting with CasaXPS: A Casa Pocket Book; Accolyte Science: Knutsford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Naumkin, A.V.; Kraut-Vass, A.; Powell, C.J.; Gaarenstroom, S.W. NIST X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Database; The National Institute of Standards and Technology NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2012.
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Babaei, F.; Fakhri, P.; Jaleh, B. Synthesis, characterization, structural, optical properties and catalytic activity of reduced graphene oxide/copper nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10782–10789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharisov, B.I.; Kharissova, O.V.; Vázquez Dimas, A.; Gómez De La Fuente, I.; Peña Méndez, Y. Review: Graphene-supported coordination complexes and organometallics: Properties and applications. J. Coord. Chem. 2016, 69, 1125–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameta, R.; Chohadia, A.K.; Jain, A.; Punjabi, P.B. Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. Adv. Oxid. Process. Waste Water Treat. 2018, 49–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiong, W.; Yining, L.; Haochuan, J.; Hongbin, Y.; Ying, L.; Mingxin, H.; Hongliang, H. Peculiar synergetic effect of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles and graphene oxide on MIL-53 (Fe) for boosting photocatalysis. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 390, 124615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, N.; Biswas, S. Synthesis of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): Routes to various MOF topologies, morphologies, and composites. Chem. Rev. 2011, 112, 933–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

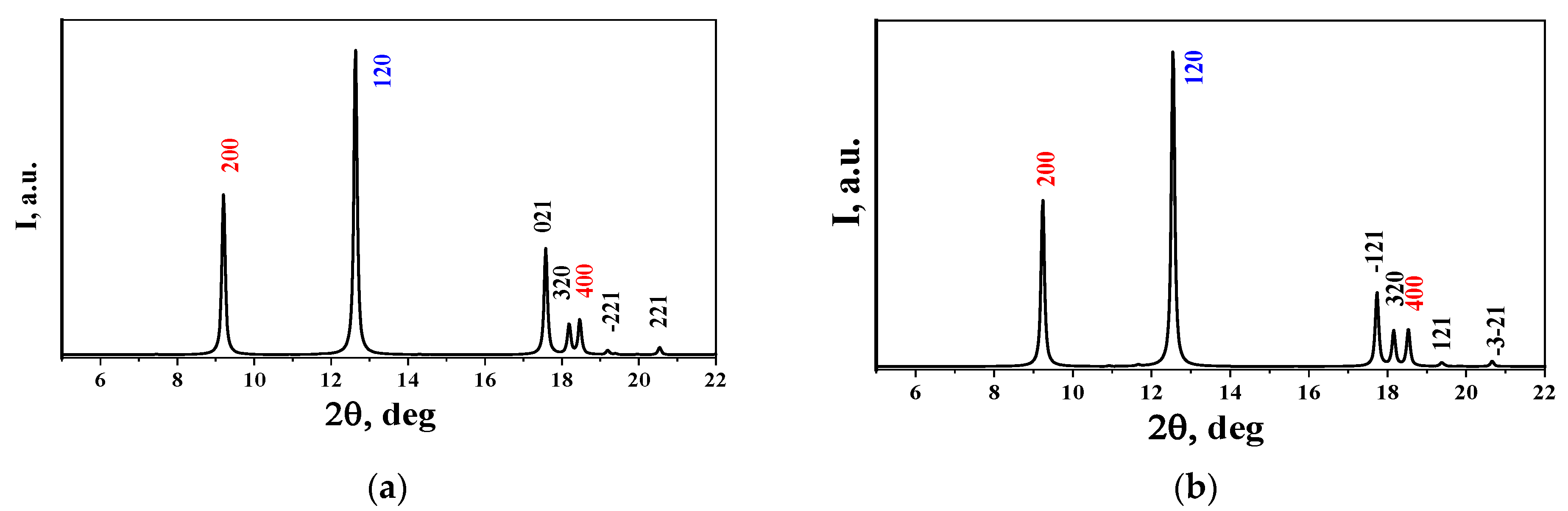
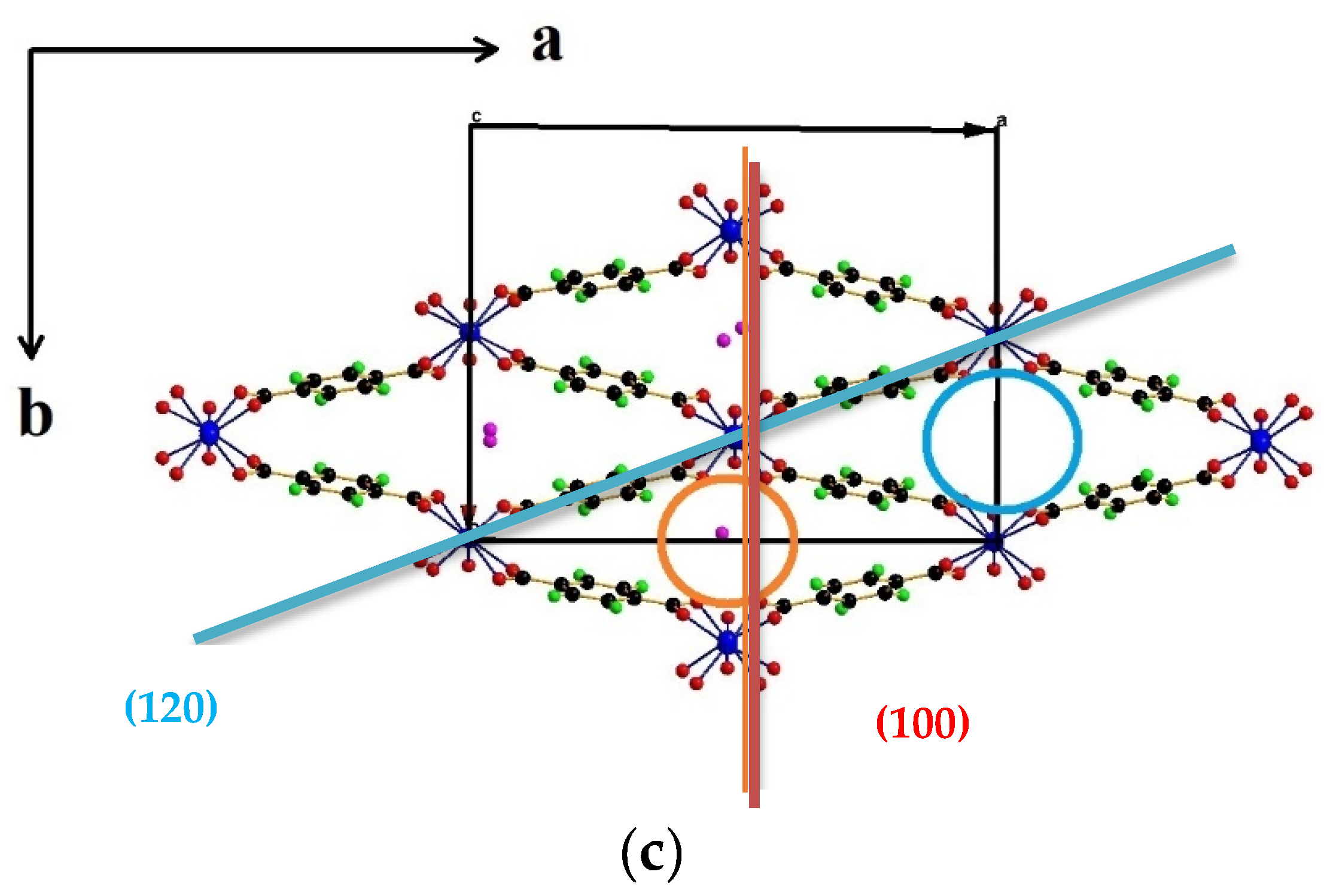
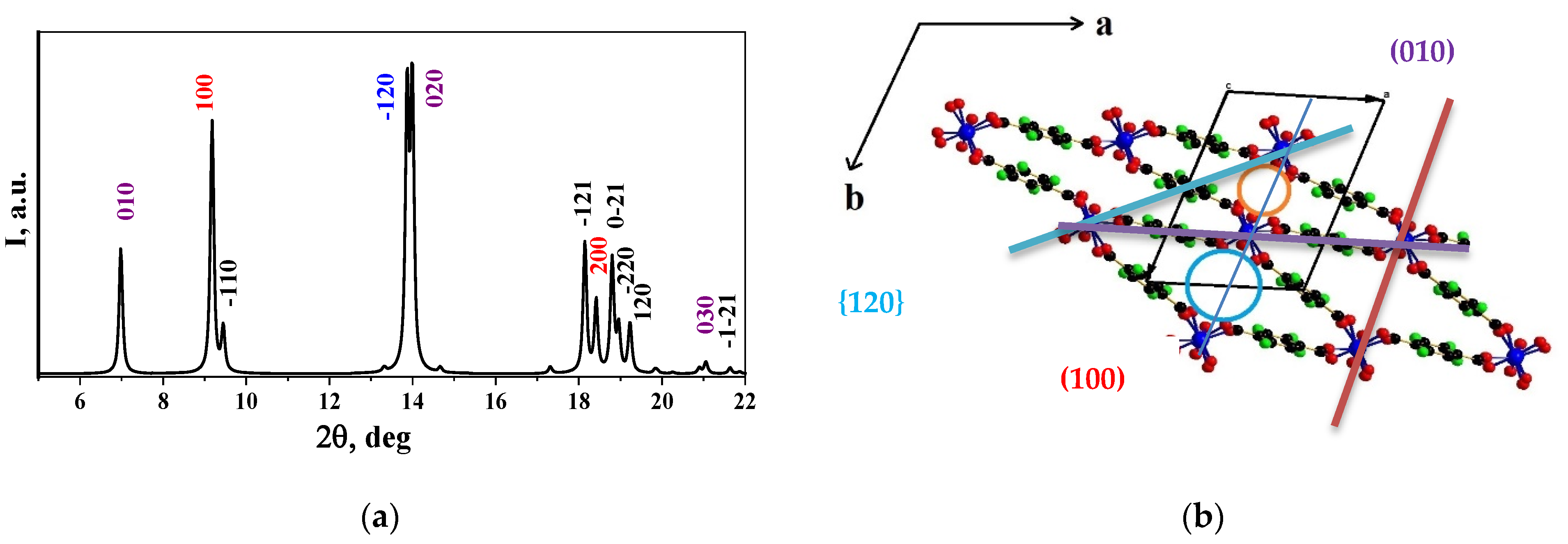





| Heating a mixture of M (NO3)3 × 9H2O c C8H6O4 (H2BDC) and water in a teflon-coated steel autoclave | ||||
| t = 220 °C, τ = 72 h | t = 200 °C, τ = 36 h | - | ||
| M (OH) (BDC)2− × (BDC)≡MIL-53(M) (as) | ||||
| Al | Cr | Ga | Fe | |
| Structure I (sp.gr. Pnma, z = 4) | - | |||
| a = 17.129, b = 12.182, c = 6.628 | a = 17.340, b = 12.178, c = 6.822 | |||
| heating in air MIL-53(M)—as | ||||
| t = 330 °C, τ = 72 h | 400° < t > 300 °C | t = 280 °C, τ = 24 h | - | |
| M (OH) (BDC)2−≡MIL-53(M) (ht) | ||||
| Al | Cr | Ga | Fe | |
| Structure II (sp.gr. Imcm, z = 4) | Structure IV (sp.gr. C 1 2/c 1; z = 4) | |||
| a = 16.675, b = 12.812, c = 6.608 | a = 16.733, b = 13.038, c = 6.812 | a = 19.8330, b = 6.8556, c = 6.7143, β = 103.88° | a = 21.2693, b = 6.7589, c = 6.8838, β = 114.625° | |
| Cooling MIL-53 (M)—ht | ||||
| to room temperature | to 150–40 °C | |||
| M (OH) (BDC)2− × (H2O)≡MIL-53(M) (lt) | MIL-53(Fe) (int) | |||
| Al | Cr | Ga | Fe | Fe |
| Structure III | Structure V—Superstructure to structure III (sp.gr. P 1 21/c 1; z = 8) | Structure VI (sp.gr. P ̅1̅ z = 8) | ||
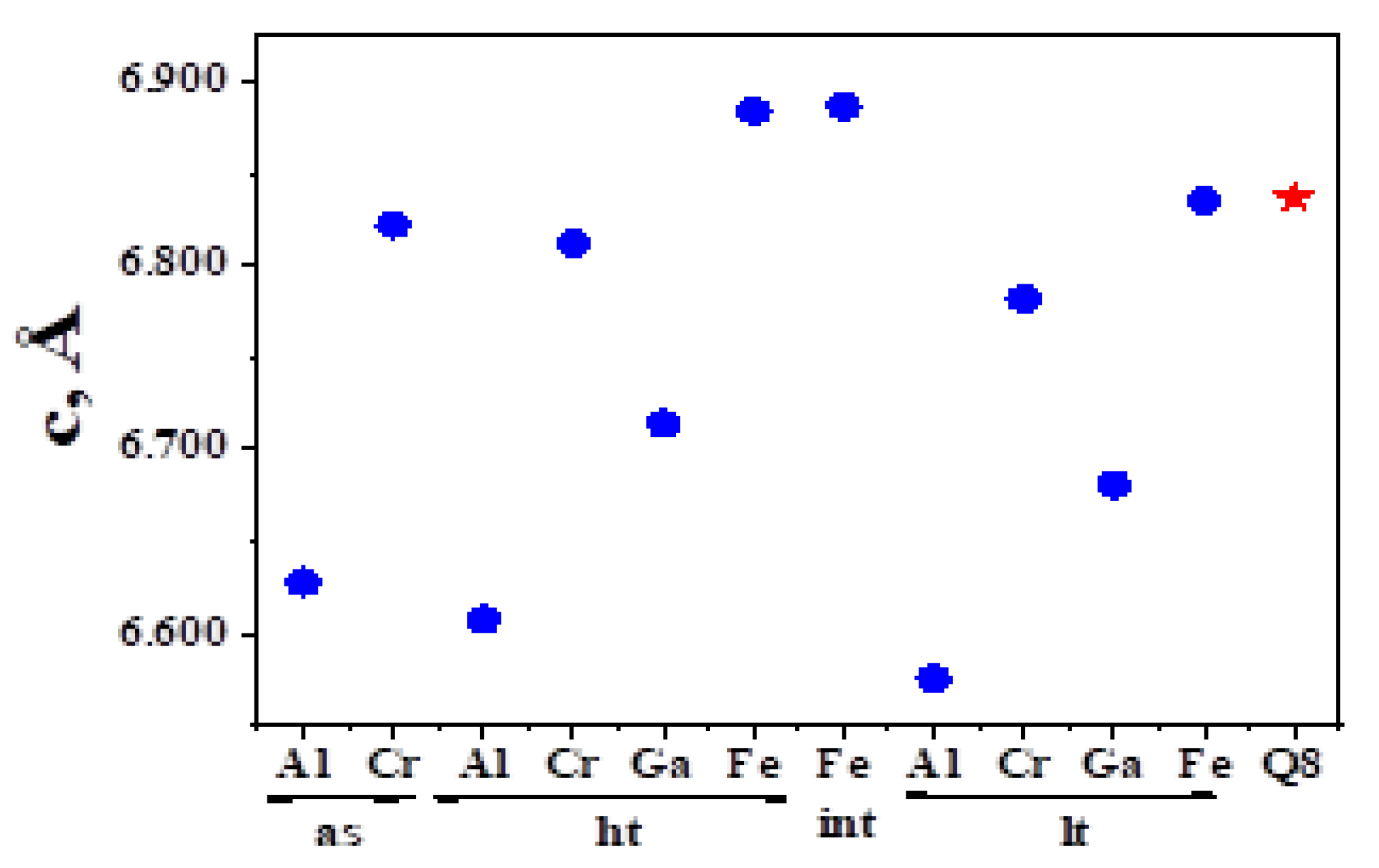
| Sp.gr. C 1 c 1; z = 4; a = 19.513, b = 7.612, c = 6.576, β = 104.24° | Sp.gr. C 1 2/c 1; z = 4; a = 19.685, b = 7.849, c = 6.782, β = 104.90° | a = 19.7053, b = 15.1642, c = 6.6812, β = 103.79° a = 19.7053, b = 7.582 × 2, c = 6.6812, β = 103.79° | a = 19.3197, b = 15.0362, c = 6.8351, β = 96.31° a = 19.3197, b = 7.518 × 2, c = 6.8351, β = 96.305° | a = 10.557, b = 13.4662, c = 6.8865, α = 88.058°, β = 103.967°, γ = 109.856° |
| Sample | MIL-53(Fe) | MIL-53(Fe)/GO |
|---|---|---|
| Space group | P21/c (#14) | P21/c (#14) |
| a, Å | 19.3284 (6) | 19.313 (2) |
| b, Å | 15.0417 (5) | 15.0190 (18) |
| c, Å | 6.8369 (2) | 6.8378 (7) |
| β, deg | 96.285 (5) | 96.487 (11) |
| Volume, Å3 | 1975.75 (11) | 1970.7 (4) |
| Sherrer size, nm | 66.3 | 296.5 |
| Microstrains, % | 0.21 | 0.10 |
| Sample | NO | RFe-O, Å | σ2, Å2 | Rf, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIL-53(Fe)/GO | 4.0 ± 0.4 | 2.01 ± 0.01 | 0.0062 | 0.5 |
| MIL-53(Fe) | 4.9 ± 0.3 | 2.00 ± 0.006 | 0.0067 | 0.2 |
| Elements and Components | Peak Position, eV | Concentration, atm. % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIL-53(Fe) | MIL-53(Fe)/GO | |||
| C 1s | C sp2 | 284.8 | - | 17.858 |
| C sp3 | 285.1–285.5 | 9.717 | 13.010 | |
| C-C-H | ~286.5 | 15.531 | 23.729 | |
| C-O | ~287.8 | 20.979 | 13.172 | |
| C = O | ~289 | 19.187 | 7.706 | |
| π-π* satellite | 291–292 | 7.873 | 5.408 | |
| O 1s | O-Fe | ~531 | 0.787 | 0.444 |
| C = O | ~532 | 0.380 | 0.903 | |
| C-O | ~532.8 | 3.789 | 2.553 | |
| C-OH | ~533.8 | 2.884 | 4.335 | |
| H2O | ~535.2 | 17.574 | 8.399 | |
| Fe 2p3/2 | Fe2+ | 712 | 0.161 | 0.158 |
| Fe3+ | ~715.4 | 1.138 | 0.324 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, Q.K.; Kuz’micheva, G.M.; Khramov, E.V.; Svetogorov, R.D.; Chumakov, R.G.; Cao, T.T. Design of Metal-Organic Polymers MIL-53(M3+): Preparation and Characterization of MIL-53(Fe) and Graphene Oxide Composite. Crystals 2021, 11, 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111281
Nguyen QK, Kuz’micheva GM, Khramov EV, Svetogorov RD, Chumakov RG, Cao TT. Design of Metal-Organic Polymers MIL-53(M3+): Preparation and Characterization of MIL-53(Fe) and Graphene Oxide Composite. Crystals. 2021; 11(11):1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111281
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Quang K., Galina M. Kuz’micheva, Evgeny V. Khramov, Roman D. Svetogorov, Ratibor G. Chumakov, and Thuy T. Cao. 2021. "Design of Metal-Organic Polymers MIL-53(M3+): Preparation and Characterization of MIL-53(Fe) and Graphene Oxide Composite" Crystals 11, no. 11: 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111281
APA StyleNguyen, Q. K., Kuz’micheva, G. M., Khramov, E. V., Svetogorov, R. D., Chumakov, R. G., & Cao, T. T. (2021). Design of Metal-Organic Polymers MIL-53(M3+): Preparation and Characterization of MIL-53(Fe) and Graphene Oxide Composite. Crystals, 11(11), 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111281