Abstract
For centuries, tuberculosis has been a worldwide burden for human health, and gaps in our understanding of its pathogenesis have hampered the development of new treatments. ESX-1 is a complex machinery responsible for the secretion of virulence factors that manipulate the host response. Despite the importance of these secreted proteins for pathogenicity, only a few of them have been structurally and functionally characterised. Here, we describe a structural study of the ESX-secretion associated protein K (EspK), a 74 kDa protein known to be essential for the secretion of other substrates and the cytolytic effects of ESX-1. Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) data show that EspK is a long molecule with a maximal dimension of 228 Å. It consists of two independent folded regions at each end of the protein connected by a flexible unstructured region driving the protein to coexist as an ensemble of conformations. Limited proteolysis identified a 26 kDa globular domain at the C-terminus of the protein consisting of a mixture of α-helices and β-strands, as shown by circular dichroism (CD) and SAXS. In contrast, the N-terminal portion is mainly helical with an elongated shape. Sequence conservation suggests that this architecture is preserved amongst the different mycobacteria species, proposing specific roles for the N- and C-terminal domains assisted by the middle flexible linker.
1. Introduction
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the causative agent of human tuberculosis (TB) and can be considered one of the most efficient pathogens in history, as it has threatened our health since the beginning of the Homo sapiens existence [1]. Nowadays, it is estimated that one-quarter of the world’s population has latent TB, from which 10 million people fell ill in 2018. Every year, 1.5 million people succumb from TB, placing it together with COVID-19 [2], as the leading cause of death from a single infectious agent [3]. Although TB chemotherapy is considered a triumph of anti-infective research [4], changing the disease from fatal to curable, it is far from optimal. The toxicity of the drugs and the length of the treatment have contributed to the rise of drug-resistant strains that threaten the global health security [4]. The need for new medicine that can cure or prevent TB is unquestionable, but gaps on the knowledge of mycobacteria pathogenesis hampers its development. Additionally, M. tuberculosis has diverged into several phylogenetic lineages with different virulence degrees hindering our further understanding of the molecular mechanisms of the pathogenesis. Nevertheless, there are essential events that contribute to the infectivity success of all pathogenic strains. Macrophages, as part of the innate immune system and first line of defence against pathogens, internalise the bacteria in a process called phagocytosis to degrade the microorganism [5]. However, M. tuberculosis and other pathogenic species evade this fate by blocking the maturation of the phagosome and disrupting the phagosomal membrane to translocate into the cytosol of the host cell [6]. This event is essential for the survival of mycobacteria, as it has been shown that non-pathogenic species are unable to translocate, leading to the lysis of the bacteria. This ability has been directly linked to the presence of the ESX-1 secretion system [7].
Mycobacteria have five different secretion systems (ESX-1 to -5) that facilitate the transport of virulence factors through a complex and almost impermeable cell wall [8]. These are paralogue protein complexes with specific functions that are unable to complement each other [9]. Despite their importance in the pathogenesis and survival of mycobacteria, the structure and mechanism of action remain poorly characterised. Only recently, the architecture of the inner-membrane complex of ESX-3 [10,11] and ESX-5 [12,13] was determined showing a protomer unit composed of the ESX-conserved components (EccB, EccC, EccD (×2) and EccE), which further oligomerise into dimers and hexamers. Each locus is composed of genes that code for the Ecc proteins and other proteins involved in their own expression and secretion regulation. These are (a) one pair of ESX proteins who provided the name for the secretion systems, (b) two or more proteins belonging to the PE/PPE family, (c) a mycosin protease (MycP), and (d) one or more ESX secretion-associated proteins (Esp) [8]. Due to the high sequence similarity and conservation between the paralogue systems [11], it is hypothesised that the substrates are directly linked to the specific function of each secretion system. Compared to its paralogues, ESX-1 contains a large number of Esp that are essential for the mycobacteria virulence [14,15,16,17]. One such protein is EspK, encoded by the espK gene (also known as Rv3879c), which is missing in the attenuated strain M. bovis bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) used worldwide as a vaccine against M. tuberculosis [18,19]. The disruption of espK has been linked with the loss of cytolytic/cytotoxic effects in mycobacterial strains [15], as well as the decreased expression and secretion of other Esp [20,21]. Physical interaction with the EspB protein has led to the hypothesis that EspK acts as a chaperone of the former, but this is yet to be proven [21].
Here, we present a structural study of the EspK protein done by limited proteolysis, Small-Angle X-ray Scattering, and circular dichroism, which revealed the presence of two well-defined domains connected by an unstructured, low complexity linker. The N-terminal region consists of an elongated shape with a predicted two-helix bundle structure characteristic of the ESX-1 substrates, while the C-terminal end comprises a globular domain composed of a mixture of α-helices and β-sheets. Sequence conservation suggests that this architecture is preserved amongst the different mycobacteria species and that specific roles for the N- and C-terminal domains are assisted by the flexible linker.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Secondary Structure Prediction
Multiple protein sequence alignment consisting of 16 representative sequences of the Mycobacterium genus was performed using ClustalW [22]. Sequence alignments were visualised with the program Jalview 2.4 (http://www.jalview.org/) [23]. The secondary structure prediction of EspK full-length was calculated using the Jpred 4 server [24].
2.2. Cloning, Expression, and Protein Purification of EspK Constructs
The coding sequence of the full-length EspK protein was amplified from genomic DNA of M. tuberculosis H37Rv (BEI Resources, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases) by PCR. The DNA fragment was cloned in the pQLinkH vector [25] using the restriction sites NsiI and HindIII. The sequence corresponding to the C-terminal region of EspK (residues 484–729) was cloned in the aforementioned vector by inverse polymerase chain reaction [26]. The constructs encode a 6×His tag followed by a TEV protease recognition site and the corresponding EspK protein. Both proteins were expressed in Rosetta (DE3) Escherichia coli cells in Overnight Express™ Instant LB Medium (EMD Millipore) supplemented with 100 μg/mL of carbenicillin and 25 μg/mL of chloramphenicol for 50 h at 25 °C. Cell pellet was resuspended in 20 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 300 mM NaCl, 40 mM imidazole supplemented with 1 mM PMSF, and 25 U/mL Benzonase® Nuclease (Merck), and lysis was performed with a C3 homogenizer (Emulsiflex, Avestin, ATA Scientific Pty Ltd., Sydney, Australia). The lysate was clarified by centrifugation at 100,000× g for 40 min and 4 °C. The soluble fraction was purified through a Ni2+ ion affinity chromatography using a 5 mL Ni-NTA Superflow column (Qiagen) and eluted with the same buffer containing 250 mM imidazole. The eluted protein was digested with TEV protease to remove the histidine tag while dialysing overnight at 4 °C against the low imidazole buffer. The protein sample was further purified through a second Ni2+ ion affinity chromatography. Aliquots containing the protein of interest were pooled together and stored at −80 °C in 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 300 mM NaCl until further use. Sample purity was assessed by SDS-PAGE.
2.3. Limited Proteolysis and N-Terminal Sequencing
A full-length EspK sample (4 µM) was incubated with trypsin for 30 min at different molar ratios following the Proti-Ace™ Kit (Hampton Research, Aliso Viejo, CA, USA) instructions. Reactions were stopped by adding SDS-PAGE loading buffer, and samples were resolved on a 12% polyacrylamide gel. Bands were transferred from the SDS-PAGE gel to a PVDF membrane and stained with 0.1% (w/v) Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250, 40% methanol, and 10% acetic acid for 5 min before cutting out the section containing the cleavage product. The first ten amino acids were determined by Edman sequencing at the Plateforme Protéomique PISSARO IRIB at the Université de Rouen, France.
2.4. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy (CD)
Circular dichroism scan measurements were obtained at 25 °C using a JASCO J-1500 spectropolarimeter equipped with a Peltier temperature controller (Jasco Inc., Easton, MD, USA). CD spectra were recorded using a 1 mm cuvette and a protein concentration of 1 µM for the full-length construct and 3 µM for the EspK C-terminal region in the far-UV (260–190 nm). Spectra were acquired in 50 mM phosphate buffer pH 8.0, 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM dithioerythritol, at a 1-nm increase per step, an averaging time of 5 s, and a spectral resolution of 1 nm. Each spectrum corresponds to the average of five repetitive scans and was corrected by subtracting the CD signal of the buffer. The temperature dependence of ellipticity was followed by monitoring the signal at 222 nm from 20 to 80 °C, with a bandwidth of 1 nm, a response time of 16 s, a sample interval of 0.2 °C, and a scan rate of 1 °C/min.
2.5. Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering (SAXS) Experiments
Structural characterisation of the EspK proteins was performed by SAXS coupled to an online size exclusion chromatography (Agilent 1200 HPLC, Santa Clara, CA, USA) equilibrated with 20 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0 and 300 mM NaCl. Experiments for the C-terminal region of EspK were collected in the bioSAXS beamline B21 at a Diamond Light Source, Harwell, United Kingdom. Protein sample consisting of 50 µL at a concentration of 13 mg mL−1 was run over a Shodex KW-403 size exclusion column at a flow rate of 0.08 mL min−1. The eluted protein was directed through a 1.6-mm diameter quartz capillary cell held in vacuum. Data acquisition consisted of 580 frames (with 3 s exposure time) using a PILATUS 2M detector at a calibrated distance of 4.014 m from the sample. Images were corrected for variations in beam current, normalized for time exposure, and processed into one-dimensional scattering curves using GDA and the DAWN software (Diamond Light Source, Didcot, UK). Data for the full-length EspK were collected in the bioSAXS beamline P12-EMBL at DESY Light Source, Hamburg, Germany. A sample consisting of 50 µL at a concentration of 3.6 mg mL−1 was run over a Superdex 200 Increase 3.2/300 size exclusion column attached to a FPLC–Malvern TDA system at a flow rate of 0.1 mL min−1. The elution output was directed through a quartz capillary cell (50 µm thick wall and a 1.7 mm path length) held in vacuum. Data acquisition consisted of 900 frames (with 1 s exposure time) using a PILATUS 2M detector at the distance of 3.0 m from the sample. Images were corrected for variations in beam current, normalised for time exposure, and processed into one-dimensional scattering curves using integrated software at the beamline [27]. Background was manually subtracted using the program CHROMIXS [28]. SAXS parameters are listed in Table 1. Low-resolution structures were constructed by ab initio modeling using the program GASBOR [29] and DAMMIF [30] by aligning, averaging, and filtering ten independently calculated dummy residue and atom models by using DAMAVER program [31]. Models for the different regions of EspK were predicted by the I-TASSER web server [32] considering residues 1–180 (N-terminus), 181–483 (flexible linker), and 484–729 (C-terminus). This division was based on the secondary structure prediction and limited proteolysis results. Then, multi-domain modeling was performed using the CORAL program [33]. As the middle part of EspK is predicted to be highly disordered, 40 residues at each end of this region were removed from the I-TASSER model and added by CORAL as linkers between the N-terminal and C-terminal regions.

Table 1.
SAXS data collection and scattering-derived parameters for the M. tuberculosis EspK proteins.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sequence Conservation of EspK Highlights Discrete Regions
Limited information exists on the structural features of EspK. Sequence analysis of the M. tuberculosis protein displays a region between residues 182 and 437 with an unusual large content of alanine and proline. Proline is an atypical amino acid due to its cyclic side chain that restricts the backbone conformation and is unable to act as a hydrogen donor: for this reason, proline is known as the “helix breaker” [34]. Based on this observation, EspK could be divided in three discrete regions: an N-terminal domain containing a WxG motif commonly found in ESX-1 proteins [35], an A/P-rich middle region, and a C-terminal domain. Comparison of the amino acid composition present in these regions with a subset of proteins taken from the protein data bank (PDB) [36] representing structured proteins, showed a similar distribution of amino acids for the N- and C-terminal ends. In contrast, the middle region lacks residues that promote order and has 5-fold more prolines than average structured proteins (Figure 1). It is noteworthy that this high proline content is also unusual for disordered proteins, as it has a 3-fold enrichment compared to the average content of intrinsically unstructured proteins [37]. Secondary structure prediction of EspK suggests that the N- and C-terminal ends are folded regions connected by a large unstructured linker (Figure 2), which is in agreement with the amino acid analysis showing an average content of order promoting residues. To determine if this organisation is peculiar for the M. tuberculosis EspK or whether it is a general characteristic of this protein, we carried out a sequence alignment of different species from the genus Mycobacterium. Analysis revealed that the N- and C-terminal domains have a high sequence conservation amongst the species, while the middle region is variable in length and sequence. Despite the sequence variation in the middle region, it retains a characteristic high alanine and proline content that would preserve its physicochemical properties (Figure 2 and Supplementary Figure S1).
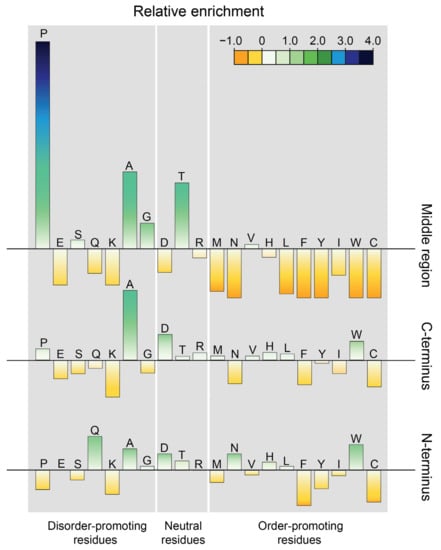
Figure 1.
Relative amino acid enrichment in the different regions of EspK compared to proteins deposited in the protein data bank [36]. Enrichment calculated as (AAEspK-AAPDB)/AAPDB, where AAEspK is the content of an amino acid in EspK, and AAPDB is the corresponding amino acid content of a subset of structured proteins. Amino acids are distributed according to their (dis)order-promoting potential.
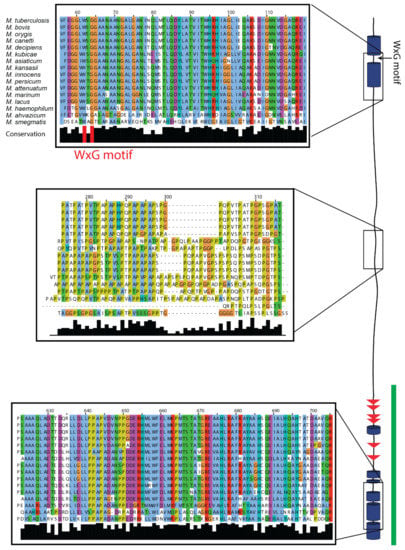
Figure 2.
Sequence alignment of EspK from different mycobacterial species and secondary structure prediction. Zoom-in displays representative regions of the different domains. The trypsin-resistant domain identified in this work is highlighted with a green line.
3.2. EspK Contains a Trypsin-Resistant Domain
To confirm the existence of the two well-defined domains, EspK full-length from M. tuberculosis H37Rv was recombinantly expressed in E. coli and further purified. Interestingly, EspK migrates anomalously in SDS-PAGE, appearing at a higher molecular weight than the expected 74 kDa (Figure 3). This has been observed in high-proline content molecules whose difference in migration is directly proportional to the percentage of prolines in the amino acid sequence [37]. The limited proteolysis of EspK at different molar ratios of protease displayed the presence of a digestion-resistant fragment, with an apparent molecular weight of 26 kDa (Figure 3). The N-terminal sequencing showed that this fragment starts at Gly484 and based on the molecular weight calculated from the amino acid sequence (26.4 kDa), it extends all the way to the C-terminus of the protein. This result agrees with the secondary structure prediction and the conservation of the respective region, suggesting that it corresponds to a folded domain of EspK. Based on the amino acid sequence, the N-terminal domain would represent an 18-kDa fragment; however, no fragments were found below the 26-kDa molecular weight marker (Figure 3). This suggests that the N-terminal domain consists of either unstructured regions or contains exposed accessible digestion sites that destabilise the structure.
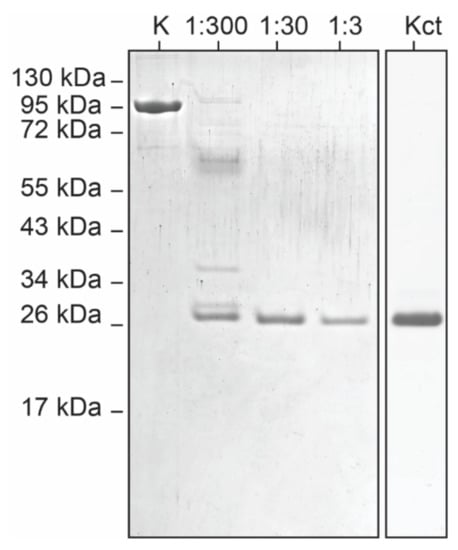
Figure 3.
Identification of a trypsin-resistant C-terminal region on EspK by limited proteolysis. First lane (K)—full-length EspK, lanes 2–4: EspK digestion using different molar ratios of trypsin, lane 5: trypsin-resistant EspK fragment recombinantly expressed.
3.3. Characterisation of Secondary Structure by Circular Dichroism (CD)
The secondary structure content of EspK and its C-terminal region was evaluated by circular dichroism (Figure 4a). Closer inspection of the far-UV CD spectrum of the C-terminal fragment shows that it consists of the typical signature of a mixed secondary structure containing both α-helices and β-sheets with two negative minima at 210 and 220 nm and a positive maximum at 197 nm. These shifted negative minima result from the combined contribution of the characteristic negative bands for α-helices present at 208 and 222 nm and those of β-sheets present between 210 and 225 nm. In addition, the presence of the intense positive signal between 195 and 200 nm is characteristic of proteins containing β-sheets. Considering that the full-length construct comprises that of the C-terminal region, this CD spectrum also resembles a mixture of β-sheets and α-helices with a well-defined negative minimum at 208 nm instead of that at 210 nm, suggesting a larger content of α-helices and a plateau between 215 and 220 nm resulting from the β-sheets contribution. The positive maxima displaced toward the lower wavelength (193 nm) also indicates a larger content α-helices contributed most likely from the N-terminal region of EspK. The overall intensity of the full-length EspK spectra is smaller (absolute value) compared to that of the C-terminal region, implying that there is less secondary structure content per residue in the full-length protein and thus a larger content of unstructured regions. The thermal stability of EspK was determined by monitoring the ellipticity at 222 nm as a function of temperature (Figure 4b). The thermal denaturation for the EspK full-length and C-terminal region corresponded to an irreversible process as the refolded spectra did not overlay with the corresponding one before the heat treatment (data not shown). Data for both constructs described a single broad transition comprising approximately 45 °C from the onset of the denaturation process until reaching the denatured state. Despite the lack of clearly identifiable intermediate transitions, this long gradual denaturation process suggests the presence of intermediate states with similar secondary structure content, which cannot be evidenced by this technique. The apparent melting temperatures corresponded to 45 and 52 °C for the full-length EspK and the C-terminal region, respectively. The decrease in the melting point for the full-length protein compared to that of the C-terminus suggests that these two regions behave independently, as an interaction between them would increase the stability of the protein and thus the melting temperature of the full-length protein.
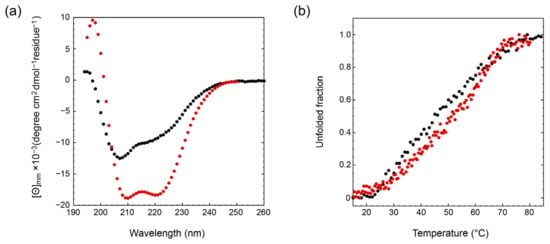
Figure 4.
Circular dichroism of the EspK full-length protein (black) and its C-terminal region (red). (a) Far-UV spectra. (b) Thermal denaturation.
3.4. Structural Analysis by Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)
We tried to gain insight into the tertiary structure of EspK by performing SAXS experiments. All parameters are listed in Table 1. The one-dimensional SAXS experimental curves were used to judge the quality of the data and obtain basic structural information related to the size and shape of the EspK protein and its C-terminal domain (Figure 5a). SAXS curve analysis confirmed that the proteins were monomeric, as the calculated molecular weight from the Porod plot corresponds to the expected value calculated from the amino acid sequence (Table 1). The full-length EspK and its C-terminal domain have a radius of gyration (Rg) of 53.53 Å and 21.70 Å, respectively, which are calculated from the slope of the Guinier plot [38], with a maximum dimension (Dmax) of 228 Å and 83 Å obtained from the Pair-Distance Distribution Function (P(r)) (Figure 5b). Based on these two parameters, it is expected that the full-length EspK represents an elongated molecule, while the C-terminal domain comprises a globular shape.
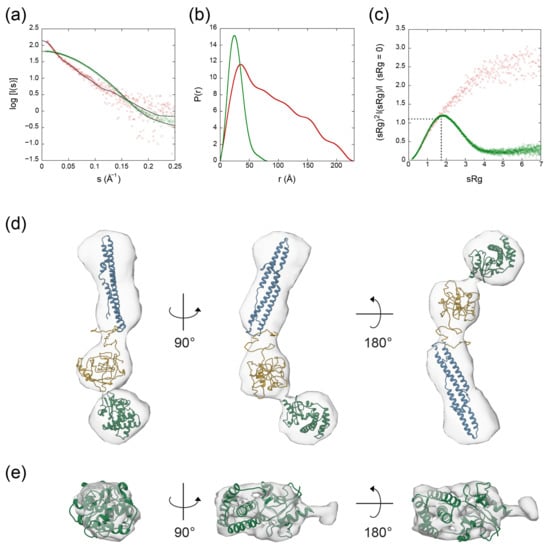
Figure 5.
SAXS data for the EspK full-length protein (red) and its C-terminal domain (green). (a) Fit of the calculated SAXS scattering curves compared to the experimental scattering signal. (b) Pair distribution function plot. (c) Dimensionless Kratky plot. The intersection of the dotted black trace corresponds to the value for the reference protein bovine serum albumin (BSA). (d) Ab initio molecular envelope of the full-length EspK showing the fit of the models corresponding to the N-terminal (residues 1–180 in blue), the flexible linker (residues 181–438 in yellow), and C-terminal region (residues 484–729 in green). (e) Ab initio molecular envelope of the C-terminal region of EspK showing the fit of the corresponding model.
Analysis of the Porod exponent, a quantitative measurement of the increase of compactness of a protein [39], confirmed the flexible nature of the full-length protein in comparison with its C-terminal domain with values of 2.4 and 4.0, respectively. This observation was in agreement with the corresponding dimensionless Kratky and P(r) distribution plots, where the C-terminal domain behaved as a globular and compact protein similar to the bovine serum albumin (BSA) used as a standard protein, compared to the highly flexible and elongated full-length EspK that seems to attain multiple conformations (Figure 5b,c). To inquire on the tertiary structure of the proteins, we obtained the SAXS ab initio models of the EspK full-length and C-terminal domain using DAMMIF and GASBOR software programs, respectively, and compared them with their corresponding I-TASSER predicted models (Figure 5d,e). The ambiguity of the obtained reconstructions, as estimated by the program AMBIMETER [40] were 1.74 for the full-length EspK and 0.0 for the C-terminal region (Table 1). These values indicate that the 3D reconstruction for the full-length protein might be ambiguous, whereas that of the C-terminal is not. The model obtained for the full-length EspK represents an average of different conformations as suggested by the Pair-Distance Distribution Function (P(r)), resulting in such ambiguity. The resolution of the models, as determined by Fourier Shell Correlation (FSC) [41] is 40 Å and 25 Å for the EspK full-length and C-terminal domain, respectively. The I-TASSER prediction for the EspK full-length protein resulted in an unstructured model. As previous data pointed to the C-terminal end being folded, we performed independent predictions for the three regions of the protein (Supplementary Figure S2). In agreement with the secondary structure prediction and circular dichroism, the model for the N-terminal region consisted of only α-helices, and seven out of the best ten templates used to build it corresponded to Pro-Pro-Glu (PPE) proteins. These proteins are characterised by its Pro-Pro-Glu (PPE) motif and are known to be secreted together with their PE protein pair by ESX-1 and its paralogues [9,42]. Despite the resemblance, the EspK N-terminal domain does not contain the PPE motif; instead, it only contains the WxG motif needed for the secretion of the protein. The top five models predicted for the middle region by I-TASSER resulted in a disordered region with different spatial distributions but no secondary structure content. In the case of the C-terminal domain, all predicted models displays a globular and compact protein composed of a mixture of α-helices and β-strands as also suggested by the circular dichroism results. For this domain, the correlation of χ2 = 11.4 between the experimental SAXS curves and the calculated one from the ab initio model (Supplementary Figure S2c) suggests a good level of confidence in the correctness of the model, which was further confirmed by calculating the normalised spatial discrepancy [43] between the SAXS and I-TASSER model (NSD = 2.48). For EspK full-length, the low-resolution envelope (DAMMIF) obtained is well described by the I-TASSER models from the three regions (Figure 5d). These models were subsequently used to build a multi-domain model with the CORAL program, which describes the experimental EspK full-length SAXS data confidently (χ2 = 1.39) (Figure 6).
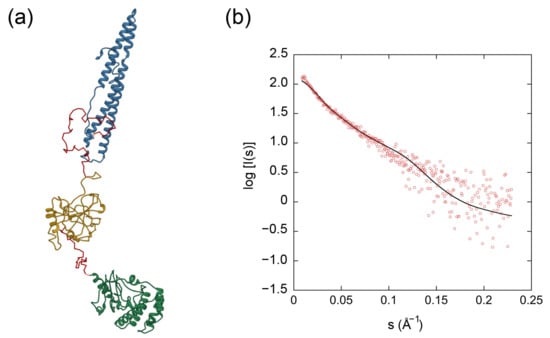
Figure 6.
Multi-domain modeling by CORAL of the full-length EspK. (a) Multi-domain model of the N-terminal domain (blue), the middle region (yellow) and the C-terminal domain (green) connected by linkers (red). (b) Fit of the calculated SAXS scattering curves from the multi-domain model (black line) compared to the experimental scattering signal (red).
The protein with the closest structural similarity found in the protein data bank which was used to build the I-TASSER model of EspK C-terminus corresponded to residues 184-410 of the Rv3899c protein from M. tuberculosis [44]. This is a protein of unknown function found in the bacteria culture filtrates [45] and infected guinea pig lungs [46]. It is noteworthy that the corresponding gene is located next to the esx-2 locus, which is a paralogue of the ESX-1 secretion system to which EspK belongs. Limited information exists on ESX-2 but its exclusive presence in slow-growing mycobacteria [47], a group of mycobacteria characterised to be pathogenic, implies a possible involvement in this process. Until now, from all five paralogues, ESX-1 is the only secretion system that contains multiple Esp-proteins. Based on the similarity found by I-TASSER between EspK and Rv3899c, and its location in the genome, it might be possible for Rv3899c to be secreted by ESX-2.
To this day, no function has been described for EspK except for a hypothetical role as a chaperone of EspB based on their interaction and that with the ESX-1 core protein EccCb1 [21]. Instrinsic disordered regions provide proteins with a unique ability to interact with several unrelated binding partners. With this in mind and based on the thermal denaturation results that suggest no interactions between the EspK domains, it is plausible that EspK assists other protein substrates such as EspB to be secreted, e.g., one domain could interact with the ESX-machinery, while the other one interacts with a substrate. EspB is homologous to the PPE-PE proteins, which are chaperoned by EspG [48]. The current model of EspK does not share structural similarity with EspG [49], implying that the system could make use of different secretion mechanism with specific chaperones. High-resolution structures are needed to test this hypothesis, leading to a better understanding of the action mechanism of ESX-1 secretory system.
4. Conclusions
Using a combined approach of SAXS, CD, and limited proteolysis, together with structure predictions, we show that EspK is formed by two discrete independent domains connected by a partially disordered region, with an unusual large content of proline that confers a high degree of flexibility to the protein. This architecture is conserved along the Mycobacterium genus, suggesting a specific function for the N- and C-terminal domain assisted by the flexible linker. To confirm the mechanism of action of such domains, high-resolution studies are needed in the presence of the binding partners.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4352/11/1/18/s1, Figure S1: Sequence alignment of EspK from different mycobacterial species, Figure S2: Tertiary structure prediction by I-TASSER.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: A.G., N.S.-P., P.J.P., R.B.G.R. and D.S.; methodology: A.G., N.S.-P., Y.G. and D.S.; formal analysis: A.G., N.S.-P. and D.S.; writing—original draft preparation: A.G., N.S.-P. and D.S.; writing—review and editing: A.G., N.S.-P., R.B.G.R. and D.S.; supervision: P.J.P. and R.B.G.R.; funding acquisition, A.G., P.J.P., R.B.G.R. and D.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is part of the M4I research programme supported by the Dutch Province of Limburg through the LINK programme. AG and RBGR acknowledge funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme under Grant Agreement No. 766970 Q-SORT (H2020-FETOPEN-1-2016-2017), and NSP acknowledges the support from the PASPA-DGAPA program from UNAM and CONACYT 283909. The SAXS experiments were performed by proposals MX21741-1 SM21035-161 and SAXS-805 iNEXT 6260 on the beamlines B21, Diamond Light Source and P12-EMBL at DESY Light Source, respectively.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The SAXS data and models for the EspK full-length protein and its C-terminal domain have been deposited in the Small Angle Scattering Biological Data Bank (SASBDB [50]) with the access code SASDKQ4 and SASDKR4, respectively (www.sasbdb.org).
Acknowledgments
We thank Alexey Kikhney from DESY Light Source, and Nathan Cowieson and Nikul Khunti from Diamond Light Source for their assistance in the preparation of the SAXS experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hershkovitz, I.; Donoghue, H.D.; Minnikin, D.E.; Besra, G.S.; Lee, O.Y.; Gernaey, A.M.; Galili, E.; Eshed, V.; Greenblatt, C.L.; Lemma, E.; et al. Detection and molecular characterization of 9000-year-old Mycobacterium tuberculosis from a Neolithic settlement in the Eastern Mediterranean. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, E.; Du, H.; Gardner, L. An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 978-92-4-156571-4. [Google Scholar]
- Zumla, A.I.; Gillespie, S.H.; Hoelscher, M.; Philips, P.P.; Cole, S.T.; Abubakar, I.; McHugh, T.D.; Schito, M.; Maeurer, M.; Nunn, A.J. New antituberculosis drugs, regimens, and adjunct therapies: Needs, advances, and future prospects. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, D.; Iida, T.; Nakase, H. The Phagocytic Function of Macrophage-Enforcing Innate Immunity and Tissue Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Wel, N.; Hava, D.; Houben, D.; Fluitsma, D.; van Zon, M.; Pierson, J.; Brenner, M.; Peters, P.J. M. tuberculosis and M. leprae translocate from the phagolysosome to the cytosol in myeloid cells. Cell 2007, 129, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, D.; Demangel, C.; van Ingen, J.; Perez, J.; Baldeon, L.; Abdallah, A.M.; Caleechurn, L.; Bottai, D.; van Zon, M.; de Punder, K.; et al. ESX-1-mediated translocation to the cytosol controls virulence of mycobacteria. Cell. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitter, W.; Houben, E.N.; Bottai, D.; Brodin, P.; Brown, E.J.; Cox, J.S.; Derbyshire, K.; Fortune, S.M.; Gao, L.Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Systematic genetic nomenclature for type VII secretion systems. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, A.M.; Gey van Pittius, N.C.; Champion, P.A.; Cox, J.; Luirink, J.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.; Appelmelk, B.J.; Bitter, W. Type VII secretion—Mycobacteria show the way. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famelis, N.; Rivera-Calzada, A.; Degliesposti, G.; Wingender, M.; Mietrach, N.; Skehel, J.M.; Fernandez-Leiro, R.; Bottcher, B.; Schlosser, A.; Llorca, O.; et al. Architecture of the mycobacterial type VII secretion system. Nature 2019, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poweleit, N.; Czudnochowski, N.; Nakagawa, R.; Trinidad, D.D.; Murphy, K.C.; Sassetti, C.M.; Rosenberg, O.S. The structure of the endogenous ESX-3 secretion system. eLife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckham, K.S.H.; Ritter, C.; Chojnowski, G.; Mullapudi, E.; Rettel, M.; Savitski, M.M.; Mortensen, S.A.; Kosinski, J.; Wilmanns, M. Structure of the mycobacterial ESX-5 Type VII Secretion System hexameric pore complex. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunduc, C.M.; Fahrenkamp, D.; Wald, J.; Ummels, R.; Bitter, W.; Houben, E.N.G.; Marlovits, T.C. Structure and dynamics of the ESX-5 type VII secretion system of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottai, D.; Majlessi, L.; Simeone, R.; Frigui, W.; Laurent, C.; Lenormand, P.; Chen, J.; Rosenkrands, I.; Huerre, M.; Leclerc, C.; et al. ESAT-6 secretion-independent impact of ESX-1 genes espF and espG1 on virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.Y.; Guo, S.; McLaughlin, B.; Morisaki, H.; Engel, J.N.; Brown, E.J. A mycobacterial virulence gene cluster extending RD1 is required for cytolysis, bacterial spreading and ESAT-6 secretion. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 1677–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassetti, C.M.; Rubin, E.J. Genetic requirements for mycobacterial survival during infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12989–12994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Saxena, R.; Tiwari, S.; Singh, D.K.; Singh, S.K.; Kumari, R.; Srivastava, K.K. RD-1 encoded EspJ protein gets phosphorylated prior to affect the growth and intracellular survival of mycobacteria. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, M.A.; Wilson, M.A.; Gill, W.P.; Salamon, H.; Schoolnik, G.K.; Rane, S.; Small, P.M. Comparative genomics of BCG vaccines by whole-genome DNA microarray. Science 1999, 284, 1520–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahairas, G.G.; Sabo, P.J.; Hickey, M.J.; Singh, D.C.; Stover, C.K. Molecular analysis of genetic differences between Mycobacterium bovis BCG and virulent M. bovis. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champion, M.M.; Williams, E.A.; Pinapati, R.S.; Champion, P.A. Correlation of phenotypic profiles using targeted proteomics identifies mycobacterial esx-1 substrates. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 5151–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, B.; Chon, J.S.; MacGurn, J.A.; Carlsson, F.; Cheng, T.L.; Cox, J.S.; Brown, E.J. A mycobacterium ESX-1-secreted virulence factor with unique requirements for export. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2—A multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdetskiy, A.; Cole, C.; Procter, J.; Barton, G.J. JPred4: A protein secondary structure prediction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W389–W394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheich, C.; Kummel, D.; Soumailakakis, D.; Heinemann, U.; Bussow, K. Vectors for co-expression of an unrestricted number of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.R.; Sambrook, J. Inverse Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, D.; Kikhney, A.G.; Svergun, D.I. Automated acquisition and analysis of small angle X-ray scattering data. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2012, 689, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjkovich, A.; Svergun, D.I. CHROMIXS: Automatic and interactive analysis of chromatography-coupled small-angle X-ray scattering data. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1944–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svergun, D.I.; Petoukhov, M.V.; Koch, M.H. Determination of domain structure of proteins from X-ray solution scattering. Biophys. J. 2001, 80, 2946–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, D.; Svergun, D.I. DAMMIF, a program for rapid ab-initio shape determination in small-angle scattering. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkov, V.V.; Svergun, D.I. Uniqueness of ab initio shape determination in small-angle scattering. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petoukhov, M.V.; Franke, D.; Shkumatov, A.V.; Tria, G.; Kikhney, A.G.; Gajda, M.; Gorba, C.; Mertens, H.D.T.; Konarev, P.V.; Svergun, D.I. New developments in the ATSAS program package for small-angle scattering data analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, M.P. The structure and function of proline-rich regions in proteins. Biochem. J. 1994, 297 Pt 2, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, C.; Panjikar, S.; Holton, S.J.; Wilmanns, M.; Song, Y.H. WXG100 protein superfamily consists of three subfamilies and exhibits an alpha-helical C-terminal conserved residue pattern. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theillet, F.X.; Kalmar, L.; Tompa, P.; Han, K.H.; Selenko, P.; Dunker, A.K.; Daughdrill, G.W.; Uversky, V.N. The alphabet of intrinsic disorder: I. Act like a Pro: On the abundance and roles of proline residues in intrinsically disordered proteins. Intrinsically Disord. Proteins 2013, 1, e24360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breibeck, J.; Skerra, A. The polypeptide biophysics of proline/alanine-rich sequences (PAS): Recombinant biopolymers with PEG-like properties. Biopolymers 2018, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinier, A. La diffraction des rayons X aux très petits angles: Application à l’étude de phénomènes ultramicroscopiques. Ann. Phys. 1939, 11, 161–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambo, R.P.; Tainer, J.A. Characterizing flexible and intrinsically unstructured biological macromolecules by SAS using the Porod-Debye law. Biopolymers 2011, 95, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petoukhov, M.V.; Svergun, D.I. Ambiguity assessment of small-angle scattering curves from monodisperse systems. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuukkanen, A.T.; Kleywegt, G.J.; Svergun, D.I. Resolution of ab initio shapes determined from small-angle scattering. IUCrJ 2016, 3, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, M.; Sawaya, M.R.; Wang, S.; Phillips, M.; Cascio, D.; Eisenberg, D. Toward the structural genomics of complexes: Crystal structure of a PE/PPE protein complex from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8060–8065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozin, M.B.; Svergun, D.I. Automated matching of high- and low-resolution structural models. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2001, 34, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, D.; Fleming, J.; Li, H.; Bi, L. Crystal structure of Rv3899c184-410, a hypothetical protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F 2016, 72, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malen, H.; Berven, F.S.; Fladmark, K.E.; Wiker, H.G. Comprehensive analysis of exported proteins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Proteomics 2007, 7, 1702–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruh, N.A.; Troudt, J.; Izzo, A.; Prenni, J.; Dobos, K.M. Portrait of a pathogen: The Mycobacterium tuberculosis proteome in vivo. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton-Foot, M.; Warren, R.M.; Sampson, S.L.; van Helden, P.D.; Gey van Pittius, N.C. The plasmid-mediated evolution of the mycobacterial ESX (Type VII) secretion systems. BMC Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekiert, D.C.; Cox, J.S. Structure of a PE-PPE-EspG complex from Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals molecular specificity of ESX protein secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14758–14763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuukkanen, A.T.; Freire, D.; Chan, S.; Arbing, M.A.; Reed, R.W.; Evans, T.J.; Zenkeviciute, G.; Kim, J.; Kahng, S.; Sawaya, M.R.; et al. Structural Variability of EspG Chaperones from Mycobacterial ESX-1, ESX-3, and ESX-5 Type VII Secretion Systems. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikhney, A.G.; Borges, C.R.; Molodenskiy, D.S.; Jeffries, C.M.; Svergun, D.I. SASBDB: Towards an automatically curated and validated repository for biological scattering data. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).