Abstract
Eight phenyl imidazolinone derivatives were synthesized from N2-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-N1-methyformamidine (DPMF) via scaffold-hopping method using the ring-closure approach. The prepared compounds were verified using 1H and 13C NMR and HRMS spectroscopies. The structure of compound 3c was confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. The mean plane of the phenyl and imidazolinone moieties was almost coplanar with an angle of 8.85(4)°. In the crystal, molecules were interlinked with intermolecular hydrogen bonds (N–H···O and C–H···O), generating a network structure. Additionally, compound 3f displayed the highest insecticidal activity (86.7%) against Plutella xylostella at 600 mg/L, which was significantly higher than the insecticidal activity (23.0%) of DPMF. Also, compound 3d displayed good fungicidal activities against Phytophthora capsici, Phytophthora sojae, and Phytophthora infestans. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations were performed to explain the insecticidal and fungicidal activities of phenyl imidazolidin-2-one derivatives, especially potent compounds 3f and 3d. Moreover, the binding modes of compounds 3a–h and DPMF against octopamine receptor of Plutella xylostella were studied by homology modeling and molecular docking. Therefore, a preliminary structure–activity relationship (SAR) was derived and discussed. These results encourage the exploration of novel insecticides and fungicides based on DPMF.
1. Introduction
Octopamine receptors (OARs) are a class of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) in invertebrates (e.g., insects). OARs can bind specifically to octopamine (OA), and regulate physiological processes, such as reproduction, feeding, flight behaviors, memory, and learning [1,2,3,4]. Since OARs do not exist in humans, they are the potential targets for novel selective insecticides. Over the past decades, many compounds, such as plant oils, clonidine, naphazoline, yohimbine, chlorpromazine, and mianserin, have been identified as octopamine receptors’ agonists and antagonists. However, further development as commercial insecticides has yet to be explored [5]. Only formamidine insecticides, such as chlordimeform (Figure 1a) and amitraz (Figure 1b), have been launched on the market successfully for controlling fleas, ticks, and mites [6,7,8]. However, chlordimeform (one of the main formamidine insecticides) and its metabolites display carcinogenicity, which limits further applications [9,10]. Amitraz is the only OARs-targeting commercial insecticide available in the market.
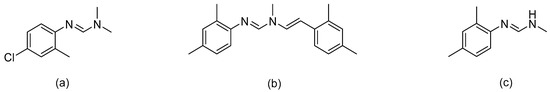
Figure 1.
(a) Chlordimeform, (b) amitraz, (c) N2-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-N1-methyformamidine (DPMF).
Diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella) is a Lepidopteran pest of cruciferous plant, which causes huge losses to agricultural production worldwide [11,12], and can be effectively controlled by commercial insecticides (tebufenozide, chlorantraniliprole, hexaflumuron, etc.) [13,14]. However, widespread and long-term applications of these insecticides promote resistance in diamondback moths, which warrants innovative novel insecticides [11,15,16]. OARs are promising molecular targets for the design and development of such insecticides against Plutella xylostella (P. xylostella). Although amitraz exhibits certain binding activity toward β-OAR of P. xylostella, its binding capacity toward PxOA2B2 is weaker than that of OA [17], indicating that amitraz may exert weak insecticidal activity against P. xylostella. Currently, there are no reports describing the insecticidal activity against P. xylostella, but amitraz shows very weak insecticidal activity against other Lepidoptera pests (Spodoptera littoralis and Heliothis virescens) [18]. N-2,4-dimethylphenyl-N’-methylformamidine (DPMF), a metabolite of amitraz (Figure 1c), exhibits acaricidal activities through targeting OARs [19]. Kita et al. reported that DPMF may possess potent β-adrenergic-like affinity for OARs in Bombyx mori (B. mori, a model insect in Lepidoptera), and is more potent than amitraz and OA [20]. This result revealed that DPMF might be more potent as an insecticide against Lepidoptera pests than amitraz. DPMF could be used as a lead compound to screen new insecticides against Lepidoptera pests.
Scaffold hopping is a popular drug discovery technique for the development of novel pesticides [21]. Hence, in this study, eight compounds were synthesized using the scaffold-hopping method via ring closure by replacing the formamidine functional group of DPMF with an imidazolinone group (Scheme 1). The structures of the prepared compounds were confirmed by 1H and 13C NMR spectrometry, HRMS (high-resolution mass spectrometry), and X-ray crystallography. Their insecticidal activities against diamondback moth were evaluated, with DPMF and amitraz as positive controls. Due to the imidazolinone group possibly possessing fungicidal activity, the fungicidal activities of these compounds against four fungal strains (Pseudoperonospora cubenis, Phytophthora capsica, Phytophthora sojae, and Phytophthora infestans) were determined, and imidazolinone-type fungicide (cyazofamid) was used as the positive control. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations were carried out to provide further clarity on the structure–activity relationship (SAR). Additionally, PxOA2B2, an octopamine receptor of Plutella xylostella, was constructed using homology modeling, and the binding modes of target compounds against PxOA2B2 were studied by molecular docking. This study offers useful guidance for the design and synthesis of new insecticides based on DPMF structure and provides the foundation for designing novel imidazolinone-type fungicides.
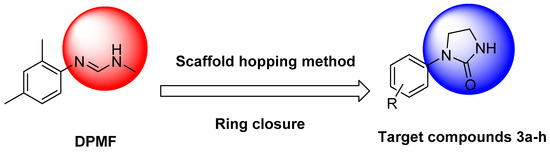
Scheme 1.
Design strategy of target compounds 3a–h.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Physical Measurements
Substituted anilines (1a–h) (purity 97–99%), 2-bromoethylamine hydrobromide (purity 98%), and triphosgene (purity 99%) were purchased from Jilin Chinese Academy of Sciences-Yanshen Technology Co., Ltd. (Jilin, Changchun, China). All other reagents used in the experiments were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China), dried, and used without further purification. Melting points were recorded using a Hanon MP100 automatic melting point apparatus (Jinan, China). The 300 MHz 1H-NMR and 75 MHz 13C-NMR spectra of the target compounds (3a–h) were recorded using a Varian Mercury-Plus 300 spectrometer (Salt Lake, UT, USA); tetramethylsilane (TMS) was used as the internal standard. High-resolution mass spectral data were obtained using an FTICR-MS Varian 7.0 T FTICR-MS instrument (Lake Forest, CA, USA). The diffraction data were collected using a Rigaku SuperNova, Dual, Cu at zero, AtlasS2 diffractometer (Agilent Technologies Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA).
2.2. Synthetic Procedures
2.2.1. Synthesis of Intermediates 2a–h
Intermediates 2a–h were synthesized via the modified method reported in reference [22]. A mixture of 2-bromoethylamine hydrobromide (10.00 g, 48.8 mmol) and substituted aniline (1a–h, 293 mmol) was dissolved in toluene (100 mL). This mixture was stirred overnight at 120 °C under nitrogen atmosphere. Then, the mixture was cooled down and filtered. The filtrate was washed twice with 20% NaOH aqueous solution (100 mL) and extracted twice with dichloromethane (100 mL). The combined organic phases were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure, giving crude intermediates 2a–h. Purification of the crude intermediates was achieved using silica gel column chromatography (methanol) producing a yellow oil (40–88%).
2.2.2. Synthesis of Target Compounds 3a–h
Target compounds (3a–h) were synthesized following the modified procedure reported in literature [23]. To a mixture of intermediates (2a–h) (41.06 mmol) in anhydrous tetrahydrofuran (73 mL) and trimethylamine (8.7 mL) a solution of triphosgene (4.06 g, 13.7 mmol) in anhydrous tetrahydrofuran (45 mL) was added dropwise over 30 min at 0 °C. Then, the reaction mixture was quenched with water (100 mL) and extracted twice with ethyl acetate (200 mL). The combined organic phases were washed twice with 10% aqueous hydrochloric acid solution (200 mL), twice with water (200 mL), and twice with saturated aqueous sodium chloride solution (200 mL). It was then dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure to afford the crude products (3a–h). Purification of crude products was achieved using silica gel column (ethyl acetate: dichloromethane, 1:2) producing the target compounds (3a–h).
2.3. Crystal Structural Determination
The molecular structure of target compound 3c was selected as a representative for X-ray analysis. Crystals of compound 3c were obtained via recrystallization from aqueous ethanol solution at room temperature. The crystal dimension of target compound 3c was 0.13 × 0.11 × 0.09 mm3. The diffraction data were collected using MoKα radiation (λ = 0.71073 Å) at 100.00(10) K using a Rigaku SuperNova, Dual, Cu at zero, AtlasS2 diffractometer (Agilent Technologies Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA). The structure was solved using SHELXT-2015 crystallographic software package and refined through full-matrix, least-squares techniques on F2 by SHELXL-2015 crystallographic software package [24]. The final cycle of refinement delivered R = 0.0469 and ωR = 0.1255 with ω = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0600 P)2 + 1.7180 P], where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3. Selected crystallographic data of compound 3c are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Selected crystallographic data of target compound 3c.
2.4. Insecticidal Activities
The insecticidal activities of target compounds 3a–h and DPMF were tested using the method reported in reference [25]. All insecticidal activity tests were conducted on representative test pests reared under laboratory conditions, which were repeated three times at 25 ± 1 °C to adhere to statistical requirements. Assessments were performed on dead/alive basis. Evaluations were based on the 0–100 percentage scale, where 0 was no activity and 100 represented total kill.
The insecticidal activities of target compounds 3a–h against Plutella xylostella were tested using the leaf disk assay method. The cabbage leaves were soaked in acetone solution containing 600 mg/L of each target compound (3a–h) for 20 s, respectively. After drying, the treated leaf was placed into a 7-cm-diameter Petri dish with 15 s-instar Plutella xylostella larvae and tested for stomach and contact toxicity. The percentage mortalities were calculated after 96-h application. DPMF was used as the positive control. All experiments were performed in triplicate and bioassay results were the average of three replications. All statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS 22.0 software package (IBM, New York, NY, USA).
2.5. Fungicidal Activities
The fungicidal activities of target compounds 3a–hand cyazofamid (a commercial fungicide and the positive control) were tested in vitro. Four fungal strains were used according to published methods, namely Pseudoperonospora cubenis (P. cubensis), Phytophthora capsica (P. capsica), Phytophthora sojae (P. sojae), and Phytophthora infestans (P. infestans) [26,27]. The solutions were prepared by dissolving 10 mg of target compound (3a–h) in DMSO (1 mL), producing a concentration of 10 mg/mL. The solution was then mixed with potato dextrose agar (PDA, 199 mL). Next, media containing target compound (3a–h) at a concentration of 50 mg/L for initial screening was poured into sterile Petri dishes (d = 9 cm) followed by cooling. Then, 0.5-cm mycelia disks in diameter were inoculated on the center of Petri dishes at 25 °C for two days. DMSO without any other compounds was employed as nontreated control. The treated hypha diameter was measured using cross-bracketing method, and commercial fungicide pyrimethanil was used as a positive control. The inhibition rate of target compounds 3a–h against fungi was calculated according to Equation (1):
where C0 is colony diameter of the control and C is colony diameter of treated. All fungicidal experiments were repeated in triplicate. All statistical analyses were performed by the SPSS 22.0 software package (IBM, New York, NY, USA).
2.6. Theoretical Calculations
Quantum chemical calculations were performed by Gaussian 16 (Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, CT, USA) [28].
2.7. Homology Modeling
At present, the crystal structure of the insect octopamine receptor has not been resolved. Therefore, we used the human-sourced octopamine (PDB entry: 5D5A) as a template to homologously model the crystal structure of Plutella xylostella octopamine receptor beta-2R-like (PxOA2B2, Sequence ID: XP_011568733.1) [29]. The homology modeling was performed using the MODELLER software [30].
2.8. Molecular Docking
AutoDock Vina software (Scripps Research Institute, San Diego, CA, USA) was used for molecular docking studies of target compounds 3a–h and DPMF with the receptor, while the receptor grid was prepared using the OPLS3e force field [31]. The grid center was set to be the centroid of ligand in homology modeling complex with a side length of 20 Å. The ligands were docked by SP (Standard Precision) mode, and all other parameters were set to defaults for the Glide docking process.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Spectroscopic Properties
The synthetic route of target compounds 3a–h is described in Scheme 2. Intermediates 2a–h were prepared via nucleophilic substitution of substituted anilines (1a–h) using 2-bromoethylamine hydrobromide. Target compounds 3a–h were obtained via cyclization reaction of intermediates 2a–h and triphosgene. The chemical structures of target compounds 3a–h were characterized by 1H and 13C NMR analysis and HRMS. Signals corresponding to C–H protons in imidazolinone ring and phenyl ring were observed at δ 3.34–3.86 ppm and δ 6.85–7.60 ppm, respectively; signal corresponding to N–H proton in imidazolinone group was observed at δ 6.78–7.06 ppm. All HRMS data for target compounds 3a–h were in agreement with the theoretical calculation values calculated by the chemical formula themselves.
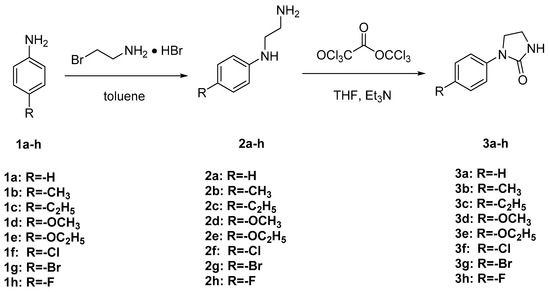
Scheme 2.
Synthetic route of target compounds 3a–h.
3.2. Crystal Structure
The crystal structure of target compound 3c, crystallized in a monoclinic system, is presented in Figure 2. The selected bond lengths and bond angles are listed in Table 2. The one-dimensional chain framework of target compound 3c is displayed in Figure 3. The crystal data have been deposited at the Cambridge crystallographic data center (CCDC) with CCDC-1878063. Crystallographic data of target compound 3c are available free of cost at CCDC (12 Union Road, Cambridge CB2 1EZ, UK; telephone number: +44-0123-7629120; fax number: +44-1223-336033; e-mail: deposit@ccdc.cam.ac.uk). These data are also available free of cost at http:www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request0.0/cif.
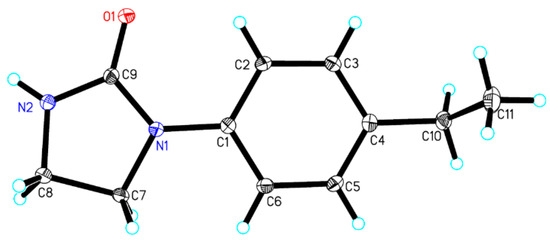
Figure 2.
Molecular structure of target compound 3c.

Table 2.
Selected bond lengths and angles of target compound 3c.
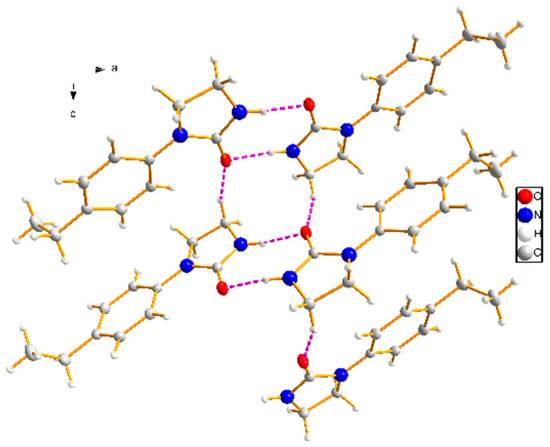
Figure 3.
The one-dimensional chain framework of target compound 3c (purple lines represent the hydrogen-bonding interactions).
The selected bond lengths and bond angles of the phenyl and imidazolinone rings in the crystal structure were in agreement with those from previous reports [32,33,34]. The bond length of O(1)–C(9) was 1.232(2) Å, which is similar to C=O bond length previously reported [25,35,36]. The ethyl-substituted phenyl and imidazolinone rings were directly connected by N(1)=C(1) bond (bond length, 1.408(2) Å). The bond angles of C(9)–N(1)–C(1) and C(9)–N(1)–C(7) were 126.9(1)° and 110.6(1)°, respectively. The mean plane of the phenyl ring, defined as C(1)–C(2)–C(3)–C(4) –C(5)–C(6), and imidazolinone ring, defined as N(2)–C(9)–N(1)–C(7)–C(8), formed angles of 8.85(4)°, revealing that the phenyl and imidazolinone rings were almost coplanar.
The 1D chain of target compound 3c in the unit cell is depicted in Figure 3. The molecules in this crystal packing were linked by intermolecular hydrogen-bonding interactions (N–H···O and C–H···O) to form network structure in the crystal structure, and intramolecular interaction (C–H···O) might have stabilized the flat conformation of the molecule (the dihedral angle between rings is 8.85) (Table 3). The N···O distances between donor (D) and acceptor (A) were 2.885(2) Å for N(2)–H(2)···O(1) and C···O distances between donor (D) and acceptor (A) were 3.358(2) Å and 2.871(2) Å for C(8)–H(8B)···O(1) and C(2)–H(2A)···O(1), respectively. As shown in Figure 4, the dimers were formed by a pair of strong N–H···O hydrogen bonds connecting the phenyl imidazolidin H atom of one molecule with the carbonyl O atom of another molecule to generate an (8) motif. Dimers connected via weak C–H···O interactions formed layers perpendicular to unit cell axis a, and the para-substituents of the studied molecules were located at the interface of the layers (Figure 5).

Table 3.
Hydrogen bond geometry of target compound 3c.
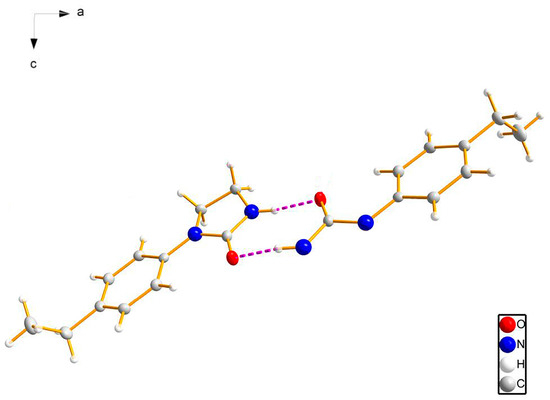
Figure 4.
The dimers formed by a pair of strong N–H···O hydrogen bonds (red, dashed lines represent hydrogen-bonding interactions).
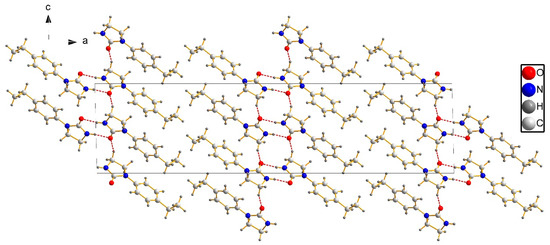
Figure 5.
Layers in the crystals of target compound 3c (red, dashed lines represent hydrogen-bonding interactions).
Symmetry transformations used to generate the equivalent atoms: #1: 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z; #2: x, 1 − y, 1/2 + z.
3.3. Quantum Chemistry Calculations of the Geometry and Electronic Structure
Computational methods were used to study the properties of potential bioactive molecules to predict their behavior in the real environment. First, we carried out the optimization of the molecules (target compounds 3a–h, DPMF, and cyazofamid) at the B3LYP/Def2SVP level by Gaussian 16 software. To obtain more accurate relative energies, single-point energies were calculated using the B3LYP/def2tzvp level by DFT calculations. The optimized conformations of target compounds 3a–h were obtained through these calculations (Figure 6). The current optimized conformations can be further used in molecular docking to study the potential interactions between target compounds 3a–h and PxOA2B2. The visual evaluation of the superimposed molecular structures of 3a–h and crystal 3c is shown in Figure 7 and the dihedral angles between the rings in 3a–h are listed in Table S1 (Supplementary Materials). Results from the molecular overlay exhibited, when the phenyl ring in the skeleton of the calculated structures of 3a–h and crystal 3c were aligned together, the imidazolinone rings in 3a–h were not coplanar with that of crystal 3c and the conformations of substituents at phenyl ring in 3d and 3e differed from that in 3a–c, 3f–h, and crystal 3c.
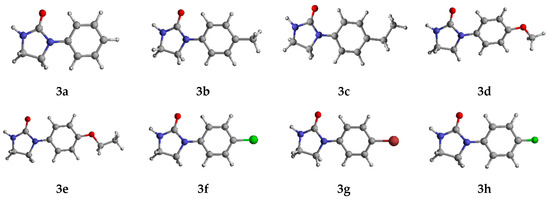
Figure 6.
Optimized conformation of target compounds 3a–h.
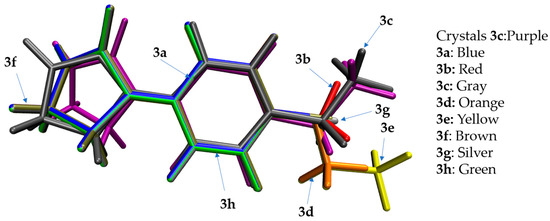
Figure 7.
Superimposed (calculated) structures of crystal 3c and target compounds 3a–h.
Factors (steric effects and electron donation/withdrawing properties) of 3a–g influencing the electron structure/insecticidal and fungicidal activities are described in Figures S1 and S2. According to molecular orbital theory, the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and the lowest occupied molecular orbital (LUMO) play key roles in the biological activities of agrochemicals [37,38]. HOMO represents the electron-donating ability of molecules and higher HOMO energy (EHOMO) indicates the electrons in molecules become unstable and, thus, result in the loss of electrons easily. LUMO shows the electron-accepting ability of molecules. The lower the LUMO energy (ELUMO) is, the more easily molecules accept electrons. EHOMO and ELUMO of agrochemicals can have a dramatic influence on their bioactivities. However, when the EHOMO is too high or the ELUMO is too low, it may lead to the strong molecular reactivity of agrochemicals, which can cause the agrochemicals to leave the receptors more easily and affect their biological activity. Moreover, the lower HOMO-LUMO gap (ΔE) represents higher insecticidal and fungicidal activities of agrochemicals in general.
Figure 8 shows the frontier molecular orbitals (FMOs) and energies of HOMO and LUMO for target compounds 3a–h, DPMF, and cyazofamid. The positive phase is symbolized with blue and the negative phase is green. Table 4 shows the insecticidal and fungicidal activity and HOMO-LUMO gaps (ΔE) of target compounds 3a–h, DPMF, and cyazofamid. Obviously, the target compound 3a had the highest ΔE of HOMO-LUMO gap, which indicated that it may have lower insecticidal and fungicidal activities, which is in agreement with the experimental data. On the contrary, the target compound 3d, which had the lowest ΔE of HOMO-LUMO gap, tends to have the highest insecticidal and fungicidal activities. It can be attributed to its strong ability to lose electrons, which can improve the stability of the complex of target compound 3d and its receptor. Notably, although target compound 3e had a similar ΔE with 3d, it exhibited the lowest activity, which can be ascribed to target compound 3e having the highest EHOMO. As above mentioned, the excessive electron-loss ability will cause it to be easily metabolized and leave the receptor, and, thus, its activity was decreased. In the case of target compound 3g, it had both the lowest ELUMO and fungicidal activity. Selected target compounds 3a-b showed lower insecticidal activity than that of DPMF, also with higher ΔE values than that of DPMF. Meanwhile, 3d and 3f-h exhibited better insecticidal activity than that of DPMF and it might be due to the reason that they have lower ΔE values than that of DPMF. Cyazofamid has a relatively lower ΔE value (0.1701 ev), compared with target compounds 3a–h, and it explains why it had the best fungicidal activity.
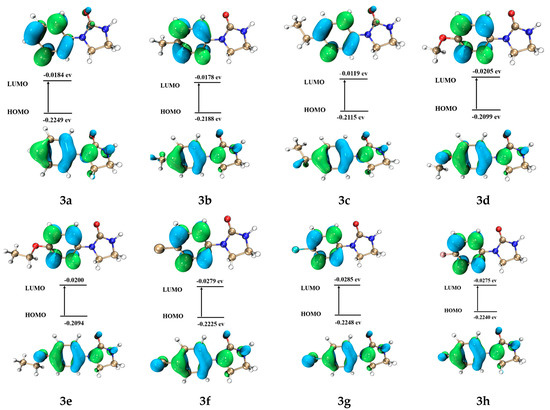
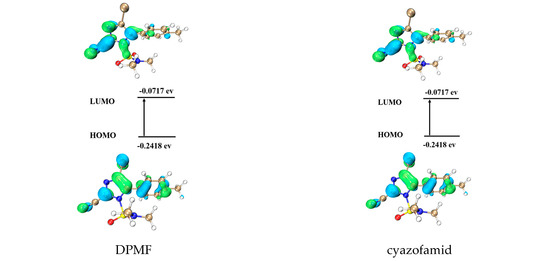
Figure 8.
Graphical representation of FMOs of target compounds 3a–h, DMPF, and cyazofamid (HOMO means the highest occupied molecular orbital and LUMO means the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital).

Table 4.
The insecticidal and fungicidal activity and HOMO-LUMO gap (ΔE) of DPMF, target compounds 3a–h.
The study of FMO energy also provides essential information that helps investigate active mechanisms. On one hand, HOMO of these compounds is mainly located on the imidazole and phenyl rings. On the other hand, LUMO of these compounds only resides on the phenyl ring. This indicates that, when these compounds interact with the receptor, the phenyl rings both provide and receive electrons, and the imidazole ring provides electrons to form the complex that promotes biological activity. This is because the imidazole ring is an electron-rich ring, so it is easier to lose electrons when it binds to the receptor, and the benzene ring is a weak electron-donating group. If the electron cloud density of the external group is large, the benzene ring will attract electrons; otherwise it will give electrons.
The insecticidal and fungicidal activity of target compounds 3a–h is shown in Table 4. Fungicidal activity of 3d/3e and 3b/3c displays that compounds with relatively smaller substituents are more active, suggesting the small steric hindrance with the receptor might benefit the fungicidal activity. It can be attributed to the big steric hindrance causing an increase of EHOMO, which can thus cause an increase of the electron-donating ability of target compounds. Despite the sizes of the substituents, the fungicidal activity of compounds with strong electron-donating groups is more potent than those possessing weak electron-donating groups (compound 3d and 3e exhibited better fungicidal activity than that of 3b and 3c, respectively). Moreover, for insecticidal activity, among all the target compounds 3f–h with strong electron-withdrawing groups, 3f with moderate steric effect and inductive effect exhibited the best activity. Additionally, the sizes of H (3a) and F atom (3h) are comparable, but their chemical nature is quite different. The insecticidal and fungicidal activity of 3h is much higher in comparison to that of 3a, which might be due to the strong inductive effect of F atom.
3.4. Molecular-Docking Stimulation
Molecular docking is a powerful tool for studying the interactions between ligands and receptors [39,40,41,42]. In order to obtain insights into the different insecticidal activity of target compounds 3a–h, their docking scores and binding modes with the active sites of PxOA2B2 were analyzed carefully. The crystal structure of PxOA2B2 was built using the crystal structure of human β2-adrenergic receptor as a template. Target compounds 3a–h and DPMF were docked into the binding pocket of PxOA2B2 using Glide and exhibited similar binding modes. The geometrical parameters for hydrogen bond interactions are listed in Table 3. For example, as shown in Figure 9a, hydrogen bonds exist between Asn61 and the carbonyl group of target compound 3c, and C–H···O interaction between the phenyl ring of compound 3f and Asn81, respectively (Figure 9b). There is also C–H···H–C interaction between the phenyl ring of compound 3f and PHE265. The predicted binding mode of DPMF is different from that of target compound 3f (Figure 9c). DPMF binds through Pi-cation interactions with Phe163 and Trp80, and hydrogen bonds with Asp84 and Tyr269. Moreover, C–H···Cring interaction was observed between the phenyl ring of DPMF and Phe163. Among the selected target compounds, compounds 3d, 3f, 3g, and 3h exhibited higher insecticidal activities against Plutella xylostella than DPMF, which is consistent with the docking scores (Table 5). However, target compound 3a had the highest docking score, but no insecticidal activity against Plutella xylostella at 600 mg/L. This may be due to the para-substituent of the benzene ring of 3b–h influencing the acyclic diene metathesis (ADMET) properties of the compound; however, this needs further study.
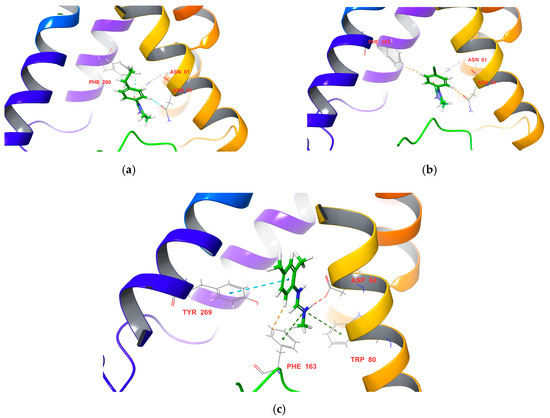
Figure 9.
Docking-predicted binding modes of compounds (a) 3c, (b) 3f, and (c) DPMF with the modeling protein of PxOA2B2.

Table 5.
The docking scores and insecticidal activities of target compounds 3a–h and DPMF against Plutella xylostella (600 mg/L).
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, different phenyl imidazolinone derivatives were synthesized using DPMF as the lead compound via ring-closure approaches using the scaffold-hopping method. Their structures were confirmed by 1H and 13C NMR, HRMS, and X-ray crystal structural analyses. The insecticidal activity results indicated that target compound 3f showed the best insecticidal activity against P. xylostella at 600 mg/L, which was considerably greater than that of DPMF. The fungicidal activity results of target compounds 3d and 3h displayed good fungicidal activities against P. capsici, P. sojae, and P. infestans. Molecular docking indicated that the structure orientations of phenyl imidazolinone derivatives fit well with P. xylostella receptor. DFT calculations suggested that when these compounds acted with the receptors, the phenyl rings both provided and received electrons, where the imidazole rings only provided electrons to form the complex that promotes biological activity. These results encourage exploration into novel insecticides and fungicides based on DPMF.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4352/10/8/713/s1, Table S1: Dihedral angles of phenyl or substituted phenyl ring and imidazolinone ring of calculated structures of compound 3a–h. Table S2: Hydrogen bond geometry. Figure S1: Steric effects of 3a–h influencing the ΔE values (a), insecticidal activities against P. xylostella (b), and fungicidal activities against P. infestans (c), P. capsic (d), P. litchi (e), and P. sojae (f). (Steric effects show the following pattern: -C2H5 > -OC2H5 > -CH3 > -OCH3; -Br > -Cl > -F > -H). Figure S2: Electron donation/withdrawing properties of 3a–h influencing the ΔE values (a), insecticidal activities against P. xylostella (b), and fungicidal activities against P. infestans (c), P. capsic (d), P. litchi (e), and P. sojae (f). (Electron donation property shows the following pattern: -OC2H5 > -OCH3 > -C2H5 > -CH3; Electron withdrawing property shows the following pattern: -Br < -Cl < -F).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.D. and Y.X.; methodology, X.D. and C.J.; synthesis, X.D.; bioassay, X.D. and Y.X.; software, Y.X.; calculation, J.G.; data curation, C.J.; writing—original draft preparation, X.D.; writing—review and editing, X.Z.; project administration, X.D.; funding acquisition, X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (No. 2018JJ3287), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31741108), State Key Laboratory of the Discovery and Development of Novel Pesticide (Shenyang Sinochem Agrochemicals R&D Co. Ltd.), the Scientific -Innovative of Hunan Agricultural Sciences and Technology (2017JC-01), and the Innovation Platform and Talent Plan of Hunan (2016RS2012).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Evans, P.D.; Maqueira, B. Insect octopamine receptors: A new classification scheme based on studies of cloned drosophila G-protein coupled receptors. Invertebr. Neurosci. 2005, 5, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Hamasaki, T.; Ozoe, F.; Ozoe, Y. Single amino acid of an octopamine receptor as a molecular switch for distinct G protein couplings. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 371, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Hamasaki, T.; Ozoe, F.; Ohta, H.; Enomoto, K.I.; Kataoka, H.; Sawa, Y.; Hirota, A.; Ozoe, Y. Identification of critical structural determinants responsible for octopamine binding to the α-adrenergic-like bombyx mori octopamine receptor. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 5896–5903. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ohta, H.; Ozoe, F.; Miyazawa, K.; Huang, J.; Ozoe, Y. Functional and pharmacological characterization of a β-adrenergic-like octopamine receptor from the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohta, H.; Ozoe, Y. Chapter two-molecular signalling, pharmacology, and physiology of octopamine and tyramine receptors as potential insect pest control targets. Adv. Insect Physiol. 2014, 46, 73–166. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, J.S.; Baggott, D.; Everett, W.R.; Fourie, J.J.; Cramer, L.G.; Yoon, S.S.; Collidor, N.; Mallouk, Y.; Lee, L.; Blair, J.; et al. Efficacy of a novel topical combination of fipronil, amitraz and (S)-methoprene for treatment and control of induced infestations of brown dog ticks (Rhipicephalus sanguineus) on dogs. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 179, 318–323. [Google Scholar]
- Martel, A.C.; Zeggane, S.; Aurieres, C.; Drajnudel, P.; Faucon, J.P.; Aubert, M. Acaricide residues in honey and wax after treatment of honey bee colonies with Apivar or Asuntol 50. Apidologie 2008, 38, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, K.; Adler, K.; Parker, L.; Pfister, K.; DeLay, R.L.; Rugg, D. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of a novel formulation of metaflumizone plus amitraz in dogs naturally infested with fleas and ticks in Europe. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 150, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.D.; Craig, G.K.; Stacey, N.H. Effects of chlordimeform and its metabolite 4-chloro-o-toluidine on rat splenic T, B and tumoricidal effector cells. Immunopharmacology 1990, 19, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, C.; Reidy, G.F.; Murray, M.; Stacey, N.H. Induction of xenobiotic biotransformation by the insecticide chlordimeform, a metabolite 4-chloro-o-toluidine and a structurally related chemical o-toluidine. Biochem. Pharmcol. 1988, 37, 2529–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallott, M.; Hamm, S.; Troczka, B.J.; Randall, E.; Pym, A.; Grant, C.; Baxter, S.; Vogel, H.; Shelton, A.M.; Field, L.M.; et al. A flavin-dependent monooxgenase confers resistance to chlorantraniliprole in the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 115, 103247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Yusoff, N.; Aizat, W.M.; Othman, N.W.; Abd Ghani, I. Optimization method for proteomic analysis of the larva and adult tissues of Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Sains Malays. 2018, 47, 2975–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, J. Optimization of artificial rearing methods for Plutella xylostella L. (Plutellidae) and its susceptibility to five types of insecticides. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2012, 13, 1713–1715, 1721. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Xiong, L.; Yang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Synthesis and structure-insecticidal activity relationship of novel phenylpyrazole carboxylic acid derivatives containing fluorine moiety. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 19, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Han, Z. Tebufenozide resistance selected in Plutella xylostella and its cross-resistance and fitness cost. Pest Manag. Sci. 2006, 62, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, X.H.; Ishaaya, I.; Cao, S.; Wu, J.J.; Yu, J.L.; Li, H.; Qian, X.H. Synthesis and insecticidal activity of heptafluoroisopropyl-containing benzoylphenylurea structures. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2736–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.T.; Ma, H.H.; Deng, X.L.; Zhu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X.M. Pharmacological characterization of a β-adrenergic-like octopamine receptor in Plutella xylostella. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 98, e21466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, A.P.; Wright, D.J. Toxicity of chlordimeform and amitraz to the egyptian cotton leafworm (Spodoptera littoralis) and the tobacco budworm (Heliothis virescens). Pestic. Sci. 1985, 16, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, C.O.; Roulston, W.J. Toxicity to boophilus microplus of formamidine acaricides and related compounds, and modification of toxicity by certain insecticide synergists. J. Econ. Entomol. 1973, 66, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, T.; Hayashi, T.; Ohtani, T.; Takao, H.; Takasu, H.; Liu, G.; Ohta, H.; Ozoe, F.; Ozoe, Y. Amitraz and its metabolite differentially activate α- and β-adrenergic-like octopamine receptors. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberth, C. Agrochemical lead optimization by scaffold hopping. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, K.; Li, L.H.; Wang, B.; Liu, M.L.; Wang, B.; Shen, W.Y.; Guo, H.Y.; Lu, Y. Design, synthesis and antimycobacterial activity of novel imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-carboxamide derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 137, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin, S.; Wei, L.H.; Moreau, E.; Lacroix, J.; Côté, M.; Petitclerc, É.; Kotra, L.P.; Gaudreault, R.C. Substituted phenyl 4-(2-oxoimidazolidin-1-yl)benzenesulfonamides as antimitotics. Antiproli ferative, antiangiogenic and antitumoral activity, and quantitative structure-activity relationships. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 5327–5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.L.; Zhou, X.M.; Wang, Z.Y.; Rui, C.H.; Yang, X.L. Synthesis, crystal structure and insecticidal activity of N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-1-phenyl-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydrocyclohepta[c]pyrazole-3-carbox amide. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2018, 37, 551–556. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.N.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Deng, Y.N.; Wu, Z.C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X.M.; Bai, L.Y.; Deng, X.L. Synthesis, crystal structure, herbicide safening, and antifungal activity of N-(4,6-dichloropyrimidine-2-yl)benzamide. Crystals 2018, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Lei, P.; Sun, T.; Jin, X.; Yang, X.L.; Ling, Y. Design, synthesis, and fungicidal activity of novel thiosemicarbazide derivatives containing piperidine fragments. Molecules 2017, 22, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Revision C.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.Y.; Olieric, V.; Ma, P.; Howe, N.; Vogeley, L.; Liu, X.; Warshamanage, R.; Weinert, T.; Panepucci, E.; Kobilka, B.; et al. In meso in situ serial X-ray crystallography of soluble and membrane proteins at cryogenic temperatures. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 2016, 72, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative protein structure modeling using modeler. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 5.6.1–5.6.32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olyaei, A.; Abbasi, A.; Ghandi, M.; Salimi, F.; Eriksson, L. 1-(1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)-4,5-dihydroxy-3- phenylimidazolidin-2-one. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E Struct. Rep. Online 2006, 62, O5326–O5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treweeke, N.R.; Hitchcock, P.B.; Pardoe, D.A.; Caddick, S. Controlling diastereoselectivity in the reactions of enantiomerically pure α-bromoacyl-imidazolidinones with nitrogen nucleophiles: Substitution reactions with retention or inversion of configuration. Chem. Commun. 2005, 1868–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegler, M.; Long, S. (4R,5R)-4,5-diphenylimidazolidin-2-one. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E Struct Rep Online 2006, 62, O5310–O5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.H.; Shi, Y.X.; Yang, M.Y.; Sun, Z.H.; Weng, J.Q.; Tan, C.X.; Liu, X.H.; Li, B.J.; Zhao, W.G. Synthesis, crystal structure, DFT studies and biological activity of a novel schiff base containing triazolo 4,3-a pyridine moiety. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2016, 35, 457–464. [Google Scholar]
- Löser, R.; Pitzschler, R.; Köckerling, M. Synthesis and X-ray crystal structure of N’-cyano-N,N’–dimethyl -4-nitrobenzohydrazide. Crystals 2017, 7, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Z.H.; Wedge, D.E.; Becnel, J.J.; Estep, A.S.; Tan, C.X.; Weng, J.Q. Synthesis and insecticidal activity of novel pyrimidine derivatives containing urea pharmacophore against Aedes aegypti. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruvilla, T.K.; Muthu, S.; Prasana, J.C.; George, J.; Saji, R.S.; Geoffrey, B.; David, R.H.A. Molecular docking, spectroscopic studies on 4-[2-(dipropylamino)ethyl]-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one and QSAR study of a group of dopamine agonists by density functional method. Spectrochim. Acta A 2018, 222, 117185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.L.; Xie, J.; Li, Y.Q.; Yuan, D.K.; Zhang, X.P.; Wang, Q.M.; Chi, M.; Yang, X.L. Design, synthesis and biological activity of novel substituted pyrazole amide derivatives targeting EcR/USP receptor. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.L.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X.P.; Yin, B.; Liang, P.; Yang, X.L. Target-based design, synthesis and biological activity of new pyrazole amide derivatives. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirashima, A.; Huang, H.W. Homology modeling, agonist binding site identification, and docking in octopamine receptor of Periplaneta americana. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2008, 32, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ohta, H.; Sasaki, K.; Ozoe, F.; Ozoe, Y. Amino acid residues involved in the interaction with the intrinsic agonist (R)-octopamine in the β-adrenergic-like octopamine receptor from the silkworm Bombyx mori. J. Pestic. Sci. 2011, 36, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).