Thermal and Photophysical Studies of Binary Mixtures of Liquid Crystal with Different Geometrical Mesogens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Preparation
2.2. Physical Characterization
2.3. Computational Method and Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
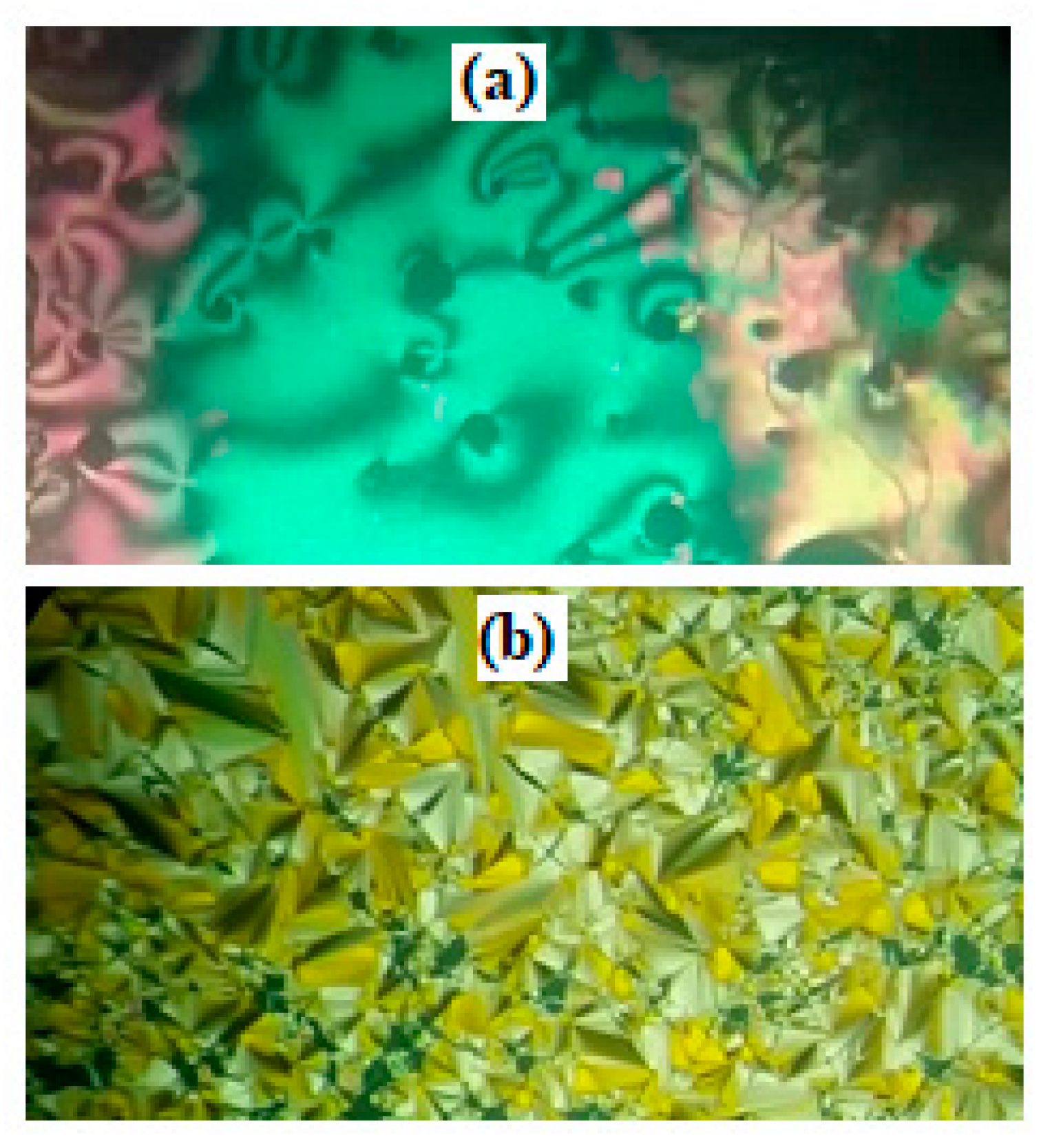
3.1. Binary Mesophase Behavior of Prepared Mixtures
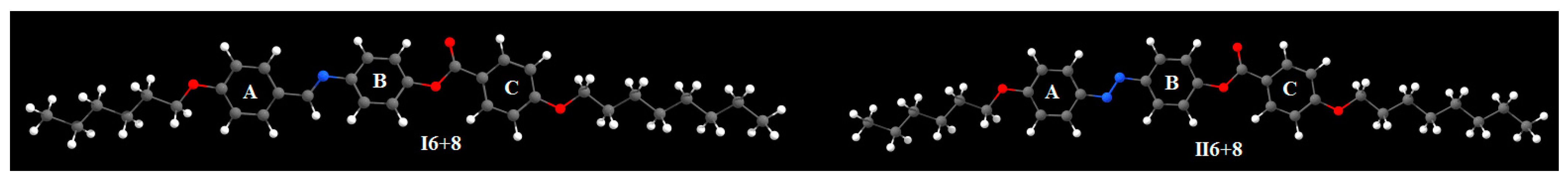
3.2. DFT Calculations
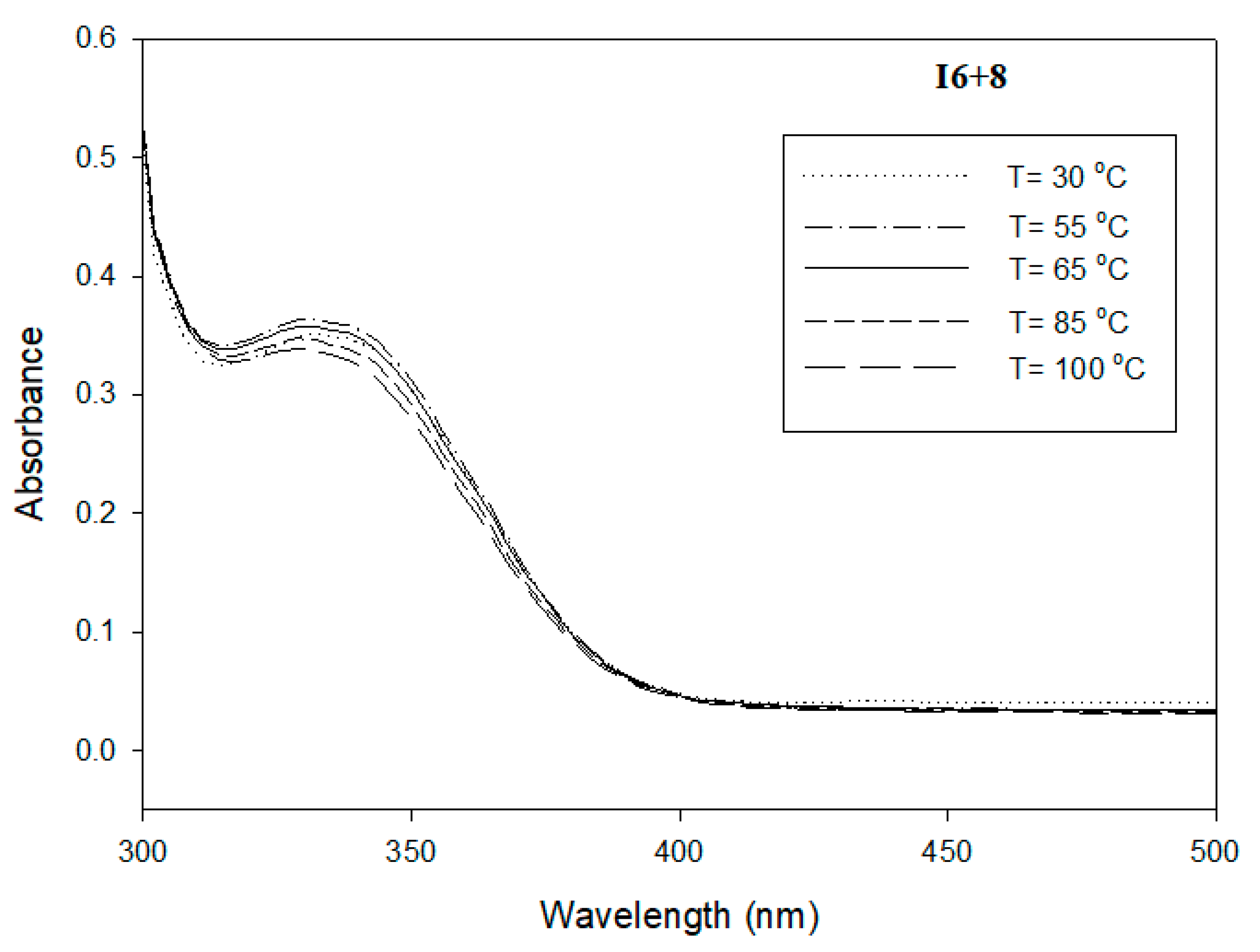
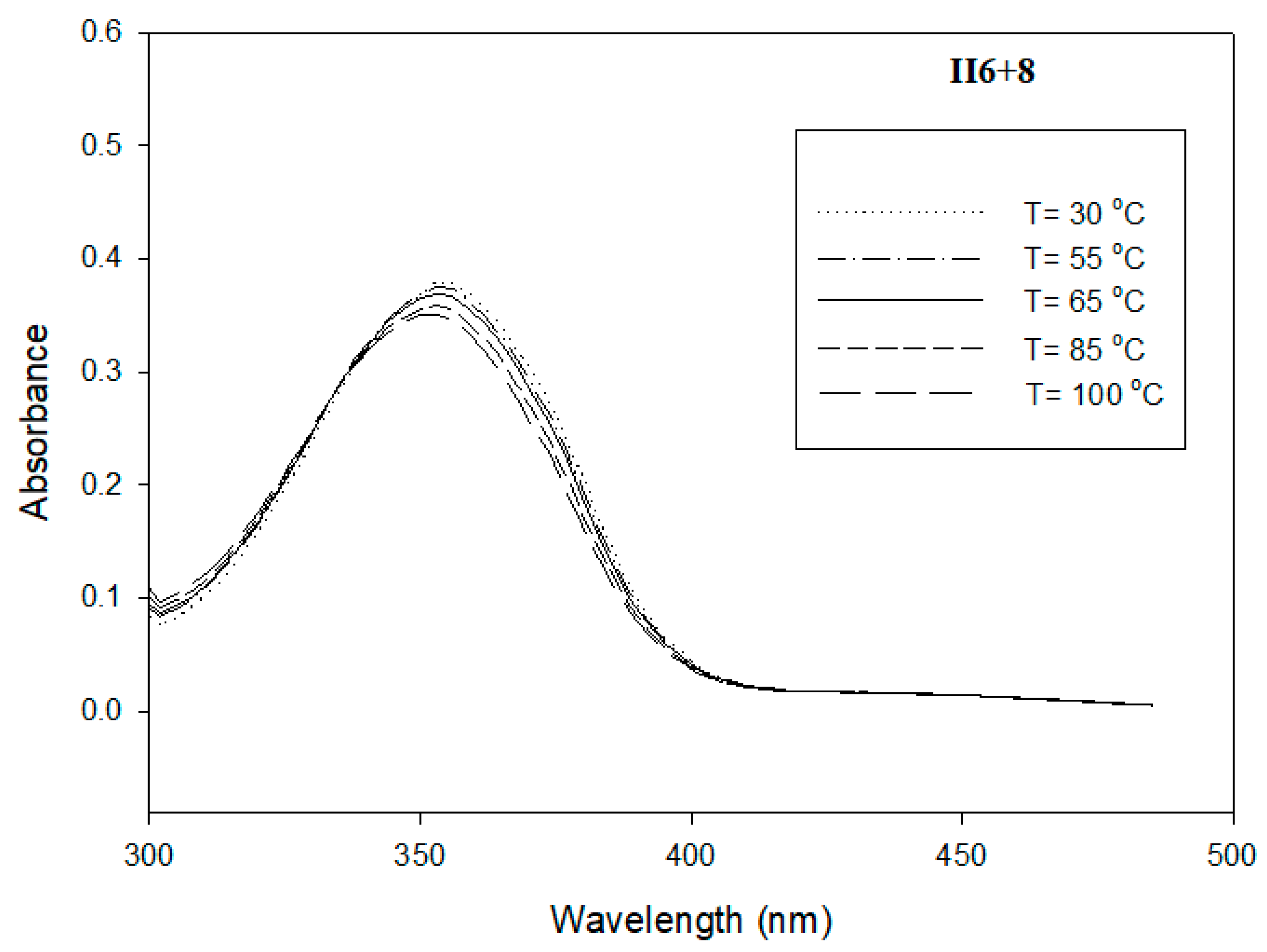
3.3. Photophysical Study
4. Conclusions
- The constructed diagrams showed enantiotropic mesomorphic behavior for all compositions.
- All systems showed nearly linear nematic-to-isotropic composition dependencies.
- The binary phase diagrams exhibited eutectic composition with high mesophase stability.
- The polarizability was highly affected by the dimensions and the type of the mesogenic core.
- The dipole moment of the Schiff base ester I6+8 was higher than that of the azo ester II6+8.
- The π-π stacking interactions in mixture enhanced the mesophase stabilities as well as their temperature ranges.
- Finally, the similar charge distribution observed in both series rationalized the enhanced mesophase stability and the mesophase range of the mixture at its eutectic compositions.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thangavel, V.; Venkataraman, B.; Prakasan, S.; Ramasamy, J.; Nallagounder, V.V. Experimental and DFT Studies on Thermochromism Induced Binary HBLC Mixture. Braz. J. Phys. 2019, 50, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamady, S.Z.; Nessim, R.I.; Shehab, O.R.; Naoum, M.M. Effect of steric factor on mesomorphic stability, II: Binary mixtures of homologues of 4-(4′-substituted phenylazo)-1-naphthyl-4″-alkoxybenzoates. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2006, 451, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoum, M.; Mohammady, S.; Ahmed, H. Lateral protrusion and mesophase behaviour in pure and mixed states of model compounds of the type 4-(4′-substituted phenylazo)-2-(or 3-) methyl phenyl-4′-alkoxy benzoates. Liq. Cryst. 2010, 37, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoum, M.; Fahmi, A.; Alaasar, M.; Abdel-Aziz, M. Effect of lateral substitution of different polarity on the mesophase behaviour in pure and mixed states of 4-(4′-substituted phenylazo)-2-substituted phenyl-4″-alkoxy benzoates. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 38, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Naoum, M.; Saad, G. Effect of alkoxy-chain length proportionation on the mesophase behaviour of terminally di-substituted phenylazo phenyl benzoates. Liq. Cryst. 2013, 40, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Naoum, M. Mesophase behavior of binary and ternary mixtures of benzoic acids bearing terminal substituents of different polarity and chain-lengths. Thermochim. Acta 2014, 575, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Naoum, M.; Saad, G. Mesophase behaviour of 1: 1 mixtures of 4-n-alkoxyphenylazo benzoic acids bearing terminal alkoxy groups of different chain lengths. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 43, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H. Mesophase stability in binary mixtures of monotropic nematogens. Liq. Cryst. 2015, 42, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, J.; Vasanth, K. Influence of molecular structure on liquid crystalline properties and phase transitions in mixed liquid crystals. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1966, 2, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, J.S.; Menon, M.R.; Patel, P.R. Chiral phases induced by doping nonmesogenic component into mesogenic esters. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2003, 392, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, R.; Gupta, R.; Patel, K. Exhibition of induced mesophases in the binary systems where one or both the components are non-mesogenic. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1991, 209, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, S.; Yamamura, Y.; Hishida, M.; Nagatomo, S.; Saito, K. Reentrant nematic phase in 4-alkyl-4′-cyanobiphenyl (n CB) binary mixtures. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 41, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Das, M.K. Determination of elastic constants of a binary system (7CPB+9.CN) showing nematic, induced smectic Ad and re-entrant nematic phases. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 41, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetinov, M.; Obadović, D.; Stojanović, M.; Lazar, D.; Vajda, A.; Éber, N.; Fodor-Csorba, K.; Ristić, I. Mesophase behaviour of binary mixtures of bent-core and calamitic compounds. Liq. Cryst. 2013, 40, 1512–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Salud, J.; Lopez, D.; Diez-Berart, S.; de la Fuente, M. Tests of the tricritical point in the SmA-to-N phase transition of binary mixtures of butyloxybenzylidene octylaniline and hexyloxybenzylidene octylaniline. Liq. Cryst. 2013, 40, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, A.K.; Patel, N.S.; Lad, V.G. Induction of chirality by doping mesogens with non-mesogenic chiral dopant. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. Sci. Technol. Sect. A. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2000, 348, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, R.; Rajput, S. Binary mesogenic systems comprised of ester mesogens and non-mesogens. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1991, 209, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaiah, T.; Nagappa; Sathyanarayana, P.; Mahadeva, J.; Sreepad, H. Induced chiral smectic phase in mixtures of mesogenic and non-mesogenic compounds. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 548, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohar, J.; Dave, J.S., Jr. Emergence of smectic mesophase in binary mixtures of pure nematogens. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1983, 103, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Henderson, P.A.; Paterson, B.J.; Imrie, C.T. Liquid crystal dimers and the twist-bend nematic phase. The preparation and characterisation of the α, ω-bis (4-cyanobiphenyl-4′-yl) alkanedioates. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 41, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.-N.; Lu, Z.; Yam, W.-S.; Yeap, G.-Y.; Imrie, C.T. Non-symmetric liquid crystal dimers containing an isoflavone moiety. Liq. Cryst. 2012, 39, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, G.-Y.; Osman, F.; Imrie, C.T. Non-symmetric dimers: Effects of varying the mesogenic linking unit and terminal substituent. Liq. Cryst. 2015, 42, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imrie, C.T.; Henderson, P.A.; Yeap, G.-Y. Liquid crystal oligomers: Going beyond dimers. Liq. Cryst. 2009, 36, 755–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoum, M.; Fahmi, A.; Ahmed, H. Liquid crystalline behaviour of model compounds di-laterally substituted with different polar groups. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 38, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niezgoda, I.; Jaworska, J.; Pociecha, D.; Galewski, Z. The kinetics of the EZE isomerisation and liquid-crystalline properties of selected azobenzene derivatives investigated by the prism of the ester group inversion. Liq. Cryst. 2015, 42, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, G.; Shanker, G.; Gan, S.; Yuvaraj, A.; Mahmood, S.; Mandal, U.K. Synthesis and liquid crystalline behaviour of substituted (E)-phenyl-4-(phenyldiazenyl) benzoate derivatives and their photo switching ability. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 43, 1578–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, D.A.; Xiang, J.; Singh, G.; Walker, R.; Agra-Kooijman, D.A.M.; Martínez-Felipe, A.; Gao, M.; Storey, J.M.; Kumar, S.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Reversible isothermal twist–bend nematic–nematic phase transition driven by the photoisomerization of an azobenzene-based nonsymmetric liquid crystal dimer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 5283–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Hasler, P.; Fierro-Armijo, A.; Soto-Bustamante, E.; Meneses-Franco, A. Synthesis and characterisation of two homologous series of LC acrylic monomers based on phenolic and resorcinic azobenzene groups. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 43, 1804–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, P.; Cook, A.; Imrie, C. Oligomeric liquid crystals: From monomers to trimers. Liq. Cryst. 2004, 31, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, F.; Yeap, G.-Y.; Nagashima, A.; Ito, M.M. Structure property and mesomorphic behaviour of S-shaped liquid crystal oligomers possessing two azobenzene moieties. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 43, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa, H. New symmetric azobenzene molecules of varied central cores: Synthesis and characterisation for liquid crystalline properties. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collings, P.J.; Hird, M. Introduction to Liquid Crystals: Chemistry and Physics; Taylor and Francis Group: London, UK; CRC Press: NewYork, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hagar, M.; Ahmed, H.; Saad, G. Synthesis and mesophase behaviour of Schiff base/ester 4-(arylideneamino) phenyl-4″-alkoxy benzoates and their binary mixtures. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.A.; Hagar, M.; Aljuhani, A. Mesophase behavior of new linear supramolecular hydrogen-bonding complexes. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 34937–34946. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, H.A.; Hagar, M.; Alhaddad, O.A. Phase behavior and DFT calculations of laterally methyl supramolecular hydrogen-bonding complexes. Crystals 2019, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagar, M.; Ahmed, H.A.; El-Sayed, T.H.; Alnoman, R. Mesophase behavior and DFT conformational analysis of new symmetrical diester chalcone liquid crystals. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 285, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Hagar, M.; Alaasar, M.; Naoum, M. Wide nematic phases induced by hydrogen-bonding. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 46, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.A.; Ahmed, H.; Hagar, M. Impact of fluorine orientation on the optical properties of difluorophenylazophenyl benzoates liquid crystal. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 216, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagar, M.; Ahmed, H.; Alhaddadd, O. DFT calculations and mesophase study of coumarin esters and its azoesters. Crystals 2018, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoum, M.M.; Metwally, N.H.; Abd Eltawab, M.M.; Ahmed, H.A. Polarity and steric effect of the lateral substituent on the mesophase behaviour of some newly prepared liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. 2015, 42, 1351–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagar, M.; Ahmed, H.; Saad, G. Mesophase stability of new Schiff base ester liquid crystals with different polar substituents. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 45, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Hagar, M.; Alhaddad, O. Mesomorphic and geometrical orientation study of the relative position of fluorine atom in some thermotropic liquid crystal systems. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Hagar, M.; El-Sayed, T.; Alnoman, R.B. Schiff base/ester liquid crystals with different lateral substituents: Mesophase behaviour and DFT calculations. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 46, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafee, S.S.; Hagar, M.; Ahmed, H.A.; El-Shishtawy, R.M.; Raffah, B.M. The synthesis of new thermal stable schiff base/ester liquid crystals: A computational, mesomorphic, and optical study. Molecules 2019, 24, 3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Hagar, M.; Alhaddad, O. New chair shaped supramolecular complexes-based aryl nicotinate derivative; mesomorphic properties and DFT molecular geometry. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 16366–16374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnoman, R.; Ahmed, H.A.; Hagar, M. Synthesis, optical, and geometrical approaches of new natural fatty acids’ esters/Schiff base liquid crystals. Molecules 2019, 24, 4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafee, S.S.; Ahmed, H.; Hagar, M. Theoretical, experimental and optical study of new thiophene-based liquid crystals and their positional isomers. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, M.; Kelly, S.M. Liquid crystals for charge transport, luminescence, and photonics. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T. Photomodulation of liquid crystal orientations for photonic applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 2037–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.K.; Nair, G.G.; Sandhya, K.; Rao, D.S. Photoinduced phase transitions in liquid crystalline systems. Curr. Sci. 2004, 86, 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Selvarasu, C.; Kannan, P. Effect of azo and ester linkages on rod shaped Schiff base liquid crystals and their photophysical investigations. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1125, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagar, M.; Ahmed, H.; Saad, G. New calamitic thermotropic liquid crystals of 2-hydroxypyridine ester mesogenic core: Mesophase behaviour and DFT calculations. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 47, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafee, S.S.; Hagar, M.; Ahmed, H.A.; Alhaddad, O.; El-Shishtawy, R.M.; Raffah, B.M. New two rings Schiff base liquid crystals; ball mill synthesis, mesomorphic, Hammett and DFT studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 299, 112161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaddad, O.; Ahmed, H.; Hagar, M. Experimental and Theoretical Approaches of New Nematogenic Chair Architectures of Supramolecular H-Bonded Liquid Crystals. Molecules 2020, 25, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagar, M.; Ahmed, H.; Alhaddad, O. Experimental and theoretical approaches of molecular geometry and mesophase behaviour relationship of laterally substituted azopyridines. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 46, 1440–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagar, M.; Ahmed, H.; Alhaddad, O. New azobenzene-based natural fatty acid liquid crystals with low melting point: Synthesis, DFT calculations and binary mixtures. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 46, 2223–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, S.; Nafee, H.A.A.; Hagar, M. New architectures of supramolecular H-bonded liquid crystal complexes based on dipyridine Derivatives. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.H.S.; Saad, G.R.; Ahmed, H.A.; Hagar, M. New wide-stability four-ring azo/ester/Schiff base liquid crystals: Synthesis, mesomorphic, photophysical, and DFT approaches. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 9643–9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.; Trucks, G.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.; Robb, M.; Cheeseman, J.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G. Gaussian 09, Revision a. 02; Gaussian. Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009; p. 200. [Google Scholar]
- Dennington, R.; Keith, T.; Millam, J. GaussView, Version 5; Semichem Inc.: Shawnee Mission, KS, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, H.; Hagar, M.; Saad, G. Impact of the proportionation of dialkoxy chain length on the mesophase behaviour of Schiff base/ester liquid crystals; experimental and theoretical study. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 46, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, C.; Rathi, N.; Dev, P.; Byrne, O.; Surolia, P.K.; Maji, P.; MacElroy, J.; Yella, A.; Grätzel, M.; Magner, E. Organic Dyes Containing Coplanar Dihexyl-Substituted Dithienosilole Groups for Efficient Dye-Sensitised Solar Cells. Int. J. Photoenergy 2017, 2017, 7594869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, M.Y.; Pan, Q.Q.; Yin, H.; Sun, G.Y.; Geng, Y.; Su, Z.M. Design of Hexabenzocoronene Derivatives as Non-Fullerene Acceptors in Organic Photovoltaics by Bridging Dimers and Modulating Structural Twists. Sol. Rrl 2017, 1, 1700060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, R.; Yamamoto, T.; Ohara, K.; Naito, T. Dye-Sensitized Molecular Charge Transfer Complexes: Magnetic and Conduction Properties in the Photoexcited States of Ni (dmit) 2 Salts Containing Photosensitive Dyes. Magnetochemistry 2017, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
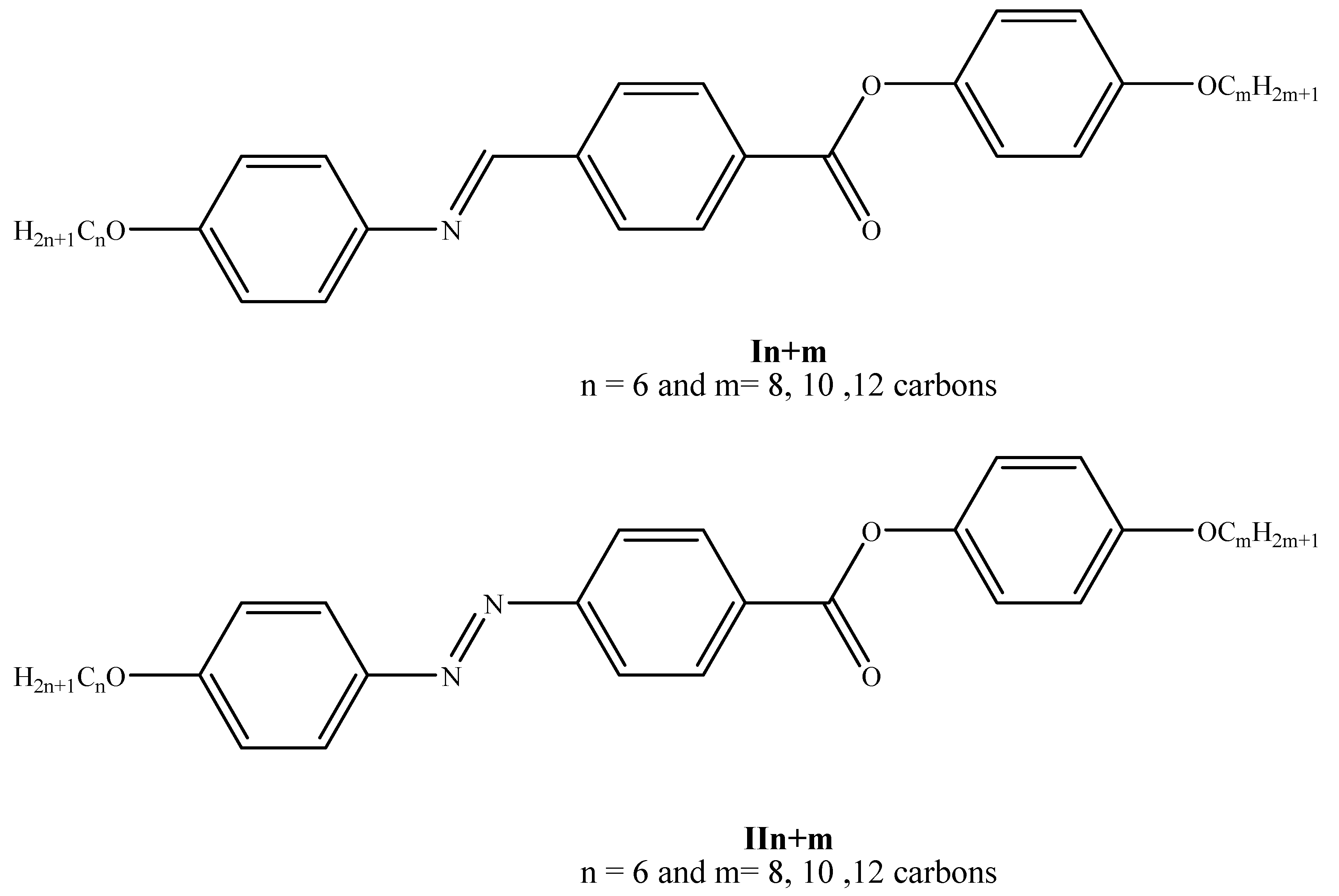
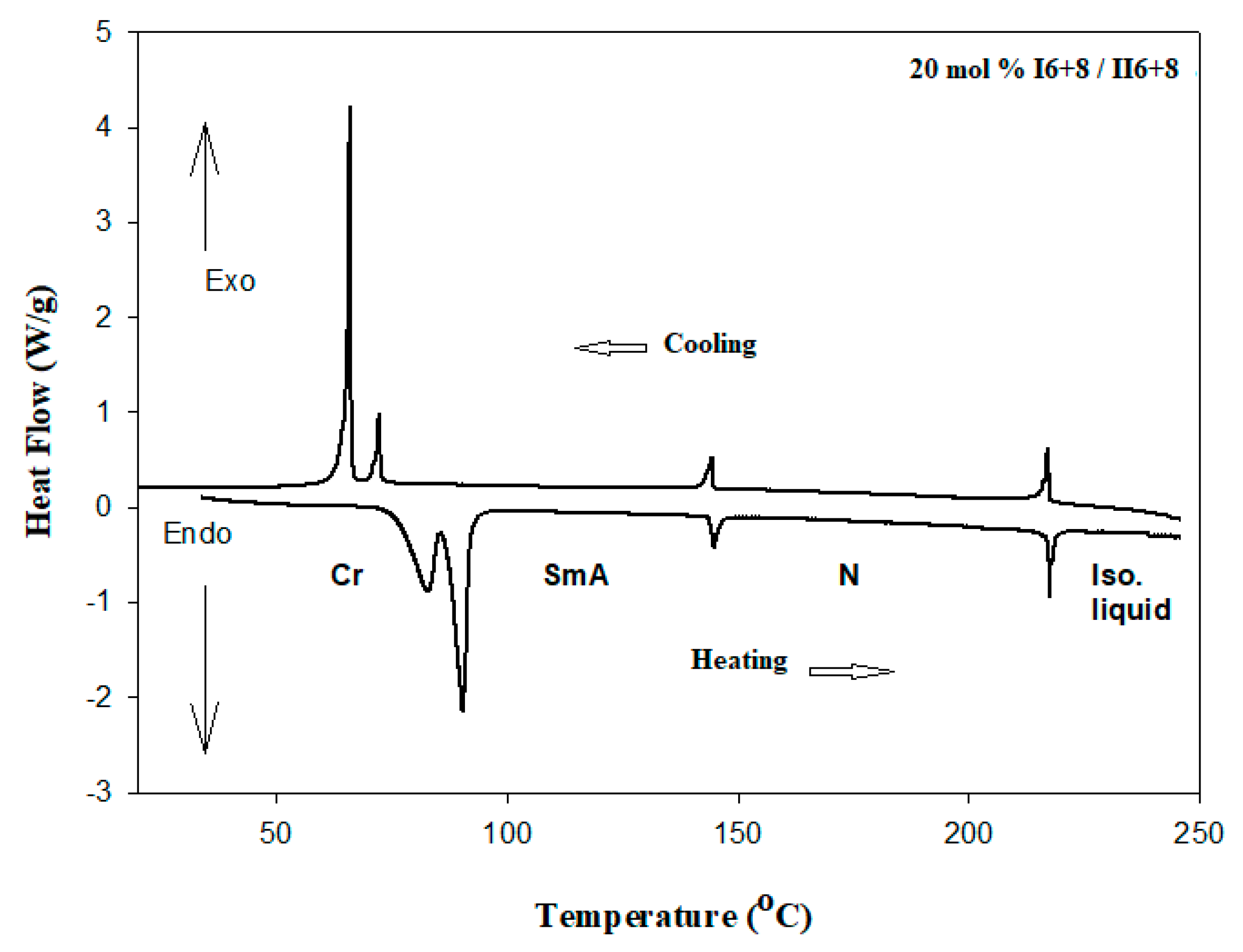



| % of Component IIn+m | TCr-SmC | TCr-SmA | TCr-N | TSmC-N | TSmA-N | TN-I |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% II6+8 | 77.5 (28.94) | 159.0 (2.24) | 218.8 (1.72) | |||
| 20% II6+8 | 90.3 (73.08) | 144.9 (3.19) | 217.6 (4.63) | |||
| 40% II6+8 | 75.9 (51.21) | 132.8 (2.83) | 217.5 (4.84) | |||
| 60% II6+8 | 102.3 (49.22) | 124.2 (2.59) | 217.1 (2.70) | |||
| 80% II6+8 | 107.5 (58.54) | 107.8 (1.87) | 215.6 (4.38) | |||
| 100% II6+8 | 113.6 (56.20) | 214.8 (2.75) | ||||
| 0% II6+10 | 93.7 (51.22) | 172.1 (1.93) | 204.7 (1.92) | |||
| 20% II6+10 | 90.9 (101.50) | 158.2 (2.77) | 202.7 (3.90) | |||
| 40% II6+10 | 91.4 (110.0) | 154.4 (2.94) | 201.3 (4.11) | |||
| 60% II6+10 | 85.3 (112.5) | 146.6 (2.83) | 201.3 (4.65) | |||
| 80% II6+10 | 92.7 (83.56) | 133.8 (1.98) | 200.0 (3.94) | |||
| 100% II6+10 | 103.5 (51.31) | 120.2 (0.93) | 195.9 (2.05) | |||
| 0% II6+12 | 92.3 (54.06) | 174.9 (2.39) | 201.9 (2.18) | |||
| 20% II6+12 | 90.9 (104.40) | 166.9 (3.36) | 199.9 (4.18) | |||
| 40% II6+12 | 88.7 (101.2) | 156.1 (2.84) | 198.2 (4.22) | |||
| 60% II6+12 | 75.4 (86.21) | 151.7 (2.68) | 197.2 (3.73) | |||
| 80% II6+12 | 97.8 (102.08) | 140.9 (1.96) | 196.1 (5.32) | |||
| 100% II6+12 | 102.4 (62.71) | 122.1 (3.66) | 186.0 (2.38) |
| Parameter | I6+8 | II6+8 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polarizability α | 470.78 | 487.25 | |
| Dipole Moment | X | −0.4716 | −0.8958 |
| Y | −3.4170 | −2.3915 | |
| Z | 0.3869 | 0.1388 | |
| Total | 3.4710 | 2.5576 | |
| Dimensions Å | Width (D) | 4.74 | 4.71 |
| Length (L) | 40.07 | 39.79 | |
| Aspect ratio (L/D) | 8.45 | 8.45 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhaddad, O.A.; Ahmed, H.A.; Hagar, M.; Saad, G.R.; Abu Al-Ola, K.A.; Naoum, M.M. Thermal and Photophysical Studies of Binary Mixtures of Liquid Crystal with Different Geometrical Mesogens. Crystals 2020, 10, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10030223
Alhaddad OA, Ahmed HA, Hagar M, Saad GR, Abu Al-Ola KA, Naoum MM. Thermal and Photophysical Studies of Binary Mixtures of Liquid Crystal with Different Geometrical Mesogens. Crystals. 2020; 10(3):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10030223
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhaddad, Omaima A., Hoda A. Ahmed, Mohamed Hagar, Gamal R. Saad, Khulood A. Abu Al-Ola, and Magdi M. Naoum. 2020. "Thermal and Photophysical Studies of Binary Mixtures of Liquid Crystal with Different Geometrical Mesogens" Crystals 10, no. 3: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10030223
APA StyleAlhaddad, O. A., Ahmed, H. A., Hagar, M., Saad, G. R., Abu Al-Ola, K. A., & Naoum, M. M. (2020). Thermal and Photophysical Studies of Binary Mixtures of Liquid Crystal with Different Geometrical Mesogens. Crystals, 10(3), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10030223







