Preparation of Few-Layered Wide Bandgap MoS2 with Nanometer Lateral Dimensions by Applying Laser Irradiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
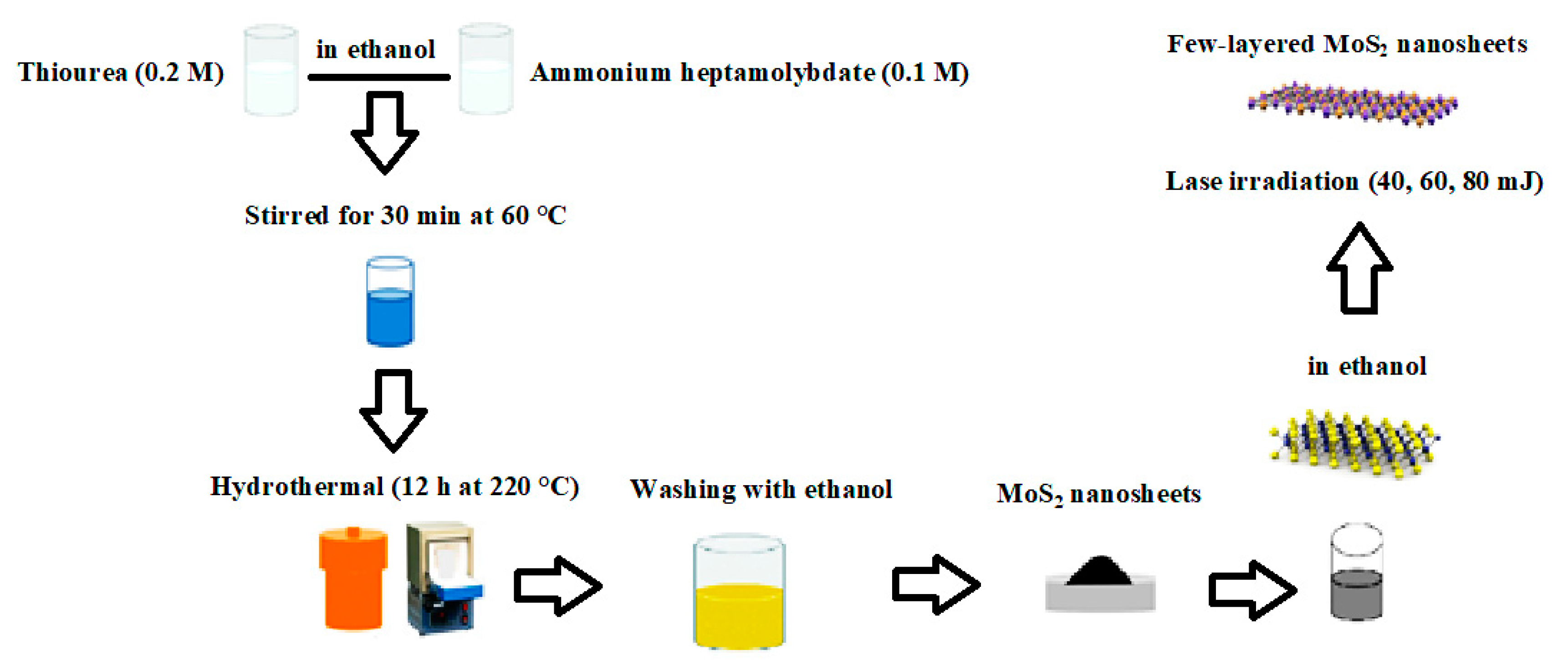
2. Experimental Details
Characterization
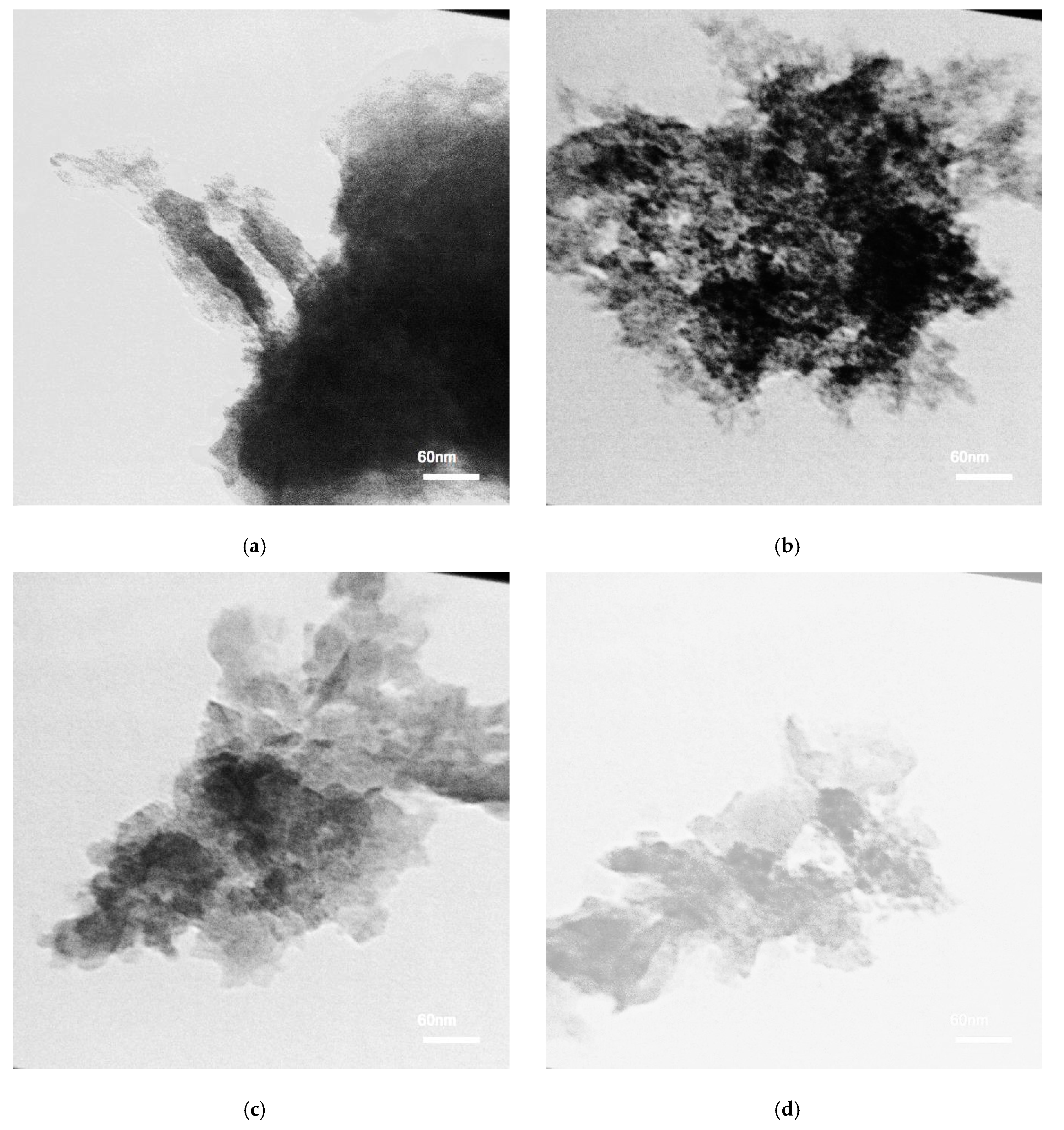
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Néstor, P.; Elías, A.L.; Berkdemir, A.; Castro-Beltran, A.; Gutiérrez, H.R.; Feng, S.; Lv, R.; Hayashi, T.; López-Urías, F.; Ghosh, S.; et al. Photosensor device based on few-layered WS2 films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 5511–5517. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Li, J.; Ren, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, X. Few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets as superior sorbents for heavy metal ion pollution management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10454–10462. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, F.; Sun, X.; Wu, C.; Peng, L.; Lin, C.; Hu, S.; Yang, J.; Xie, Y. Metallic few-layered VS2 ultrathin nanosheets: High two-dimensional conductivity for in-plane supercapacitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 17832–17838. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, M.; Asadpour, M.; Majelan, N.A.; Faghihnasiri, M. Effect of boron and nitrogen doping on electro-optical properties of armchair and zigzag graphyne nanoribbons. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2014, 82, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Wang, J. Graphene-based materials for supercapacitor electrodes—A review. J. Mater. 2016, 2, 37–54. [Google Scholar]
- Francesco, B.; Bartolotta, A.; Coleman, J.N.; Backes, C. 2D-crystal-based functional inks. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6136–6166. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, L.; Zhou, L.; Wu, D.; Peng, H.; Yan, K.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z. Photochemical chlorination of graphene. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5957–5961. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G.; Song, H.; Chen, X. Electrochemical performance of graphene nanosheets as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 1320–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Wu, J.; Xu, X.; Ho, Y.; Ni, G.; Zou, Q.; Koon, G.K.W.; Zhao, W.; Neto, A.H.C.; Eda, G.; et al. An innovative way of etching MoS2: Characterization and mechanistic investigation. Nano Res. 2013, 6, 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Yu, Y.; Ye, G.J.; Ge, Q.; Ou, X.; Wu, H.; Feng, D.; Chen, X.H.; Zhang, Y. Black phosphorus field-effect transistors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 372. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Su, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, L. Controlled scalable synthesis of uniform, high-quality monolayer and few-layer MoS2 films. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1866. [Google Scholar]
- Novoselov Kostya, S.; Jiang, D.; Schedin, F.; Booth, T.J.; Khotkevich, V.V.; Morozov, S.V.; Geim, A.K. Two-dimensional atomic crystals. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10451–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman Jonathan, N.; Lotya, M.; O’Neill, A.; Bergin, S.D.; King, P.J.; Khan, U.; Young, K.; Gaucher, A.; De, S.; Smith, R.J.; et al. Two-dimensional nanosheets produced by liquid exfoliation of layered materials. Science 2011, 331, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, M.; Khan, U.; Hughes, J.M.; Coleman, N.J. Role of solubility parameters in understanding the steric stabilization of exfoliated two-dimensional nanosheets by adsorbed polymers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 11393–11400. [Google Scholar]
- Eswaraiah, V.; Backes, C.; Paton, K.R.; Harvey, A.; Gholamvand, Z.; McCauley, J.; Coleman, J.N. Large-scale production of size-controlled MoS2 nanosheets by shear exfoliation. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zeng, Z.; Cao, X.; Lu, G.; Wang, L.H.; Fan, Q.L.; Huang, W.; Zhang, H. Preparation of MoS2-polyvinylpyrrolidone nanocomposites for flexible nonvolatile rewritable memory devices with reduced graphene oxide electrodes. Small 2012, 8, 3517–3522. [Google Scholar]
- Chouhan Raghuraj, S.; Žitko, G.; Fajon, V.; Živković, I.; Pavlin, M.; Berisha, S.; Jerman, I.; Vesel, A.; Horvat, M. A Unique Interactive Nanostructure Knitting based Passive Sampler Adsorbent for Monitoring of Hg2+ in Water. Sensors 2019, 19, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, H.; Chen, Y.; Lu, C.H.; Chi, Y.; Yang, H.H. Graphitic carbon nitride materials: Sensing, imaging and therapy. Small 2016, 12, 5376–5393. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Liu, Q.; Asiri, A.M.; Qusti, A.H.; Al-Youbi, A.O.; Sun, X. Ultrathin graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets: A novel peroxidase mimetic, Fe doping-mediated catalytic performance enhancement and application to rapid, highly sensitive optical detection of glucose. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 11604–11609. [Google Scholar]
- Manish, C.; Shin, H.S.; Eda, G.; Li, L.; Loh, K.P.; Zhang, H. The chemistry of two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 263. [Google Scholar]
- Fai, M.K.; Shan, J. Photonics and optoelectronics of 2D semiconductor transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 216. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, W.Q.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kis, A.; Coleman, J.N.; Strano, M.S. Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 699. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Yan, R.; Bertolazzi, S.; Brivio, J.; Gao, B.; Kis, A.; Jena, D.; Xing, H.G.; Huang, L. Exciton dynamics in suspended monolayer and few-layer MoS2 2D crystals. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Erwin, P.; Gelato, L.; Chabot, B.; Penzo, M.; Cenzual, K.; Gladyshevskii, R. TYPIX Standardized Data and Crystal Chemical Characterization of Inorganic Structure Types; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lebegue, S.; Eriksson, O. Electronic structure of two-dimensional crystals from ab initio theory. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 115409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fai, M.K.; Lee, C.; Hone, J.; Shan, J.; Heinz, T.F. Atomically thin MoS2: A new direct-gap semiconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 136805. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Zhou, W.; Lu, A.; Fang, W.; Lee, Y.; Hsu, A.L.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, K.K.; Yang, H.Y.; Li, L.; et al. van der Waals epitaxy of MoS2 layers using graphene as growth templates. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2784–2791. [Google Scholar]
- John, B.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, P.; Papakonstantinou, P. Electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction on edges of a few layer molybdenum disulfide nanodots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 14113–14122. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, B.; Moses, P.G.; Jaramillo, T.F.; Nørskov, J.K.; Chorkendorff, I. Hydrogen evolution on nano-particulate transition metal sulfides. Faraday Discuss. 2009, 140, 219–231. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, X.; Du, Z.; Jia, B.; Gu, M.; Hong, M. A frozen matrix hybrid optical nonlinear system enhanced by a particle lens. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 14982–14988. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, M.L.; Su, S.H.; Chang, J.K.; Tsai, D.S.; Chen, C.H.; Wu, C.I.; Li, L.J.; Chen, L.J.; He, J.H. Monolayer MoS2 heterojunction solar cells. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 8317–8322. [Google Scholar]
- Mariyappan, S.; Bansal, T.; Durcan, C.A.; Yu, B. Molybdenum disulphide/titanium dioxide nanocomposite-poly 3-hexylthiophene bulk heterojunction solar cell. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 153901. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, W.; Yu, J.C.; Lin, J.; Yu, J.; Li, P. Preparation and photocatalytic behavior of MoS2 and WS2 nanocluster sensitized TiO2. Langmuir 2004, 20, 5865–5869. [Google Scholar]
- Benavente, E.; Ana, M.A.S.; Mendizábal, F.; González, G. Intercalation chemistry of molybdenum disulfide. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 224, 87–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Zhang, X.Q.; Zhang, W.; Chang, M.T.; Lin, C.T.; Chang, K.D.; Yu, Y.C.; Wang, J.T.; Chang, C.S.; Li, L.J.; et al. Synthesis of large-area MoS2 atomic layers with chemical vapor deposition. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2320–2325. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Wang, R.; Sun, X.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, J.; Lou, X.W.; Xie, Y. Defect-rich MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets with additional active edge sites for enhanced electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5807–5813. [Google Scholar]
- Afanasiev, P. Synthetic approaches to the molybdenum sulfide materials. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2008, 11, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindhu, B.; Sharu, B.K.; Gopika, M.S.; Praseetha, P.K.; Veluraja, K. Molybdenum disulfide nanoflakes through Li-AHA assisted exfoliation in an aqueous medium. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 22026–22033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.V.; Kim, K.; Jung, D.; Singh, K.; Oh, E.; Chung, J.S. Liquid phase co-exfoliated MoS2–graphene composites as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 244, 280–286. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.; Santhana, A.; Jiang, S.; Warchoł, J.K. Synthesis and characterization of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide magnetic MoS2@ Fe3O4 nanoparticles for adsorption of Cr (VI)/Cr (III). ACS Omega 2017, 2, 6187–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawula Tobile, N.Y.; Raju, K.; Franklyn, P.J.; Sigalas, I.; Ozoemena, K.I. The effects of morphology re-arrangements on the pseudocapacitive properties of mesoporous molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanoflakes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A1927–A1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, K.; Heydrich, S.; Hirmer, M.; Schmutzler, J.; Schüller, C. Low-temperature photocarrier dynamics in monolayer MoS2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 102109. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer Jannik, C.; Geim, A.K.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Novoselov, K.S.; Booth, T.J.; Roth, S. The structure of suspended graphene sheets. Nature 2007, 446, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagar, P.; Harle, A.; Sathaye, S.; Patil, K. Development of a novel method to grow mono-/few-layered MoS 2 films and MoS2—Graphene hybrid films for supercapacitor applications. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 10845–10855. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.H.; Han, D.J.; Choi, J.S.; Park, M.; Seo, T.S. Dual role of blue luminescent MoS2 quantum dots in fluorescence resonance energy transfer phenomenon. Small 2014, 10, 3858–3862. [Google Scholar]
- Deepesh, G.; Damien, D.; Shaijumon, M.M. MoS2 quantum dot-interspersed exfoliated MoS2 nanosheets. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5297–5303. [Google Scholar]
- Chikan, V.; Kelley, D.F. Size-dependent spectroscopy of MoS2 nanoclusters. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 3794–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo Thomas, F.; Jørgensen, K.P.; Bonde, J.; Nielsen, J.H.; Horch, S.; Chorkendorff, I. Identification of active edge sites for electrochemical H2 evolution from MoS2 nanocatalysts. Science 2007, 317, 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, S.; Li, D.; Wu, P. One-pot, facile, and versatile synthesis of monolayer MoS2/WS2 quantum dots as bioimaging probes and efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, W.; Dong, H.; Fugetsu, B.; Cao, Y.; Lu, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X. Tunable fabrication of molybdenum disulfide quantum dots for intracellular microRNA detection and multiphoton bioimaging. Small 2015, 11, 4158–4164. [Google Scholar]
- Bojana, V.; Dominko, R.; Gunde, M.K.; Hauptman, N.; Skapin, S.D.; Remskar, M. Optical properties of exfoliated MoS2 coaxial nanotubes-analogues of graphene. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 593. [Google Scholar]
- Václav, Š.; Henych, J. Strongly luminescent monolayered MoS2 prepared by effective ultrasound exfoliation. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3387–3394. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, H.; Du, C.; Shi, H.; Feng, X.; Li, J.; Tan, Y.; Song, W. Water-Soluble Monolayer Molybdenum Disulfide Quantum Dots with Upconversion Fluorescence. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2015, 32, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Pang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, X.; Fan, H.; Liu, S.F. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of monolayer MoS2 quantum dots for highly efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 10693–10697. [Google Scholar]
- Prestopino, G.; Marinelli, M.; Milani, E.; Verona, C.; Verona-Rinati, G. Transient lateral photovoltaic effect in synthetic single crystal diamond. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 143504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eva, M.; Omnès, F.; Calle, F. Wide-bandgap semiconductor ultraviolet photodetectors. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2003, 18, R33. [Google Scholar]
- Andrea, S.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Kim, J.; Chim, C.; Galli, G.; Wang, F. Emerging photoluminescence in monolayer MoS2. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Yafei, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Z. MoS2 nanoribbons: High stability and unusual electronic and magnetic properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16739–16744. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Birdwell, A.G.; Amani, M.; Burke, R.A.; Ling, X.; Lee, Y.; Liang, X.; Peng, L.; Richter, C.A.; Kong, J.; et al. Broadband optical properties of large-area monolayer CVD molybdenum disulfide. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 195434. [Google Scholar]
- Subhrajit, M.; Maiti, R.; Midya, A.; Das, S.; Ray, S.K. Tunable direct bandgap optical transitions in MoS2 nanocrystals for photonic devices. ACS Photonics 2015, 2, 760–768. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ma, X.D.; Qiu, Y.P.; Zhang, T. High quantum-yield luminescent MoS2 quantum dots with variable light emission created via direct ultrasonic exfoliation of MoS2 nanosheets. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 95178–95182. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Pan, H.; Zhang, Y.W.; Yakobson, B.I. Quasiparticle band structures and optical properties of strained monolayer MoS2 and WS2. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 155304. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.A.B.; Chemla, D.S.; Schmitt-Rink, S. Relation between electroabsorption in bulk semiconductors and in quantum wells: The quantum-confined Franz-Keldysh effect. Phys. Rev. B 1986, 33, 6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde Dhanraj, B.; Vijayamohanan, K.P. Electrochemical preparation of luminescent graphene quantum dots from multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 12522–12528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepesh, G.; Damien, D.; Li, B.; Gullappalli, H.; Pillai, V.K.; Ajayan, P.M.; Shaijumon, M.M. Electrochemical synthesis of luminescent MoS2 quantum dots. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6293–6296. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Lin, Y.; Qi, B.; Pang, D. Electrochemical tuning of luminescent carbon nanodots: From preparation to luminescence mechanism. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5801–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, L.; Li, X.; Ran, P.; Zuo, P.; Wang, A.; Qu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Lu, Y. Preparation of monolayer MoS2 quantum dots using temporally shaped femtosecond laser ablation of bulk MoS2 targets in water. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, E.; Chow, T.P. Silicon carbide benefits and advantages for power electronics circuits and systems. Proc. IEEE 2002, 90, 969–986. [Google Scholar]
- Burak, O.; Tolbert, L.M. Comparison of Wide-Bandgap Semiconductors for Power Electronics Applications; Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.; Dorn-Gomba, L.; Mak, C.; Emadi, A. Automotive traction inverters: Current status and future trends. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 3337–3350. [Google Scholar]


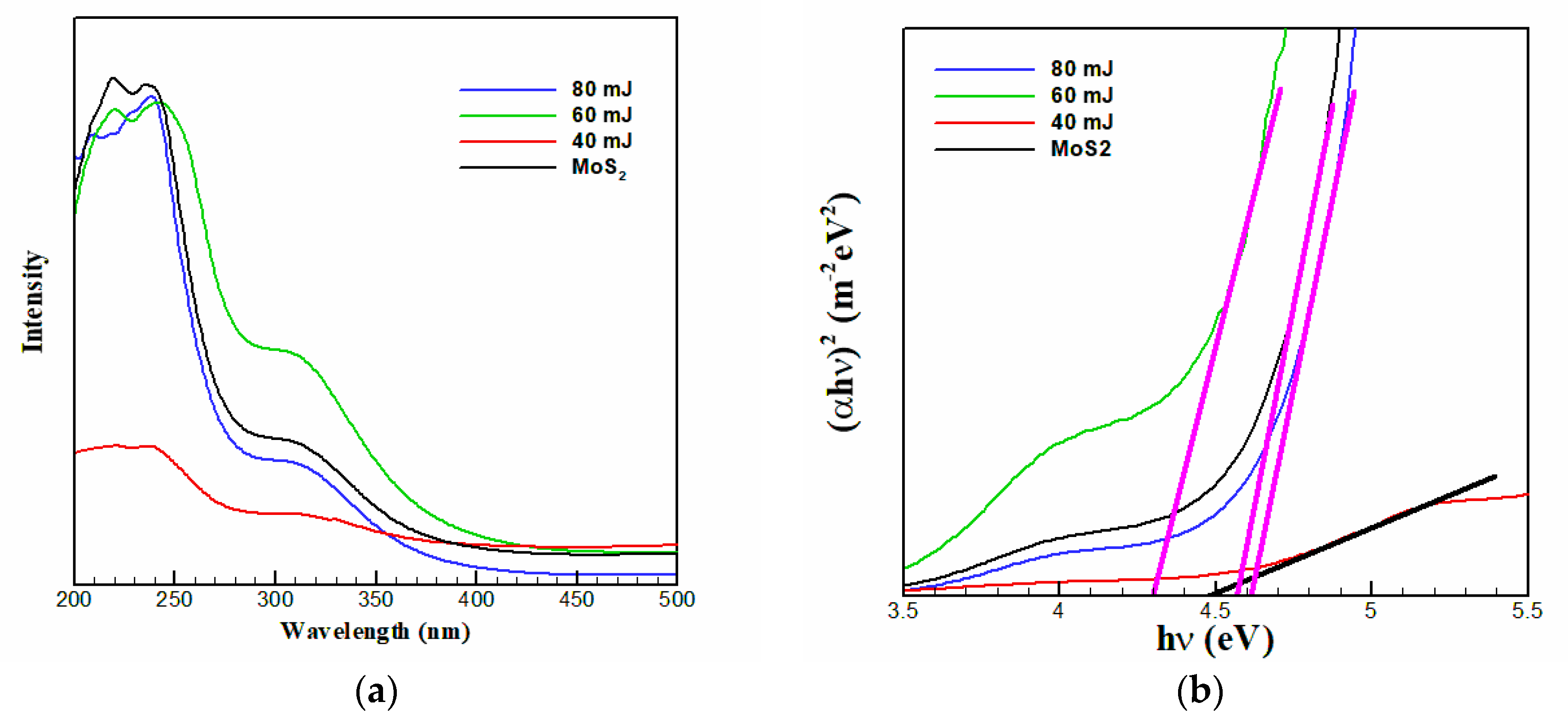

| Sample | MoS2 | 40 mJ | 60 mJ | 80 mJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bandgap (eV) | 4.6 | 4.5 | 4.3 | 4.7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahdavi, M.; Kimiagar, S.; Abrinaei, F. Preparation of Few-Layered Wide Bandgap MoS2 with Nanometer Lateral Dimensions by Applying Laser Irradiation. Crystals 2020, 10, 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10030164
Mahdavi M, Kimiagar S, Abrinaei F. Preparation of Few-Layered Wide Bandgap MoS2 with Nanometer Lateral Dimensions by Applying Laser Irradiation. Crystals. 2020; 10(3):164. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10030164
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahdavi, Mitra, Salimeh Kimiagar, and Fahimeh Abrinaei. 2020. "Preparation of Few-Layered Wide Bandgap MoS2 with Nanometer Lateral Dimensions by Applying Laser Irradiation" Crystals 10, no. 3: 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10030164
APA StyleMahdavi, M., Kimiagar, S., & Abrinaei, F. (2020). Preparation of Few-Layered Wide Bandgap MoS2 with Nanometer Lateral Dimensions by Applying Laser Irradiation. Crystals, 10(3), 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10030164





