Biomineralization of Carbonate Minerals Induced by The Moderate Halophile Staphylococcus Warneri YXY2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture Medium and Bacterial Strain
2.2. Preparation of Bacterial Seed
2.3. Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of YXY2 Bacteria
2.4. Formation of Biotic and Abiotic Carbonate Minerals
2.5. Characterization of Biominerals Induced by YXY2 Bacteria
2.6. Analyses of Intracellular Biomineralization
2.7. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3. Results
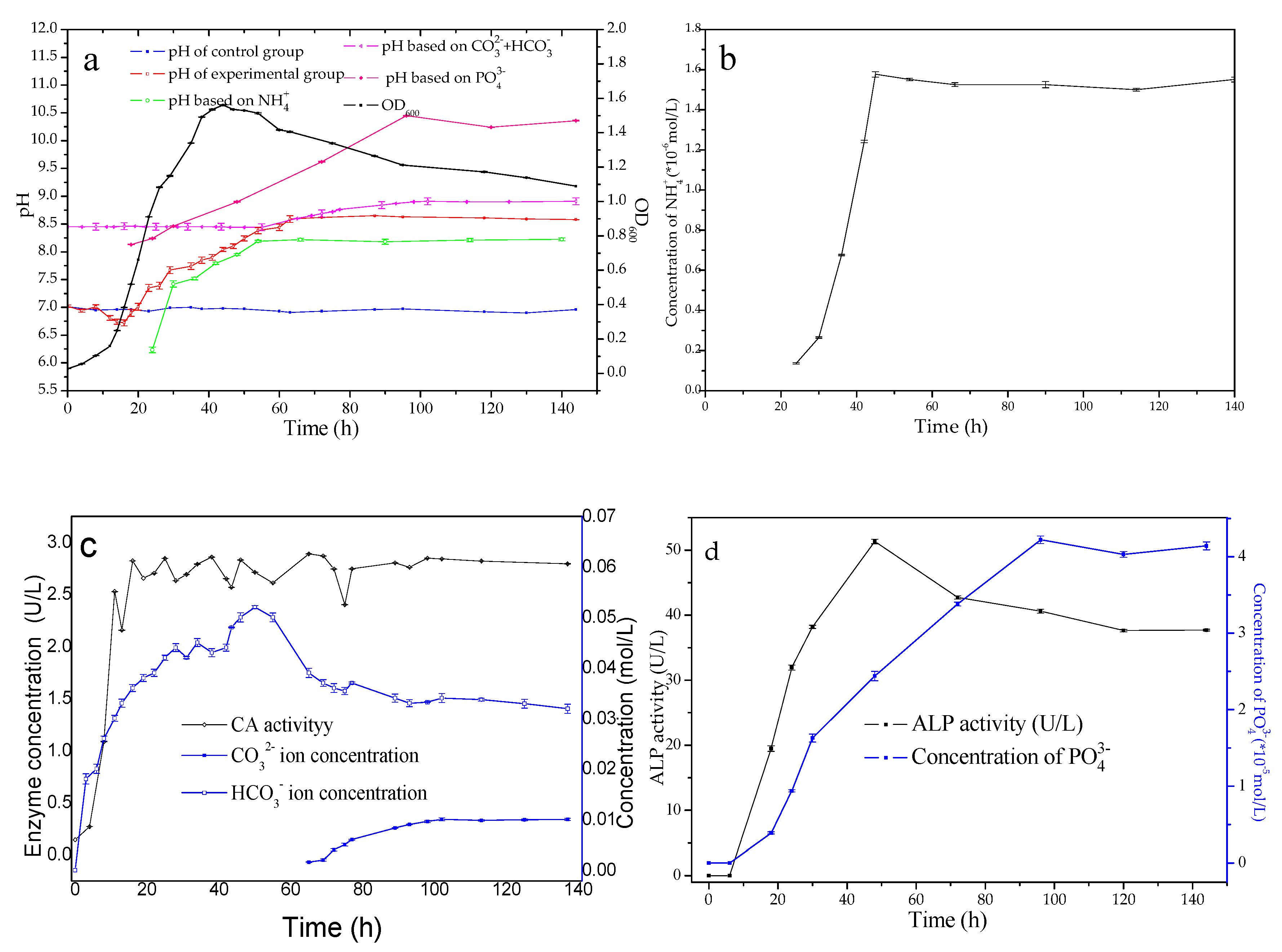
3.1. Hydro-Chemical Parameters’ Evolutions
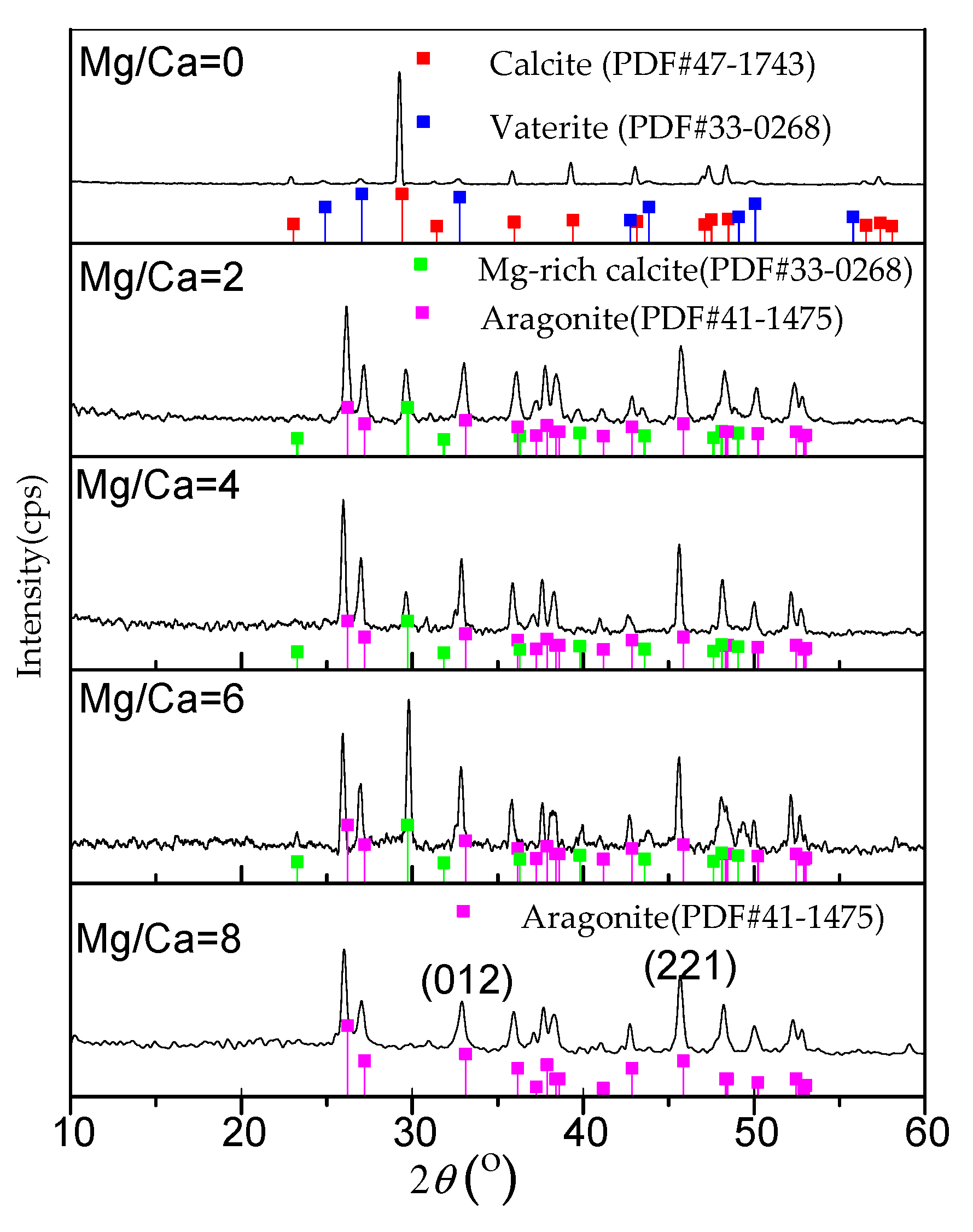
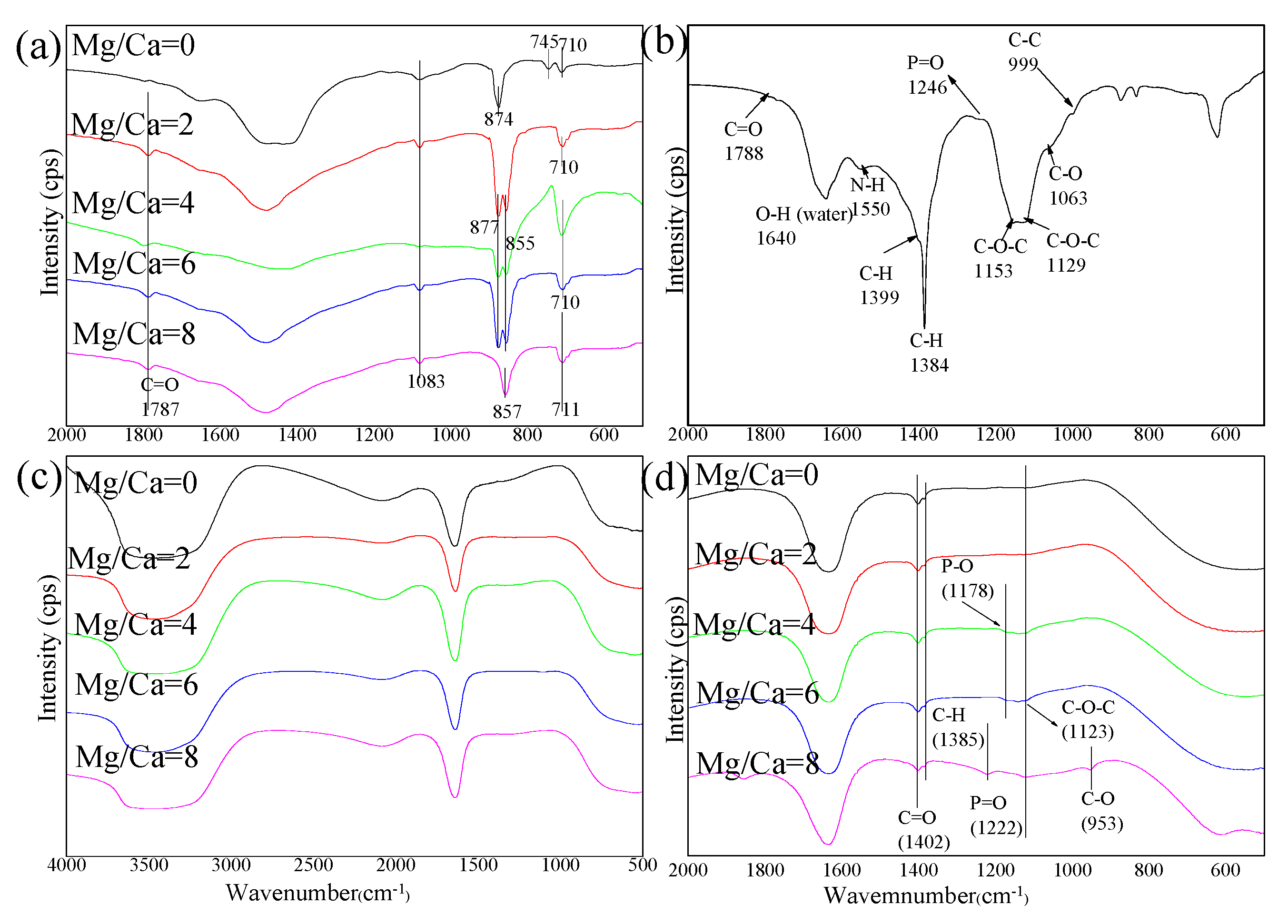
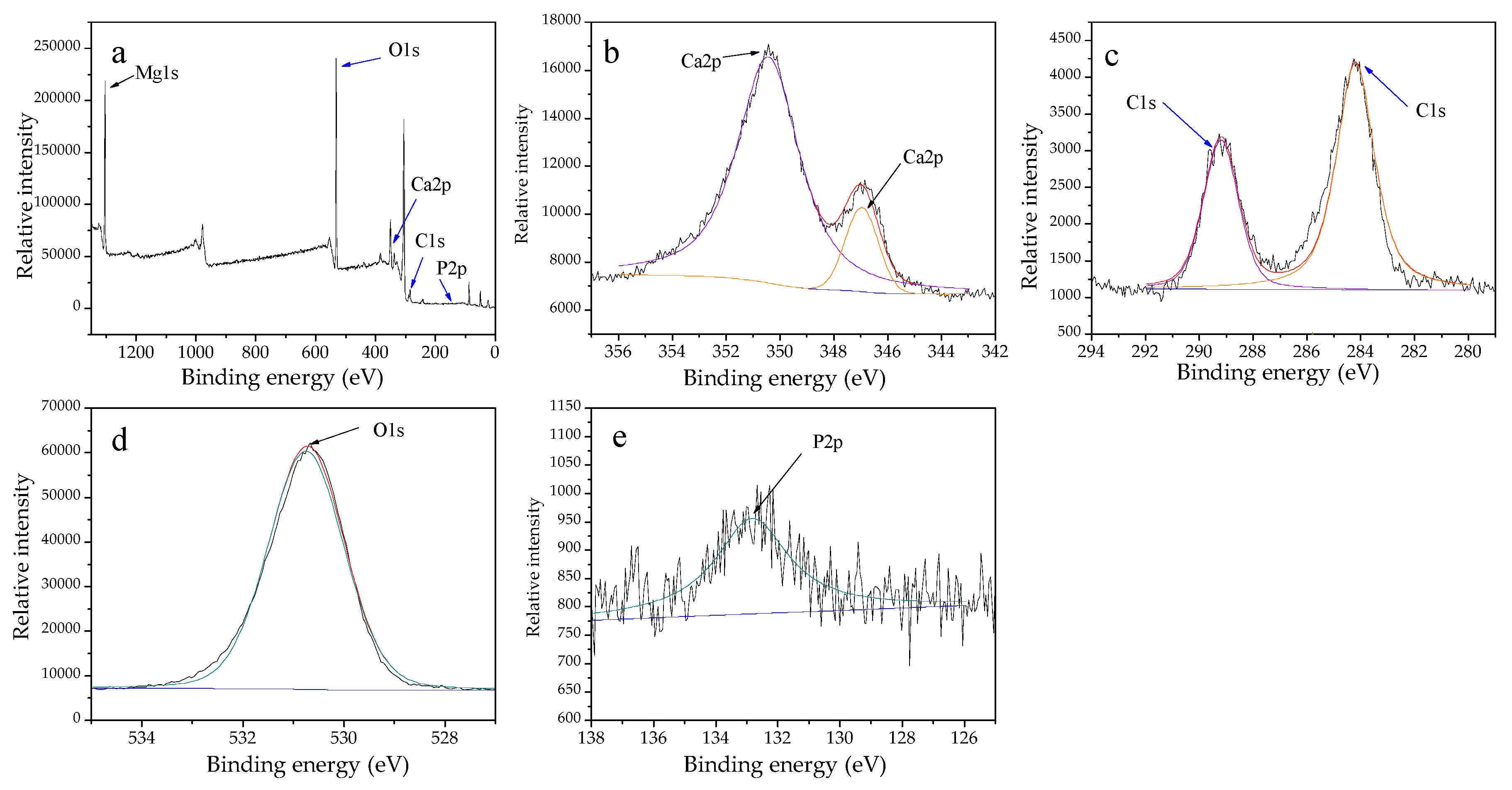
3.2. Characteristics of Biominerals
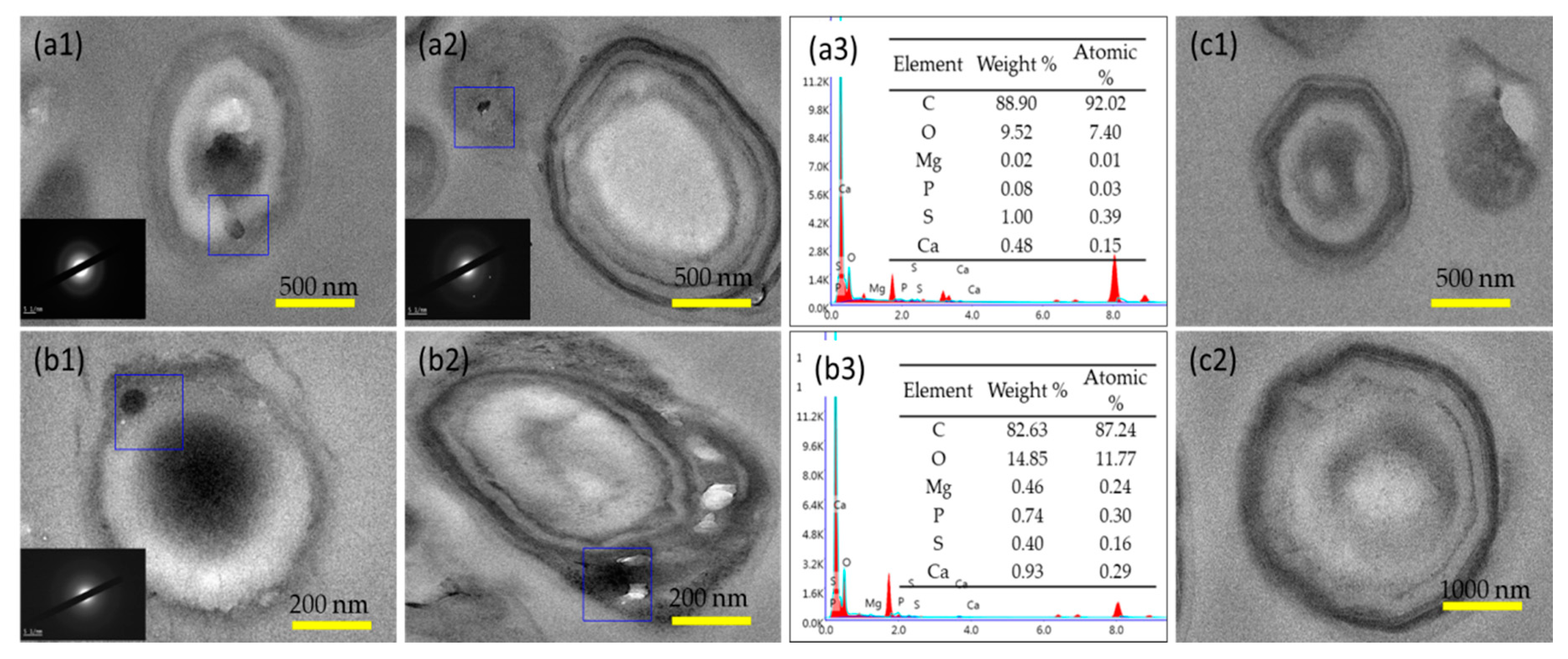
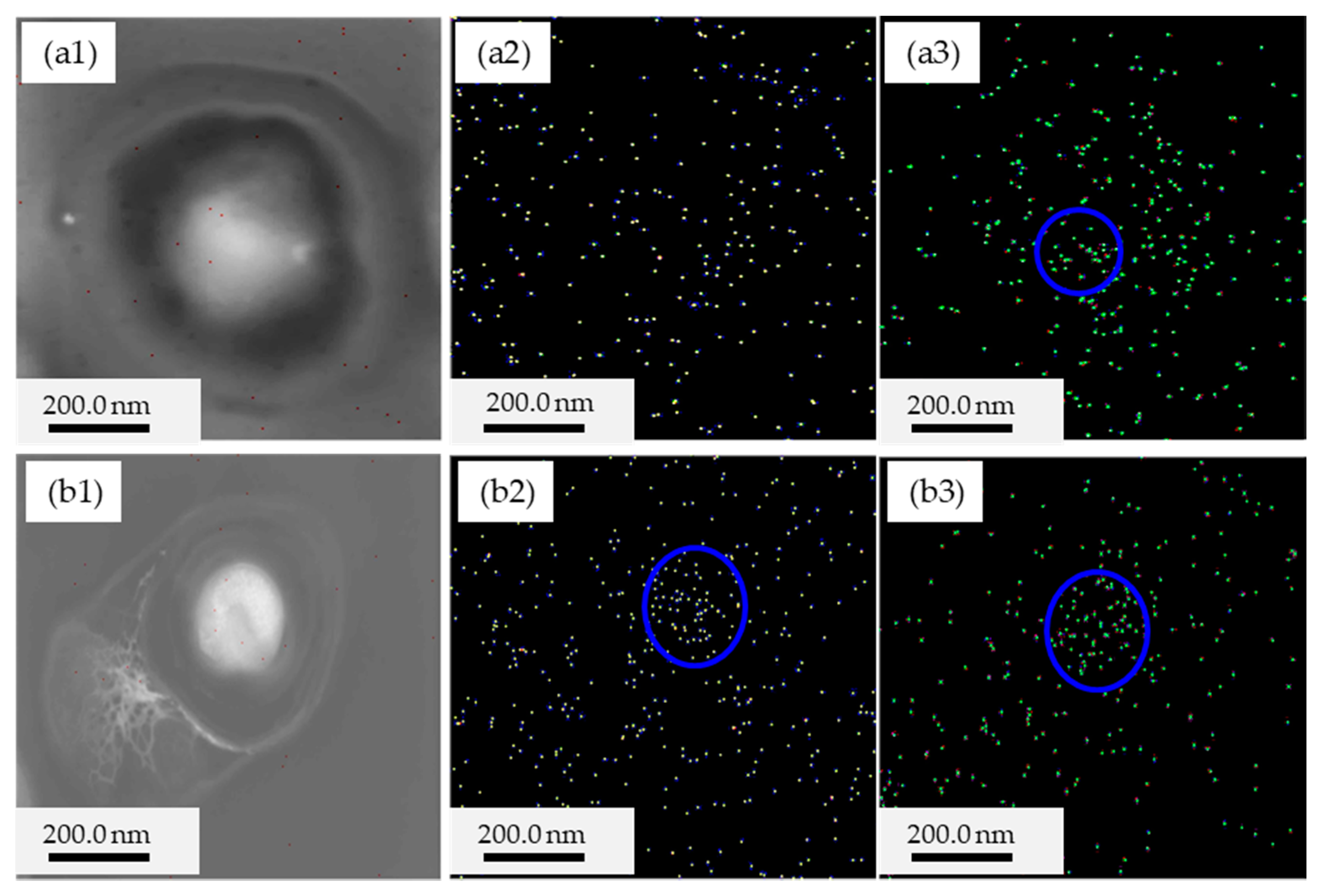
3.3. Intracellular Biomineralization Induced by S. Warneri YXY2 Bacteria
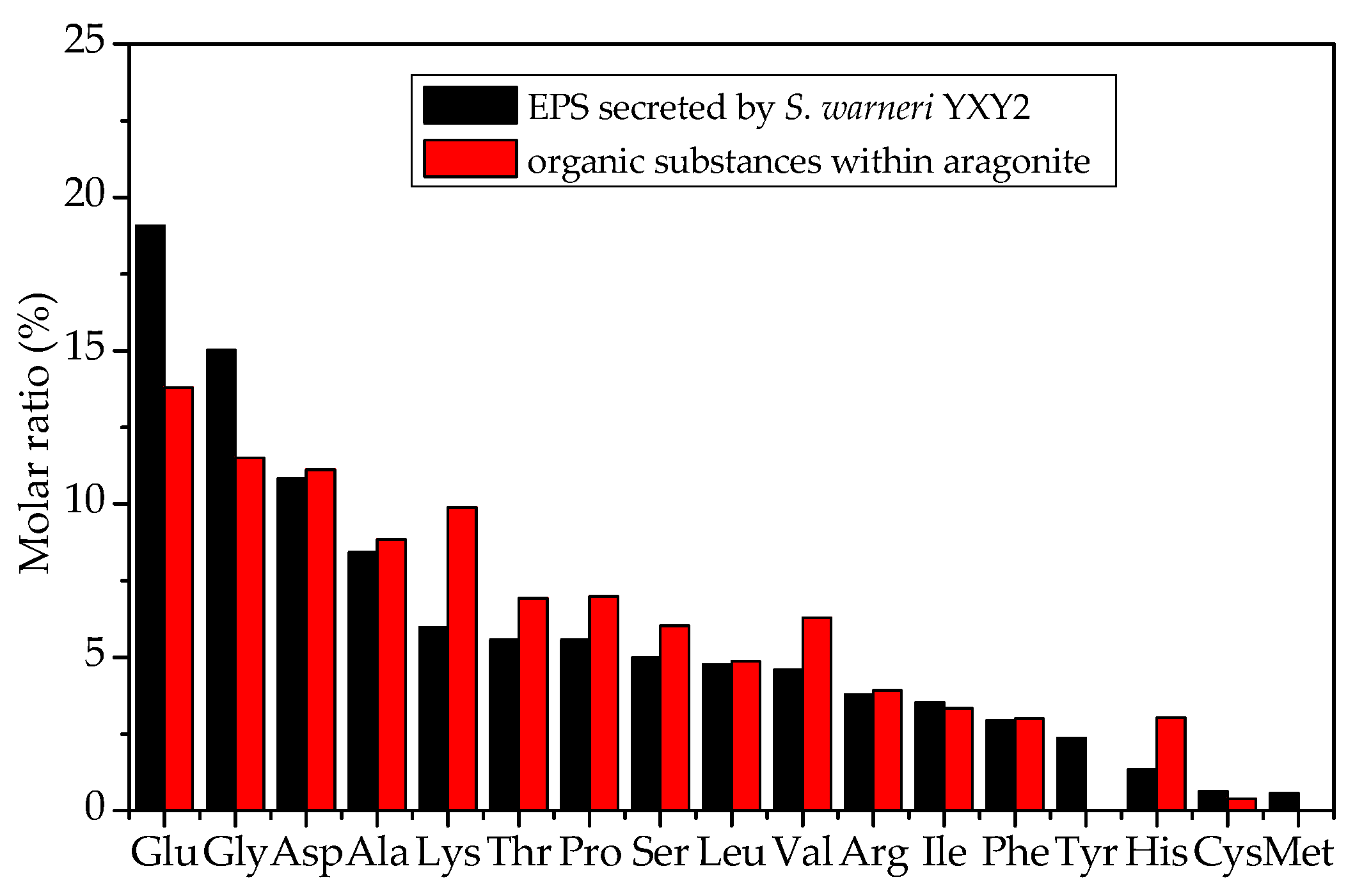
3.4. Amino Acid Composition of EPS
3.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
4. Discussion
4.1. S. Warneri YXY2 Creating the Suitable Conditions for Biomineralization
4.2. EPS Serving as the Nucleation Site and the Preferred Orientation of Aragonite
4.3. The Role of Mg/Ca Molar Ratios in Calcium Carbonate Polymorphs
4.4. Possible Mechanism of Mg Entry into the Biotic Aragonite
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, W.; Ma, H.; Li, F.; Jin, Z.D.; Li, J.; Ma, F.; Wang, C. Citrobacter sp. strain GW-M mediates the coexistence of carbonate minerals with various morphologies. Geomicrobiol. J. 2013, 30, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epple, M. Buchbesprechung: Biomineralization principles and concepts in bioinorganic materials chemistry. Von Stephen Mann. Angew. Chem. 2003, 115, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Valiyaveettil, S.; Wopenka, B.; Morse, D. CaCO3 biomineralization: Acidic 8-kDa proteins isolated from aragonitic abalone shell nacre can specifically modify calcite crystal morphology. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb, M.; Cohen, A.; Gabitov, R.; Hutter, J. Compositional and morphological features of aragonite precipitated experimentally from seawater and biogenically by corals. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 4166–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Li, D.; Zhao, H.; Yan, H.; Li, P. Precipitation of carbonate minerals induced by the halophilic Chromohalobacter Israelensis under high salt concentrations: Implications for natural environments. Minerals 2017, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Yao, Y.; Wang, H.; Shen, A.; Zhang, J. Halophilic archaea mediate the formation of proto-dolomite in solutions with various sulfate concentrations and salinities. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, B.; Hu, Q.; Chen, J.; Ji, J.; Teng, H.H. Carbonate biomineralization induced by soil bacterium Bacillus megaterium. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2006, 70, 5522–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Sun, B.; Zhao, H.; Yan, H.; Han, M.; Zhao, Y.; Meng, R.; Zhuang, D.; Li, D.; Ma, Y.; et al. Isolation of Leclercia adcarboxglata strain JLS1 from dolostone sample and characterization of its induced struvite minerals. Geomicrobiol. J. 2017, 34, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Yu, W.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Tucker, M.; Yan, H. The significant roles of Mg/Ca ratio, Cl− and SO42− in carbonate mineral precipitation by the halophile Staphylococcus epidermis Y2. Minerals 2018, 8, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Jiang, J.; Sun, H.; Huang, Y.; Tao, F.; Lian, B. Carbonate mineral formation under the influence of limestone-colonizing actinobacteria: Morphology and polymorphism. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rivadeneyra, M.; Martín-Algarra, A.; Sánchez-Navas, A.; Martín-Ramos, D. Carbonate and phosphate precipitation by Chromohalobacter marismortui. Geomicrobiol. J. 2006, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Román, M.; Romanek, C.; Fernández-Remolar, D.; Sánchez-Navas, A.; McKenzie, J.; Amils, R.; Vasconcelos, C. Aerobic biomineralization of Mg-rich carbonates: Implications for natural environments. Chem. Geol. 2011, 281, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Wang, H.; Yao, Y.; Duan, Y. High salinity facilitates dolomite precipitation mediated by Haloferax volcanii DS52. Earth. Planet. Sc. Lett. 2017, 472, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Dong, H.; Lv, G.; Jiang, H.; Yu, B.; Bishop, M. Microbial dolomite precipitation using sulfate reducing and halophilic bacteria: Results from Qinghai Lake, Tibetan Plateau, NW China. Chem. Geol. 2010, 278, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Turchyn, A.; Steiner, Z.; Bots, P.; Lampronti, G.; Tosca, N. The role of microbial sulfate reduction in calcium carbonate polymorph selection. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2018, 237, 184–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.; Yan, H.; Tucker, M.E.; Zhao, H.; Han, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, B.; Li, D.; Pan, J.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Calcite precipitation induced by Bacillus cereus MRR2 cultured at different Ca2+ concentrations: Further insights into biotic and abiotic calcite. Chem. Geol. 2018, 500, 64–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perri, E.; Tucker, M.; Slowakiewicz, M.; Whitaker, F.; Bowen, L.; Perrotta, I. Carbonate and silicate biomineralization in a hypersaline microbial mat (Mesaieed sabkha, Qatar): Roles of bacteria, extracellular polymeric substances and viruses. Sedimentology 2017, 65, 1213–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zeng, C.; Liu, Q.; Liu, D.; Xuan, Q.; Gong, L. Calcium carbonate precipitation induced by a bacterium strain isolated from an oligotrophic cave in Central China. Front. Earth. Sci. China 2010, 4, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakimoto, S.; Okazaki, K.; Sakane, T.; Imai, K.; Sumino, Y.; Akiyama, S.-I.; Nakao, Y. Isolation and taxonomic characterization of urease-producing bacteria. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1989, 53, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vasconcelos, C.; McKenzie, J.A.; Bernasconi, S.; Grujic, D.; Tien, A.J. Microbial mediation as a possible mechanism for natural dolomite formation at low-temperatures. Nature 1995, 377, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achal, V.; Pan, X. Characterization of urease and carbonic anhydrase producing bacteria and their role in calcite precipitation. Curr. Microbiol. 2010, 62, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, S.; Liebetrau, V.; Löscher, C.; Böhm, F.; Gorb, S.; Eisenhauer, A.; Treude, T. Marine ammonification and carbonic anhydrase activity induce rapid calcium carbonate precipitation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2018, 243, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Ge, S.-S.; Shao, Q.; Liu, M.; Liu, Q.Y. Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of CeO2 hollow microspheres via yeast template route. Chinese J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 32, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, T.; Zengping, N.; Li, H.; Tang, J.; Zhou, G. High cadmium concentration in soil in the three Gorges region: Geogenic source and potential bioavailability. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 37, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, H.; Zhou, J.; Tucker, M.E.; Han, M.; Zhao, H.; Mao, G.; Zhao, Y.; Han, Z. Bio-precipitation of calcium and magnesium ions through extracellular and intracellular process induced by Bacillus Licheniformis SRB2. Minerals 2019, 9, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhao, H.; Tucker, M.E.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, B.; Han, Z.; Yan, H. Biomineralization of monohydrocalcite induced by the halophile Halomonas smyrnensis WMS-3. Minerals 2019, 9, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhao, H.; Tucker, M.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, Z.; Pan, J.; Wu, G.; Yan, H. Extracellular and intracellular biomineralization induced by Bacillus licheniformis DB1-9 at different Mg/Ca molar ratios. Minerals 2018, 8, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocker, Y.; Stone, J. The catalytic versatility of erythrocyte carbonic anhydrase. III. Kinetic studies of the enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl acetate. Biochemistry 1967, 6, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Tucker, M.E.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhou, J.; Yin, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Mechanism of biomineralization induced by Bacillus subtilis J2 and characteristics of the biominerals. Minerals 2019, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Garnier, G. Direct measurement of alkaline phosphatase kinetics on bioactive paper. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 87, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J. A single-solution method for the determination of soluble phosphate in sea water. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. Uk. 1958, 37, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.-T.; Yao, Q.Z.; Ni, J.; Jin, G. Formation of aragonite mesocrystals and implication for biomineralization. Amer. Mineral. 2009, 94, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, R.; Shao, Q.; Yang, S.; Xu, J. NiO nanoparticles modified with5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-carboxyl pheyl)-porphyrin: Promising peroxidase mimetics for H2O2 and glucose detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Chiang, C.-Y.; Zhou, W. Formation Mechanism of CaCO3 Spherulites in the Myostracum Layer of Limpet Shells. Crystals 2017, 7, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braissant, O.; Cailleau, G.; Dupraz, C.; Verrecchia, A. Bacterially induced mineralization of calcium carbonate in terrestrial environments: The role of exopolysaccharides and amino acids. J. Sediment. Res. 2003, 73, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Bratos Perez, M.A.; Martin-Gil, F.J.; Díez, A.; Rodríguez, J.; Rodríguez, P.; Domingo, A.; Torres, A. Identification of species of Brucella using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2003, 55, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Ratner, B. Differentiation of calcium carbonate polymorphs by surface analysis techniques - an XPS and TOF-SIMS study. Surf. Interface. Anal. 2008, 40, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, Q.-Z.; Wang, F.-P.; Huang, Y.-R.; Fu, S.-Q.; Zhou, G.-T. Insights into the formation mechanism of vaterite mediated by a deep-sea bacterium Shewanella piezotolerans WP3. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2019, 256, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadier, S.; Rokidi, S.; Rey, C.; Combes, C.; Koutsoukos, P. Crystal growth of aragonite in the presence of phosphate. J. Cryst. Growth. 2017, 458, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, Q.-Z.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Li, Y.-L.; Zhou, G.-T. Biomimetic synthesis of struvite with biogenic morphology and implication for pathological biomineralization. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Roman, M.; Rivadeneyra, M.A.; Vasconcelos, C.; McKenzie, J.A. Biomineralization of carbonate and phosphate by moderately halophilic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 61, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Cui, H.; Zhenglong, J.; Liu, H.; He, H.; Fang, N. Biomineralization processes of calcite induced by bacteria isolated from marine sediments. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Lian, B. Heterologously expressed carbonic anhydrase from Bacillus mucilaginosus promoting CaCO3 formation by capturing atmospheric CO2. Carbonate. Evaporite. 2016, 31, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenti, A.; Mühlschlegel, F.; Hall, R.; Steegborn, C.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Inhibition of the ??-class enzymes from the fungal pathogens Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans with simple anions. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 5066–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, S.; Archibald, D.; Didymus, J.; Douglas, T.; Heywood, B.; Meldrum, F.; Reeves, N. Crystallization at inorganic-organic interfaces: Biominerals and biomimetic synthesis. Science 1993, 261, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bains, A.; Dhami, N.K.; Mukherjee, A.; Reddy, M.S. Influence of exopolymeric materials on bacterially induced mineralization of carbonates. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2015, 175, 3531–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silyn-Roberts, H.; Sharp, R. Preferred orientation of calcite and aragonite in the reptilian eggshells. P. Roy. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 1985, 225, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.T.; Feng, Q. Crystal orientation preference and formation mechanism of nacreous layer in mussel. J. Cryst. Growth. 2003, 258, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Dove, P.; Yoreo, J. Understanding the molecular-scale processes of biomineralization: The role of Mg2+ and Sr2+ in calcite growth. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts; Wiley: Hoboken, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Robach, J.S.; Stock, S.R.; Veis, A. Mapping of magnesium and of different protein fragments in sea urchin teeth via secondary ion mass spectroscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 2006, 155, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Aichmayer, B.; Paris, O.; Fratzl, P.; Meibom, A.; Metzler, R.A.; Politi, Y.; Addadi, L.; Gilbert, P.U.P.A.; Weiner, S. The grinding tip of the sea urchin tooth exhibits exquisite control over calcite crystal orientation and Mg distribution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6048–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, A.; Allison, N. Mg structural state in coral aragonite and implications for the paleoenvironmental proxy. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meibom, A.; Cuif, J.-P.; Hillion, F.O.; Constantz, B.; Anne, J.-L.; Dauphin, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Dunbar, R.B. Distribution of magnesium in coral skeleton. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L23306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, G.A.; Cohen, A.L.; Wang, Z.; Crusius, J. Rayleigh-based, multi-element coral thermometry: A biomineralization approach to developing climate proxies. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2011, 75, 1920–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollion-Bard, C.; Blamart, D. Possible controls on Li, Na, and Mg incorporation into aragonite coral skeletons. Chem. Geol. 2015, 396, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuguchi, T.; Uchida, T.; Matsumoto, E.; Isdale, P.; Kawana, T. Variations in Mg/Ca, Na/Ca, and Sr/Ca ratios of coral skeletons with chemical treatments: Implications for carbonate geochemistry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2001, 65, 2865–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchitto, T.M.; Bryan, S.P.; Doss, W.; McCulloch, M.T.; Montagna, P. A simple biomineralization model to explain Li, Mg, and Sr incorporation into aragonitic foraminifera and corals. Earth. Planet. Sc. Lett. 2018, 481, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokroy, B.; Fitch, A.N.; Lee, P.L.; Quintana, J.P.; Caspi, E.a.N.; Zolotoyabko, E. Anisotropic lattice distortions in the mollusk-made aragonite: A widespread phenomenon. J. Struct. Biol. 2006, 153, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Mg/Ca Ratios | Biotic Minerals | Abiotic Minerals | Organic Carbon Source | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcite | Aragonite | Beef Extract | Tryptone | ||
| 0 | −15.27 | −11.19 | −12.41 | −18.86 | −21.56 |
| 2 | −16.47 | ||||
| 4 | −17.01 | ||||
| 6 | −17.45 | ||||
| 8 | −17.93 | ||||
| Surfaces | (111) | (221) | (012) | (021) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Etotal | 747,500.50 | 369,6261.00 | 481,336.50 | 696,041.50 |
| Esurface | 214.16 | 140.70 | 66.39 | 73.27 |
| EGlu | 749,137.00 | 369,7010.00 | 481,873.00 | 696,442.00 |
| Eadsorption | −1850.66 | −889.70 | −602.89 | −473.77 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Sun, B.; Yan, H.; Tucker, M.E.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H. Biomineralization of Carbonate Minerals Induced by The Moderate Halophile Staphylococcus Warneri YXY2. Crystals 2020, 10, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10020058
Han Y, Sun B, Yan H, Tucker ME, Zhao Y, Zhou J, Zhao Y, Zhao H. Biomineralization of Carbonate Minerals Induced by The Moderate Halophile Staphylococcus Warneri YXY2. Crystals. 2020; 10(2):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10020058
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yu, Bin Sun, Huaxiao Yan, Maurice E. Tucker, Yanhong Zhao, Jingxuan Zhou, Yifan Zhao, and Hui Zhao. 2020. "Biomineralization of Carbonate Minerals Induced by The Moderate Halophile Staphylococcus Warneri YXY2" Crystals 10, no. 2: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10020058
APA StyleHan, Y., Sun, B., Yan, H., Tucker, M. E., Zhao, Y., Zhou, J., Zhao, Y., & Zhao, H. (2020). Biomineralization of Carbonate Minerals Induced by The Moderate Halophile Staphylococcus Warneri YXY2. Crystals, 10(2), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10020058




