Transverse Scaling of Schottky Barrier Charge-Trapping Cells for Energy-Efficient Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
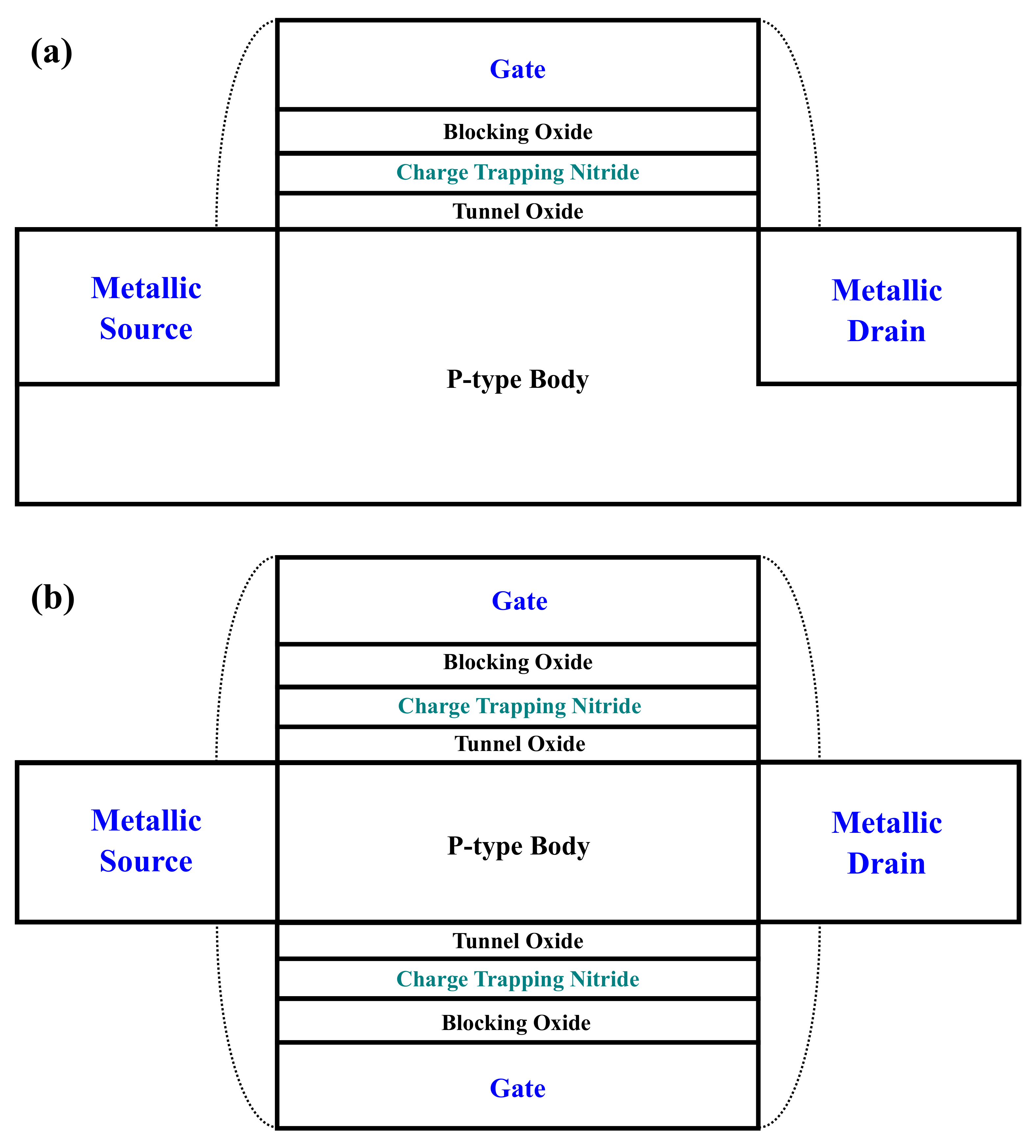
2. Device Structures and Numerical Parameters
3. Gate Structures and Scaled Dielectrics
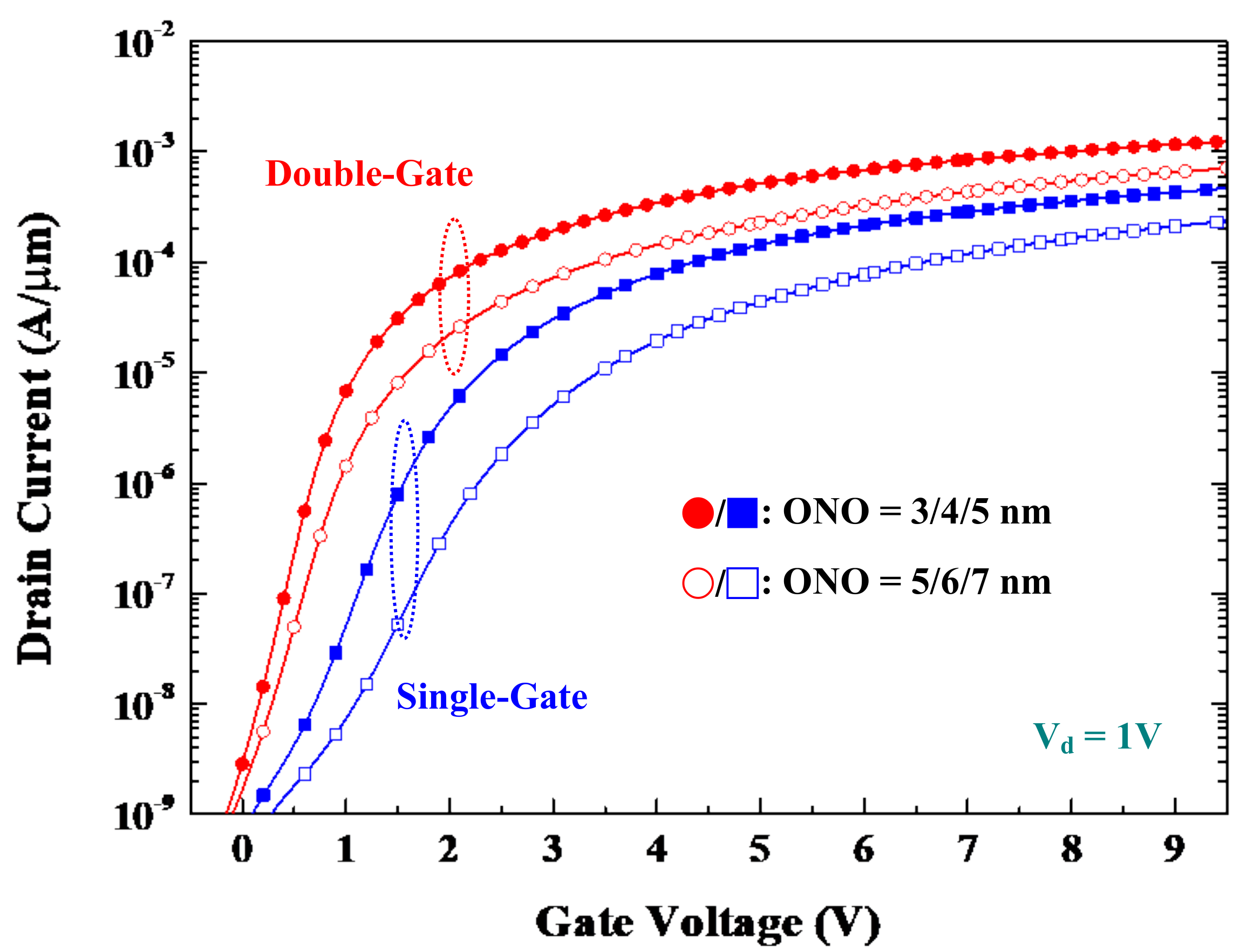
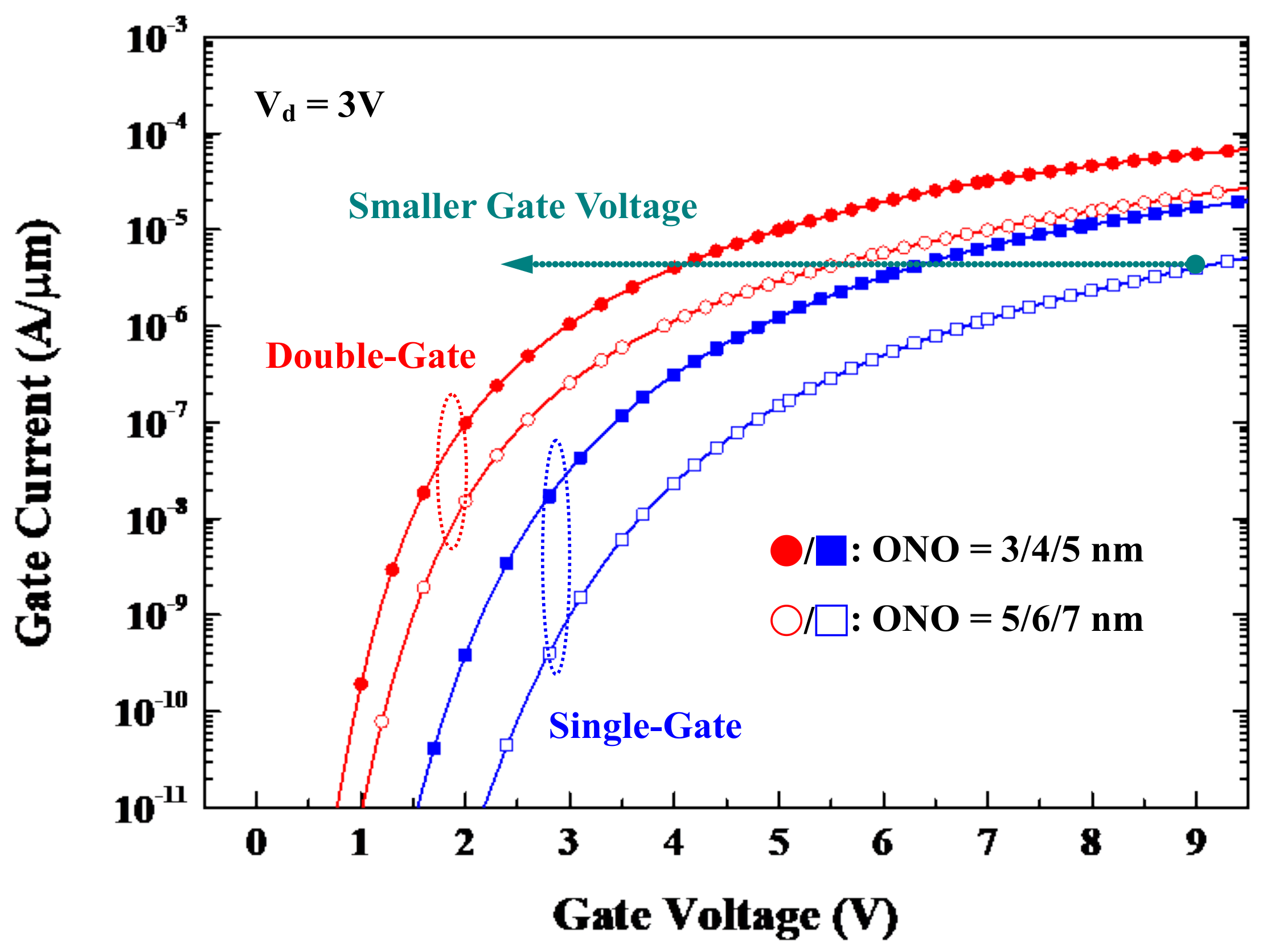
3.1. Drain and Gate Currents
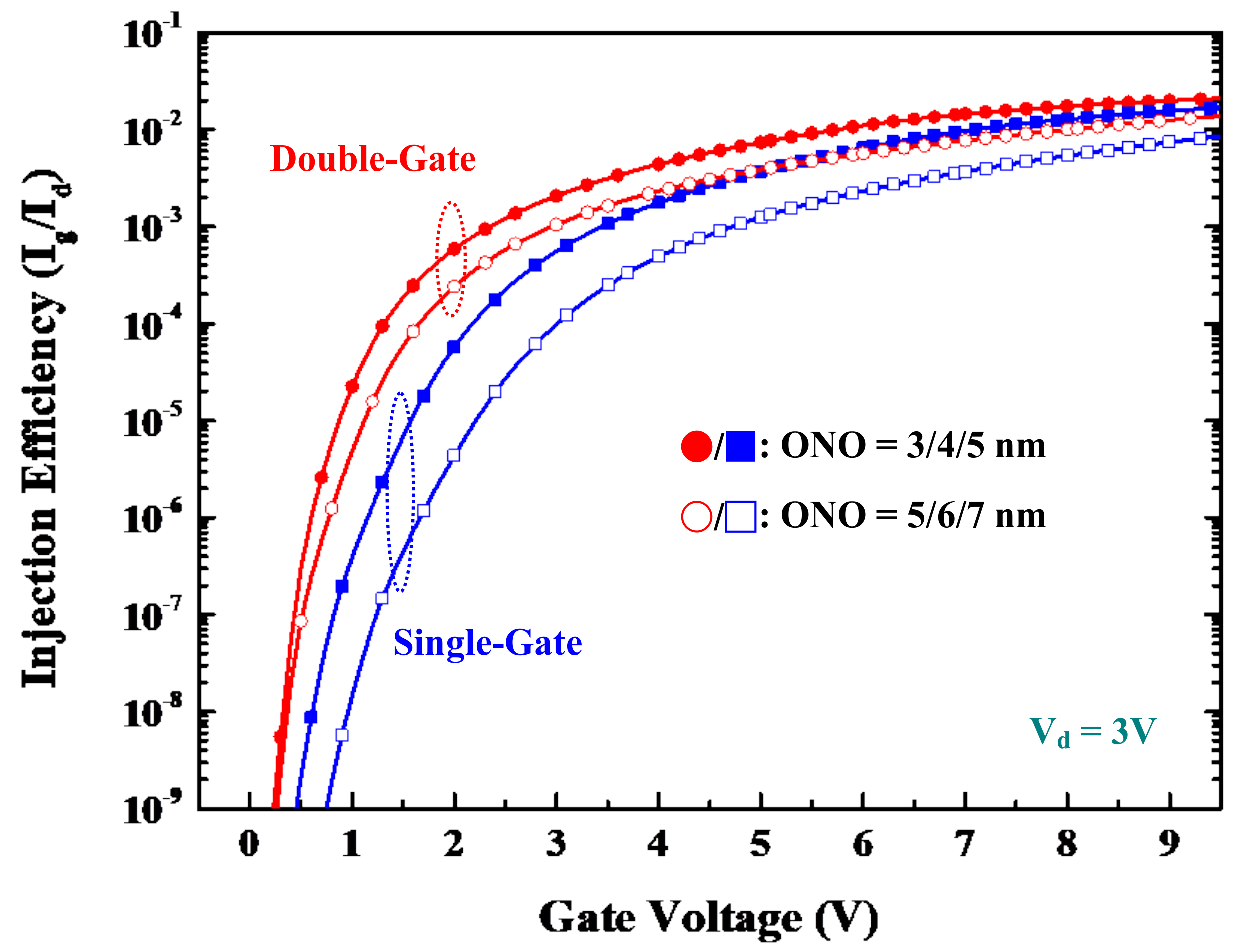
3.2. Source-Side Injection
4. Operation Voltages of Scaled Cells
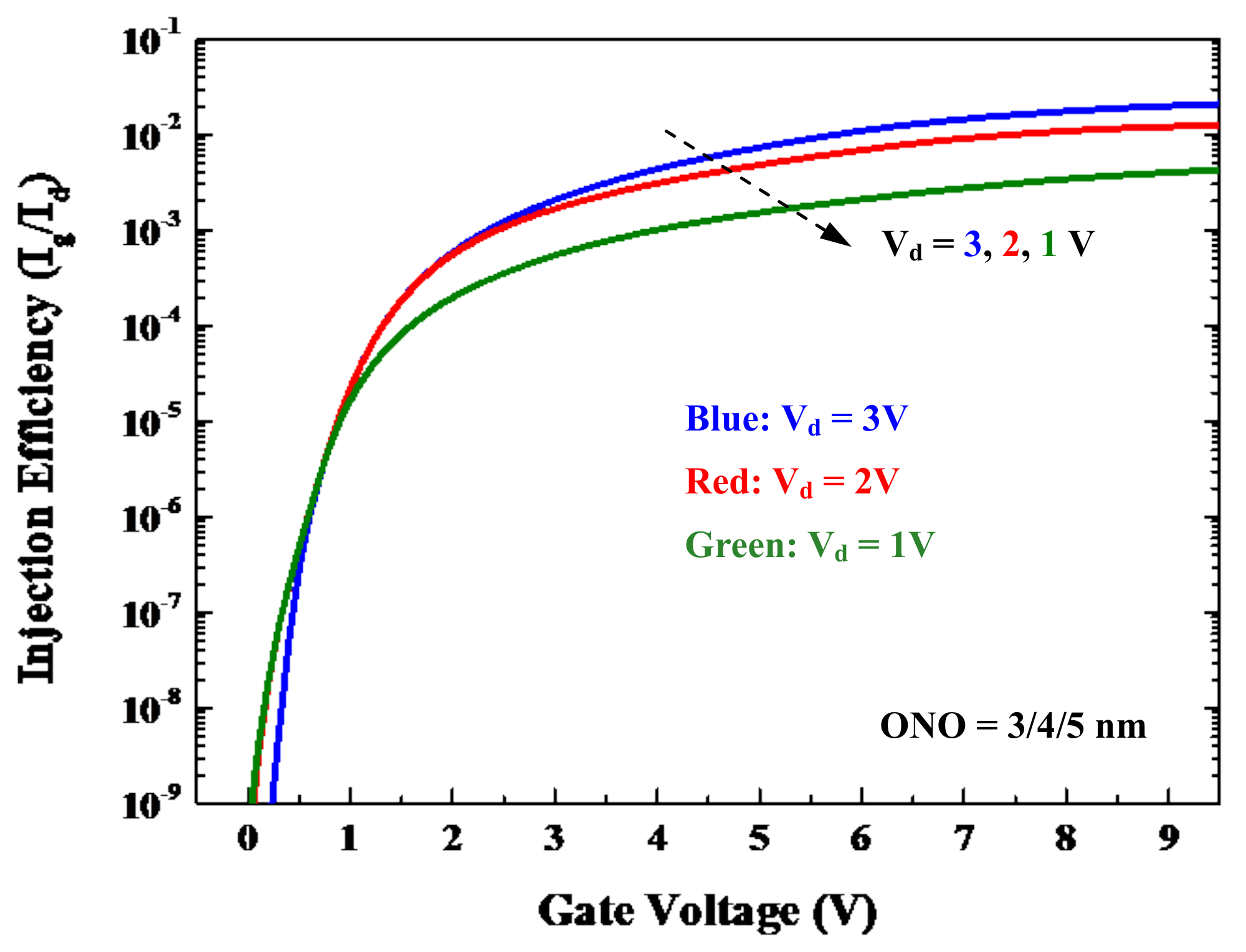
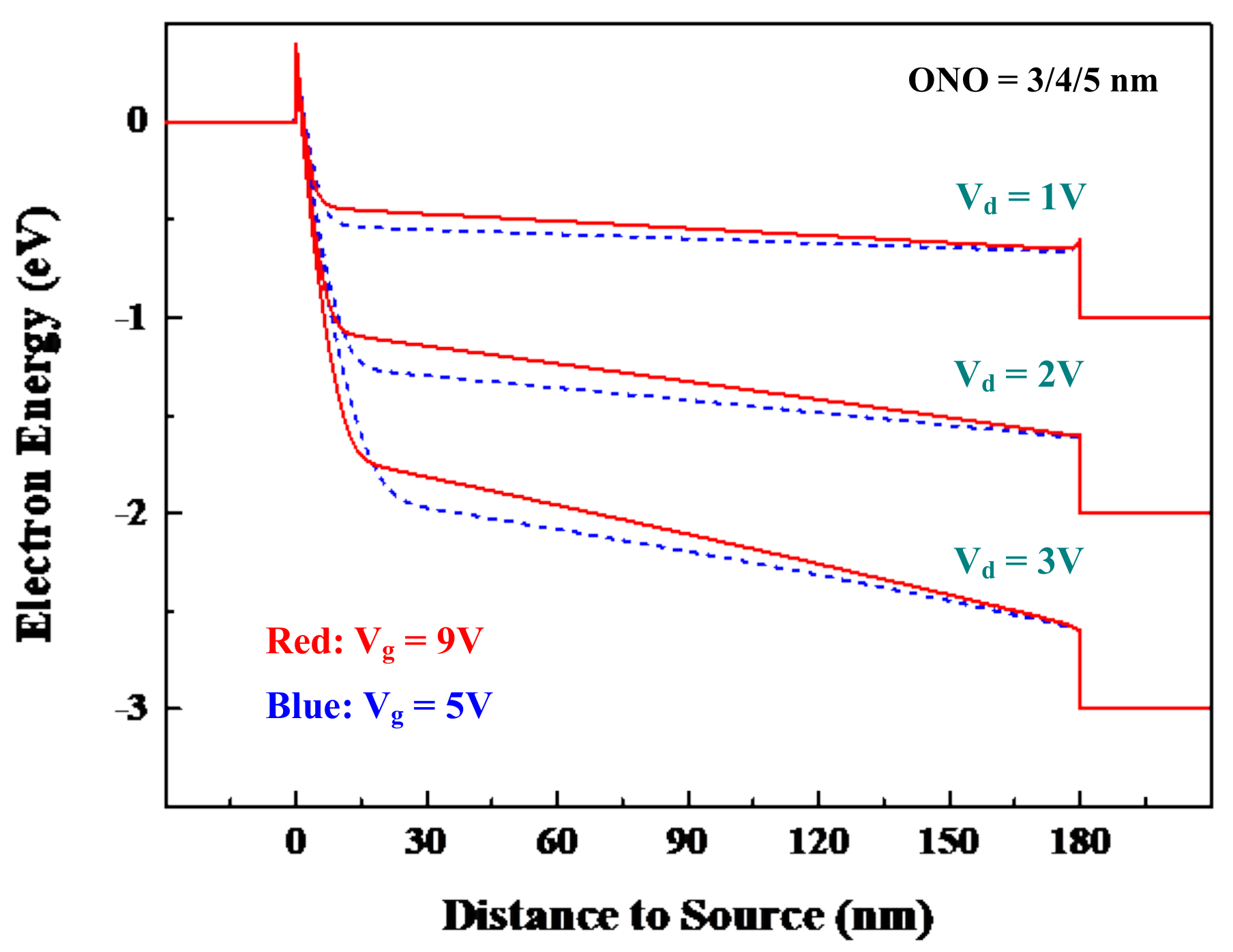
4.1. Drain Voltage
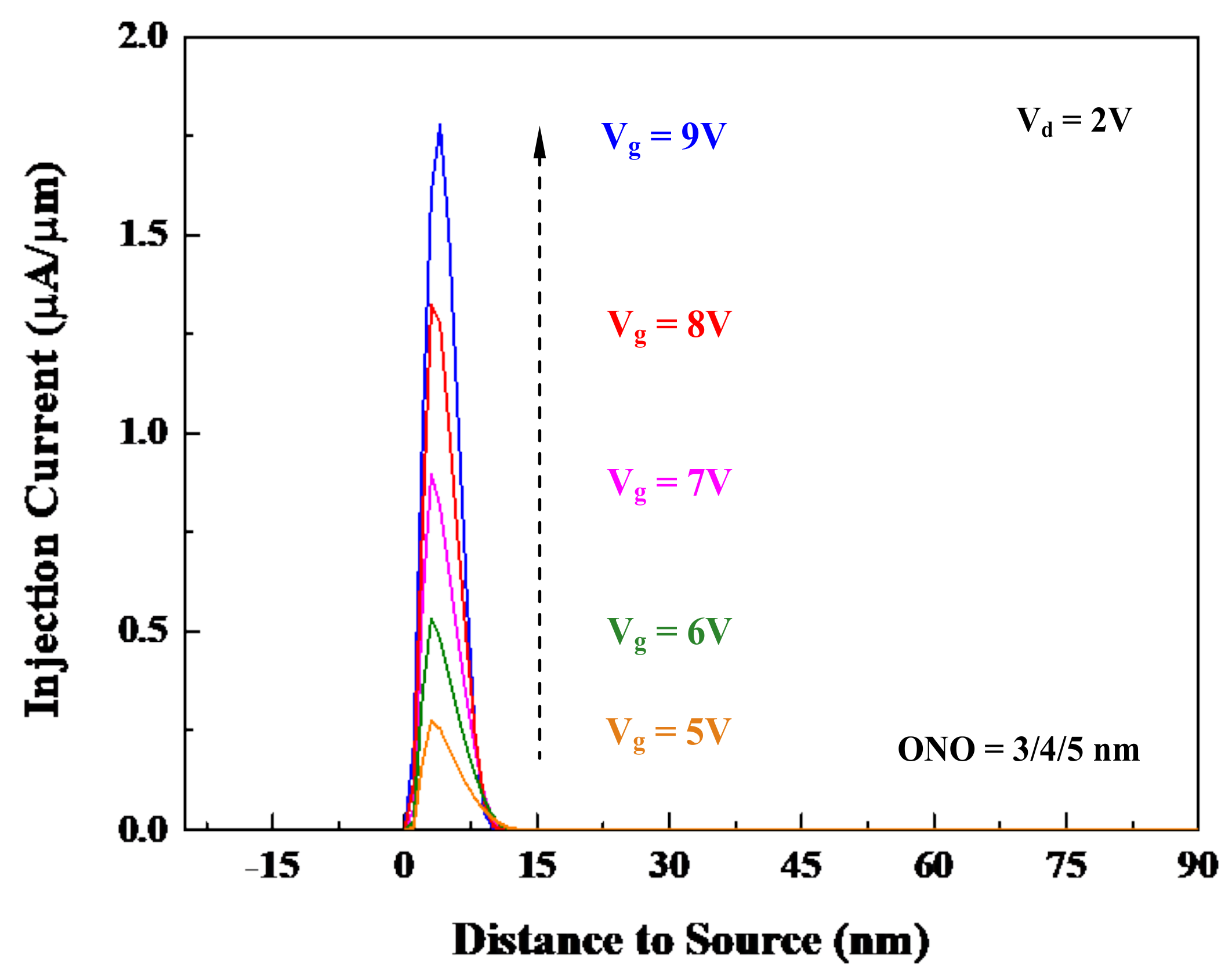
4.2. Gate Voltage
5. Low-Power and High-Efficiency Cells
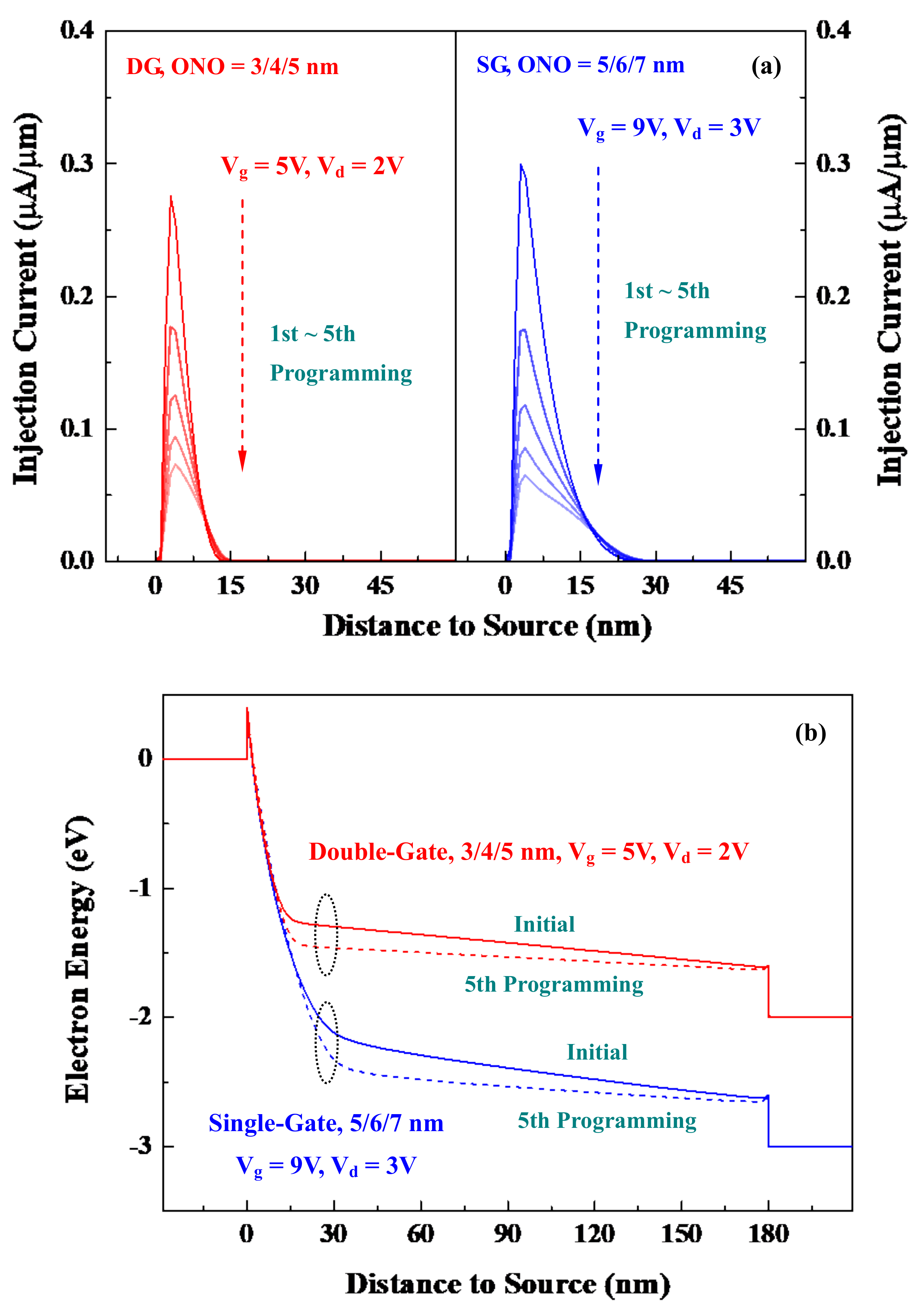
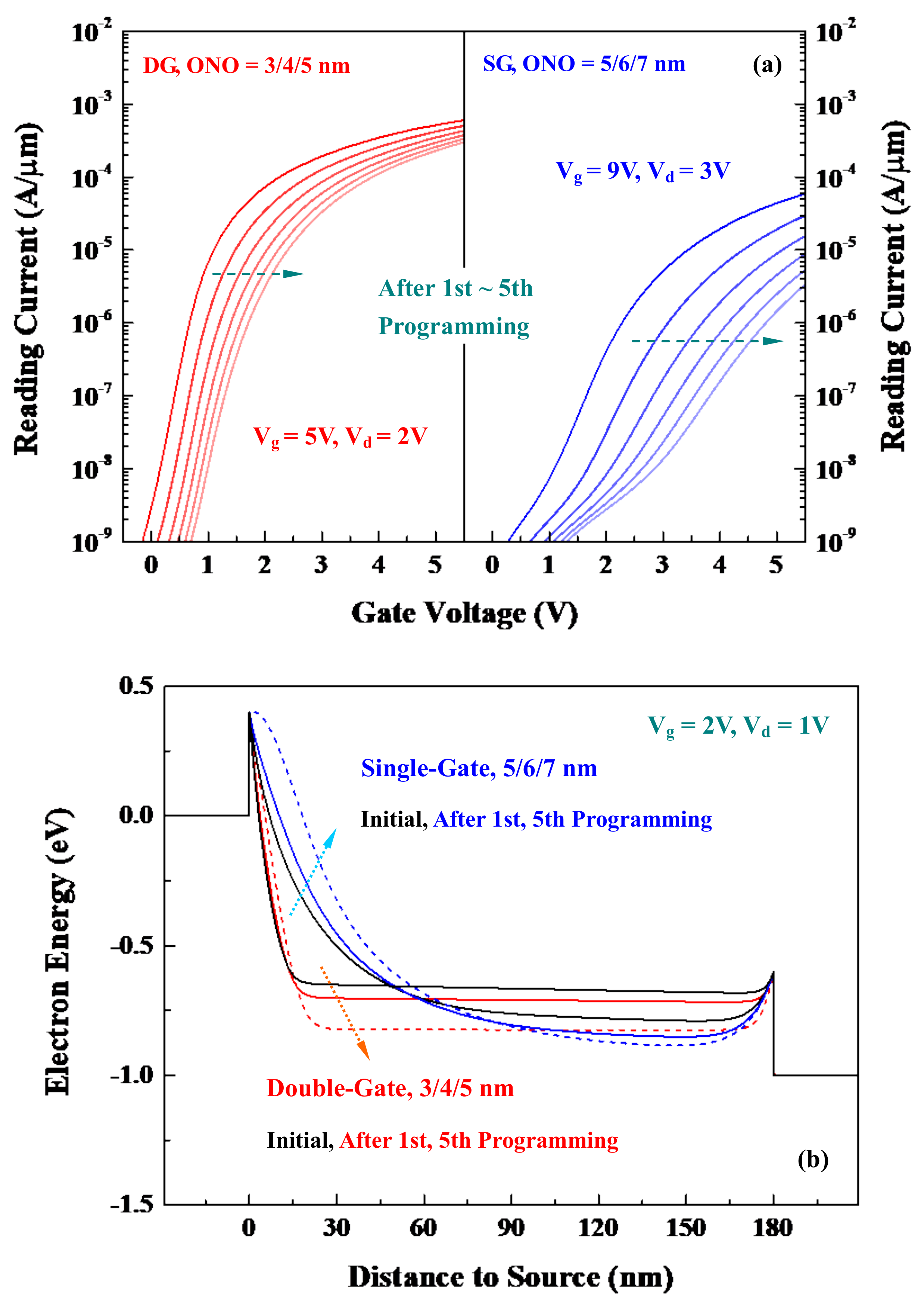
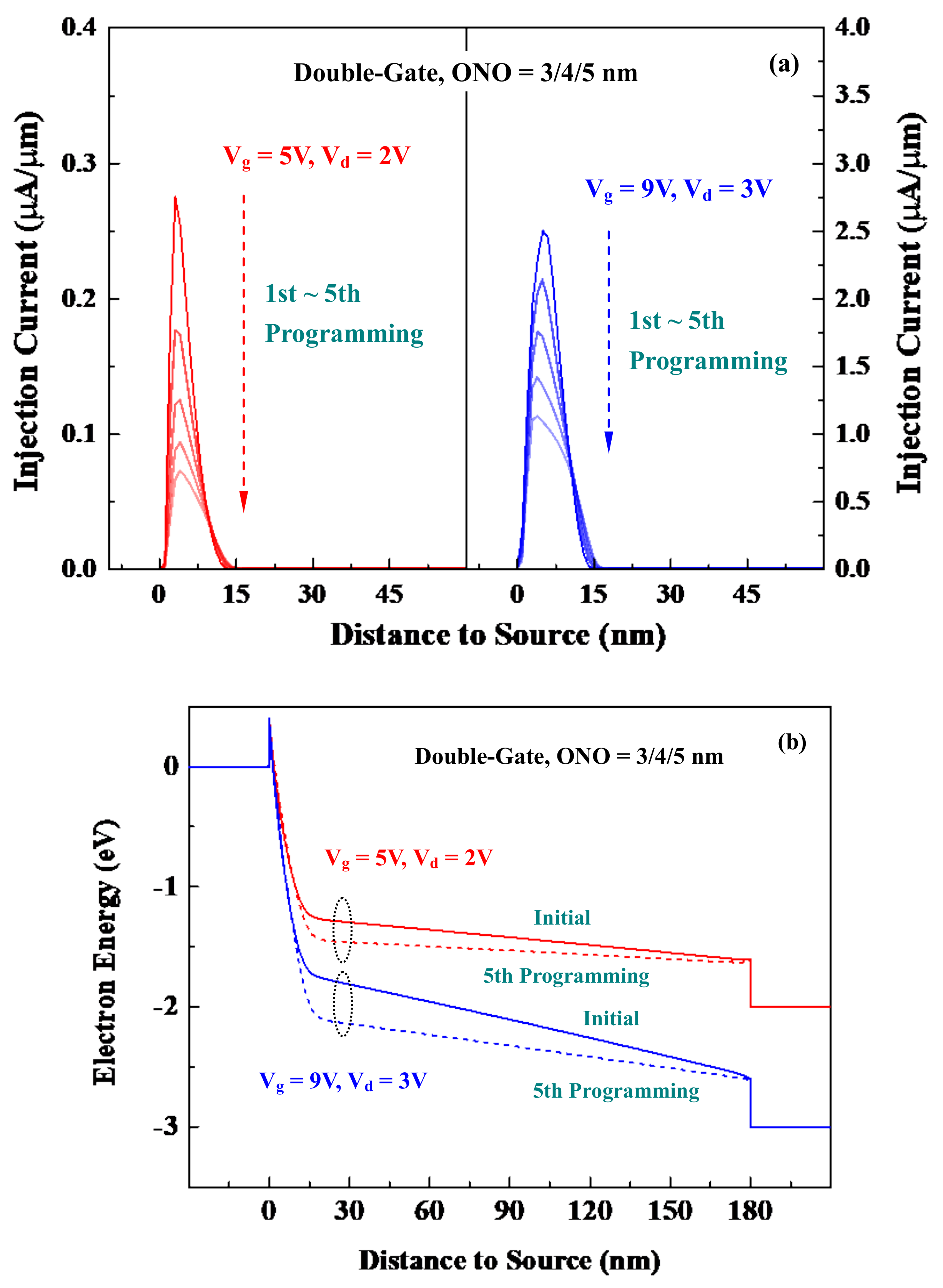
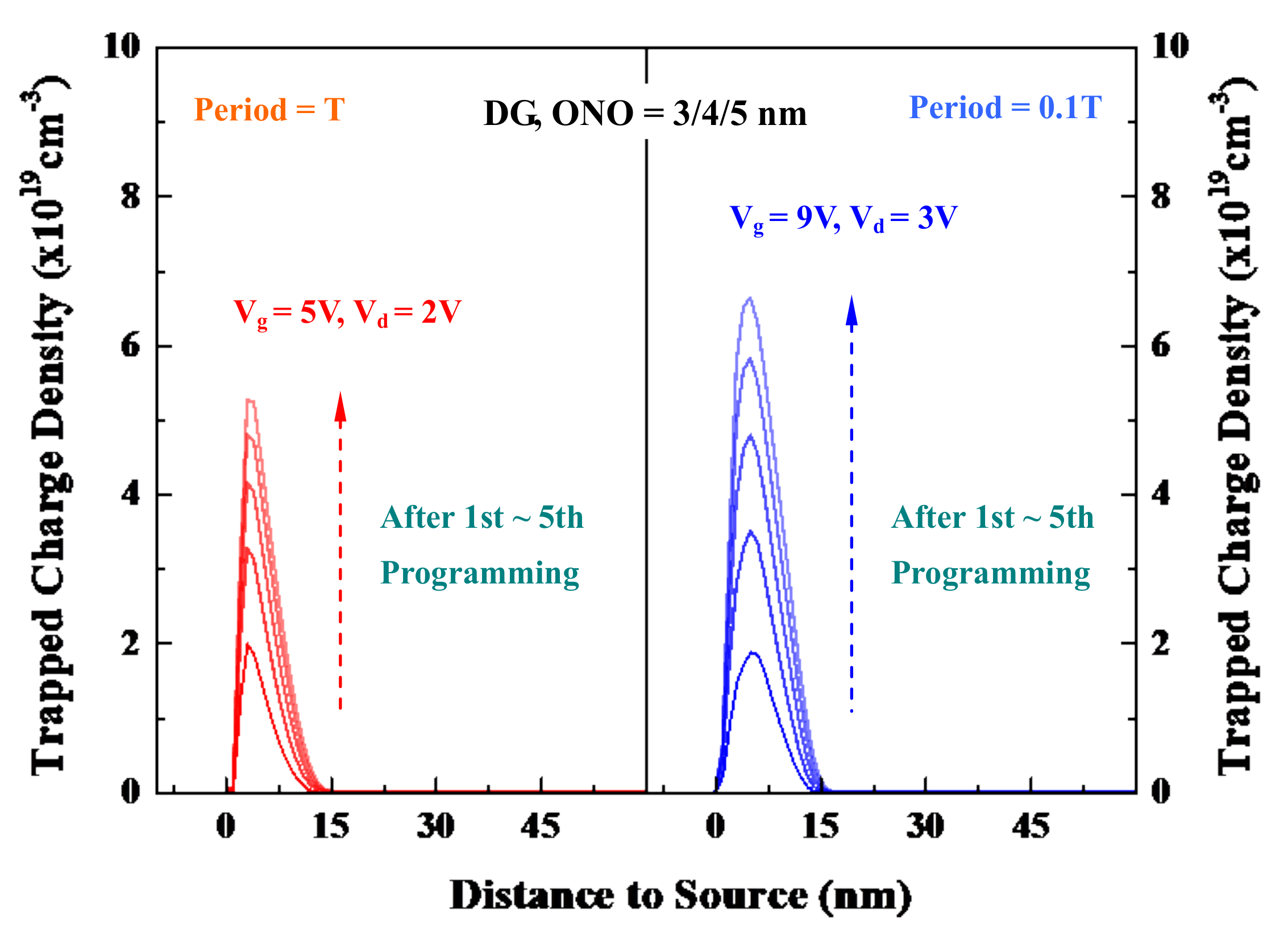
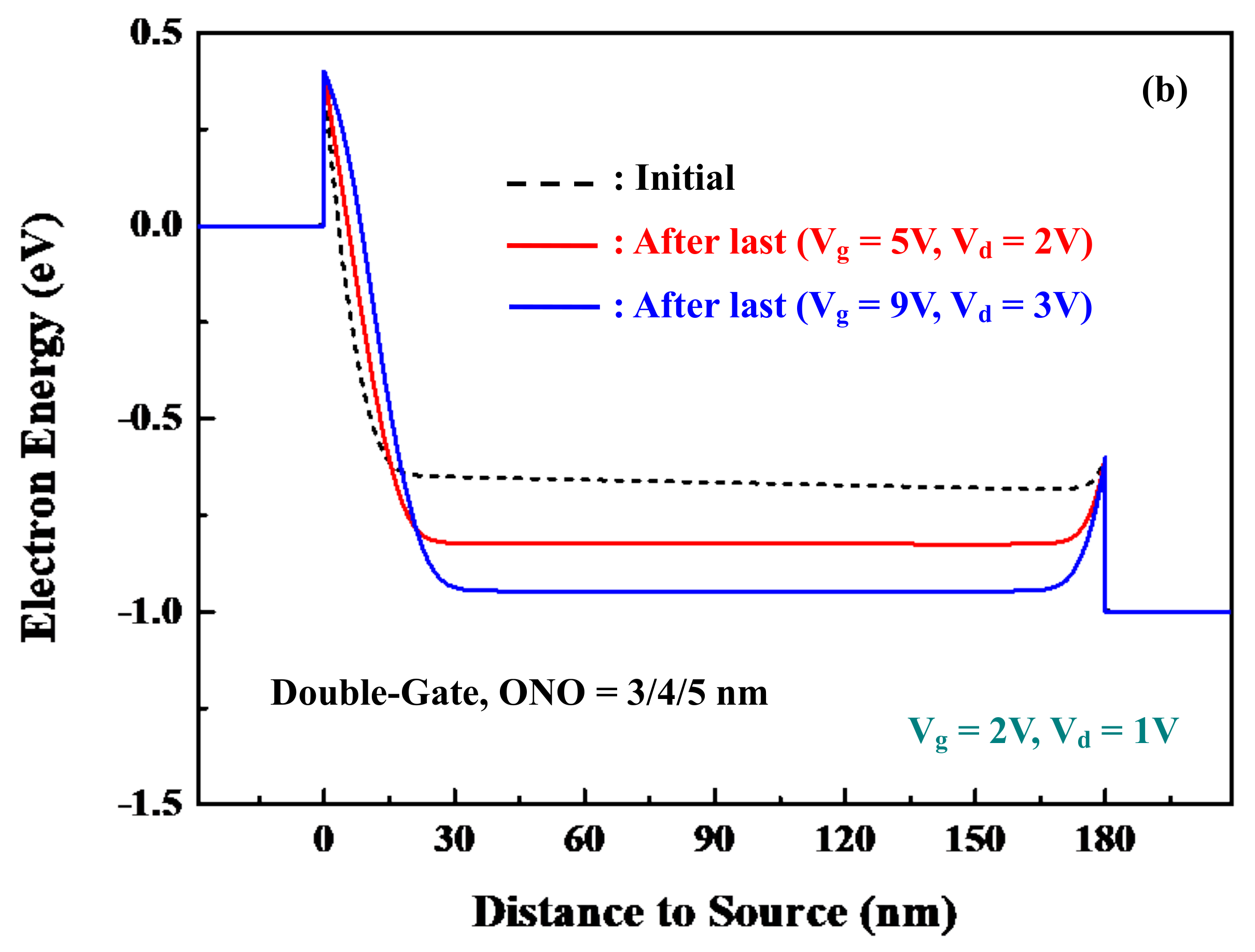
5.1. Successive Injection-Trapping Iterations
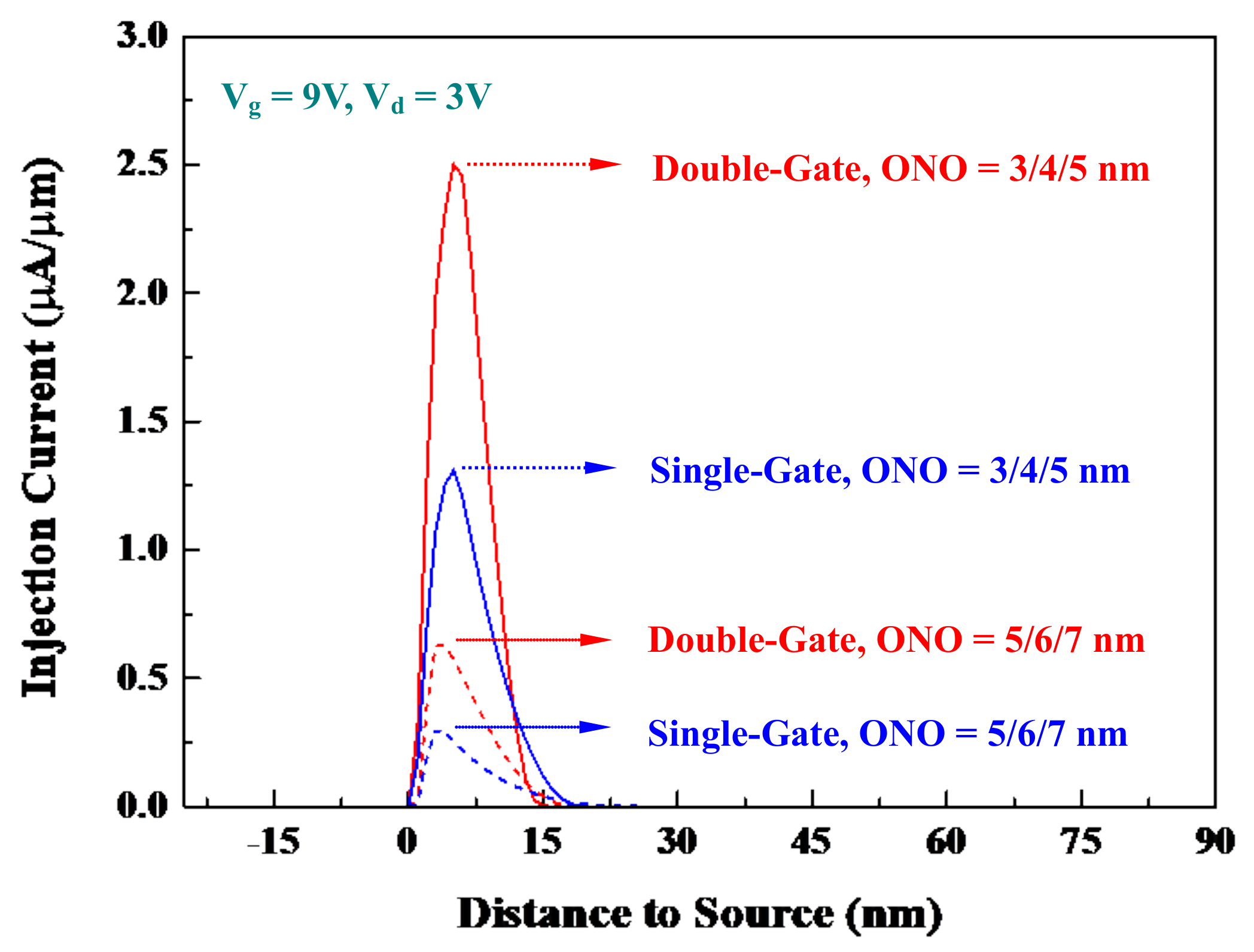
5.2. Scaled Double-Gate and Non-Scaled Single-Gate Cells
5.3. Low-Power and High-Efficiency Cells
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pak, J.; Chen, C.; Chang, K.-T.; Shetty, S.; Tu, A.; Neo, J.; Singh, P.; Amato, S.; Givant, A.; Thurgate, T.; et al. 40 nm & 22 nm Embedded Charge Trap Flash for Automotive Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Memory Workshop (IMW), Kyoto, Japan, 13–16 May 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, B.; Zhou, J.; Wu, S.; Jiang, H.; Chen, X.; Yang, W. Improving Flash Memory Performance and Reliability for Smartphones With I/O Deduplication. IEEE Trans. Comput. Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2019, 38, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Lee, Y.; Min, S.L. Framework for efficient and flexible scheduling of flash memory operations. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 6th Non-Volatile Memory Systems and Applications Symposium (NVMSA), Hsinchu, Taiwan, 16–18 August 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Park, B.-G.; Kim, Y. Implementation of Boolean Logic Functions in Charge Trap Flash for In-Memory Computing. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2019, 40, 1358–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, K.; Nagasawa, T.; Kaneda, Y.; Mitani, H.; Iwase, T.; Aoki, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Morioka, T.; Maekawa, K.; Ito, T.; et al. A 2T-MONOS Embedded Flash Macro With 65-nm SOTB Technology Achieving 0.15-pJ/bit Read Energy With 80-MHz Access for IoT Applications. IEEE Solid State Circuits Lett. 2020, 3, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nii, K.; Taniguchi, Y.; Okuyama, K. A Cost-Effective Embedded Nonvolatile Memory with Scalable LEE Flash®-G2 SONOS for Secure IoT and Computing-in-Memory (CiM) Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Symposium on VLSI Design, Automation and Test (VLSI-DAT), Hsinchu, Taiwan, 10–13 August 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, C.-X.; Chang, M.-F. Challenges in Circuit Designs of Nonvolatile-memory based computing-in-memory for AI Edge Devices. In Proceedings of the 2019 International SoC Design Conference (ISOCC), Jeju, Korea, 6–9 October 2019; pp. 164–165. [Google Scholar]
- Lue, H.-T.; Chen, W.; Chang, H.-S.; Wang, K.-C.; Lu, C.-Y. A Novel 3D AND-type NVM Architecture Capable of High-density, Low-power In-Memory Sum-of-Product Computation for Artificial Intelligence Application. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology, Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 177–178. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, C.-H.; Liang, J.-T. Nonvolatile Schottky Barrier Multibit Cell With Source-Side Injected Programming and Reverse Drain-Side Hole Erasing. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2010, 57, 1774–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.-H.; Liang, J.-T.; Luo, Y.-X. Reading Operation and Cell Scalability of Nonvolatile Schottky barrier Multibit Charge-Trapping Memory Cells. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2012, 59, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.-H.; Chang, W.; Luo, Y.-X.; Liang, J.-T.; Huang, M.-K.; Chien, N.D.; Shia, R.-K.; Tsai, J.-J.; Wu, W.-F.; Lien, C. Schottky Barrier Silicon Nanowire SONOS Memory With Ultralow Programming and Erasing Voltages. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2011, 32, 1477–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.-H.; Chang, W.; Wu, W.-F.; Lien, C. Multilevel Schottky Barrier Nanowire SONOS Memory with Ambipolar n- and p-Channel Cells. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2012, 59, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Shih, C.-H.; Luo, Y.-X.; Hsia, J.-K.; Wu, W.-F.; Lien, C. A Localized Two-Bit/Cell Nanowire SONOS Memory Using Schottky Barrier Source-Side Injected Programming. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2013, 12, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.-J.; Wu, W.F.; Chen, Y.H.; Teng, H.J.; Chien, N.D.; Shih, C.-H.; Tsai, J. Effects of High Temperatures on Cell Reading, Programming, and Erasing of Schottky Barrier Charge-Trapping Memories. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2019, 19, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, K.; Matsuzawa, K.; Koga, J.; Takagi, S.-I.; Toriumi, A. Enhancement of hot-electron generation rate in Schottky source metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 76, 3992–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.-H.; Liang, J.-T.; Wang, J.-S.; Chien, N.D. A Source-Side Injection Lucky Electron Model for Schottky Barrier Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor Devices. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2011, 32, 1331–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, J.; Snyder, J. Overview and status of metal S/D Schottky-barrier MOSFET technology. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2006, 53, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, R.T. The physics and chemistry of the Schottky barrier height. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2014, 1, 011304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Lee, J.; Shin, M. p-Type Nanowire Schottky Barrier MOSFETs: Comparative Study of Ge- and Si-Channel Devices. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2013, 61, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appenzeller, J.; Knoch, J.; Björk, M.T.; Riel, H.; Schmid, H.; Riess, W. Toward Nanowire Electronics. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2008, 55, 2827–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synopsys Inc. Synopsys MEDICI User’s Manual; Synopsys Inc.: Mountain View, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.-X.; Shih, C.-H. Coupling of carriers injection and charges distribution in Schottky barrier charge-trapping memories using source-side electrons programming. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2014, 29, 115006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.-H.; Lo, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Tsai, J.-J. Impact of gate-to-source/drain misalignments on source-side injection Schottky barrier charge-trapping memory cells evaluated using numerical programming-trapping iterations. Microelectron. Reliab. 2017, 74, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.-H.; Huang, M.-K.; Tsai, J.-J.; Chen, Y.-H.; Wu, W.-F. Metallic Schottky barrier source/drain nanowire transistors using low-temperature microwave annealed nickel, ytterbium, and titanium silicidation. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 70, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.-C.; Seol, M.-L.; Hur, J.; Moon, D.-I.; Lee, B.-H.; Han, J.-W.; Park, J.-Y.; Jeon, S.-B.; Choi, Y.-K. Ultra-Fast Erase Method of SONOS Flash Memory by Instantaneous Thermal Excitation. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2015, 37, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-H.; Jiang, C.-M.; Chen, W.-C.; Wang, T.; Tsai, W.-J.; Lu, T.-C.; Chen, K.-C.; Lu, C.-Y. Electric Field Induced Nitride Trapped Charge Lateral Migration in a SONOS Flash Memory. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2016, 38, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohara, P.; Vishvakarma, S.K. Self-Amplified Tunneling-Based SONOS Flash Memory Device With Improved Performance. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2018, 65, 4297–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, K.; Uchida, K.; Nishiyama, A. A unified simulation of Schottky and ohmic contacts. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2000, 47, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieong, M.; Solomon, P.; Laux, S.; Wong, H.-S.; Chidambarrao, D. Comparison of raised and Schottky source/drain MOSFETs using a novel tunneling contact model. In Proceedings of the International Electron Devices Meeting 1998. Technical Digest (Cat. No.98CH36217), San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–9 December 1998; pp. 733–736. [Google Scholar]
- Iwai, H.; Ohguro, T.; Ohmi, S.-I. NiSi salicide technology for scaled CMOS. Microelectron. Eng. 2002, 60, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, H.; Ohguro, T.; Ohmi, S.-I. Challenges of nickel silicidation in CMOS technologies. Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 137, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, T.; Ko, P.; Hu, C. A simple method to characterize substrate current in MOSFET’s. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 1984, 5, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, S.; Ko, P.-K.; Hu, C. Lucky-electron model of channel hot-electron injection in MOSFET’S. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1984, 31, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnat, K.; Yeap, C.-F.; Jallepalli, S.; Shih, W.-K.; Hareland, S.; Agostinelli, V.; Tasch, A.; Maziar, C. A pseudo-lucky electron model for simulation of electron gate current in submicron NMOSFET’s. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1996, 43, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igura, Y.; Matsuoka, H.; Takeda, E. New device degradation due to “cold” carriers created by band-to-band tunneling. IEEE Electron Devices Lett. 1989, 10, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teng, H.-J.; Chen, Y.-H.; Tsai, J.-J.; Chien, N.D.; Lien, C.; Shih, C.-H. Transverse Scaling of Schottky Barrier Charge-Trapping Cells for Energy-Efficient Applications. Crystals 2020, 10, 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10111036
Teng H-J, Chen Y-H, Tsai J-J, Chien ND, Lien C, Shih C-H. Transverse Scaling of Schottky Barrier Charge-Trapping Cells for Energy-Efficient Applications. Crystals. 2020; 10(11):1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10111036
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeng, Hung-Jin, Yu-Hsuan Chen, Jr-Jie Tsai, Nguyen Dang Chien, Chenhsin Lien, and Chun-Hsing Shih. 2020. "Transverse Scaling of Schottky Barrier Charge-Trapping Cells for Energy-Efficient Applications" Crystals 10, no. 11: 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10111036
APA StyleTeng, H.-J., Chen, Y.-H., Tsai, J.-J., Chien, N. D., Lien, C., & Shih, C.-H. (2020). Transverse Scaling of Schottky Barrier Charge-Trapping Cells for Energy-Efficient Applications. Crystals, 10(11), 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10111036





