Effect of Transition Metal Additives on the Catalytic Performance of Cu–Mn/SAPO-34 for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3 at Low Temperature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Calculation of NH3, NO, H2O, or SO2 Adsorption on Different Transition Metal Oxides
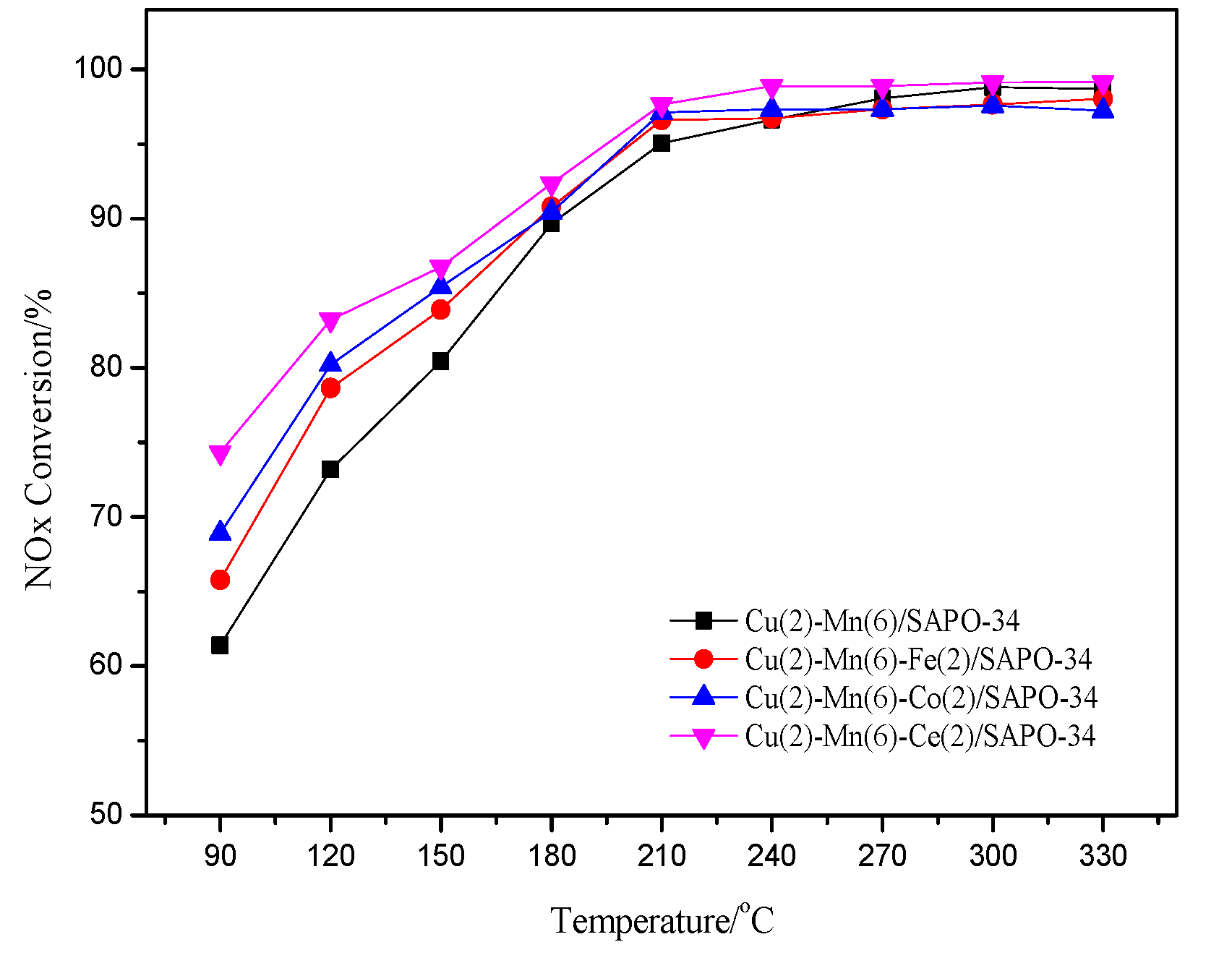
2.2. Changes of Catalyst Activity after Adding Transition Metals
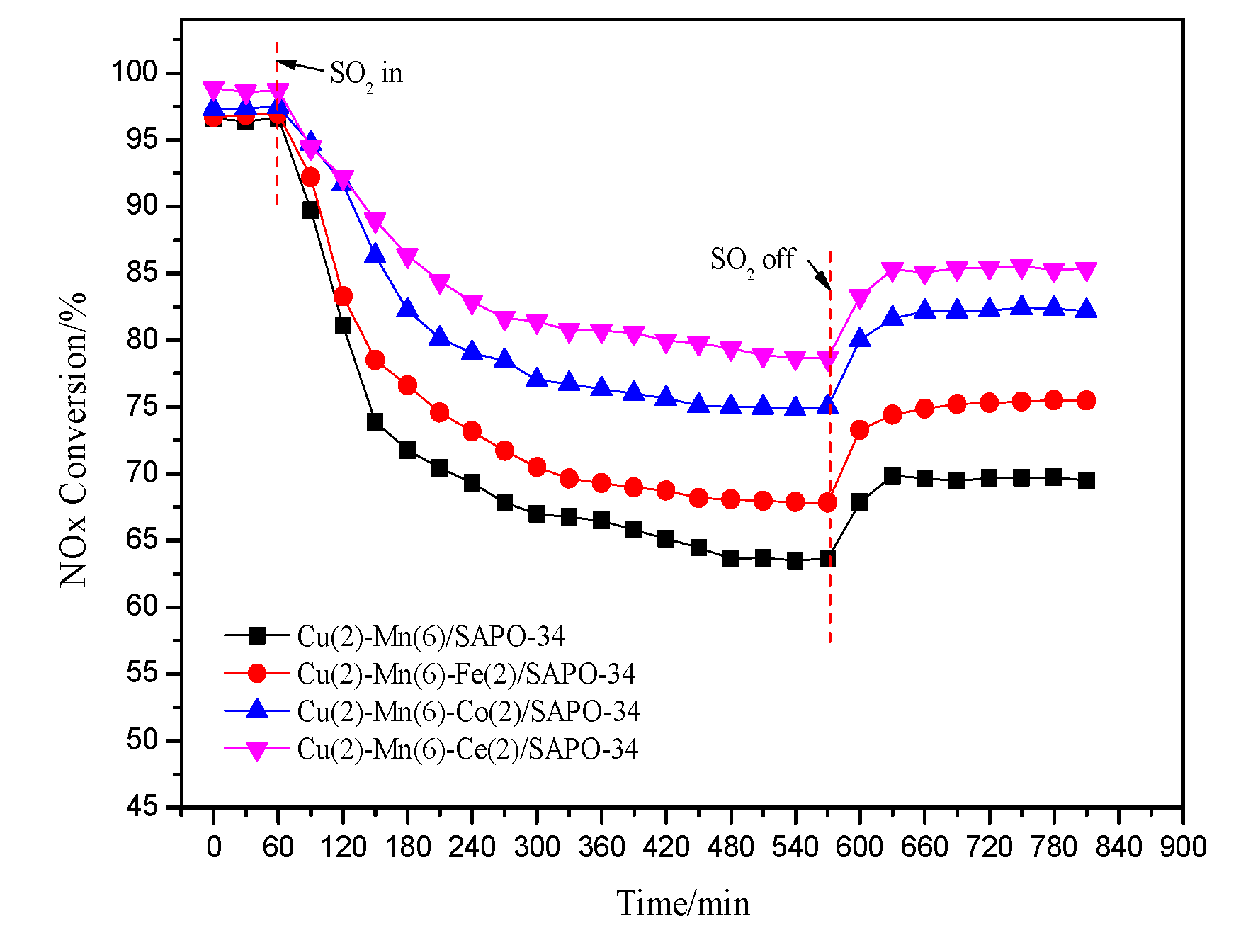
2.3. Changes of SO2 Resistance Performance of Catalyst after Adding Different Transition Metal Additive
2.4. Catalyst Characterization
2.4.1. BET Analysis
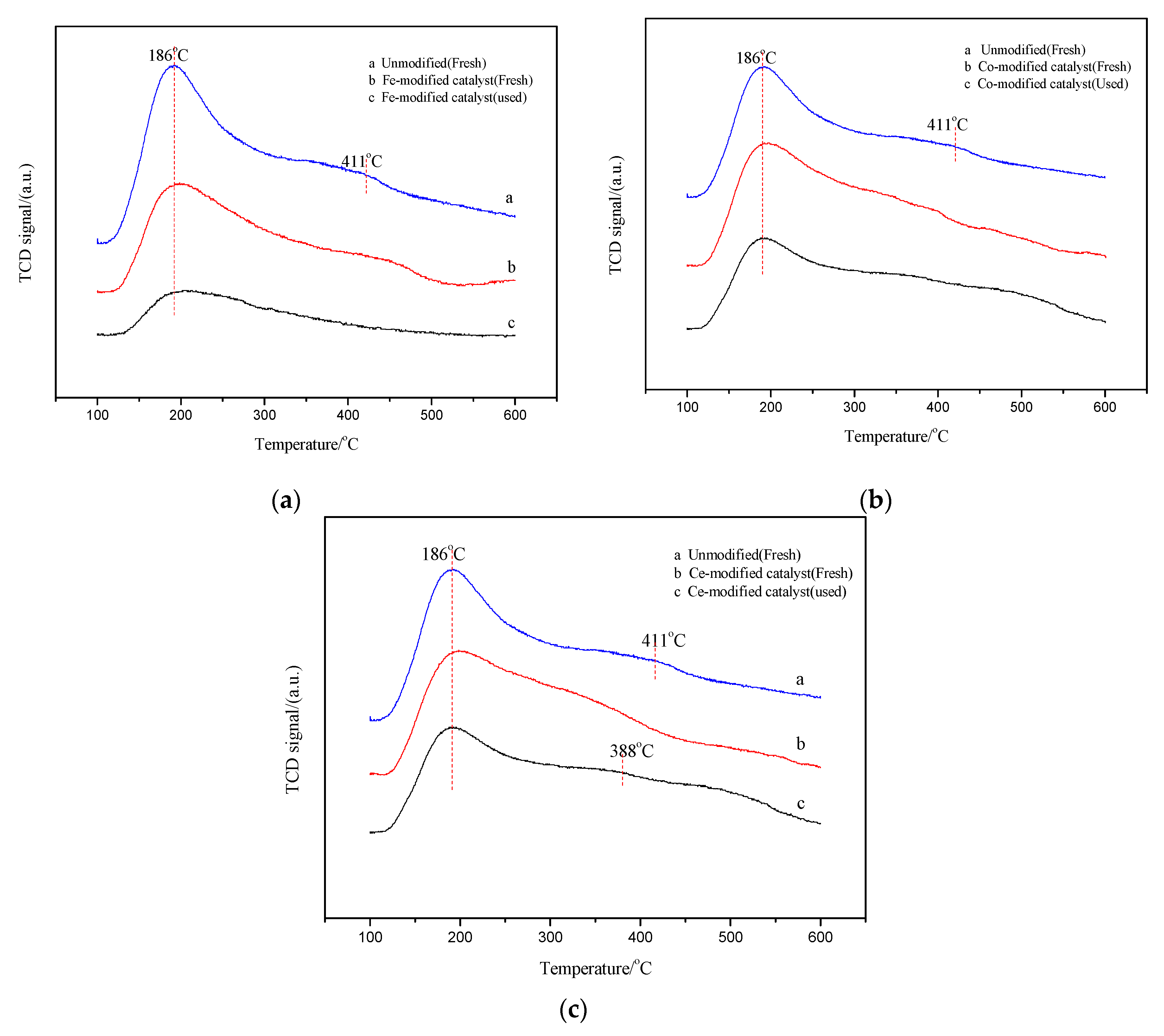
2.4.2. Temperature Programmed Desorption of Ammonia (NH3-TPD) Analysis
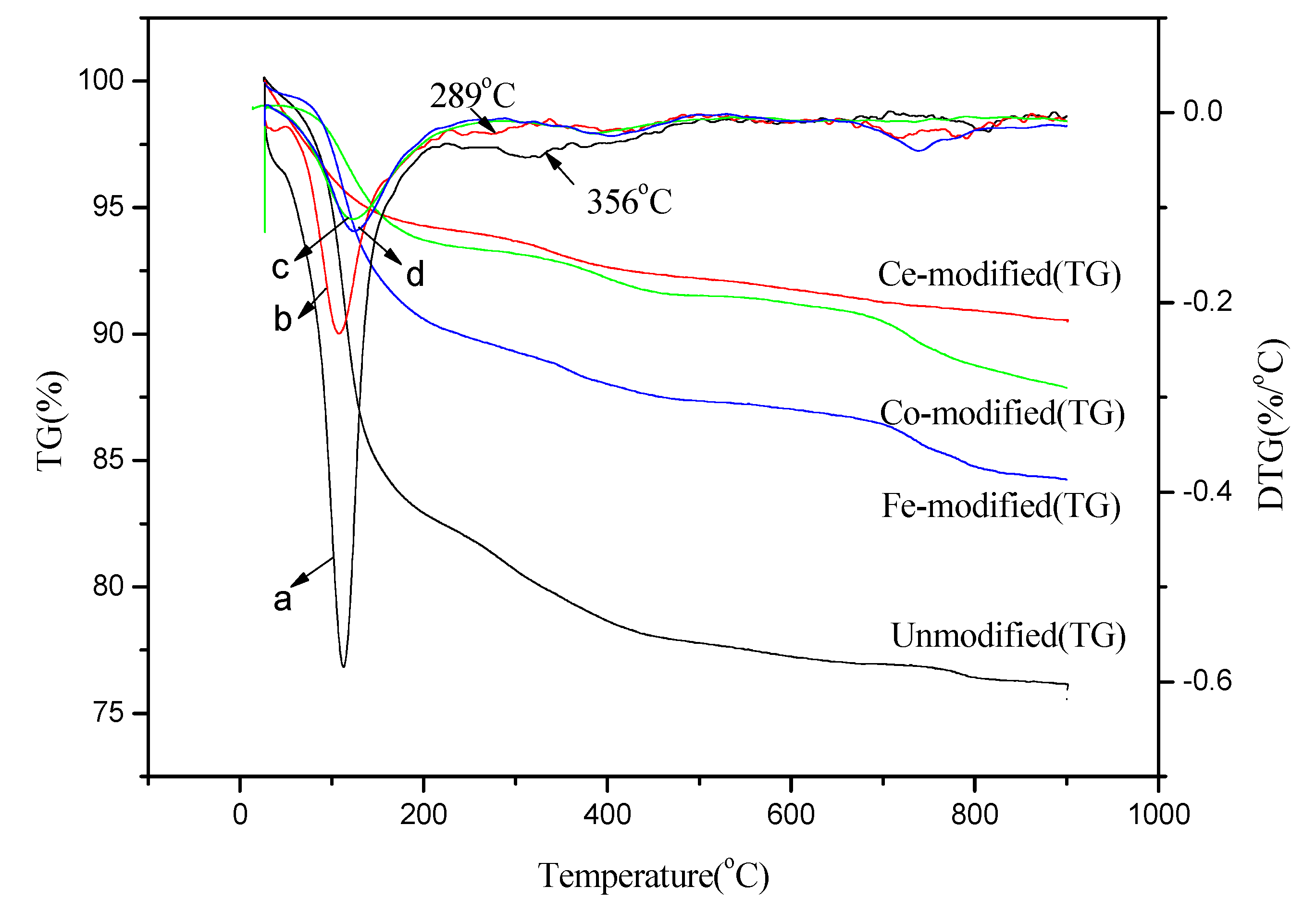
2.4.3. TG-differential thermal gravity (DTG) Analysis
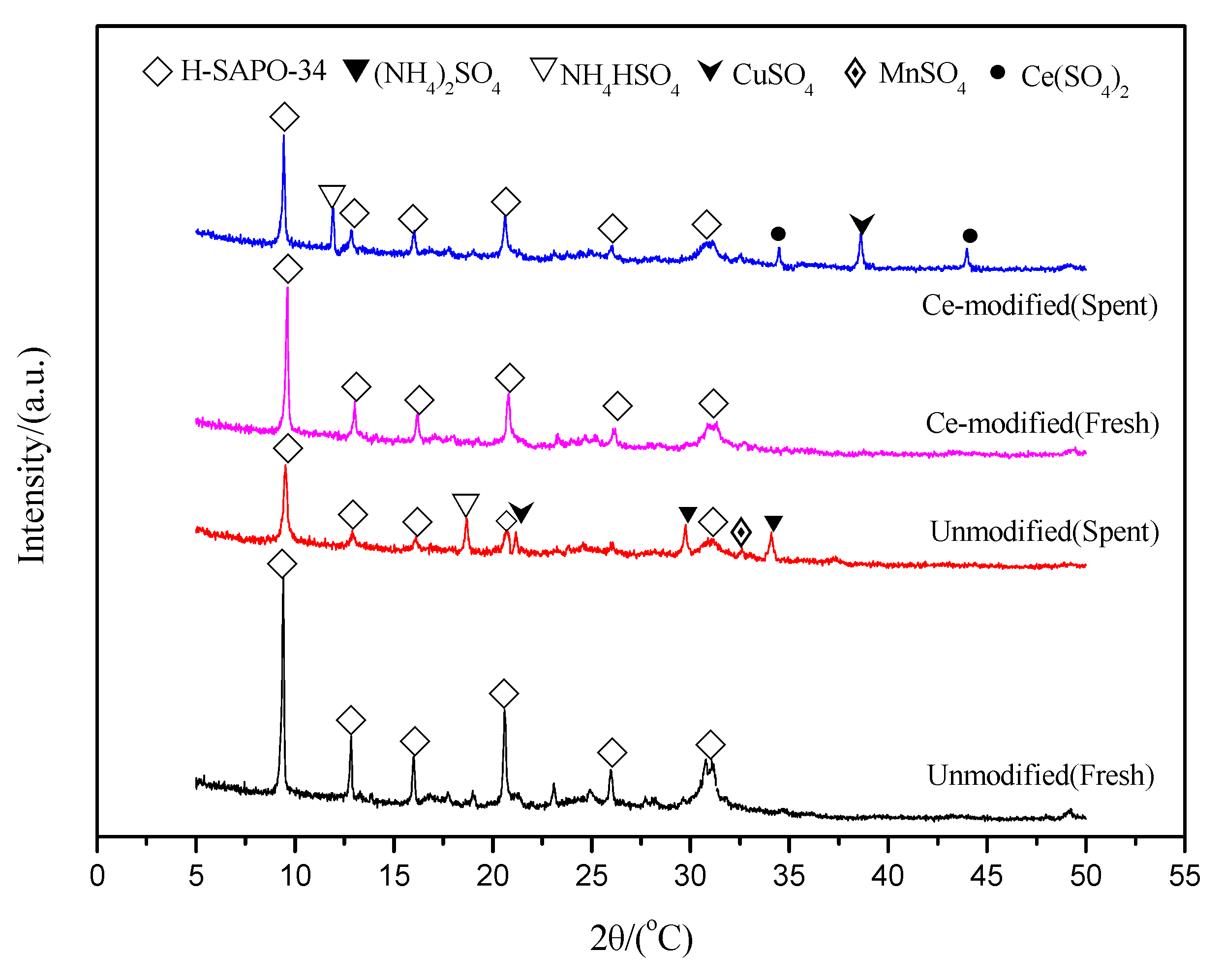
2.4.4. XRD Analysis
2.4.5. SEM and EDX Analysis
3. Experimental
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.2. Catalytic Activity Measurement
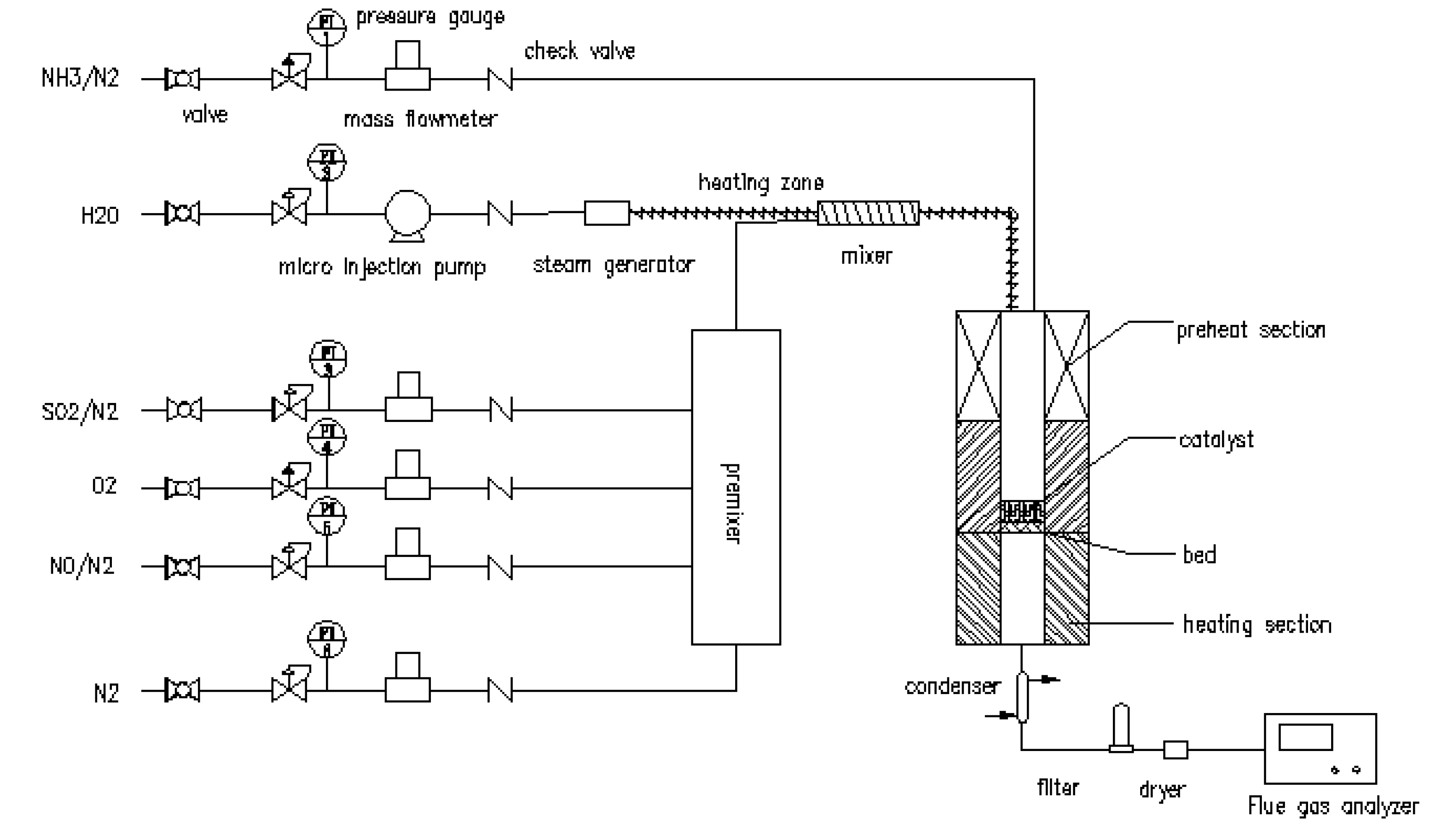
3.3. Catalyst Characterization
3.4. Calculation Details
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Q. Formation and reaction of ammonium sulfate salts on V2O5/AC catalyst during selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide by ammonia at low temperatures. J. Catal. 2003, 214, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G.; Lietti, L.; Ramis, G.; Berti, F. Chemical and mechanistic aspects of the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by ammonia over oxide catalysts: A review. Appl. Catal. B 1998, 18, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.P.; Stenger, H.G., Jr.; Wachs, I.E. Oxidation of SO2 over Supported Metal Oxide Catalysts. J. Catal. 1999, 181, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Tong, Z.; Huang, Y. Selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperatures over iron and manganese oxides supported on mesoporous silica. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 78, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.S.; Gao, X.; Cui, L.W.; Fu, Y.C.; Luo, Z.Y.; Cen, K.F. Investigation of the effect of Cu addition on the SO2-resistance of a CeTi oxide catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Fuel 2012, 92, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; He, H. Structure−Activity Relationship of Iron Titanate Catalysts in the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 16929–16936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Cai, S.; Li, H.; Huang, L.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D. Mechanistic Aspects of deNO x Processing over TiO2 Supported Co–Mn Oxide Catalysts: Structure–Activity Relationships and In Situ DRIFTs Analysis. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6069–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Zhong, Q. Promotional effect of F-doped V2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalyst for NH3-SCR of NO at low-temperature. Appl. Catal. A 2012, 435, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, M.; Forser, S.; Thormählen, P.; Skoglundh, M. Screening of TiO2-supported catalysts for selective NOx reduction with ammonia. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 7723–7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantcheva, M. FT-IR spectroscopic investigation of the reactivity of NOx species adsorbed on Cu2+/ZrO2 and CuSO4/ZrO2 catalysts toward decane. Appl. Catal. B 2003, 42, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Cheng, Y.; Cavataio, G.; McCabe, R.W.; Fu, L.; Li, J. Characterization of commercial Cu-SSZ-13 and Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts with hydrothermal treatment for NH3-SCR of NOx in diesel exhaust. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ling, W.; Huang, B.; Dong, L.; Yu, C.; Xi, H. The synergistic effects of cerium presence in the framework and the surface resistance to SO2 and H2O in NH3-SCR. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 56, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, W.; He, P.; Guan., S.; Yuan, B.; Li, R.; Shen, D. H2O and/or SO2 Tolerance of Cu-Mn/SAPO-34 Catalyst for NO Reduction with NH3 at Low Temperature. Catalysts 2019, 9, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyoura, R.; Urano, K. Mechanism, kinetics, and equilibrium of thermal decomposition of ammonium sulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1970, 9, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Niu, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S. Decomposition and reactivity of NH4HSO4 on V2O5/AC catalysts used for NO reduction with ammonia. J. Catal. 2000, 195, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayanti, K.; Andonova, S.; Kumar, A.; Li, J.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.W.; Yezerets, A.; Olsson, L. Impact of sulfur oxide on NH3-SCR over Cu-SAPO-34. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 166, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.Q.; Wu, Z.B.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, W.K. DRIFT study of the SO2 effect on low-temperature SCR reaction over Fe− Mn/TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 4961–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Ma, L.; Yang, S.; Schwank, J.W.; Hao, J. Effect of Sn on MnOx–CeO2 catalyst for SCR of NOx by ammonia: Enhancement of activity and remarkable resistance to SO2. Catal. Commun. 2012, 27, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Tang, X.; Yi, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Chu, C.; Li, C. Promotional mechanisms of activity and SO2 tolerance of Co-or Ni-doped MnOx-CeO2 catalysts for SCR of NOx with NH3 at low temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Huang, X.; Yang, X.; Tang, Z. Comprehensive study of the promotional mechanism of F on Ce–Mo/TiO 2 catalysts for wide temperature NH 3-SCR performance: the activation of surface [triple bond, length as m-dash] Ti–F bonds. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 2231–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Kong, T.; Chen, L.; Ding, S.; Yang, F.; Dong, L. Enhanced low-temperature NH3-SCR performance of MnOx/CeO2 catalysts by optimal solvent effect. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 420, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Su, F.; Gao, S.; Xu, G. Sulfur poisoning resistant mesoporous Mn-base catalyst for low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 95, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Xiao, X.; Liao, Y.; Dang, H.; Shan, W.; Yang, S. Global kinetic study of NO reduction by NH3 over V2O5–WO3/TiO2: Relationship between the SCR performance and the key factors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 11011–11023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Chang, H.; Ma, L.; Peng, Y.; Qu, Z.; Yan, N.; Wang, C.; Li, J. Novel effect of SO2 on the SCR reaction over CeO2: Mechanism and significance. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 136, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Jin, R.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Effect of ceria doping on SO2 resistance of Mn/TiO2 for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperature. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cen, W.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Weng, X. The role of cerium in the improved SO2 tolerance for NO reduction with NH3 over Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst at low temperature. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 148, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Gu, T. Relationship between SO2 poisoning effects and reaction temperature for selective catalytic reduction of NO over Mn–Ce/TiO2 catalyst. Catal. Today 2010, 153, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, B.; Shi, K.; He, S.; Liu, X.; Du, Z.; Yang, K. Preparation and characterization of nanocrystal grain TiO2 porous microspheres. Appl. Catal. B 2003, 40, 253–258. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.J.; Shu, H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Yang, H.M.; Yang, L.J. Formation and decomposition of NH4HSO4 during selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 150, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemany, L.J.; Berti, F.; Busca, G.; Ramis, G.; Robba, D.; Toledo, G.P.; Trombetta, M. Characterization and composition of commercial V2O5&z. sbnd; WO3&z. sbnd; TiO2 SCR catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 1996, 10, 299–311. [Google Scholar]
- Long, R.Q.; Yang, R.T. Characterization of Fe-ZSM-5 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide by ammonia. J. Catal. 2000, 194, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, M.; Murata, Y.; Kishikawa, K.; Zhang, D.; Ikeue, K. On the reasons for high activity of CeO2 catalyst for soot oxidation. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 4489–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.W.; Nam, K.B.; Hong, S.C. The role of ceria on the activity and SO2 resistance of catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 196, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
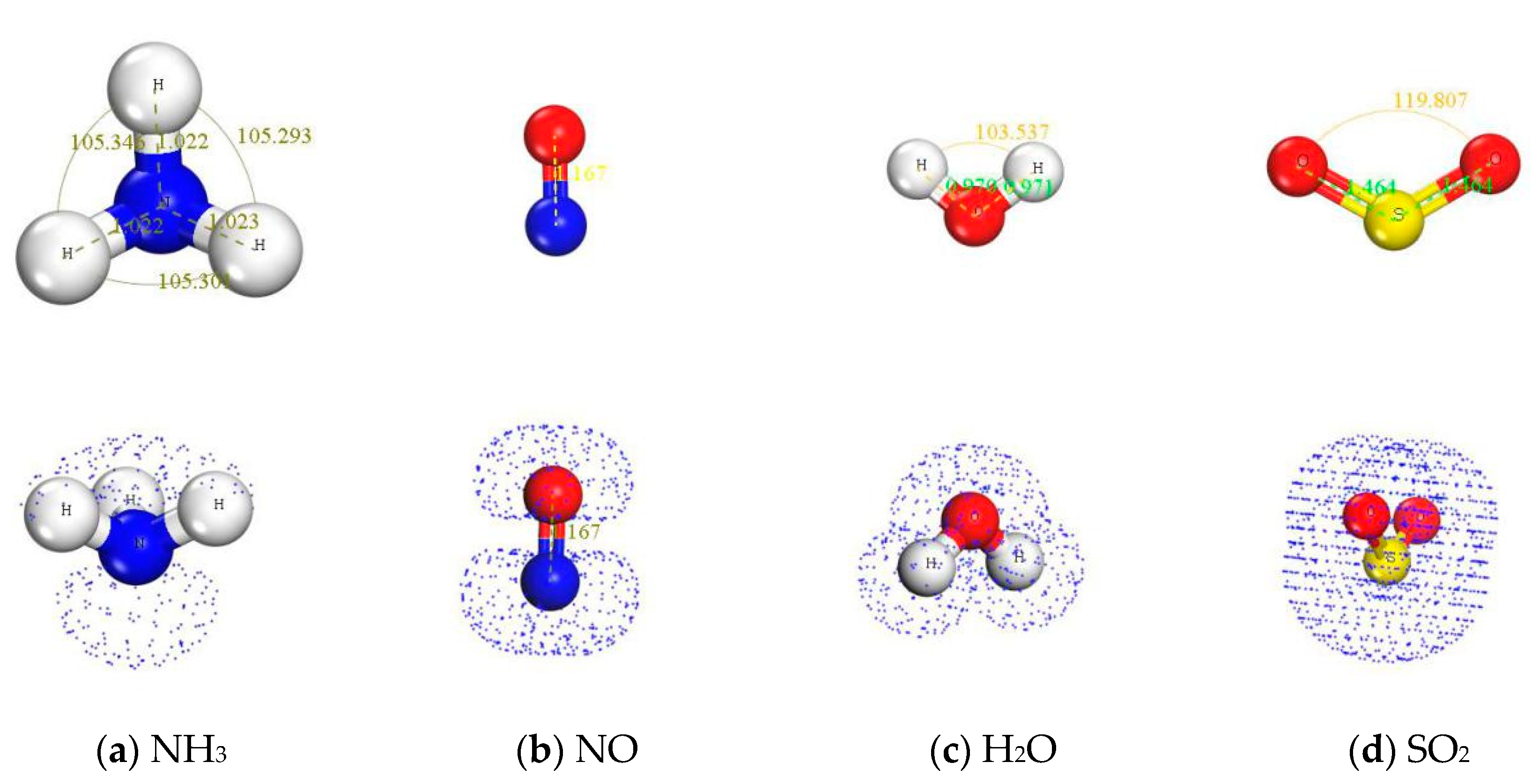

| Adsorption Base | Adsorbents | Adsorption Energy/eV | Bond length/Å | Bond Angle/° | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Adsorption | After Adsorption | Before Adsorption | After Adsorption | |||
| MnOx(001) | NH3 | −2.03875 | 1.022 | 1.023 | 105.293 | 108.475 |
| 1.022 | 1.023 | 105.346 | 108.497 | |||
| 1.023 | 1.023 | 105.301 | 108.309 | |||
| NO | −1.05696 | 1.167 | 1.224 | 180 | 180 | |
| H2O | −1.10298 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 103.537 | 103.317 | |
| 0.971 | 1 | |||||
| SO2 | −2.20810 | 1.464 | 1.572 | 119.807 | 112.639 | |
| 1.464 | 1.572 | |||||
| CuOx(001) | NH3 | −3.52843 | 1.022 | 1.036 | 105.293 | 106.817 |
| 1.022 | 1.036 | 105.346 | 106.817 | |||
| 1.023 | 1.037 | 105.301 | 106.742 | |||
| NO | −1.76270 | 1.167 | 1.201 | 180 | 180 | |
| H2O | −1.11959 | 0.97 | 0.988 | 103.537 | 106.312 | |
| 0.971 | 0.979 | |||||
| SO2 | −6.13501 | 1.464 | 1.614 | 119.807 | 107.336 | |
| 1.464 | 1.614 | |||||
| CeOx(001) | NH3 | −3.25139 | 1.022 | 1.034 | 105.293 | 107.880 |
| 1.022 | 1.034 | 105.346 | 107.872 | |||
| 1.023 | 1.034 | 105.301 | 107.791 | |||
| NO | −1.60770 | 1.167 | 1.205 | 180 | 180 | |
| H2O | −0.86146 | 0.97 | 0.991 | 103.537 | 105.937 | |
| 0.971 | 0.991 | |||||
| SO2 | −2.57682 | 1.464 | 1.558 | 119.807 | 112.783 | |
| 1.464 | 1.557 | |||||
| FeOx(001) | NH3 | −3.16140 | 1.022 | 1.033 | 105.293 | 108.603 |
| 1.022 | 1.033 | 105.346 | 108.636 | |||
| 1.023 | 1.033 | 105.301 | 108.564 | |||
| NO | −1.59895 | 1.167 | 1.20 | 180 | 180 | |
| H2O | −1.29654 | 0.97 | 0.987 | 103.537 | 104.996 | |
| 0.971 | 1.030 | |||||
| SO2 | −2.69020 | 1.464 | 1.554 | 119.807 | 113.179 | |
| 1.464 | 1.555 | |||||
| CoOx(001) | NH3 | −2.79458 | 1.022 | 1.033 | 105.293 | 108.971 |
| 1.022 | 1.034 | 105.346 | 109.051 | |||
| 1.023 | 1.034 | 105.301 | 108.835 | |||
| NO | −1.59260 | 1.167 | 1.208 | 180 | 180 | |
| H2O | −1.02839 | 0.97 | 0.993 | 103.537 | 104.911 | |
| 0.971 | 0.994 | |||||
| SO2 | −2.37824 | 1.464 | 1.629 | 119.807 | 113.453 | |
| 1.464 | 1.630 | |||||
| MoOx(001) | NH3 | −1.86400 | 1.022 | 1.028 | 105.293 | 110.208 |
| 1.022 | 1.028 | 105.346 | 110.182 | |||
| 1.023 | 1.029 | 105.301 | 110.251 | |||
| NO | −1.02833 | 1.167 | 1.180 | 180 | 180 | |
| H2O | −1.16968 | 0.97 | 0.987 | 103.537 | 105.752 | |
| 0.971 | 0.987 | |||||
| SO2 | −3.07422 | 1.464 | 1.540 | 119.807 | 113.453 | |
| 1.464 | 1.540 | |||||
| CrOx(001) | NH3 | −2.75508 | 1.022 | 1.027 | 105.293 | 107.530 |
| 1.022 | 1.028 | 105.346 | 107.433 | |||
| 1.023 | 1.029 | 105.301 | 107.470 | |||
| NO | −1.49119 | 1.167 | 1.206 | 180 | 180 | |
| H2O | −1.12858 | 0.97 | 0.995 | 103.537 | 106.029 | |
| 0.971 | 0.995 | |||||
| SO2 | −3.22779 | 1.464 | 1.559 | 119.807 | 113.015 | |
| 1.464 | 1.560 | |||||
| RuOx(001) | NH3 | −1.11775 | 1.022 | 1.032 | 105.293 | 109.292 |
| 1.022 | 1.031 | 105.346 | 109.044 | |||
| 1.023 | 1.032 | 105.301 | 109.714 | |||
| NO | −0.87561 | 1.167 | 1.200 | 180 | 180 | |
| H2O | −0.10325 | 0.97 | 0.971 | 103.537 | 103.537 | |
| 0.971 | 0.970 | |||||
| SO2 | −2.65537 | 1.464 | 1.549 | 119.807 | 112.669 | |
| 1.464 | 1.553 | |||||
| Catalyst | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Diameter (nm) | BET Relative Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh catalyst | 457 | 0.23 | 2.08 | 27.4 |
| Used catalyst | 332 | 0.16 | 2.15 | |
| Fe-modified catalyst (Fresh) | 399 | 0.21 | 2.03 | 18.6 |
| Fe-modified catalyst (Used) | 325 | 0.14 | 3.34 | |
| Co-modified catalyst (Fresh) | 402 | 0.17 | 2.22 | 11.1 |
| Co-modified catalyst (Used) | 357 | 0.15 | 2.35 | |
| Ce-modified catalyst (Fresh) | 423 | 0.19 | 2.14 | 7.8 |
| Ce-modified catalyst (Used) | 390 | 0.16 | 2.18 |
| O | Si | Al | P | Cu | Mn | Ce | Co | Fe | S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unmodified (Fresh) | 62.57 | 3.51 | 16.47 | 13.98 | 1.11 | 2.36 | – | – | – | – |
| Unmodified (Spent) | 59.54 | 3.19 | 16.42 | 14.76 | 1.24 | 3.37 | – | – | – | 1.48 |
| Ce-modified (Spent) | 57.09 | 4.33 | 19.74 | 10.62 | 1.46 | 4.52 | 1.89 | – | – | 0.35 |
| Co-modified (Spent) | 55.63 | 4.71 | 18.77 | 12.31 | 1.28 | 4.82 | – | 1.84 | – | 0.64 |
| Fe-modified (Spent) | 55.94 | 4.13 | 16.32 | 14.49 | 1.45 | 4.63 | – | – | 1.91 | 1.13 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, G.; Zhang, W.; He, P.; Shen, D.; Wu, C.; Gong, C. Effect of Transition Metal Additives on the Catalytic Performance of Cu–Mn/SAPO-34 for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3 at Low Temperature. Catalysts 2019, 9, 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080685
Liu G, Zhang W, He P, Shen D, Wu C, Gong C. Effect of Transition Metal Additives on the Catalytic Performance of Cu–Mn/SAPO-34 for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3 at Low Temperature. Catalysts. 2019; 9(8):685. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080685
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Guofu, Wenjie Zhang, Pengfei He, Dekui Shen, Chunfei Wu, and Chenghong Gong. 2019. "Effect of Transition Metal Additives on the Catalytic Performance of Cu–Mn/SAPO-34 for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3 at Low Temperature" Catalysts 9, no. 8: 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080685
APA StyleLiu, G., Zhang, W., He, P., Shen, D., Wu, C., & Gong, C. (2019). Effect of Transition Metal Additives on the Catalytic Performance of Cu–Mn/SAPO-34 for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3 at Low Temperature. Catalysts, 9(8), 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080685






