The Low Temperature Solvent-Free Aerobic Oxidation of Cyclohexene to Cyclohexane Diol over Highly Active Au/Graphite and Au/Graphene Catalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Catalyst Preparation
4.2.1. Impregnation
4.2.2. Sol Immobilisation
4.3. Catalyst Characterization
4.4. Catalyst Testing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheldon, R.A. Fundamentals of green chemistry: Efficiency in reaction design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1437–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellan, A.; Bart, J.C.J.; Cavallaro, S. Synthesis of adipic acid via nitric acid oxidation of cyclohexanol in a two-step continuous process. Catal. Today 1991, 9, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, A.F. Nitric acid oxidation design in the manufacture of adipic acid from cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1954, 3, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, R.A.; Slaten, C.S.; Seapan, M.; Lower, M.W.; Tomlinson, P.E. Abatement of N2O emissions produced in the adipic acid industry. Environ. Prog. 1994, 13, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Luo, G.; Chu, Y.; Wei, F. Experimental and modeling analysis of NO reduction by CO for a FCC regeneration process. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 184, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, R.E.; Cicerone, R.J. Future global warming from atmospheric trace gases. Nature 1986, 319, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravishankara, A.R.; Daniel, J.S.; Portmann, R.W. Nitrous Oxide (N2O): The Dominant Ozone-Depleting Substance Emitted in the 21st Century. Science 2009, 326, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahara, H.; Ono, M.; Konishi, M.; Fukuoka, Y. Partial hydrogenation of benzene to cyclohexene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1997, 121, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obara, N.; Hirasawa, S.; Tamura, M.; Nakagawa, Y. Oxidative Cleavage of Vicinal Diols with the Combination of Platinum and Vanadium Catalysts and Molecular Oxygen. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozhko, E.; Raabova, K.; Macchia, F.; Malmusi, A.; Righi, P.; Accorinti, P.; Alini, S.; Babini, P.; Cerrato, G. Oxidation of 1, 2-Cyclohexanediol to Adipic Acid with Oxygen: A Study Into Selectivity-Affecting Parameters. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 1998–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishopp, S.D.; Scott, J.L.; Torrente-murciano, L. Insights into biphasic oxidations with hydrogen peroxide; towards scaling up. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 3281–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, C.H.A.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z.; Ma, D.D.D.; Wong, N.-B.; Lee, S.-T. Metal (Cu, Au)-modified silicon nanowires for high-selectivity solvent-free hydrocarbon oxidation in air. Chem. Commun. 2009, 5829–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suri, R.P.S.; Christensen, G.L. Hazardous and Industrial Wastes: Proceedings of the Thirtieth Mid-Atlantic Industrial and Hazardous Waste Conference; Technomic Pub. Co.: Lancaster, PA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.D.; Xu, Y.-J.; Jenkins, P.; McMorn, P.; Landon, P.; Enache, D.I.; Carley, A.F.; Attard, G.A.; Hutchings, G.J.; King, F.; et al. Tunable gold catalysts for selective hydrocarbon oxidation under mild conditions. Nature 2005, 437, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biella, S.; Rossi, M. Gas phase oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones catalysed by supported gold. Chem. Commun. 2003, 3, 378–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enache, D.I.; Edwards, J.K.; Landon, P.; Solsona-Espriu, B.; Carley, A.F.; Herzing, A.A.; Watanabe, M.; Kiely, C.J.; Knight, D.W.; Hutchings, G.J. Solvent-Free Oxidation of Primary Alcohols to Aldehydes Using Au-Pd/TiO2 Catalysts. Science 2006, 311, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.-Y.; Zhu, M.-Q.; Chen, J.; Shen, Y.-Y.; Zhao, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, X.-Z. Solvent-free oxidation of cyclohexene over catalysts Au/OMS-2 and Au/La-OMS-2 with molecular oxygen. Catal. Commun. 2010, 12, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoeva, B.G.; Ovoshchnikov, D.S.; Golovko, V.B. Establishing a Au Nanoparticle Size Effect in the Oxidation of Cyclohexene Using Gradually Changing Au Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 2986–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Aoki, M.; Noyori, R. A “Green” Route to Adipic Acid: Direct Oxidation of Cyclohexenes with 30 Percent Hydrogen Peroxide. Science 1998, 281, 1646–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruta, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Sano, H.; Yamada, N. Novel Gold Catalysts for the Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide at a Temperature far Below 0 °C. Chem. Lett. 1987, 16, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, G.J. Vapor phase hydrochlorination of acetylene: Correlation of catalytic activity of supported metal chloride catalysts. J. Catal. 1985, 96, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.S.; Goodman, D.W. The Structure of Catalytically Active Gold on Titania. Science 2004, 306, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, N.A.; Kiely, C.J.; Whyman, R.; Siddiqui, M.R.H.; Hutchings, G.J.; Pankhurst, Q.A.; Wagner, F.E.; Rajaram, R.R.; Golunski, S.E. Microstructural comparison of calcined and uncalcined gold/iron-oxide catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation. Catal. Today 2002, 72, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Arellano, C.; Abad, A.; Corma, A.; García, H.; Iglesias, M.; Sánchez, F. Catalysis by Gold(I) and Gold(III): A Parallelism between Homo- and Heterogeneous Catalysts for Copper-Free Sonogashira Cross-Coupling Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1536–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashmi, A.S.K.; Weyrauch, J.P.; Rudolph, M.; Kurpejović, E. Gold Catalysis: The Benefits of N and N,O Ligands. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 6545–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boronat, M.; Concepción, P.; Corma, A.; González, S.; Illas, F.; Serna, P. A Molecular Mechanism for the Chemoselective Hydrogenation of Substituted Nitroaromatics with Nanoparticles of Gold on TiO2 Catalysts: A Cooperative Effect between Gold and the Support. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 16230–16237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corma, A.; Serna, P. Chemoselective Hydrogenation of Nitro Compounds with Supported Gold Catalysts. Science 2006, 313, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milone, C.; Tropeano, M.L.; Gulino, G.; Neri, G.; Ingoglia, R.; Galvagno, S. Selective liquid phase hydrogenation of citral on Au/Fe2O3 catalysts. Chem. Commun. 2002, 868–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavan, L.; Tiruvalam, R.; Ab Rahim, M.H.; bin Saiman, M.I.; Enache, D.I.; Jenkins, R.L.; Dimitratos, N.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.A.; Taylor, S.H.; Knight, D.W.; et al. Solvent-free oxidation of primary carbon-hydrogen bonds in toluene using Au-Pd alloy nanoparticles. Science 2011, 331, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.-X.; He, C.-H.; Zhu, M.-Q.; Wu, K.-J.; Lai, Y.-L. Silica-Supported Gold Catalyst Modified by Doping with Titania for Cyclohexane Oxidation. Catal. Lett. 2007, 118, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovoshchnikov, D.S.; Donoeva, B.G.; Williamson, B.E.; Golovko, V.B. Tuning the selectivity of a supported gold catalyst in solvent- and radical initiator-free aerobic oxidation of cyclohexene. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Yu, H.; Peng, F.; Wang, H. Confined iron nanowires enhance the catalytic activity of carbon nanotubes in the aerobic oxidation of cyclohexane. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.; Golovko, V.B.; Vaughan, O.P.H.; Abdulkin, P.; Berenguer-murcia, A.; Tikhov, M.S.; Johnson, B.F.G.; Lambert, R.M. Selective oxidation with dioxygen by gold nanoparticle catalysts derived from 55-atom clusters. Nature 2008, 454, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Cui, Y.-T.; Xu, Z.-B.; Qu, J. Hot Water-Promoted Ring-Opening of Epoxides and Aziridines by Water and Other Nucleopliles. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 2270–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.J.; Fang, L.; Fan, Z.; Albela, B.; Bonneviot, L.; De Campo, F.; Pera-Titus, M.; Clacens, J.M. Tunable catalysts for solvent-free biphasic systems: Pickering interfacial catalysts over amphiphilic silica nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4869–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wu, F.; Sun, X.; Li, R.; Guo, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Xing, F.; Wang, W.; Gao, J. Factors that affect pickering emulsions stabilized by graphene oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 4843–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, N.; Freakley, S.J.; Mcvicker, R.U.; Althahban, S.M.; Dimitratos, N.; Morgan, D.J.; Jenkins, R.L.; Willock, D.J.; Taylor, S.H.; Kiely, C.J.; et al. Aqueous Au-Pd colloids catalyze selective CH4 oxidation to CH3OH with O2 under mild conditions. Science 2017, 358, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
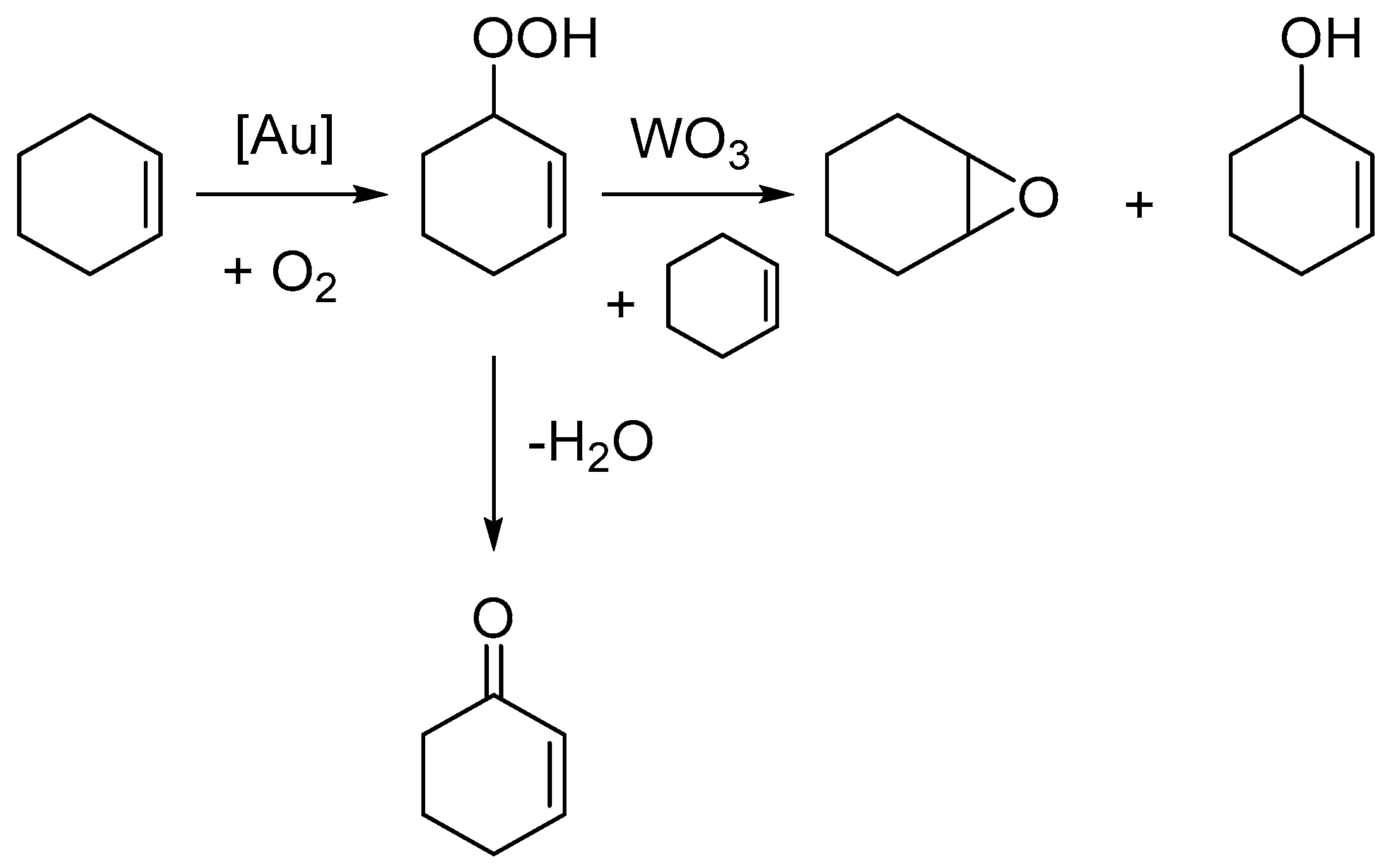
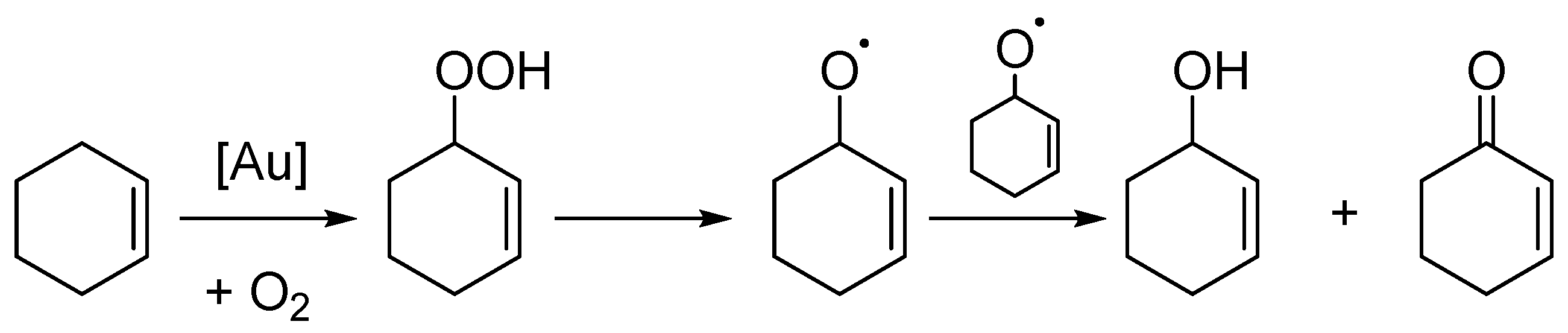
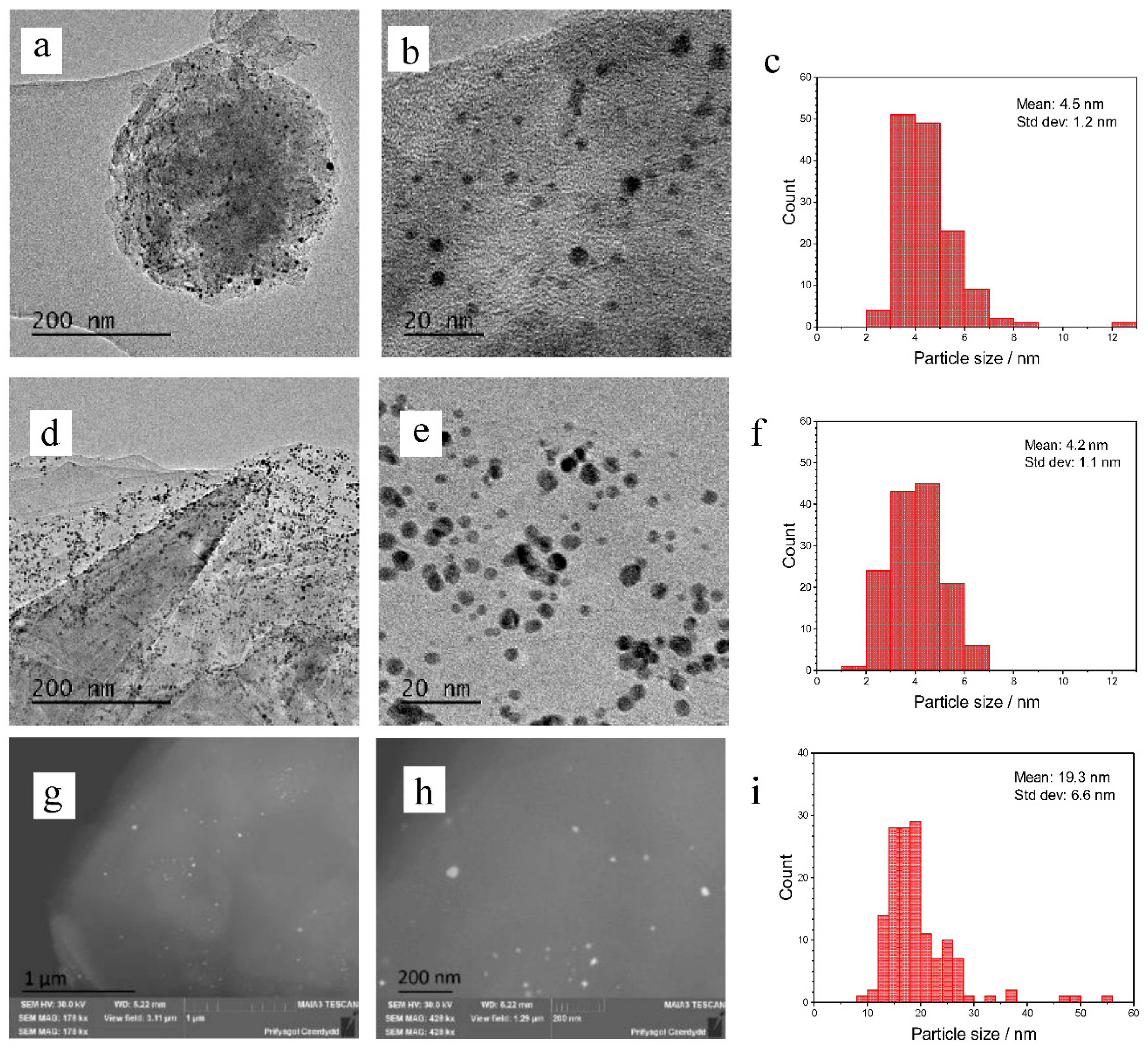
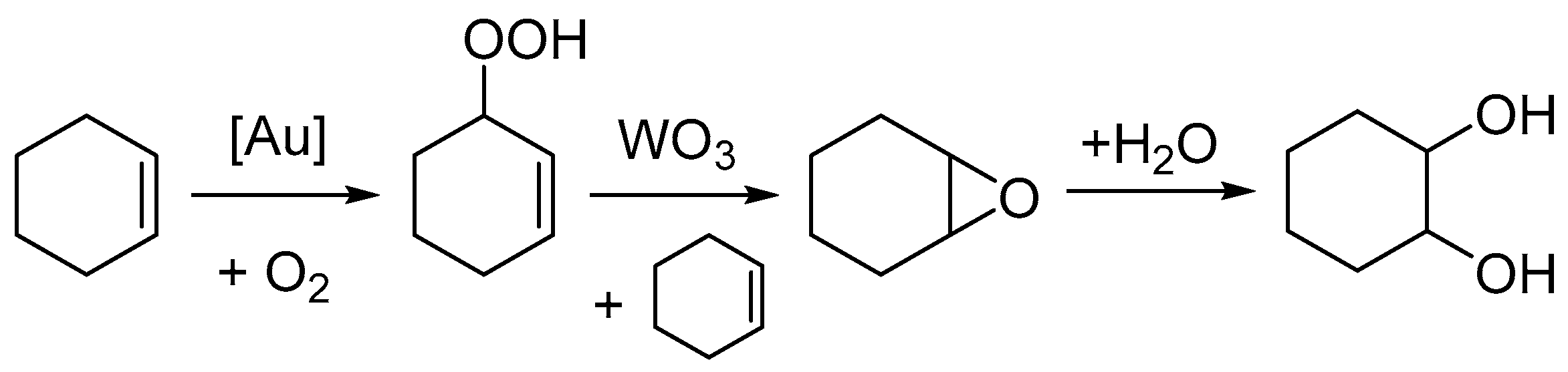
| Catalyst | Conversion (%) | Selectivity (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cy–Oxide | Cy–Ol | Cy–One | Cy–Diol | |||
| Blank | - | 1.7 | 3.2 | 41.6 | 47.5 | 2.3 |
| Graphite | - | 0.6 | 3.6 | 20.1 | 29.2 | 2.7 |
| Graphene | - | 4.3 | 13.4 | 26.9 | 48.7 | 0.1 |
| WO3 | - | 10.3 | 37.0 | 39.5 | 12.4 | 5.2 |
| 1% Au/graphite | I | 8.5 | 13.7 | 17.3 | 38.4 | 1.4 |
| S | 61.4 | 3.9 | 15.6 | 55.3 | 4.5 | |
| 1% Au/graphite + WO3 b | I | 17.7 | 29.8 | 31.1 | 22.2 | 5.1 |
| S | 75.2 | 0.4 | 16.4 | 37.0 | 13.7 | |
| 1% Au/graphene | I | 25.9 | 10.1 | 18.2 | 53.3 | 3.1 |
| S | 73.2 | 0.0 | 18.6 | 56.0 | 7.8 | |
| 1% Au/graphene + WO3 b | I | 41.6 | 7.1 | 21.3 | 46.4 | 5.2 |
| S | 76.1 | 0.0 | 17.0 | 48.8 | 9.0 | |
| Catalyst | Con (%) | Selectivity (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cy–Oxide | Cy–Ol | Cy–One | Cy–Diol | |||
| 1% Au/graphite | I | 8.5 | 13.7 | 17.3 | 38.4 | 1.4 |
| 1% Au/graphite + WO3 b | I | 17.7 | 29.8 | 31.1 | 22.2 | 5.1 |
| 1% Au/graphite + WO3 + H2O c | I | 11.8 | 2.0 | 22.5 | 46.3 | 17.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rogers, O.; Pattisson, S.; Macginley, J.; Engel, R.V.; Whiston, K.; Taylor, S.H.; Hutchings, G.J. The Low Temperature Solvent-Free Aerobic Oxidation of Cyclohexene to Cyclohexane Diol over Highly Active Au/Graphite and Au/Graphene Catalysts. Catalysts 2018, 8, 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8080311
Rogers O, Pattisson S, Macginley J, Engel RV, Whiston K, Taylor SH, Hutchings GJ. The Low Temperature Solvent-Free Aerobic Oxidation of Cyclohexene to Cyclohexane Diol over Highly Active Au/Graphite and Au/Graphene Catalysts. Catalysts. 2018; 8(8):311. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8080311
Chicago/Turabian StyleRogers, Owen, Samuel Pattisson, Joseph Macginley, Rebecca V. Engel, Keith Whiston, Stuart H. Taylor, and Graham J. Hutchings. 2018. "The Low Temperature Solvent-Free Aerobic Oxidation of Cyclohexene to Cyclohexane Diol over Highly Active Au/Graphite and Au/Graphene Catalysts" Catalysts 8, no. 8: 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8080311
APA StyleRogers, O., Pattisson, S., Macginley, J., Engel, R. V., Whiston, K., Taylor, S. H., & Hutchings, G. J. (2018). The Low Temperature Solvent-Free Aerobic Oxidation of Cyclohexene to Cyclohexane Diol over Highly Active Au/Graphite and Au/Graphene Catalysts. Catalysts, 8(8), 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8080311






