Three-Dimensional TiO2 Structures Incorporated with Tungsten Oxide for Treatment of Toxic Aromatic Volatile Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
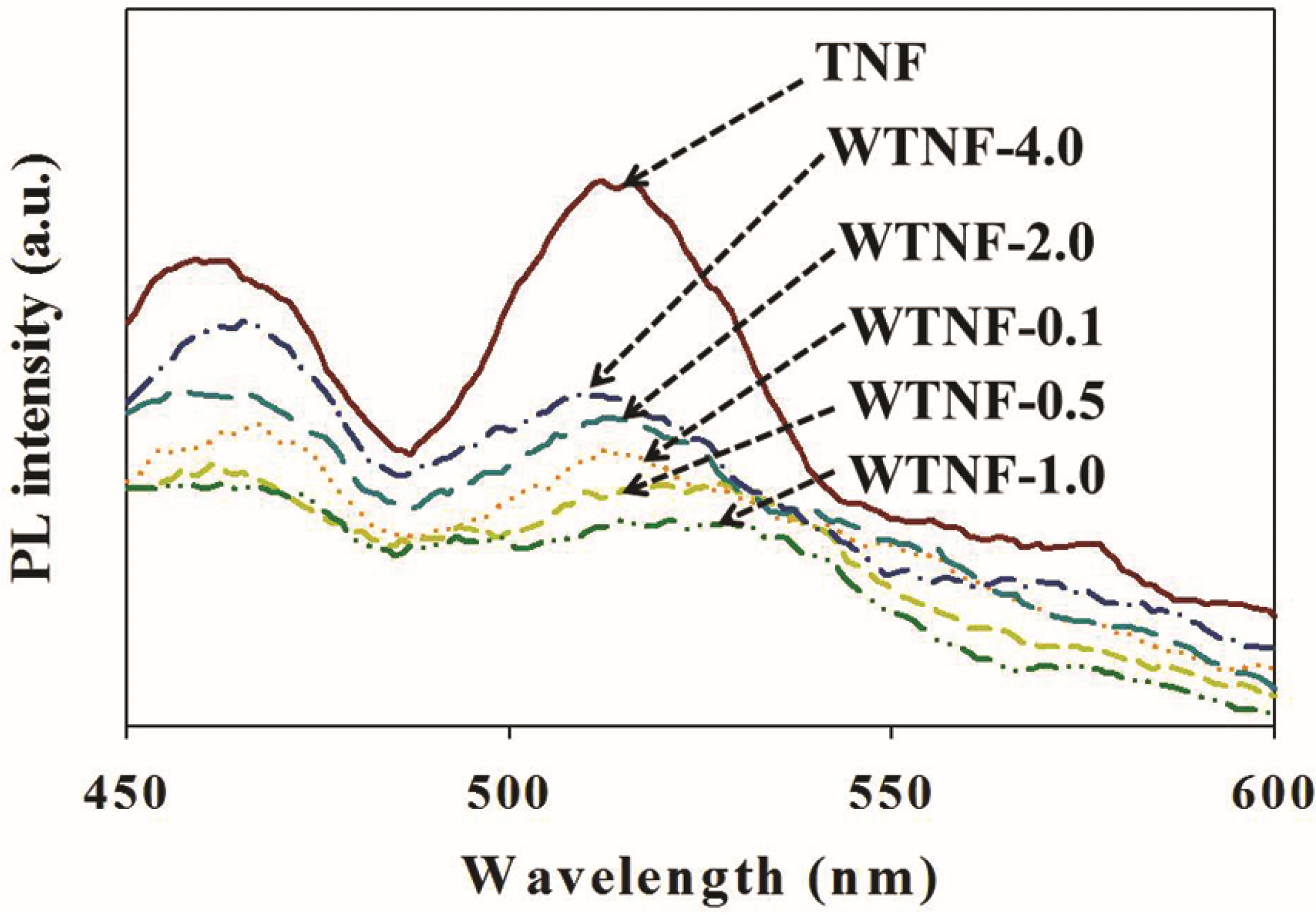
2.1. Fabricated Photocatalysts
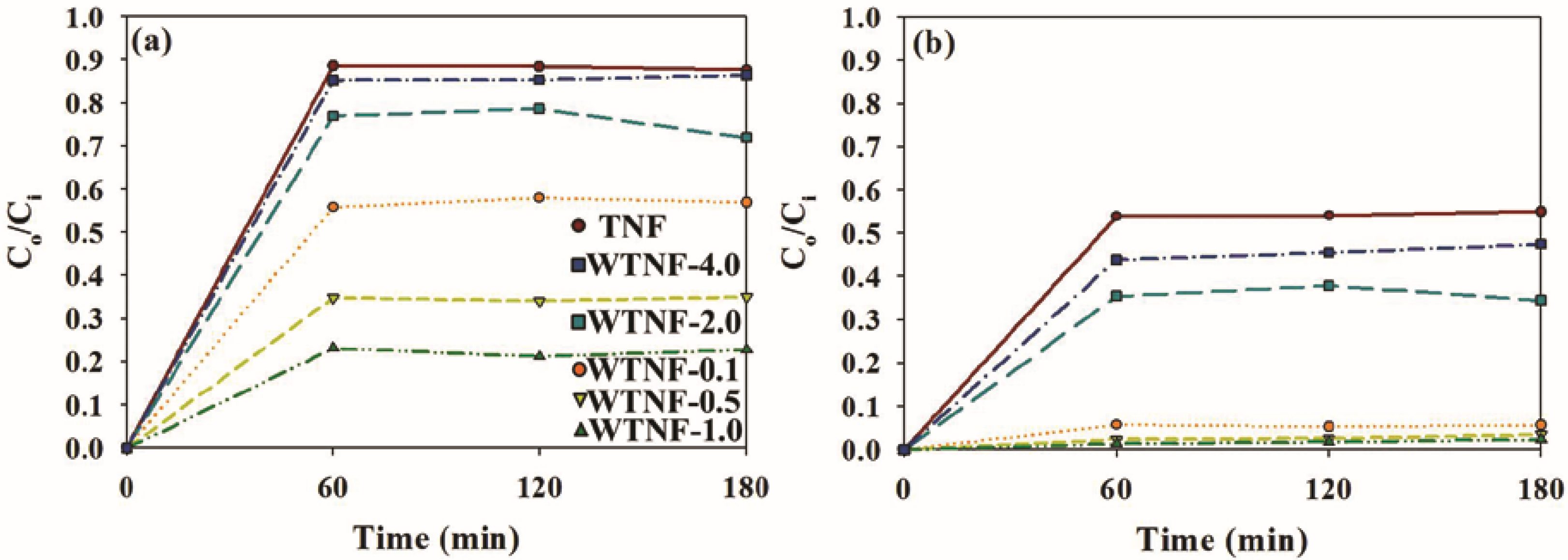
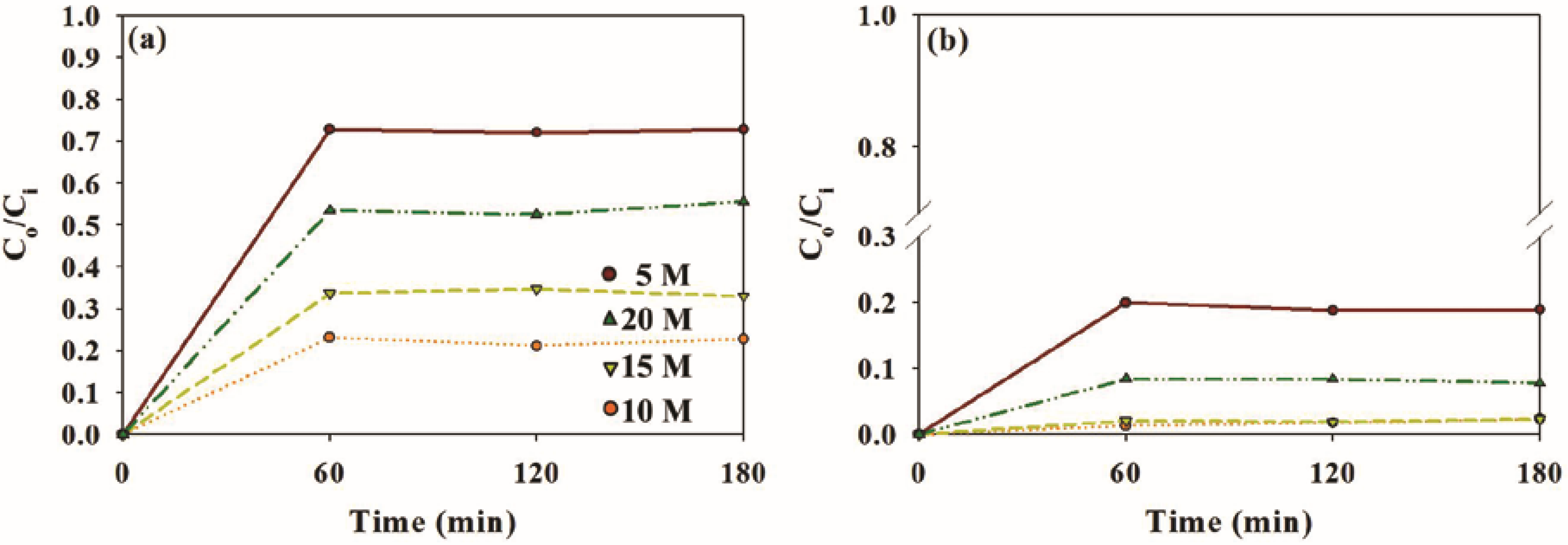
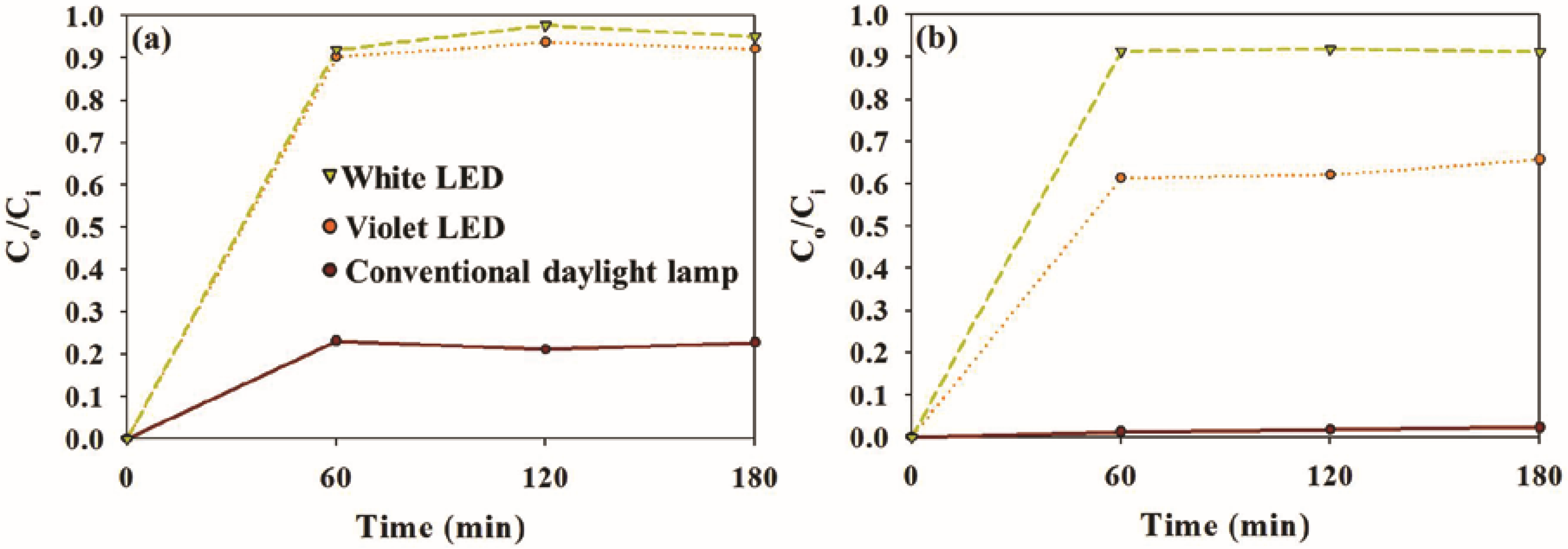
2.2. Photocatalytic Activity of Sample Photocatalysts
3. Materials and Methods
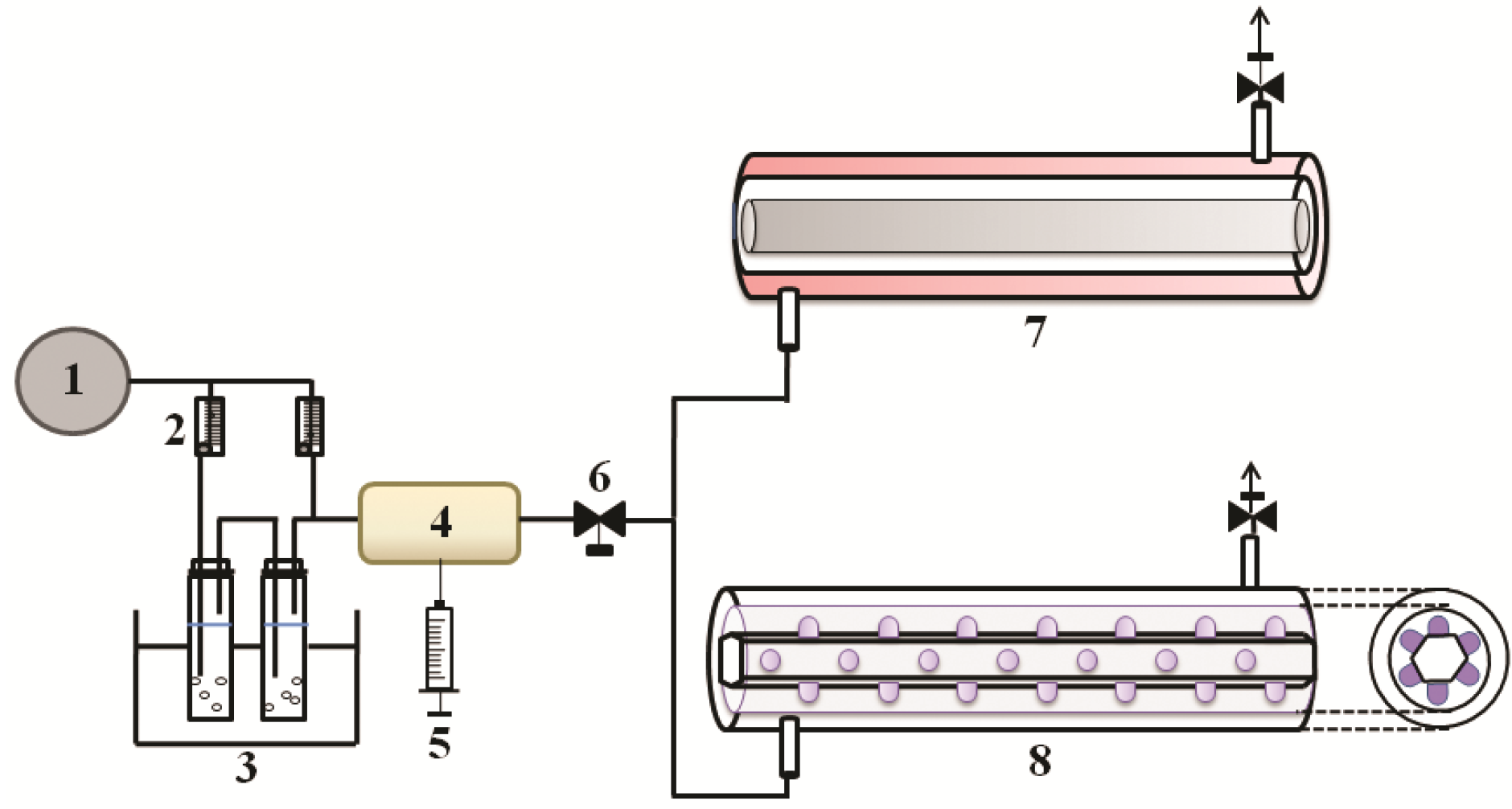
3.1. Preparation of Samples
3.2. Photocatalysis of Aromatic Compounds
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, F.-C.; Mukherjee, B.; Batterman, S. Determinants of personal, indoor and outdoor VOC concentrations: An analysis of the RIOPA data. Environ. Res. 2013, 126, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, N.; Cuadras, A.; Rovira, E.; Borrull, F.; Marcé, R.M. Chronic risk assessment of exposure to volatile organic compounds in the atmosphere near the largest Mediterranean industrial site. Environ. Int. 2012, 39, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer). Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Available online: http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php (accessed on 5 January 2016).
- Grabowska, E.; Reszczyńska, J.; Zaleska, A. Mechanism of phenol photodegradation in the presence of pure and modified-TiO2: A review. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5453–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Jo, W.K. Control of methyl tertiary-butyl ether via carbon-doped photocatalysts under visible-light irradiation. Environ. Eng. Res. 2012, 17, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, T.; Fujishima, A. Photoelectrochemical properties of TiO2 photocatalyst and its applications for environmental purification. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2012, 13, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.K.; Lee, J.Y. Degradation of chlorinated hydrocarbons via a light-emitting-diode (LED) derived photocatalyst. Environ. Eng. Res. 2013, 18, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zou, J.-J. Controlling surface and interface of TiO2 toward highly efficient photocatalysis. Mater. Lett. 2015, 160, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, S.W. TiO2 photocatalysis for the degradation of pollutants in gas phase: From morphological design to plasmonic enhancement. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2015, 24, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaez, M.; Nolan, N.T.; Pillai, S.C.; Seery, M.K.; Falaras, P.; Kontos, A.G.; Dunlop, P.S.M.; Hamilton, J.W.J.; Byrne, J.A.; O’Shea, K.; et al. A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 125, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Qiu, F.; Xu, W.; Cao, S.; Zhu, H. Recent progress in enhancing photocatalytic efficiency of TiO2-based materials. Appl. Catal. A 2015, 495, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Liu, H.; Sun, J.; Tian, Y.; Chen, S.; Song, J.; Luo, R.; Li, D.; Chen, A.; Liu, C.-C. Improvement of TiO2 photocatalytic properties under visible light by WO3/TiO2 and MoO3/TiO2 composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 338, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.G.; Rao, K.S.R.K. Tungsten-based nanomaterials (WO3 & Bi2WO6): Modifications related to charge carrier transfer mechanisms and photocatalytic applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 355, 939–958. [Google Scholar]
- Riboni, F.; Bettini, L.G.; Bahnemann, D.W.; Selli, E. WO3−TiO2 vs. TiO2 photocatalysts: Effect of the W precursors and amount on the photocatalytic activity of mixed oxides. Catal. Today 2013, 209, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Delgado, N.A.; Gracia-Pinilla, M.A.; Maya-Treviño, L.; Hinojosa-Reyes, L.; Guzman-Mar, J.L.; Hernández-Ramírez, A. Solar photocatalytic activity of TiO2 modified with WO3 on the degradation of an organophosphorus pesticide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.A.; Madras, G. Photocatalytic degradation with combustion synthesized WO3 and WO3‒TiO2 mixed oxides under UV and visible light. Sep. Purif, Technol. 2013, 105, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, K.; Ochiai, T.; Murakami, T.; Fujishima, A. Photoenergy conversion with TiO2 photocatlysis: New materials and recent applications. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 84, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, E.; Szilágyi, I.; Forró, L.; Magrez, A. Probing titanate nanowire surface acidity through methylene blue adsorption in colloidal suspension and on thin films. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2014, 416, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouster, P.; Pavlovic, M.; Szilagyi, I. Improving the stability of titania nanosheets by functionalization with polyelectrolytes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 97322–97330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, E.; Ribič, P.R.; Hashemi, F.; Forró, L.; Magrez, A. Dye metachromasy on titanate nanowires: Sensing humidity with reversible molecular dimerization. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 8778–8784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenczek-Zajac, A.; Kusior, A.; Lacz, A.; Radecka, M.; Zakrzewska, K. TiO2 flower-like nanostructures decorated with CdS/PbS nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 60, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, H. Highly active and durable Bi2O3/TiO2 visible photocatalyst in flower-like spheres with surface-enriched Bi2O3 quantum dots. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 102, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.-G.; Xu, Y.-Q.; Pan, J.; Gu, H.; Qin, C.-Y.; Zhou, P. Glycine assisted synthesis of flower-like TiO2 hierarchical spheres and its application in photocatalysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2012, 177, 1664–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Chen, T.; Sun, Y.-L.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Jia, X.-H. Controlled synthesis of porous flower-like TiO2 nanostructure with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 11015–11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, T.; Liu, H.; Huang, B.; Zhang, Q. Hierarchical flower-like nanostructures of anatase TiO2 nanosheets dominated by {001} facets. J. Alloy Compd. 2016, 657, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, A.; García-López, E.; Marcì, G.; Palmisano, L. A survey of photocatalytic materials for environmental remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211–212, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhyapak, P.V.; Meshram, S.P.; Tomar, V.; Amalnerkar, D.P.; Mulla, I.S. Effect of preparation parameters on the morphologically induced photocatalytic activities of hierarchical zinc oxide nanostructures. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 7367–7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.K.; Won, Y.S.; Hwang, I.; Tayade, R. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of aqueous nitrobenzene using graphitic carbon–TiO2. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 3455–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Duan, W.; Liu, B.; Chen, X.; Yang, F.; Guo, J. Fabrication of efficient visible light activated Cu–P25–grapheneternary composite for photocatalytic degradation of methyl blue. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 356, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.K.; Park, G.T.; Tayade, R.J. Synergetic effect of adsorption on degradation of malachite green dye under blue LED irradiation using spiral-shaped photocatalytic reactor. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 2280–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.K.; Kang, H.J. Photocatalysis of sub-ppm limonene over multiwalled carbon nanotubes/titania composite nanofiber under visible-light irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, H.H.; Jo, W.K. Adsorption and photocatalysis of 2-ethyl-1-hexanol over graphene oxide–TiO2 hybrids post-treated under various thermal conditions. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 180, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.K.; Natarajan, T.S. Influence of TiO2 morphology on the photocatalytic efficiency of direct Z-scheme g-C3N4/TiO2 photocatalysts for isoniazid degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 281, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
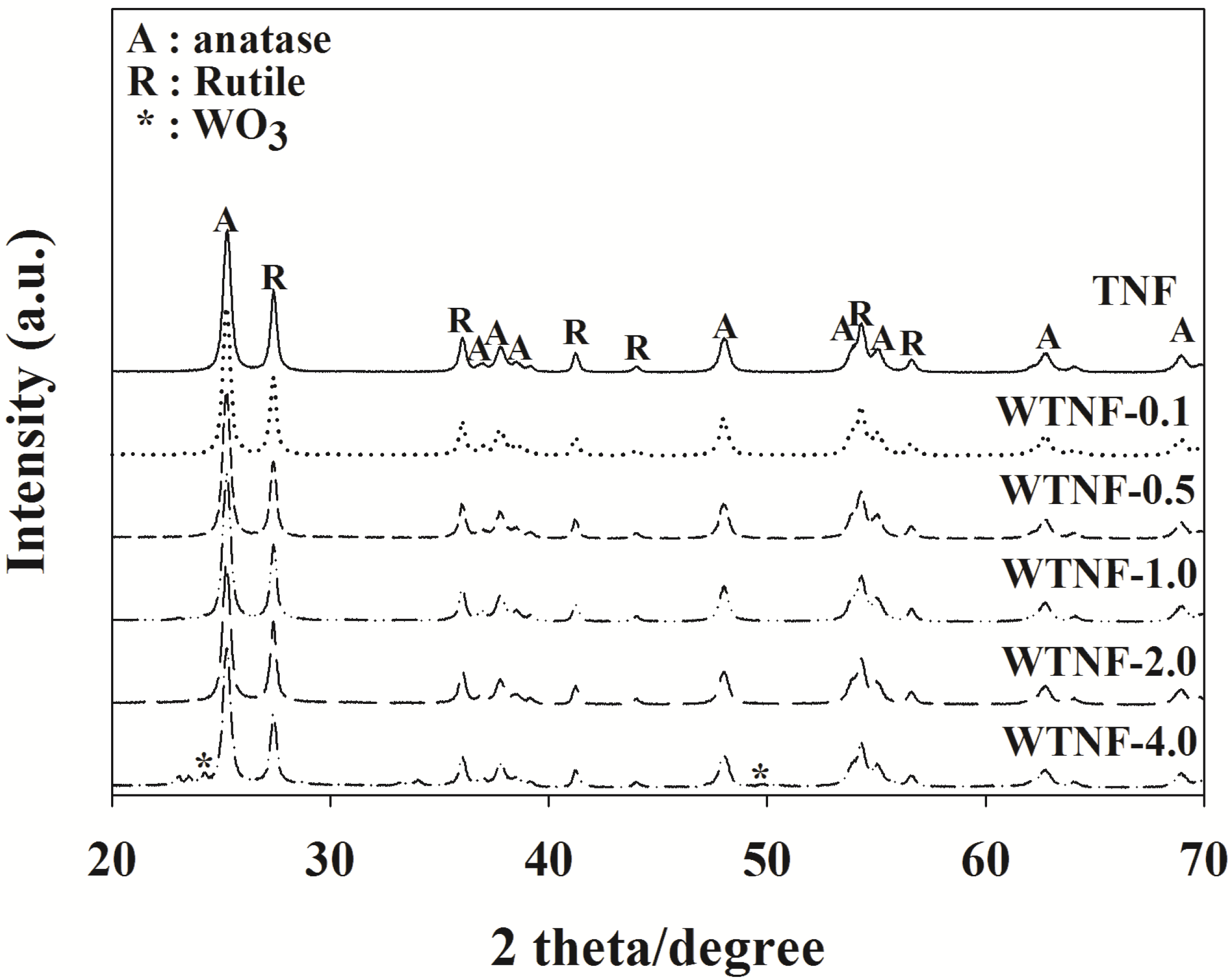
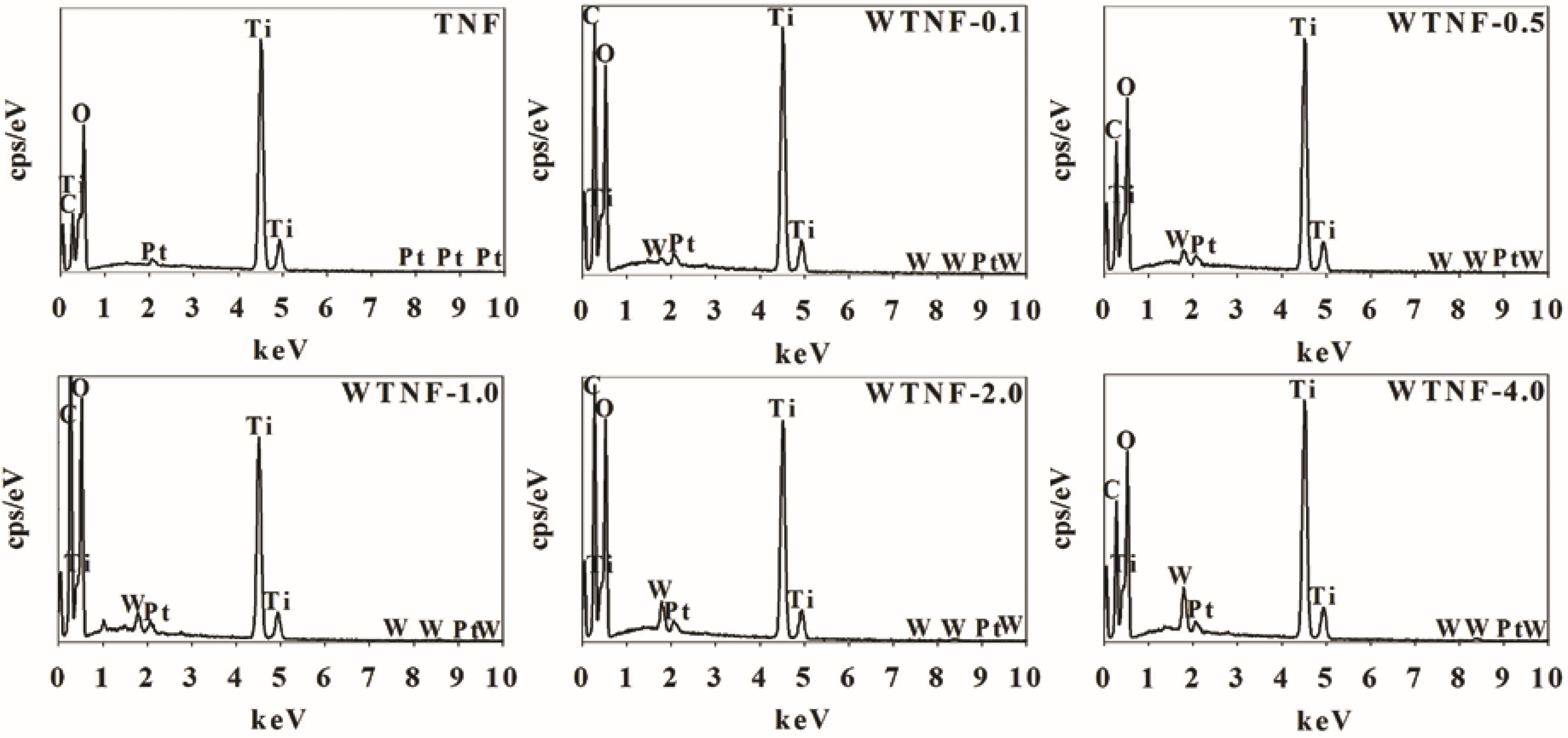
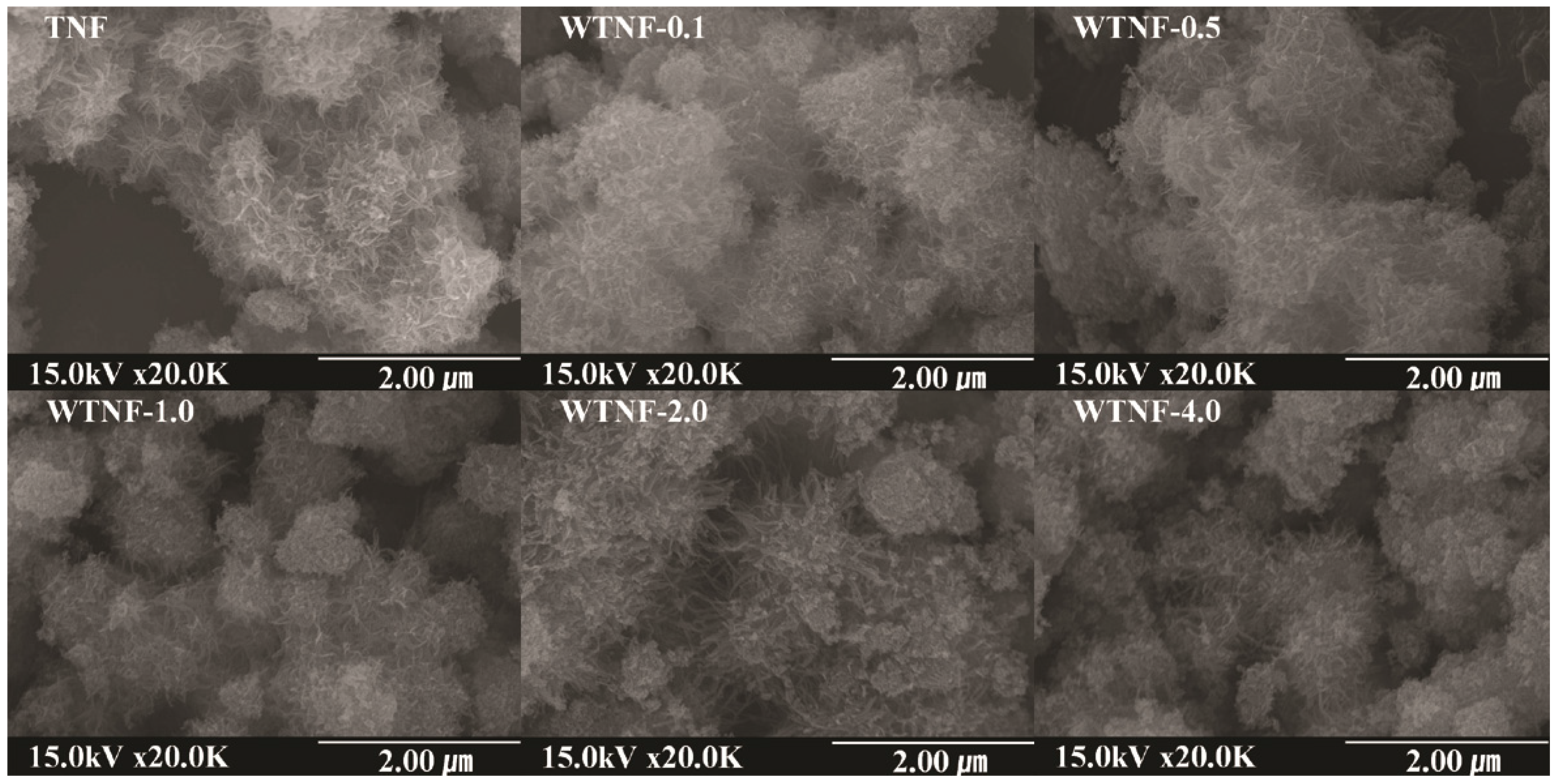
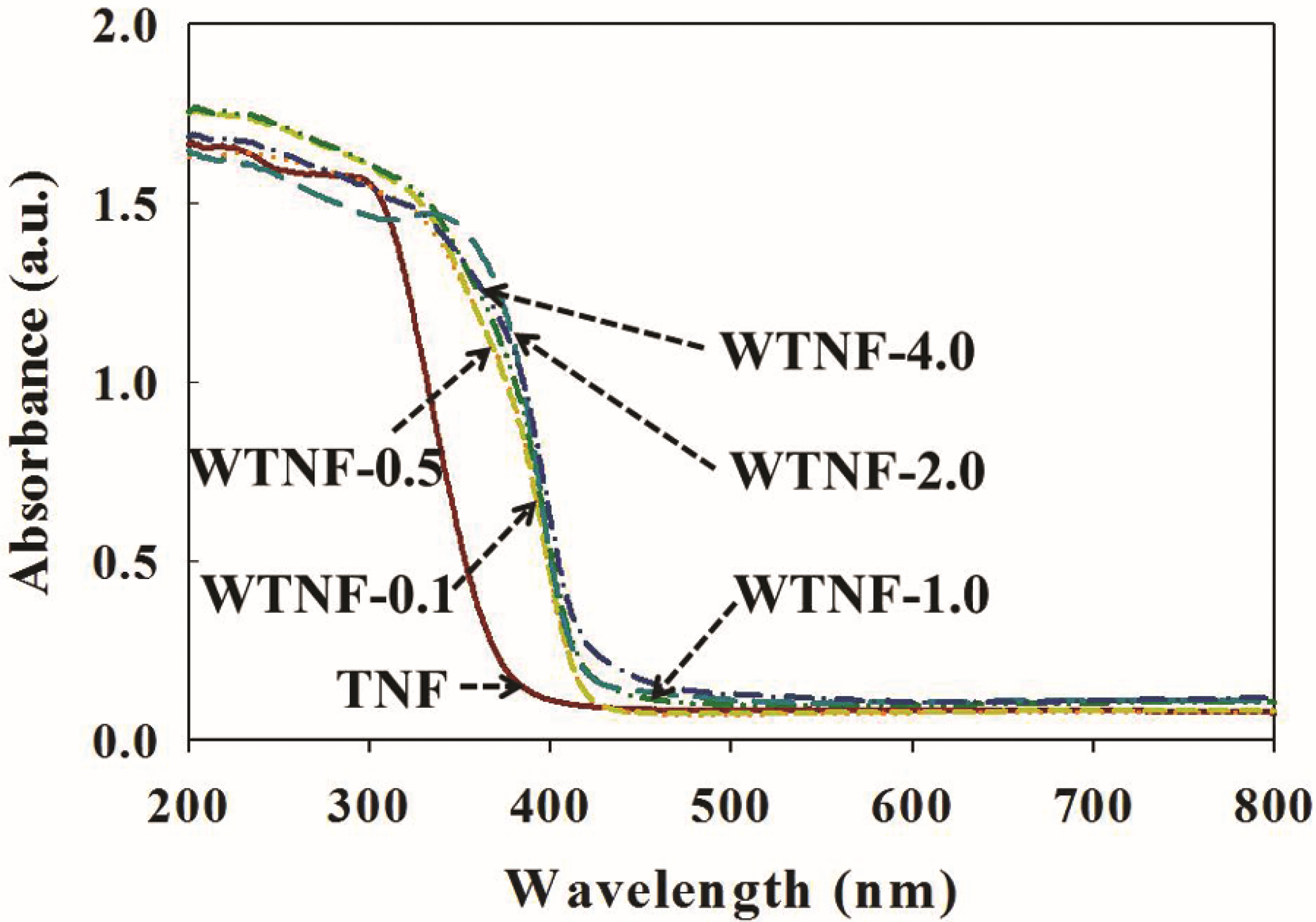
| Photocatalyst | SBET, m2 g−1 | Total Pore Volume, cm3 g−1 | Band Gap, eV |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNF | 102.1 | 0.30 | 3.30 |
| WTNF-0.1 | 122.6 | 0.37 | 2.97 |
| WTNF-0.5 | 133.4 | 0.31 | 2.96 |
| WTNF-1.0 | 135.4 | 0.36 | 2.96 |
| WTNF-2.0 | 107.4 | 0.25 | 2.95 |
| WTNF-4.0 | 104.8 | 0.22 | 2.92 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.Y.; Jo, W.-K. Three-Dimensional TiO2 Structures Incorporated with Tungsten Oxide for Treatment of Toxic Aromatic Volatile Compounds. Catalysts 2017, 7, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7040097
Lee JY, Jo W-K. Three-Dimensional TiO2 Structures Incorporated with Tungsten Oxide for Treatment of Toxic Aromatic Volatile Compounds. Catalysts. 2017; 7(4):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7040097
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Joon Yeob, and Wan-Kuen Jo. 2017. "Three-Dimensional TiO2 Structures Incorporated with Tungsten Oxide for Treatment of Toxic Aromatic Volatile Compounds" Catalysts 7, no. 4: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7040097
APA StyleLee, J. Y., & Jo, W.-K. (2017). Three-Dimensional TiO2 Structures Incorporated with Tungsten Oxide for Treatment of Toxic Aromatic Volatile Compounds. Catalysts, 7(4), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7040097





