The Use of Palladium on Magnetic Support as Catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reactions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Palladium on Magnetically Supports
2.1. The Magnetic Particle
2.2. Palladium Deposited Directly onto the Iron Oxide Nanoparticle
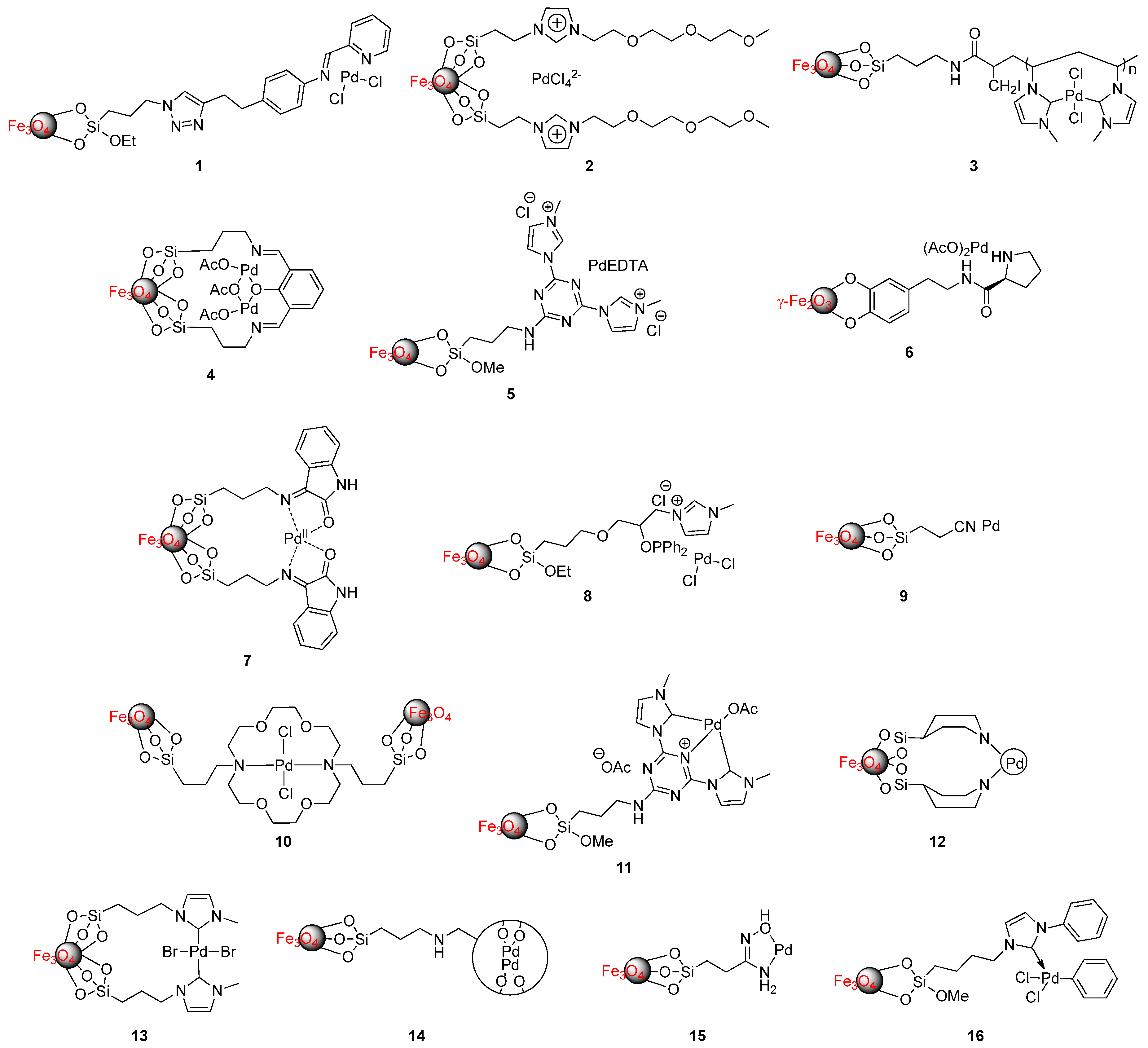
2.3. Iron Oxide with Ligands Holding Palladium
2.4. The Use of Palladium Chelated to Magnetic Nanoparticles
2.5. Recycling
2.6. Catalyst Leaching
3. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miyaura, N.; Suzuki, A. Stereoselective synthesis of arylated (E)-alkenes by the reaction of alk-1-enylboranes with aryl halides in the presence of palladium catalyst. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1979, 19, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaura, N.; Yamada, K.; Suzuki, A. A new stereospecific cross-coupling by the palladium-catalyzed reaction of 1-alkenylboranes with 1-alkenyl or 1-alkynyl halides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979, 20, 3437–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaura, N.; Suzuki, A. Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of organoboron compounds. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 2457–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaura, N. Cross-coupling reaction of organoboron compounds via base-assisted transmetalation to palladium(II) complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2002, 653, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A. Cross-coupling reactions via organoboranes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2002, 653, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildner, P.G.; Colacot, T.J. Reactions of the 21st Century: Two Decades of Innovative Catalyst Design for Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Couplings. Organometallics 2015, 34, 5497–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrounig, P.; Trobe, M.; Breinbauer, R. Sequential and iterative Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions in organic synthesis. Monatsh. Chem. 2017, 148, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A. Cross-coupling reactions of organoboranes: An easy way to construct C–C Bonds (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 6723–6737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negishi, E. Magical power of transition metals: Pas, present, and future (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 6738–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seechurn, C.C.C.J.; Kitching, M.O.; Colacot, T.J.; Snieckus, V. Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling: A historical contextual perspective to the 2010 Nobel Prize. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5062–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarasen, A.; Kuse, M.; Nishikawa, T.; Isobe, M. Substituent effect of imino-O-arenesulfonates, a coupling partner in Suzuki–Miyaura reaction for substitution of the pyrazine ring: Study for the synthesis of coelenterazine analogs. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 82, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roglans, A.; Pla-Quintana, A.; Moreno-Mañas, M. Diazonium salts as substrates in palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4622–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.G.; Moro, A.V.; Correia, C.R.D. Evolution and Synthetic applications of the Heck-Matsuda reaction: The return of arenediazonium salts to prominence. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 1403–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felpin, F.-X.; Nassar-Hardy, L.; Le Callonnec, F.; Fouquet, E. Recent advances in the Heck-Matsuda reaction in heterocyclic chemistry. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 2815–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, F.; Dong, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Recent applications of arene diazonium salts in organic synthesis. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 1582–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Astruc, D. Fast-growing field of magnetically recyclable nanocatalysts. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6949–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deraedt, C.; Astruc, D. “Homeopathic” palladium nanoparticle catalysis of cross carbon-carbon coupling reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Islam, M.M.; Islam, S.M. Suzuki–Miyaura reaction by heterogeneously supported Pd in water: Recent studies. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 42193–42221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marck, G.; Villiger, A.; Buchecker, R. Aryl couplings with heterogeneous palladium catalysts. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 3277–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydnes, M.O. Recent Developments in the use of palladium on solid support in organic synthesis. Curr. Org. Synth. 2011, 8, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydnes, M.O. Use of nanoparticles as catalysts in organic synthesis—Cross-coupling reactions. Curr. Org. Chem. 2014, 18, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.N.; Mohsin, M.A.; Danish, M.; Nazar, M.F.; Murtaza, S. Palladium catalyzed Heck-Mizoroki and Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions (review). Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 2014, 40, 781–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felpin, F.-X.; Ayad, T.; Mitra, S. Pd/C: An old catalyst for new applications—Its use for the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. Eur. J. Chem. 2006, 2679–2690. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, F. Multiple roles of graphene in heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3023–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santra, S.; Hota, P.K.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Bera, P.; Chosh, P.; Mandal, S.K. Palladium nanoparticles on graphite oxide: A recyclable catalyst for the synthesis of biaryl cores. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 2776–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbhar, A.; Salunkhe, R. Recent advances in biopolymer supported palladium in organic synthesis. Curr. Org. Chem. 2015, 19, 2075–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebaschi, S.; Hekmati, M.; Veisi, H. Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles mediated by black tea leaves (Camellia sinensis) extract: Catalytic activity in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction under ligand-free conditions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 485, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Lu, Z.; Li, Y. Carboxymethylcellulose-supported palladium nanoparticles generated in situ from palladium(II) carboxymethylcellulose: An efficient and reusable catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura and Mizoroki-Heck reactions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Huang, M.; Li, Y. Synthesis of a novel cellulose microencapsulated palladium nanoparticle and its catalytic activities in Suzuki–Miyaura and Mizoroki-Heck reactions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 8339–8345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghipor, A.; Fakhri, A. Heterogeneous Fe3O4@chitosan-Schiff base Pd nanocatalyst: Fabrication, characterization and application as highly efficient and magnetically-recoverable catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura and Heck-Mizoroki C–C coupling reactions. Catal. Commun. 2016, 73, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.; Kumbhar, A.; Salunkhe, R. Palladium supported on silica-chitosan hybrid material (Pd-CS@SiO2) for Suzuki–Miyaura and Mizoroki-Heck cross-coupling reactions. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2015, 29, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, H.L.; Rylott, E.L.; Hunt, A.J.; Dodson, J.R.; Taylor, A.F.; Bruce, N.C.; Clark, J.H. Supported palladium nanoparticles synthesized by living plants as a catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura reactions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikata, T.; Tsutsumi, H.; Gao, L.; Kojima, K.; Chikama, K.; Nagashima, H. Adhesive catalyst immobilization of palladium nanoparticles on cotton and filter Paper: Applications to reusable catalysts for sequential catalytic reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariprasad, E.; Radhakrishnan, T.P. Palladium nanoparticle-embedded polymer thin film “dip catalyst” for Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.K.; Radhakrishnan, T.P. Hollow bimetallic nanoparticles generated in situ inside a polymer thin film: fabrication and catalytic application of silver-palladium-poly(vinyl alcohol). J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 13612–13618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.G.M.; Alvarenga, G.; Scheeren, C.W.; Rosa, G.R. Densenvovimento de reator tipo «dip catalyst» para filmes poliméricos contendo nanoparticulas de metais de transição. Quim. Nova 2014, 37, 1401–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Rao, G.K.; Kumar, S.; Singh, A.K. Formation and role of palladium chalcogenide and other species in Suzuki–Miyaura and Heck C–C coupling reactions catalyzed with palladium(II) complexes of organochalcogen ligands: realities and speculations. Organometallics 2014, 33, 2921–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Asiri, A.M.; Garcia, H. Metal-organic frameworks catalyzed C–C and C-heteroatom coupling reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1922–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Hosmane, N.S. Nanocatalysis: Recent advances and applications in boron chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 293–294, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Deraedt, C.; Ruiz, J.; Astruc, D. Magnetic and dendritic catalysts. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Patzig, C.; Hu, Y.; Scott, R.W.J. In Situ X-ray absorption spectroscopic study of Fe@FexOy/Pd and Fe@FexOy/Cu nanoparticle catalysts prepared by galvanic exchange reactions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 21209–21218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, S.; Majoral, J.-P.; Grass, R.N.; Stark, W.J.; Reiser, O. Carbon coated magnetic nanoparticles as supports in microwave-assisted palladium catalyzed Suzuki-Miyarura coupling. Green Process. Synth. 2012, 1, 275–279. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Kaliaguine, S.; Hou, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, D. A versatile designed synthesis of magnetically separable nano-catalysts with well-defined core-shell nanostructures. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 6071–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.; Lee, K.; Park, J.C.; Park, K.H. Facile synthesis of Pd/Fe3O4/charcoal bifunctional catalyst with high metal loading for high product yields in Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 5626–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, J.; Ye, M. Hierarchical nanospheres based on Pd nanoparticles dispersed on carbon coated magnetic cores with a mesoporours ceria shell: A highly intergrated multifunctional catalyst. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 16592–16601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappelletti, A.L.; Uberman, P.M.; Martín, S.E.; Sateta, M.E.; Troiani, H.E.; Sánchez, R.D.; Carbonio, R.E.; Strumia, M.C. Synthesis, characterization, and nanocatalysis application of core-shell superparamagnetic nanoparticles of Fe3O4@Pd. Aust. J. Chem. 2015, 68, 1492–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Sarvari, M.; Khanivar, A.; Moeini, F. Palladium immobilized on Fe3O4/ZnO nanoparticles: A novel magnetically recyclable catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura and Heck reactions under ligand-free conditions. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2016, 13, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, T.; Li, X.; Dong, P.; Baines, R.; Shen, J.; Ye, M. Magnetic core-shell to yolk-shell structures in palladium-catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura reactions: Heterogeneous versus homogeneous nature. ChemPlusChem 2016, 81, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Fu, Y.; He, G.; Sun, X.; Wang, X. Core-shell-like Ni-Pd nanoparticles supported on carbon black as a magnetically separable catalyst for green Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 200, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Su, H.; Luo, J.; Wei, Y. “Click” magnetic nanoparticle-supported palladium catalyst: A phosphine-free, highly efficient and magnetically recoverable catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaicharoenwimolkul, L.; Chairam, S.; Namkajorn, M.; Khamthip, A.; Kamonsatikul, C.; Tewasekson, U.; Jindabot, S.; Pon-On, W.; Somsook, E. Effect of ferrocene substituents and ferricinium additive on the properties of polyaniline derivatives and catalytic activities of palladium-doped poly(m-ferrocenylaniline)-catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, B.; Mansouri, F.; Vali, H. A highly water-dispersible/magnetically separable palladium catalyst based on a Fe3O4@SiO2 anchored TEG-imidazolium ionic liquid for the Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction in water. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2587–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilpour, M.; Javidi, J.; Dodeji, F.N.; Hassannezhad, H. Fe3O4@SiO2-polymer-imid-Pd magnetic porous nanosphere as magnetically separable catalyst for Mizoroki-Heck and Suzuki–Miyaura coupling ractions. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2014, 11, 1703–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.; Dong, Z.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ma, J. Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions catalyzed by efficient and recyclable Fe3O4@SiO2@SiO2-Pd(II) catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2014, 53, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghotbinejad, M.; Khosropour, A.R.; Mohammadpoor-Baltork, I.; Moghadam, M.; Tangestaninejad, S.; Mirkhani, V. Ultrasound-assisted C–C coupling reactions catalyzed by unique SPION-A-Pd(EDTA) as a robust nanocatalyst. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 8590–8596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehlig, E.; Waggeh, B.; Millot, N.; Lalatonne, Y.; Motte, L.; Guénin, E. Immobilized Pd on magnetic nanoparticles bearing proline as a highly efficient and retrievable Suzuki–Miyaura catalyst in aqueous media. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeilpour, M.; Javidi, J. Magnetically-recoverable Schiff Base Complex of Pd(II) immobilized on Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles: An efficient catalyst for Mizoroki-Heck and Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2015, 62, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholinejad, M.; Razeghi, M.; Ghaderi, A.; Biji, P. Palladium supported on phosphinite functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a new magnetically separable catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions in aqueous media. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 3117–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakiani, B.A.; Pourshamsian, K.; Veisi, H. A highly stable and efficient magnetically recoverable and reusable Pd nanocatalyst in aqueous media heterogeneously catalyzed Suzuki C–C cross-coupling reactions. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2015, 29, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, K.; Ghonchepour, E.; Karimi, M.; Heydari, A. Encapsulation of Pd(II) into superparamagnetic nanoparticles grafted with EDTA and their catalytic activity towards reduction of nitroarenes and Suzuki–Miyaura coupling. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2015, 29, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowassagh, B.; Takallou, A.; Mobaraki, A. Magnetic nanoparticle-supported Pd(II)-cryptand 22 complex: An efficient and reusable heterogeneous precatalyst in the Suzuki–Miyaura coupling and the formation of aryl-sulfur bonds. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 401, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, S.J.; Heidari, V.; Nasrabadi, H. Magnetic Pd/Fe3O4/reduced-graphene oxide nanohybrid as an efficient and recoverable catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction in water. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 396, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Li, Z.; Qian, H.; Lin, Z.Y. A magnetically separable palladium catalyst containing a bulky N-heterocyclic carbine ligand for the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghotbinejad, M.; Khosropour, A.R.; Mohammadpoor-Baltork, I.; Moghadam, M.; Tangestaninejad, S.; Mirkhani, V. SPIONs-bis(NHC)-palladium(II): A novel, powerful and efficient catalyst for Mizoroki-Heck and Suzuki–Miyaura C–C coupling reactions. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2014, 385, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Lu, M. A highly water-dispersible and magnetically separable palladium catalyst based on functionalized poly(ethylene glycol)-supported iminophosphine for Suzuki–Miyaura coupling in water. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2015, 29, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, G.; Ghorbani-Choghamarani, A. Immobilized palladium on modified magnetic nanoparticles and study of its catalytic activity in Suzuki–Miyaura C–C coupling reaction. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2016, 30, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Olid, F.; Andrés, R.; de Jesus, E.; Flores, J.C.; Gȯmez-Sal, P.; Heuze, K.; Vellutini, L. Magnetically recoverable catalysts base don mono- or bis-(NHC) complexes of palladium for the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction in aqueous media: Two NHC-Pd linkages are better than one. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 11633–11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salemi, H.; Kaboudin, B.; Kazemi, F.; Yokomatsu, T. Highly water-dispersible magnetite nanoparticle supported-palladium-β-cyclodextrin as an efficient catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura and Sonogashira coupliong reactions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 52656–52664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani-Vaghei, R.; Hemmati, S.; Hekmati, M. Pd immobilized on modified magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Magnetically recoverable and reusable Pd nanocatalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions and Ullmann-type N-arylation of indoles. J. Chem. Sci. 2016, 128, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajipour, A.R.; Tadayoni, N.S.; Khorsandi, Z. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles-N-heterocyclic carbine-palladium(II): A new, efficient and robust recyclable catalyst for Mizoroki-Heck and Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2016, 30, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.V.; Kumar, A.V. A biomimetic magnetically recoverable palladium nanocatalyst for the Suzuki cross-coupling reaction. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 46864–46870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, N.T.S.; Van Der Sluys, M.; Jones, C.W. On the nature of the active species in palladium catalyzed Mizoroki-Heck and Suzuki–Miyaura couplings—Homogeneous or heterogeneous catalysis, a critical review. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2006, 348, 609–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
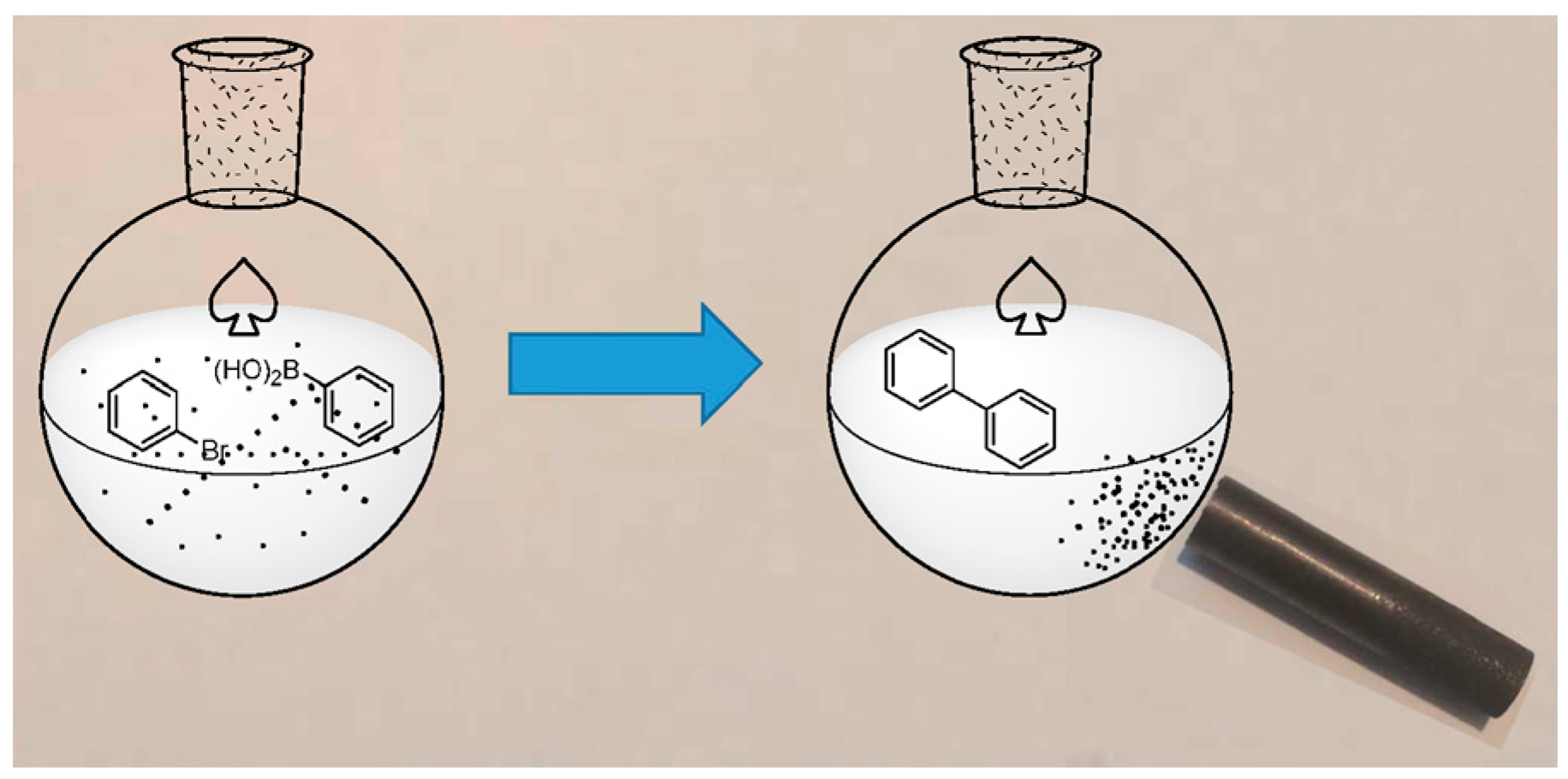
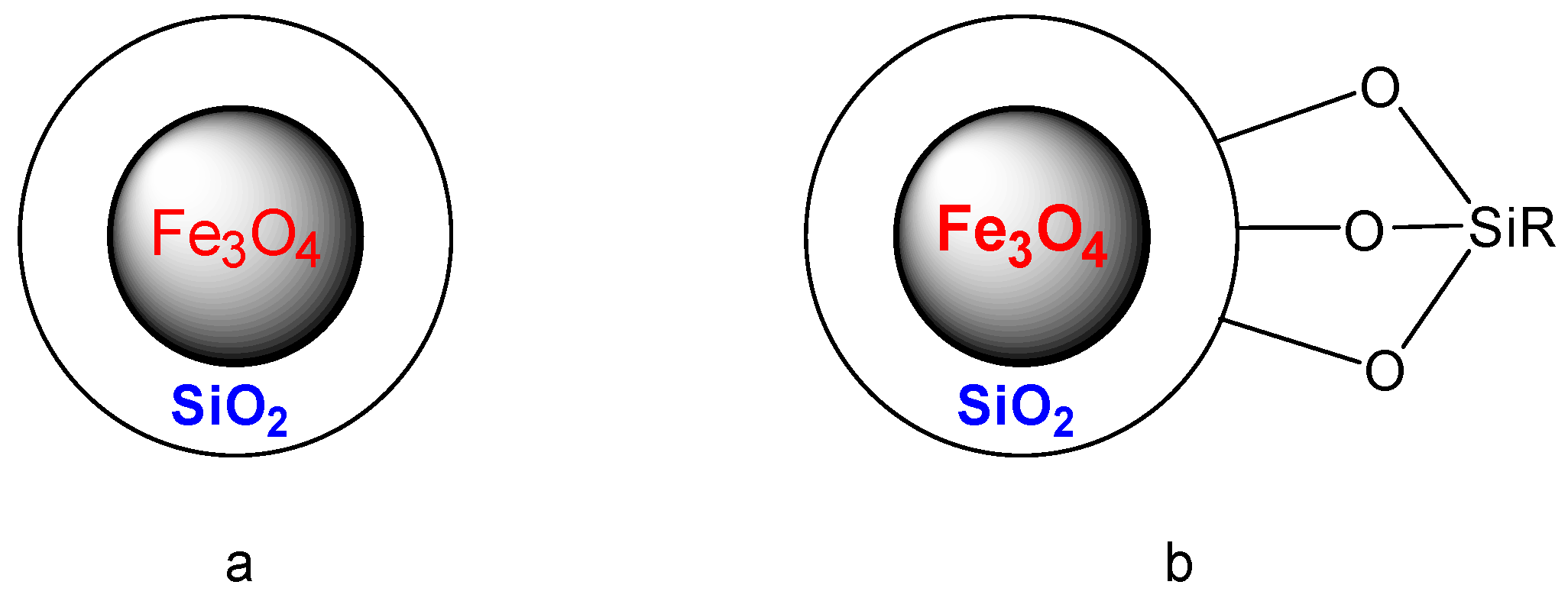
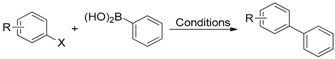
| Entry | Catalyst | Conditions | R | ArB(OH)2 | X | Yield | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fe3O4@C-Pd@mSiO2 | ArB(OH)2 (1.5 equiv.), ArX (1.0 equiv.), Cat. (1.5 mol% Pd), K2CO3, iPrOH, 70 °C, 6 h | H, 4-OMe, 4-NO2, 4-COMe | Ph, 3-pyridyl, 2-thiophenyl, 1-naphthalene | I | 73%–99% (for Ar = Ph) 19%–38% (for the heterocycles) | [43] |
| 2 | Pd@Fe3O4@C | ArB(OH)2 (1.2 equiv.), ArX (1.0 equiv.), Cat. (1.0 mol%), K2CO3, DMF/H2O 4:1, 100 °C, 4 h | H, 4-F, 4-OMe, 2-Me, 4-COMe, 2-COMe | Ph (for all X), 4-Me-Ph, 4-CF3-Ph | Cl, Br, OTf | >99% (for PhX with Ar = Ph) 45%–99% | [44] |
| 3 | Fe3O4@C-Pd@mCeO2 | ArB(OH)2 (1.2 mmol), ArX (1.0 mmol), Cat. (Pd 3.05 wt%), K2CO3, EtOH/H2O (1:1), 80 °C, 3 h | H, OMe, OEt, OCF3, OH, NH2, Me | Ph, 3-MePh, 4-MePh, 4-F, 4-OMe, 2-naphthyl | Cl, Br, I | 68%–99% (X = Br and I) 50%–58% (X = Cl) | [45] |
| 4 | Fe3O4@Pd-OA a | ArB(OH)2 (1.5 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), K3PO4, DMF, 115 °C, 5 h | 4-OMe | Ph, 4-FPh | I | 80%–94%b | [46] |
| 5 | Pd@ Fe3O4@ZnO | ArB(OH)2 (1 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (Pd 0.1 mol%), K2CO3, H2O, 100 °C, 1–3 h (for X = Br, I), 7–14 h (for X = Cl) | 4-Me, 4-COMe, 4-Cl, 4-F, 4-NO2, 4-NH2, 4-CN, 4-pyridin | Ph, 2-FPh, 3-FPh, 4-FPh, 4-EtPh | Cl, Br, I | 70%–95% (X = Br and I) 25%–53% (X = Cl) | [47] |
| 6 | Fe3O4@SiO2-Pd@mCeO2 | ArB(OH)2 (1.2 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (Pd 0.5 mmol%), K2CO3, EtOH/H2O (9:1) (for Br, I), 80 °C (for Br, I), DMF/H2O (9:1), 100 °C (for Cl), 3 h | H, 3-Me, 4-OMe, 4-OCF3, 4-COCH3 | Ph, 3-MePh, 4-MePh, 4-OMePh, 4-FPh | Cl, Br, I | 75%–99% (X = Br and I) 68%–88% (X = Cl) | [48] |
| 7 | Fe3O4@h-Pd@mCeO2 | ArB(OH)2 (1.2 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (Pd 0.5 mmol%), K2CO3, EtOH/H2O (9:1) (for Br, I), 80 °C (for Br, I), DMF/H2O (9:1), 100 °C (for Cl), 3 h | H, 3-Me, 4-OMe, 4-OCF3, 4-COCH3 | Ph, 3-MePh, 4-MePh, 4-OMePh, 4-FPh | Cl, Br, I | 82%–99% (X = Br and I) 72%–92% (X = Cl) | [48] |
| 8 | Pd@Ni@CB CB = carbon black | ArB(OH)2 (1.1 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (Pd 0.1 mol%), K2CO3, EtOH/H2O (1:1), 30 °C (for X = Br, I), 80 °C (for X = Cl), 45 min–1.5 h | H, 2-NO2, 3-NO2, 4-NO2, 2-OMe, 3-OMe, 4-OMe, 4-Me, 4-OH, 4-CN, 4-CHO | Ph | Cl, Br, I | 79%–95% (X = Br and I) 5%–60% (X = Cl) | [49] |
| Entry | Catalyst # | Conditions | R | ArB(OH)2 | X | Yield | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | ArB(OH)2 (1.2 equiv.), ArX (1.0 equiv.), Cat. (0.2 mol% Pd), K2CO3, EtOH/H2O (1:1), 60 °C, 3–12 h | H, 4-Me, 4-COCH3, 4-NO2, 4-CF3, 4-CN, 4-NH2, 4-OH, 3-OMe, 3-CHO, 2-OMe | Ph, 4-MePh, 4-OMePh, 4-ClPh | Cl, Br, I | 80%–99% (X = Br and I) 5%–12% (X = Cl) | [50] |
| 2 | Pd/Poly(m-ferrocenyl-aniline | ArB(OH)2 (1 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (2.0 mol% Pd), KOH, toluene, reflux, 20 h | 4-Me | Ph, 4-MePh, 3-MePh, 2-MePh, 4-CHOPh | Br | 67%–98% 26% (for ArB(OH)2 = 4-CHOPh) | [51] |
| 3 | 2 | ArB(OH)2 (1.2 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.025 mol% Pd), K2CO3, H2O, 60–80 °C, 4–15 h (for Br, I), 24 h (for Cl) a | H, 4-NO2, 4-OMe, 4-CHO, 4-OH, 4-NH2, 3-OH, 2-CHO, 2-Me, 2-Et, 2,6-Me, 2-thiophenyl, 5-pyrimidinyl, 3-pyridyl, 2-pyridil | Ph, 4-MePh, 2-MePh, 3-pyridyl | Cl, Br, I (three examples with Cl) | 72%-quant. (X = Br and I) 85%–96% (X = Cl) | [52] |
| 4 | 3 | ArB(OH)2 (1.2 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.0049 mol% Pd), K2CO3, NMP, 90 °C, 0.5–2.5 h (for X = Br or I), 2.5–9 h (for X = Cl) | H, 4-Me, 4-OMe, 4-CHO, 4-COCH3, 4-CN, 4-NO2, 4-Cl, 3-Me, 2-Me, 3-pyridyl, 5-pyrimidine, 3-thiophenyl | Ph, | Cl, Br, I | 77%–95% | [53] |
| 5 | 4 | ArB(OH)2 (1.5 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.5 mol%), K2CO3, EtOH, 80 °C, 3–10 h | H, 4-Me, 2-Me, 4-OH, 2-NO2 | Ph, 4-ClPh ( X = I) | Cl, Br, I | 95%–99% (X = Br and I) 16%–64% (X = Cl) | [54] |
| 6 | 5 | ArB(OH)2 (1.1 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.003 mol% Pd), K2CO3, DMF/H2O (1:2), 70 °C, 2–14 h Ultrasound applied power 160 W, 30 °C, 7–35 min | H, 4-Me, 4-OMe, 4-CHO, 4-Ac, 4-F | Ph, 4-OMePh | Br, I | 82%–93% (70 °C, conventional heating) 87%–96% (ultrasound conditions) | [55] |
| 7 | 6 | ArB(OH)2 (1.1 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.1 mol%), Na2CO3, EtOH/H2O (1:1), 80 °C, 30 min | H, 4-NO2 | 4-COMe, 4-COOEt, 4-CHO, 4-ethenyl, 4-tolyl, 4-ethenyl, 2-furanyl, 2-thiophenyl | Cl, Br, I (only one example with X = Cl and Br) | 60%–99% (for X = I) | [56] |
| 8 | 7 | ArB(OH)2 (1.2 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.3 mol%), K2CO3, NMP, 100 °C, 0.5–4.5 h (for Br, I), 4–12 h (for Cl) | H, 4-Me, 3-Me, 2-Me, 4-OMe, 4-NO2, 2-Me- 4-NO2, 4-NH2, 4-COMe, 4-CN, 1-naphthyl | Ph | Cl, Br, I | 77%–96% | [57] |
| 9 | 8 | ArB(OH)2 (1.5 equiv.), ArX (1.0 equiv.), Cat. (0.3 mol%), K2CO3, EtOH/H2O (1:1) , 30 °C (for X = I), 60 °C (for X = Br), 120 °C (for X = Cl), 1–24 h (for X = Br or I), 48 h (for X = Cl) | H, 4-OH, 4-OMe, 4-CHO, 4-NO2, 4-CN, 4-COMe, 4-biphenyl, 1-naphthalen, 5-pyrimidine | Ph, 4-ClPh, 4-MePh, 3,5-diFPh, 2-FPh, 2-NO2Ph, 1-naphthalene | Cl, Br, I | 74%–98% | [58] |
| 10 | 9 | ArB(OH)2 (1.1 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.2 mol%), K2CO3, EtOH/H2O, 20–25 °C, 0.2–6 h (for X = Br or I), 10–12 h (for X = Cl) | H, 4-Me, 4-COCH3, 4-OMe, 4-Cl, 3-NO2, 2-CHO, 1-naphthyl, 2-thienyl | Ph | Cl, Br, I | 88%–98% (X = Br and I) 20%–25% (X = Cl) | [59] |
| 11 | Fe3O4@EDTA-PdCl2 | ArB(OH)2 (1.1 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), K2CO3, TBABa, H2O, 80 °C, 2–6 h | H, 3-Me, 3-CF3, 1-naphthyl, 2-thienyl, (for X = Br) H, 4-Me, 4-OMe, 4-NO2, 4-CHO (for X = I) | Ph | Br, I | 76%–95% | [60] |
| 12 | 10 | ArB(OH)2 (1.2 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.5 mol%), Et3N, TBAB b, DMF/H2O (1:1), 75 °C, 1–6 h (X = Br and I), 24 h ( X = Cl) | H, 4-Br, 2-thiophenyl, 1-naphthyl, 4-CN, 4-NO2, 4-Me | Ph, 4-OMePh | Cl, Br, I | 47%–94% (X = Br and I) 35%–37% (X = Cl) | [61] |
| 13 | Pd/Fe3O4/r-GO c | ArB(OH)2 (1.5 equiv.), ArX (1.0 equiv.), Cat. (0.36 mol% Pd), K2CO3, H2O, 80 °C, 15 min–2.5 h | H, 4-Me, 4-CN, 4-NO2 | Ph | Cl, Br, I | 78%–99% | [62] |
| 14 | Fe3O4-NHC-Pd | ArB(OH)2 (1.2 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.02 mol%), K2CO3, EtOH/H2O (3:1), 70 °C, 12 h | H, 4-Me, 4-OMe, 4-COMe, 4-CHO, 4-CO2H, 4-CN, 4-NO2 | Ph, 4-MePh, naphthyl, 2,6-diMePh | Br | 87%–99% 61% for 2,6-diMePh | [63] |
| 15 | 11 | ArB(OH)2 (1.1 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.002 mol%), K2CO3, DMF/H2O (1:2), 70 °C, 4–14 h, microwave irradiation 200 W, 70 °C, 2–7 min | H, 4-Me, 4-OMe, 4-CHO | Ph, 4-OMePh | Br, I | 81%–91% (conventional heating) 85%–95% (microwave irradiation) | [64] |
| 16 | Fe3O4@PEG-iminophosphine-Pd | ArB(OH)2 (1.2 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.05 mol%), K2CO3, H2O, 65 °C, 5–8 h (for Br, I) 24 h (for Cl) | 4-Me, 3-Me, 2-Me, 4-OMe, 4-CH2OH, 4-NO2, 4-COMe, 4-F, 4-CN | Ph, 4-OMePh, 4-CF3Ph | Cl (only one example), Br, I | 89%–99% (X =Br and I) 88% (X =Cl, R = 4-NO2, Ar = Ph) | [65] |
| 17 | 12 | ArB(OH)2 (1.0 equiv.), ArX (1.0 equiv.), Cat. (0.37 mol%), Na2CO3, PEG, 100 °C, 20–150 min | H, 4-Me, 4-OMe, 4-CN, 4-CN, 4-Cl, 4-NO2, 3-CHO, 3-CF3, | Ph, 4-OMePh, 3,4-diFPh | Br, I | 88%–98% | [66] |
| 18 | 13 | ArB(OH)2 (1.2 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.024 mol%), K2CO3, Tx d/THF (9:1) , 65 °C, 30 h (for Br) 80 °C, 90 h (for Cl) | 4-Me | Ph | Cl, Br | 100% conv.e | [67] |
| 19 | 14 | ArB(OH)2 (1.2 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.03–0.30 mol%) f K2CO3, H2O, reflux, 4–12 h (for X = Br or I), 24 h (for X = Cl) | H, 4-OMe, 4-CHO, 4-NO2, 4-Cl, 2-Me, 5-pyrimidine, | Ph, 4-MePh, 4-OMePh, 3-NO2Ph, 2,6-diMePh, 3,5-diFPh, 2-benzofuranyl, 2-naphtyl, 1-naphthyl | Cl, Br, I | 75%–99% (X = Br and I) 36%–65% (X = Cl) | [68] |
| 20 | 15 | ArB(OH)2 (1.2 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.1 mol%), K2CO3, EtOH/H2O (1:1), 25 °C, 1–5 h (for Br, I), 15–24 h (for Cl) | H, 4-Me, 4-OMe, 2-OMe, 4-F, 4-NO2, 4-COMe | Ph | Cl, Br, I | 85%–96% (X =Br and I) 60%–70% (X = Cl) | [69] |
| 21 | 16 | ArB(OH)2 (1.1 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.036 mol%), K2CO3, EtOH/H2O (1:1), rt, 0.5–2 h | H,g 4-OMe,g 3-OMe, 2-OMe, 4-NO2,g 4-CHO 4-Cl, m-Cl, o-Cl (X = Br) | Ph | Cl, Br, I | 75%-98% (X = Br and I) 65%–74% (X = Cl) | [70] |
| 22 | Pd/Fe3O4@PDA h | ArB(OH)2 (1.1 equiv.), ArX (1 equiv.), Cat. (0.46 mol% for X = I and 0.27 for X = N2+BF4−), K2CO3, EtOH/H2O (1:1) (for X = Br and I), 100 °C (for X = Br), 80 °C (for X = I), rt (for X = N2+BF4−), 10 h (for X = I) and 2–3.5 h (for X = N2+BF4−) | H (for X = I) 4-OMePh, 4-BrPh, 4-NO2Ph (for X = N2+BF4−) | Br, I, N2+BF4− | 77%–98% | [71] |
© 2017 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sydnes, M.O. The Use of Palladium on Magnetic Support as Catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reactions. Catalysts 2017, 7, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7010035
Sydnes MO. The Use of Palladium on Magnetic Support as Catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reactions. Catalysts. 2017; 7(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7010035
Chicago/Turabian StyleSydnes, Magne O. 2017. "The Use of Palladium on Magnetic Support as Catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reactions" Catalysts 7, no. 1: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7010035
APA StyleSydnes, M. O. (2017). The Use of Palladium on Magnetic Support as Catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reactions. Catalysts, 7(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7010035