Noble Metal-Free Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions Templated by Tobacco Materials for Catalytic Oxidation of CO
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
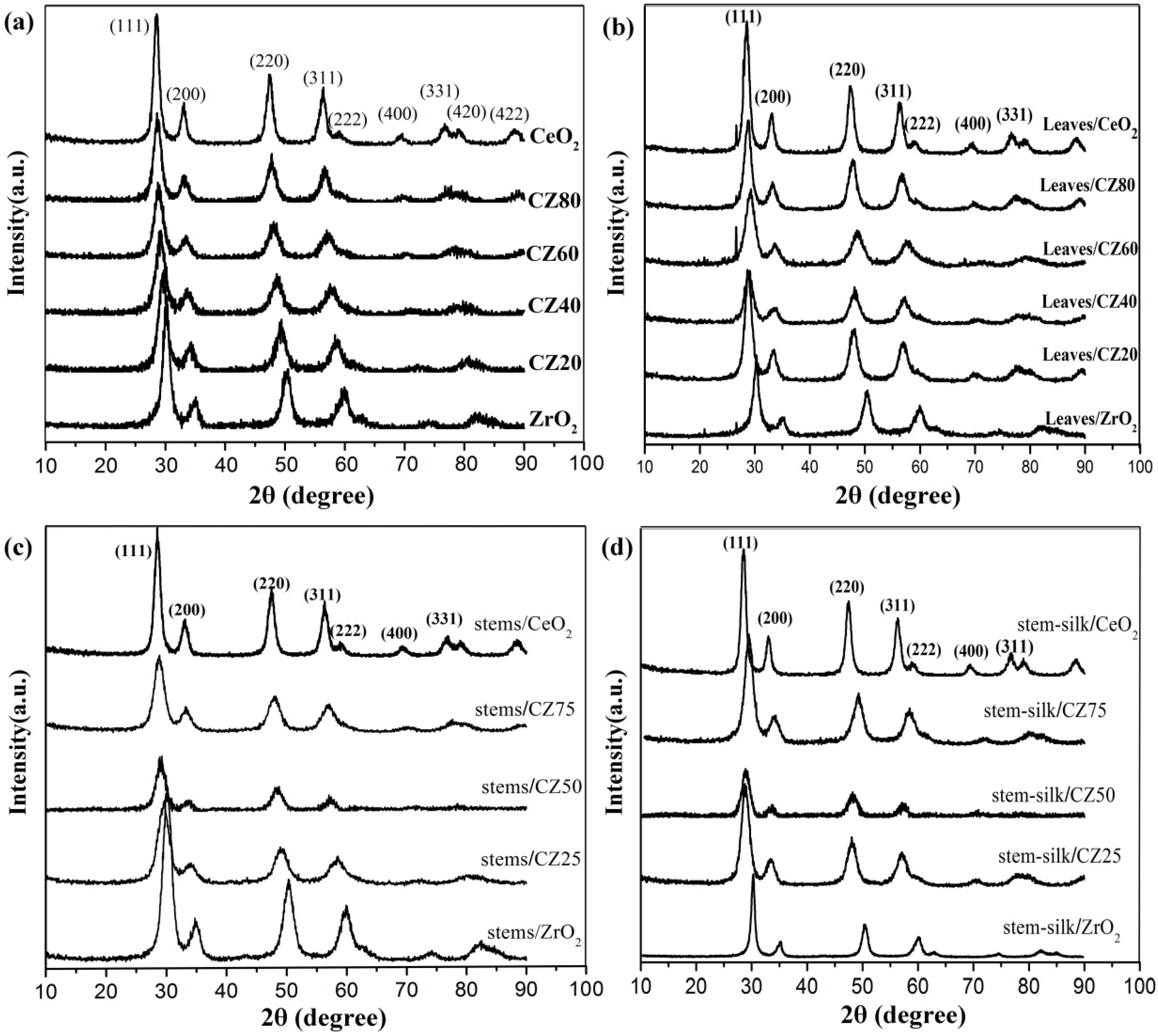
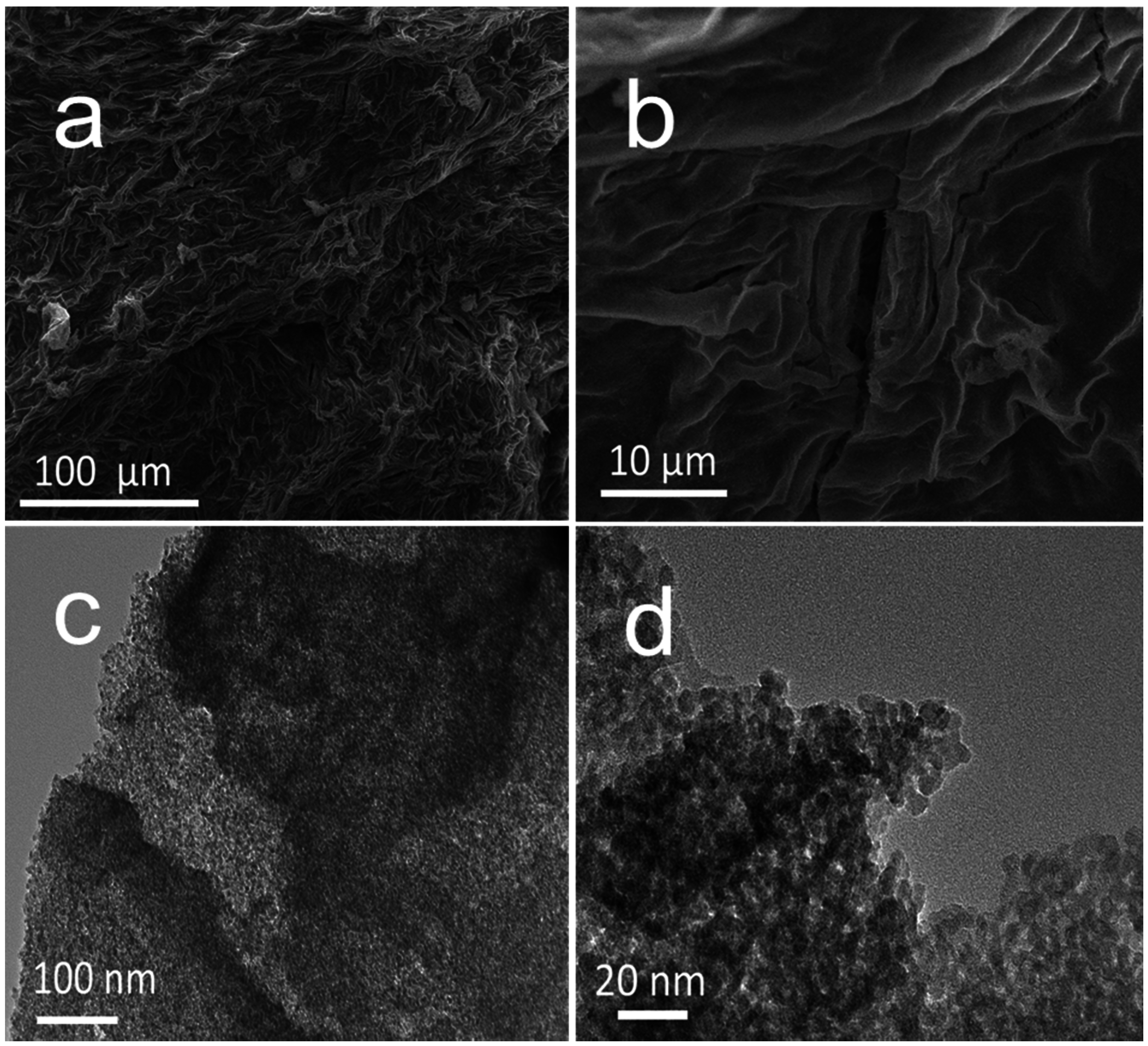
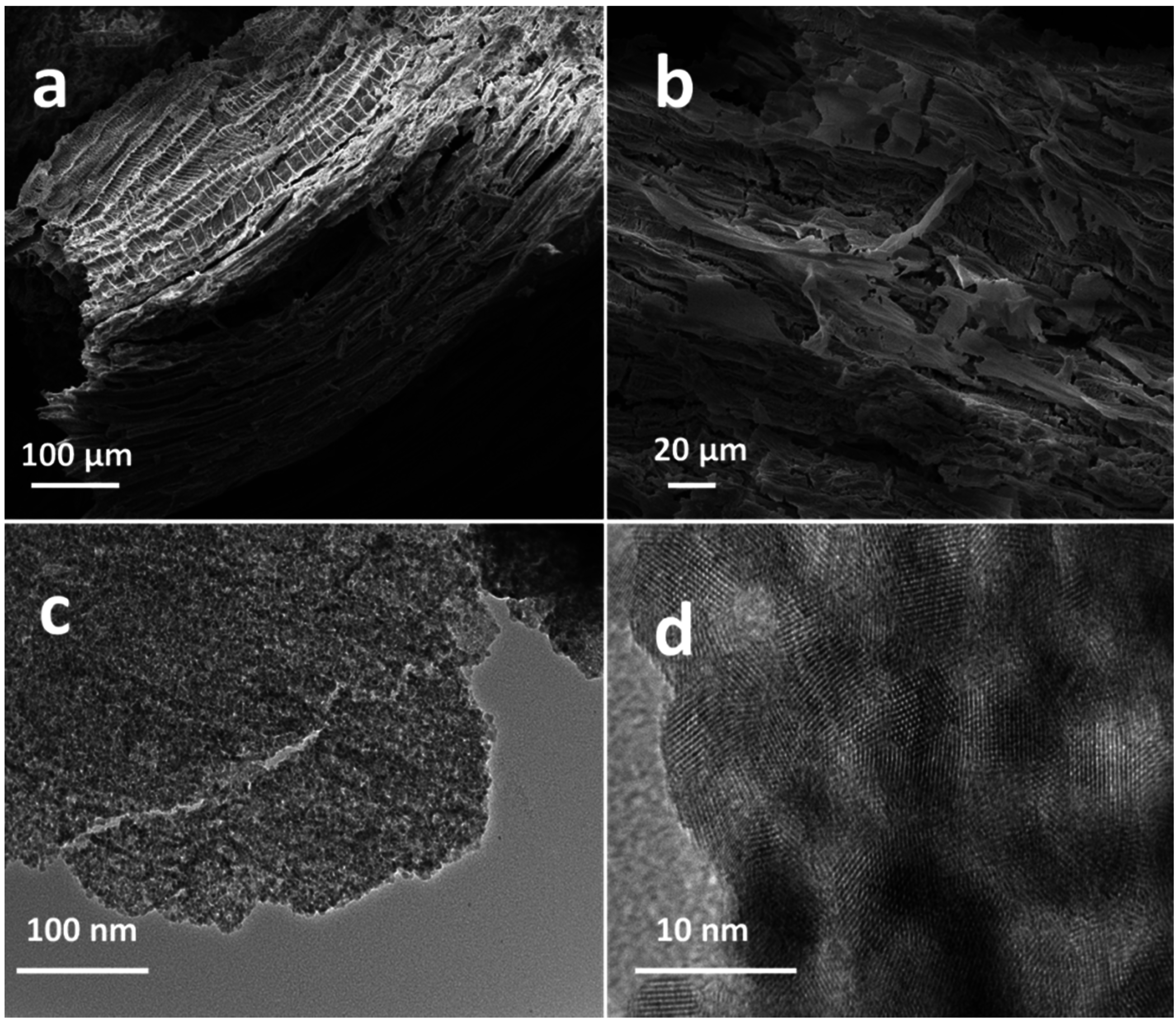
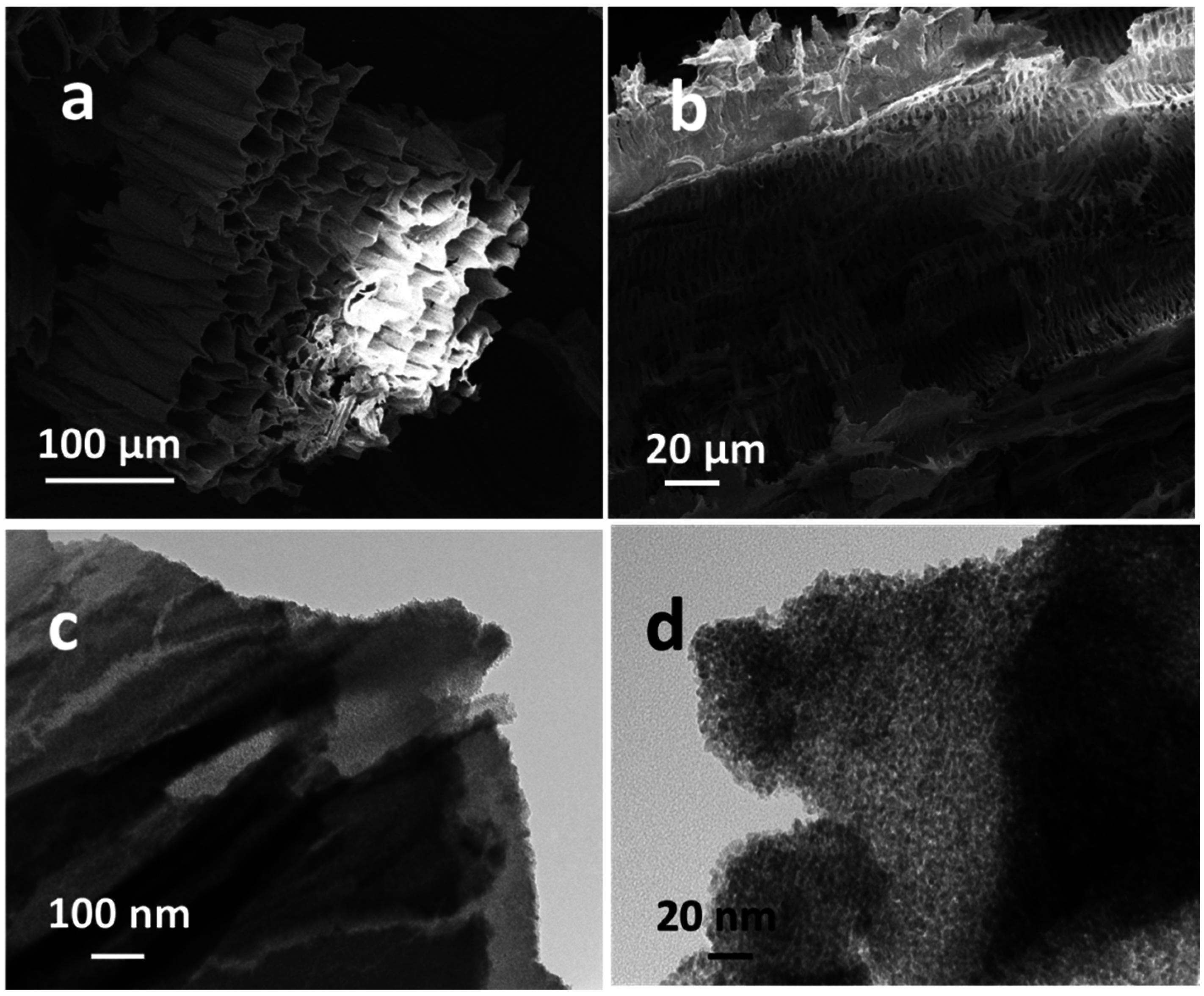
2.1. Characterizations
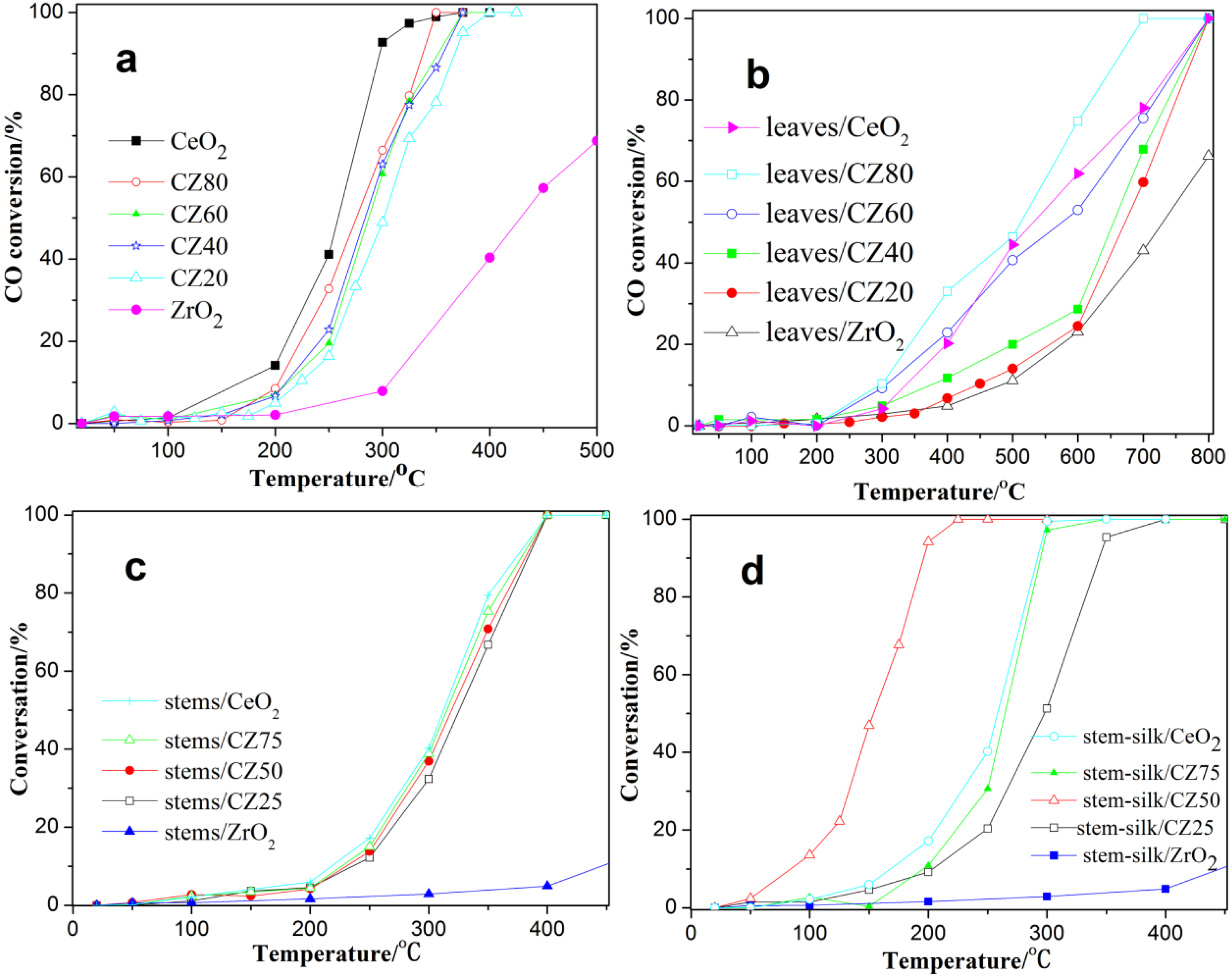
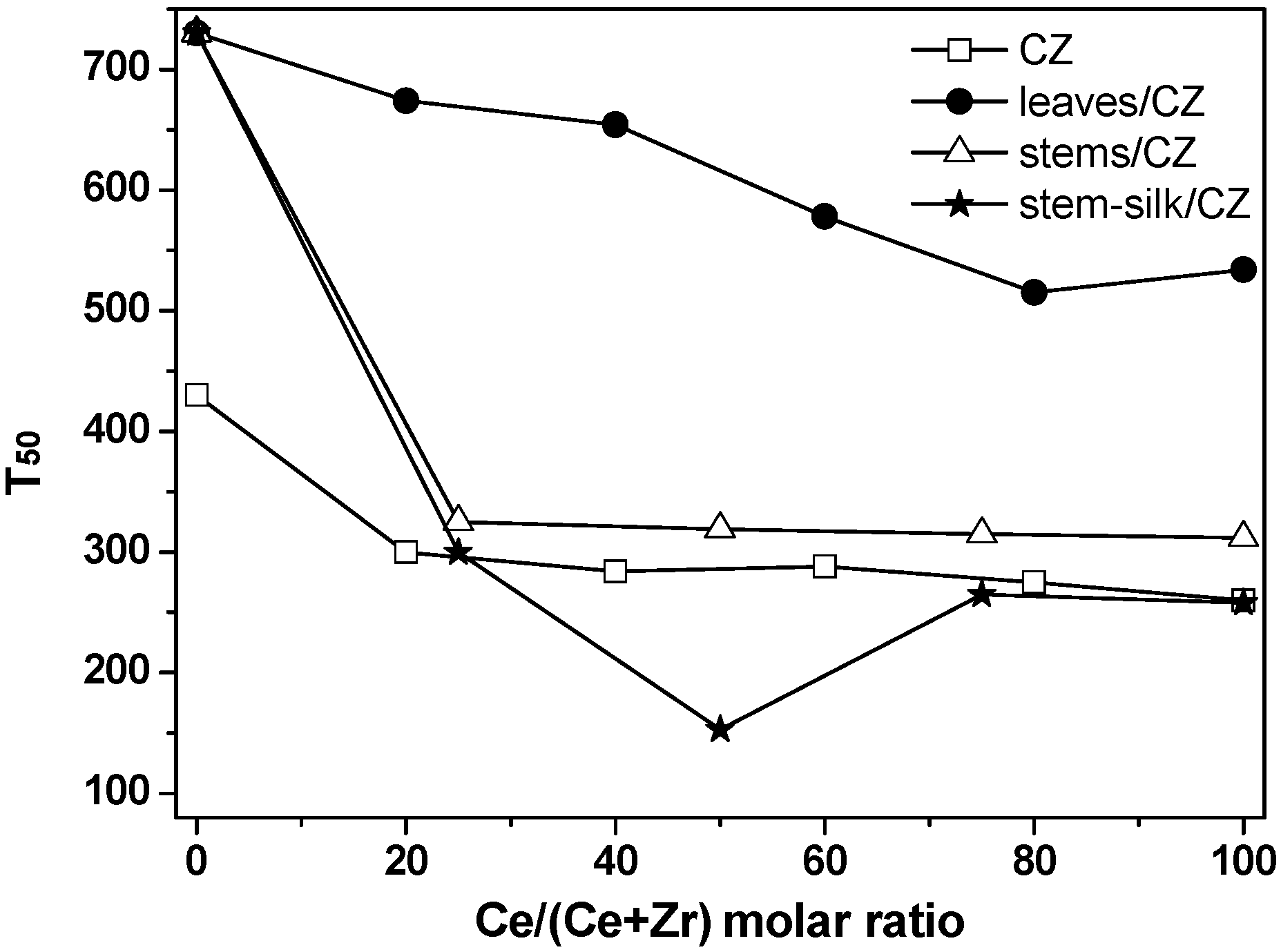
2.2. Catalytic Activity
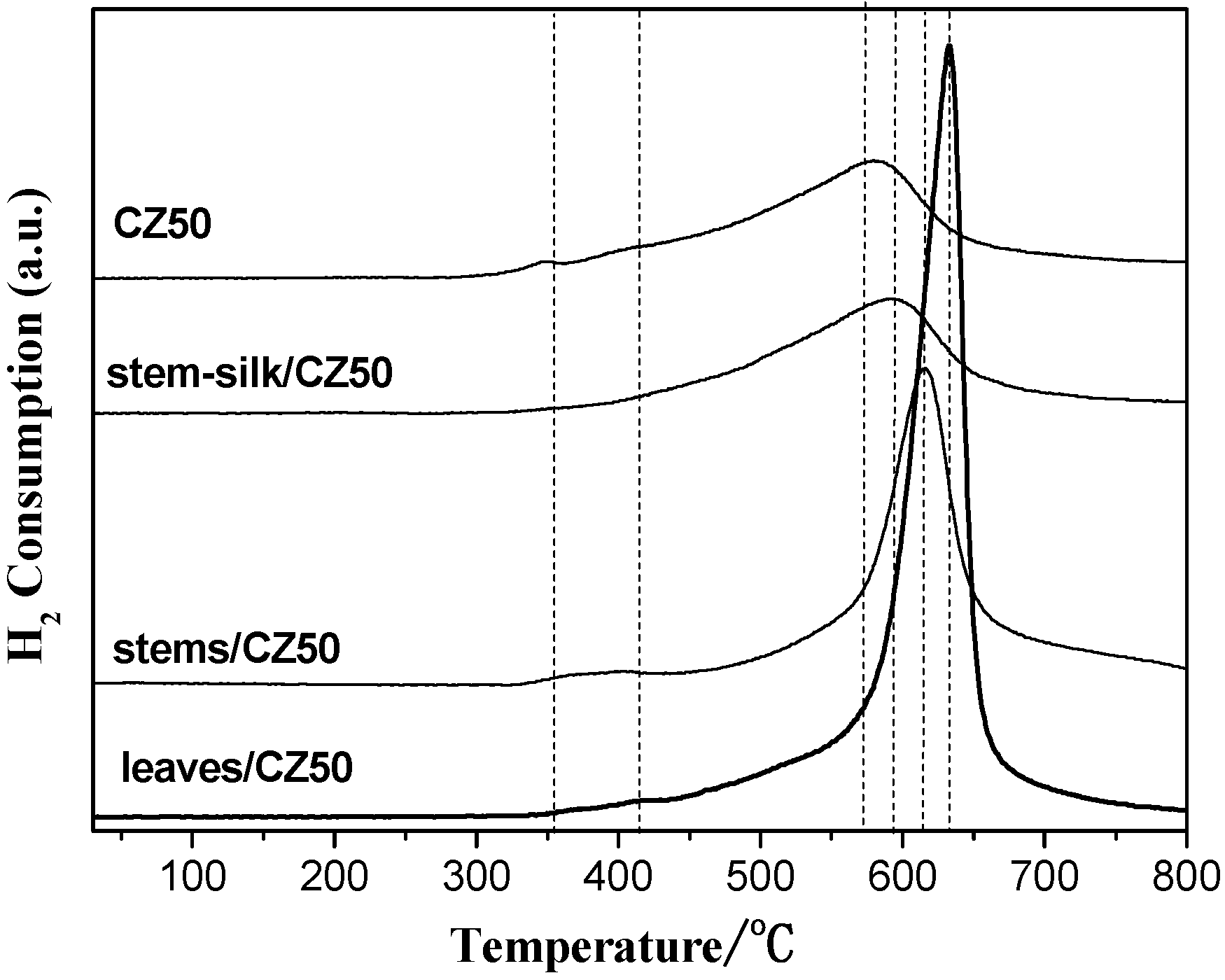
2.3. Oxygen Storage Capacity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis
3.2. Characterizations
3.3. Catalytic Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shelef, M.; McCabe, R.W. Twenty-five years after introduction of automotive catalysts: What next? Catal. Today 2000, 62, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twigg, M.V. Progress and future challenges in controlling automotive exhaust gas emissions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 70, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.C.; Yao, Y.F.Y. Ceria in automotive exhaust catalysts: I. Oxygen storage. J. Catal. 1984, 86, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, B.C.; Heinzel, A. Materials for fuel-cell technologies. Nature 2001, 414, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Minamidate, Y.; Tonouchi, S.; Goto, T.; Dong, Q.; Yamane, H.; Sato, T. Solution synthesis of homogeneous plate-like multifunctional CeO2 particles. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 5976–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laachir, A.; Perrichon, V.; Badri, A.; Lamotte, J.; Catherine, E.; Lavalley, J.C.; Fallah, J.E.; Hilaire, L.; Normand, F.L.; Quéméré, E.; et al. Reduction of CeO2 by hydrogen. Magnetic susceptibility and Fourier-transform infrared, ultraviolet and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy measurements. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1991, 87, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Farrauto, R.; Deeba, M. Part II: Oxidative Thermal Aging of Pd/Al2O3 and Pd/CexOy-ZrO2 in Automotive Three Way Catalysts: The Effects of Fuel Shutoff and Attempted Fuel Rich Regeneration. Catalysts 2015, 5, 1797–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Farrauto, R.; Deeba, M.; Valsamakis, I. Part I: A Comparative Thermal Aging Study on the Regenerability of Rh/Al2O3 and Rh/CexOy-ZrO2 as Model Catalysts for Automotive Three Way Catalysts. Catalysts 2015, 5, 1770–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varez, A.; Garcia-Gonzalez, E.; Sanz, J. Cation miscibility in CeO2-ZrO2 oxides with fluorite structure. A combined TEM, SAED and XRD Rietveld analysis. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 4249–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovarelli, A.; Zamar, F.; Llorca, J.; Leitenburg, C.D.; Dolcetti, G.; Kiss, J.T. Nanophase Fluorite-Structured CeO2-ZrO2 Catalysts Prepared by High-Energy Mechanical Milling. J. Catal. 1997, 169, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.S.; Walton, R.I.; Thompsett, D.; Fisher, J.; Ashbrook, S.E. One-Step Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Ceria-Zirconia Mixed Oxides: The Beneficial Effect of Sodium Inclusion on Redox Properties. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 4500–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, T.; Watanabe, T.; Matsushita, N.; Yoshimura, M. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Monodisperse Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 Metastable Solid Solution Nanocrystals. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2009, 2054–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masui, T.; Nakano, K.; Ozaki, T.; Adachi, G.-Y.; Kang, Z.; Eyring, L. Redox Behavior of Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions Modified by the Chemical Filing Process. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 1834–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Yang, H. Investigation of the Oxygen Exchange Property and Oxygen Storage Capacity of CexZr1−xO2 Nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 6921–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, J.; Fornasiero, P.; Balducci, G.; Di Monte, R.; Hickey, N.; Sergo, V. Effect of ZrO2 content on textural and structural properties of CeO2-ZrO2 solid solutions made by citrate complexation route. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2003, 349, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Shen, M.; Wang, J. Comparison of the microstructure and oxygen storage capacity modification of Ce0.67Zr0.33O2 from CaO and MgO doping. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 441, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghom, S.A.; Zamani, C.; Nazarpour, S.; Andreu, T.; Morante, J.R. Oxygen sensing with mesoporous ceria-zirconia solid solutions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 140, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.T.; Chen, K.B.; Wang, M.F.; Weng, S.F.; Lee, C.S.; Lin, M.C. Enhanced catalytic activity of Ce1−xMxO2 (M = Ti, Zr, and Hf) solid solution with controlled morphologies. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3286–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zhan, W.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Lu, G. Preparation of high oxygen storage capacity and thermally stable ceria-zirconia solid solution. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thammachart, M.; Meeyoo, V.; Risksomboon, T.; Osuwan, S. Catalytic activity of CeO2-ZrO2 mixed oxide catalysts prepared via sol–gel technique: CO oxidation. Catal. Today 2001, 68, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Rosei, F.; Ma, D. Template engaged synthesis of hollow ceria-based composites. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 5578–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahzadeh-Ghom, S.; Zamani, C.; Andreu, T.; Epifani, M.; Morante, J.R. Improvement of oxygen storage capacity using mesoporous ceria-zirconia solid solutions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 108–109, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.W.; Holmes, S.M.; Hanif, N.; Cundy, C.S. Hierarchical Pore Structures through Diatom Zeolitization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 2707–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.-X.; Chow, S.-K.; Zhang, D. Biomorphic mineralization: From biology to materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 542–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Zhai, Z.; He, J.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Synthesis, characterizations and photocatalytic studies of mesoporous titania prepared by using four plant skins as templates. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, A.; Mabande, G.T.P.; Selvam, T.; Schwieger, W.; Rudolph, A.; Hermann, R.; Sieber, H.; Greil, P. Biotemplating of Luffa cylindrica sponges to self-supporting hierarchical zeolite macrostructures for bio-inspired structured catalytic reactors. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2006, 26, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Miao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Tao, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, J. Synthesis of Cobalt Doped Porous Titania-Silica Prepared by Using the Rice Husks as Both Silicon Source and Template and its Catalytic Oxidation of 4-Methyl Pyridine. Catal. Lett. 2009, 131, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zeng, M.; He, J.; Duan, L.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Syntheses and characterizations of cobalt doped mesoporous alumina prepared using natural rubber latex as template and its catalytic oxidation of tetralin to tetralone. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 396, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Zi, G.; Yao, Z.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xue, D.; Wang, B.; Wang, J. Synthesis, characterizations and catalytic allylic oxidation of limonene to carvone of cobalt doped mesoporous silica templated by reed leaves. Catal. Commun. 2015, 59, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Song, H.; Chou, L. Mesoporous nanocrystalline ceria-zirconia solid solutions supported nickel based catalysts for CO2 reforming of CH4. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 18001–18020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Hoflund, G. Low-temperature catalytic carbon monoxide oxidation over hydrous and anhydrous palladium oxide powders. J. Catal. 2007, 245, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fally, F.; Perrichon, V.; Vidal, H.; Kaspar, J.; Blanco, G.; Pintado, J.M.; Bernal, S.; Colon, G.; Daturi, M.; Lavalley, J.C. Modification of the oxygen storage capacity of CeO2-ZrO2 mixed oxides after redox cycling aging. Catal. Today 2000, 59, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornasiero, P.; Balducci, G.; di Monte, R.; Kašpar, J.; Sergo, V.; Gubitosa, G.; Ferrero, A.; Graziani, M. Modification of the Redox Behaviour of CeO2 Induced by Structural Doping with ZrO2. J. Catal. 1996, 164, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Yu, J.C.; Kwong, T.; Mak, A.C.; Lai, S. Morphology-Controllable Synthesis of Mesoporous CeO2 Nano- and Microstructures. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 4514–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Peng, Q.; Li, Y. Enhanced catalytic activity of ceria nanorods from well-defined reactive crystal planes. J. Catal. 2005, 229, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Fu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Hermansson, K. The electronic and reduction properties of Ce0.75Zr0.25O2(110). Chem. Phys. Lett. 2008, 450, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Zhou, Y.; Ta, N.; Li, Y.; Shen, W. Redox properties and catalytic performance of ceria-zirconia nanorods. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 4184–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiuchi, N.; Haneda, M.; Ozawa, M. Enhancement of OSC property of Zr rich ceria-zirconia by loading a small amount of platinum. Catal. Today 2014, 232, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | SBET (m2·g−1) | Samples | SBET (m2·g−1) | Samples | SBET (m2·g−1) | Samples | SBET (m2·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CeO2 | 58.78 | leaves/CeO2 | 41.37 | stems/CeO2 | 22.95 | stem-silk/CeO2 | 48.35 |
| CZ80 | 76.55 | leaves/CZ80 | 95.61 | stems/CZ75 | 55.93 | stem-silk/CZ75 | 77.89 |
| CZ60 | 91.80 | leaves/CZ60 | 70.88 | stems/CZ50 | 66.15 | stem-silk/CZ50 | 99.47 |
| CZ40 | 112.08 | leaves/CZ40 | 66.24 | stems/CZ25 | 42.73 | stem-silk/CZ25 | 75.71 |
| CZ20 | 96.31 | leaves/CZ20 | 60.84 | stems/ZrO2 | 39.56 | stem-silk/ZrO2 | 22.49 |
| ZrO2 | 55.03 | leaves/ZrO2 | 42.02 | - | - | - | - |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, D.; Duan, D.; Han, Y.; He, J.; He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yan, Z.; Wang, J.; Yuan, F. Noble Metal-Free Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions Templated by Tobacco Materials for Catalytic Oxidation of CO. Catalysts 2016, 6, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6090135
Zhu D, Duan D, Han Y, He J, He Y, Chen Y, Zhang W, Yan Z, Wang J, Yuan F. Noble Metal-Free Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions Templated by Tobacco Materials for Catalytic Oxidation of CO. Catalysts. 2016; 6(9):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6090135
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Donglai, Deliang Duan, Yi Han, Jiao He, Yi He, Yongjuan Chen, Wei Zhang, Zhiyin Yan, Jiaqiang Wang, and Fagui Yuan. 2016. "Noble Metal-Free Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions Templated by Tobacco Materials for Catalytic Oxidation of CO" Catalysts 6, no. 9: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6090135
APA StyleZhu, D., Duan, D., Han, Y., He, J., He, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, W., Yan, Z., Wang, J., & Yuan, F. (2016). Noble Metal-Free Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions Templated by Tobacco Materials for Catalytic Oxidation of CO. Catalysts, 6(9), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6090135







