Solvent-Free Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Technical-Grade Sugar Esters and Evaluation of Their Physicochemical and Bioactive Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
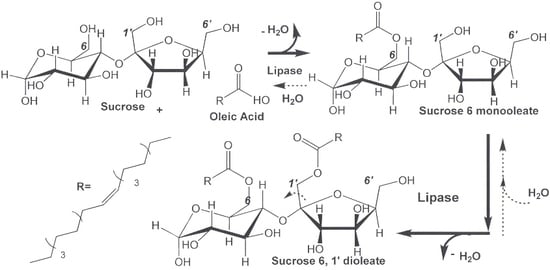
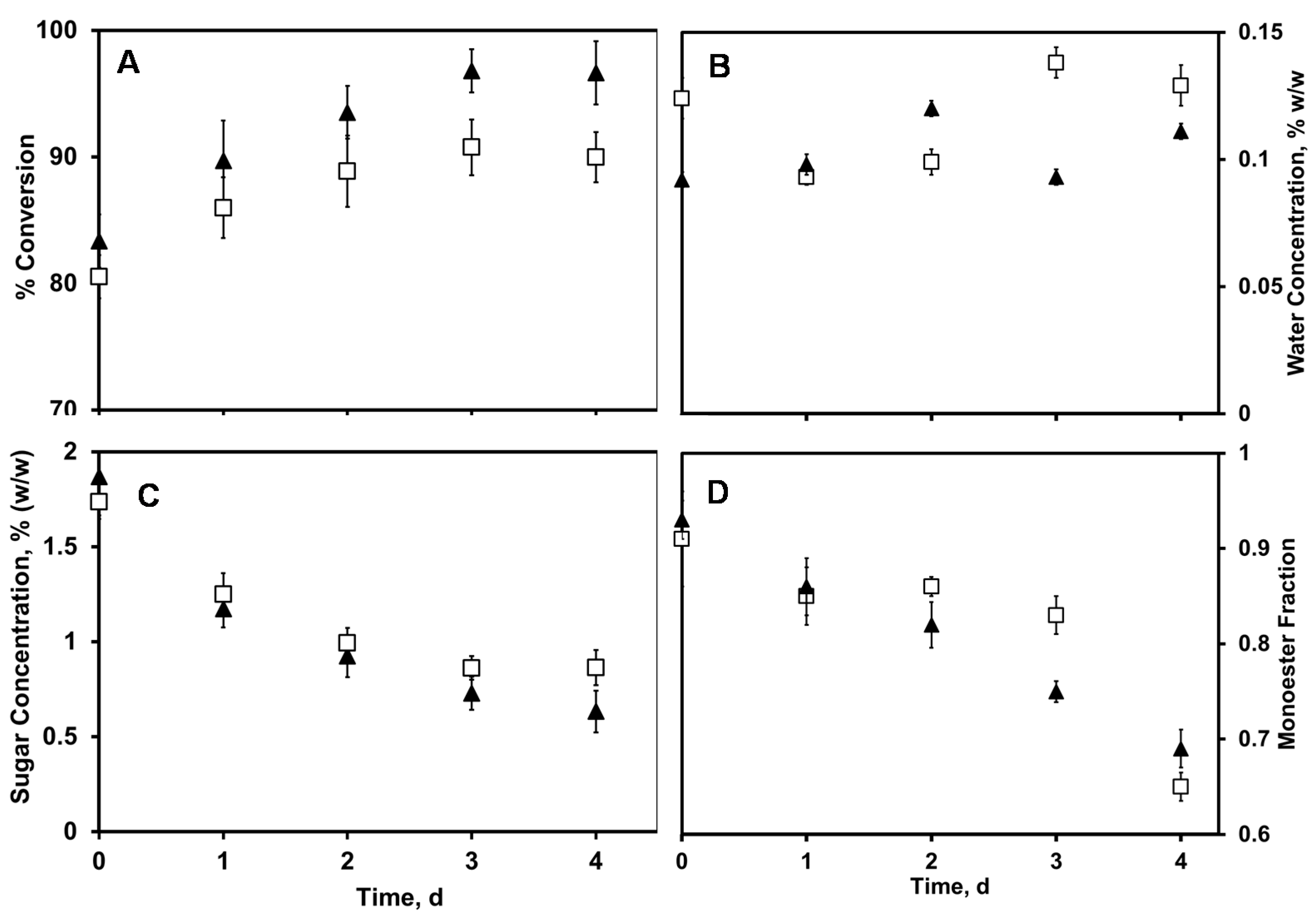
2.1. Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Technical-Grade Sucrose and Fructose Oleate
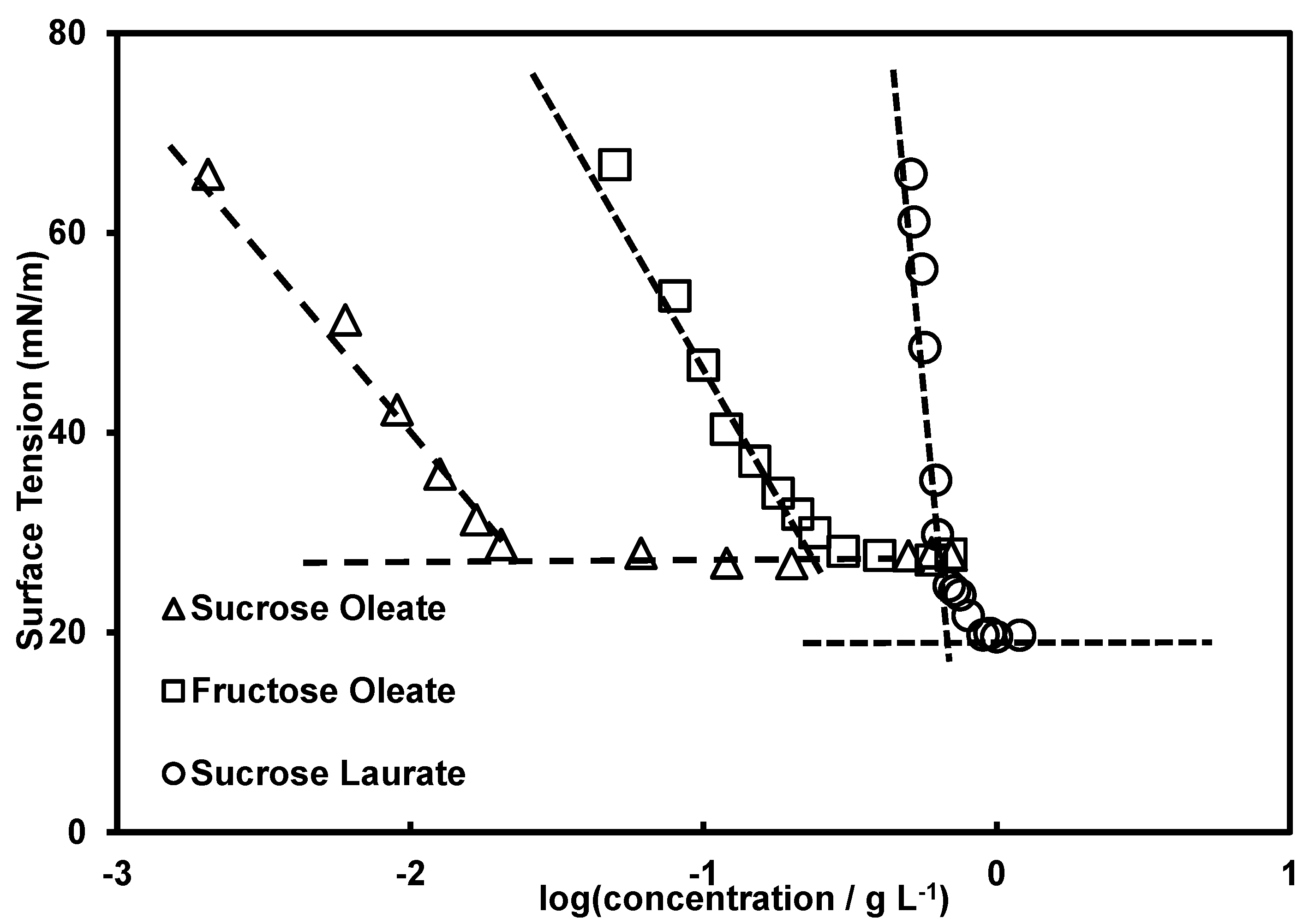
2.2. Composition and Surface Activity
2.3. Composition and Surface Activity
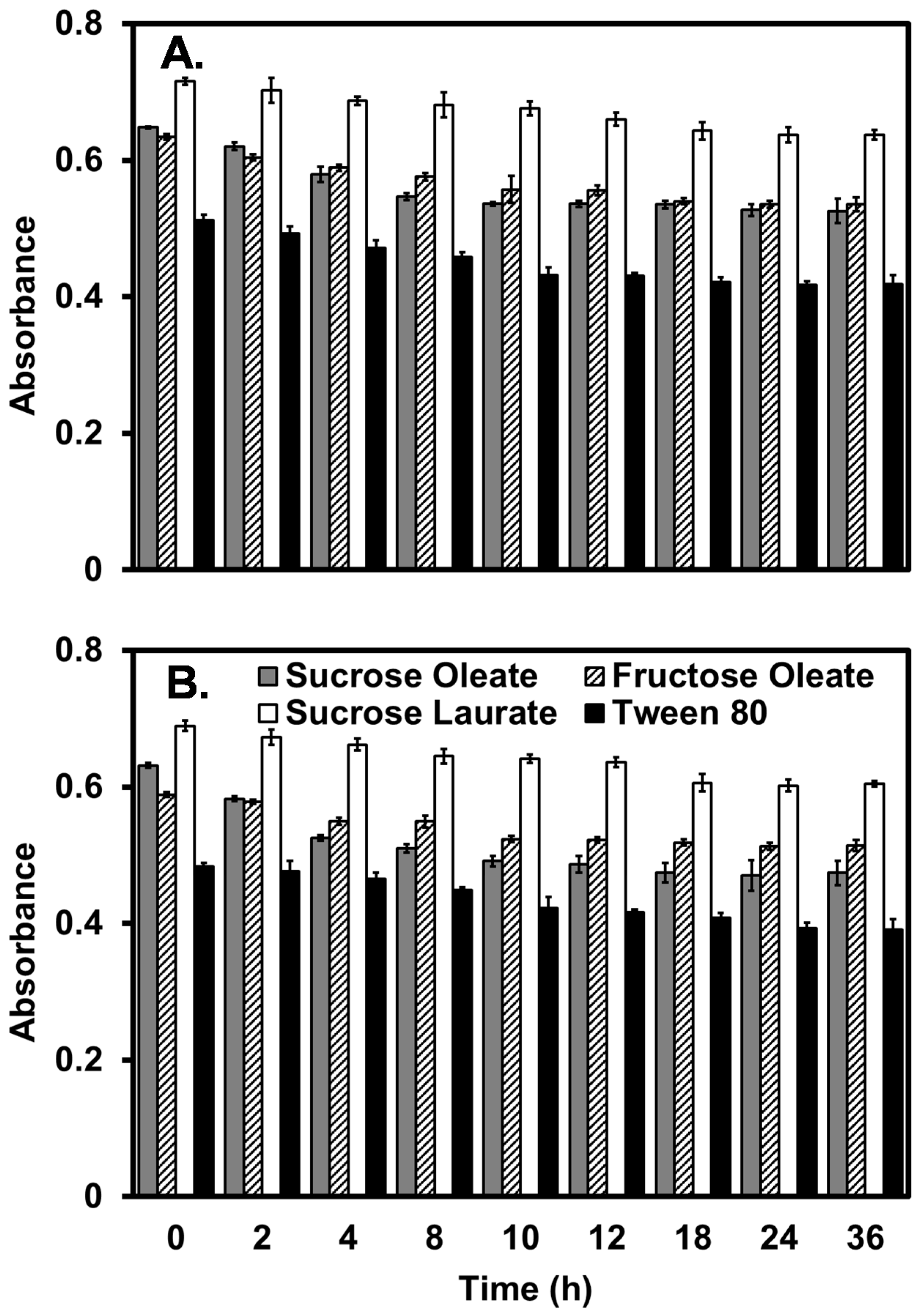
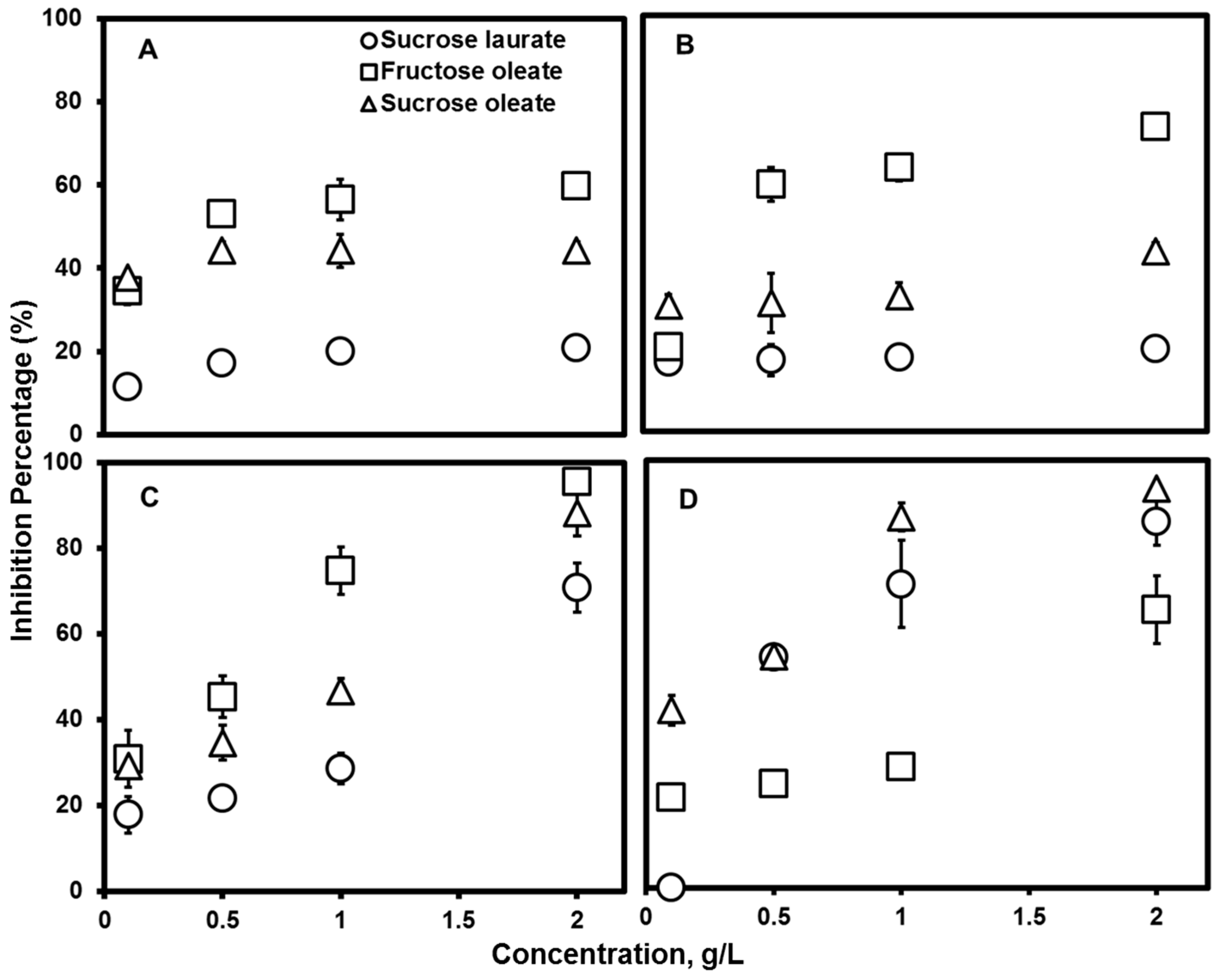
2.4. Antimicrobial Activity
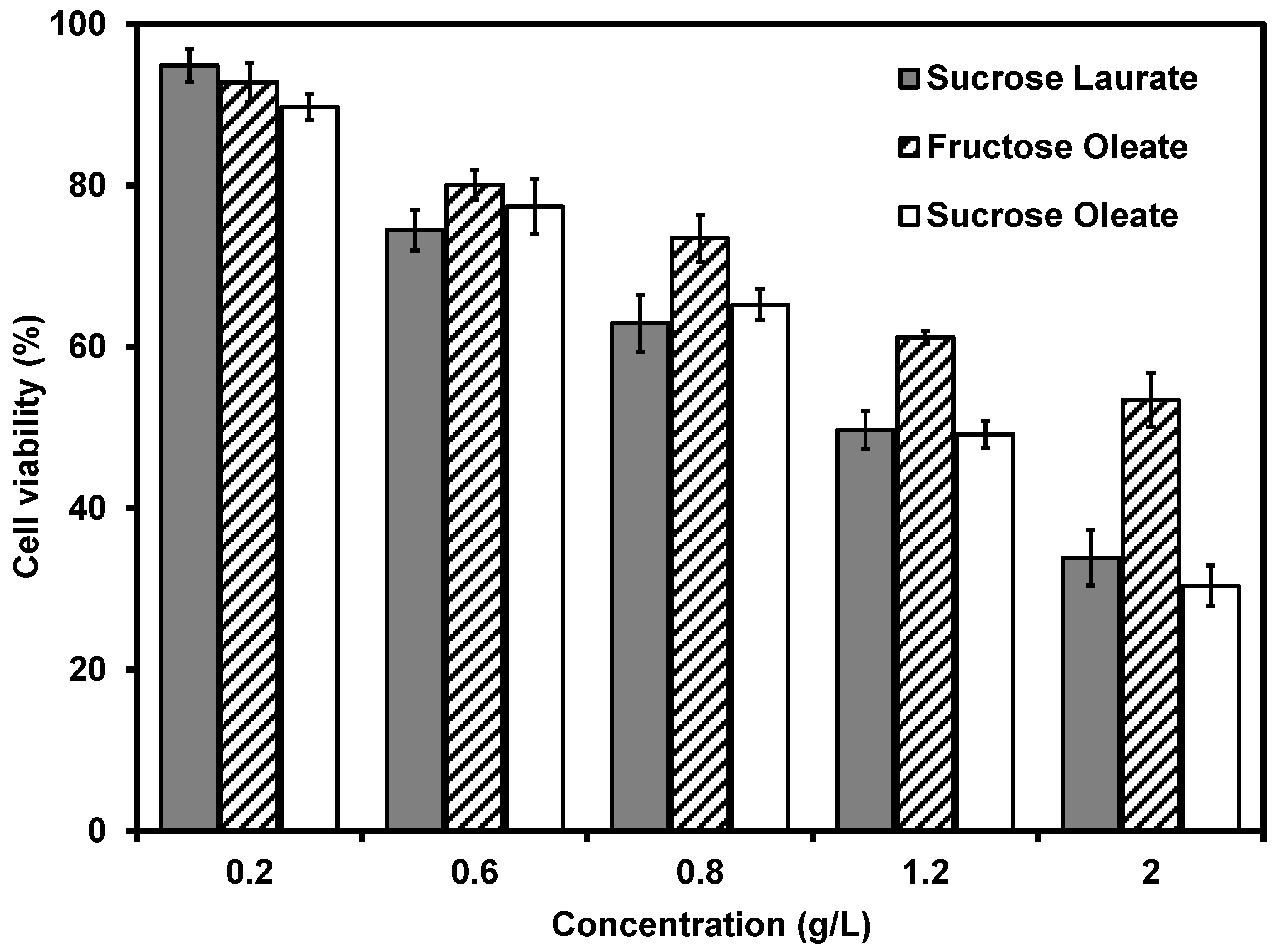
2.5. Antitumor Activity
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Methods
3.2. Formation of Supersaturated Solutions of Size-Reduced Sucrose Using High Pressure Homogenization
3.3. Lipase-Catalyzed Sugar Oleate Synthesis Using Solvent-Free Suspensions
3.4. Composition of Reaction Medium
3.5. Specific Gravity and Surface Tension
3.6. Emulsification Capacity and Stability
3.7. Antimicrobial Activity
3.8. Antitumor Activity
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HIV | Anti-human immunodeficiency virus |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| HPH | High pressure homogenization |
| RML | Rhizomucor miehei lipase |
| CALB | Candida antarctica lipase B |
| PBBR | A packed-bed bioreactor |
| STBR | A stirred tank bioreactor |
| HLB | Hydrophilic–lipophilic balance |
| CMC | Critical micellar concentration |
| OD | Optical density |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
References
- Pyo, S.; Hayes, D. Synthesis of saccharide–fatty acid ester biosurfactants catalyzed by lipase. In Biobased Surfactants and Detergents: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications; Hayes, D., Kitamoto, D., Solaiman, D., Ashby, D., Eds.; AOCS Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 2009; pp. 323–350. [Google Scholar]
- Gumel, A.M.; Annuar, M.S.M.; Heidelberg, T.; Chisti, Y. Lipase mediated synthesis of sugar fatty acid esters. Proc. Biochem. 2011, 46, 2079–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, P.; Beach, E.S.; Zimmerman, J.B. Derivation and synthesis of renewable surfactants. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1499–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, S.A.; Gratton, E.; Zanocco, A.L.; Lemp, E.; Gunther, G. Sucrose monoester micelles size determined by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaoka, M.; Imamura, K.; Hirakawa, Y.; Tahara, Y.; Kamiya, N.; Goto, M. Sucrose laurate-enhanced transcutaneous immunization with a solid-in-oil nanodispersion. MedChemComm 2014, 5, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Sang, Z.; Sun, C.; Dai, Y.; Deng, Y. Synthesis, characterization, antibacterial and antifungal evaluation of novel monosaccharide esters. Molecules 2012, 17, 8661–8673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Ye, R.; Davidson, P.M.; Hayes, D.G.; Golden, D.A.; Zhong, Q. Sucrose monolaurate improves the efficacy of sodium hypochlorite against Escherichia coli O157:H7 on spinach. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 145, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoydonckx, H.E.; de Vos, D.E.; Chavan, S.A.; Jacobs, P.A. Esterification and transesterification of renewable chemicals. Top. Catal. 2004, 27, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Callow, N.; Dashtbozorg, S.S.; Salager, J.-L.; Ju, L.-K. Ethylation of di-rhamnolipids: A green route to produce novel sugar fatty acid nonionic surfactants. J. Surf. Deterg. 2014, 17, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Yin, B. Sugar-based ester quaternary ammonium compounds and their surfactant properties. J. Surf. Deterg. 2014, 17, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, J.; Lv, F.; Ye, R.; Bie, X.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Z. Enzymatic synthesis of lard-based ascorbyl esters in a packed-bed reactor: Optimization by response surface methodology and evaluation of antioxidant properties. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, S.-H.; Hayes, D.G. Designs of bioreactor systems for solvent-free lipase-catalyzed synthesis of fructose–oleic acid esters. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2009, 86, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganske, F.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Lipase-catalyzed glucose fatty acid ester synthesis in ionic liquids. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 3097–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Yan, R.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y. Synthesis and characterization of raffinose fatty acid monoesters under ultrasonic irradiation. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2013, 237, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Pyo, S.-H.; Hayes, D.G. Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of saccharide–fatty acid esters using suspensions of saccharide crystals in solvent-free media. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2010, 87, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Hayes, D.G. Optimization of the solvent-free lipase-catalyzed synthesis of fructose-oleic acid ester through programming of water removal. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Hayes, D.G. Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of saccharide-fatty acid esters utilizing solvent-free suspensions: Effect of acyl donors and acceptors, and enzyme activity retention. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Hayes, D.G. Solvent-free lipase-catalysed synthesis of saccharide-fatty acid esters: Closed-loop bioreactor system with in situ formation of metastable suspensions. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2012, 30, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Hayes, D.G. Recent progress for lipase-catalyzed synthesis of sugar fatty acid esters. J. Oil Plam Res. 2014, 26, 355–365. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, R.; Hayes, D.G.; Burton, R. Effects of particle size of sucrose suspensions and pre-incubation of enzymes on lipase-catalyzed synthesis of sucrose oleic acid esters. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (FAO); World Health Organization (WHO). Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants: Seventy-Third [73rd] Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Technical Report Series 960; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Song, Z. Migration of reactive trace compounds from Novozym® 435 into organic solvents and ionic liquids. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 49, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Duarte, D.; Lopez-Cortes, N.; Ferrer, M.; Plou, F.J.; Ballesteros, A. Parameters affecting productivity in the lipase-catalysed synthesis of sucrose palmitate. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2005, 23, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, R.J.; Graber, M.; Denis, V.; Pleiss, J. Molecular mechanism of the hydration of Candida antarctica lipase B in the gas phase: Water adsorption isotherms and molecular dynamics simulations. ChemBioChem 2009, 10, 2913–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uppenberg, J.; Hansen, M.T.; Patkar, S.; Jones, T.A. The sequence, crystal structure determination and refinement of two crystal forms of lipase B from Candida antarctica. Structure 1994, 2, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Lipase from Rhizomucor miehei as a biocatalyst in fats and oils modification. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2010, 66, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, A.E.; Sjursnes, B.J.; Vakurov, A.V.; Halling, P.J. Kinetics of lipase-catalyzed esterification in organic media: Correct model and solvent effects on parameters. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1999, 24, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorzelski, S.; Watrobska-Swietlikowska, D.; Sznitowska, M. Surface tensometry studies on formulations of surfactants with preservatives as a tool for antimicrobial drug protection characterization. J. Biophys. Chem. 2012, 3, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, R.M.C.; Elliott, D.C.; Elliott, W.H.; Jones, K.M.U. Data for Biochemical Research; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1986; p. 580. [Google Scholar]
- Soultani, S.; Ognier, S.; Engasser, J.-M.; Ghoul, M. Comparative study of some surface active properties of fructose esters and commercial sucrose esters. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 227, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalakis, G.; Murray, B.S.; Sarney, D.B. Surface activity and critical aggregation concentration of pure sugar esters with different sugar headgroups. J. Coll. Int. Sci. 2000, 229, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheckermann, C.; Schlotterbeck, A.; Schmidt, M.; Wray, V.; Lang, S. Enzymatic monoacylation of fructose by two procedures. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1995, 17, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husband, F.; Sarney, D.; Barnard, M.; Wilde, P. Comparison of foaming and interfacial properties of pure sucrose monolaurates, dilaurate and commercial preparations. Food Hydrocoll. 1998, 12, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, A.; Gast, A. Physical Chemistry of Surfaces; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Neta, N.A.S.; dos Santos, J.C.S.; de Oliveira Sancho, S.; Rodrigues, S.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; Rodrigues, L.R.; Teixeira, J.A. Enzymatic synthesis of sugar esters and their potential as surface-active stabilizers of coconut milk emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habulin, M.; Šabeder, S.; Knez, Ž. Enzymatic synthesis of sugar fatty acid esters in organic solvent and in supercritical carbon dioxide and their antimicrobial activity. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2008, 45, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagh, A.; Shen, S.; Shen, F.A.; Miller, C.D.; Walsh, M.K. Effect of lactose monolaurate on pathogenic and nonpathogenic bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 3465–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Song, F.; Taxipalati, M.; Wei, W.; Feng, F. Comparative study of surface-active properties and antimicrobial activities of disaccharide monoesters. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, M.; Soliveri, J.; Plou, F.J.; López-Cortés, N.; Reyes-Duarte, D.; Christensen, M.; Copa-Patiño, J.L.; Ballesteros, A. Synthesis of sugar esters in solvent mixtures by lipases from Thermomyces lanuginosus and Candida antarctica B, and their antimicrobial properties. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2005, 36, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwami, Y.; Schachtele, C.; Yamada, T. Effect of sucrose monolaurate on acid production, levels of glycolytic intermediates, and enzyme activities of Streptococcus mutans NTCT 10449. J. Dental Res. 1995, 74, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-Y.; Tsuchido, T.; Ono, H.; Takano, M. Cell death of Bacillus subtilis caused by surfactants at low concentrations results from induced cell autolysis. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1990, 70, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Ando, K.; Tamura, G.; Arima, K. Effects of some fatty acid esters on the viability and transplantability of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1971, 31, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, M.; Perez, G.; Plou, F.J.; Castell, J.V.; Ballesteros, A. Antitumour activity of fatty acid maltotriose esters obtained by enzymatic synthesis. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2005, 42, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, Y.; Yoshimoto, K.; Okabe, M.; Fukuoka, F. Chemical and biochemical studies on carbohydrate esters. III. Antitumor activity of unsaturated fatty acids and their ester derivatives against Ehrlich ascites carcinoma. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1976, 24, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Property | Fructose Oleate | Sucrose Oleate | Sucrose Laurate | Tween® 80 1–3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free fatty acid, wt % | 3.4 | 10.0 | 0.1 | ND |
| Saccharide, wt % | 0.63 | 0.86 | <0.10 | ND |
| Moisture, wt % | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.05 | ND |
| Monoester among the esters, wt % | 69 | 65 | 86 | ND |
| Hydrophilic–Lipophilic Balance (Griffin HLB) 4 | 7.2 | 10.1 | 11.2 | 15.0 |
| Density, g/mL | 934 | 952 | 689 | 1070 |
| Critical Micellar Concentration (CMC), g/L | 0.18 | 0.021 | 0.63 | 0.014 |
| Surface tension (γ) at C = CMC, mN/m) | 27.9 | 29.6 | 19.7 | 38.0 |
| Surface excess (Γ), mol·m−2 × 106 | 1.91 | 0.849 | 8.19 | 0.74 |
| Specific surface area (As), nm2 | 0.87 | 1.96 | 0.20 | 2.24 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, R.; Hayes, D.G.; Burton, R.; Liu, A.; Harte, F.M.; Wang, Y. Solvent-Free Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Technical-Grade Sugar Esters and Evaluation of Their Physicochemical and Bioactive Properties. Catalysts 2016, 6, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6060078
Ye R, Hayes DG, Burton R, Liu A, Harte FM, Wang Y. Solvent-Free Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Technical-Grade Sugar Esters and Evaluation of Their Physicochemical and Bioactive Properties. Catalysts. 2016; 6(6):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6060078
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Ran, Douglas G. Hayes, Rachel Burton, Anjun Liu, Federico M. Harte, and Yuemeng Wang. 2016. "Solvent-Free Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Technical-Grade Sugar Esters and Evaluation of Their Physicochemical and Bioactive Properties" Catalysts 6, no. 6: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6060078
APA StyleYe, R., Hayes, D. G., Burton, R., Liu, A., Harte, F. M., & Wang, Y. (2016). Solvent-Free Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Technical-Grade Sugar Esters and Evaluation of Their Physicochemical and Bioactive Properties. Catalysts, 6(6), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6060078