N-acetylglucosamine 2-Epimerase from Pedobacter heparinus: First Experimental Evidence of a Deprotonation/Reprotonation Mechanism
Abstract
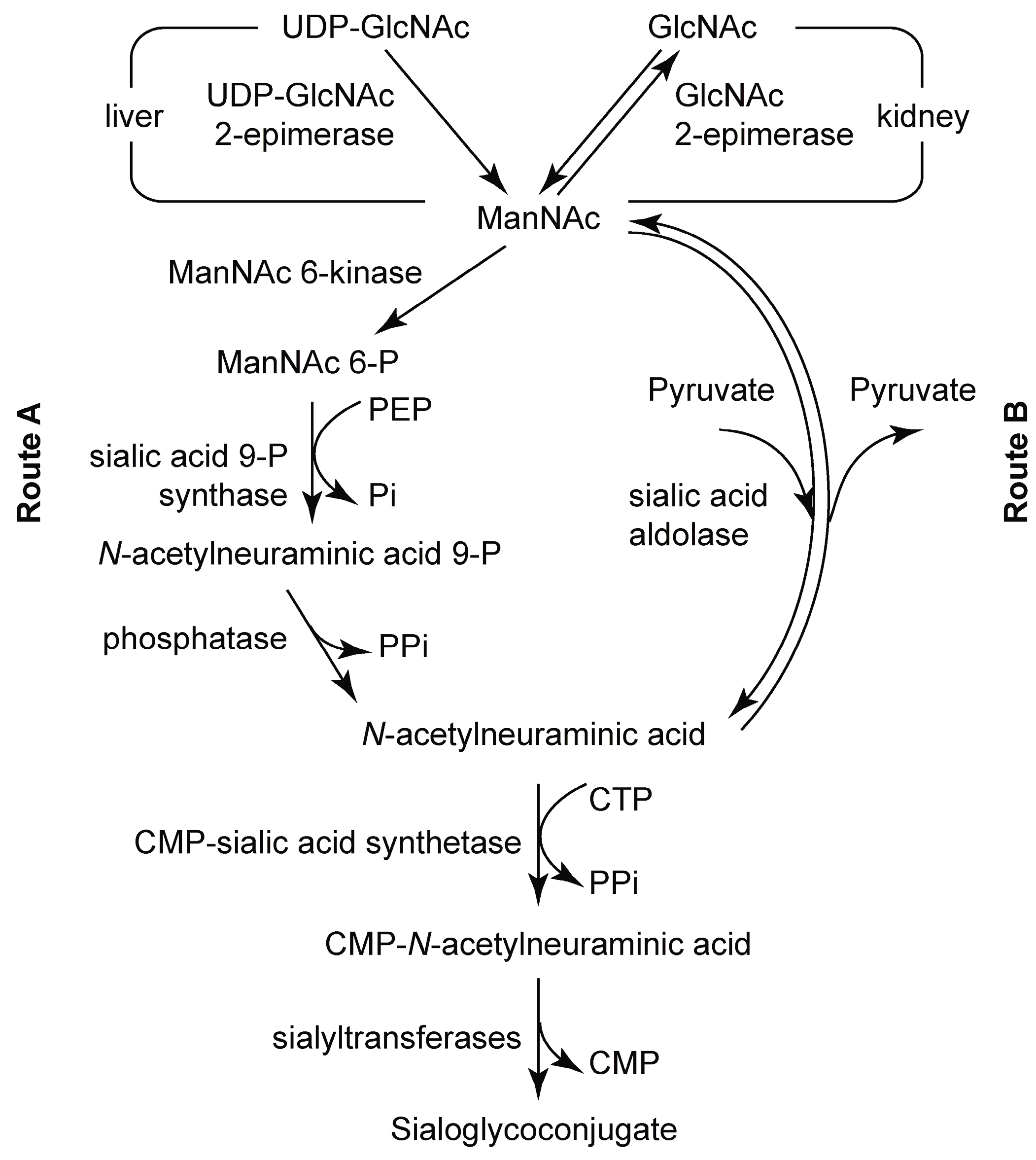
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cloning and Homology Analysis of PhGn2E Gene
2.2. Protein Expression and Purification
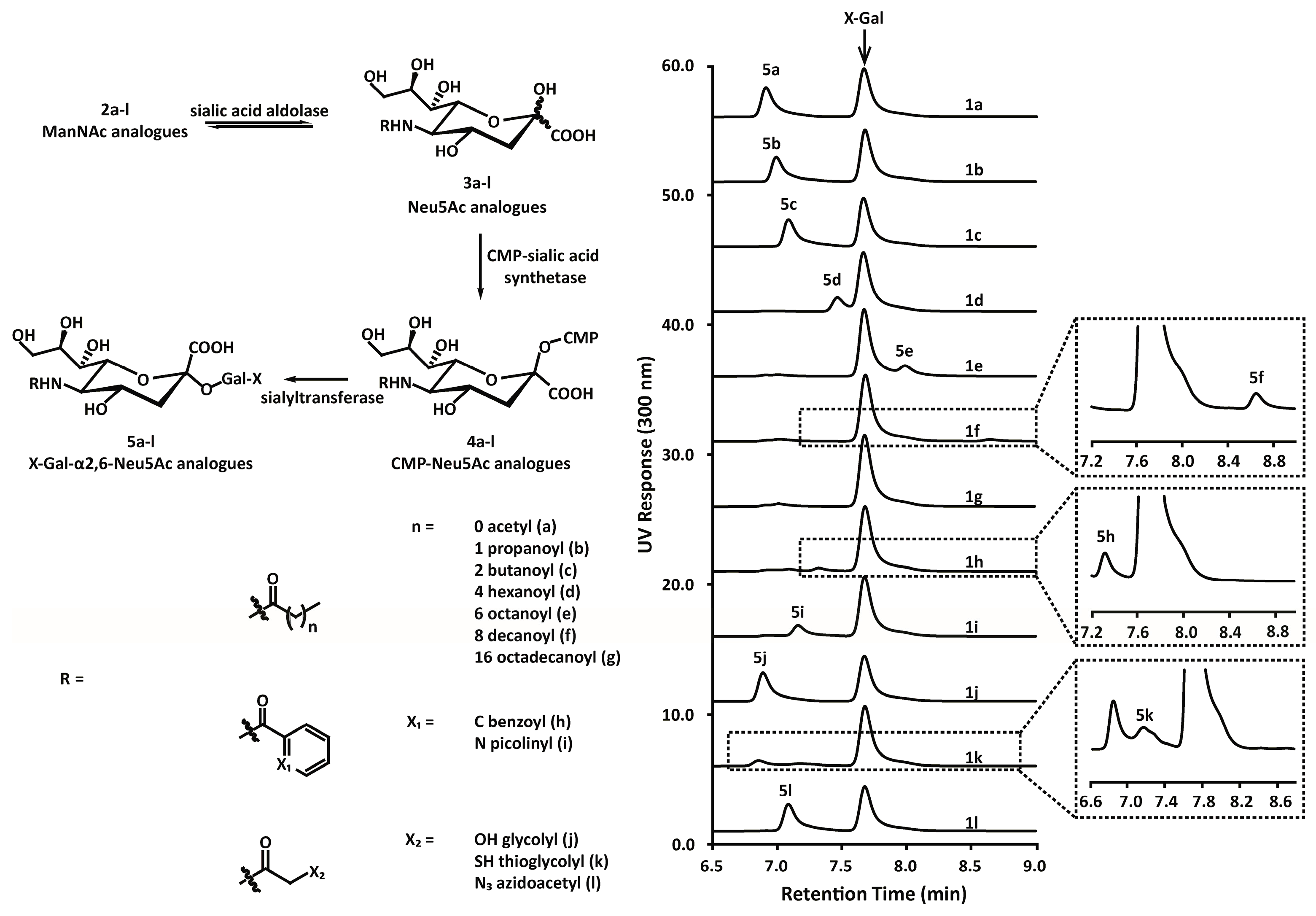
2.3. Substrate Specificity
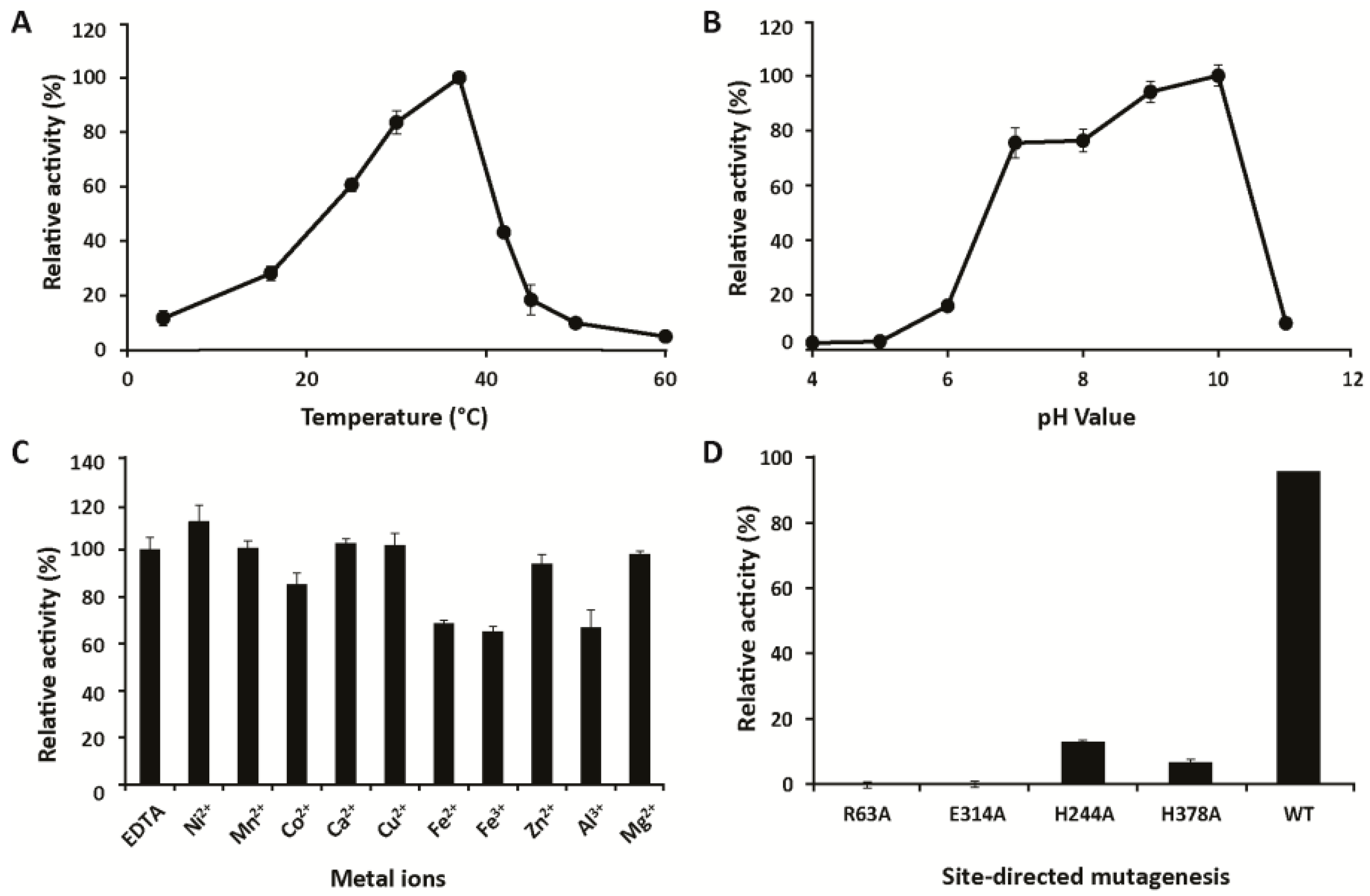
2.4. Biochemical Characterization
2.5. Hydrogen/Deuterium Exchange Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Characterization
3.2. Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Mannosamine and Sialic Acid Derivatives
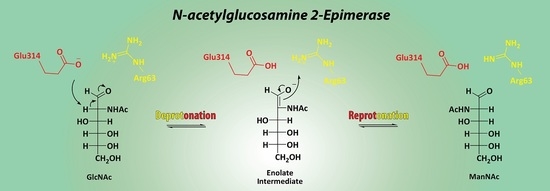
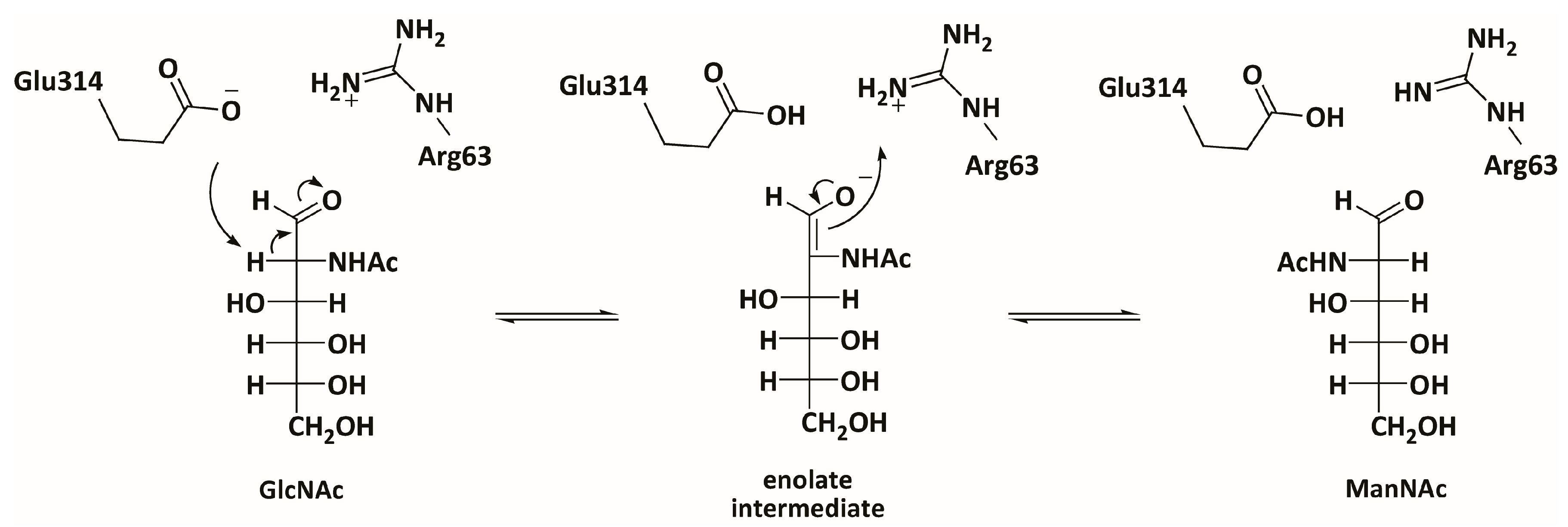
3.3. Mechanistic Studies
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General
4.2. Bacterial Strains
4.3. Gene Cloning and Construction of the Expression Vector
4.4. Expression and Protein Purification
4.5. Enzymatic Assay
4.6. Biochemical Characterization
4.7. Synthesis of N-Substituted Glucosamine Derivatives and Determination of PhGn2E Substrate Promiscuity
4.8. Enzymatic Synthesis and Analysis of Indoxylsialosides
4.9. Mechanistic NMR Studies
4.10. Activity Screening Using PhGn2E Mutants
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inoue, S.; Kitajima, K. KDN (deaminated neuraminic acid): Dreamful past and exciting future of the newest member of the sialic acid family. Glycoconj. J. 2006, 23, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, R. Chemistry, metabolism, and biological functions of sialic acids. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 1982, 40, 131–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tzanakakis, G.N.; Syrokou, A.; Kanakis, I.; Karamanos, N.K. Determination and distribution of N-acetyl- and N-glycolylneuraminic acids in culture media and cell-associated glycoconjugates from human malignant mesothelioma and adenocarcinoma cells. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2006, 20, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devine, P.L.; Clark, B.A.; Birrell, G.W.; Layton, G.T.; Ward, B.G.; Alewood, P.F.; McKenzie, I.F.C. The breast tumor-associated epitope defined by monoclonal-antibody 3E1.2 is an O-linked mucin carbohydrate containing N-glycolilneuraminic acid. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 5826–5836. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hedlund, M.; Tangvoranuntakul, P.; Takematsu, H.; Long, J.M.; Housley, G.D.; Kozutsumi, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Ryan, A.F.; Gallo, R.L.; et al. N-glycolylneuraminic acid deficiency in mice: Implications for human biology and evolution. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 4340–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasonkin, I.O.; Koliatsos, V.E. Nonhuman sialic acid Neu5Gc is very low in human embryonic stem cell-derived neural precursors differentiated with B27/N2 and noggin: Implications for transplantation. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 201, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Meledeo, M.A.; Wang, Z.Y.; Khanna, H.S.; Paruchuri, V.D.P.; Yarema, K.J. Metabolic glycoengineering: Sialic acid and beyond. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 1382–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keppler, O.T.; Horstkorte, R.; Pawlita, M.; Schmidts, C.; Reutter, W. Biochemical engineering of the N-acyl side chain of sialic acid: Biological implications. Glycobiology 2001, 11, 11R–18R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, S.M.; Huddleston, K.A.; Pitts, L.R.; Nguyen, N.; Lee, Y.C.; Vann, W.F.; Coleman, T.A.; Betenbaugh, M.J. Cloning and expression of the human N-acetylneuraminic acid phosphate synthase gene with 2-keto-3-deoxy-d-glycero-d-galacto-nononic acid biosynthetic ability. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17869–17877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasche, R.; Hinderlich, S.; Weise, C.; Effertz, K.; Lucka, L.; Moormann, P.; Reutter, W. A bifunctional enzyme catalyzes the first two steps in N-acetylneuraminic acid biosynthesis of rat liver—Molecular cloning and functional expression of UDP-N-acetyl-glucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 24319–24324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blick, T.J.; Tiong, T.; Sahasrabudhe, A.; Varghese, J.N.; Colman, P.M.; Hart, G.J.; Bethell, R.C.; McKimmBreschkin, J.L. Generation and characterization of an influenza virus neuraminidase variant with decreased sensitivity to the neuraminidase-specific inhibitor 4-guanidino-Neu5Ac2en. Virology 1995, 214, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, S.M.; Huddleston, K.A.; Tomiya, N.; Nguyen, N.; Lee, Y.C.; Vann, W.F.; Coleman, T.A.; Betenbaugh, M.J. Cloning and expression of human sialic acid pathway genes to generate CMP-sialic acids in insect cells. Glycoconj. J. 2001, 18, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varki, A. Radioactive tracer techniques in the sequencing of glycoprotein oligosaccharides. FASEB J. 1991, 5, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luchansky, S.J.; Yarema, K.J.; Takahashi, S.; Bertozzi, C.R. GlcNAc 2-epimerase can serve a catabolic role in sialic acid metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 8035–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Roseman, S. The sialic acids. V. N-acyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerase. J. Biol. Chem. 1965, 240, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Hori, K.; Ogasawara, H.; Hiwatashi, K.; Sugiyama, T. Effects of Nucleotides on the interaction of renin with G1cNAc 2-epimerase (Renin binding protein, RnBP). J. Biochem. 2006, 140, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Ogasawara, H.; Takahashi, K.; Hori, K.; Saito, K.; Mori, K. Identification of a domain conferring nucleotide binding to the N-acetyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerase (renin binding protein). J. Biochem. 2002, 131, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, T.; Mikami, B.; Maru, I.; Ohta, Y.; Hashimoto, W.; Murata, K. Crystal structure of N-acyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerase from porcine kidney at 2.0 angstrom resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 303, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klermund, L.; Groher, A.; Castiglione, K. New N-acyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerases from cyanobacteria with high activity in the absence of ATP and low inhibition by pyruvate. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 168, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.C.; Chien, H.C.R.; Hsu, W.H. Production of N-acetyl-d-neuraminic acid by recombinant whole cells expressing Anabaena sp. CH1N-acetyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerase and Escherichia coli N-acetyl-d-neuraminic acid lyase. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 129, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klermund, L.; Riederer, A.; Groher, A.; Castiglione, K. High-level soluble expression of a bacterial N-acyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerase in recombinant Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2015, 111, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sola-Carvajal, A.; Sanchez-Carron, G.; Garcia-Garcia, M.I.; Garcia-Carmona, F.; Sanchez-Ferrer, A. Properties of BoAGE2, a second N-acetyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerase from Bacteroides ovatus ATCC 8483. Biochimie 2012, 94, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.F.; Kao, C.H.; Lin, W.D.; Hsiao, N.W.; Hsu, W.H.; Lee, Y.C. N-Acetyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerase from Anabaena sp. CH1 contains a novel ATP-binding site required for catalytic activity. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, J.; Tanner, M.E. Mechanistic aspects of enzymatic carbohydrate epimerization. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2002, 19, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.C.; Wu, H.M.; Chang, Y.N.; Wang, W.C.; Hsu, W.H. The central cavity from the (alpha/alpha)(6) barrel structure of Anabaena sp. CH1N-acetyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerase contains two key histidine residues for reversible conversion. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 367, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, E.L.; Akutsu, H.; Doreleijers, J.F.; Harano, Y.; Ioannidis, Y.E.; Lin, J.; Livny, M.; Mading, S.; Maziuk, D.; Miller, Z. BioMagResBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D402–D408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, K.; Koizumi, S.; Endo, T.; Ozaki, A. Production of N-acetyl-d-neuraminic acid by coupling bacteria expressing N-acetyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerase and N-acetyl-d-neuraminic acid synthetase. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2002, 30, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncla, B.; Braham, P.; Hillier, S. Sialidase (neuraminidase) activity among gram-negative anaerobic and capnophilic bacteria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maru, I.; Ohta, Y.; Murata, K.; Tsukada, Y. Molecular cloning and identification of N-acyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerase from porcine kidney as a renin-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 16294–16299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Hori, K.; Takahashi, K.; Ogasawara, H.; Tomatsu, M.; Saito, K. Effects of nucleotides on N-acetyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerases (renin-binding proteins): Comparative biochemical studies. J. Biochem. 2001, 130, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, W.K.; Hinderlich, S.; Reutter, W.; Tanner, M.E. Sialic acid biosynthesis: Stereochemistry and mechanism of the reaction catalyzed by the mammalian UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 2455–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wratil, P.R.; Rigol, S.; Solecka, B.; Kohla, G.; Kannicht, C.; Reutter, W.; Giannis, A.; Nguyen, L.D. A novel approach to decrease sialic acid expression in cells by a C-3-modified N-acetylmannosamine. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 32056–32063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahal, L.K.; Yarema, K.J.; Bertozzi, C.R. Engineering chemical reactivity on cell surfaces through oligosaccharide biosynthesis. Science 1997, 276, 1125–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, E.L.; Hadfield, A.F.; Brown, A.E.; Sartorelli, A.C. Modification of sialic acid metabolism of murine erythroleukemia cells by analogs of N-acetylmannosamine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1983, 762, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aich, U.; Meledeo, M.A.; Sampathkumar, S.G.; Fu, J.; Jones, M.B.; Weier, C.A.; Chung, S.Y.; Tang, B.C.; Yang, M.; Hanes, J.; et al. Development of delivery methods for carbohydrate-based drugs: Controlled release of biologically-active short chain fatty acid-hexosamine analogs. Glycoconj. J. 2010, 27, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Sampathkumar, S.G.; Jones, M.B.; Rhee, J.K.; Baskaran, G.; Goon, S.; Yarema, K.J. Characterization of the metabolic flux and apoptotic effects of O-hydroxyl- and N-acyl-modified N-acetylmannosamine analogs in Jurkat cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 18342–18352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborda, P.; Wang, S.-Y.; Voglmeir, J. Influenza Neuraminidase Inhibitors: Synthetic Approaches, Derivatives and Biological Activity. Molecules 2016, 21, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.Z.; Li, Y.H.; Lau, K.; Muthana, S.; Yu, H.; Cheng, J.S.; Chokhawala, H.A.; Sugiarto, G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X. Sialidase substrate specificity studies using chemoenzymatically synthesized sialosides containing C5-modified sialic acids. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 5137–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Karpel, R.; Chen, X. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of CMP-sialic acid derivatives by a one-pot two-enzyme system: Comparison of substrate flexibility of three microbial CMP-sialic acid synthetases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 6427–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, C.L.; Goon, S.; Yarema, K.J.; Hinderlich, S.; Hang, H.C.; Chai, D.H.; Bertozzi, C.R. Substrate specificity of the sialic acid biosynthetic pathway. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 12864–12874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampathkumar, S.G.; Li, A.V.; Yarema, K.J. Synthesis of non-natural ManNAc analogs for the expression of thiols on cell-surface sialic acids. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ress, D.K.; Linhardt, R.J. Sialic acid donors: Chemical synthesis and glycosylation. Curr. Org. Synth. 2004, 1, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meo, C.; Priyadarshani, U. C-5 modifications in N-acetyl-neuraminic acid: Scope and limitations. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 1540–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keppler, O.T.; Herrmann, M.; von der Lieth, C.W.; Stehling, P.; Reutter, W.; Pawlita, M. Elongation of the N-acyl side chain of sialic acids in MDCK II cells inhibits influenza A virus infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 253, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, B.R.; Boddy, C.N. Sialic acid and N-acyl sialic acid analog production by fermentation of metabolically and genetically engineered Escherichia coli. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Chokhawala, H.A.; Huang, S.; Chen, X. One-pot three-enzyme chemoenzymatic approach to the synthesis of sialosides containing natural and non-natural functionalities. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, P.M.; Sala, R.F.; Tanner, M.E. Eliminations in the reactions catalyzed by UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 10269–10277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahuku, G.S. A simple extraction method suitable for PCR-based analysis of plant, fungal, and bacterial DNA. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2004, 22, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Huang, S.; Chokhawala, H.; Sun, M.; Zheng, H.; Chen, X. Highly efficient chemoenzymatic synthesis of naturally occurring and non-natural alpha-2,6-linked sialosides: A P. damsela alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase with extremely flexible donor-substrate specificity. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3938–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.L.; Conway, L.P.; Wang, M.M.; Huang, K.; Liu, L.; Voglmeir, J. Quantification of sialic acids in red meat by UPLC-FLD using indoxylsialosides as internal standards. Glycoconj. J. 2016, 33, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laver, W.G. Purification, N-terminal amino acid analysis, and disruption of an influenza virus. Virology 1961, 14, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.-Y.; Laborda, P.; Lu, A.-M.; Duan, X.-C.; Ma, H.-Y.; Liu, L.; Voglmeir, J. N-acetylglucosamine 2-Epimerase from Pedobacter heparinus: First Experimental Evidence of a Deprotonation/Reprotonation Mechanism. Catalysts 2016, 6, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6120212
Wang S-Y, Laborda P, Lu A-M, Duan X-C, Ma H-Y, Liu L, Voglmeir J. N-acetylglucosamine 2-Epimerase from Pedobacter heparinus: First Experimental Evidence of a Deprotonation/Reprotonation Mechanism. Catalysts. 2016; 6(12):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6120212
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Su-Yan, Pedro Laborda, Ai-Min Lu, Xu-Chu Duan, Hong-Yu Ma, Li Liu, and Josef Voglmeir. 2016. "N-acetylglucosamine 2-Epimerase from Pedobacter heparinus: First Experimental Evidence of a Deprotonation/Reprotonation Mechanism" Catalysts 6, no. 12: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6120212
APA StyleWang, S.-Y., Laborda, P., Lu, A.-M., Duan, X.-C., Ma, H.-Y., Liu, L., & Voglmeir, J. (2016). N-acetylglucosamine 2-Epimerase from Pedobacter heparinus: First Experimental Evidence of a Deprotonation/Reprotonation Mechanism. Catalysts, 6(12), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6120212