Single-Atom and Sub-Nano Ruthenium Cluster Catalysts—Application to Biomass Upgrading into Biofuel Additive
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Influence of the Synthesis Route
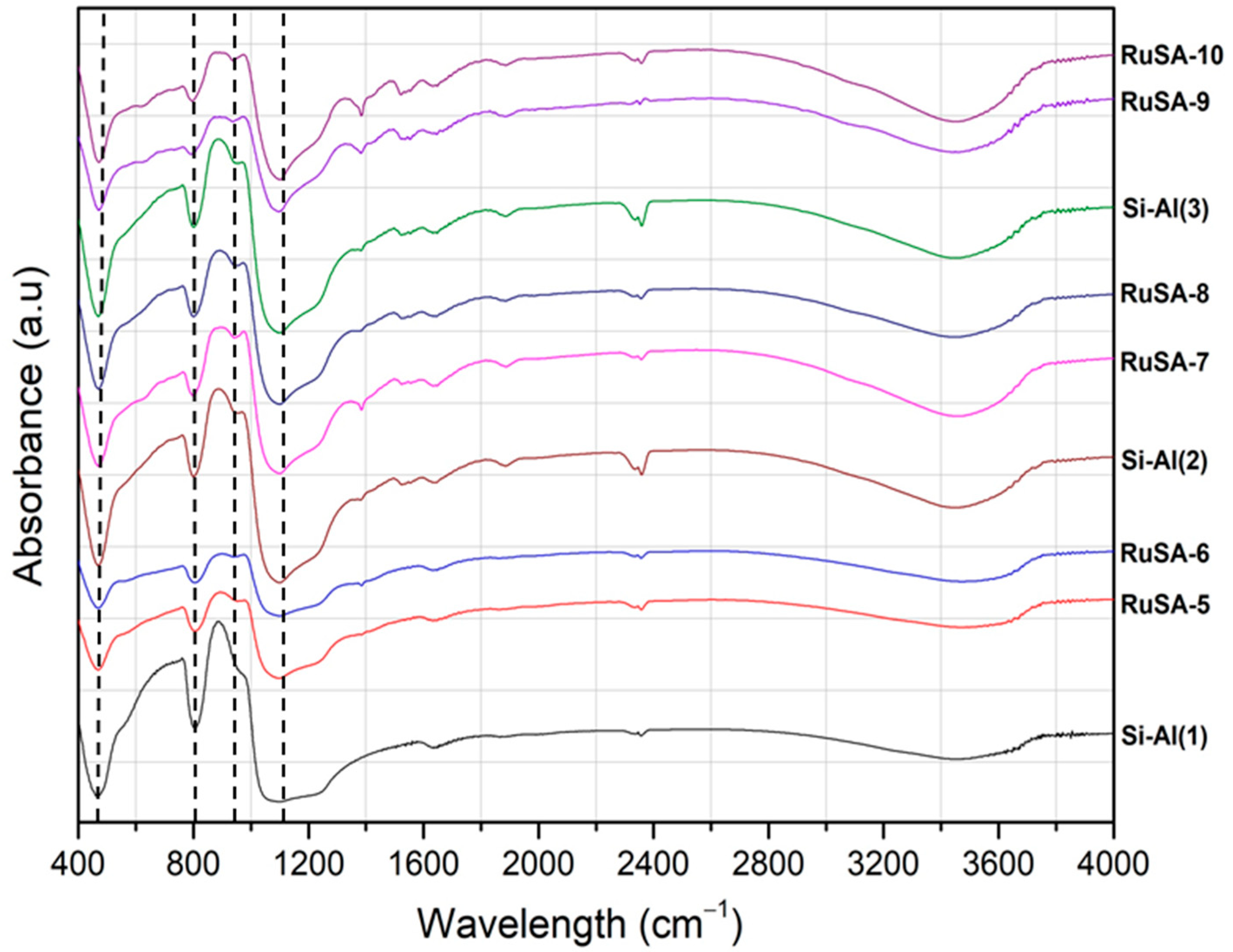
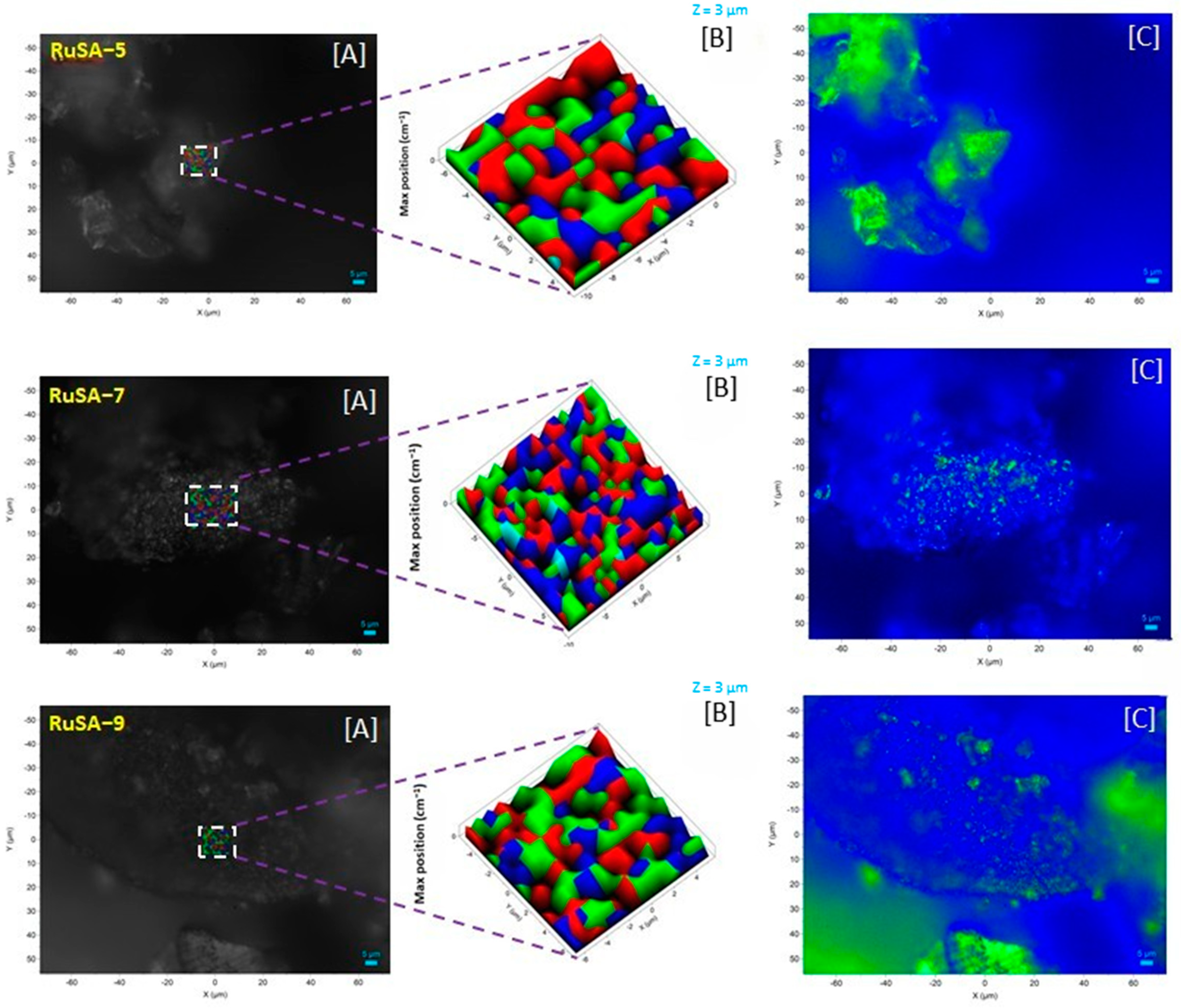
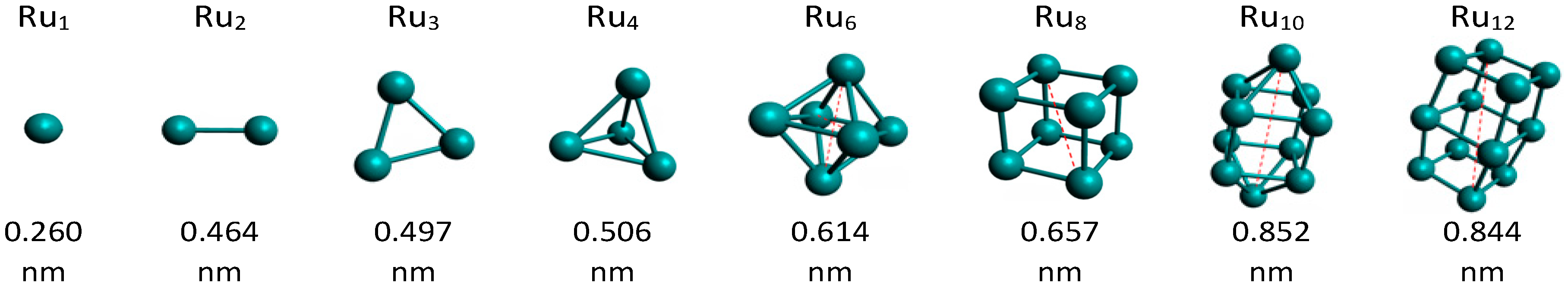
2.2. Catalysts Characterization
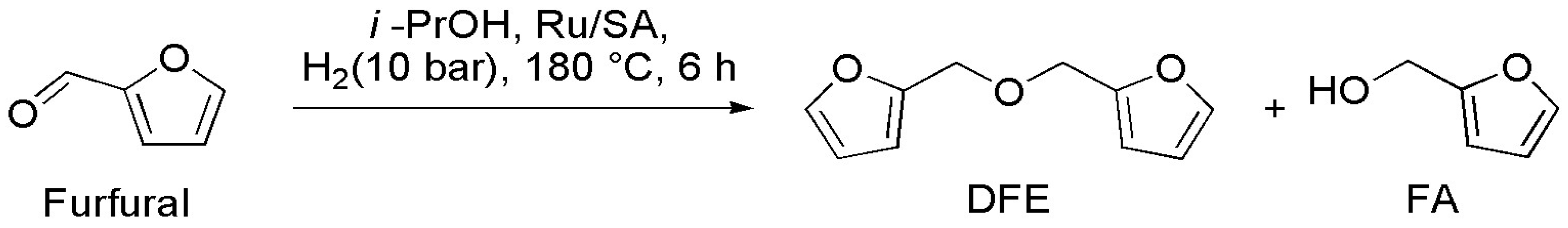
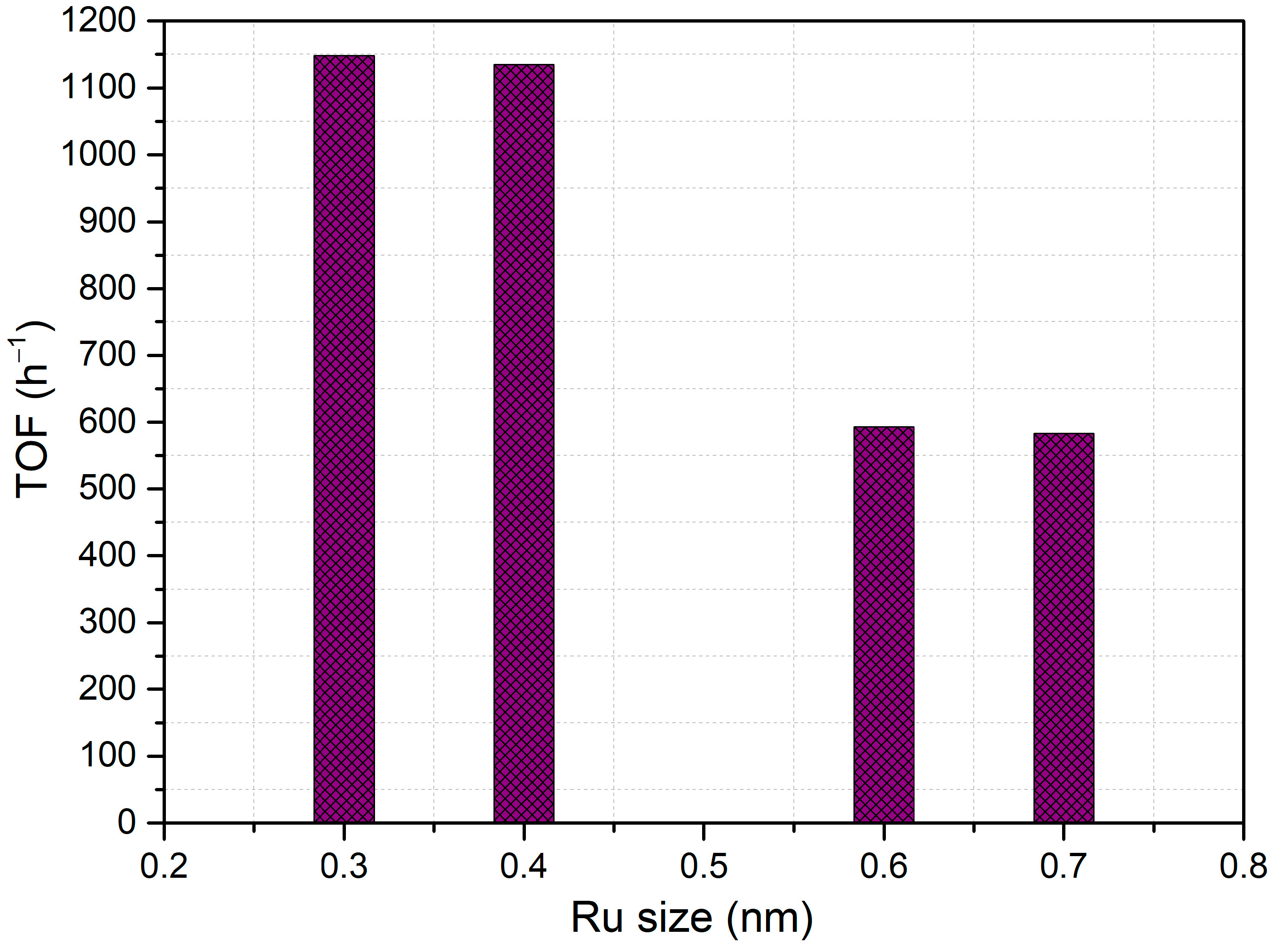
2.3. Catalytic Tests
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials Synthesis
3.2. Catalytic Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lei, Y.; Mehmood, F.; Lee, S.; Greeley, J.; Lee, B.; Seifert, S.; Winans, R.E.; Elam, J.W.; Meyer, R.J.; Redfern, P.C.; et al. Increased Silver Activity for Direct Propylene Epoxidation via Subnanometer Size Effects. Science 2010, 328, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketoshi, A.; Haruta, M. Size-and Structure-specificity in Catalysis by Gold Clusters. Chem. Lett. 2014, 43, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, W. Sub-nanometre sized metal clusters: From synthetic challenges to the unique property discoveries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3594–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Corma, A. Metal Catalysts for Heterogeneous Catalysis: From Single Atoms to Nanoclusters and Nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 4981–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, J.; Bilal, M.; Rasool, N.; Hafeez, U.; Shah, S.A.A.; Imran, S.; Zakaria, Z.A. Synthesis of ruthenium complexes and their catalytic applications: A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lopez-Haro, M.; Lopes, C.W.; Li, C.; Concepcion, P.; Simonelli, L.; Calvino, J.J.; Corma, A. Regioselective generation and reactivity control of subnanometric platinum clusters in zeolites for high-temperature catalysis. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Quan, X.; Yu, H.; Chen, S.; Choi, W.; Kim, B.; Zhang, S. Alkali-metal-oxides coated ultrasmall Pt sub-nanoparticles loading on intercalated carbon nitride: Enhanced charge interlayer transportation and suppressed backwark reaction for overall water splitting. J. Catal. 2019, 377, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.; Rivero-Crespo, M.A.; Domínguez, I.; Rubio-Marqués, P.; Oliver-Meseguer, J.; Liu, L.; Cabrero-Antonino, M.; Gavara, R.; Hernández-Garrido, J.C.; Boronat, M.; et al. Base-Controlled Heck, Suzuki, and Sonogashira Reactions Catalyzed by Ligand-Free Platinum or Palladium Single Atom and Sub-Nanometer Clusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 1928–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensaad, M.; Berrichi, A.; Bachir, R.; Bedrane, S. Nano and Sub-nano Gold–Cobalt Particles as Effective Catalysts in the Synthesis of Propargylamines via AHA Coupling. Catal. Lett. 2020, 151, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiburcio, E.; Zheng, Y.; Bilanin, C.; Hernández-Garrido, J.C.; Vidal-Moya, A.; Oliver-Meseguer, J.; Martín, N.; Mon, M.; Ferrando-Soria, J.; Armentano, D.; et al. MOF-Triggered Synthesis of Subnanometer Ag02 Clusters and Fe3+ Single Atoms: Heterogenization Led to Efficient and Synergetic One-Pot Catalytic Reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 10342–10354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, M.; Kitanaka, T.; Nakagawa, Y.; Tomishige, K. Cu Sub-Nanoparticles on Cu/CeO2 as an Effective Catalyst for Methanol Synthesis from Organic Carbonate by Hydrogenation. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axet, M.R.; Philippot, K. Catalysis with Colloidal Ruthenium Nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 1085–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naota, T.; Takaya, H.; Murahashi, S.-I. Ruthenium-catalyzed reactions for organic synthesis. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 2599–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Bhutto, S.U.A.; Aftab, S.; Wang, F.; Xu, X.; Xia, M. Ruthenium based with carbon supported catalysts for the catalytic transfer hydrogenation of furfural: A review. Nano Energy 2023, 117, 108808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordet, A.; El Sayed, S.; Sanger, M.; Boniface, K.J.; Kalsi, D.; Luska, K.L.; Jessop, P.G.; Leitner, W. Selectivity control in hydrogenation through adaptive catalysis using ruthenium nanoparticles on a CO2-responsive support. Nat. Chem. 2021, 13, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ruan, H.; Feng, M.; Qin, Y.; Job, H.; Luo, L.; Wang, C.; Engelhard, M.H.; Kuhn, E.; Chen, X.; et al. One-Pot Process for Hydrodeoxygenation of Lignin to Alkanes Using Ru-Based Bimetallic and Bifunctional Catalysts Supported on Zeolite Y. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 1846–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendeddouche, W.; Bedrane, S.; Zitouni, A.; Bachir, R. Highly efficient catalytic one-pot biofuel production from lignocellulosic biomass derivatives. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 2148–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yamaguchi, D.; Tang, L.; Periasamy, S.; Ma, H.; Hart, J.N.; Chiang, K. Enhancement of oxygen exchanging capability by loading a small amount of ruthenium over ceria-zirconia on dry reforming of methane. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Besson, M.; Descorme, C. Catalytic wet air oxidation of succinic acid over Ru and Pt catalysts supported on CexZr1−xO2 mixed oxides. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 165, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dali, A.; Rekkab-Hammoumraoui, I.; Choukchou-Braham, A.; Bachir, R. Allylic oxidation of cyclohexene over ruthenium-doped titanium-pillared clay. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 29167–29178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedrane, S.; Descorme, C.; Duprez, D. 16O/18O isotopic exchange: A powerful tool to investigate oxygen activation on M/CexZr1−xO2 catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 289, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Xue, Y.; Chen, W.; Qiu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Horike, S.; Tang, L. MOFs-Based Heterogeneous Catalysts: New Opportunities for Energy-Related CO2 Conversion. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1801587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Liu, L.; Yu, P.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; He, T.; Wu, G.; Chen, P. Mesoporous Ru/MgO prepared by a deposition-precipitation method as highly active catalyst for producing COx-free hydrogen from ammonia decomposition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 211, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.K.; Torrente-Murciano, L. Low temperature H2 production from ammonia using ruthenium-based catalysts: Synergetic effect of promoter and support. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 172–173, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yati, I.; Dwiatmoko, A.A.; Yoon, J.S.; Choi, J.-W.; Suh, D.J.; Jae, J.; Ha, J.-M. One-pot catalytic reaction to produce high-carbon-number dimeric deoxygenated hydrocarbons from lignin-derived monophenyl vanillin using Al2O3-cogelled Ru nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2016, 524, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najarnezhadmashhadi, A.; Eränen, K.; Engblom, S.; Aho, A.; Murzin, D.; Salmi, T. Continuous Hydrogenation of Monomeric Sugars and Binary Sugar Mixtures on a Ruthenium Catalyst Supported by Carbon-Coated Open-Cell Aluminum Foam. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 13450–13459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Ma, N.; Yu, C.; Ding, N.; Chen, J.-L.; Pao, C.-W.; Lee, J.-F.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, B.H. Tuning the interfaces in the ruthenium-nickel/carbon nanocatalysts for enhancing catalytic hydrogenation performance. J. Catal. 2019, 377, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Shan, S.; Petkov, V.; Hu, W.; Kroner, A.; Zheng, J.; Yu, C.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Luque, R.; et al. Ruthenium–nickel–nickel hydroxide nanoparticles for room temperature catalytic hydrogenation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 7869–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Bernal, Z.; Lillo-Ródenas, M.Á.; Román-Martínez, M.C. Effect of the carbon surface chemistry on the metal speciation in Ru/C catalysts. Impact on the transformation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 681, 161554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedrane, S.; Descorme, C.; Duprez, D. Investigation of the oxygen storage process on ceria-and ceria–zirconia-supported catalysts. Catal. Today 2002, 75, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedraogo, A.S.; Bhoi, P.R. Recent progress of metals supported catalysts for hydrodeoxygenation of biomass derived pyrolysis oil. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 119957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, C.M.; Al-Shaal, M.G.; Gu, D.; Joshi, H.; Ciptonugroho, W.; Schüth, F. Ruthenium Supported on High-Surface-Area Zirconia as an Efficient Catalyst for the Base-Free Oxidation of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-Furandicarboxylic Acid. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, X.; Jiang, K.; Wang, J.; Ren, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhuang, X.; Wang, T. Efficient Catalytic Conversion of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-Furandicarboxylic Acid over Ruthenium Cluster-Embedded Ni(OH)2 Catalyst. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, e202200863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Fang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. Synergistic interaction of Ru clusters and nanoparticles on WO3 nanorods for highly selective hydrogenation of furfural. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 42, 111160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Dhepe, P.L. Understanding the influence of alumina supported ruthenium catalysts synthesis and reaction parameters on the hydrodeoxygenation of lignin derived monomers. Mol. Catal. 2020, 480, 110525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Du, H.; Wei, B.; Zhu, J.; Li, M.; Shan, Y.; Shen, J.; Song, C. Hydrodeoxygenation of Guaiacol on Ru Catalysts: Influence of TiO2–ZrO2 Composite Oxide Supports. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 12070–12079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.N.; Park, Y.-K.; Lee, I.-G.; Ko, C.H. Enhancement of CO bond cleavage to afford aromatics in the hydrodeoxygenation of anisole over ruthenium-supporting mesoporous metal oxides. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 544, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, E.; Escobedo, J.L.G.; Lindblad, M.; Käldström, M.; Meriö-Talvio, H.; Jiang, H.; Puurunen, R.L.; Karinen, R. Hydrodeoxygenation of Levulinic Acid Dimers on a Zirconia-Supported Ruthenium Catalyst. Catalysts 2020, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczyglewska, P.; Feliczak-Guzik, A.; Nowak, I. A support effect on the hydrodeoxygenation reaction of anisole by ruthenium catalysts. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 293, 109771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plößer, J.; Lucas, M.; Claus, P. Highly selective menthol synthesis by one-pot transformation of citronellal using Ru/H-BEA catalysts. J. Catal. 2014, 320, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Mensah, J.; Drewery, M.; Kennedy, E.; Maschmeyer, T.; Stockenhuber, M. Role of metal support during ru-catalysed hydrodeoxygenation of biocrude oil. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 281, 119470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, T.; Tsutsui, K.; Matsui, T.; Kikuchi, R.; Eguchi, K. Support effect on complete oxidation of volatile organic compounds over Ru catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 81, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Lee, F.Y.; Lv, L.; Liu, J.; Tian, X.N.; Zhao, X.S. Sandwiched Ruthenium/Carbon Nanostructures for Highly Active Heterogeneous Hydrogenation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 1926–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.-W.; Chen, H.-Y.; Wei, W.-H.; Chen, G.-C.; Yamanaka, I.; Liu, B.-T.; Hong, T.-F.; Chiang, T.-C.; Huang, H.-C.; Wang, C.-H. Novel ruthenium-based catalysts with atomic dispersion for oxygen evolution reaction in water electrolysis. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 35, 101857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Cui, Y.; Qian, W.; Peng, Q.; Wang, J.; Gong, H.; Fang, J.; Dai, S.; Hou, Z. Thermoregulated Ionic Liquid-Stabilizing Ru/CoO Nanocomposites for Catalytic Hydrogenation. Langmuir 2020, 36, 11589–11599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, S.-M.; Xu, Y.; Tan, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Duan, H.; Song, Y.-F. Single Ru atoms with precise coordination on a monolayer layered double hydroxide for efficient electrooxidation catalysis. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldosari, O.F.; Iqbal, S.; Miedziak, P.J.; Brett, G.L.; Jones, D.R.; Liu, X.; Edwards, J.K.; Morgan, D.J.; Knight, D.K.; Hutchings, G.J. Pd–Ru/TiO2 catalyst–an active and selective catalyst for furfural hydrogenation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Martínez, O.U.; Suárez-Toriello, V.A.; Reyes, J.A.D.L.; Pawelec, B.; Fierro, J.L.G. Support effect and metals interactions for NiRu/Al2O3, TiO2 and ZrO2 catalysts in the hydrodeoxygenation of phenol. Catal. Today 2017, 296, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iroegbu, A.O.C.; Ray, S.S. On the chemistry of furfuryl alcohol polymerization: A review. J. Polym. Sci. 2024, 62, 1044–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principe, M.; Martínez, R.; Ortiz, P.; Rieumont, J. The polymerization of furfuryl alcohol with p-toluenesulfonic acid: Photocross-linkeable feature of the polymer. Polímeros 2000, 10, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, R.; Martínez, R.; Ortiz, P. Polymerization of furfuryl alcohol with trifluoroacetic acid: The influence of experimental conditions. Die. Makro. Chem. 1992, 193, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Assary, R.S.; Marshall, C.L.; Gosztola, D.J.; Curtiss, L.A.; Stair, P.C. Acid-Catalyzed Furfuryl Alcohol Polymerization: Characterizations of Molecular Structure and Thermodynamic Properties. ChemCatChem 2011, 3, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choura, M.; Belgacem, N.M.; Gandini, A. Acid-Catalyzed Polycondensation of Furfuryl Alcohol: Mechanisms of Chromophore Formation and Cross-Linking. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 3839–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, A.; Peters, F. The furans. Reinhold Pub Corp. N. Y. 1953, 447, 867. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Song, H.; Li, C. Catalytic transfer hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol over Fe3O4 modified Ru/Carbon nanotubes catalysts. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, Á.; Curtin, T.; Hernández, W.Y.; Van Der Voort, P.; Leahy, J.J. Hydrogenation of Furfural with a Pt–Sn Catalyst: The Suitability to Sustainable Industrial Application. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2016, 20, 1917–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, Á.; Leahy, J.J.; Curtin, T. The influence of metal selection on catalyst activity for the liquid phase hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol. Catal. Today 2017, 279, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarouni, D.; Evgenidi, C.D.; Kordulis, C.; Dourtoglou, V. Catalytic conversion of biomass-derived compounds to high added value products using an acid treated natural mordenite. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 33, 101125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Hao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, B. Selective catalytic dehydration of furfuryl alcohol to 2, 2′-difurfuryl ether using a polyoxometalate catalyst. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzada, L.A.; Louis, C.; Han, C.W.; Ortalan, V.; Zanella, R. Au-Ru/TiO2 prepared by deposition-precipitation with urea: Relevant synthesis parameters to obtain bimetallic particles. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camposeco, R.; Miguel, O.; Torres, A.E.; Armas, D.E.; Zanella, R. Highly active Ru/TiO2 nanostructures for total catalytic oxidation of propane. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 98076–98090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Mejia, C.; Gnanakumar, E.S.; Olivos-Suarez, A.; Gascon, J.; Greer, H.F.; Zhou, W.; Rothenberg, G.; Shiju, N.R. Ru/TiO2-catalysed hydrogenation of xylose: The role of the crystal structure of the support. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X. Theoretical investigation on RuO2 nanoclusters adsorbed on TiO2 rutile (110) and anatase (101) surfaces. Theor. Chem. Accounts 2014, 133, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, W. Total Oxidation of Propane over a Ru/CeO2 Catalyst at Low Temperature. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9531–9541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirichenko, O.; Redina, E.; Davshan, N.; Mishin, I.; Kapustin, G.; Brueva, T.; Kustov, L.; Li, W.; Kim, C.H. Preparation of alumina-supported gold-ruthenium bimetallic catalysts by redox reactions and their activity in preferential CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 134-135, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Bai, X. Preparation of SBA-15 supported Ru nanocatalysts by electrostatic adsorption–ultrasonic in situ reduction method and its catalytic performance for hydrogen storage of N-ethylcarbazole. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 98034–98047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, Y.; Yamazaki, H.; Yokoi, T.; Tatsumi, T.; Kondo, J.N. IR Characterization of Homogeneously Mixed Silica–Alumina Samples and Dealuminated Y Zeolites by Using Pyridine, CO, and Propene Probe Molecules. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 14043–14050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendahou, K.; Cherif, L.; Siffert, S.; Tidahy, H.; Benaïssa, H.; Aboukaïs, A. The effect of the use of lanthanum-doped mesoporous SBA-15 on the performance of Pt/SBA-15 and Pd/SBA-15 catalysts for total oxidation of toluene. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 351, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, R.R.; Santoyo, V.R.; Sánchez, C.D.M.; Rosales, M.M. Effect of aluminum precursor on physicochemical properties of Al2O3 by hydrolysis/precipitation method. Nova Sci. 2018, 10, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.I.; Jahin, H.S.; Dessouki, H.A.; Nassar, M.Y. Synthesis and characterization of γ-Al2O3 and α-Al2O3 nanoparticles using a facile, inexpensive auto-combustion approach. Egypt. J. Chem. 2021, 64, 2509–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riad, M. Influence of magnesium and chromium oxides on the physicochemical properties of γ-alumina. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 327, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun-Cheng, L.; Lan, X.; Feng, X.; Zhan-Wen, W.; Fei, W. Effect of hydrothermal treatment on the acidity distribution of γ-Al2O3 support. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidi, A.; Sadeghi, N. Application of RuO2 Nanoparticles as Catalyst in Preparation of Indolo[3,2-a]Carbazoles. J. Clust. Sci. 2016, 27, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Kaden, W.E.; Yu, X.; Boscoboinik, J.A.; Martynova, Y.; Lichtenstein, L.; Heyde, M.; Sterrer, M.; Włodarczyk, R.; Sierka, M.; et al. Thin silica films on Ru(0001): Monolayer, bilayer and three-dimensional networks of [SiO4] tetrahedra. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 11344–11351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukawa, Y.; Handa, M.; Hoshino, Y. Resonance Raman spectra of tris(acetylacetonato)iron(III) and ruthenium(III) complexes and their solvent effect. J. Solut. Chem. 1995, 24, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, B.; Joshi-Imre, A.; Cogan, S.F. Charge injection characteristics of sputtered ruthenium oxide electrodes for neural stimulation and recording. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 110, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherepy, N.J.; Shen, T.H.; Esposito, A.P.; Tillotson, T.M. Characterization of an effective cleaning procedure for aluminum alloys: Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy and zeta potential analysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 282, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pešková, Š.; Machovič, V.; Procházka, P. Raman Spectroscopy Structural Study Of Fired Concrete. Ceram. Silikáty 2011, 55, 410–417. [Google Scholar]
- Bin Mukhlish, M.Z.; Horie, Y.; Nomiyama, T. Flexible Alumina-Silica Nanofibrous Membrane and Its High Adaptability in Reactive Red-120 Dye Removal from Water. Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benattia, F.K.; Arrar, Z.; Dergal, F. Methods and Applications of Raman Spectroscopy: A Powerful Technique in Modern Research, Diagnosis, and Food Quality Control. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2024, 20, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherigui, S.; Dergal, F.; Chikhi, I.; Chaker, H.; Chabane, N. Detection of Algerian Honey Adulteration by Raman Spectroscopy and Chemometrics Methods. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2023, 88, 231–240. [Google Scholar]
- Chabane, N.; Dergal, F.; Attar, T.; Belarbi, N.; Chikhi, I.; Charigui, S.; Mustapha, M.A.; Lerari, D.; Bachari, K. Green inhibition of copper corrosion by ammoides verticillata oil in 1M nitric acid: Weight lossand Raman spectroscopic mapping studies. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2023, 68, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benladghem, Z.; Seddiki, S.M.L.; Dergal, F.; Mahdad, Y.M.; Aissaoui, M.; Choukchou-Braham, N. Biofouling of reverse osmosis membranes: Assessment by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and microscopic imaging. Biofouling 2022, 38, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L. The Simple Cubic Structure of Ruthenium Clusters. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 2140–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, S.; Jansen, A.P.J.; van Santen, R.A. Magnetic, bonding and structural behavior of Ru12 and Ru13 clusters: Is Ru12 magic? J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 2010, 954, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soini, T.M.; Ma, X.; Aktürk, O.Ü.; Suthirakun, S.; Genest, A.; Rösch, N. Extending the cluster scaling technique to ruthenium clusters with hcp structures. Surf. Sci. 2016, 643, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Zheng, W.-H.; Guo, X. Sub-nanometric ruthenium clusters prepared by solid-state dispersion for catalytic selective aerobic oxidation of aromatic alcohols. Appl. Catal. O Open 2024, 194, 207006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Lin, L.; Qiao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xu, Z.; Gong, H.; Li, D.; Chen, M.; Huang, R.; Hou, Z. Ru subnanoparticles on N-doped carbon layer coated SBA-15 as efficient Catalysts for arene hydrogenation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2019, 585, 117183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, N.; Li, W.; Sun, M.; Wu, T.; Huang, B.; Yong, X.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, L.; Song, H.; et al. Engineering the synergistic effect of carbon dots-stabilized atomic and subnanometric ruthenium as highly efficient electrocatalysts for robust hydrogen evolution. SmartMat 2022, 3, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Biswal, S.; Tripathi, B.P. Ultrasmall Ruthenium Nanoclusters Anchored on Thiol-Functionalized Metal–Organic Framework as a Catalyst for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 5317–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Gao, K.; Wang, X.; Zheng, H.; Cao, J.; Mi, L.; Huo, Q.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; He, C. Subnanometric Ru clusters with upshifted D band center improve performance for alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ishii, H.; Liao, Y.-F.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.-Y.; Pang, H. Synergistic Mechanism of Sub-Nanometric Ru Clusters Anchored on Tungsten Oxide Nanowires for High-Efficient Bifunctional Hydrogen Electrocatalysis. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2206096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Deng, B.; Jiang, Z.-J. High activity and excellent durability of oxygen-vacancy-rich ruthenium manganese oxide solid-solution nanowires for the oxygen evolution reaction in acidic media. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 25252–25261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.J.; Luque, R.; Budarin, V.L.; Clark, J.H.; Macquarrie, D.J. Supported metal nanoparticles on porous materials. Methods and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, I.; Chen, M.; Dyer, J.; Kletnieks, P.W.; Haw, J.F.; Dixon, D.A.; Gates, B.C. A Zeolite-Supported Molecular Ruthenium Complex with η6-C6H6 Ligands: Chemistry Elucidated by Using Spectroscopy and Density Functional Theory. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2010, 16, 7427–7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Du, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Tang, J.; Qin, C.; Liang, C.; Huang, C.; Yao, S. Furfural production from lignocellulosic biomass: One-step and two-step strategies and techno-economic evaluation. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 6318–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaswal, A.; Singh, P.P.; Mondal, T. Furfural—A versatile, biomass-derived platform chemical for the production of renewable chemicals. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 510–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, C.C.; Nie, R. Surface Synergetic Effects of Ni–ReOx for Promoting the Mild Hydrogenation of Furfural to Tetrahydrofurfuryl Alcohol. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 11256–11267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ye, J.; Yang, Y.; Yin, P.; Feng, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Wei, M.; Truhlar, D.G. Catalytic Conversion Furfuryl Alcohol to Tetrahydrofurfuryl Alcohol and 2-Methylfuran at Terrace, Step, and Corner Sites on Ni. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 7240–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihel, D.; Redouane, B.; Amina, B.; Ginesa, B.; Sumeya, B.; Juan, C.J. Zr-doped MgAl-LDH@Au nano-catalysts for selective and efficient oxidation of biomass-derived furfural. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Fagúndez, N.; Agirrezabal-Telleria, I.; Arias, P.L.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Mariscal, R.; Granados, M.L. Aqueous-phase catalytic oxidation of furfural with H2O2: High yield of maleic acid by using titanium silicalite-1. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 54960–54972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douthwaite, M.; Huang, X.; Iqbal, S.; Miedziak, P.J.; Brett, G.L.; Kondrat, S.A.; Edwards, J.K.; Sankar, M.; Knight, D.W.; Bethell, D. The controlled catalytic oxidation of furfural to furoic acid using AuPd/Mg(OH)2. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 5284–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Wei, M. A Control over Hydrogenation Selectivity of Furfural via Tuning Exposed Facet of Ni Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 4226–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Asensio, R.; Gómez, C.P.J.; Sancho, C.G.; Moreno-Tost, R.; Cecilia, J.A.; Maireles-Torres, P. Influence of Structure-modifying Agents in the Synthesis of Zr-doped SBA-15 Silica and Their Use as Catalysts in the Furfural Hydrogenation to Obtain High Value-added Products through the Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley Reduction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, E.; Vijlbrief, T.; Hijkoop, R.; Gruter, G.-J.M.; Van der Waal, J.C. Promising results with YXY Diesel components in an ESC test cycle using a PACCAR Diesel engine. Biomass-Bioenergy 2012, 36, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeeb, M.A.; Akih-Kumgeh, B. Recent Trends in the Production, Combustion and Modeling of Furan-Based Fuels. Energies 2018, 11, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D.A.; Brandt, P.; Nordin, S.J.M.; Andersson, P.G. Ru(arene)(amino alcohol)-Catalyzed Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones: Mechanism and Origin of Enantioselectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 9580–9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, M.; Yamada, I.; Noyori, R. CH/π Attraction: The Origin of Enantioselectivity in Transfer Hydrogenation of Aromatic Carbonyl Compounds Catalyzed by Chiral η6-Arene-Ruthenium(II) Complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2001, 40, 2818–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiguchi, S.; Fujii, A.; Haack, K.J.; Matsumura, K.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Kinetic Resolution of Racemic Secondary Alcohols by RuII-Catalyzed Hydrogen Transfer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1997, 36, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.H.; Park, J.Y.; Renzas, J.R.; Butcher, D.R.; Huang, W.; Somorjai, G.A. Size Effect of Ruthenium Nanoparticles in Catalytic Carbon Monoxide Oxidation. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2709–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, K.; Joo, S.H.; Mun, B.S.; Butcher, D.R.; Renzas, J.R.; Aksoy, F.; Liu, Z.; Somorjai, G.A.; Park, J.Y. Intrinsic Relation between Catalytic Activity of CO Oxidation on Ru Nanoparticles and Ru Oxides Uncovered with Ambient Pressure XPS. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5761–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillo, F.; Moulijn, J.A.; Kreutzer, M.T.; van Ommen, J.R. Nanoparticle sintering in atomic layer deposition of supported catalysts: Kinetic modeling of the size distribution. Catal. Today 2018, 316, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Richards, V.N.; Shields, S.P.; Buhro, W.E. Kinetics and Mechanisms of Aggregative Nanocrystal Growth. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.J.F. Growth and structure of supported metal catalyst particles. Int. Mater. Rev. 1995, 40, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedrane, S.; Descorme, C.; Duprez, D. An optimized route for the preparation of well dispersed supported ruthenium catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 1563–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameur, N.; Bedrane, S.; Bachir, R.; Choukchou-Braham, A. Influence of nanoparticles oxidation state in gold based catalysts on the product selectivity in liquid phase oxidation of cyclohexene. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2013, 374-375, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, R.; Järås, S.; Canu, P. Partial oxidation of methane over supported ruthenium catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 325, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Cui, J.; Deng, T.; Cui, X.; Ding, G.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y. Water-Promoted Hydrogenation of Levulinic Acid to γ-Valerolactone on Supported Ruthenium Catalyst. ChemCatChem 2014, 7, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
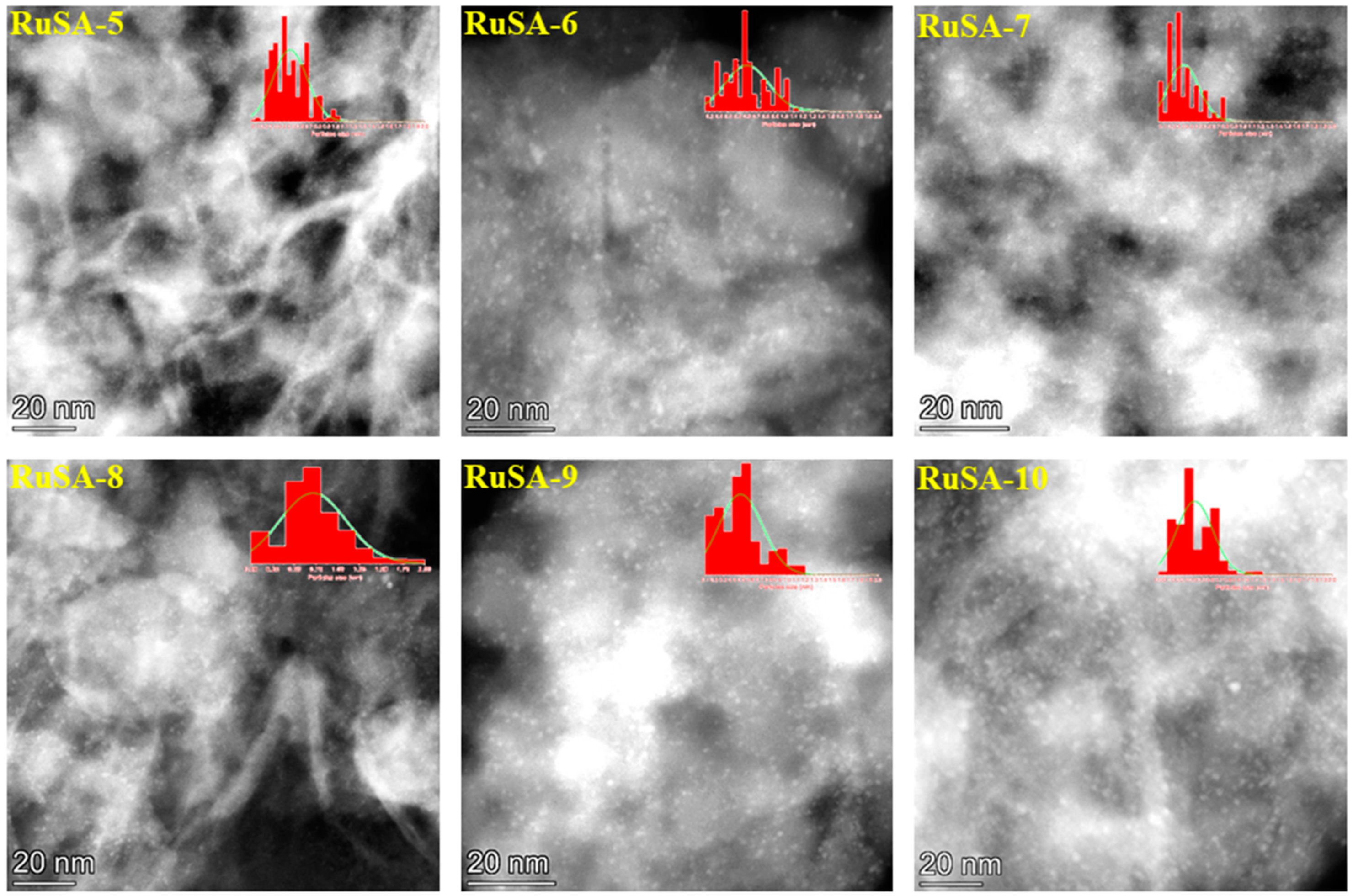


| Samples | Synthesis Route | Support | Ru Loading (%) | Ru Particle Size (nm) | Ru Single Atoms (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RuSA-5 | S | Si-Al (1) | 0.94 | 0.4 ± 0.06 | 35 |
| RuSA-6 | S | Si-Al (1) | 1.80 | 0.6 ± 0.05 | 24 |
| RuSA-7 | S | Si-Al (2) | 0.93 | 0.3 ± 0.07 | 74 |
| RuSA-8 | S | Si-Al (2) | 1.83 | 0.7 ± 0.04 | 27 |
| RuSA-9 | S | Si-Al (3) | 0.97 | 0.4 ± 0.06 | 35 |
| RuSA-10 | S | Si-Al (3) | 2.00 | 0.4 ± 0.06 | 57 |
| Catalysts | Ru Loading (%) |
Ru Average Particle Size (nm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ru/CD | n.d | 2.3 * | [89] |
| Ru/Ni(OH)2 | n.d | 1.5–2 * | [33] |
| Ru/Ni-MOF-SH | 3.5 | 1.5 * | [90] |
| Ru/PC | 2 | 1–3.1 * | [91] |
| Ru SNC/W18O49 | very low | 1 * | [92] |
| Ru/Al2O3-SSD | 0.98 | 0.97 | [87] |
| Rux/Mn1−xO2 NWs | 1.5 | n.d | [93] |
| Ru/NC-SBA-15 | 0.1 | 0.5 | [88] |
| Ru/SiO2-Al2O3 | 1 | 0.3–0.4 | Present work |
| Ru/SiO2-Al2O3 | 2 | 0.4–0.7 | Present work |
| Entry | Catalyst | TOF (h−1) | Yield (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DFE | FA | Other | |||
| 1 | Blank test | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | Si-Al (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | Si-Al (2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | Si-Al (3) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | RuSA-5 | 1135 | 92 | 0 | 8 |
| 6 | RuSA-6 | 593 | 97 | 3 | 0 |
| 7 | RuSA-7 | 1148 | 95 | 0 | 5 |
| 8 | RuSA-8 | 583 | 93 | 0 | 7 |
| 9 | RuSA-9 | 1100 | 92 | 2 | 6 |
| 10 | RuSA-10 | 1067 | 86 | 5 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tabet-Zatla, C.Z.; Bedrane, S.; Calvino, J.J.; Cauqui, M.Á.; Dergal, F.; Bachir, R.; Ziani-Cherif, C.; Hernández-Garrido, J.C. Single-Atom and Sub-Nano Ruthenium Cluster Catalysts—Application to Biomass Upgrading into Biofuel Additive. Catalysts 2025, 15, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050449
Tabet-Zatla CZ, Bedrane S, Calvino JJ, Cauqui MÁ, Dergal F, Bachir R, Ziani-Cherif C, Hernández-Garrido JC. Single-Atom and Sub-Nano Ruthenium Cluster Catalysts—Application to Biomass Upgrading into Biofuel Additive. Catalysts. 2025; 15(5):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050449
Chicago/Turabian StyleTabet-Zatla, Chaima Z., Sumeya Bedrane, José Juan Calvino, Miguel Ángel Cauqui, Fayçal Dergal, Redouane Bachir, Chewki Ziani-Cherif, and Juan Carlos Hernández-Garrido. 2025. "Single-Atom and Sub-Nano Ruthenium Cluster Catalysts—Application to Biomass Upgrading into Biofuel Additive" Catalysts 15, no. 5: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050449
APA StyleTabet-Zatla, C. Z., Bedrane, S., Calvino, J. J., Cauqui, M. Á., Dergal, F., Bachir, R., Ziani-Cherif, C., & Hernández-Garrido, J. C. (2025). Single-Atom and Sub-Nano Ruthenium Cluster Catalysts—Application to Biomass Upgrading into Biofuel Additive. Catalysts, 15(5), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050449









