Unravel the Roles of the Acid Sites in Different Pore Channels of HZSM-5 Catalyst on Ethanol Conversion to Light Olefin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
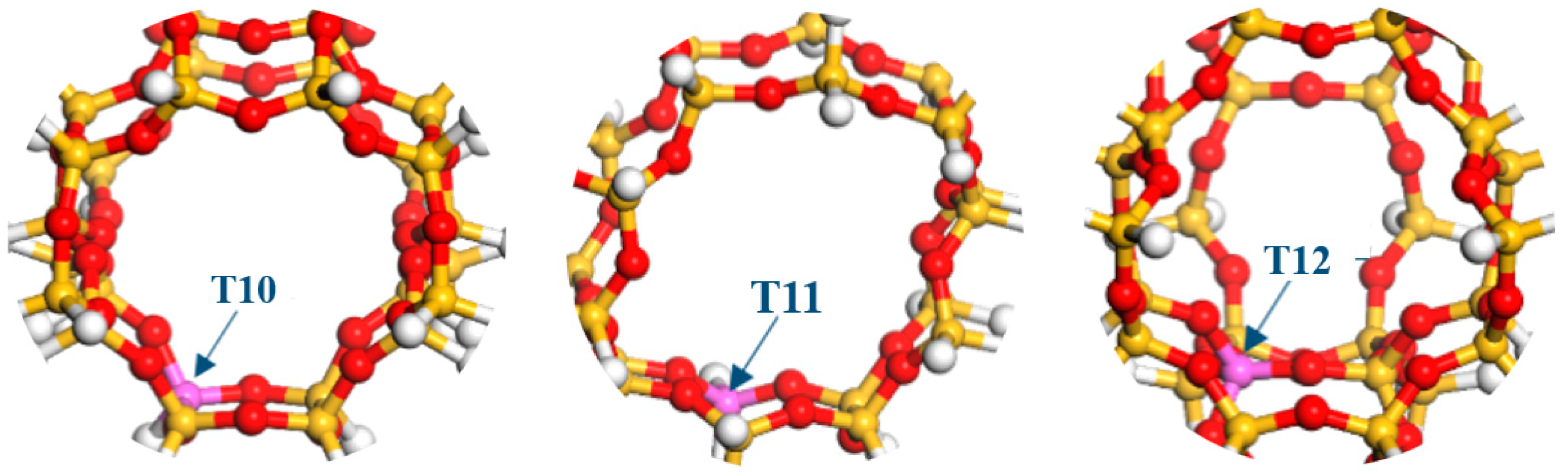
2.1. DFT Simulation Results
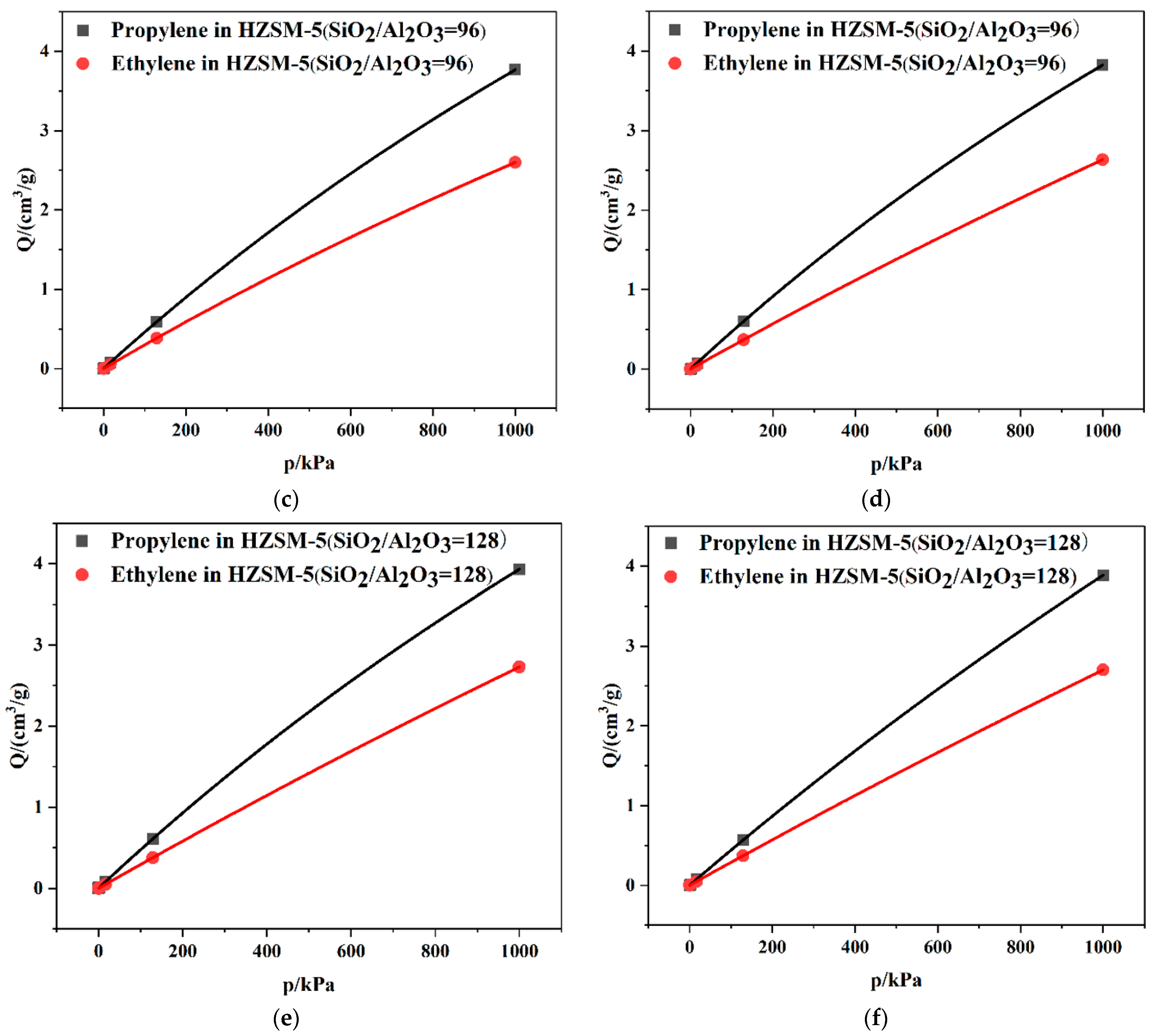
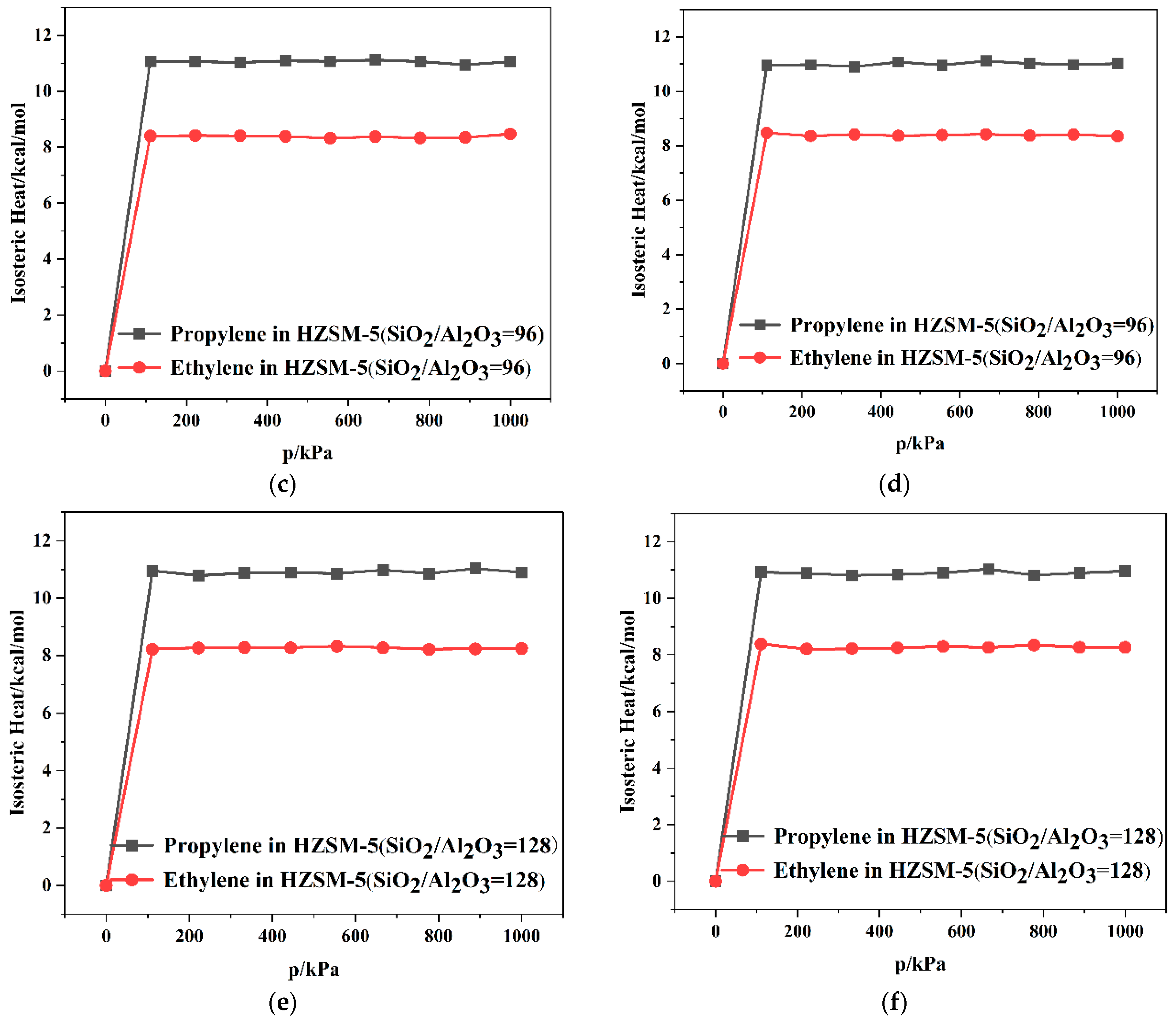
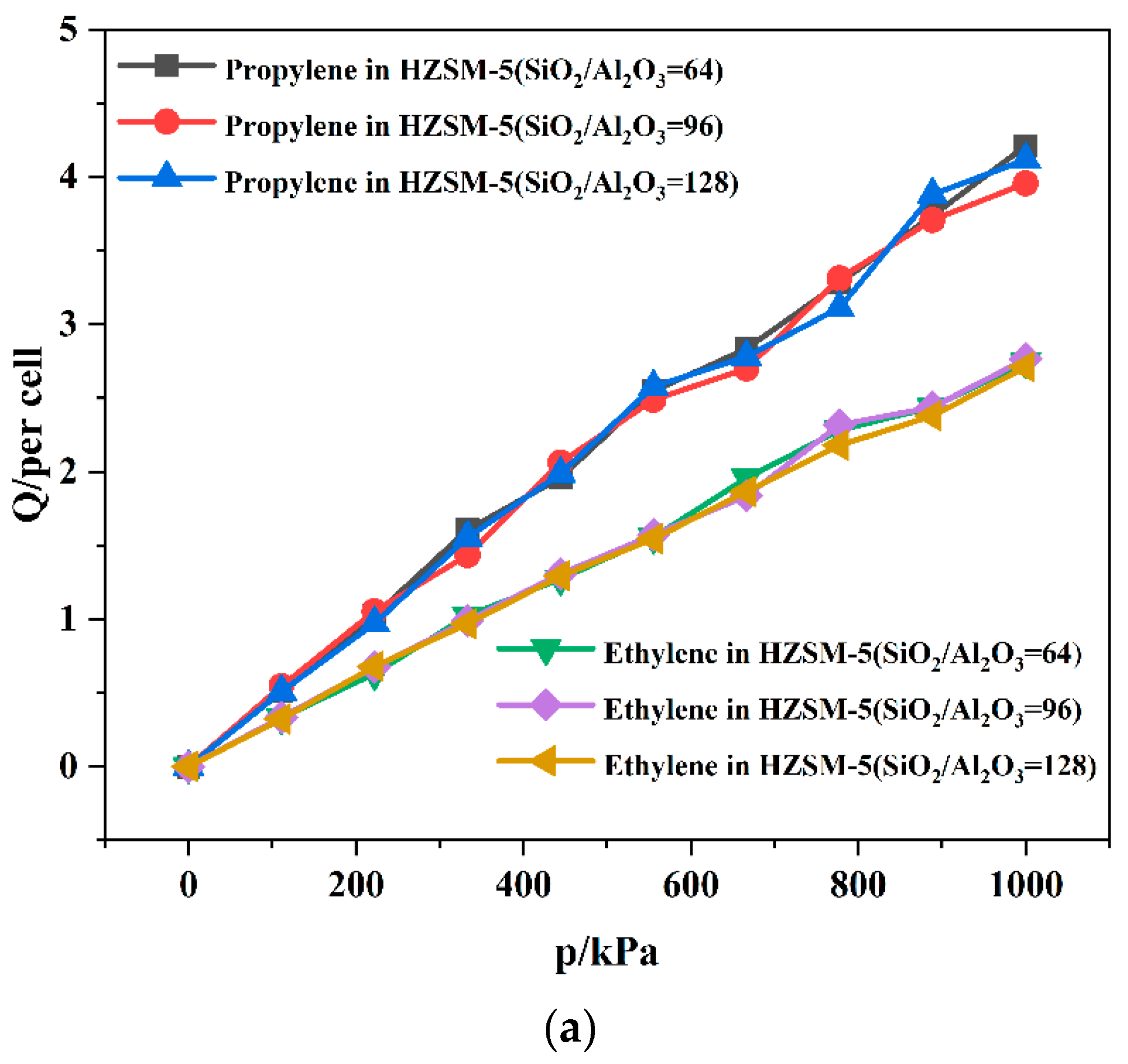
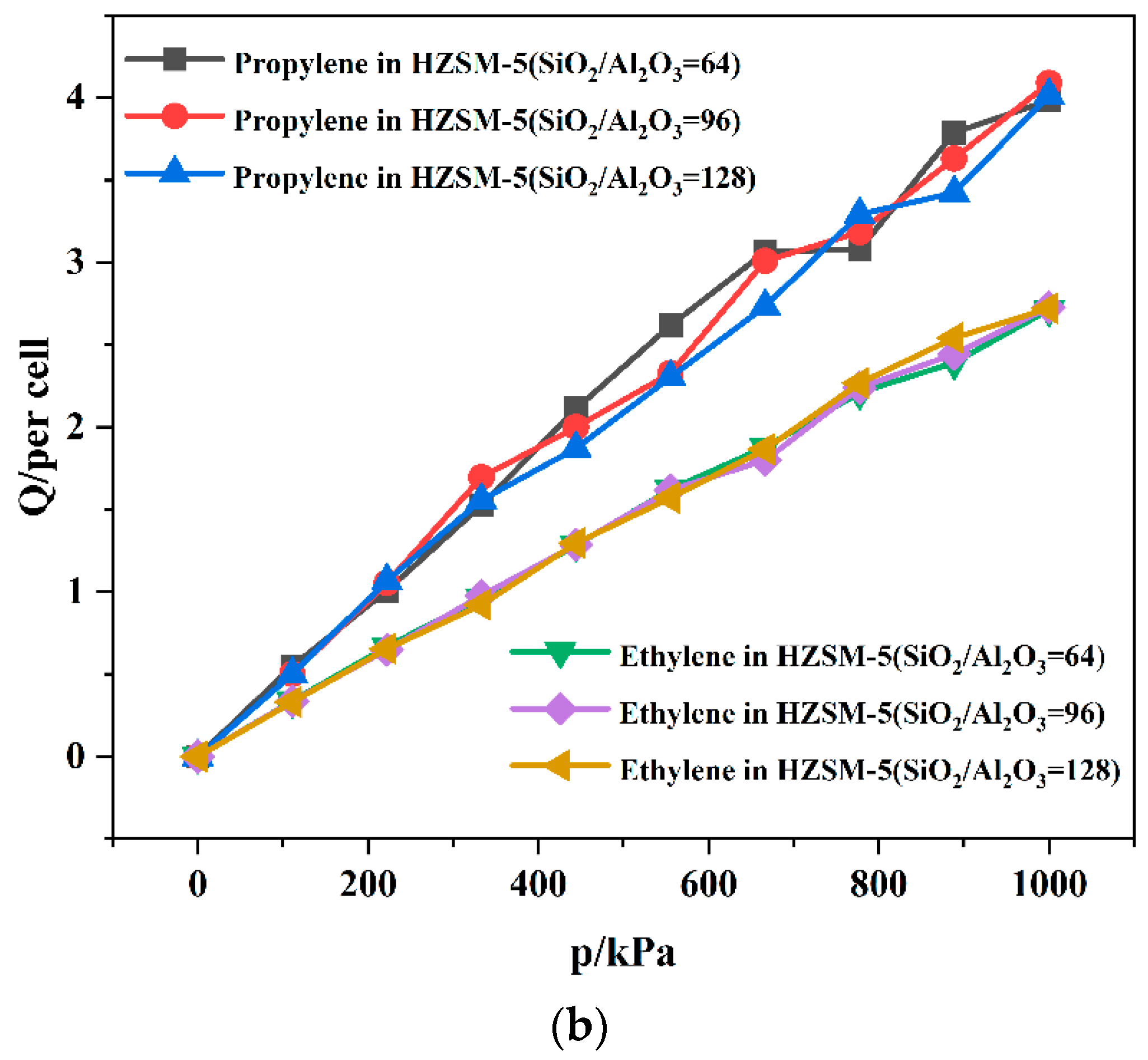
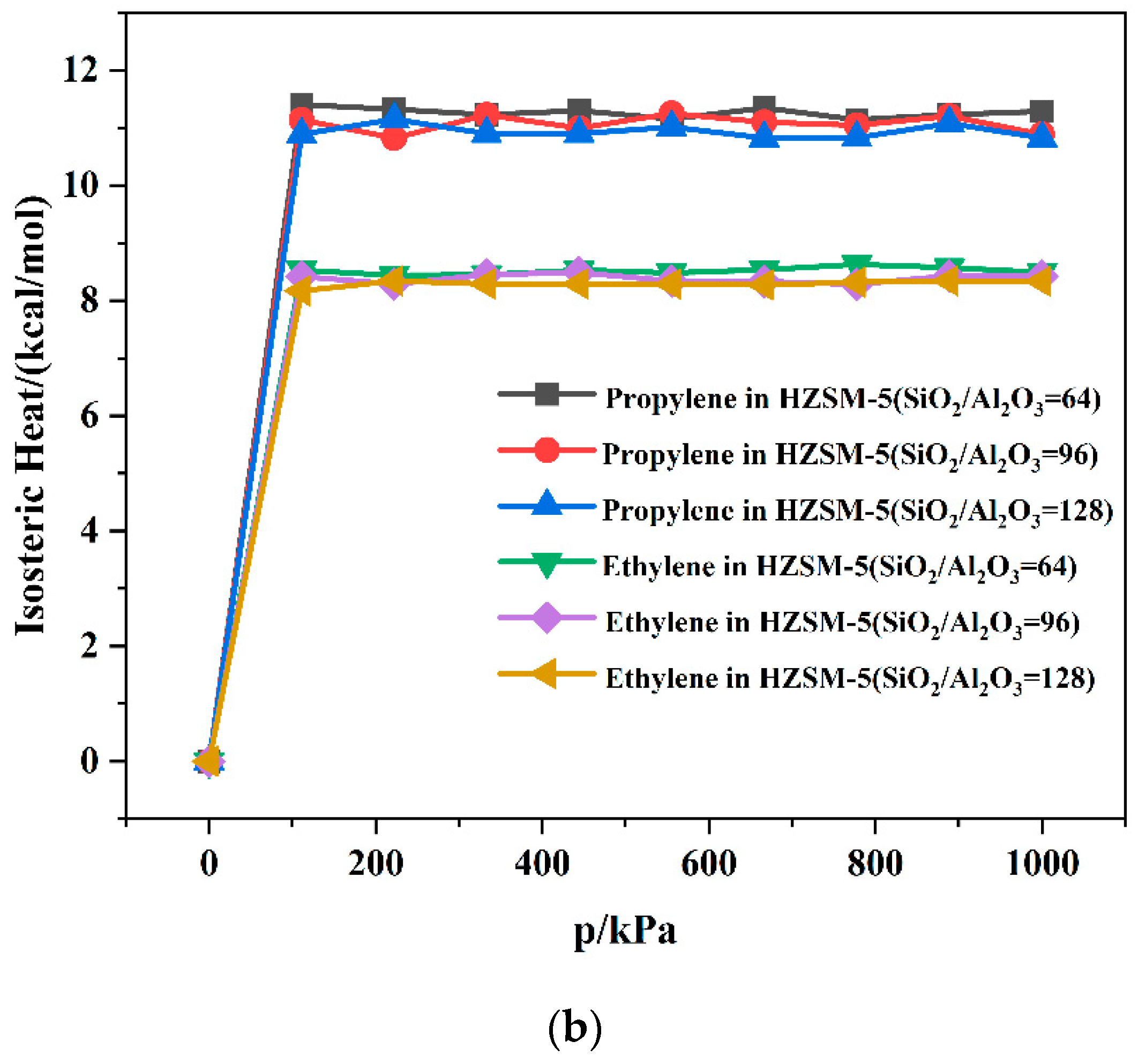
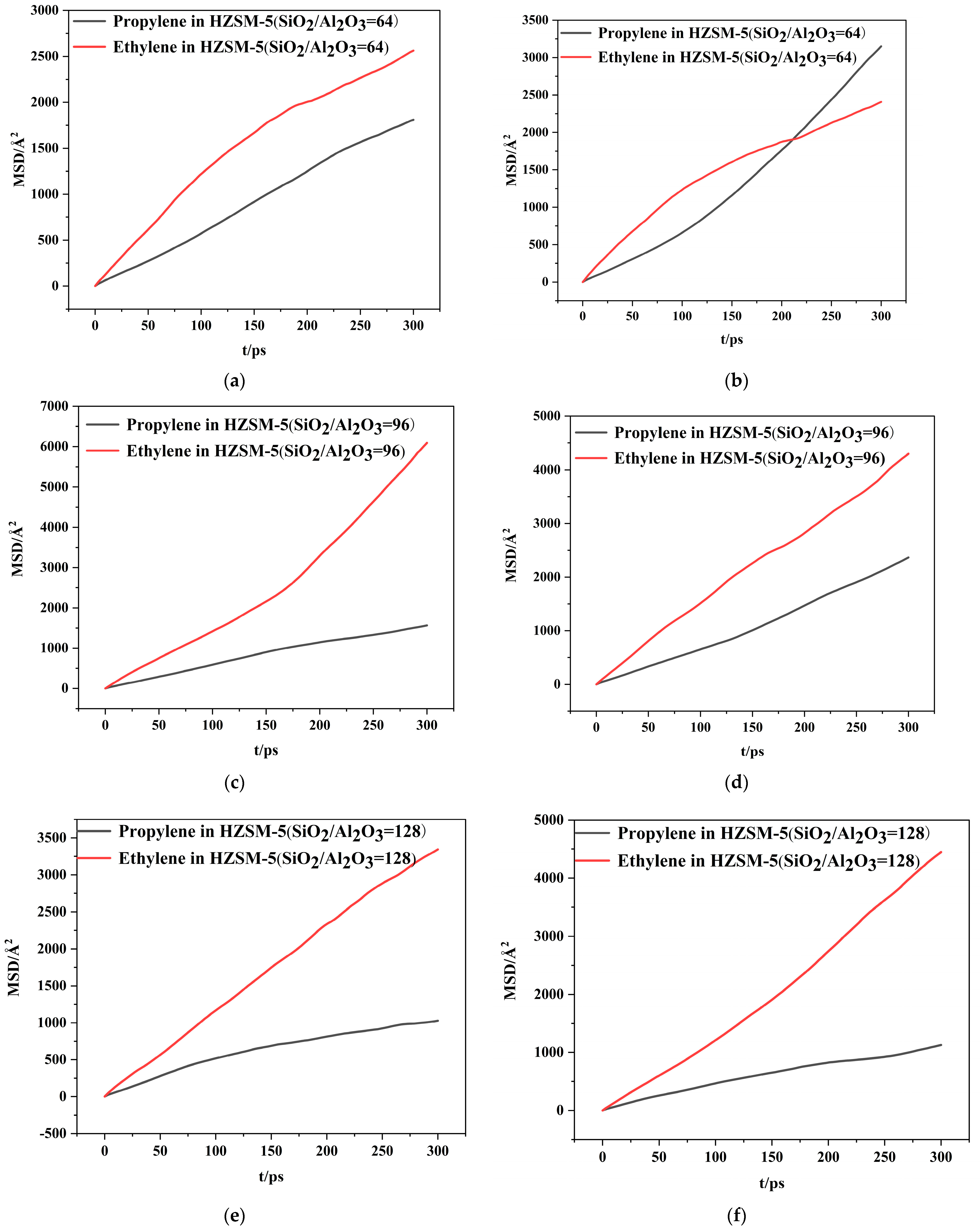
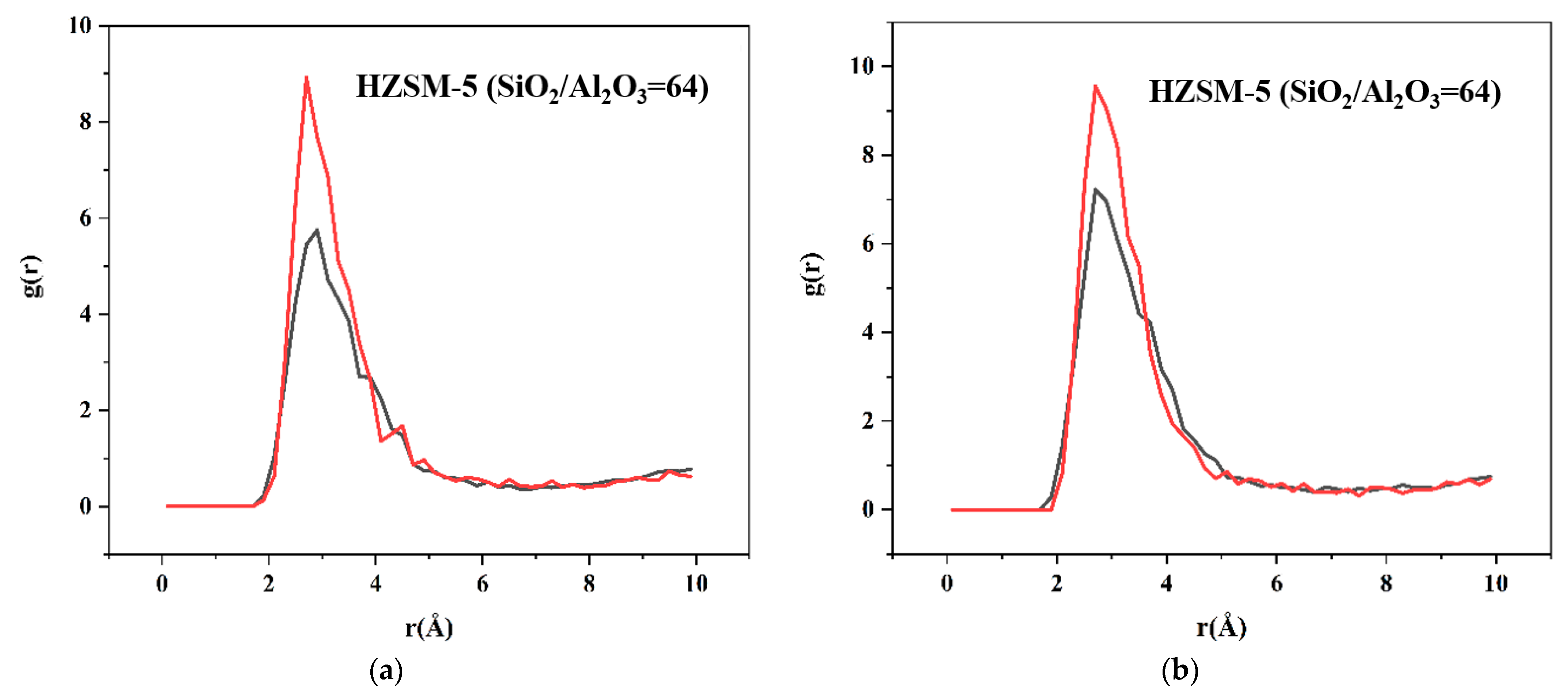
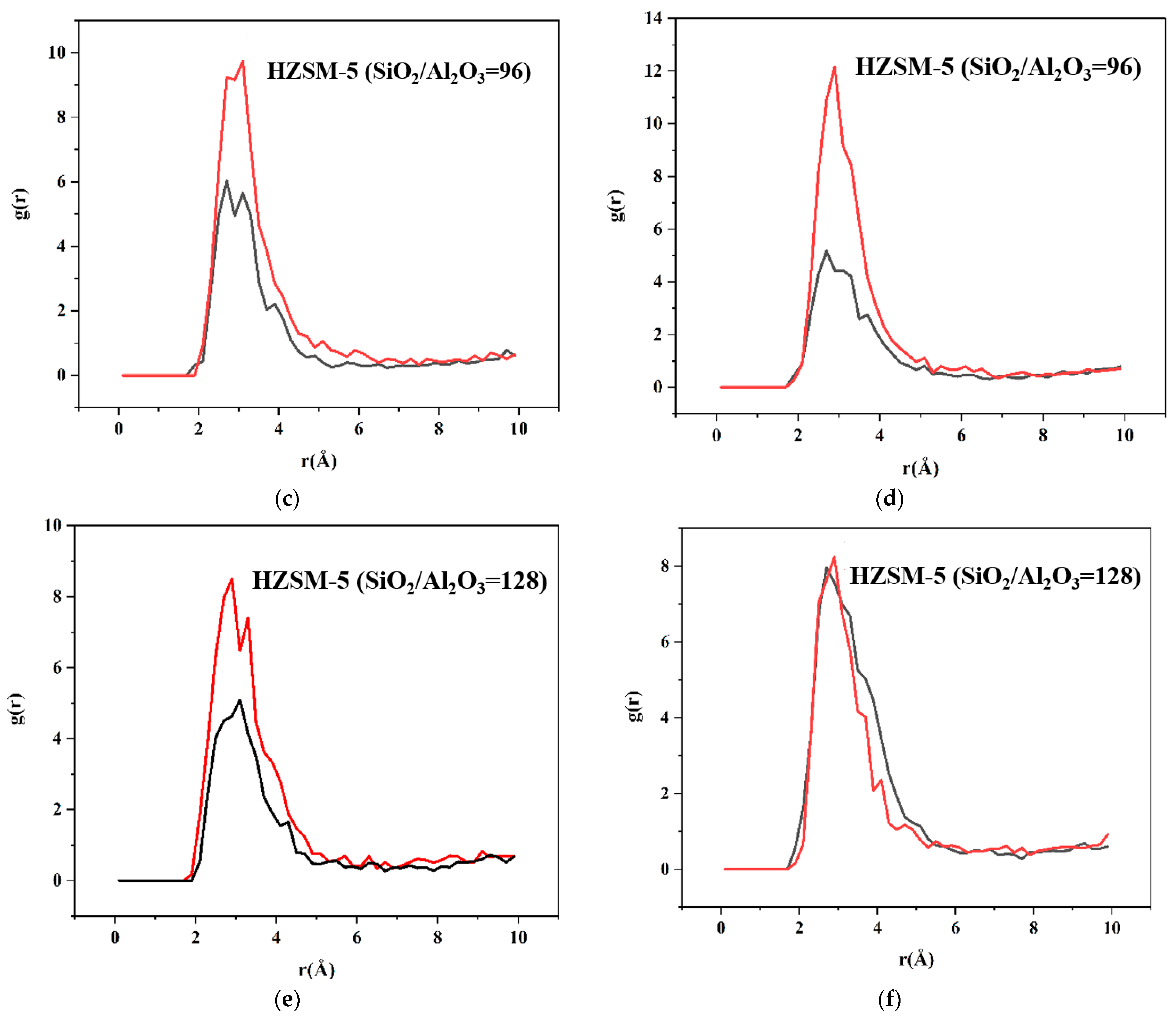
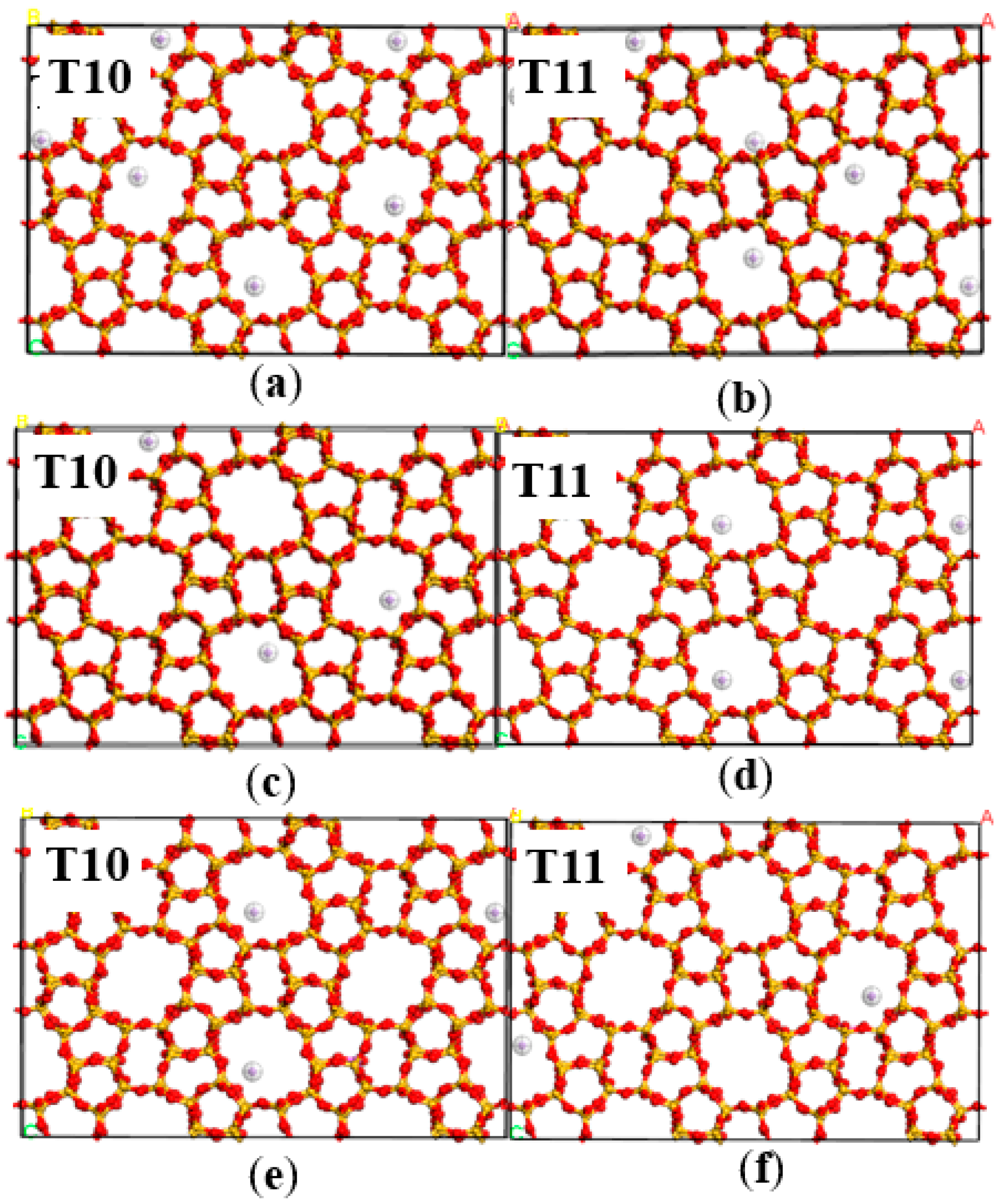
2.2. Dynamics Simulation Result
3. Computational Methods
3.1. DFT Simulation Calculation
3.2. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alotibi, M.F.; Alshammari, B.A.; Alotaibi, M.H.; Alotaibi, F.M.; Alshihri, S.; Navarro, R.M. ZSM-5 zeolite based additive in FCC process: A review on modifications for improving propylene production. Catal. Surv. Asia 2020, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Corresa, E.; Mathieu, Y.; Sauvanaud, L.; Al-Bogami, S.; Al-Ghrami, M.S.; Bourane, A. Crude oil to chemicals: Light olefins from crude oi. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 12–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louwen, J.N.; Van Eijck, L.; Vogt, C.; Vogt, E.T.C. Understanding the activation of ZSM-5 by phosphorus: Localizing phosphate groups in the pores of phosphate-stabilized ZSM-5. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 9390–9403. [Google Scholar]
- Degnan, T.; Chitnis, G.; Schipper, P.H. History of ZSM-5 fluid catalytic cracking additive development at Mobil. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000, 35, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan, J.J.C.T. The chemistry of olefins production by ZSM-5 addition to catalytic cracking units. Catal. Today 2000, 55, 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Zafar, F.; Shen, D.; Wang, X.; Bae, J.W. Contributions of ZSM-5 morphology over hybridized ZnO-ZrO2/ZSM-5 for direct CO2 hydrogenation activity to aromatics. Fuel 2024, 378, 132925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Sugiarto, J.R.; Yoon, W.; Irshad, M.; Jo, H.; Bibi, S.S.; Kim, S.K.; Khan, M.K.; Kim, J. High-yield pentanes-plus production via hydrogenation of carbon dioxide: Revealing new roles of zirconia as promoter of iron catalyst with long-term stability. J. Energy Chem. 2025, 102, 431–442. [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto, M.J. Selective catalytic conversion of bio-ethanol to propene: A review of catalysts and reaction pathways. Catal. Today 2015, 242, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Sazama, P.; Dědeček, J.; Gábová, V.; Wichterlová, B.; Spoto, G.; Bordiga, S. Effect of aluminium distribution in the framework of ZSM-5 on hydrocarbon transformation. Cracking of 1-butene. J. Catal. 2008, 254, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoi, T.; Mochizuki, H.; Namba, S.; Kondo, J.N.; Tatsumi, T. Control of the Al distribution in the framework of ZSM-5 zeolite and its evaluation by solid-state NMR technique and catalytic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 15303–15315. [Google Scholar]
- Janda, A.; Bell, A.T. Effects of Si/Al ratio on the distribution of framework Al and on the rates of alkane monomolecular cracking and dehydrogenation in H-MFI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 19193–19207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Chen, J.; Qin, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, S.; Wang, G.; Dong, M.; Fan, W.; Wang, J. Conversion of methanol to olefins over H-ZSM-5 zeolite: Reaction pathway is related to the framework aluminum siting. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 7311–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungtak, K.; Gyungah, P.; Hee, W.M.; Geunjae, K.; Ki, K.S. Control of hierarchical structure and framework-Al distribution of ZSM-5 via adjusting crystallization temperature and their effects on methanol conversion. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 2880–2892. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Z.; Qin, Z.; Ma, H.; Dong, M.; Li, J.; Fan, W.; Wang, J. Polymethylbenzene or alkene cycle theoretical study on their contribution to the process of methanol to olefins over H-ZSM-5 zeolite. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 28482–28498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Ma, C.; Huang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, K.; Liu, D. Bioethanol conversion into propylene over various zeolite catalysts: Reaction optimization and catalyst deactivation. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Guo, X.; Sun, Y.; Han, S.; Li, Q. Understanding the nanoconfinement effect on the ethanol-to-propene mechanism catalyzed by acidic ZSM-5 and FAU zeolites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 310–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Lobo, R.F.J.M.; Materials, M. Adsorption equilibria of CO2 and small hydrocarbons in AEI, CHA, STT, and RRO-type siliceous zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 236, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyvanloo, Z.; Pour, A.N.; Moosavi, F.; Shahri, S.M.K. Molecular dynamic simulation studies of adsorption and diffusion behaviors of methanol and ethanol through ZSM-5 molecular sieve. J. Mol. Graph. Modell. 2022, 110, 108048. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Z. Insight into the topology effect on the diffusion of ethene and propene in zeolites: A molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Energy Chem. 2013, 22, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Calvo, A.; Van der Perre, S.; Claessens, B.; Calero, S.; Denayer, J.F.M. Unravelling the influence of carbon dioxide on the adsorptive recovery of butanol from fermentation broth using ITQ-29 and ZIF-8. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 9957–9964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, J.A.; Chung, J.; Nair, S.; Sholl, D.S. Adsorption and diffusion of small alcohols in zeolitic imidazolate frameworks ZIF-8 and ZIF-90. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 3169–3176. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Qin, Z.; Dong, M.; Li, J.; Fan, W.; Wang, J. Catalytic roles of the acid sites in different pore channels of H-ZSM-5 zeolite for methanol-to-olefins conversion. Chin. J. Catal. 2021, 42, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Qin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Dong, M.; Li, J.; Fan, W.; Wang, J. Mechanistic insights into the catalytic role of various acid sites on ZSM-5 zeolite in the carbonylation of methanol and dimethyl ether. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 3193–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

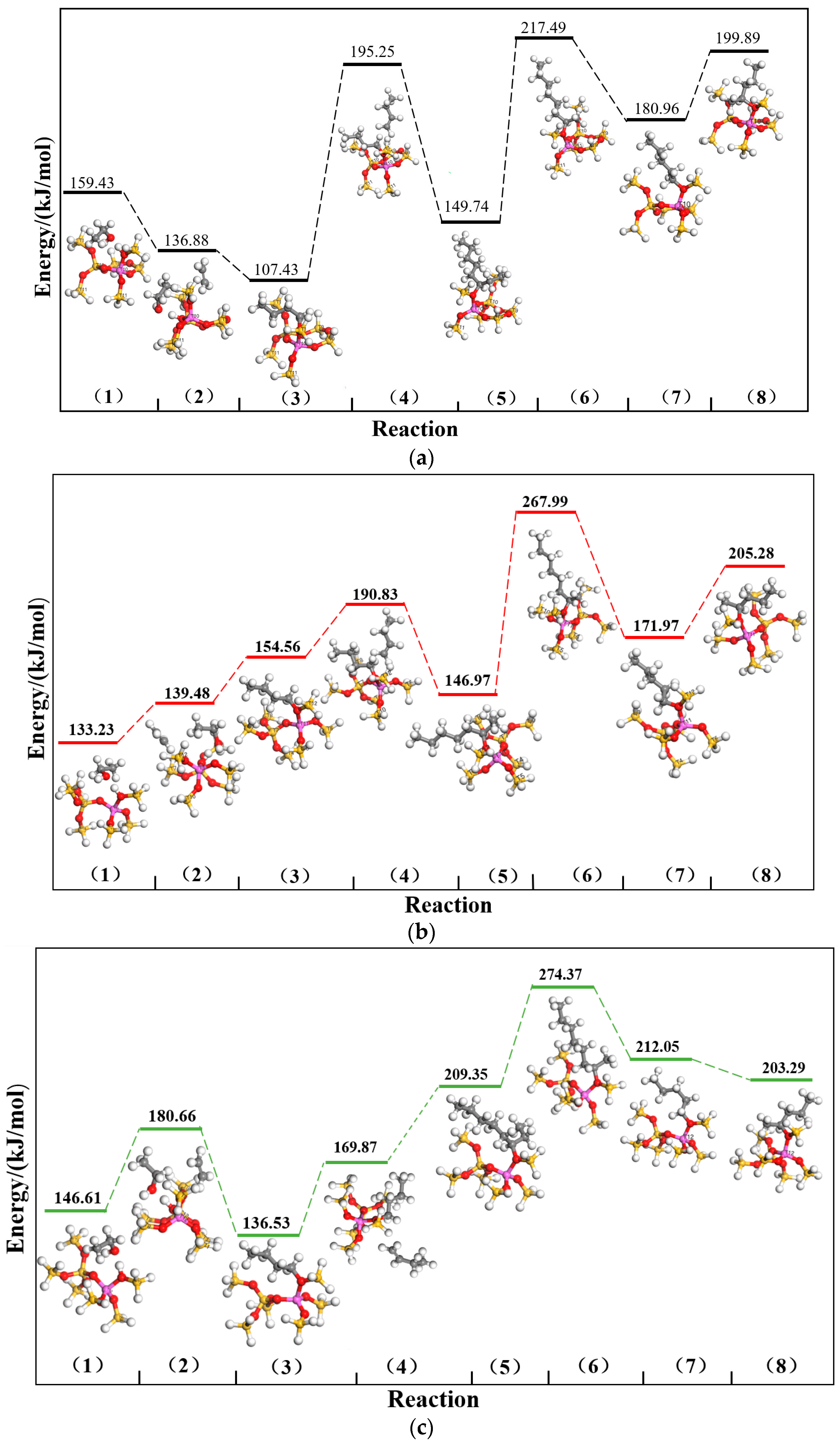
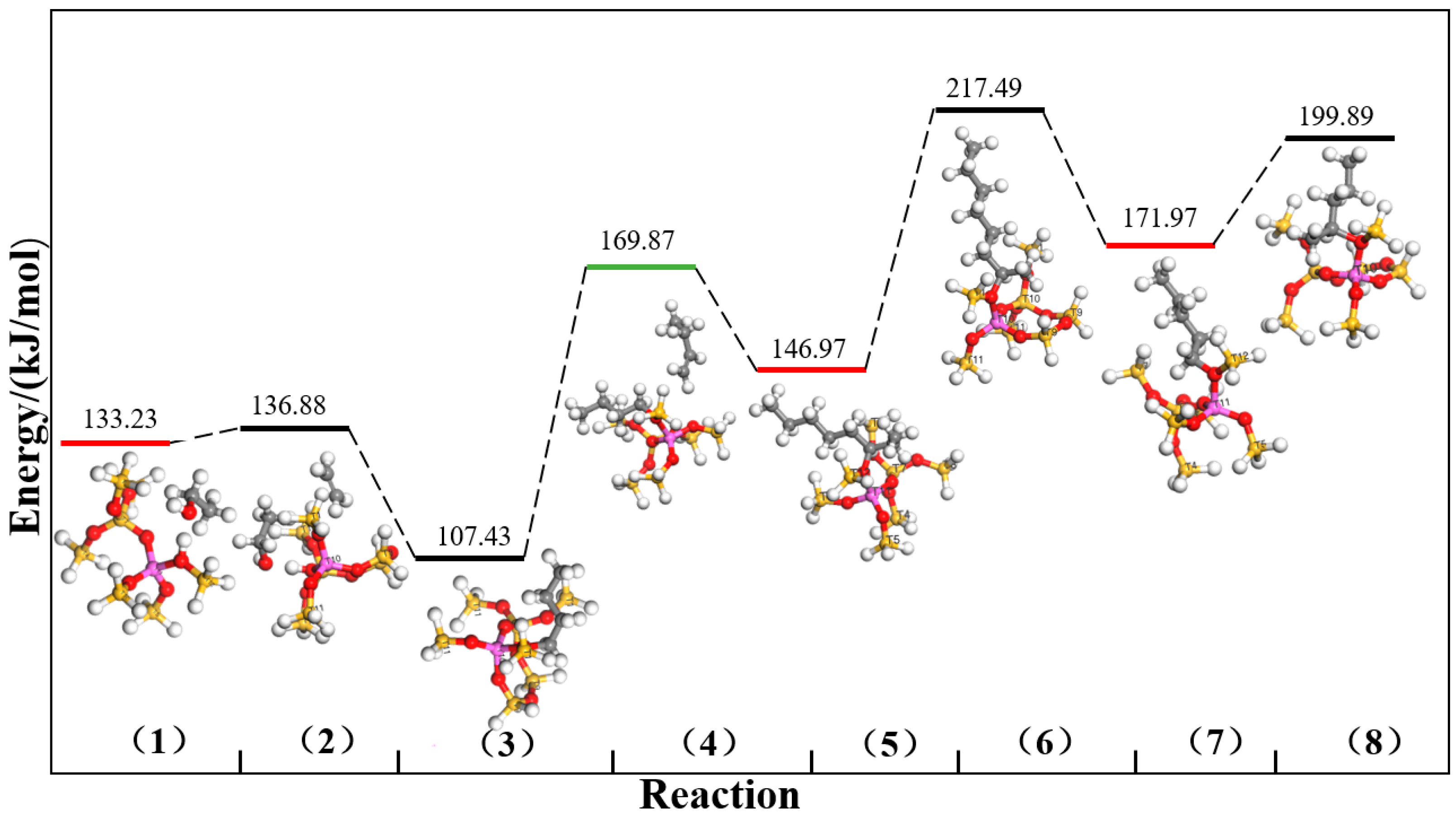



| Channels | ∆E (kJ/mol) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dehydration | Ethylation | Deprotonation | Dimerization | Proton Transfer | β-Scission | Proton Transfer | β-Scission | |
| Straight channel | 499.03 | 474.25 | 456.06 | 478.90 | 469.82 | 463.29 | 470.74 | 456.34 |
| Sinusoidal channel | 486.05 | 483.46 | 470.54 | 463.20 | 460.45 | 467.68 | 465.16 | 482.78 |
| Intersection channel | 498.93 | 494.57 | 480.54 | 440.86 | 490.83 | 476.20 | 482.77 | 480.04 |
| SiO2/Al2O3 | Channel | Langmuir Constant b (kPa−1 × 10−4) | Isosteric Heat (kcal/mol) | Average Loading (per cell) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3H6 | C2H4 | C3H6 | C2H4 | C3H6 | C2H4 | ||
| 64 | T10 | 2.78 | 2.55 | 11.10 | 8.86 | 7.65 | 5.73 |
| T11 | 2.80 | 2.63 | 11.34 | 8.51 | 8.19 | 5.78 | |
| 96 | T10 | 2.60 | 2.52 | 11.06 | 8.47 | 7.91 | 5.84 |
| T11 | 2.63 | 2.58 | 11.01 | 8.34 | 7.68 | 5.66 | |
| 128 | T10 | 2.73 | 2.38 | 10.89 | 8.25 | 8.00 | 5.56 |
| T11 | 2.70 | 2.48 | 10.56 | 8.26 | 7.97 | 5.58 | |
| SiO2/Al2O3 | Channel | Langmuir Constant b (kPa−1 × 10−4) | Isosteric Heat (kcal/mol) | Average Loading (per Cell) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3H6 | C2H4 | C3H6 | C2H4 | C3H6 | C2H4 | ||
| 64 | T10 | 1.61 | 1.14 | 11.24 | 8.49 | 4.21 | 2.75 |
| T11 | 3.21 | 1.49 | 11.19 | 8.53 | 3.98 | 2.71 | |
| 96 | T10 | 2.29 | 1.04 | 10.91 | 8.44 | 3.95 | 2.76 |
| T11 | 2.53 | 1.07 | 10.90 | 8.30 | 4.09 | 2.73 | |
| 128 | T10 | 1.50 | 1.30 | 10.96 | 8.33 | 3.88 | 2.71 |
| T11 | 1.91 | 0.64 | 10.96 | 8.35 | 4.02 | 2.72 | |
| SiO2/Al2O3 | Channel | Diffusion Coefficients × 10−8(cm2/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| C3H6 | C2H4 | ||
| 64 | T10 | 1.05 | 1.38 |
| T11 | 1.77 | 1.24 | |
| 96 | T10 | 0.87 | 3.27 |
| T11 | 1.32 | 2.30 | |
| 128 | T10 | 0.55 | 1.89 |
| T11 | 0.59 | 2.50 | |
| SiO2/Al2O3 | Channel | Diffusion Coefficient × 10−8(cm2/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| C3H6 | C2H4 | ||
| 64 | T10 | 0.69 | 2.51 |
| T11 | 0.85 | 2.48 | |
| 96 | T10 | 0.47 | 1.55 |
| T11 | 1.00 | 2.69 | |
| 128 | T10 | 1.36 | 1.12 |
| T11 | 1.58 | 1.58 | |
| SiO2/Al2O3 | Channel | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 64 | T10 | 0.27 | 1.53 |
| T11 | 0.34 | 1.47 | |
| 96 | T10 | 0.30 | 1.43 |
| T11 | 0.37 | 1.50 | |
| 128 | T10 | 1.21 | 1.43 |
| T11 | 1.00 | 1.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Dong, M.; Chen, K.; Liu, D. Unravel the Roles of the Acid Sites in Different Pore Channels of HZSM-5 Catalyst on Ethanol Conversion to Light Olefin. Catalysts 2025, 15, 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15040302
Xia W, Wang X, Wang D, Jiang Z, Zhang Y, Li S, Dong M, Chen K, Liu D. Unravel the Roles of the Acid Sites in Different Pore Channels of HZSM-5 Catalyst on Ethanol Conversion to Light Olefin. Catalysts. 2025; 15(4):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15040302
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Wei, Xinrui Wang, Di Wang, Zhenhua Jiang, Yanli Zhang, Shuangshuang Li, Mingyuan Dong, Kun Chen, and Dong Liu. 2025. "Unravel the Roles of the Acid Sites in Different Pore Channels of HZSM-5 Catalyst on Ethanol Conversion to Light Olefin" Catalysts 15, no. 4: 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15040302
APA StyleXia, W., Wang, X., Wang, D., Jiang, Z., Zhang, Y., Li, S., Dong, M., Chen, K., & Liu, D. (2025). Unravel the Roles of the Acid Sites in Different Pore Channels of HZSM-5 Catalyst on Ethanol Conversion to Light Olefin. Catalysts, 15(4), 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15040302








