Abstract
Methylamines, including monomethylamine (MMA), dimethylamine (DMA), and trimethylamine (TMA), are essential industrial intermediates. However, traditional catalysts suffer from poor product selectivity and are being phased out due to shifting market demands. Zeolites have emerged as promising alternatives due to their high activity and superior selectivity. Large- and medium-pore zeolites require modifications to enhance MMA- and DMA-selectivity by reducing pore size, whereas small-pore zeolites inherently exhibit high selectivity for MMA and DMA without modification. However, their high production costs have hindered large-scale commercialization. Research efforts are now focused on developing cost-effective catalysts to shift methylamine synthesis from equilibrium-driven (balancing) to selective (unbalancing) processes. This review explores the performance of zeolite-based catalysts in methylamine synthesis, highlighting key factors influencing selectivity. Additionally, it examines the challenges associated with small-pore zeolites and discusses strategies to enhance their application.
1. Introduction
Methylamines are synthesized through the methylation of ammonia (NH3), where hydrogen atoms are replaced by methyl groups (-CH3) in the presence of Brønsted acid catalysts [1]. Based on the number of methyl groups, they are classified as MMA, DMA, or TMA. These compounds serve as critical industrial intermediates in pharmaceuticals, pesticides, solvents, defense chemicals, surfactants, explosives, chemical fibers, synthetic resins, feed additives, lithium batteries, and other applications [2,3].
Early methylamine production involved batch processes using methanol (MeOH) and NH3 with zinc chloride as a dehydrating agent [4]. Later, Brown et al. developed gas-phase catalytic methods using alumina and silica–alumina catalysts, significantly improving reaction efficiency and reducing costs [5,6,7]. This process was subsequently commercialized and remains the foundation of modern methylamine production. The reaction occurs at high temperatures and is exothermic, producing a mixture of MMA, DMA, and TMA. After synthesis, crude methylamines are separated into individual products [1].
Due to the thermodynamic equilibrium (Figure 1a), TMA is the predominant product. However, MMA and DMA are more commercially valuable as key precursors for N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) and N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF), respectively. In contrast, TMA has faced oversupply issues. To enhance MMA and DMA selectivity [8], industrial processes adjust reaction conditions by increasing the temperature and the NH3-to-MeOH molar ratio (N/C ratio) (Figure 1b) [9,10]. However, at high MeOH conversion rates near equilibrium, TMA remains the dominant product. Many processes, therefore, rely on recovering and recycling TMA, a method known as the balancing production process. This approach is complex, costly, and poses significant operational risks [11].
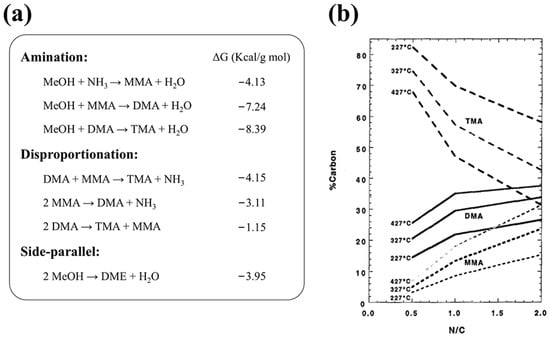
Figure 1.
(a) Equilibrium reactions in the synthesis of methylamine from methanol and ammonia; (b) thermodynamic equilibrium in methylamines synthesis. Reprinted/adapted with permission from Ref. [1]. Copyright (1997) Elsevier.
Zeolites have played a transformative role in the chemical industry. Their first major application was in fluid catalytic cracking (FCC), where Y-type (FAU) zeolites significantly improved gasoline yields and quality [12]. Later, Mobil Oil introduced high-silica zeolites such as ZSM-5 [13], which enhanced cracking efficiency and enabled new catalytic processes, including methanol-to-gasoline (MTG) conversion [14,15]. Zeolites’ ability to control methylene chain growth within confined pore structures has inspired their use in methylamine synthesis [16,17]. Researchers have explored the use of zeolites such as MOR, MFI, and RHO to improve catalytic efficiency and reduce costs associated with the balancing production process which traditionally relies on inefficient amorphous catalysts.
Today, zeolite-based catalysts for methylamine synthesis have been extensively studied [2,18], with increasing demands for higher selectivity and cost efficiency. This review provides an overview of the historical development of zeolite catalysts in methylamine synthesis, their reaction mechanisms, by-product formation, and strategies to enhance catalytic performance. Additionally, it discusses future trends in process optimization and catalyst development. Advancing zeolite-based catalysts can facilitate the industrialization of methylamine production while reducing manufacturing costs.
2. Zeolite Catalysts
2.1. Historical Overview
Zeolites are kinetically stable, three-dimensional porous materials composed primarily of (SiO4) and (AlO4)− tetrahedra. The incorporation of Al introduces a negative framework charge, which is balanced by cations such as protons, alkali metals, or alkaline earth metals. In their protonated form, zeolites function as solid acids, making them highly effective catalysts for methylamine synthesis [19].
The (SiO4) and (AlO4)− tetrahedra interconnect to form channels and cavities, with pore size determined by the number of tetrahedra units in the ring structure [20]. Based on pore size, zeolites are classified into three categories, small-pore zeolites with 8-membered rings (3~4.5 Å), medium-pore zeolites with 10-membered rings (4.5~6.5 Å), and large-pore zeolites with 12-membered rings (6.5~8 Å). Figure 2 illustrates representative structures of these zeolite types.
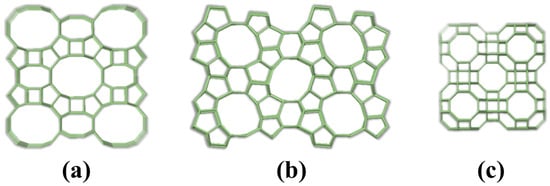
Figure 2.
Structures of typical zeolites with different pore sizes: (a) large-pore mordenite, (b) medium-pore ZSM-5, and (c) small-pore rho zeolite.
Early methylamine synthesis catalysts were largely adapted from developments in the petroleum industry. Large-pore and medium-pore zeolites were commonly used but lacked sufficient steric constraints to restrict TMA formation (3.9 × 5.4 × 6.1 Å). Consequently, selectivity for DMA (3.9 × 4.7 × 6.0 Å) and MMA (3.7 × 3.9 × 4.4 Å) remained low. To address this limitation, post-synthesis modifications were introduced to reduce pore size, thereby enhancing DMA and MMA selectivity while suppressing TMA formation [21]. However, these modification processes are complex and costly.
To overcome these challenges, researchers have increasingly focused on small-pore zeolites, which naturally exhibit high selectivity for MMA and DMA due to their intrinsic pore structure [22,23]. Despite their superior performance, small-pore zeolites have not been widely adopted in industrial methylamine production. The primary barrier remains their high synthetic cost, which limits large-scale implementation.
Definitions and Equations
For clarity, the following definitions and equations will be used throughout this review:
where Equation (1) is methanol conversion, representing the single-pass conversion rate of methanol. Equations (2) and (3) are product selectivity. Before 2000, Equation (2) was widely used in scientific literature and patents, expressing selectivity in terms of carbon atom distribution. However, Equation (3), which defines selectivity on a molar basis, has become the industry standard. Since molar selectivity better reflects the individual selectivity of each product, this review will primarily use Equation (3). Nevertheless, both carbon atom selectivity and molar selectivity are provided in Table 1 and Table 2 for comparison. Equation (4) is the true single-pass yield of each product. Equation (5) is the by-product formation, which is relevant to the discussions on reaction efficiency and process optimization.
2.2. Catalytic Mechanism
2.2.1. Eley-Rideal Mechanism
Ercher et al. investigated the methanol amination process using in situ infrared (IR) spectroscopy and found that both methanol and ammonia adsorb onto the Brønsted acid sites of H-MOR. However, ammonia exhibits a stronger affinity for these sites than methanol. As the temperature increases, most methanol desorbs from the Brønsted acid sites and reacts with ammonia at other locations to form methylamines [24].
All three methylamines—monomethylamine (MMA), dimethylamine (DMA), and trimethylamine (TMA)—can adsorb onto the Brønsted acid sites. However, ammonia readily displaces these adsorbed methylamines, facilitating their desorption. The desorption rate of methylamines closely matches their formation rate in the gas phase, suggesting that ammonia-assisted desorption is the rate-determining step in methylamine synthesis.
Based on these observations, researchers proposed an Eley-Rideal (E-R) mechanism for methanol amination over zeolites, which is as follows:
- (1)
- Ammonia Occupation: Under reaction conditions, ammonia predominantly occupies Brønsted acid sites, while methanol remains in the gas-phase. The reaction between gas-phase methanol and ammonia leads to methylamine formation (Figure 3a).
- (2)
- NH3-Assisted Desorption: adsorbed methylamines undergo desorption facilitated by ammonia molecules, preventing site blockage and enabling continuous catalysis (Figure 3b).
- (3)
- Sequential Methylation: lower-substituted methylamines, such as MMA and DMA, remain adsorbed and undergo further methylation, leading to the formation of DMA and TMA (Figure 3c).
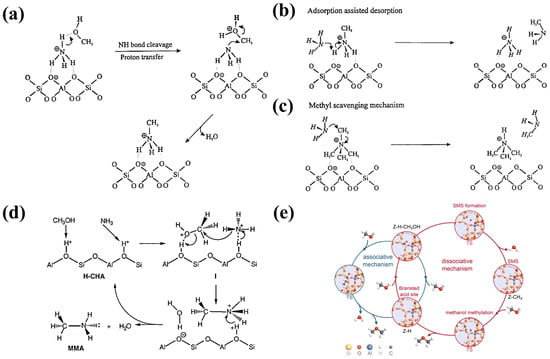
Figure 3.
(a) Proposed reaction mechanism for the formation of methylamines on Bronsted acid zeolites, (b) adsorption assisted desorption, and (c) methyl scavenging mechanism. Reprinted/adapted with permission from Ref. [24]. Copyright (1997) Springer. (d) Proposed mechanism for methylamine synthesis. Methanol and ammonia are adsorbed on adjacent Brønsted acid sites to give proximally bound species (I). Reprinted/adapted with permission from Ref. [25]. Copyright (1996) Elsevier. (e) Optimized geometries for the two reaction paths employing H-SSZ-13. Reprinted/adapted with permission from Ref. [26]. Copyright (2020) ACS.
2.2.2. Langmuir–Hinshelwood Mechanism
Segawa et al. proposed that methanol amination over CHA-type zeolite catalysts follows a Langmuir–Hinshelwood (L-H) mechanism. In this pathway, methanol and ammonia adsorb onto adjacent acid sites and undergo an SN2-like reaction to form methylamines (Figure 3d) [25].
Additionally, methanol adsorption on zeolite acid sites can lead to the formation of surface methoxide species. These methoxide species may react with another methanol molecule, forming dimethyl ether (DME) as a by-product (Figure 3e) [26]. However, in methanol amination, ammonia competes with methanol for adsorption, inhibiting methoxide formation. This competition explains the low selectivity for DME in methanol amination reactions.
Notably, the E-R mechanism was primarily observed in hydrogen-based zeolites, whereas the L-H mechanism was identified in CHA zeolites containing K+ ions. Studies suggest that metal ions enhance methanol adsorption, influencing the reaction pathway [27].
2.2.3. By-Product Formation Mechanism
Ammonia formation is suppressed when the methanol concentration becomes too high at certain reaction sites. At acidic sites, adsorbed methanol reacts with another methanol molecule to produce DME as a by-product. Fritz et al. proposed that methanol displaces the oxygen from another methanol molecule, whose oxygen is activated either by protonation of the hydroxyl group or by coordination with a Lewis acid site [9].
DME is generally considered the main contributor to coke deposition [26,28]. Therefore, minimizing DME formation is essential for improving methylamine synthesis. Hellman et al. reported that stronger acidity in zeolites increases coke formation, which poisons Brønsted acid sites [29,30]. Hong et al. found that increasing intergranular mesopores effectively reduces coke formation, thereby enhancing catalyst stability [28].
2.3. Large-Pore and Medium-Pore Zeolites
2.3.1. Unmodified Large-Pore and Medium-Pore Zeolites
Table 1 summarizes the most representative zeolite topologies for methylamine synthesis, comparing their performance with conventional amorphous solid acid catalysts. Zeolites such as Y (FAU), Mordenite (MOR), Ferrierite (FER), and ZSM-5 (MFI) exhibit lower TMA selectivity than amorphous-solid acid catalysts (MgO-SiO2 and Al2O3-SiO2).
Among these zeolites, MOR-type zeolites demonstrated the best performance, achieving 34.6% MMA selectivity, 41.8% DMA selectivity, and 22.6% TMA selectivity at 400 °C and a weight hourly space velocity (WHSV) of 1.25 h−1. Zeolite T (OFF) also exhibited low TMA selectivity (13.7%), but its practical application is limited due to its excessively low DMA selectivity (23.7%).

Table 1.
Summary of amorphous solid acid catalysts, large-pore, and medium-pore zeolites used for methanol conversion in the presence of ammonia. The table includes conversion (L), carbon-based selectivity (C), mole-based selectivity (M), and reaction conditions.
Table 1.
Summary of amorphous solid acid catalysts, large-pore, and medium-pore zeolites used for methanol conversion in the presence of ammonia. The table includes conversion (L), carbon-based selectivity (C), mole-based selectivity (M), and reaction conditions.
| Sample | Top. a | Si/Al Si/Mg | LR b | N/C c | T/WHSV d °C/h−1 | LMeOH e/% | CSelectivity f/C% | MSelectivity g/% | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMA | DMA | TMA | MMA | DMA | TMA | ||||||||
| MgO-SiO2 | - | 2 | - | 1 | 400/1.25 | 66 | 3.7 | 11.9 | 84.8 | 9.4 | 15.0 | 71.2 | [8] |
| Al2O3-SiO2 | - | 2 | - | 1 | 400/1.25 | 90 | 9.8 | 14.6 | 70.7 | 22.8 | 16.9 | 54.6 | [8] |
| H-Y | FAU | 2.8 | 12 | 1 | 380/0.156 | >90 | 15.5 | 25.5 | 59.0 | 28.8 | 23.7 | 36.5 | [2] |
| H-Mor | MOR | 9.7 | 12 | 1 | 380/0.0445 | >90 | 26.6 | 25.7 | 47.7 | 38.9 | 18.8 | 23.3 | [2] |
| H-ZSM-5 | MFI | 12.5 | 10 | 1 | 380/0.03 | >90 | 10.9 | 21.5 | 67.5 | 19.6 | 19.3 | 40.4 | [2] |
| H-SiCl4-Mor | MOR | 10.5 | 12 | 1 | 380/0.0388 | >90 | 33.3 | 65.3 | 1.4 | 49.8 | 48.9 | 0.7 | [2] |
| TEOS-H-Mor | MOR | 10.0 | 12 | 1 | 360/0.4 | 90 | 19.5 | 75.8 | 4.7 | 32.4 | 63.0 | 2.6 | [31] |
| H-Zeolon | MOR | 5.0 | 12 | 1 | 400/1.25 | 86 | 18.7 | 44.9 | 36.4 | 34.6 | 41.8 | 22.6 | [8] |
| Na-Zeolon | MOR | 5.0 | 12 | 1 | 400/1.25 | 86 | 10.8 | 36.2 | 53.0 | 23.3 | 38.0 | 37.0 | [8] |
| Mg-Zeolon | MOR | 5.0 | 12 | 1 | 400/1.25 | 91 | 21.1 | 54.7 | 24.2 | 37.2 | 48.3 | 14.2 | [8] |
| Mg,H-Zeolon | MOR | 5.0 | 12 | 1 | 400/1.25 | 76 | 18.4 | 56.8 | 24.8 | 33.3 | 51.3 | 14.9 | [8] |
| La, H-Zeolon | MOR | 5.0 | 12 | 1 | 400/1.25 | 95 | 20.7 | 58.9 | 20.4 | 36.1 | 51.5 | 11.9 | [8] |
| Cu-Zeolon | MOR | 5.0 | 12 | 1 | 400/1.25 | 82 | 16.1 | 22.1 | 61.8 | 32.2 | 22.0 | 41.0 | [8] |
| H-Mor-unsteamed | MOR | - | 12 | 1.9 | 310/2.18 | 90 | 19.6 | 26.6 | 53.9 | 37.8 | 25.6 | 34.6 | [32] |
| H-Mor-steamed | MOR | - | 12 | 1.9 | 310/1.99 | 89 | 26.2 | 52.2 | 21.6 | 43.2 | 43.0 | 11.9 | [32] |
| Na,H-Mor SiO2 binder | MOR | 5.5 | 12 | 1.1 | 390/6.64 | 94 | 17.0 | 77.5 | 5.5 | 29.0 | 66.0 | 3.1 | [33] |
| Na,H-Mor-Al2O3 binder | MOR | 5.5 | 12 | 1.1 | 390/6.64 | 96 | 13.5 | 46.2 | 32.2 | 27.3 | 46.7 | 21.7 | [33] |
| H-Fer | FER | 6.0 | 10 | 1 | 400/0.12 | 94 | 13.0 | 28.0 | 59.0 | 26.6 | 28.7 | 40.2 | [34] |
| Ca-Fer | FER | 6.0 | 10 | 0.83 | 400/1.32 | 83 | 22.0 | 48.0 | 30.0 | 39.3 | 42.9 | 17.9 | [35] |
| H-T | OFF | - | 12 | 1.7 | 430/3.32 | 85 | 41.4 | 31.4 | 27.2 | 62.6 | 23.7 | 13.7 | [36] |
a Top. = topology. b LR = Largest ring. c N/C = NH3/CH3OH. d WHSV = weight hourly space velocity. e LMeOH = MeOH conversion. f CSelectivity =. g MSelectivity = .
2.3.2. Modification Strategy for Large-Pore and Medium-Pore Zeolites
Solvent treatment
Segawa and Tachibana analyzed H-MOR before and after SiCl4 vapor treatment using infrared (IR) spectroscopy with pyridine and ammonia as probe molecules. They found that Si-(O-Si)4 species formed inside the main channels of H-MOR after treatment (Figure 4a). As a result, large base molecules such as pyridine and TMA could no longer access the active sites, whereas smaller molecules like NH3, MMA, and DMA remained accessible (Figure 4b). This modification increased MMA and DMA selectivity from 76.4% to 98.7% [2]. Despite the low WHSV used in the study, these findings highlight the critical role of pore size in controlling product selectivity.
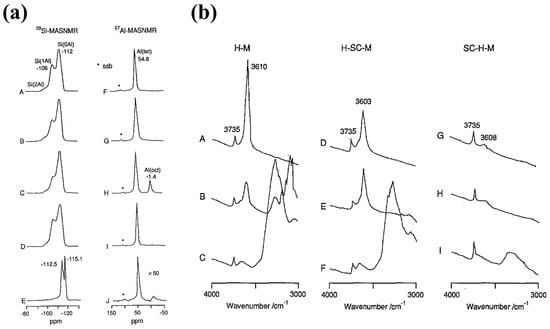
Figure 4.
(a) 29Si- and 27A1-MAS NMR spectra of mordenites before or after treatments with SiC14, (A,F) Na-M (Si/A1 = 9.0); (B,G) Na-SC-M (Si/A1 = 9.1); (C,H) H-SC-M (Si/AI = 11.4); (D,I) H-M (Si/A1 = 9.3); (E,J) SC-H-M (Si/A1 = 58.0); The asterisks represent spinning sidebands (ssb). (b) IR spectra of OH stretching region of H-M (Si/Al = 9.7), H-SC-M (Si/Al = 10.5), and SC-H-M (Si/Al = 21.2) (A,D,G); after evacuation at 773 K, (B,E,H); pyridine adsorbed and evacuated at 473 K, (C,F,I). Reprinted/adapted with permission from Ref. [2]. Copyright (1991) Elsevier.
Lercher et al. treated H-MOR with tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) and examined the effects using in situ ammonia adsorption IR spectroscopy. They observed that the diffusion of TMA was significantly hindered in the modified zeolite, leading to its decomposition into DMA and MMA. This treatment increased DMA and MMA selectivity to 95.4%, demonstrating that product diffusion plays a key role in reaction selectivity [31].
Ion exchange
Takeshita et al. found that alkaline-earth metal-exchanged mordenite (Mg2+ and La3+) exhibited high DMA selectivity (>50%) at 400 °C and WHSV = 1.25 h−1 [8]. Their acidity analysis revealed the following trends: weak and medium Brønsted acid sites favor stepwise methylation of ammonia with methanol, leading to MMA and DMA formation; strong Brønsted acid sites (e.g., in H+-ZSM-5 and Al2O3-SiO2) promote excessive methylation, increasing the formation of TMA and DME (Figure 5); larger alkaline-earth metal cations reduce pore size, limiting TMA diffusion and modifying acidity to enhance DMA selectivity.
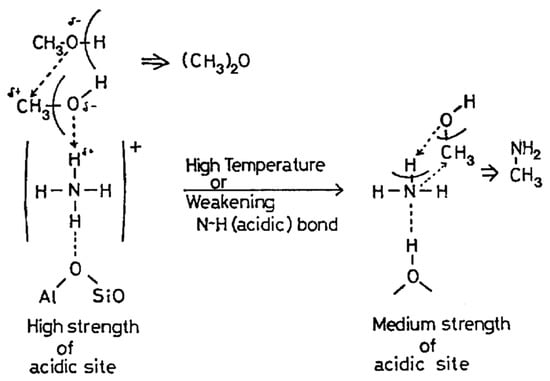
Figure 5.
A schematic explanation of the influences of the acid strength of the catalyst and the reaction temperature on the production of methylamines. Reprinted/adapted with permission from Ref. [8]. Copyright (1983) Elsevier.
Baiker et al. investigated methylamine synthesis using modulation excitation diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) combined with periodic isotopic perturbation using CD3OD (Figure 6) [37]. They found that Na-MOR adsorbed MMA less strongly than H-MOR, leading to enhanced MMA desorption and reduced formation of highly methylated products (DMA and TMA). These findings suggest that modifying the zeolite cation composition can tune the adsorption strength and improve selectivity.
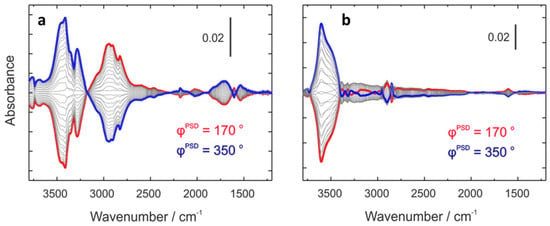
Figure 6.
Phase-domain IR spectra during (a) NH3 modulation (NH3 + MMA ↔ MMA) and (b) MeOH modulation (MeOH + MMA ↔ MMA) at 623 K. Reprinted/adapted with permission from Ref. [37]. Copyright (2013) ACS.
Schmal et al. introduced Cu2+ into H-ZSM-5 and found that the 3.7%Cu/H-ZSM-5 catalyst exhibited high MMA selectivity in methanol amination [38]. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and ammonia temperature-programmed desorption (NH3-TPD) revealed that Cu2+ introduction reduced Brønsted acid strength, preventing excessive methylation, and enhanced Lewis acid sites, facilitating amine product desorption and suppressing TMA formation.
Steam treatment and Binder effects
In addition to these modification strategies, Ashina reported in a patent that steam-treated H-MOR exhibited higher MMA and DMA selectivity (86.2%) [32]. However, the underlying mechanism for this improvement was not specified at the time.
Zhang et al. studied the effects of different binders on Na,H-ZSM-5 and found that using silica sol as a binder significantly increased DMA selectivity to 66.0% under harsh reaction conditions (WHSV = 6.64 h−1) [33]. This enhancement improves the industrial applicability of the catalyst.
2.4. Small-Pore Zeolite
2.4.1. Catalytic Performance
Small-pore zeolites exhibit higher selectivity for MMA and DMA than large- and medium-pore zeolites due to their naturally restricted pore sizes. This advantage allows them to achieve high selectivity without requiring complex modifications. Common small-pore zeolites used in methanol ammonification include SSZ-13 (CHA) [39], SAPO-34 (CHA) [40,41], SSZ-16 (AFX) [39], rho (RHO) [28,42,43], and ZK-5 (KFI) [44,45]. These materials demonstrate excellent shape selectivity, achieving high methanol conversion and superior DMA selectivity in single-pass reactions (Table 2). Among them, zeolites with RHO, KFI, and CHA topologies exhibit the best performance, with methanol conversion rates exceeding 80% and DMA selectivity approaching 60%.

Table 2.
Summary of different small-pore zeolites used for methanol conversion in the presence of ammonia. The table includes conversion (L), carbon-based selectivity (C), mole-based selectivity (M), and reaction conditions.
Table 2.
Summary of different small-pore zeolites used for methanol conversion in the presence of ammonia. The table includes conversion (L), carbon-based selectivity (C), mole-based selectivity (M), and reaction conditions.
| Sample | Top.a | Si/Al | TOS b /h | N/C c | T/WHSV d °C/h−1 | LMeOH e /% | CSelectivity f/C% | MSelectivity g/% | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMA | DMA | TMA | MMA | DMA | TMA | ||||||||
| H-RHO-8.7 | RHO | 9.3 | 10 | 1 | 400/4.3 | 95.9 | - | - | - | 68.2 | 11.1 | [43] | |
| H-RHO-7.3 | RHO | 7.5 | 10 | 1 | 400/4.3 | 97.0 | - | - | - | 71.6 | 13.3 | [43] | |
| H-KFI-5.4 | KFI | 5.4 | 10 | 2 | 350/0.813 | 95.2 | 13.0 | 59.2 | 27.7 | 24.1 | 54.8 | 17.1 | [45] |
| Na(22%)-KFI-5.4 | KFI | 5.4 | 10 | 2 | 350/0.813 | 95.0 | 13.8 | 59.8 | 26.4 | 26.0 | 56.4 | 16.6 | [45] |
| H-ECR-18 | PAU | 4.4 | 10 | 1 | 400/1.7 | ~59 | 55.7 | 29.5 | 14.8 | ~34 | ~9 | ~3 | [46] |
| D-20 | CHA | -h | 20 | 2 | 320/0.813 | 90.8 | 12.8 | 68.5 | 18.7 | 22.7 | 61.0 | 11.1 | [41] |
| H-ZK-5 | KFI | 3.2 | 3 | 2 | 350/0.813 | 63.4 | 21.9 | 68.2 | 9.9 | 33.7 | 52.5 | 5.1 | [44] |
| H-RHO | RHO | 4.1 | 10 | 1 | 400/4.3 | ~50 | - | - | - | ~90 | ~10 | [28] | |
| H-PST-29 | PWN | 5.0 | 10 | 1 | 400/4.3 | ~48 | - | - | - | ~83 | ~17 | [28] | |
| DNL-6 | RHO | -i | 2.4 | 2 | 260/0.813 | 49.7 | 32.8 | 56.4 | 10.8 | 42.1 | 36.2 | 4.6 | [42] |
| DNL-6 | RHO | -i | 2.4 | 2 | 300/0.813 | 88.3 | 16.8 | 59.1 | 24.1 | 26.1 | 45.9 | 12.5 | [42] |
| SAPO-34 | CHA | -j | 2.8 | 2 | 380/0.813 | 82.0 | 14.9 | 60.9 | 24.2 | 26.8 | 54.7 | 14.5 | [40] |
| H-SSZ-16 | AFX | 6.1 | 3 | 1 | 400/4.3 | 88.9 | 26.6 | 62.6 | 10.8 | 40.9 | 48.2 | 5.5 | [39] |
| H-SSZ-13 | CHA | 5.1 | 3 | 1 | 400/1.7 | 92.8 | 38.7 | 48.8 | 12.5 | 56.4 | 35.5 | 6.1 | [39] |
| H-levyne | LEV | 7.9 | 3 | 1 | 400/0.34 | 38.9 | 63.3 | 22.2 | 14.5 | 62.3 | 10.9 | 4.8 | [39] |
| H-rho | RHO | 3.9 | 3 | 1 | 400/4.3 | 78.6 | 31.3 | 61.0 | 7.7 | 44.6 | 43.4 | 3.7 | [39] |
| H-Cha | CHA | - | - | 1 | 400/0.93 | 98 | 16.0 | 51.0 | 33.0 | 29.0 | 46.1 | 19.9 | [34] |
| H-ZK-5,SDB | KFI | - | 10 | 1 | 350/0.4 | 95 | 13.9 | 77.8 | 8.3 | 20.2 | 56.5 | 4.0 | [47] |
a Top. = topology. b TOS = time of stream. c N/C = NH3/CH3OH. d WHSV = weight hourly space velocity. e LMeOH = MeOH conversion. f CSelectivity = . g MSelectivity = . h Elemental composition: Si0.216Al0.461P0.323. i Elemental composition: Si0.364Al0.414P0.222O2. j Elemental composition: Si0.189Al0.463P0.348.
2.4.2. Factors Affecting Product Selectivity in Small-Pore Zeolites
Effect of ion exchange
Yan et al. synthesized high-silica KFI zeolite (Si/Al = 5.4) using a dual-template system containing potassium cations and an 18-crown-6 ether complex [45]. The catalyst exhibited excellent performance in methanol ammonification, achieving 95.2% methanol conversion and 78.9% MMA + DMA selectivity at 350 °C and WHSVMeOH = 0.813 h−1. The study found that Na+ incorporation suppressed DME formation, a common by-product. Controlled Na+ introduction further enhanced MMA and DMA selectivity to 82.4%, while maintaining high methanol conversion.
Lercher and Kogelbauer investigated co-adsorption behavior on Na-ERI and H-ERI zeolites [27]. They found that methanol preferentially adsorbed on Na-ERI, while ammonia favored H-ERI. This selective adsorption suggests that Na+ ions inhibit excessive methylation by promoting methanol adsorption, thereby reducing TMA formation.
Effect of Si/Al ratios
As shown in Table 2, RHO zeolites with different Si/Al ratios (Si/Al = 9.3, 7.5, and 3.9) exhibit distinct selectivity under identical conditions (400 °C, WHSV= 4.3 h−1). Low-silica RHO shows higher MMA and DMA selectivity due to the abundance of weak acidic sites [39]. In contrast, high-silica RHO exhibits higher TMA selectivity and lower MMA and DMA selectivity. Weak acid sites in high-silica RHO account for less than 15% of the total acidic sites [43]. This suggests that high-Si/Al ratio zeolites possess stronger acidic sites that favor TMA formation. Furthermore, high-Si/Al ratio zeolites exhibit greater structural stability than low-Si/Al ratio zeolites due to their more stable framework.
Effect ofcrystal size
Schwarz et al. examined the impact of crystal size on ZK-5 (KFI) by modifying its crystal size with K+, Sr2+, and Cs+ ions [48]. Their findings revealed that smaller crystals exhibited higher catalytic activity but lower selectivity, leading to increased TMA formation; and larger crystals enhanced selectivity, reducing TMA formation to just 1%, though at the cost of lower methanol conversion.
Similarly, Yan et al. found that small-sized RHO crystals increased MMA and DMA yield by 10–16% compared to larger crystals in high-silica RHO zeolites [43]. These findings highlight the crucial role of crystal size in tuning product selectivity.
Effect of spatial positional resistance
Segawa et al. compared the catalytic performance of K-CHA and H-CHA zeolites [25]. When K+ ions fully blocked the CHA pores, only surface acid sites remained accessible, leading to low methanol conversion and a 1:1:1 methylamine distribution. However, replacing K+ with H+ reactivated the cha cage, enabling TMA molecules to undergo reverse reactions. This modification significantly improved MMA and DMA selectivity. H-CHA achieved 96% methanol conversion and 97% MMA and DMA selectivity at 340 °C and when weight/flow = 67 g h mol−1, demonstrating the importance of spatial constraints in product selectivity.
Callanan et al. found that hydrothermal treatment of RHO-type zeolites enhanced DMA selectivity through structural modifications [49]. During hydrothermal treatment, dealumination generated extra-framework aluminum (EFAl) species, leading to two key changes: redistribution of acid site strength, favoring medium-strength Brønsted acid sites; and increased steric constraints within micropores, which suppressed TMA formation by optimizing transition-state selectivity. These combined effects—adjusted acid site strength and enhanced spatial confinement—promoted DMA production via shape-selective catalysis.
3. Future Development Directions
The demand for MMA remains strong across various industries, including coatings, adhesives, new energies, and medical devices [50,51]. DMA, a specialty chemical intermediate, is widely used in pigments, pharmaceuticals, polymers, textiles, and coatings [52]. With industrialization accelerating in the Asia–Pacific region, DMA consumption is expected to rise steadily, with green chemistry and sustainable production becoming competitive priorities. TMA demand is also expected to remain stable, driven by its applications in environmentally friendly plasticizers, powder coatings, and high-performance insulation materials. To meet these evolving needs, MMA production must expand, DMA synthesis must transition to greener processes, and TMA output must be optimized.
3.1. Process Optimization
Traditional methylamine synthesis follows a balancing production process, such as the A-6 process (China) and the Nitto process (Japan)) [53]. These methods regulate MMA and TMA yields based on market demand. However, thermodynamic equilibrium constraints result in high recycle volumes, increased separation loads, and multiple reaction towers, leading to safety risks and high maintenance costs. These challenges are driving the shift toward a non-balancing production process.
The non-balancing approach disrupts the thermodynamic equilibrium distribution, allowing production to align more closely with market demand while improving energy efficiency and safety. Small-pore zeolites are the preferred catalysts for this method. However, achieving low cost, high activity, and high selectivity catalysts requires either improving existing small-pore zeolites or developing novel materials for methanol ammoniation reactions.
3.2. Small-Pore Zeolite Catalyst Development
Enhancing the activity, selectivity, and cost-effectiveness of small-pore zeolites is essential for advancing non-equilibrium methylamine production [54]. However, economic feasibility remains a primary challenge as small-pore zeolites are more expensive to produce than traditional catalysts. Reducing synthesis costs is critical for their widespread industrial adoption.
3.2.1. Optimization of Synthesis Methods
Lowering catalyst preparation costs is essential for commercial viability. Optimizing the synthesis process and utilizing inexpensive raw materials can significantly reduce production expenses [55,56,57], improving market competitiveness and facilitating green technology adoption [58,59,60,61].
Liu et al. developed a cost-effective SAPO-34 synthesis method using n-butylamine as an OSDA, achieving an 84% yield and significantly reducing the preparation cost [40]. The catalyst demonstrated excellent performance in methanol ammoniation, with 82% methanol conversion and 81.5% selectivity for MMA and DMA at 380 °C with WHSVMeOH = 0.813 h−1. In 2023, Liu et al. further reduced costs by using spent MTO catalyst as a raw material and diethylamine as the OSDA for SAPO-34 synthesis [41]. After 20 h at 320 °C and WHSVMeOH = 0.813 h−1, the catalyst maintained 90.8% methanol conversion and 83.7% selectivity for MMA and DMA, demonstrating excellent stability and industrial potential.
Yan et al. developed an OSDA-free method for ZK-5 synthesis using SAPO-34 as a seed. The presence of Si(3Al), P-containing species, and morpholine released from the seed accelerated crystallization (Figure 7) [44]. The resulting ZK-5 catalyst achieved 63.4% methanol conversion and 86.2% selectivity for MMA and DMA at 350 °C and WHSVMeOH = 0.813 h−1, with minimal TMA formation (5.1%), making it a cost-effective alternative.
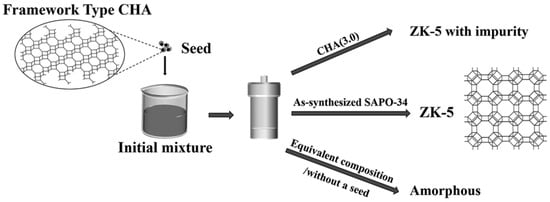
Figure 7.
Crystallization behavior of the initial mixtures without a seed, with a low-silica CHA (CHA (3.0)) seed, and with the equivalent chemicals of the as-synthesized SAPO-34. Reprinted/adapted with permission from Ref. [44]. Copyright (2022) RSC.
3.2.2. Enhanced Catalyst Lifespan
Extending the catalyst lifespan is crucial for improving industrial feasibility. A longer catalyst life reduces replacement frequency, lowers operational costs, minimizes raw material consumption, and decreases waste generation [62,63]. These benefits collectively enhance overall plant efficiency and profitability [64].
Yan et al. synthesized a high-silica RHO zeolite (Si/Al = 8.7) with reduced OSDA usage, employing SSZ-13 as a crystallization promoter [43]. Under accelerated aging conditions, the catalyst exhibited 93.0% methanol conversion (Figure 8a) and nearly 90.0% MMA and DMA yield (Figure 8b) at 350 °C with LHSV = 11.7 h−1, maintaining performance for 6 h without significant degradation.
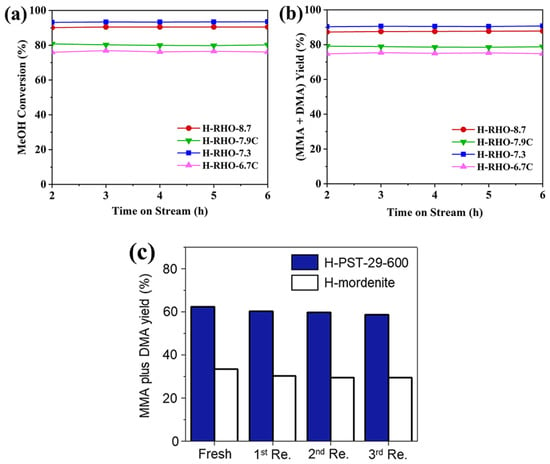
Figure 8.
(a) MeOH conversion and (b) MMA and DMA yield during the selective synthesis of methylamine over high-silica H-RHO zeolites at 350 °C, 2 MPa, N/C = 1.9, and LHSV(MeOH+ammonia) = 11.7 h−1 (GHSV(MeOH+ammonia) = 7488 h−1). Reprinted/adapted with permission from Ref. [43]. Copyright (2024) RSC. (c) Yields of MMA and DMA at 2 h on stream in methylamine synthesis over H-PST-29-600 (navy) and H-mordenite (white) in four successive runs at 400 °C, 4.3 h−1 WHSVMeOH, and 10.1 Kpa NH3 and MeOH for 50 h. Both catalysts were regenerated by calcination at 550 °C in the air for 8 h. Reprinted/adapted with permission from Ref. [28]. Copyright (2020) Elsevier.
Hong et al. compared first-generation (rho, RHO) and second-generation (H-PST-29, PWN) isoreticular zeolites for selective methylamine synthesis at 400 °C and WHSVMeOH = 4.3 h−1 [28]. Both H-rho and H-PST-29 exhibited 93.0% methanol conversion, with an MMA and DMA selectivity of 85.4% and 75.0%, respectively. Circularity is one of the most important indicators for evaluating catalyst economics. After hydrothermal treatment at 600 °C, H-PST-29-600 maintained stable MMA and DMA yields over three regeneration cycles (Figure 8c). The performance was comparable to traditional H-MOR while retaining high MMA and DMA selectivity. The high stability of PST-29-600 is attributed to the weakening of strong acidic sites and the formation of intergranular mesopores through high-temperature treatment. This reduces coke formation and increases gas diffusion capacity, making it a promising candidate for long-lifespan catalysts in methanol ammoniation.
Liu et al. compared the performance of SAPO-34 synthesized using diethylamine (DEA) and tetraethylammonium hydroxide (TEAOH) [41]. SAPO-34-D, synthesized with DEA, exhibited excellent catalytic activity and high selectivity for MMA and DMA in methanol amination. In contrast, SAPO-34-T, synthesized with TEAOH, showed significantly lower MMA and DMA selectivity. However, at 450 °C and WHSV = 3.65 h−1, SAPO-34-T demonstrated twice the lifespan of SAPO-34-D. This suggests that the same topology, when synthesized with different OSDAs, can exhibit substantial differences in catalysis performance. Enhancing catalyst lifespan may justify a moderate increase in OSDA cost.
3.2.3. Increasing Single-Pass Selectivity of the Desired Product
Enhancing single-pass selectivity improves the reaction efficiency, reduces by-product formation, and minimizes separation and purification costs [65,66]. Higher selectivity optimizes raw material utilization, lowers waste production, and improves the overall economic and environmental sustainability of industrial processes [59,67]. The factors influencing MMA and DMA selectivity in small-pore zeolites have been discussed in Section 2.4.2 and will not be repeated here.
4. Conclusions
This review provides a comprehensive analysis of recent advancements in zeolite materials for selective methylamine synthesis, including reaction mechanisms, factors affecting product selectivity, and catalyst modification strategies. The primary challenge hindering the commercialization of small-pore zeolites is their high production cost. The following three key approaches have been proposed to address this issue: reducing synthesis costs, extending catalyst lifespan, and improving single-pass product selectivity. Combining these strategies could significantly reduce the industrialization costs of small-pore zeolites and accelerate the transition from balancing to non-balancing production processes.
Although small-pore zeolites have demonstrated excellent catalytic performance, they still fall short of meeting industrial targets. The desired MMA and DMA yield exceeds 80% [3], while the highest single-pass yield achieved under industrial conditions is only 79.2%, below expectations. Developing green synthesis methods, such as template-free or energy-efficient processes, remains a key challenge. Additionally, further research is needed to explore the potential of novel small-pore zeolites, including SSZ-39 (AEI) and SSZ-98 (ERI), for methanol ammoniation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.J. and W.Y.; validation, Y.Y. and J.P.; formal analysis, J.-Y.L.; investigation, K.J.; data curation, K.J.; writing—original draft preparation, K.J.; writing—review and editing, W.Y.; visualization, K.J. and W.Y.; supervision, W.Y.; project administration, W.Y.; funding acquisition, W.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFA1500401), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22288101), and the ‘111 Center’ (B17020).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Corbin, D.R.; Schwarz, S.; Sonnichsen, G.C. Methylamines synthesis: A review. Catal. Today 1997, 37, 71–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, K.; Tachibana, H. Highly Selective Methylamine Synthesis over Modified Mordenite Catalysts. J. Catal. 1991, 131, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, D.G. Working with Zeolites: A Reflection on Catalyst Development in Industry. Top. Catal. 2021, 64, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, W.D.; Howald, A.M. Methyl amines from methyl alcohol and ammonium chloride. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1920, 42, 2663–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.B.; Reid, E.E. The Catalytic Alkylation of Ammonia. J. Phys. Chem. 1924, 28, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.L.; Elderfield, R.C. The catalytic preparation of methylamine from methyl alcohol and ammonia1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1928, 50, 1786–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briner, E.; Gandillon, J. Recherches sur l’obtention des méthylamines par déshydratation catalytique du système ammoniac-alcool méthylique. Helv. Chim. Acta 1931, 14, 1283–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, I.; Yasutake, A.; Fujitsu, H.; Takeshita, K. Selective synthesis of dimethylamine (DMA) from methanol and ammonia over zeolites. J. Catal. 1983, 82, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetting, F.; Dingerdissen, U. Production of methylamines over ZK-5 zeolite treated with tetramethoxysilane. Chem. Eng. Techno. 1992, 15, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.T.; Zhang, L.; Kobe, J.M.; Yi, C.; Dumesic, J.A. Methylamine synthesis over solid acid catalysts: Reaction kinetic measurements. J. Mol. Catal. 1994, 93, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, K.S. Industrial processes for manufacturing amines. Appl. Catal. A 2001, 221, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerlocher, C.; McCusker, L.B.; Olson, D.H. Atlas of Zeolite Framework Types; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 140–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argauer, R.J.; Landolt, G.R. Crystalline Zeolite zsm-5 and Method of Preparing the Same. U.S. Patent 3702886, 14 November 1972. Available online: https://image-ppubs.uspto.gov/dirsearch-public/print/downloadPdf/3702886 (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Meisel, S.L. Gasoline from methanol in one step. Chem. Technol. Chemtech 1976, 6, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.D.; Silvestri, A.J. The conversion of methanol and other O-compounds to hydrocarbons over zeolite catalysts. J. Catal. 1977, 47, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frilette, V.J.; Weisz, P.B.; Golden, R.L. Catalysis by crystalline aluminosilicates I. Cracking of hydrocarbon types over sodium and calcium “X” zeolites. J. Catal. 1962, 1, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisz, P.B.; Frilette, V.J.; Maatman, R.W.; Mower, E.B. Catalysis by crystalline aluminosilicates II. Molecular-shape selective reactions. J. Catal. 1962, 1, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigert, F.J. Selective synthesis and equilibration of methylamines on sodium mordenite. J. Catal. 1987, 103, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Pang, W.; Yu, J.; Huo, Q.; Chen, J. Chemistry of Zeolites and Related Porous Materials: Synthesis and Structure; John Wiley & Sons (Asia) Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2007; Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/book/10.1002/9780470822371 (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Yan, W.; Yu, J. Our journey in zeolite science. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2023, 358, 112368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, K.; Tachibana, H.; Holderich, W.; Prins, R.; Howe, R.F.; Haaq, W.V. Shape-Selective Reactions for Methylamine Synthesis from Methanol and Ammonia. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1993, 75, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, K.; Ilao, M.C. Methanol amination over small-pore zeolite catalysts. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1997, 105, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Bu, L.; Huang, Y.; Guo, N.; Qu, L.; Sang, J.; Li, Y.; Su, X.; et al. Organic-free, Ultrafast Synthesis of K-CHA Nano-aggregates with Various Morphologies and Their Adsorption Performances. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2024, 40, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gründling, C.; Eder-Mirth, G.; Lercher, J.A. Surface species in the direct amination of methanol over Brønsted acidic mordenite catalysts. Res. Chem. Intermed. 1997, 23, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilao, M.C.; Yamamoto, H.; Segawa, K. Shape-Selective Methylamine Synthesis over Small-Pore Zeolite Catalysts. J. Catal. 1996, 161, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvidsson, A.A.; Plessow, P.N.; Studt, F.; Hellman, A. Influence of Acidity on the Methanol-to-DME Reaction in Zeotypes: A First Principles-Based Microkinetic Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 14658–14663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogelbauer, A.; Lercher, J.A. Surface chemistry of methanol and ammonia on HNaK erionites. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1992, 88, 2283–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, K.; Shin, J.; Hong, S.B. A comparative study of methylamines synthesis over zeolites H-rho and H-PST-29. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 300, 110150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mores, D.; Kornatowski, J.; Olsbye, U.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Coke formation during the methanol-to-olefin conversion: In Situ microspectroscopy on individual H-ZSM-5 crystals with different Brønsted acidity. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 2874–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisnet, M.; Costa, L.; Ribeiro, F.R. Prevention of zeolite deactivation by coking. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 305, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundling, C.; EderMirth, G.; Lercher, J.A. Selectivity enhancement in methylamine synthesis via postsynthesis modification of Bronsted acidic mordenite—An infrared spectroscopic and kinetic study on the reaction mechanism. J. Catal. 1996, 160, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashina, Y.; Fujita, T.; Fakatsu, M.; Yagi, J. Process for Producing Dimethylamine in Preference to Mono- and Trimethylamines by Gas Phase Catalytic Reaction of Ammonia with Methanol. U.S. Patent 4582936, 15 April 1986. Available online: https://image-ppubs.uspto.gov/dirsearch-public/print/downloadPdf/4582936 (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ke, Y. Preparation of Moulded Zeolite Catalysts for the Selective Synthesis of Dimethylamine. CN Patent 1095645, 30 November 1994. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=Zw74qSZOFghc7uYpZoHdNRAEc-1q1Uo_JD7utOoXxhs52jhWnSgCTNlQms9INFCBcYGsHUYbakJMscXb95p5c5zFcuCPQXwlYRIxtUTB9nPHTroY48vPu3o_byG8r9oXdR91MQJH4lSWMrWPKbEaiXFH8XjEuR2I&uniplatform=NZKPT (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Abrams, L.; Shannon, R.D.; Sonnichsen, G.C. Selected Chabazite Zeolites as Catalysts for Conversion of Methanol and Ammonia to Diemethylamine. U.S. Patent 4737592, 12 April 1988. Available online: https://image-ppubs.uspto.gov/dirsearch-public/print/downloadPdf/4737592 (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Weigert, F.J. Preparation of Monomethylamine. U.S. Patent 4254061, 3 March 1981. Available online: https://image-ppubs.uspto.gov/dirsearch-public/print/downloadPdf/4254061 (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Herrmann, C.; Fetting, F.; Plog, C. Amine production from methanol and ammonia over ZSM-5 and T-zeolite catalysts. Appl. Catal. 1988, 39, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, N.; Meemken, F.; Hungerbühler, K.; Baiker, A. Selectivity-Controlling Factors in Catalytic Methanol Amination Studied by Isotopically Modulated Excitation IR Spectroscopy. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.H.O.; da Silva, V.T.; Schmal, M. The effect of copper loading on the acidity of Cu/HZSM-5 catalysts: IR of ammonia and methanol for methylamines synthesis. Appl. Catal. A 2005, 294, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.-Y.; Shin, C.-H.; Jung, H.J.; Hong, S.B. Catalytic evaluation of small-pore molecular sieves with different framework topologies for the synthesis of methylamines. Appl. Catal. A 2006, 305, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wu, P.; Xiang, X.; Yang, M.; Wang, Q.; Tian, P.; Liu, Z. SAPO-34 synthesized with n-butylamine as a template and its catalytic application in the methanol amination reaction. Chin. J. Catal. 2017, 38, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Yang, M.; Fan, D.; Zhu, D.; Tian, P.; Liu, Z. Synthesis of SAPO-34 by utilizing spent industrial MTO catalyst and their catalytic applications. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023, 21, 100302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Yang, M.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, S.; Gao, M.; Xu, S.; Tian, P.; Liu, Z. Silicoaluminophosphate molecular sieve DNL-6: Synthesis with a novel template, N′,N′-dimethylethylenediamine, and its catalytic application. Chin. J. Catal. 2018, 39, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Jin, K.; Liu, S.; Li, Q.; Hou, P.; Liu, S.; Song, Q.; Wang, Z.; Tian, P.; et al. Fluoride-free synthesis of high-silica RHO zeolite for the highly selective synthesis of methylamine. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2024, 11, 5473–5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Han, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Tian, P.; Zhou, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yan, W. Exclusive SAPO-seeded synthesis of ZK-5 zeolite for selective synthesis of methylamines. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 5766–5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Han, J.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Tian, P.; Yan, W. High-silica KFI zeolite: Highly efficient synthesis and catalysis in methanol amination reaction. Chem. Synth. 2024, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.H.; Shu, D.; Hong, S.B. Synthesis of stable ECR-18 zeolite and its catalytic properties in methanol amination. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2024, 364, 112875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D.; Keane, M.; Abrams, L.; Staley, R.H.; Gier, T.E.; Sonnichsen, G.C. Selective synthesis of dimethylamine over small-pore zeolites: III. H-ZK-5. J. Catal. 1989, 115, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Corbin, D.R.; Sonnichsen, G.C. The effect of crystal size on the methylamines synthesis performance of ZK-5 zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1998, 22, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callanan, L.H.; van Steen, E.; O’Connor, C.T. Improved selectivity to lower substituted methylamines using hydrothermally treated zeolite Rho. Catal. Today 1999, 49, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinderslev, J.B.; Skov, L.N.; Andreasen, J.G.; Ghorwal, S.; Skibsted, J.; Jensen, T.R. Methylamine Lithium Borohydride as Electrolyte for All-Solid-State Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202203484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Kong, W.; Liu, Y.; Ren, W.; Wang, H. Redox Mediator as Highly Efficient Charge Storage Electrode Additive for All-Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 15, 2404046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bras, J.; Muzart, J. Recent Uses of N,N-Dimethylformamide and N,N-Dimethylacetamide as Reagents. Molecules 2018, 23, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiro, A.; Takeyuki, F.; Michio, F.; Junsuke, Y. Process for Producing Dimethylamine. EP 0125616, 15 November 1988. Available online: https://register.epo.org/application?number=EP84105217&tab=main (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Dusselier, M.; Davis, M.E. Small-Pore Zeolites: Synthesis and Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 5265–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Su, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.-N.; Xu, J.; Pan, Q.; Yan, W. Mild activation of spent fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts for the pilot synthesis of zeolite a with commercial quality and excellent Co2+ removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.Y.; Chen, H.W.; Wang, S.J.; Pan, H.N.; Yang, Z.; Su, H.P.; Zhang, H.Y.; Pan, J.Y.; Zhang, J.N.; Li, L.B.; et al. Synthesis of customized zeolite X with outstanding CO2 selectivity over CH4 and N2 using facile activated spent fluid catalytic cracking catalysts. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Yang, W. Impact of Various Silicon Sources on the Synthesis of Mordenite and Differences in the Carbonylation Reaction of Dimethyl Ether. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2025, 41, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Wu, Z.J.; Yip, A.C.K. Advances in the Green Synthesis of Microporous and Hierarchical Zeolites: A Short Review. Catalysts 2019, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Ali, S.; Zaman, W. Recent Advancements in Catalysts for Petroleum Refining. Catalysts 2024, 14, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Tang, S.W.; Yin, S.H.; Li, S.W. Research progress on green synthesis of various high-purity zeolites from natural material-kaolin. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 306, 127248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, F.-S. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Wastes. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2024, 40, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Sun, F.; Qu, Z.B.; Wang, J.J.; Xu, Y.H.; Gao, J.H.; Zhao, G.B. A review of porous catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: Insights into the role of mass transfer within nanopores. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 359, 130678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, J.L.; Li, L.; Yu, J.H. Zeolite-based materials for greenhouse gas capture and conversion. Sci. China Chem. 2024, 67, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaji, S.; Hussain, I.; Malaibari, Z.; Hossain, M.M.; Qureshi, Z.S.; Ahmed, S. Catalytic Cracking of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) to Light Olefins Using Zeolite-based Materials: Recent Advances, Trends, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Chem. Rec. 2024, 24, e202400110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Alshafei, F.H.; Zones, S.I.; Davis, M.E. Cage-Defining Ring: A Molecular Sieve Structural Indicator for Light Olefin Product Distribution from the Methanol-to-Olefins Reaction. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 6012–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soheili, S.; Nakhaei Pour, A. Controlling product selectivity and catalyst lifetime by altering acid strength, cavity size of SAPO, and diffusion rate of methanol in the MTO reaction: DFT and MD calculations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 5226–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenasheva, M.V.; Gorbunov, D.N. Recent Progress and Strategies on the Design of Zeolite-Based Catalysts for Hydroformylation of Olefins. Catalysts 2024, 14, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).