Abstract
In the study presented herein, a series of TiO2-supported Ru catalysts were prepared through over-impregnation with different amounts of H2O2 and applied to the catalytic combustion of dichloromethane (DCM). The experimental results show that the optimal (1 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst sample yields 90% DCM conversion at 301 °C, which is 40 °C lower than the temperature required by the (0 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst. This good activity is related to its high number of acid sites (especially Brønsted acid sites), an appropriate amount of uniformly dispersed RuO2 particles, and strong interaction between RuO2 and the TiO2 support. In addition, excessive H2O2 leads to the growth and phase segregation of RuO2, which weakens the interaction between RuO2 and the TiO2 support and decreases catalytic activity. Moreover, H2O2 addition also contributes to the stability of catalysts, which possibly results from the re-dispersion of RuO2 on the TiO2 support during the reaction.
1. Introduction
Chlorinated volatile organic compounds (CVOCs) are widely used in industry as solvents and degreasing and cleaning agents; however, they pose considerable harm to human health and the environment [1,2,3]. Catalytic oxidation is considered an advantageous technique to eliminate CVOCs due to its high conversion rate, low ignition temperature, low operating energy consumption, and limited number of by-products [4,5].
The catalysts used for catalytic oxidation mainly consist of noble metal catalysts (e.g., Pt, Pd, and Ru) [6,7,8] and transition metal oxides (e.g., CeO2-ZrO2, Cr2O3, and MnO2) [9,10,11,12]. Supported Pt or Pd catalysts demonstrate relatively higher catalytic activity than transition metal oxides; however, they are expensive and sensitive to high temperatures and chlorine poisoning. Transition metal oxide catalysts are relatively inexpensive and have good resistance to chlorine poisoning; however, their low catalytic activity and poor selectivity limit their wider application [13]. In contrast, supported Ru catalysts have been demonstrated to be highly active and stable components for CVOCs oxidation due to their excellent catalytic dechlorination activity via the Deacon pathway [14].
TiO2, ZnO [15], CeO2 [16,17], WO3 [18], and LaMnO3 [19] are often employed as catalyst supports. Among these, TiO2 is one of the classical acid catalysts, which is considered an important factor for the degradation of short-chain CVOCs (e.g., DCM) due to its high surface area, large number of pores for the dispersal of active particles, and remarkable interaction between group 8 noble metals [6,20]. At present, researchers mainly focus their attention on the effect of catalyst support behavior (e.g., the hierarchical structure of the support [13] and chemical modification of the support [21]) on the performance of catalysts. However, the behavior of active species [22], such as the valence and dispersion as reported in several works [23,24,25], also plays an important role in catalytic activity [26]. Ru species are considered as the active sites in the catalytic combustion of CVOCs [27], and H2O2 is a green and moderate oxidant used to change the valence of Ru, which is also beneficial to the catalyst’s surface dispersion [28]. In the following paper, we propose a simple and feasible method to oxidize Ru species through the addition of different amounts of H2O2, aiming to prepare catalysts with varying behavior of Ru species. Moreover, the structural and chemical properties of these catalysts were characterized using XRD, BET, TEM, XPS, H2-TPR, NH3-TPD, and pyridine-IR methods to determine the effects of the morphology, acidity, and valence of Ru species and interaction between RuO2 species and TiO2 on catalytic activities.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalyst Analysis
Figure 1 presents the XRD diffraction patterns of the (0, 1, and 3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalysts, where 2θ = 25.3°, 37.8°, 48.1°, 53.9°, 55.1°, and 62.7° represent the diffraction peak of the typical anatase phases (JCPDS No. 21-1272) and 2θ = 27.9° and 35.1° are assigned to RuO2 (JCPDS No. 40-1290). All samples show almost identical XRD diffraction patterns, indicating that all catalysts maintain the initial support TiO2 crystal structure (the raw material P25, mostly anatase TiO2) after Ru impregnation and H2O2 treatment. The Ru content of (0, 1, and 3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalysts measured by ICP-OES are 0.28 wt%, 0.26 wt%, and 0.26 wt% (see Table 1), respectively, which are close to the theoretical value. The specific surface area of P25 is 58.5 m2·g−1, and all three catalysts exhibit a slight decrease. Regardless of whether H2O2 is added, all samples have extremely poor XRD peaks for RuO2, owing to the low loading amount of Ru. A further analysis revealed that the RuO2 crystallite sizes of the (0, 1, and 3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalysts are 6.4, 7.0, and 8.5 nm (see Table 1), respectively, as calculated using Scherrer’s equation (see Table S1). Using the above results, it was possible to prove that H2O2 treatment promotes the growth of RuO2 crystallite, especially the (3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst when the amount of H2O2 present is excessive.
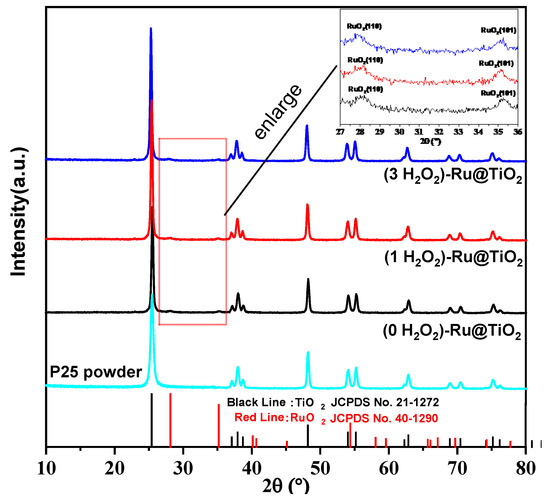
Figure 1.
X-ray diffraction patterns of the various samples.

Table 1.
Different properties of P25 and catalysts.
The HRTEM images of different samples are provided in Figure 2. The morphologies of the (0 and 1 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalysts are almost identical, as shown in Figure 2a–d, where their mainly exposed lattice fringe at around 0.35 nm corresponds to anatase (1 0 1) facets and at 0.24 nm corresponds to anatase (0 0 4) facets [29]. Moreover, the EDS mapping images illustrate that the Ru species of the (1 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst disperse more uniformly than those of the (0 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst (Figure S1a,b), which might result from the formation of RuO2 nanoparticles during oxidation with H2O2.
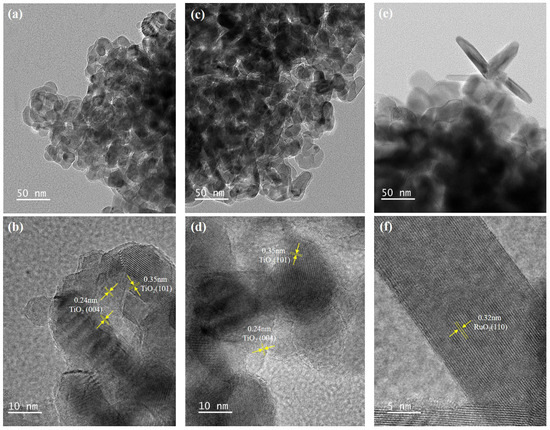
Figure 2.
HRTEM mapping images of the 0 (a,b), 1 (c,d), and 3 (e,f) H2O2-Ru@TiO2 catalysts.
With the increased addition of excess H2O2, a new structure of RuO2 nanorods emerges in the (3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst, where their mainly exposed lattice fringe at around 0.32 nm corresponds to RuO2 (1 1 0) facets [30] (Figure 2e,f). The EDS mapping images (Figure S1c) indicate that the nanorods were enriched in Ru and O species but not Ti species, which also proves that the nanorods comprised RuO2. Furthermore, the XRD analysis results also proved the growth of RuO2 nanorods, and this growth was found to eventually cause the phase segregation of RuO2 at higher H2O2 concentrations.
The XPS results for Ti 2p provided in Figure 3a show two main peaks centered at 458.5–458.8 eV and 464.6–465.0 eV, which could be ascribed to the typical Ti4+ oxidation state in a tetragonal structure [21]. It can be clearly seen that the binding energy shifts to a lower energy level after H2O2 treatment for the (1 and 3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 samples compared with the (0 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst. This binding energy shift indicates the chemical attachment of the Ru species to the TiO2 surface, probably resulting in a changed electron atmosphere and stronger interaction with the support following H2O2 treatment [31,32,33].
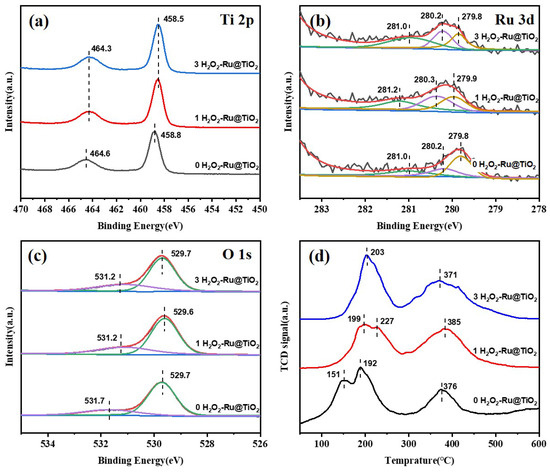
Figure 3.
XPS spectra of Ti 2p (a), Ru 3d (b), O 1s (c), and H2-TPR profiles (d) of the various samples.
Figure 3b shows the Ru 3d5/2 XPS profiles of the studied catalysts. The peaks centered at 279.8 and 279.9 eV can be attributed to Ru0 [21]. The second peak at around 208.3 eV is assigned to RuOx species. The third peak centered at 281.0 and 281.2 eV is ascribed to RuO2 [34]. All species of Ru exist in each catalyst; however, the amount of RuO2 in the (0 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst is significantly lower than that in the (1 and 3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalysts (see Table 2), which indicates that H2O2 treatment could oxidize Ru3+ species to a higher valence state of RuO2 and prevent the generation of excess Ru0 following heating. Furthermore, a greater amount of RuO2 was observed in the (3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst compared to the (1 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst, which also proves the growth and phase segregation of RuO2 in accordance with the XRD and TEM results.

Table 2.
The content of different Ru species from fresh and spent samples analyzed by XPS.
As the O1s XPS results displayed in Figure 3c show, the peaks centered at around 529.6 eV can be assigned to oxygen ions in the crystal lattice (O2−), and the peaks presented at 531.2 and 531.7 eV can be ascribed to adsorbed oxygen species (O−/O22−) [35]. The amount of adsorbed oxygen species for the (1 and 3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalysts is higher than that of the (0 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst (see Table S2), suggesting that the H2O2 treatment of RuO2 increases the adsorption of hydroxyl groups on the surface of TiO2, which might create abundant active oxygen species to improve catalytic activity during the progression of the oxidation reaction [36,37].
The H2-TPR profiles of the catalysts are shown in Figure 3d. H2-TPR profiles are mainly used to obtain the interaction information between metal oxides with carriers and to analyze the content of different species of metal oxides. The reduction peak between 150–250 °C and 300–450 °C can be attributed to the reduction in RuO2 species interacting with the TiO2 support weakly and strongly, respectively [38]. The reduction temperature increased for the (1 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst compared to the (0 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 sample, implying that the interaction between RuO2 species and the TiO2 support increased, which corresponds to the XPS analysis results for Ti 2p. However, the reduction temperature decreased slightly for the (3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst compared to the (1 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 sample, indicating that interaction between RuO2 species and the TiO2 support decreased. It can be inferred that the phase segregation of RuO2 nanorods, as shown in the TEM images, results in weakened interaction.
The total acid intensity of the catalysts was evaluated using NH3-TPD (see Figure 4a). The peaks at 120–300 °C and 300–400 °C are attributed to NH3 desorption from weak and moderate acidic sites, respectively. The NH3 desorption peaks of the (0 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst are observed at 188 °C and 351 °C, which are assigned to weak and moderate acidic sites, respectively. With the increased addition of H2O2, the weak acidic site disappears and the moderate acidic site shifts to a higher temperature. The peaks of the (1 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 and (3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalysts were found to shift to 366 °C and 375 °C, respectively, suggesting that the catalysts have an increased number of moderate acidic sites.
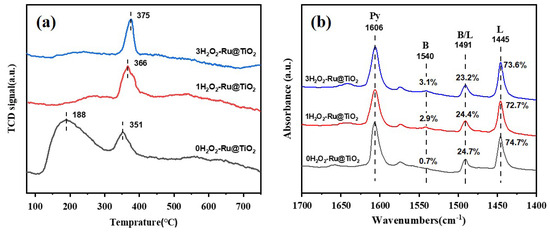
Figure 4.
NH3-TPD profiles (a) and pyridine-IR (b) of various samples.
The pyridine-IR spectra of catalysts with different H2O2 additions are used to distinguish Brønsted and Lewis acids (see Figure 4b). The peaks at 1606 cm−1 are ascribed to the physical adsorption of pyridine. The bands at 1445 and 1540 cm−1 are assigned to Lewis and Brønsted acid sites [21], respectively, and the information on the percentage of different acid sites on the catalysts is also presented in Figure 4b. It can be seen that all catalysts contain mostly Lewis acid sites and generate more Brønsted acid sites with H2O2 treatment.
2.2. Catalytic Activity and Discussion
The activities of the different samples are presented in Figure 5. The activities of pure TiO2 and pure RuO2 samples were carried out separately, using an identical amount of TiO2 or RuO2 as they are present in the catalyst. Pure TiO2 showed extremely poor activity due to its small active sites. The activity of the pure RuO2 sample increased due to its high catalytic dechlorination activity via the Deacon pathway, reaching 90% conversion (T90) at 413 °C. When TiO2 and RuO2 were physically mixed, the activity further improved with a T90 value of 369 °C. However, the activity of this mixed sample is lower than that of the (0, 1, and 3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalysts, although they have identical amounts of TiO2 and RuO2. Comparing the activities of the prepared catalysts, the (0 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst showed a lower activity with a T90 value of 344 °C than that of the (1 and 3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalysts which had T90 values of 301 °C and 317 °C, respectively.
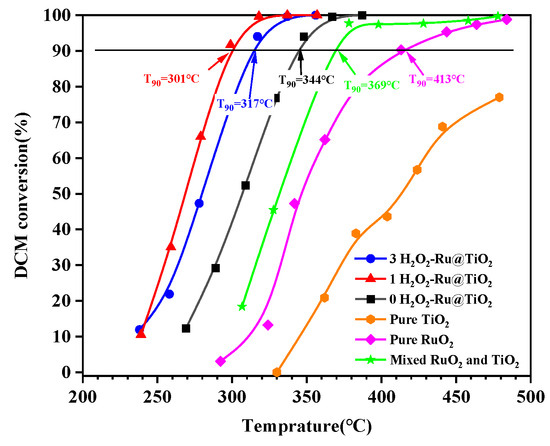
Figure 5.
DCM conversion curves over various samples.
It is widely accepted that there exist two important steps during the CVOCs catalytic combustion process [39,40]: (a) the adsorption, dissociation, and oxidation of the C−Cl/C-C bond at acidic sites and (b) the desorption of products such as CO2, H2O, HCl, and Cl2. The chlorine species that are dissociatively adsorbed on the active sites can be removed in the form of Cl2 via the Deacon pathway catalyzed by RuO2 species rather than Ru0 species [38,41]. The H2O2 treatment catalysts, the (1 and 3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalysts, contain more RuO2 species than the (0 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst, as shown in the XPS results, which contribute to the increasing the catalytic activity.
The EDS mapping images illustrate that the Ru species of the (1 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst were dispersed more uniformly than those of the (0 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst and strengthened the interaction between RuO2 species and the TiO2 support analyzed using their H2-TPR profiles. It can be inferred that the increased interaction can also promote the catalytic combustion activity of DCM.
The NH3-TPD results prove that the increased acidity of (1 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst can facilitate the adsorption and dissociation of CVOCs whilst simultaneously increasing catalytic activity, as reported [42,43]. Furthermore, the pyridine-IR characterization results illustrate that three catalysts contain a similar percentage of Lewis acid sites, where it is generally believed that the C−Cl bonds cleave and the intermediates are eventually oxidized to CO2 [44]. However, the (1 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst generates a higher percentage of Brønsted acid sites than the (0 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst, with this process providing sufficient H protons to react with Cl, forming HCl at low temperatures and facilitating Cl desorption [44,45]. The increased number of Brønsted acid sites is conducive to accelerating the catalytic cycle whilst simultaneously increasing catalytic activity.
Moreover, the activity of the (3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst with greater H2O2 addition was lower than that of the (1 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst. It can be inferred that the phase segregation of RuO2 nanorods under excess H2O2 conditions might weaken the interaction between RuO2 and the TiO2 support and decrease the catalytic combustion activity of DCM.
2.3. Stability Tests
The stability tests of the (0, 1, and 3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalysts were carried out and the results are presented in Figure 6. The catalysts were evaluated at different temperatures due to the difference in catalytic activities, which makes certain that each catalyst degrades roughly the same amount of DCM. It can be found that the DCM conversion over (1 and 3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalysts only decreased by 0.2–0.3% and 0.1–0.2% after a 150 h reaction at 320 °C and 330 °C, respectively. By contrast, the (0 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst decreased 0.6–0.7% after a 150 h reaction at 360 °C, showing more obvious deactivation. These results implied that the addition of H2O2 contributes to the catalytic stability, which may be ascribed to the uniformly dispersed RuO2 and strong interaction between RuO2 and the TiO2 support.
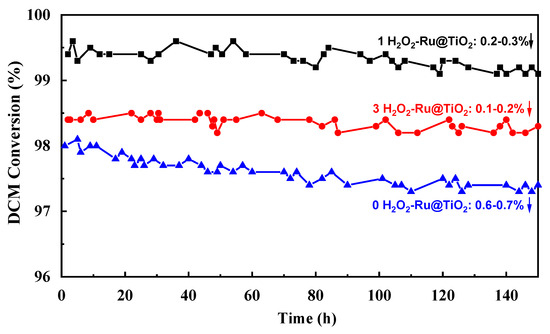
Figure 6.
The stability test for DCM catalytic combustion over various samples.
The spent catalysts (after 150 h reaction) are analyzed by XRD, as shown in Figure S2. The XRD patterns of spent catalysts are similar to the fresh catalysts, implying that the anatase TiO2 cannot transfer to the rutile phase during the stability test because the reaction temperature is lower than its transition temperature.
The spent catalysts are characterized by XPS, as shown in Figure 7. The binding energies of Ti 2p change by only a little, as shown in Figure 7a, which indicates that the TiO2 support is stable in its reaction. Figure 7b shows the O1s XPS profiles of the spent catalysts; the changes in peaks centered at 529.6 eV (assigned to oxygen ions in the crystal lattice) are negligible. The peak assigned to adsorbed oxygen species for the (0 H2O2)-Ru@ TiO2 catalyst shifts to the lower binding energy form 531.7 eV to 531.1 eV, which might be related to its greater decrease during the stability test. Furthermore, the amount of adsorbed oxygen species (generally considered as surface active oxygen species) for all spent catalysts decreased compared to fresh catalysts (see Table S2), which is probably associated with the decrease in DCM conversion.
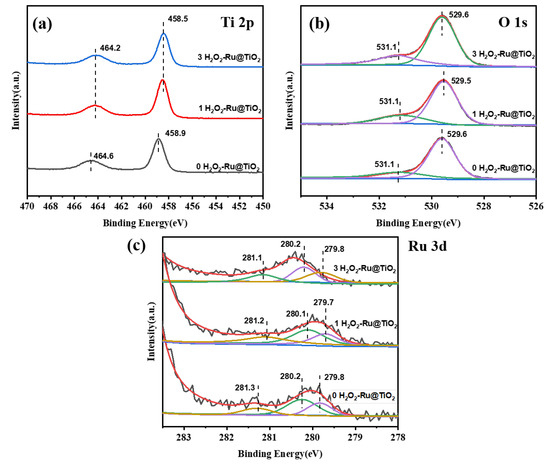
Figure 7.
XPS spectra of Ti 2p (a), O 1s (b), and Ru 3d (c) of the spent samples.
As the Ru 3d XPS results displayed in Figure 7c show, the binding energies of all species of Ru almost remain unchanged. The amount of Ru0 and RuO2 in the 0 H2O2-Ru@TiO2 catalyst shows a greater increase and decrease, respectively. However, this change is not obvious for the (1 and 3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalysts (see Table 2). It is inferred that a part of RuO2 is reduced to Ru0 during the stability test, which might cause a decrease in DCM conversion. Notably, the decrease in the amount of RuO2 as well as the DCM conversion is at a minimum in the (3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst during stability tests, which possibly results from the re-dispersion of RuO2 on the TiO2 support in the reaction [38].
3. Experiment
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
The catalysts were prepared using the over-impregnation method. A total of 0.0762 g of RuCl3·H2O (37.5–41.0 wt% Ru, Aladdin, Shanghai, China) was added to 80 mL deionized water, whereby the concentration of Ru was 0.0037 mol·min−1. Subsequently, 10 g of TiO2 (P25, Macklin, Shanghai, China) and different amounts of 30 wt% H2O2 solution (0 g, 0.0335 g, and 0.1005 g) were added to the solution separately, maintaining the molar ratio of Ru: H2O2 at 1:0, 1:1, and 1:3, respectively. The solution was stirred for 2 h at 95 °C and then cooled to 80 °C. Subsequently, the solutions were stirred and evaporated at 80 °C until they were completely evaporated. Finally, the obtained samples were dried in an oven at 80 °C for 12 h and calcined in a muffle furnace at 450 °C for 4 h. The resulting catalysts were denoted as (0 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2, (1 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2, and (3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2, respectively, and each catalyst contained a theoretical 0.30 wt% loading amount of Ru.
Moreover, three samples (“Pure RuO2”, “Pure TiO2”, and mixed “RuO2 and TiO2”) were synthetized in a similar process to catalyst preparation. For “Pure RuO2” samples, H2O2 solution and 10 g of TiO2 were not added and the other steps were exactly the same as the catalyst preparation method. Similarly, 0.0762 g of RuCl3·H2O was not added in the preparation of “Pure TiO2” samples. A total of 0.015 g of pure RuO2 and 4.985g of pure TiO2 were ground mechanically together to obtain the sample of “mixed RuO2 and TiO2”.
3.2. Catalyst Characterization
The crystal phases of the samples were analyzed using an X-ray powder diffractometer (Bruker-AXS D8 Advance, Karlsruhe, Germany). The operating speed is 10 degree·min−1 in the 2θ range of 5–90°. A high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) was performed on JEM-F200 (Tokyo, Japan) to examine the morphologies of different catalysts. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS, JED-2300T, Tokyo, Japan) was applied to determine the element types on the observed region of the catalysts. The valence band of the catalysts was obtained though X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) using a Thermal Scientific ESCALAB 250Xi instrument with an Al Kα X-ray. The Ru content of each catalyst was determined by an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES, Spectro Arcos FHX22, Kleve City, Germany). The specific surface area was analyzed by N2 adsorption on Quadrasorb-SI instrument (Quantachrome, Boynton Beach, FL, USA).
The H2-TPR and NH3-TPD profiles of the catalysts were measured on Auto Chem II 2920 (Micromeritics, Atlanta, GA, USA). The samples were pretreated with pure He at 300 °C for 30 min and then cooled to 30 °C. Thereafter, 10% H2/He was applied through the reactor for the H2-TPR experiments, and then the temperature was increased at a rate of 10 °C·min−1 from 30 to 800 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C·min−1. In the NH3-TPD experiments, the sample was flushed with 5% NH3/He for 30 min, and then treated with pure He at 100 °C for 30 min to remove the physically adsorbed NH3. Thereafter, chemically adsorbed NH3 was detected with the same temperature programs of H2-TPR. The pyridine-IR spectra of the catalysts were performed on a Thermo Fisher Nicolet iS50 model Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (Waltham, MA, USA) with pyridine/2,4,6-trimethylpyridine adsorption between 1350 and 1750 cm−1.
3.3. Activity and Stability Tests
Catalytic activities during DCM oxidation were carried out in a microreactor. The inner diameter and length of the reactor are 6 mm and 70 cm, respectively. A quantity of 0.2 g (0.0008 g for the sample of RuO2 only) catalyst (40–60 mesh) mixed with quartz (0.3 g, 20–40 mesh) was loaded in the microreactor. The flow rates of DCM, N2, and O2 were 0.05 mL·min−1, 90 mL·min−1, and 10 mL·min−1, respectively, where the concentration of DCM was 500 mg·L−1 with GHSV 30,000 mL·g−1·h−1. The product was sampled online at 120 °C through a six-way valve and analyzed using a gas chromatograph (GC, 9790IIT-2, FULI, Zhejiang, China) equipped with an FID detector and a capillary column (624, 30 m × 0.32 mm ×1.0 μm, Lanzhou Donglilong Information Technology Co. Ltd., Lanzhou, China).
The conversion of DCM is calculated as follows:
where [DCM]in and [DCM]out are the inlet DCM concentration and the outlet DCM concentration, respectively.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we investigated TiO2-supported Ru catalysts through treatment involving various H2O2 concentrations and examined the catalytic combustion activity of DCM. The activity of the (0 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst with a T90 value of 344 °C was lower than the (1 and 3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalysts with T90 values of 301 °C and 317 °C, respectively. The effect of H2O2 treatment on the morphology, dispersion, and valence of Ru species was verified using our TEM and XPS results; in addition, the acidity and interaction between RuO2 species and the TiO2 support were analyzed using NH3-TPD, pyridine-IR spectra, and H2-TPR characterization. With the addition of H2O2, the (1 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst was found to comprise a higher number of acid sites (especially Brønsted acid sites), an appropriate amount of uniformly dispersed RuO2, and strong interaction between RuO2 and the TiO2 support, which are characteristics conducive to improving the catalytic combustion activity and stability of DCM. However, excess H2O2 addition on the (3 H2O2)-Ru@TiO2 catalyst led to phase segregation forming RuO2 nanorods, which weakened the interaction between RuO2 and the TiO2 support and decreased catalytic activity.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal14120886/s1: Table S1: The parameters using in Scherrer’s equation; Table S2: The content of different O species from various samples analyzed by XPS; Figure S1: EDS particle atomic mapping of (0 H2O2) (a), (1 H2O2) (b), and (3 H2O2) (c) -Ru@TiO2-catalysts; Figure S2: X-ray diffraction patterns of the spent catalysts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, investigation, methodology, and resources, X.S.; validation, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, and writing—review and editing, Z.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The completion of the above research was the authors’ personal choice, and no funding was received from any agency.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the discussion of the results with our group members.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- Nevanperä, T.K.; Pitkäaho, S.; Ojala, S.; Keiski, R.L. Oxidation of Dichloromethane over Au, Pt, and Pt-Au Containing Catalysts Supported on γ-Al2O3 and CeO2-Al2O3. Molecules 2020, 25, 4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Li, H.; Li, C.J.C. A review and perspective of recent research in biological treatment applied in removal of chlorinated volatile organic compounds from waste air. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126338–126349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Xue, X.; Meng, Z.; Zhou, R. Enhanced catalytic activity and stability of Ce doping on Cr supported HZSM-5 catalysts for deep oxidation of chlorinated volatile organic compounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 234, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.S.; Razzak, S.A.; Hossain, M.M. Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)—A review. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Miao, G.; Pi, Y.; Xia, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Xiao, J. Abatement of various types of VOCs by adsorption/catalytic oxidation: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 1128–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Fei, X.; Wen, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z. Bimodal mesoporous TiO2 supported Pt, Pd and Ru catalysts and their catalytic performance and deactivation mechanism for catalytic combustion of Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2). Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 550, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraudon, J.-M.; Nguyen, T.; Leclercq, G.; Siffert, S.; Lamonier, J.-F.; Aboukaïs, A.; Vantomme, A.; Su, B.-L. Chlorobenzene total oxidation over palladium supported on ZrO2, TiO2 nanostructured supports. Catal. Today 2008, 137, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brink, R.W.; Louw, R.; Mulder, P. Formation of polychlorinated benzenes during the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene using a Pt/γ-Al2O3 catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 1998, 16, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.-H.; Ihm, S.-K. Development of new vanadium-based oxide catalysts for decomposition of chlorinated aromatic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Meng, Z.; Yang, S.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, R. Highly active behaviors of CeO2–CrOx mixed oxide catalysts in deep oxidation of 1, 2-dichloroethane. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2014, 393, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, M.; Wei, Z.; Xin, Q.; Ying, P.; Li, C. Catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene on supported manganese oxide catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 29, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Hu, P.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Luo, M. Characterization of CrOx/Al2O3 catalysts for dichloromethane oxidation. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Shang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C. Micro-meso hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite supported RuOx nanoparticles for activity enhancement of catalytic vinyl chloride oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 606, 154906–154916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Over, H. Atomic-scale understanding of the HCl oxidation over RuO2, a novel deacon process. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 6779–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada-Pérez, S.; Solà, M.; Poater, A. Carbon dioxide conversion on supported metal nanoparticles: A brief review. Catalysts 2023, 13, 305–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ding, M.; Li, M.; Guo, X.; Dai, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhan, W.; Guo, Y.; et al. Morphology effect of cerium dioxide on the catalytic performance of Ru/CeO2 catalyst for the oxidation of different CVOCs. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 345, 127428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Ding, Q.; Fan, H.; Pan, F.; Shou, Y.; Jiao, K.; Xia, C.; Xie, B.; Zhan, W.; Guo, Y.; et al. Biotemplate preparation of Ru/CeO2 catalysts for the catalytic combustion of vinyl chloride. Catal. Commun. 2023, 184, 106801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Lim, Y.H.; Pophali, A.; Lee, E.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.S.; Suh, J.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, S.; Bang, J.; et al. Promotional effect of WO3 in V2O5–WO3/TiO2 on low-temperature activity in the catalytic oxidation of 1, 2-dichloroethane. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 494, 153029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, C.; Zeng, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xie, X. Research progress of catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds over Mn-based catalysts—A review. Rev. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauster, S.J.; Fung, S.C.; Garten, R.L. Strong metal-support interactions. Group 8 noble metals supported on titanium dioxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978, 100, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z. The superior performance of dichloromethane oxidation over Ru doped sulfated TiO2 catalysts: Synergistic effects of Ru dispersion and acidity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 515, 145971–145978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Douthwaite, M.; Pattisson, S.; Hao, Z. Recent advances in the catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds: A review based on pollutant sorts and sources. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4471–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Kong, M.; Hua, Z.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yan, X.; Gao, X. The Study on the Active Site Regulated RuOx/Sn0.2Ti0.8O2 Catalysts with Different Ru Precursors for the Catalytic Oxidation of Dichloromethane. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1306–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Nie, L.; Zhou, X.; Yang, W.; Li, W.; Chen, Y. Abatement of dichloromethane with high selectivity over defect-rich MOF-derived Ru/TiO2 catalysts. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 15724–15734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Jiang, M.; Chen, J.; Yan, D.; Jia, H.J.A.C.B.E. Unveiling the lead resistance mechanism and interface regulation strategy of Ru-based catalyst during chlorinated VOCs oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 315, 121592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Su, W. Progress of catalytic oxidation of typical chlorined volatile organic compounds (CVOCs): A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Xin, Q.; Fu, Y.; Hua, Z.; Dong, Y.; Ran, M.; Song, H.; Liu, S.; Qu, R.; Yang, Y.; et al. Efficient catalytic oxidation of chlorinated volatile organic compounds over RuO2-WOx/Sn0.2Ti0.8O2 catalysts: Insight into the Cl poisoning mechanism of acid sites. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiragond, C.B.; Biswas, S.; Powar, N.S.; Lee, J.; Gong, E.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, J.W.; Cho, C.H.; Wong, B.M.; et al. Surface—modified Ag@ Ru-P25 for photocatalytic CO2 conversion with high selectivity over CH4 formation at the solid–gas interface. Carbon Energy 2024, 6, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Pan, F.; Wang, H. Investigation of facets-dependent photoactivity of anatase TiO2 nanobelt with high percentage of {100} facets. Funct. Mater. Lett. 2017, 10, 1750059–1750062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.-Z.; Jiang, Y.-F.; Zhao, Z.-W.; Zhao, S.-J.; Zhou, X.; Cheang, T.-Y.; Xu, A.-W. Molecule-Assisted Synthesis of Highly Dispersed Ultrasmall RuO2 Nanoparticles on Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Matrix as Ultraefficient Bifunctional Electrocatalysts for Overall Water Splitting. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 11529–11535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, I.M.; Albetran, H.; Prida, V.M.; Vega, V.; Manurung, P.; Ionescu, M. A comparative study on crystallization behavior, phase stability, and binding energy in pure and Cr-doped TiO2 nanotubes. J. Mater. Res. 2013, 28, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, N.T.T.; Tuan, P.D.; Dzung, N.V. The shifts of band gap and binding energies of titania/hydroxyapatite material. J. Compos. 2014, 2014, 283034–283038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmasides, C.; Kondarides, D.; Grünert, W.; Verykios, X. XPS and FTIR study of Ru/Al2O3 and Ru/TiO2 catalysts: Reduction characteristics and interaction with a methane-oxygen mixture. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 5227–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z. Highly efficient and selective Ru and Ce modified ZSM-5 catalysts for catalytic oxidation of toluene. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 651, 129709–129720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Han, M. Effect of Mo Dispersion on the Catalytic Properties and Stability of Mo–Fe Catalysts for the Partial Oxidation of Methanol. Molecules 2020, 25, 2410–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Huang, J.; Liu, F.; Xu, X.; Fang, X.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Wang, X. Rutile RuO2 dispersion on rutile and anatase TiO2 supports: The effects of support crystalline phase structure on the dispersion behaviors of the supported metal oxides. Catal. Today 2020, 339, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, B.; Xie, Z.; Li, Y.; Shen, Z.-Y. Preparation and photocatalytic properties of RuO2/TiO2 composite nanotube arrays. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 13664–13669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Bai, S.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Lu, G. The effect of TiO2 doping on catalytic performances of Ru/CeO2 catalysts during catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 142, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miran, H.A.; Altarawneh, M.; Jiang, Z.-T.; Oskierski, H.; Almatarneh, M.; Dlugogorski, B.Z. Decomposition of selected chlorinated volatile organic compounds by ceria (CeO2). Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 3902–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Luo, J.; Liu, S. Novel metal loaded KIT-6 catalysts and their applications in the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 294, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, N.; Gómez-Segura, J.; Marín, R.P.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. Mechanism of HCl oxidation (Deacon process) over RuO2. J. Catal. 2008, 255, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhai, S.; Chen, J.; Yuan, J.; Wu, Z.; Weng, X. Development of a multi-active center catalyst in mediating the catalytic destruction of chloroaromatic pollutants: A combined experimental and theoretical study. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 272, 119015–119023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Shi, M.; Wang, H.; Yu, F.; Weng, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z. A two-stage Ce/TiO2–Cu/CeO2 catalyst with separated catalytic functions for deep catalytic combustion of CH2Cl2. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 290, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Fu, K.; Pang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Song, C.; Ji, N.; Ma, D.; Lu, X.; Liu, C.; Han, R.; et al. Recent Advances of Chlorinated Volatile Organic Compounds’ Oxidation Catalyzed by Multiple Catalysts: Reasonable Adjustment of Acidity and Redox Properties. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 9854–9871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z. A comparative study of the dichloromethane catalytic combustion over ruthenium-based catalysts: Unveiling the roles of acid types in dissociative adsorption and by-products formation. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2022, 605, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).