Synthesis, Material Properties, and Organocatalytic Performance of Hypervalent Iodine(III)-Oxidants in Core–Shell-Structured Magnetic Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
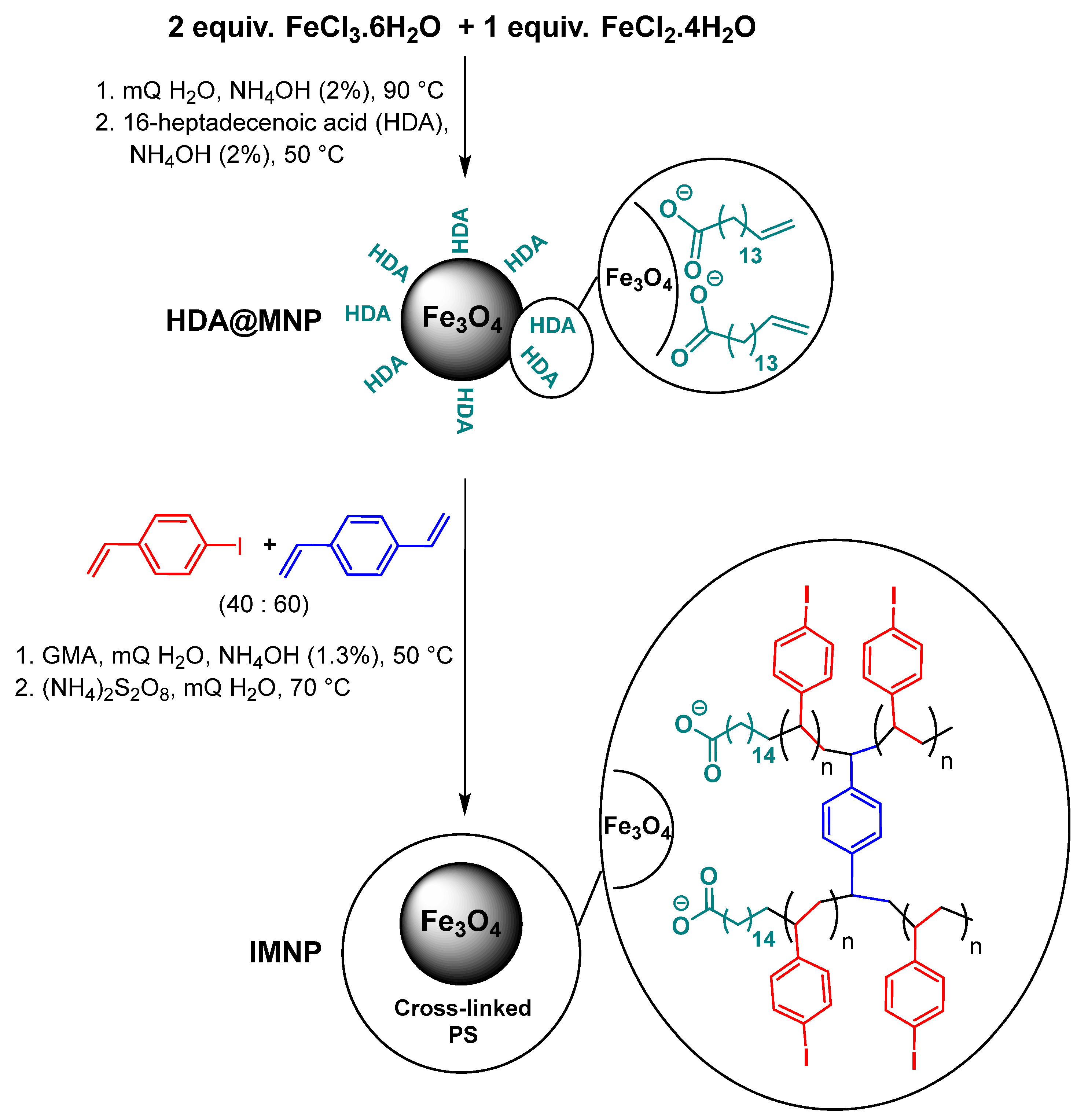
2.1. Synthesis of Iodinated Core–Shell Type Magnetic Nanoparticles (IMNPs)
2.2. Characterization of Core–Shell Type IMNPs by Analytical and Spectroscopic Means
2.3. Morphology, Particle Size, and Imaging of IMNPs by SEM and DLS Investigation
2.4. TEM Investigations of MNPs and IMNPs
2.5. Evaluation of IMNPs as Suitable Organocatalysts for Oxidative Transformations
2.5.1. α-Tosyloxylation of Propiophenone with IMNPs
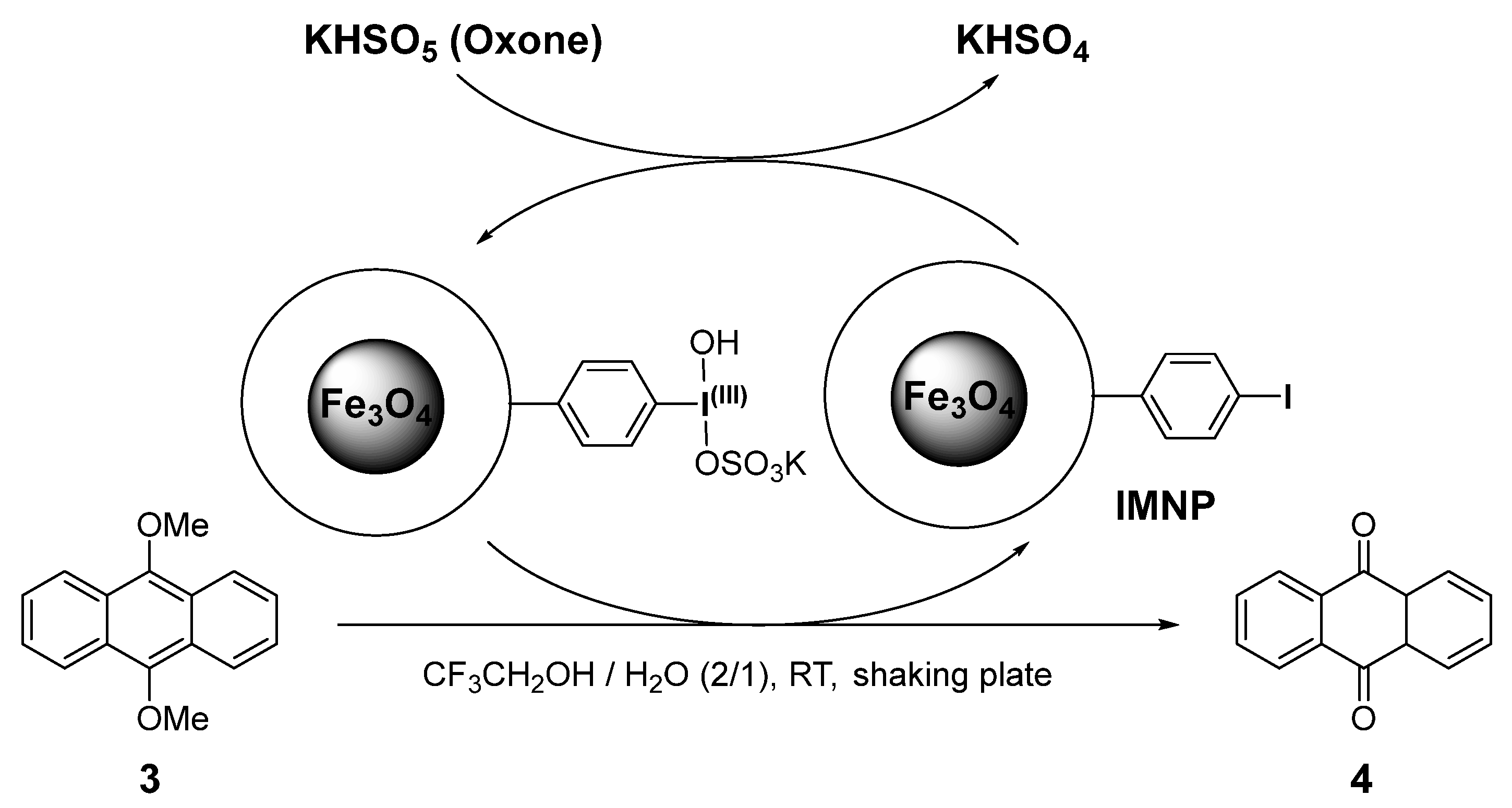
2.5.2. IMNP-Mediated Organocatalytic Oxidation of 9,10-Dimethoxyanthracene
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wirth, T. (Ed.) Hypervalent Iodine Chemistry—Modern Developments in Organic Synthesis; Topics in Current Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tohma, H.; Kita, Y. Hypervalent Iodine Reagents for the Oxidation of Alcohols and Their Application to Complex Molecule Synthesis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdankin, V.V.; Stang, P.J. Chemistry of Polyvalent Iodine. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 5299–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küpper, F.C.; Feiters, M.C.; Olofsson, B.; Kaiho, T.; Yanagida, S.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Carpenter, L.J.; Luther, G.W., III; Lu, Z.; Jonsson, M.; et al. Commemorating Two Centuries of Iodine Research: An Interdisciplinary Overview of Current Research. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11598–11620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhdankin, V.V. Hypervalent Iodine Chemistry: Preparation, Structure, and Synthetic Applications of Polyvalent Iodine Compounds; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yusubov, M.S.; Zhdankin, V.V. Iodine Catalysis: A Green Alternative to Transition Metals in Organic Chemistry and Technology. Resour.-Effic. Technol. 2015, 1, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, A.; Zhdankin, V.V. Advances in Synthetic Applications of Hypervalent Iodine Compounds. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3328–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, F.V.; Wirth, T. “Stereoselective Reactions” Patai’s Chemistry of Functional Groups, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, F.V.; Shetgaonkar, S.E.; Krishnan, M.; Wirth, T. Progress in Organocatalysis with Hypervalent Iodine Catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 8102–8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohi, T.; Maruyama, A.; Yoshimura, M.; Morimoto, K.; Tohma, H.; Kita, Y. Versatile Hypervalent-Iodine(III)-Catalyzed Oxidations with m-Chloroperbenzoic Acid as a Cooxidant. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6193–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, M.; Takeuchi, Y.; Katayama, T.; Sueda, T.; Miyamoto, K. Iodobenzene-Catalyzed α-Acetoxylation of Ketones. In Situ Generation of Hypervalent (Diacyloxyiodo)benzenes Using m-Chloroperbenzoic Acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12244–12245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, R.D.; Wirth, T. Hypervalent Iodine Goes Catalytic. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4402–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkbeiner, P.; Nachtsheim, B.J. Iodine in Modern Oxidation Catalysis. Synthesis 2013, 45, 979–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimi; Uttam, B.; Zhdankin, V.V.; Kumar, R. New Isoxazole-Substituted Aryl Iodides: Metal-Free Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 27, e202301191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimi; Soni, S.; Uttam, B.; China, H.; Dohi, T.; Zhdankin, V.V.; Kumar, R. Recyclable Hypervalent Iodine Reagents in Modern Organic Synthesis. Synthesis 2022, 54, 2731–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okawara, M.; Mizuta, K. Synthesis and Some Reactions of Polystyrene Iodosoacetate. Kogyo Kagaku Zasshi 1961, 64, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togo, H.; Sakuratani, K. Polymer-Supported Hypervalent Iodine Reagents. Synlett 2002, 2002, 1966–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.P.; Chen, Z. Hypervalent Iodine in Synthesis XXVIII: The Preparation and Utility of Polymer-Supported Phenyliodine(III) Diacetate. Synth. Commun. 1999, 29, 2859–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, S.V.; Thomas, A.W.; Finch, H. Polymer-Supported Hypervalent Iodine Reagents in ‘Clean’ Organic Synthesis with Potential Application in Combinatorial Chemistry. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1999, 1, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, S.; Sakuratani, K.; Togo, H. Synthetic Use of Poly[4-hydroxy(tosyloxy)iodo]styrenes. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 6174–6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficht, S.; Mülbaier, M.; Giannis, A. Development of New and Efficient Polymer-Supported Hypervalent Iodine Reagents. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 4863–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohma, H.; Maegawa, T.; Kita, Y. Facile and Efficient Oxidative Transformation of Primary Alcohols to Methyl Esters in Water Using Hypervalent Iodine(III) Reagents. Synlett 2003, 2003, 723–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.-B.; Chen, J.-M. Poly{[4-(Hydroxy)(Tosyloxy)Iodo]Styrene}-Promoted Direct α-Hydroxylation of Ketones to α-Hydroxyketones. J. Chem. Res. 2006, 2006, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalberer, E.W.; Whitfield, S.R.; Sanford, M.S. Application of Recyclable Polymer-Immobilized Iodine(III) Oxidants in Catalytic C-H Bond Functionalization. J. Mol. Catal. A. 2006, 251, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; But, T.Y.S.; Togo, H.; Toy, P.H. Macroporous Polystyrene-Supported (Diacetoxyiodo)benzene: An Efficient Heterogeneous Oxidizing Reagent. Synlett 2007, 2007, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Maurya, R.; Ahmad, P.J. Diversity Oriented Synthesis of Benzimidazole and Benzoxa/(thia)zole Libraries through Polymer-Supported Hypervalent Iodine Reagent. Comb. Chem. 2009, 11, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Phillips, J.A. The Synthesis and Application of Polymer-Supported Hypervalent Iodine Reagent in the Organic Chemistry Laboratory. J. Chem. Educ. 2010, 87, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-M.; Zeng, X.-M.; Zhdankin, V.V. Preparation and Reactivity of Polystyrene-Supported Iodosylbenzene Sulfate: An Efficient Recyclable Oxidizing System. Synlett 2010, 2010, 2771–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Jin, E.; Bao, W.; Zhang, Y. Clean and Highly Selective Oxidation of Alcohols in an Ionic Liquid by Using an Ion-Supported Hypervalent Iodine(III) Reagent. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 952–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handy, S.T.; Okello, M.J. Homogeneous Supported Synthesis Using Ionic Liquid Supports: Tunable Separation Properties. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 2874–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.N.; Poupon, J.C.; Charette, A.B. Tetraarylphosphonium Salts as Soluble Supports for Oxidative Catalysts and Reagents. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 8510–8515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Y.; Kuang, H.; Jia, H. A Facile Synthesis of Ionic Liquid-Supported Iodosylbenzenes. J. Chem. Res. 2011, 35, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Yoshimura, A.; Wei, Y.; Nemykin, N.V.; Zhdankin, V.V. Facile Preparation and Reactivity of Bifunctional Ionic Liquid-Supported Hypervalent Iodine Reagent: A Convenient Recyclable Reagent for Catalytic Oxidation. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iinuma, M.; Moriyama, K.; Togo, H. Various Oxidative Reactions with Novel Ion-Supported (Diacetoxyiodo)benzenes. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 2961–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Pan, H. Regioselective Acetylate of 1,3-Disubstituted Selenoureas Promoted by Recyclable Ion-Supported Hypervalent Iodine(III) Reagent. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2014, 189, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Gan, B.; Mi, Z.; Xie, Y. Synthesis of Cyanamides from Isoselenocyanates Promoted by Recyclable Ionic Liquid-Supported (Diacetoxyiodo)benzene. J. Chem. Res. 2015, 39, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocaboy, C.; Gladysz, J.A. Convenient Syntheses of Fluorous Aryl Iodides and Hypervalent Iodine Compounds: ArI(L)n Reagents that are Recoverable by Simple Liquid/Liquid Biphase Workups, and Applications in Oxidations of Hydroquinones. Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesevic, V.; Gladysz, J.A. An Easily Accessed Class of Recyclable Hypervalent Iodide Reagents for Functional Group Oxidations: Bis(trifluoroacetate) Adducts of Fluorous Alkyl Iodides, CF3(CF2)n−1I(OCOCF3)2. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesevic, V.; Gladysz, J.A. Oxidations of Secondary Alcohols to Ketones Using Easily Recyclable Bis(trifluoroacetate) Adducts of Fluorous Alkyl Iodides, CF3(CF2)n−1I(OCOCF3)2. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 7433–7440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podgorsek, A.; Jurisch, M.; Stavber, S.; Zupan, M.; Iskra, J.; Gladysz, J.A. Synthesis and Reactivity of Fluorous and Nonfluorous Aryl and Alkyl Iodine(III) Dichlorides: New Chlorinating Reagents that are Easily Recycled using Biphasic Protocols. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 3133–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohma, H.; Maruyama, A.; Maeda, A.; Maegawa, T.; Dohi, T.; Shiro, M.; Morita, T.; Kita, Y. Preparation and Reactivity of 1,3,5,7-Tetrakis[4-diacetoxyiodo)phenyl]adamantane, a Recyclable Hypervalent Iodine(III) Reagent. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 3595–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohi, T.; Maruyama, A.; Yoshimura, M.; Morimoto, K.; Tohma, H.; Shiro, M.; Kita, Y. A Unique Site-Selective Reaction of Ketones with New Recyclable Hypervalent Iodine(III) Reagents Based on a Tetraphenylmethane Structure. Chem. Commun. 2005, 17, 2205–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroda, A.; Togo, H. Biphenyl- and Terphenyl-Based Recyclable Organic Trivalent Iodine Reagents. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 12408–12414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohi, T.; Fukushima, K.I.; Kamitanaka, T.; Morimoto, K.; Takanaga, K.; Kita, Y. An Excellent Dual Recycling Strategy for the Hypervalent Iodine/Nitroxyl Radical Mediated Selective Oxidation of Alcohols to Aldehydes and Ketones. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorat, P.B.; Bhong, B.Y.; Shelke, A.V.; Karade, N.N. 2,4,6-Tris(4-iodophenoxy)-1,3,5-triazine as a New Recyclable “Iodoarene” for In Situ Generation of Hypervalent Iodine(III) Reagent for α-Tosyloxylation of Enolizable Ketones. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 3332–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Wei, Y. Facile Preparation of Magnetic Nanoparticle-Supported Hypervalent Iodine Reagent: A Convenient Recyclable Reagent for Oxidation. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2012, 354, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahamat, Z.; Nemati, F.; Elhampour, A. Highly Effective Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohols to Benzaldehydes Over a New Hypervalent Iodine(III) Reagent with the Polymeric Framework and Magnetic Feature as Reusable Heterogeneous Nanocatalyst. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 146, 104415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambu, H.; Shimokawa, I.; Fujiwara, T.; Yakura, T. Recyclable Magnetic Nanoparticle-Supported Iodoarene Catalysts for Oxidation of 4-Alkoxyphenols to Quinones. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2016, 5, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diles, D.C. Recent Advances and Future Directions in Magnetic Materials. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 5907–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polshettiwar, V.; Luque, R.; Fihri, A.; Zhu, H.; Bouhrara, M.; Basset, J.-M. Magnetically Recoverable Nanocatalysts. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3069–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, M.J.; Branco, P.S.; Varma, R.S. Nano-Magnetite (Fe3O4) as a Support for Recyclable Catalysts in the Development of Sustainable Methodologies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3371–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, R.B.N.; Varma, R.S. Magnetically Retrievable Catalysts for Organic Synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 752–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrowczynski, R.; Nan, A.; Liebscher, J. Magnetic Nanoparticle-Supported Organocatalysts—An Efficient Way of Recycling and Reuse. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 5927–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Astruc, D. Fast-Growing Field of Magnetically Recyclable Nanocatalysts. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6949–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushra, R.; Ahmad, M.; Alam, K.; Seidi, F.; Qurtulen; Shakeel, S.; Song, J.; Jin, Y.; Xiao, H. Recent Advances in Magnetic NanoParticles: Key Applications, Environmental Insights, and Future Strategies. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 40, e00985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre, S.H. Recent Developments of Supported and Magnetic Nanocatalysts for Organic Transformations: An Up-To-Date Review. Appl. Nanosci. 2023, 13, 15–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovejero, J.G.; Gallo-Cordova, A.; Roca, A.G.; Morales, M.P.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S. Reproducibility and Scalability of Magnetic Nanoheater Synthesis. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.D.; Deng, L.; Lee, J.M.; Resendez, K.M.; Fuller, M.; Hoijang, S.; Robles-Hernandez, F.; Chu, C.-W.; Litvinov, D.; Hadjiev, V.G.; et al. Magnetic Tunability via Control of Crystallinity and Size in Polycrystalline Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Small 2024, 20, 2402940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, H.; Sharma, R. A Review on Functionalization and Potential Application Spectrum of Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs) Based Systems. Chem. Inorg. Mater. 2024, 2, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.-H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Protection, Functionalization, and Application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feyen, M.; Weidenthaler, C.; Schüth, F.; Lu, A.H. Synthesis of Structurally Stable Collodial Composites as Magnetically Recyclable Acid Catalysts. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 2955–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirfakhraei, S.; Hekmati, M.; Eshbala, F.H.; Veisi, H. Fe3O4/PEG-SO3H as a Heterogeneous and Magnetically-Recyclable Nanocatalyst for the Oxidation of Sulfides to Sulfones or Sulfoxides. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 1757–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wu, J.; Hou, Y. Fe3O4 Nanostructures: Synthesis, Growth Mechanism, Properties and Applications. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5130–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonidis, K.; Liébana-Viñas, S.; Wiedwald, U.; Ma, Z.; Li, Z.-A.; Spasova, M.; Patsia, O.; Myrovali, E.; Makridis, A.; Sakellari, D.; et al. A Versatile Large-Scale and Green Process for Synthesizing Magnetic Nanoparticles with Tunable Magnetic Hyperthermia Features. RSC. Adv. 2016, 6, 53107–53117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, D.; Kale, S.N.; Kaul-Ghanekar, R.; Xue, J.-M.; Ding, J. Studies of Magnetite Nanoparticles Synthesized by Thermal Decomposition of Iron(III) Acetylacetonate in Tri(ethylene Glycol). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 3093–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Palma, R.; Peeters, S.; Van Bael, M.J.; Van den Rul, H.; Bonroy, K.; Laureyn, W.; Mullens, J.; Borghs, G.; Maes, G. Silane Ligand Exchange to Make Hydrophobic Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles Water-Dispersible. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Togo, H. PhI-Catalyzed α-Tosyloxylation of Ketones with m-Chloroperbenzoic Acid and p-Toluenesulfonic Acid. Synlett 2006, 2006, 798–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, E.A.; Olofsson, B. α-Functionalization of Carbonyl Compounds Using Hypervalent Iodine Reagents. Synthesis 2011, 2011, 517–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, R.M.; Prakash, O. Oxidation of Phenolic Compounds with Organohypervalent Iodine Reagents. Org. Reac. 2001, 57, 327–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armarego, W.L.F.; Chai, C.L.L. Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Oxford UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, H.J.; Kennedy, E.R.; Forno, M.W. Iodosobenzene. Org. Synth. 1942, 22, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Kondo, Y. Transition-Metal-Free Carboxylation of Organozinc Reagents Using CO2 in DMF Solvent. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 2035–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everson, D.A.; Shrestha, R.; Weix, D.J. Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive Cross-Coupling of Aryl Halides with Alkyl Halides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 920–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partridge, B.M.; Hartwig, J.F. Sterically Controlled Iodination of Arenes via Iridium-Catalyzed C–H Borylation. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, M.; Nabana, T.; Togo, H. Novel Oxidative α-Tosyloxylation of Alcohols with Iodosylbenzene and p-Toluenesulfonic Acid and Its Synthetic Use for Direct Preparation of Heteroaromatics. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 6424–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, L.M.; Paulick, R.C.; Whitlock, H.W. Carbon-13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study of the Biosynthesis of Daunomycin and Islandicin. J. Org. Chem. 1978, 43, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Entry | Run | Iodine Source | Yield of 2 a [%] | Recovered IMNPs b [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | iodobenzene | 87 | - |
| 2 | 1 | IMNPs | 85 | 98 |
| 3 | 2 | IMNPs | 39 | 98 |
| 4 | 3 | IMNPs | 15 | 91 |
| Entry | Run | Reagent (mol%) | Yield of 4 a [%] | Recovered IMNPs b [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | IMNPs (30) | 85 | 97 |
| 2 | 2 | IMNPs (30) | 77 | 81 |
| 3 | 3 | IMNPs (30) | 75 | 80 |
| 4 | 4 | IMNPs (30) | 75 | 92 |
| 5 | 1 | Iodobenzene (100) | 88 | - |
| 6 | 1 | MNP (100) | <10 | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grand, J.; Alayrac, C.; Moldovan, S.; Witulski, B. Synthesis, Material Properties, and Organocatalytic Performance of Hypervalent Iodine(III)-Oxidants in Core–Shell-Structured Magnetic Nanoparticles. Catalysts 2024, 14, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14100677
Grand J, Alayrac C, Moldovan S, Witulski B. Synthesis, Material Properties, and Organocatalytic Performance of Hypervalent Iodine(III)-Oxidants in Core–Shell-Structured Magnetic Nanoparticles. Catalysts. 2024; 14(10):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14100677
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrand, Julien, Carole Alayrac, Simona Moldovan, and Bernhard Witulski. 2024. "Synthesis, Material Properties, and Organocatalytic Performance of Hypervalent Iodine(III)-Oxidants in Core–Shell-Structured Magnetic Nanoparticles" Catalysts 14, no. 10: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14100677
APA StyleGrand, J., Alayrac, C., Moldovan, S., & Witulski, B. (2024). Synthesis, Material Properties, and Organocatalytic Performance of Hypervalent Iodine(III)-Oxidants in Core–Shell-Structured Magnetic Nanoparticles. Catalysts, 14(10), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14100677






