Nucleophilic Reactions Using Alkali Metal Fluorides Activated by Crown Ethers and Derivatives
Abstract
1. Introduction
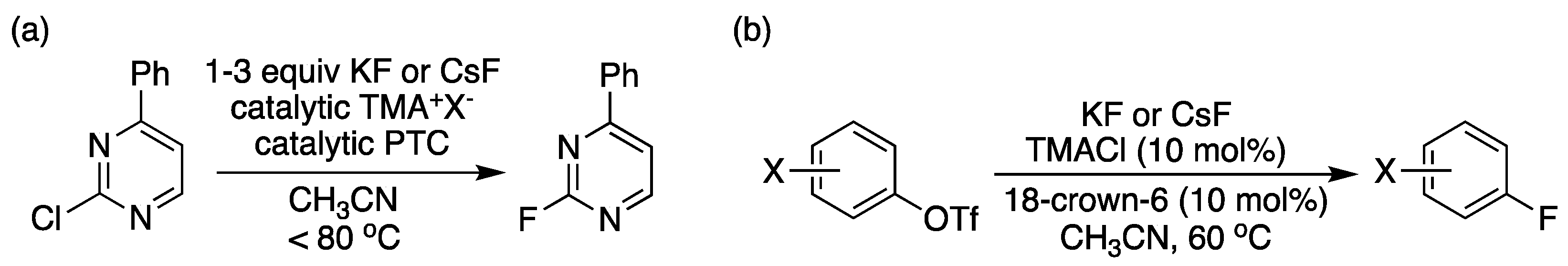
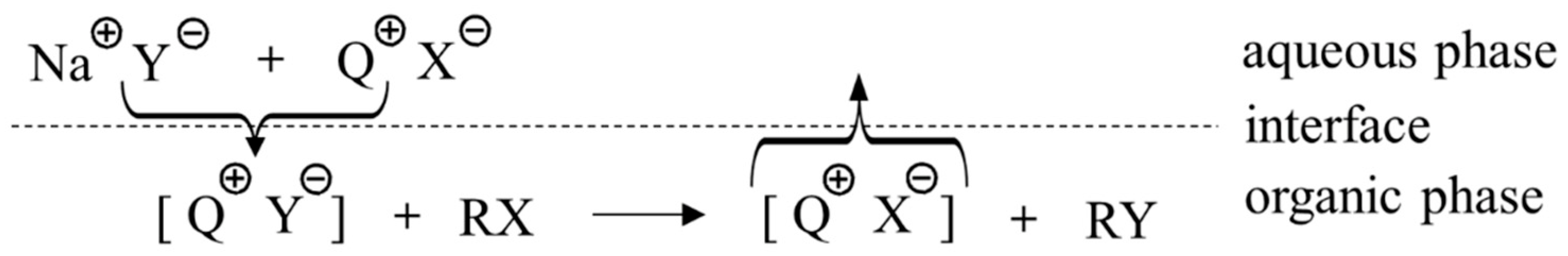
2. Earlier Works on Crown Ethers and Derivatives as PTCs
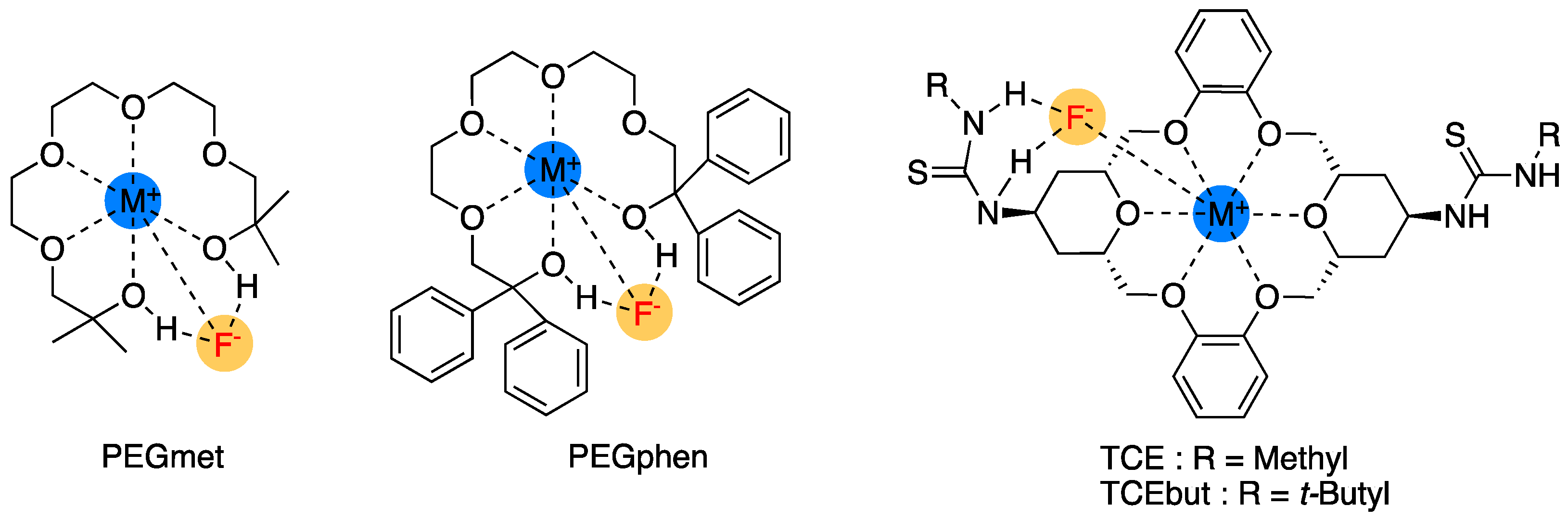
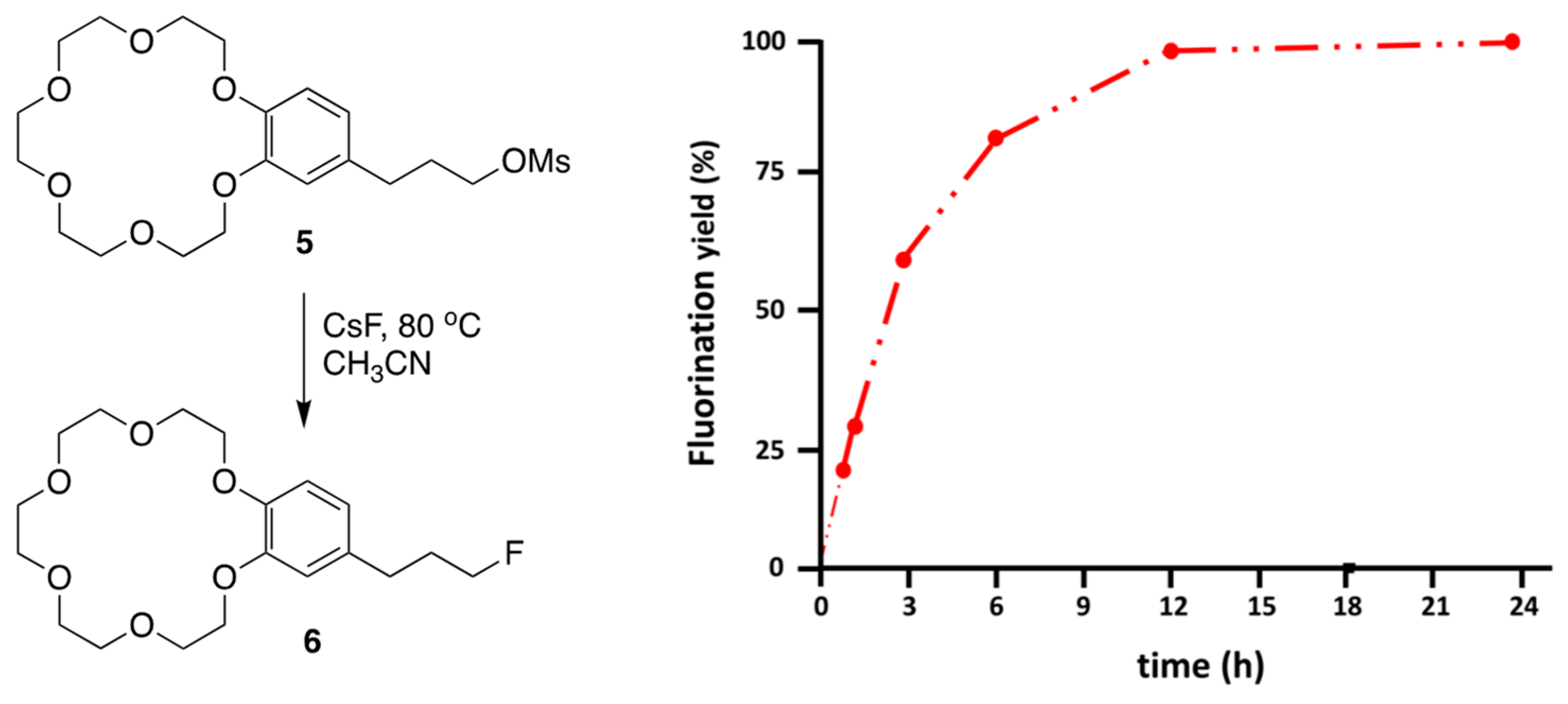
3. Functionalized Crown Ethers
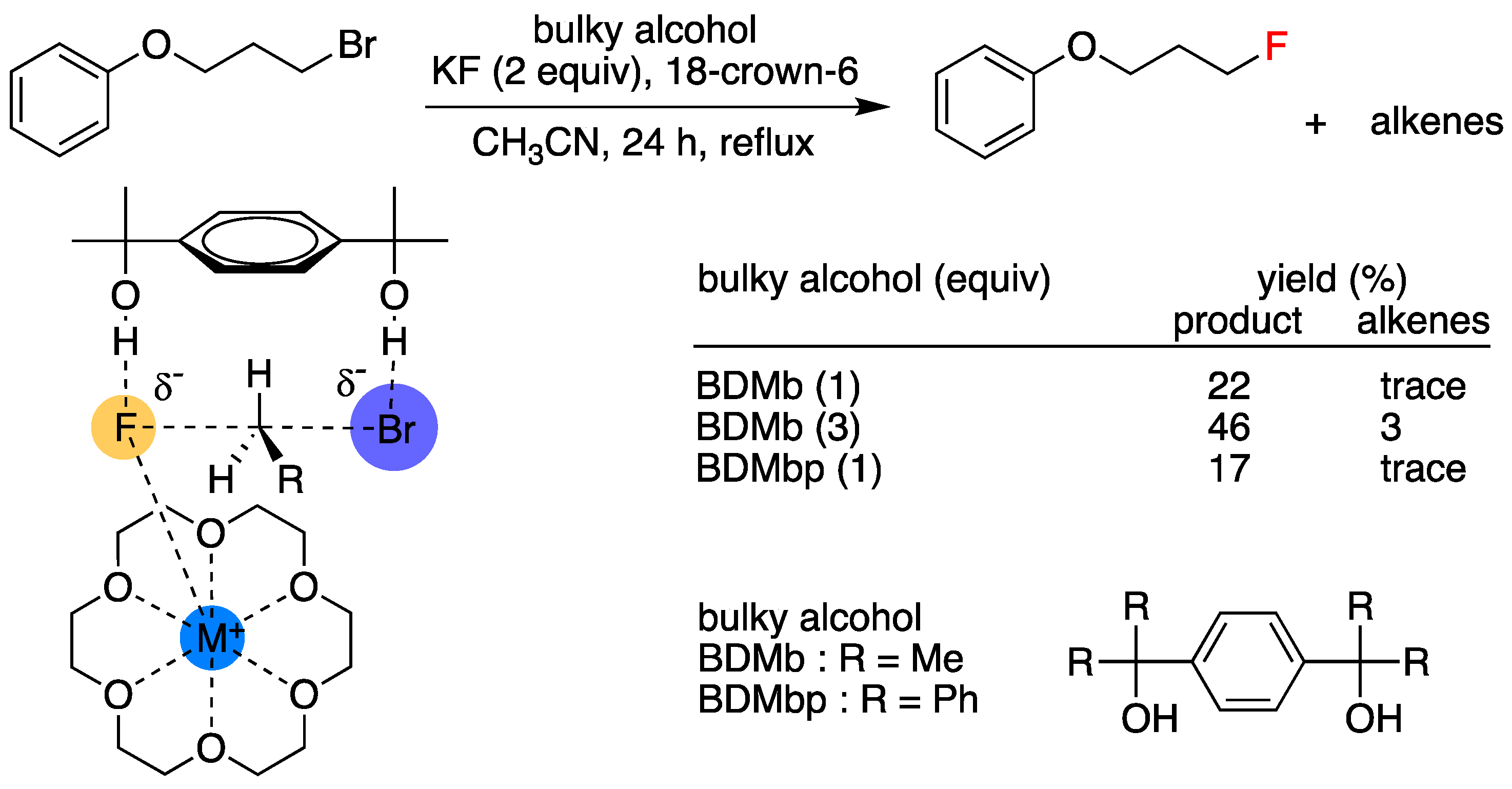
4. Synergetic Effects of Crown Ether/Alcohol and/Ammonium Combination
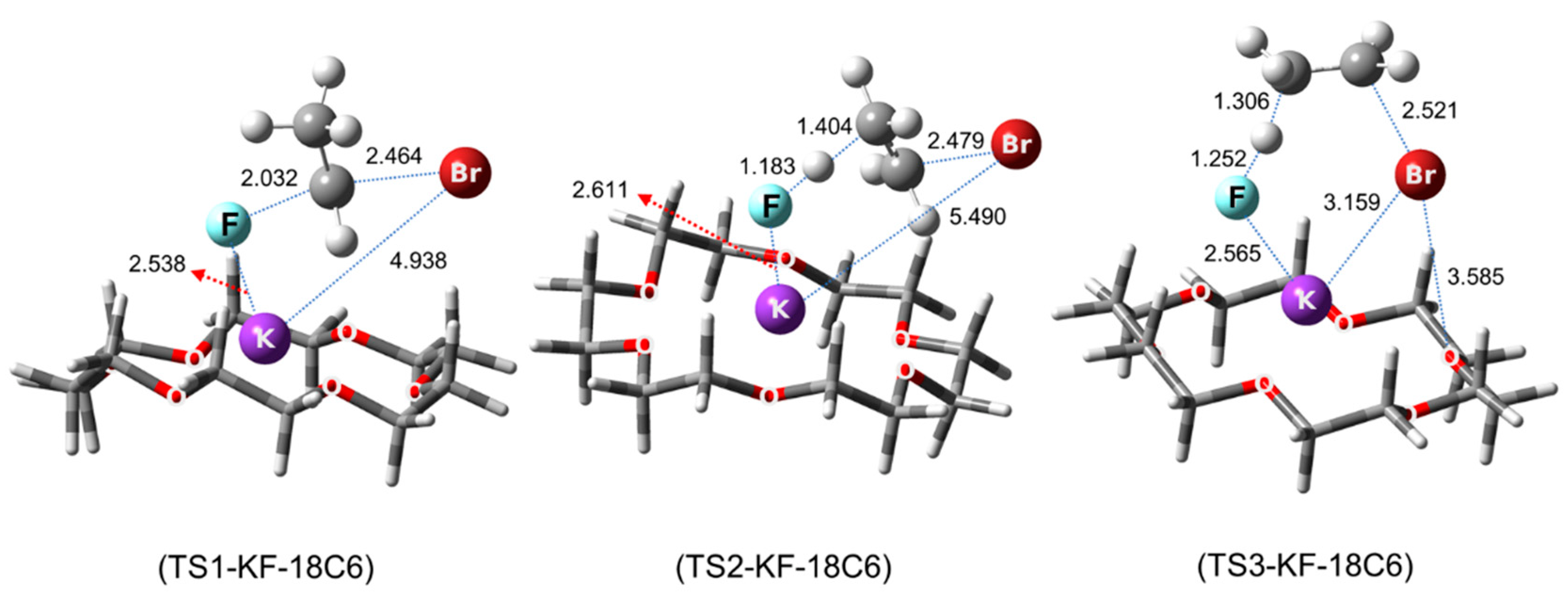
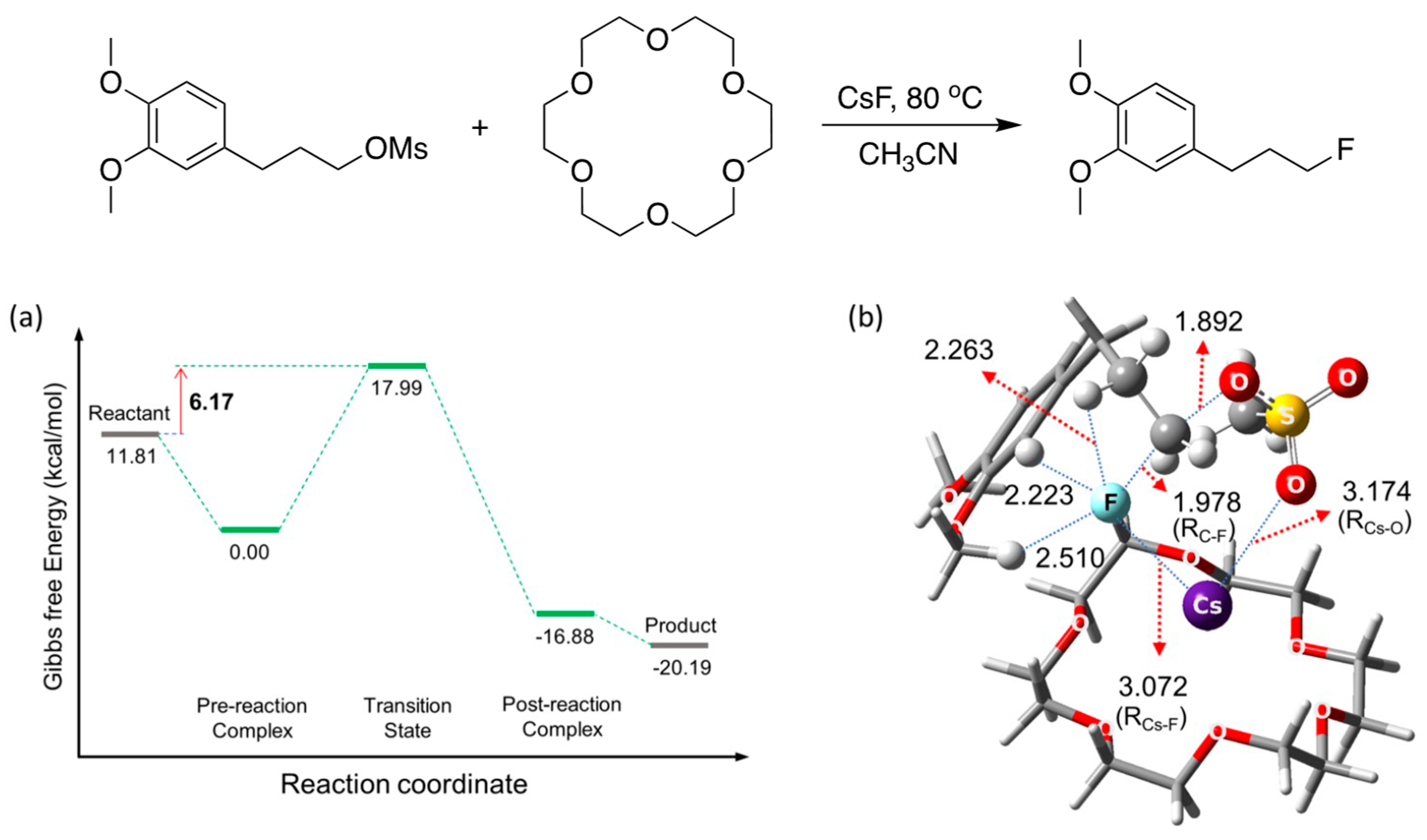
5. Mechanistic Features for Crown Ether-Facilitated SN2 Reactions
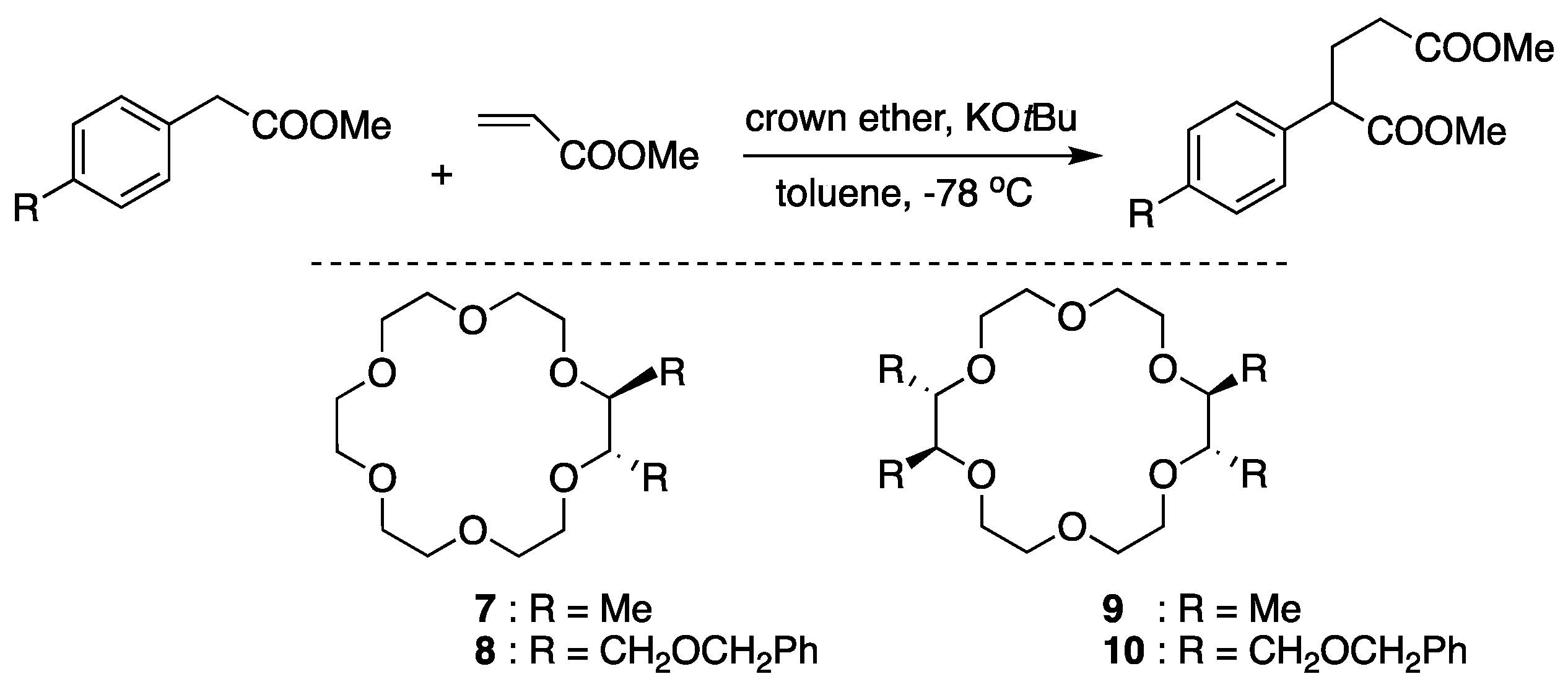
6. Chiral Crown Ethers and Derivatives for Asymmetric Synthesis
7. Concluding Remarks
8. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pedersen, C.J. The Discovery of Crown Ethers. Science 1988, 241, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, C.J. Cyclic Polyethers and Their Complexes with Metal Salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89, 7017–7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokel, G.W. Crown Ethers and Cryptands; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 1991; ISBN 0851869963. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, Y.; Gokel, G.W. Cation Binding by Macrocycles: Complexation of Cationic Species by Crown Ethers, 1st ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1990; ISBN 0824781872. [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw, J.S.; Izatt, R.M. Crown Ethers: The Search for Selective Ion Ligating Agents. Acc. Chem. Res. 1997, 30, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokel, G.W.; Leevy, W.M.; Weber, M.E. Crown Ethers: Sensors for Ions and Molecular Scaffolds for Materials and Biological Models. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 2723–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Xu, C.; Ren, J.; Xu, B.; Qu, X. Sensing Metal Ions with Ion Selectivity of a Crown Ether and Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer between Carbon Dots and Graphene. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1284–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnock, S.J.; Sujanani, R.; Zofchak, E.S.; Zhao, S.; Dilenschneider, T.J.; Hanson, K.G.; Mukherjee, S.; Ganesan, V.; Freeman, B.D.; Abu-Omar, M.M. Engineering Li/Na Selectivity in 12-Crown-4–Functionalized Polymer Membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022197118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Shionoya, M.; Koga, K. Functionalized Crown Ethers as an Approach to the Enzyme Model for the Synthesis of Peptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 3371–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, F.Z.; Wu, J.Y.; Xie, J.Q.; Li, S. Development of the Aza-Crown Ether Metal Complexes as Artificial Hydrolase. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 154, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yan, X.; Huang, F.; Niu, Z.; Gibson, H.W. Stimuli-Responsive Host–Guest Systems Based on the Recognition of Cryptands by Organic Guests. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1995–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.-H.; Wang, Q.-C.; Zhang, Q.-W.; Ma, X.; Tian, H. Photoresponsive Host–Guest Functional Systems. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 7543–7588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Ahn, D.-S.; Oh, Y.-H.; Lee, S.; Kil, H.S.; Oh, S.J.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Ryu, J.S.; Moon, D.H.; et al. A New Class of SN2 Reactions Catalyzed by Protic Solvents: Facile Fluorination for Isotopic Labeling of Diagnostic Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 16394–16397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-W.; Oliveira, M.T.; Jang, H.B.; Lee, S.; Chi, D.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Song, C.E. Hydrogen-Bond Promoted Nucleophilic Fluorination: Concept, Mechanism and Applications in Positron Emission Tomography. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 4638–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.-H.; Ahn, D.-S.; Chung, S.-Y.; Jeon, G.-H.; Park, S.-W.; Oh, S.J.; Kim, D.W.; Kil, H.S.; Chi, D.Y.; Lee, S. Facile SN2 Reaction in Protic Solvent: Quantum Chemical Analysis. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 10152–10161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laloo, J.Z.A.; Rhyman, L.; Larrañaga, O.; Ramasami, P.; Bickelhaupt, F.M.; de Cózar, A. Ion-Pair SN2 Reaction of OH− and CH3Cl: Activation Strain Analyses of Counterion and Solvent Effects. Chem. Asian J. 2018, 13, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laloo, J.Z.A.; Rhyman, L.; Ramasami, P.; Bickelhaupt, F.M.; de Cózar, A. Ion-Pair SN2 Substitution: Activation Strain Analyses of Counter-Ion and Solvent Effects. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 4431–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harder, S.; Streitwieser, A.; Petty, J.T.; Ragué Schleyer, P. von Ion Pair SN2 Reactions. Theoretical Study of Inversion and Retention Mechanisms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 3253–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Gai, J.-G.; Xiong, Y.; Lee, K.-H.; Chu, S.-Y. Theoretical Study on the Identity Ion Pair SN2 Reactions of LiX with CH3SX (X = Cl, Br, and I): Structure, Mechanism, and Potential Energy Surface. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 6615–6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalessandro, E.V.; Pliego, J.R. Reactivity and Stability of Ion Pairs, Dimers and Tetramers versus Solvent Polarity: SNAr Fluorination of 2-Bromobenzonitrile with Tetramethylammonium Fluoride. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2020, 139, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, P.E.; Bradshaw, J.S.; Parish, W.W. Modified Crown Ether Catalysts. 3. Structural Parameters Affecting Phase Transfer Catalysis by Crown Ethers and a Comparison of the Effectiveness of Crown Ethers to That of Other Phase Transfer Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 4810–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, W.C.; Mathre, D.J. Phase-Transfer Alkylation of Heterocycles in the Presence of 18-Crown-6 and Potassium Tert-Butoxide. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 3172–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciapaglia, R.; Mandolins, L. Catalysis by Metal Ions in Reactions of Crown Ether Substrates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1993, 22, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, S.; Capocasa, G.; Mandolini, L. Supramolecular Catalysts Featuring Crown Ethers as Recognition Units. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 23, 3340–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, Z.; Richter, D.; Nagy, S.; Bagi, P.; Rapi, Z.; Simon, A.; Drahos, L.; Huszthy, P.; Bakó, P.; Kupai, J. Synthesis of Novel Crown Ether-Squaramides and Their Application as Phase-Transfer Catalysts. Molecules 2021, 26, 6542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landini, D.; Montanari, F.; Pirisi, F.M. Crown Ethers as Phase-Transfer Catalysts in Two-Phase Reactions. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1974, 21, 879–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landini, D.; Maia, A.; Montanari, F.; Pirisi, F.M. Crown Ethers as Phase-Transfer Catalysts. A Comparison of Anionic Activation in Aqueous–Organic Two-Phase Systems and in Low Polarity Anhydrous Solutions by Perhydrodibenzo-18-Crown-6, Lipophilic Quaternary Salts, and Cryptands. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1980, 2, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehmlow, E. V Advances in Phase-Transfer Catalysis [New Synthetic Methods (20)]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1977, 16, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, C.L.; Harris, H.P. Chemistry of Naked Anions. I. Reactions of the 18-Crown-6 Complex of Potassium Fluoride with Organic Substrates in Aprotic Organic Solvents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1974, 96, 2250–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsher, U.; Frolow, F.; Dalley, N.K.; Jiang, W.; Yu, Z.Y.; Knobeloch, J.M.; Bartsch, R.A. Crown Ether Alcohols as Bifunctional Ligands for Simultaneous Cation Complexation and Anion Solvation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 6570–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, N.F.; Pliego, J.R. Theoretical Design and Calculation of a Crown Ether Phase-Transfer-Catalyst Scaffold for Nucleophilic Fluorination Merging Two Catalytic Concepts. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 8455–8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iashin, V.; Wirtanen, T.; Perea-Buceta, J.E. Tetramethylammonium Fluoride: Fundamental Properties and Applications in CF Bond-Forming Reactions and as a Base. Catalysts 2022, 12, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Morales-Colón, M.T.; Brooks, A.F.; Wright, J.S.; Makaravage, K.J.; Scott, P.J.H.; Sanford, M.S. SNAr Radiofluorination with in Situ Generated [18F]Tetramethylammonium Fluoride. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 14121–14130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimler, S.D.; Froese, R.D.J.; Bland, D.C.; Sanford, M.S. Reactions of Arylsulfonate Electrophiles with NMe4F: Mechanistic Insight, Reactivity, and Scope. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 11178–11190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, S.S.; Bolik, K.-V.; Maschauer, S.; Prante, O. 18F-Fluorination Using Tri-Tert-Butanol Ammonium Iodide as Phase-Transfer Catalyst: An Alternative Minimalist Approach. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starks, C.M. Phase-Transfer Catalysis. I. Heterogeneous Reactions Involving Anion Transfer by Quaternary Ammonium and Phosphonium Salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1971, 93, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kumatabara, Y.; Shirakawa, S. Chiral Quaternary Phosphonium Salts as Phase-Transfer Catalysts for Environmentally Benign Asymmetric Transformations. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Ding, C.; Maruoka, K. Phosphonium Salts as Chiral Phase-Transfer Catalysts: Asymmetric Michael and Mannich Reactions of 3-Aryloxindoles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4559–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Yan, H.; Jang, H.B.; Kim, H.K.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Chi, D.Y.; Song, C.E. Bis-Terminal Hydroxy Polyethers as All-Purpose, Multifunctional Organic Promoters: A Mechanistic Investigation and Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7683–7686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Song, C.E.; Chi, D.Y. New Method of Fluorination Using Potassium Fluoride in Ionic Liquid: Significantly Enhanced Reactivity of Fluoride and Improved Selectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 10278–10279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.-H.; Jang, H.B.; Im, S.; Song, M.J.; Kim, S.-Y.; Park, S.-W.; Chi, D.Y.; Song, C.E.; Lee, S. SN2 Fluorination Reactions in Ionic Liquids: A Mechanistic Study towards Solvent Engineering. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.-H.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, S. Ionic Liquids as Organocatalysts for Nucleophilic Fluorination: Concepts and Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietraszkiewicz, M.; Jurczak, J. Synthesis of Chiral Diaza-Crown Ethers Incorporating Carbohydrate Units. Tetrahedron 1984, 40, 2967–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérubé, C.; Voyer, N. Crown-Ether-Modified Cyclic Dipeptides as Supramolecular Chiral Catalysts. Supramol. Chem. 2018, 30, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérubé, C.; Barbeau, X.; Cardinal, S.; Boudreault, P.L.; Bouchard, C.; Delcey, N.; Lagüe, P.; Voyer, N. Interfacial Supramolecular Biomimetic Epoxidation Catalysed by Cyclic Dipeptides. Supramol. Chem. 2017, 29, 330–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, B.; Lehn, J.M.; Sauvage, J.P. Les Cryptates. Tetrahedron Lett. 1969, 10, 2889–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehn, J.M. Accounts of Chemical Research Cryptates: The Chemistry of Macropolycyclic Inclusion Complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 1978, 11, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.O.; Llinares, J.M.; Day, V.W.; Bowman-James, K. Cryptand-like Anion Receptors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3980–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landini, D.; Maia, A.; Montanari, F.; Tundo, P. Lipophilic [2.2.2] Cryptands as Phase-Transfer Catalysts. Activation and Nucleophilicity of Anions in Aqueous-Organic Two-Phase Systems and in Organic Solvents of Low Polarity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1979, 101, 2526–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliego, J.R. Potassium Fluoride Activation for the Nucleophilic Fluorination Reaction Using 18-Crown-6,[2.2.2]-Cryptand, Pentaethylene Glycol and Comparison with the New Hydro-Crown Scaffold: A Theoretical Analysis. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 3127–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, A.P.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.-W.; Yan, H.; Song, C.E. Cooperative Asymmetric Cation-Binding Catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 4319–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalessandro, E.V.; Pliego, J.R. Theoretical Design of New Macrocycles for Nucleophilic Fluorination with KF: Thiourea-Crown-Ether Is Predicted to Overcome [2.2.2]-Cryptand. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2020, 5, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, V.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Choi, W.; Kim, D.W. Crown Ether Metal Complex Fluoride Salt as a Facile and Low Hygroscopic Fluoride Source for Nucleophilic Fluorination. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.-H.; Yun, W.; Kim, C.-H.; Jang, S.-W.; Lee, S.-S.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.-W. Inter-and Intra-Molecular Organocatalysis of SN2 Fluorination by Crown Ether: Kinetics and Quantum Chemical Analysis. Molecules 2021, 26, 2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Yun, W.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.W. Kinetics and Quantum Chemical Analysis of Intramolecular SN2 Reactions by Using Metal Salts and Promoted by Crown Ethers: Contact Ion Pair vs. Separated Nucleophile Mechanism. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202104431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliego, J.R., Jr.; Riveros, J.M. New Insights on Reaction Pathway Selectivity Promoted by Crown Ether Phase-Transfer Catalysis: Model Ab Initio Calculations of Nucleophilic Fluorination. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2012, 363, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.L.; Valle, M.S.; Pliego, J.R., Jr. Micro-Solvation and Counter Ion Effects on Ionic Reactions: Activation of Potassium Fluoride with 18-Crown-6 and Tert-Butanol in Aprotic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 319, 114211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.L.; Valle, M.S.; Pliego, J.R., Jr. Nucleophilic Fluorination with KF Catalyzed by 18-Crown-6 and Bulky Diols: A Theoretical and Experimental Study. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 15457–15465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.M.; Whittaker, A.M.; Schultz, D.M. Nucleophilic Fluorination of Heteroaryl Chlorides and Aryl Triflates Enabled by Cooperative Catalysis. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 3999–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Kitamura, M.; Ooi, T.; Maruoka, K. Dramatic Rate Enhancement of Asymmetric Phase-Transfer-Catalyzed Alkylations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, V.H.; Choi, W.; Lee, S.-S.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.W. Bis-tert-Alcohol-Functionalized Crown-6-Calix[4]arene: An Organic Promoter for Nucleophilic Fluorination. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 4515–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schettini, R.; Sicignano, M.; De Riccardis, F.; Izzo, I.; Della Sala, G. Macrocyclic Hosts in Asymmetric Phase-Transfer Catalyzed Reactions. Synthesis 2018, 50, 4777–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shao, Y.; Tang, J.; Jiang, J.; Wang, L.; Li, S. Supramolecular Asymmetric Catalysis Mediated by Crown Ethers and Related Recognition Systems. Green Synth. Catal. 2021, 2, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Sasaki, S.; Koga, K. Simple Chiral Crown Ethers Complexed with Potassium Tert-Butoxide as Efficient Catalysts for Asymmetric Michael Additions. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 7229–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicignano, M.; Schettini, R.; Sica, L.; Pierri, G.; De Riccardis, F.; Izzo, I.; Maity, B.; Minenkov, Y.; Cavallo, L.; Della Sala, G. Unprecedented Diastereoselective Arylogous Michael Addition of Unactivated Phthalides. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 7131–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Sala, G.; Sicignano, M.; Schettini, R.; De Riccardis, F.; Cavallo, L.; Minenkov, Y.; Batisse, C.; Hanquet, G.; Leroux, F.; Izzo, I. Switchable Diastereoselectivity in the Fluoride-Promoted Vinylogous Mukaiyama–Michael Reaction of 2-[(Trimethylsilyl) Oxy] Furan Catalyzed by Crown Ethers. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 6629–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
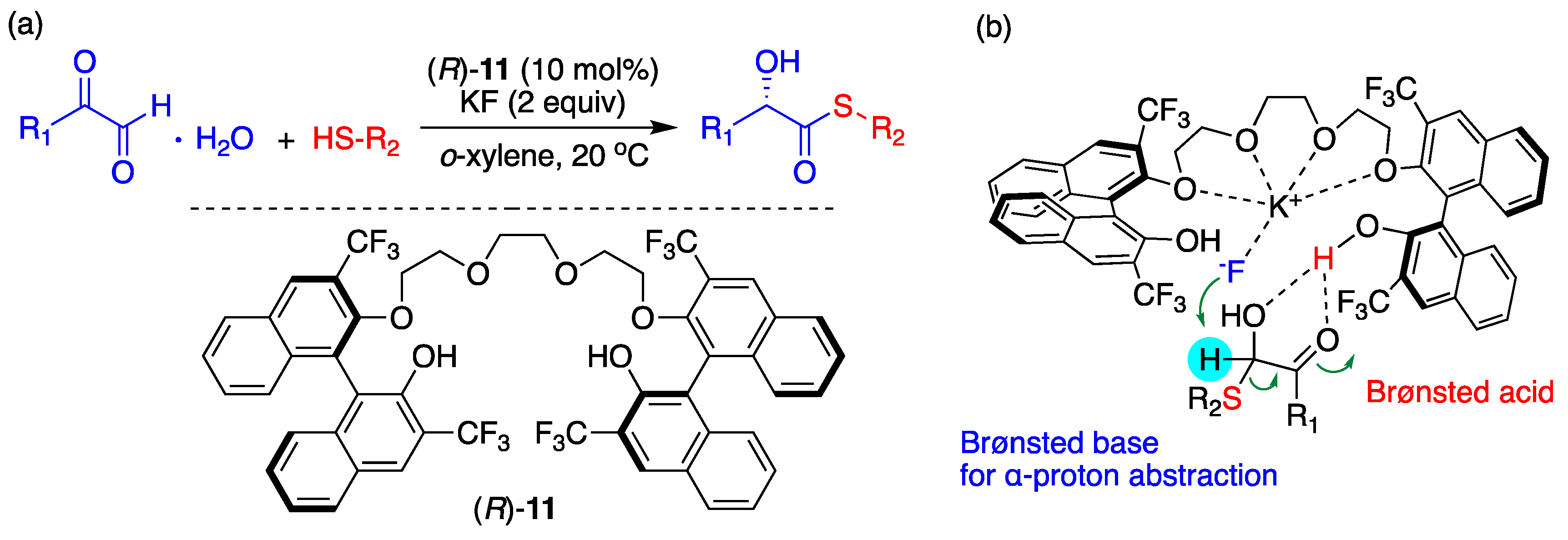
- Park, S.Y.; Hwang, I.S.; Lee, H.J.; Song, C.E. Biomimetic Catalytic Transformation of Toxic α-Oxoaldehydes to High-Value Chiral α-Hydroxythioesters Using Artificial Glyoxalase I. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
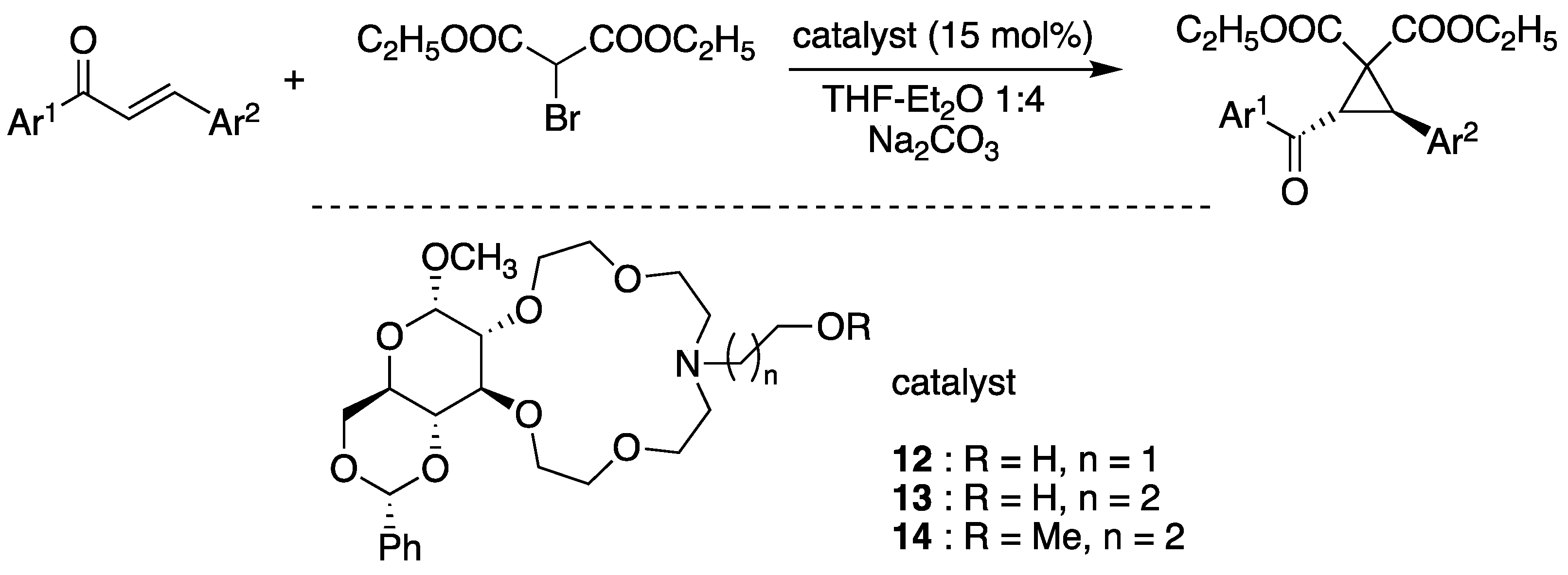
- Rapi, Z.; Grün, A.; Nemcsok, T.; Hessz, D.; Kállay, M.; Kubinyi, M.; Keglevich, G.; Bako, P. Crown Ether Derived from D-Glucose as an Efficient Phase-Transfer Catalyst for the Enantioselective Michael Addition of Malonates to Enones. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2016, 27, 960–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbán, I.; Bakó, P.; Rapi, Z. Carbohydrate-Based Azacrown Ethers in Asymmetric Syntheses. Chemistry 2021, 3, 550–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other function. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, P.J.; Wadt, W.R. Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for the transition metal atoms Sc to Hg. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
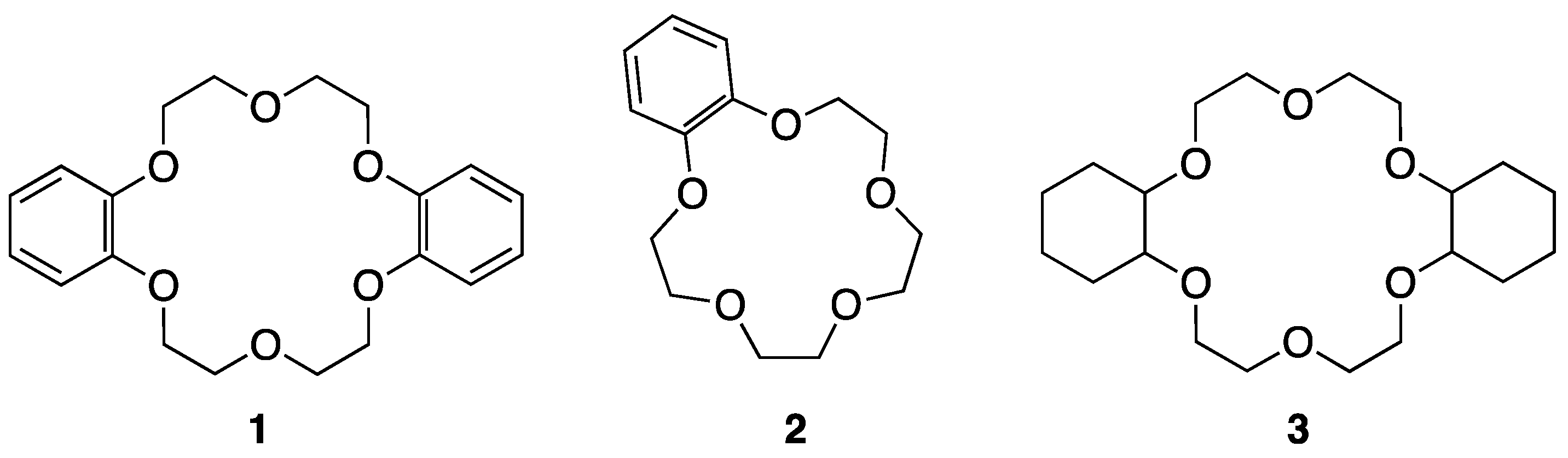
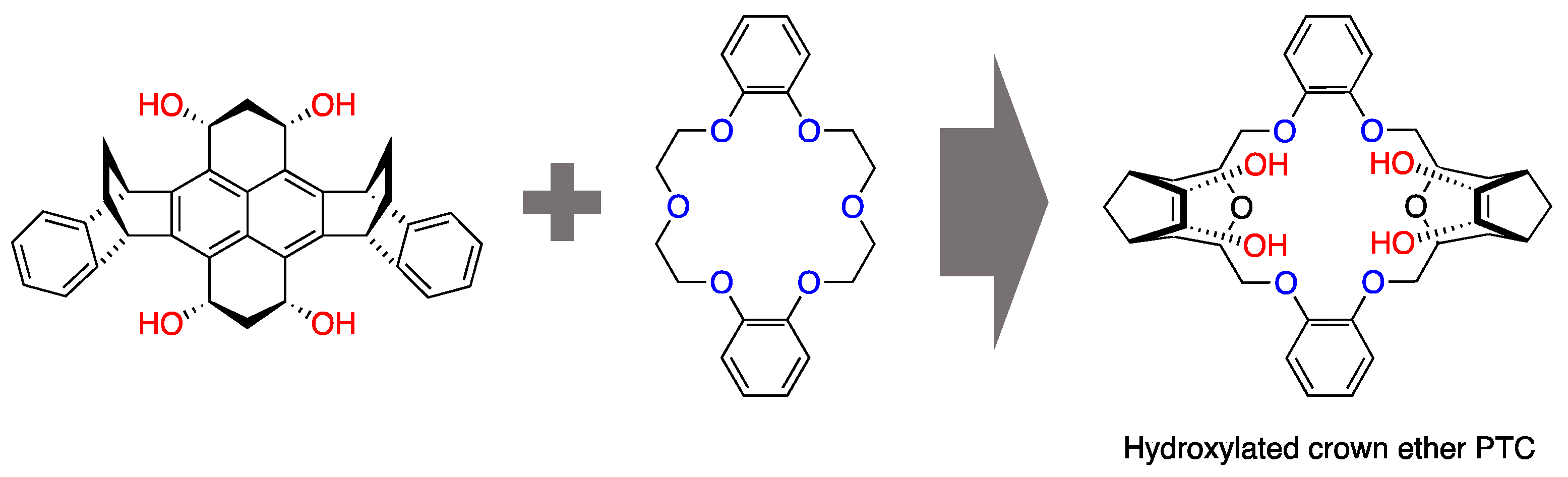
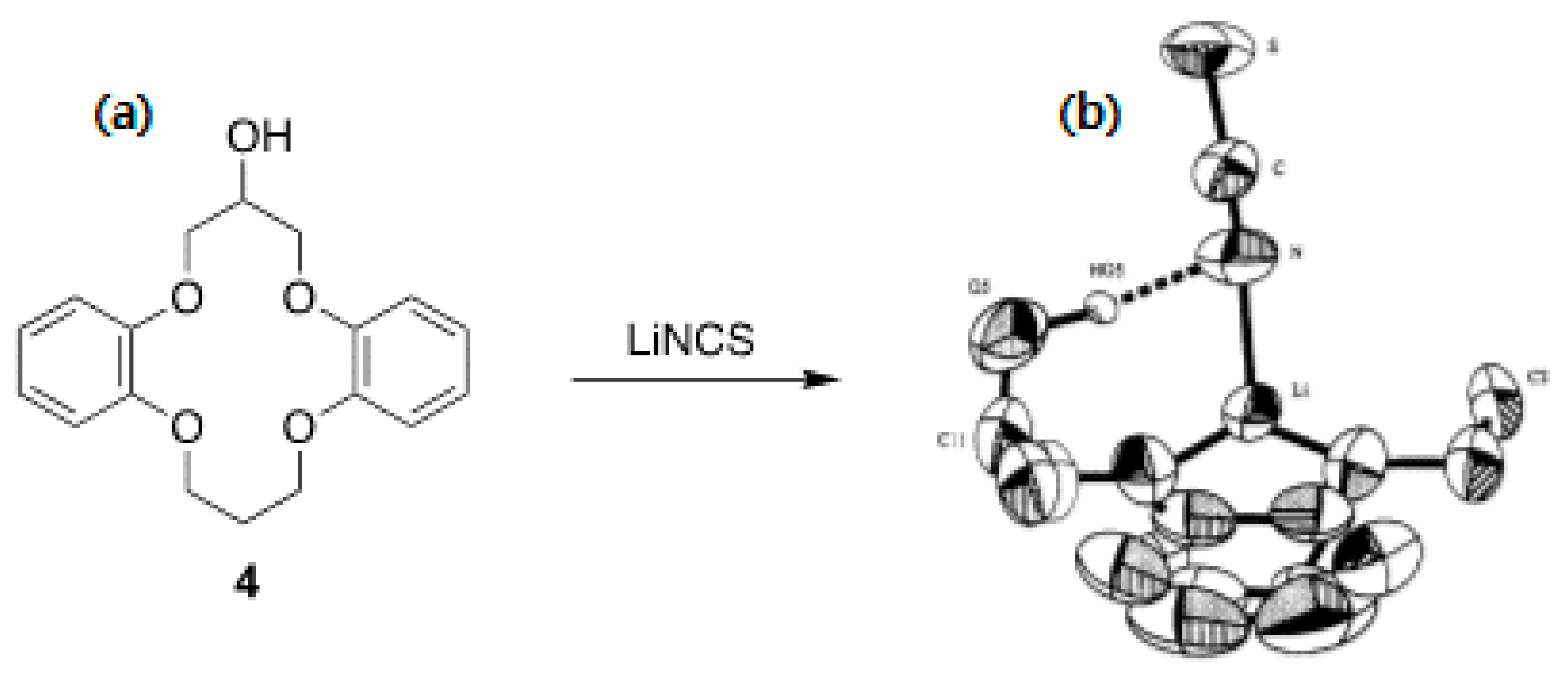




| Metal Salt | Crown Ether | Reaction Time (h) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| KI | 1 | 40 | 80 |
| NaI | 2 | 21 | 80 |
| KI | 3 | 3 | 100 |
| KI | - | 24 | <4 |
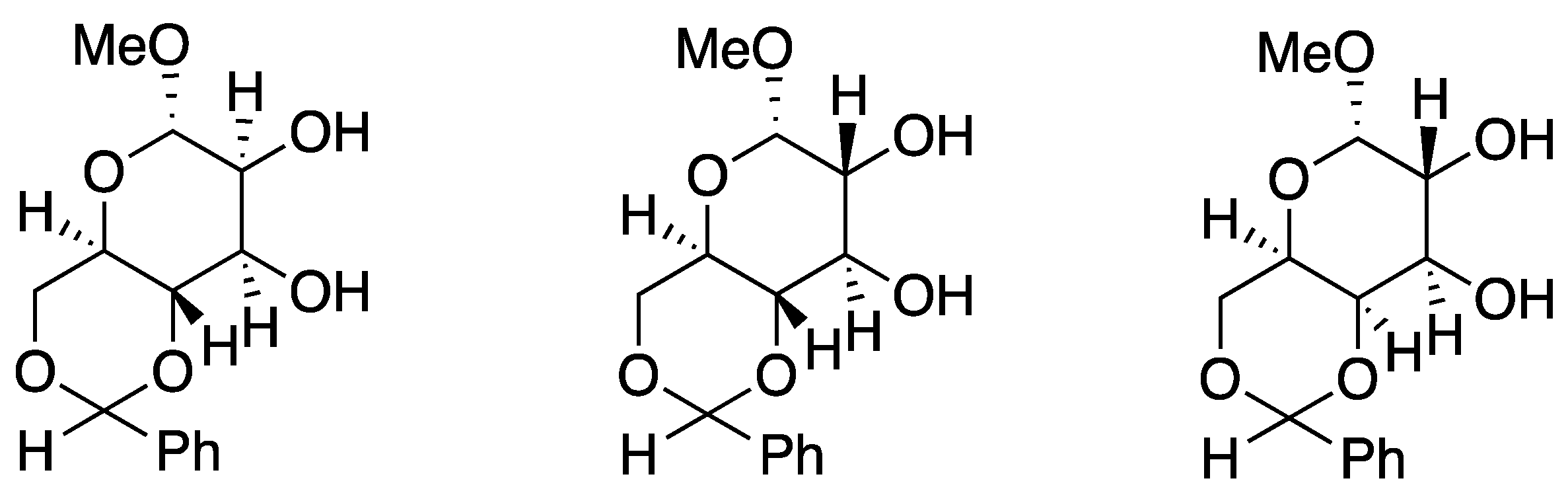
| Entry | Ar1 * | Ar2 * | Catalyst | Yield (%) | ee (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C6H5 | C6H5 | 12 | 28 | 88 |
| 2 | 4-O2N-C6H4 | C6H5 | 12 | 77 | 99 |
| 3 | C6H5 | Thiophen-2-yl | 12 | 57 | 94 |
| 4 | C6H5 | C6H5 | 13 | 32 | 98 |
| 5 | C6H5 | C6H5 | 14 | 35 | 99 |
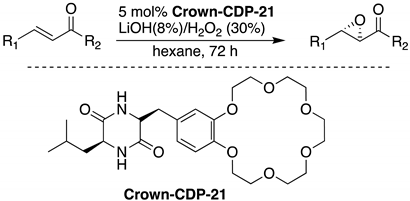 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | R1 | R2 | Yield (%) | ee (%) |
| 1 | Ph | Ph | 93 | 34 |
| 2 | p-Cl- Ph | Ph | 32 | 27 |
| 3 | p-F- Ph | Ph | 31 | 30 |
| 4 | Ph | p-F- Ph | 67 | 18 |
| 5 | p-NO2- Ph | p-CH3- Ph | 54 | 40 |
| 6 | p-NO2- Ph | Ph | 81 | 21 |
| 7 | o-NO2- Ph | Ph | 54 | 15 |
| 8 | p-OMe- Ph | Ph | 43 | 6 |
| 9 | o-OMe- Ph | Ph | 10 | 13 |
| 10 | 2-naphtyl | Ph | 45 | 19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, Y.-H.; Jeong, J.G.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, S. Nucleophilic Reactions Using Alkali Metal Fluorides Activated by Crown Ethers and Derivatives. Catalysts 2023, 13, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030479
Oh Y-H, Jeong JG, Kim DW, Lee S. Nucleophilic Reactions Using Alkali Metal Fluorides Activated by Crown Ethers and Derivatives. Catalysts. 2023; 13(3):479. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030479
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Young-Ho, Ju Gyeong Jeong, Dong Wook Kim, and Sungyul Lee. 2023. "Nucleophilic Reactions Using Alkali Metal Fluorides Activated by Crown Ethers and Derivatives" Catalysts 13, no. 3: 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030479
APA StyleOh, Y.-H., Jeong, J. G., Kim, D. W., & Lee, S. (2023). Nucleophilic Reactions Using Alkali Metal Fluorides Activated by Crown Ethers and Derivatives. Catalysts, 13(3), 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030479








